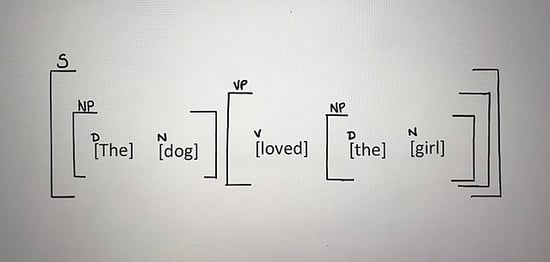
State to what part of speech the following words belong and translate them into Russian science – scientist – scientifically; geology – geological – geologist; develop – development – developed; compose – composer – composition; sculpt – sculpture – sculptor; evidence – evidently; occur – occurrence – occurring
Суффиксы существительных -er (-or), -ist, -ian, -ity, -ing, -hood, ment, -ness, -y, -th, -ant, -ism, -ure, ship • Суффиксы «er, or» присоединяются к глаголам для обозначения действующих лиц. to buy — a buyer покупать — покупатель to translate — a translator переводить — переводчик
Суффикс –ist, -ian • Суффикс –ist — для обозначения профессионалов, сторонников общественного или научного направления. physicist – физик • Суффикс –ian – для обозначения национальности, звания и профессии Russian — русский, academician — академик, musician — музыкант Слова, образованные присоединением суффикса -ian, могут переводиться и прилагательными, например: the Russian language — русский язык
Суффикс -ity • Суффикс -ity (орфографические варианты -ety, -iety) образует абстрактные существительные со значением состояния, качества, условия. • Суффиксу -ity соответствует суффикс -ость, например: able (способный) — ability (способность); active (активный) — activity (активность, деятельность); valid (имеющий силу, обоснованный, действенный) validity (действенность, справедливость, законность, обоснованность).
Суффикс -ing • Суффикс -ing образует существительные от глаголов, например: to meet (встречать) — meeting (встреча), to proceed (продолжать) — proceeding (практика, proceedings труды, записки (научного общества) Не путайте существительные с окончанием -ing с причастием и герундием
Суффикс -hood • Суффикс -hood образует существительные со значением «состояние, положение, качество», например: child (ребенок) — childhood (детство), man (мужчина) — manhood (мужественность)
Суффикс -ment • Суффикс -ment образует существительные, обозначающие действие, результат действия, например: to move (двигаться) — movement (движение) Некоторые слова с этим суффиксом приобретают значение совокупности предметов, например: equipment (оборудование).
Суффикс -ness • Суффикс -ness образует существительные со значением «состояние, качество», например: dark (темный) — darkness (темнота), good (хороший) — goodness (доброта), great (великий) — greatness (величие).
Суффикс -у • Суффикс -у образует абстрактные существительные от глаголов, например: to discover (открывать) — discovery (открытие); to inquire (спрашивать, узнавать) — inquiry (вопрос, запрос)
Суффикс -ant • Суффикс -ant образует существительные со значением лица и вещества, например: to assist (помогать) — assistant помощник, to serve (служить) — servant (слуга), an oxidant (окислитель)
Суффикс -th • Суффикс -th образует существительные со значением качества, например: true (верный, правдивый) — truth (правда), Deep (глубокий) – depth (глубина)
Суффикс –ism • Суффикс –ism употребляют для образования существительного в английском языке (от простых существительных или прилагательных), имеющих значение обобщения типичных свойств или идейного направления: a hero – heroism a patriot – patriotism social – socialism Buddha – Buddhism
Суффикс -age • Суффикс -age образует существительные с различными значениями, например: to break (ломать) — breakage (поломка); to marry (жениться) — marriage (свадьба); courage (храбрость, смелость, мужество)
Суффикс -urе (-ture, -sure) • Суффикс -urе (-ture, -sure) образует существительные, обозначающие процесс, например: to press – pressure — давление, to mix — mixture — смешивание
Суффикс -(a)tion • Суффикс «(a)ion (tion, ssion)»-tion – для обозначения «состояние, характеристика, процесс» . to expect — expectation ожидать — ожидание to produce — production производить — продукция to exclude — exclusion исключать — исключение to permit — permission разрешать — разрешение
Суффикс -ion. • Суффикс –ion — образует из глаголов существительное: invent- invention
Суффиксы «ness, (ance, ence)» • Суффиксы «ness, существительные прилагательных: (ance, от ence)» образуют соответствующих happy — happiness счастливый — счастье important — importance важный — важность different — difference различный — различие
Form nouns from the following words: modify, move, compose, translate, relate, observe, divide, different, mix, constitute, develop
The word “THE” is a Definite Article and an Adverb.Take a look at the definitions and examples below and you will see how this little word can be used as different parts of speech.
1. Definite Article
This word “The” is considered as a definite article because it is used to refer to something specific. It is also placed before a noun, if the audience already knows what is being referred to (there is only one or the subject has already been mentioned). For example, let’s look at the sentence below:
“The pope will visit the Philippines in 2015.”
“The” is used because there is only one pope in the whole world.
Definition:
a. used to indicate a person or thing that has already been mentioned or seen or is clearly understood from the situation
- Joe is the tallest boy in class.
b. used to refer to things or people that are common in daily life
- The moon is aligned between the Sun and the Earth.
c. used to refer to things that occur in nature
- The inner planets of the solar system are denser compared to the outer planets.
2. Adverb
Aside from acting as a definite article, “The” can also be used as an adverb. Take for example the sentence below:
“Since getting a new computer, he was able to produce outputs all the quicker.”
In that sentence, “the” serves as an adverb because it modifies the adjective quicker. Take note that the word can only be used as an adverb if it is used together with an adjective or another adverb which is in the comparative degree.
Definition:
a. than before: than otherwise —used before a comparative
- The sooner the better.
b. to what extent
- Mercury is the most cratered planet in our Solar System.
c. beyond all others
- The more the merrier.
Parts of Speech
Every word is a part of speech, each playing a specific role in a sentence. There are 8 different parts of speech including noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Each word in a sentence plays a vital role in conveying the meaning and intent of the sentence.
What is Part of Speech?
The English language has thousands of words and every word has some function to perform. Some words are there to show action, some to join, and some to name something. And together, all the functions performed by words in the English language fall under Parts of speech.
Parts of Speech Definition
The parts of speech are the “traditional grammatical categories to which words are assigned in accordance with their syntactic functions, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on.” In other words, they refer to the different roles that words can play in a sentence and how they relate to one another based on grammar and syntax.
Parts of Speech Table
| Types | Function | Examples | Sentences |
| Noun | Refers Things or person | Pen, Chair, Ram, Honesty |
Cars are expensive. This chair is of wood. Ram is a topper. Honesty is the best policy. |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, it, they |
They are expensive. It is of wood. He is a topper. It is the best policy |
| Adjective | Describes a noun |
Super, Red, Our, Big, Great class |
Super cars are expensive Red chair is for kids Ram is a class topper. Great things take time. |
| Verb | Describes action or state | Play, be, work, love, like |
I play football I will be a doctor I like to work I love writing poem. |
| Adverb | Describes a verb, adjective or adverb | Silently, too, very |
I love reading silently. It is too tough to handle. He can speak very fast. |
| Preposition | Links a noun to another word | at, in, of, after, under, |
The ball is under the table. I am at a restaurant. she is in trouble. I am going after her. It is so nice of him |
| Conjunction | Joins clauses and sentences | and, but, though, after |
First, I will go to college and then I may go to fest. I don’t have a car but I know how to drive. She failed the exam though she worked hard. He will come after he finish his match. |
| Interjection | Shows exclamation | oh!, wow!, alas! Hurray! |
Oh! I got fail again. Wow! I got the job. Alas! She is no more. Hurray! we are going to party. |
Parts of Speech Examples with Sentences
Noun
Examples: Luggage, Cattle.
Sentence: Never leave your luggage unattended.
In some places, cattle are fed barely.
Pronoun
Examples: who, either, themselves
Sentence: I know a man who plays the guitar very well.
Either of the two cars is for sale.
They enjoyed themselves at the party.
Adjective
Examples: kind, moving, wounder.
Sentence:
She is a kind person.
Boarding a moving bus can be dangerous.
Never poke a wounded animal.
Verb
Examples: Praise, Hate, Punish
Sentence: She always praises her friends.
I don’t hate anybody.
The boy has been punished by his teacher
Adverb
Examples: Always, enough, immediately
Sentence: we should always help each other.
We should be wise enough to understand what is good for us.
We should leave bad habits immediately.
Preposition
Examples: Off, Below, From. to
Sentence:
He plunged off the cliff
I live below the 9th floor.
I travel daily from Delhi to Noida.
Conjunction
Examples: whereas, as well as, so,
Sentence: The new software is fairly simple whereas the old one was a bit complicated.
The finance company is not performing well as well as some of its competitors.
He was ready so he may come.
Interjection
Examples: oops! whoa! phew!
Sentence: Oops! I forgot to mention her name.
Whoa! you drive fast.
Phew! That was close call, we had a narrow escape.
Parts of Speech Quiz
Choose the correct Parts of Speech of the BOLD word from the following questions.
1. Let us play, Shall We?
a. Conjunction
b. Pronoun
c. Verb
2. It is a good practice to arrange books on shelves.
a. Verb
b. Noun
c. Adjective
3. Whose books are these?
a. Pronoun
b. Preposition
c. verb
4. Father, please get me that toy.
a. Pronoun
b. Adverb
c. Adjective
5. His mentality is rather obnoxious.
a. Adverb
b. Adjective
c. Noun
6. He is the guy whose money got stolen.
a. Pronoun
b. Conjunction
c. Adjective
7. I will have finished my semester by the end of this year.
a. Interjection
b. Conjunction
c. Preposition
8. Bingo! That’s the one I have been looking for
a. Interjection
b. Conjunction
c. Preposition
Quiz Answers
1. c, 2. b, 3. a, 4. c, 5. a, 6. b, 7. c, 8. a
FAQs on Parts of Speech
Q1. What are Parts of Speech?
Ans. A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech.
Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech?
Ans. Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection.
Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there?
Ans. There are a total of 8 parts of Speech.
Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
Ans. Adjective. Eg. Our car.
Q5. What Part of Speech is “Quickly”?
Ans. Adverb. let us understand it with this example – Milk sours quickly in warm weather.
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)
What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words. All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech. There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns…you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.
There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
#1: Nouns
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. It’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona.
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace.
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team, crowd, and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator…which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma,” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas,” or, “They’ve got several charismas.” It just doesn’t make sense!
Verbs are all about action…just like these runners.
#2: Verbs
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being. In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran,” “We arrived,” and, “The car stopped” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence. One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal. The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.
Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words. Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence.. For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance (higher, lower, farther), age (younger, older), size and dimensions (bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter), and quality or feeling (better, cleaner, happier, angrier).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects. Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est:
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject—story—is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest…though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles: a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers: a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words: other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech…which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up.
Adverbs can be used to answer questions like «when?» and «how long?»
#4 Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence. These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless, she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead, they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens. In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
|
Adverbs of Place |
Adverbs of Time |
Adverbs of Manner |
Adverbs of Degree |
Adverbs of Frequency |
|
Above |
Afterwards |
Badly |
Almost |
Again |
|
Below |
Already |
Happily |
Much |
Always |
|
Here |
Always |
Sadly |
Nearly |
Ever |
|
Outside |
Immediately |
Slowly |
Quite |
Frequently |
|
Over there |
Last (month, week, year) |
Quickly |
Really |
Generally |
|
There |
Now |
Well |
So |
Hardly ever |
|
Under |
Soon |
Hard |
Too |
Nearly |
|
Upstairs |
Then |
Fast |
Very |
Never |
|
Yesterday |
Occasionally |
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
Here’s a helpful list of pronouns.
(Attanata / Flickr)
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs. Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets? We already bought ours.
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here…you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby…maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing. The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone. That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.
Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock.)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences. Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense—they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence. Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.
Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences. While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well, look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.
This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases.
(attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places. Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people—you and I—are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair.
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field.
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.
10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples (a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection
b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition
c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs
b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions
c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities.
b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities.
c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film.
b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through.
c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases.
b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs.
c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty.
b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject.
c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those
b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them
c) Who, what, which, whose

a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences.
b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences.
c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail.
b) The cow jumped over the moon.
c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling.
c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!
What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT, and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
Have friends who also need help with test prep? Share this article!
About the Author
Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
поделиться знаниями или
запомнить страничку
- Все категории
-
экономические
43,633 -
гуманитарные
33,652 -
юридические
17,917 -
школьный раздел
611,709 -
разное
16,898
Популярное на сайте:
Как быстро выучить стихотворение наизусть? Запоминание стихов является стандартным заданием во многих школах.
Как научится читать по диагонали? Скорость чтения зависит от скорости восприятия каждого отдельного слова в тексте.
Как быстро и эффективно исправить почерк? Люди часто предполагают, что каллиграфия и почерк являются синонимами, но это не так.
Как научится говорить грамотно и правильно? Общение на хорошем, уверенном и естественном русском языке является достижимой целью.
The words
of language, depending on various formal and semantic features, are
divided into classes. The traditional grammatical classes of words
are called “parts of speech”, since the word is distinguished not
only by grammatical, but also by semantico-lexemic properties, some
scholars also refer to parts of speech as lexico-grammatical
categories (Смирницкий).
It should
be noted that the term “parts of speech” is purely traditional
and conventional. This name was introduced in the grammatical
teaching of Ancient Greece, where no strict differenciation was drawn
between the word as a vocabulary unit and the word as a functional
element of the sentence.
In modern
linguistics, parts of speech are discriminated on the basis of the
three criteria: “semantic, formal and functional” (Щерба).
The
semantic criterion presupposes (предполагать,
заключать
в
себя)
the generalized meaning, which is characteristic of all the words
constituting (составлять)
a given part of speech. This meaning is understood as the categorical
meaning of the part of speech.
The formal
criterion exposes (выставлять
на
показ)
the specific inflexional and derivational (word-building) features of
part a part of speech.
The
functional criterion concerns the syntactic role of words in the
sentence, typical of a part of speech.
These
three factors of categorical characterization of words are referred
to as ‘meaning’, form and function.
The
three-criteria characterization of parts of speech was developed and
applied to practice in Soviet linguistics. Three names are especially
notable for the elaboration of these criteria: V.V. Vinogradov
in connection with the study of Russian Grammar, A.I. Smirnitskyand
B.A. Ilyish in connection with their study of English Grammar.
Alongside
of the three-criteria principle of dividing the words into
grammatical classes modern linguistics has developed another,
narrower principle based on syntactic featuring of words only.
On
the material of Russian, the principle of syntactic approach to the
classification of word-stock were outlined in the works of A.M.
Peshkovsky. The principles of syntactic classification of English
words were worked out by L. Bloomfield and his followers L. Harris
and especially Ch. Fries.
Here
is how Ch. Fries presents his scheme of English word-classes.
For
his materials he chooses tape-recorded spontaneous conversations
which last 50 hours.
The
three typical sentences are:
Frames:
A.
The concert was good (always).
B.
The clerk remembered the tax (suddenly).
C.
The team went there.
As
a result he divides the words into 4 classes: class I, II, III, IV,
which correspond to the traditional nouns, verbs, adjectives and
adverbs.
Thus,
class I includes all words which can be used in the position of the
words ‘concert’ (frame A), clerk and tax (frame B), team (frame C),
i.e. in the position of subject and object.
Class
II includes the words which have the position of the words ‘was’,
‘remembered’, ‘went’ in the given frames, i.e. in the position of the
predicate or part of the predicate.
Class
III includes the words having the position of ‘good’, and ‘new’, i.e.
in the position of the predicative or attribute.
And
the words of class IV are used in the position of ‘there’ in Frame C,
i.e. of an adverbial modifier.
These
classes are subdivided into subtypes.
Ch.
Fries sticks to the positional approach. Thus such words as man, he,
the others, another belong to class I as they can take the position
before the words of class II, i.e. before the finite verb.
Besides
the 4 classes, Fries finds 15 groups of function words. Following the
positional approach, he includes into one and the same group the
words of quite different types.
Thus,
group A includes all words, which can take the position of the
definite article ‘the’, such as: no, your, their, both, few, much,
John’s, our, four, twenty.
But
Fries admits, that some of these words may take the position of class
I in other sentences.
Thus,
this division is very complicated, one and the same word may be found
in different classes due to its position in the sentence. So Fries’
idea, though interesting, doesn’t reach its aim to create a new
classification of classes of words, but his material gives
interesting data concerning the distribution of words and their
syntactic valency.
Today
many scholars believe that it is difficult to classify English parts
of speech using one criterion.
Some
Soviet linguists class the English parts of speech according to a
number of features.
1.
Lexico-grammatical meaning: (noun — substance, adjective — property,
verb — action, numeral — number, etc).
2.
Lexico — grammatical morphemes: (-er, -ist, -hood — noun; -fy, -ize —
verb; -ful, -less — adjective, etc).
3.
Grammatical categories and paradigms.
4.
Syntactic functions
5.
Combinability (power to combine with other words).
In
accord with the described criteria, words are divided into notional
and functional, which reflects their division in the earlier
grammatical tradition into changeable and unchangeable.
To
the notional parts of speech of the English language belong the noun,
the adjective, the numeral, the pronoun, the verb, the adverb.
To
the basic functional series of words in English belong the article,
the preposition, the conjunction, the particle, the modal word, the
interjection.
The
difference between them may be summed up as follows:
1) Notional
parts
of speech express notions and function as sentence parts (subject,
object, attribute, adverbial modifier).
2) Notional
parts
of speech have a naming function and make a sentence by themselves:
Go!
***
1)
Functional
words
(or form-words) cannot be used as parts of the sentence and cannot
make a sentence by themselves.
2)
Functional
words
have no naming function but express relations.
3)
Functional
words
have a negative combinability but a linking or specifying function.
E.g. prepositions and conjunctions are used to connect words, while
particles and articles — to specify them.
Each
part of speech is further subseries in accord with various particular
semantico-functional and formal features of the words.
Thus,
nouns are subdivided into proper and common, animate and unanimate,
countable and uncountable, conctrete and abstract.
E.g.
Mary-girl, man-earth, can-water, stone-honesty.
This
proves that the majority of English parts of speech has a field-like
structure.
The
theory of grammatical fields was worked out by V.G. Admoni on the
material of the German language.
The
essence of this theory is as follows. Every part of speech has words,
which obtain all the features of this part of speech. They are its
nucleus. But there are such words which don’t have all the features
of this part of speech, though they belong to it.
Consequently,
the field includes central and peripheral elements.
Because
of the rigid word-order in the English sentence and scantiness of
inflected forms, English parts of speech have developed a number of
grammatical meanings and an ability to be converted.
E.g.
It’s better to be a has-been than a never-was.
He
grows old. He grows roses.
The
conversation may be written one part of speech.
She
took off her glasses.
Give
me a glass of water.
The
person in the glass was making faces.
Don’t
break the glass when cleaning the window.
They
are called variants of one part of speech. Because of homonymy and
polysemy many notional words may have the same form as functional
words.
E.g.
He grows roses — He grows old.
Professor
Ilyish objects to the division of words into notional and functional
(formal) parts of speech. He says that prepositions and conjunctions
are no less notional than nouns and verbs, as they also express some
relations and connections existing independently.
Соседние файлы в папке Gosy
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- nouns
- pronouns
- verbs
- adjectives
- adverbs
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won’t make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won’t even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics, the label part of speech has generally been discarded in favor of the term word class or syntactic category. These terms make words easier to qualify objectively based on word construction rather than context. Within word classes, there is the lexical or open class and the function or closed class.
Read about each part of speech below and get started practicing identifying each.
Noun
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they’re the official name of something or someone, called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronoun
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence. They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verb
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject’s state of being (is, was). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became
Adjective
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverb
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Examples: softly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, softly, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spacial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase, which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet, with.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples: articles: a, an, the; determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners, which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections (Hooray!) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun [or converted adjective] work modifies the noun permit.
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
- Birds fly.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it’s a command to an understood «you».
- Go!
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, «(You) go!»
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what’s happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it’s a preposition because it’s followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time (before winter) that answers the question of when the birds migrate. Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.