From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In digital audio electronics, a word clock or wordclock (sometimes sample clock, which can have a broader meaning)[further explanation needed] is a clock signal used to synchronise other devices, such as digital audio tape machines and compact disc players, which interconnect via digital audio signals. Word clock is so named because it clocks each audio sample. Samples are represented in data words.
S/PDIF, AES/EBU, MADI, ADAT, and TDIF are some of the formats that use a word clock. Various audio over Ethernet systems use communication protocols to distribute word clock. The device which generates the word clock is the clock source for all the other audio devices.
Comparison to timecode[edit]
Word clock should not be confused with timecode; word clock is used entirely to keep a perfectly timed and constant bitrate to avoid timing errors that can cause data transmission errors. Timecode is metadata about the media data being transmitted. Time code can be used as an initial phase reference for jam sync using the word clock as the frequency reference.
Over coax cable[edit]
Professional digital audio equipment may have a word clock input or output to synchronize timing between multiple devices. Although the electrical characteristics of the word clock signal have not been completely standardized, some characteristics should always apply. Items that should remain consistent are TTL level, a 75ohm output impedance, 75ohm cables and a 75ohm terminating resistor at the end of a chain or cable.
Proper termination of the word clock signal with a 75ohm resistor is important. It prevents the clock signal from reflecting back into the cable and causing false detection of extra 1’s and 0’s. Some digital equipment includes a switchable terminator, some include a hardwired terminator and others have no terminator at all. An unfortunate aspect is that some equipment manuals do not indicate whether a hardwired terminator is included.[1]
A chain connection from the source through the receivers may increase jitter. Using clock distributing devices for parallel transmission is a better method. The length and quality of coaxial cables are important.
Over AES3[edit]
The AES11 standard defines a means for carrying a word clock over an AES3 connection. In this context, the word clock is known as a Digital Audio Reference Signal (DARS).
In annex B, the AES11 standard also describes common practice in transmitting and receiving a plain word clock signal. This is not an attempt to standardize it, the annex is informative only.
See also[edit]
- Phase-locked loop
References[edit]
- ^ Section 9.1.3 of Ardour manual
- Word clock
-
A word clock or wordclock (sometimes sample clock, which can have a broader meaning) is a clock signal (not the actual device) used to synchronise other devices, such as digital audio tape machines and compact disc players, which interconnect via digital audio. S/PDIF, AES/EBU, ADAT, TDIF and other formats use a word clock. Various audio over Ethernet protocols use broadcast packets for the word clock. The device which maintains the word clock on a network is the master clock.
Word clock should not be confused with timecode; word clock is used entirely to keep a perfectly-timed and constant bitrate to avoid data errors. The word clock generator, usually built-in to analog-to-digital converters, creates digital pulses which contain no other data, and is considered essential to avoid frequency drift between the internal oscillators of each device. Timecode is actual data (technically metadata) «about» the media content being transmitted, and is optional, being sent in a higher layer.
ee also
* data word
* clock
* transport stream
* digital-to-analog converter
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
-
Word Clock — Wordclock ist ein Basistakt in der digitalen Audiotechnik, um Bearbeitungs und Übertragungsvorgänge zwischen verschiedenen Audiokomponenten synchron zu halten. Der Wordclock hat genau die Periodendauer welcher von einem Abtastwert (Samplerate)… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
Clock — (englisch: Uhr) steht für CLOCK, Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput, Gensequenz Clock (Lied), 1997 von Coal Chamber Clock (Band), The Clock, Comicfigur The Clock (OT, 1945) US Film, dt: Urlaub für die Liebe Clock (Restaurant), schwedische… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
Clock — For other uses, see Clock (disambiguation). Timepiece redirects here. For the Kenny Rogers album, see Timepiece (album). Platform clock at King s Cross railway station, London … Wikipedia
-
clock-watching — UK [ˈklɒkˌwɒtʃɪŋ] / US [ˈklɑkˌwɑtʃɪŋ] noun [uncountable] the practice of not concentrating on your work because you wish it was time to stop Derived word: clock watcher noun countable Word forms clock watcher : singular clock watcher plural clock … English dictionary
-
clock-watching — noun paying excessive attention to the clock (in anticipation of stopping work) • Hypernyms: ↑attention, ↑attending * * * clock watcher, clock watching see ↑watch the clock below. • • • Main Entry: ↑clock * * * clock watching UK … Useful english dictionary
-
Clock DVA — Origin Sheffield, England Genres Industrial music/Post punk/EBM Years active 1978–1981, 1982–1984, 1988–1994, 2008–present Labels … Wikipedia
-
Word game — Word games and puzzles are generally engaged as a source of entertainment, but they have been found to serve a very useful and progressive educational purpose as well. For instance, young children can find enjoyment playing modestly competitive… … Wikipedia
-
clock — I UK [klɒk] / US [klɑk] noun [countable] Word forms clock : singular clock plural clocks ** an object that shows the time. The object like a clock that you wear on your wrist is called a watch. Clocks either have a background called a face with… … English dictionary
-
Clock signal — In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is a particular type of signal that oscillates between a high and a low state and is utilized like a metronome to coordinate actions of circuits. Although the word signal… … Wikipedia
-
Clock rate — Clocking redirects here. For tampering with vehicle odometers, see Odometer fraud. The clock rate is the rate in cycles per second (measured in hertz) or the frequency of the clock in any synchronous circuit, such as a central processing unit… … Wikipedia
В цифровой аудиоэлектронике, word clock или wordclock (иногда образцы часов , которые могут иметь более широкое значение) — это тактовый сигнал, используемый для синхронизации других устройств, таких как цифровые аудиомагнитофоны и проигрыватели компакт-дисков , которые соединяются через цифровые аудиосигналы . Word Clock назван так потому, что он синхронизирует каждый аудиосэмпл . Образцы представлены словами данных .
S / PDIF , AES / EBU , ADAT и TDIF — это некоторые из форматов, в которых используется синхронизация слов. Различные системы передачи звука через Ethernet используют протоколы связи для распределения синхронизации слов. Устройство, которое генерирует синхронизацию слов, является единственным основным источником синхронизации для всех подчиненных аудиоустройств.
Сравнение с таймкодом
Word Clock не следует путать с тайм-кодом ; word clock полностью используется для поддержания идеально синхронизированного и постоянного битрейта, чтобы избежать ошибок синхронизации, которые могут вызвать ошибки передачи данных. Временной код — это метаданные о передаваемых мультимедийных данных. Временный код может быть использован в качестве начальной опорной фазы для джема синхронизации , используя синхронизирующие импульсы слов в качестве опорной частоты.
По коаксиальному кабелю
Профессиональное цифровое аудиооборудование может иметь вход или выход Word Clock для синхронизации времени между несколькими устройствами. Хотя электрические характеристики сигнала синхронизации слов не полностью стандартизированы, некоторые характеристики должны применяться всегда. Пункты, которые должны оставаться постоянными, — это уровень TTL , выходное сопротивление 75 Ом, кабели 75 Ом и согласующий резистор 75 Ом на конце цепи или кабеля.
Правильное завершение сигнала синхронизации слов с помощью резистора 75 Ом имеет важное значение. Это предотвращает отражение тактового сигнала обратно в кабель и ложное обнаружение лишних единиц и нулей. Некоторое цифровое оборудование включает в себя переключаемый терминатор, некоторые включают зашитый терминатор, а у других терминатор отсутствует вообще. К сожалению, в некоторых руководствах по оборудованию не указывается, включен ли проводной терминатор или нет.
Цепное соединение от источника (ведущего) к приемникам (ведомым) может увеличить джиттер. Лучше использовать устройства распределения часов для параллельной передачи. Длина и качество коаксиальных кабелей важны.
Более AES3
Стандарт AES11 определяет средства для передачи тактового сигнала через соединение AES3 . В этом контексте слово Clock известен как цифровой опорный звуковой сигнал (DARS).
В приложении B стандарт AES11 также описывает обычную практику передачи и приема синхросигнала в виде простого слова. Это не попытка стандартизации, приложение носит информативный характер.
Смотрите также
- Петля фазовой автоподстройки частоты
Рекомендации

What is Word Clock?
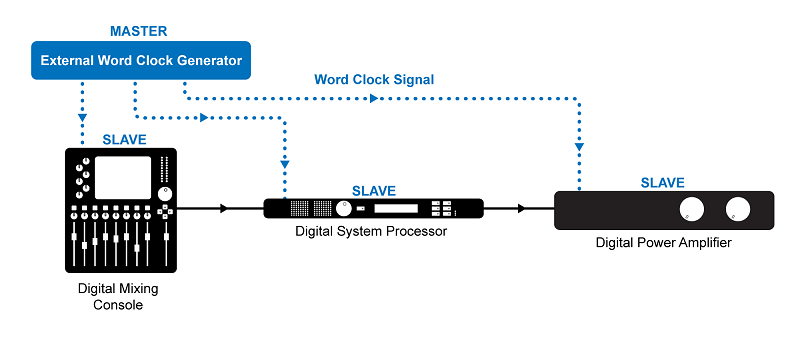
In order that two or more digital audio units such as effects items or digital preamps can easily work collectively in a group, a master device should set the so-called word clock rate and all different units (the slaves) should comply with this clock rate.
That is so because every of those digital audio units has an integrated clock generator that gives the fundamental clock rate for processing the audio information. While we’re on the topic: the act of shifting media (video and film or pc animation) should even be synchronized.
A number of units interacting, therefore, want synchronization of their base clock rates. That is performed via the word clock, the base clock signal that permits the transmission of information streams between the units.
Simply setting all related units to the identical frequency (sample rate) wouldn’t be adequate, because the smallest inaccuracies would generate noise interference and even signal failure. Fluctuations of the sign are known as jitter. An exterior word clock “tells” the units when the clock pulses begin and when they cease.
All digital units must be referenced to the same clock, in any other case, one among two things will occur, relying on the units in question:
- The receiving gadget will see incoming audio information, that isn’t referenced to its personal clock cycles, so the info is reflected. Consequence? Audio doesn’t pass.
- The receiving gadget sees incoming audio information and makes an attempt to pass audio, however attributable to differing tolerances within the clock timing, pops and clicks are heard within the audio
How Does Word Clock Work?
Word Clock is a steady square wave pulse operating at the sampling frequency. Word Clock signals are often generated by oscillators, which use quartz that resonates at an exact frequency.
The digital audio machine locks onto it and takes every maximum and minimal worth of the wave as the ‘ticking’ of the clock, marking the place every slice of audio begins and ends. It’s very important that this clock be as steady and freed from variations, known as jitter, as potential. Irregularities within the clock signal will end in much less high-frequency definition, poor stereo imaging, and dullness.
Word Clock turns into much more essential when connecting two or extra digital audio units which might be sending signals to one another. All of them should synchronize to at least one ‘Master Clock’.
Not establishing Word clock settings accurately will both end in no sign passing, or sign errors together with drop-outs, pops, clicks, or huge bursts of full-range white noise which might blow loudspeakers. Now that almost all live sound instruments share signals digitally, it’s essential to be across set-up and administer your clock.
Easy digital set-ups like ‘audio desk and remote stage box’ often handle the clock settings for you. Most digital stage boxes are constructed to only be able to be a clock slave and take the clock from the digital connection to their desk. Most desks have their clock set to their inside generator by default. Altering the sample rate in your desk’s setting from 44.1kHz to 48kHz won’t trigger any drama in this situation.
Does the Word Clock Improve the Sound?
Well originally, word clock only serves the purpose of syncing two or more digital devices together and they do not serve as a converter or have any units inside that can improve the sound.
On other hand, the word clock will help you to avoid any troubles that can come down the road if you are not using one to sync your digital gadgets. As we previously mentioned, there are some troubles that can happen if you are not using one – and that is why we can state that the word clock is important to avoid failures of the sound quality, but does not improve already good sounding signals.
In terms of getting a better and more expensive word clock for your studio will improve the stability of the signals. Again, it will not improve the signals but will provide more stable clocking which will result in stable audio without any issues – which will give you great results without any jitter.
Conclusion
This was a brief one, but certainly, we believe that we provided all the needed info on the word clocks for newcomers and experienced mixers as well. If you go back in the text above, you will be able to notice that we bolded some words and phrases that had the word digital. The reason for that is that you will need a word clock if you are running only digital devices or using digital devices with a digital mixer.
If you are going with the old-school and trusted analog signal with regular cables, then the clocking is not needed. But if you decided to use some digital devices, most certainly you will need one for your studio.
In case you are having any questions in regards to this topic, please let us know in the comment section below and we will be more than happy to provide you with some answers!
Overview
The term «Word Clock» is used to describe a one cycle per sample period «square wave» signal used for synchronization of digital audio equipment. The signal is typically “TTL level” which is nominally 5 volt p-p and is carried on 75 Ohm coaxial cable with BNC connectors.
History
Earlier digital audio systems employed a number of formats of interconnection, many of which were proprietary. Some were parallel; in which case each bit was carried on a separate conductor and a Word Clock signal was used to synchronize the timing of the transmission of each complete word of 16 bits, once per sample period.
In other systems; the left and right channel’s digital audio data was transmitted in a serial manner, in parallel with a Word Clock signal which was used to synchronize the receiver with the beginning of the transmission of each serial word.
As digital audio systems grew in complexity and the need for synchronization with video equipment arose, Word Clock was used as the system «clock» even though newer formats, such as the AES3 digital audio format were «self-clocking.»
Due to the fact that the Word Clock format is a relatively low frequency signal compared to the serial formats with an embedded bit clock, with two transitions per sample period as versus hundreds of transitions per sample period; the Word Clock signal did offer advantages in terms of jitter issues. With reasonable care to use of the proper cable and termination; cable reflections (one of the main sources of jitter) have the time to decay before the next transition occurs; which is not the case with serial formats.
Technology advanced; and as the speed of circuitry increased it became commonplace for digital systems to use high-speed serial transmission with the obvious advantage of fewer conductors needed to move the data from device to device. As Wordlength increased from 16, to 32, to 64 bits; the advantages of serial transmission became even greater. Contemporary digital audio equipment commonly uses serial data transmission internally as well as externally; and this makes it necessary to have an internal bit clock which is in the range of 64 to 128 times the sample frequency.
Due to advances in serial transmission technology and the fact that contemporary digital audio systems operate with a much higher frequency bit clock, the internal clock frequency is significantly higher than the one cycle per sample Word Clock frequency and better methods are available to deal with issues related to very high frequency transmission. The result is that many contemporary digital audio devices do at least as good a job, if not a better, sync’ing to an AES digital audio input than to a lower frequency Word Clock signal that requires generation of a synchronized much higher frequency bit clock. For these reasons, Lavry DA converters all “lock” to the incoming digital audio and use sophisticated methods of effectively “de-coupling” the internal clock used for conversion from the jitter in the incoming digital audio signal. Lavry AD converters also offer the option of synchronizing to AES sync, in addition to Word Clock.
Basics
See termination for important information on proper termination.
“Proper” termination requires two things:
- Both the sending end and the receiving end must have termination at exactly one place.
- The termination must be the correct value; which is the same as the characteristic impedance of the cable.
In (1) the sending end is generally a «given» as all Word Clock outputs have fixed internal termination by design. The important issue is termination of the receiving device(s).
There are three basic approaches to using Word Clock in systems larger than two devices:
a.) Use a Word Clock source with multiple outputs. The Word Clock source must have as many outputs as there are «slave» devices with Word Clock inputs. The Lavry Synchrony-16 is an example of this type of source.
b.) Use one Word Clock source and «chain» the same signal using BNC «T» connectors on the inputs of the receiving devices. The slave devices in middle of the chain must not have fixed internal termination so the only receiving device with termination is the last slave device in the chain. The last device can either have fixed internal termination or a BNC «T» connector on its input with a BNC terminator on the «T» opposite in the incoming Word Clock cable.
c.) A «mixed» approach. This can be a combination of (a) and (b) or a combination of Word Clock connections to synchronize all external AD converters and AES synchronization of the «master» AD converter to the digital audio interface.
Lavry Products
- Synchrony-16- Master Clock with 12 BNC Word Clock output and 4 BNC SuperClock outputs. Features Termination Diagnostic indicators for each output.
- LavryGold AD122-96 MkIII- BNC Word Clock input and output + XLR AES Sync input; BNC input is not internally terminated
- LavryBlue 4496 with MSYNC- BNC Word Clock output, BNC Sync input accepts Word Clock and AES3 Sync; not internally terminated
- LavryBlack AD10- BNC Sync In accepts Word Clock and AES3 Sync; fixed internal termination selectable between 75 and 110 Ohms
- LavryBlack AD11- BNC Word Clock output, BNC Clock input accepts Word Clock, AES3, and S-PDIF sync; fixed 75 Ohm internal termination.