We normally use WILL to speak about the future. It is always combined with another verb. Since WILL is classified as a modal verb (like can, would, could, should) it has the same characteristics: It does not change in the third person (i.e. he, she, it)
Contents
- 1 What part of grammar is the word will?
- 2 What type of word is will?
- 3 What tense is the word will?
- 4 Will be usage in English grammar?
- 5 How will Grammar?
- 6 Will or Wills?
- 7 What is my will?
- 8 Can will be an adverb?
- 9 Is Will a modal verb?
- 10 Is Will a future tense verb?
- 11 Is Would a future tense?
- 12 Will have noun examples?
- 13 Will sentences in English examples?
- 14 What is the difference will and would?
- 15 Will and will be examples?
- 16 Will modals example?
- 17 Can will be used as a verb?
- 18 Is will a verb or adverb?
- 19 How do you write your will?
- 20 Why have a will?
As detailed above, ‘will’ can be a noun or a verb. Noun usage: He felt a great will to make a pilgrimage to the Holy Land. Noun usage: Of course, man’s will is often regulated by his reason.
What type of word is will?
Will and shall are modal verbs. They are used with the base form of the main verb (They will go; I shall ask her).
What tense is the word will?
Will is used for the future, but also for the present
Many people consider will to be the present form (its past form is would), and like all present forms, it can be used to talk about the present or future.The term ‘future tenses’ is used because these forms are often used when talking about the future.
Will be usage in English grammar?
Will comes first in the verb phrase in a statement (after the subject and before another verb). It is often contracted to ‘ll in informal situations: The next Olympic Games will be in London. I’ll give you a call at about 6 o’clock.
How will Grammar?
It is always combined with another verb. Since WILL is classified as a modal verb (like can, would, could, should) it has the same characteristics: It does not change in the third person (i.e. he, she, it)
Contractions.
| Positive Contraction | |
|---|---|
| I will | I’ll |
| You will | you’ll |
| He will | he’ll |
| She will | she’ll |
Will or Wills?
A will or testament is a legal document that expresses a person’s (testator) wishes as to how their property (estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person (executor) is to manage the property until its final distribution.
What is my will?
1 : a legal declaration of a person’s wishes regarding the disposal of his or her property or estate after death especially : a written instrument legally executed by which a person makes disposition of his or her estate to take effect after death. 2 : desire, wish: such as.
Can will be an adverb?
When modifying an entire sentence, adverbs can be placed in four positions: at the beginning; at the end; after the verb to be and all auxiliary verbs: can, may, will, must, shall, and have, when have is used as an auxiliary (for example in I have been in Spain twice);
Is Will a modal verb?
These are verbs that indicate likelihood, ability, permission or obligation. Words like: can/could, may/might, will/would, shall/should and must.
Is Will a future tense verb?
There are two basic future tenses used to describe things that happen in the future.The first future tense is the future with “will.” Use the future with will to talk about an event in the future that you have just decided to do, for predictions and for promises. Examples: I think I’ll go to that party next week.
Is Would a future tense?
We use ‘would’ in future tense when we want to present a possibility of activity. Ex: I would rather go to Paris for a holiday in the month of July than London. In the above example I give two possible holiday destination to which I would like to go. We use ‘will go’ for definite future action.
Will have noun examples?
We use will have when we are looking back from a point in time in the future: By the end of the decade, scientists will have discovered a cure for influenza. I will phone at six o’clock. He will have got home by then.
Will sentences in English examples?
Will sentence example
- If the people of Boston must fight for their liberty, we will help them. 427.
- If you panic, she will be frightened. 349.
- When will supper be ready?
- Things will get better.
- If he does not take the inheritance, we will not have a home.
- One day he will know.
- He will be pleased.
- I will lead you to it.
What is the difference will and would?
The main difference between will and would is that will is used for real possibilities while would is used for imagined situations in the future.
Will and will be examples?
Will signifies future perfect tense that is an event which will complete within a timespan- I will go to my native home in summers- while will be refers to future continuous tense that is something which will take place in the near future but no specific time period can be deduced at the point-I will be going to my
Will modals example?
More Examples of “Will”
| Modal Use | Positive Forms | Negative Forms |
|---|---|---|
| will volunteering, promising | I will take care of everything for you. I will make the travel arrangements. There’s no need to worry. | I will never forget you. I will never give up the fight for freedom. |
Can will be used as a verb?
verb (used with object), willed, will·ing. to decide, bring about, or attempt to effect or bring about by an act of the will: He can walk if he wills it.verb (used without object), willed, will·ing. to exercise the will: To will is not enough, one must do.
Is will a verb or adverb?
Will and shall are modal verbs. They are used with the base form of the main verb (They will go; I shall ask her).
How do you write your will?
Writing Your Will
- Create the initial document. Start by titling the document “Last Will and Testament” and including your full legal name and address.
- Designate an executor.
- Appoint a guardian.
- Name the beneficiaries.
- Designate the assets.
- Ask witnesses to sign your will.
- Store your will in a safe place.
Why have a will?
A will allows you to direct how your belongings—such as bank balances, property, or prized possessions—should be distributed. If you have a business or investments, your will can specify who will receive those assets and when. A will also allows you to direct assets to a charity (or charities) of your choice.
Глагол will (would — в прошедшем времени) — является одним из самых употребительных глаголов в английском языке и служит в большинстве случаев для построения форм будущего времени.
Глагол will имеет только две формы: will и would. Обе формы не являются смысловыми глаголами, то есть сами по себе не обозначают какое-то действие, а поэтому вне контекста не переводятся.
Читайте также:
- Глагол в английском языке — общие сведения.
- Все времена глагола в таблицах.
Содержание:
- Вспомогательный глаголы will (would).
- Модальный глагол will (would).
- Will и Shall.
- Will или Going to?
Глагол will может использоваться как вспомогательный и модальный.
В качестве вспомогательного, глагол will/would нужен в двух случаях: для построения будущего времени и условных предложений. Глагол выполняет чисто техническую, вспомогательную функцию построения грамматической конструкции, не добавляя в предложение особого смысла или эмоционального оттенка.
1. Образование будущего времени
Вспомогательный глагол will используется для образования будущего форм времени всех видовременных форм глагола, самый простой пример — Future Simple, простое будущее время. Will ставится перед смысловым глаголом, который в простом будущем времени используется в начальной форме, без окончаний.
He will move to the capital. — Он скоро переедет в столицу.
I will come to see you tomorrow. — Я приду навестить тебя завтра.
Глагол would используется для образования формы «будущее в прошедшем» (Future in the Past).
He said that he would move to the capital soon. — Он сказал, что скоро переедет в столицу.
I said that I would come to see you. — Я сказал, что приду навестить тебя.
2. Образование условных предложений
Подробнее об условных предложениях читайте здесь: https://langformula.ru/english-grammar/conditional.
Глагол will используется в условных предложениях первого типа:
If I find the phone number, I will call him. — Если найду номер телефона, я ему позвоню.
If you help me, I will not forget it. — Если ты поможешь мне, я не забуду этого.
Глагол would нужен для построения форм сослагательного наклонения в условных предложениях второго и третьего типа:
If I were you, I would think twice. — Я бы на твоем месте подумал дважды. (второй тип)
If you had betrayed me, I would have not forgiven you. — Если бы ты меня предал, я бы не простил тебя. (третий тип)
Модальный глагол WILL
В отличие от вспомогательного, модальный глагол will добавляет к высказыванию отношение говорящего к действию. Иначе говоря, здесь речь идет не просто о будущем времени, а о придаче выражению эмоциональной окраски.
1. Решимость, уверенность в совершении действия.
I will take what is mine. — Я заберу то, что принадлежит мне.
I will not surrender. — Я не сдамся.
2. Уверенность в совершении действия другим лицом, угроза.
You will release the prisoners. — Вы отпустите пленников.
You will accept our offer. — Вы примите наше предложение.
They will give us what we want. — Они отдадут нам то, что мы хотим.
3. Вежливая просьба или вопрос, просьба в вопросительной форме.
Will you write your name here? — Не могли бы вы написать ваше имя здесь?
Will you give me a hand? — Не мог бы ты мне помочь?
Will you marry me? — Ты выйдешь за меня замуж?
Вопросы можно задать и с would — они будут звучать мягче, вежливее и с меньшей уверенностью.
Would you help me with my car? — Ты не мог бы помочь мне с моей машиной?
4. В отрицательных предложениях — упорство в совершении действия.
This man will not stop. — Этот человек все никак не остановится.
The window will not open. — Окно все никак не откроется.
5. Упорное нежелание чего-то делать в прошлом
Это значение присуще только прошедшему времени, поэтому используется would.
I told you you not to take my car but you wouldn’t listen! — Я же говорил тебе не брать мою машину, но ты же не слушал!
Why she had to go? I don’t know, she wouldn’t say. — Почему она должна была уйти? Я не знаю, она бы ни за что не сказала.
6. Повторяющееся действие в прошлом (с глаголом would)
В таких выражениях часто присутствует оттенок ностальгии.
That old actor would sit and rewatch his old movies for hours. — Этот старый актер частенько сидел и пересматривал свои старые фильмы часами.
Will и Shall
В старых учебниках английского можно прочитать, что наряду с глаголом will в качестве вспомогательного (не путать с модальным) для образования форм будущего времени в 1-ом лице единственного и множественного числа используется shall.
I shall go. — Я пойду.
We shall go. — Мы пойдем.
В современном английском языке shall как вспомогательный уже практически не используется, можно смело говорить I will go, We will go.
Однако shall используется как модальный глагол, то есть для выражения отношения говорящего к действию. Вот примеры таких случаев:
1. Вопрос с целью получить инструкцию, распоряжение (в предложениях от первого лица):
Shall I bring you water? — Мне принести тебе воды?
Shall I go? — Я пошел?
Shall I call you the manager? — Позвать вам менеджера?
2. Угроза, обещание (обращение ко второму, третьему лицу)
This is the last warning. You shall bring me the money. — Это последнее предупреждение. Ты принесешь мне деньги.
I’m fired. My boss shall regret his decision. — Я уволен. Мой босс пожалеет о своем решении.
3. Долженствование, обязательство выполнить действие (как правило, в официальных документах, договорах)
The contractor shall provide them with housing. — Подрядчик обязан обеспечить их жильем.
Примечание: У глагола shall тоже есть форма прошедшего времени — should, подробнее об употреблении should в качестве модального глагола написано в статье «Модальные глаголы в английском языке.»
Will или Going to?
Намерение совершить действие в будущем можно выразить не только с помощью will, но и используя оборот to be going to. В употреблении этих двух способов много тонких нюансов, зависящих от ситуации, контекста, интонации. Но наиболее общее правило такое:
- will — выражение уверенности в совершении действия, что-то вроде «я СДЕЛАЮ это», «это ПРОИЗОЙДЕТ».
- to be going to — запланированное, предполагаемое действие, обычно в ближайшем будущем, что-то вроде «я СОБИРАЮСЬ сделать это».
I will tell my girlfriend the truth tonight. — Сегодня вечером я СКАЖУ своей девушке всю правду.
I am goint to tell my girlfriend the truth tonight. — Сегодня вечером я собираюсь рассказать своей девушке всю правду.
Другие случаи использования will и to be going to:
| Will | To be going to |
| Решение совершить действие в будущем принято в момент речи: | Решение совершить действие в будущем принято до момента речи (запланировано): |
|---|---|
| — There’s no milk. — Молоко закончилось. — Really? I’ll go and get some. — Правда? Тогда я пойду куплю. |
— There’s no milk. — Молоко закончилось. — I know. I’m going to go and get some when this TV show finishes. — А я знаю. Я пойду куплю молока, когда передача закончится. |
| Предсказание будущих событий, основанное на мнении: | Предсказание будущих событий, основанное на том, что в настоящем есть что-то указывающее на эти события: |
| — I think the cop will spot us. — Я думаю, коп нас заметит. | — The cop has got a flashlight! He is going to spot us. — У копа фонарик! Он нас заметит. |
Здравствуйте! Меня зовут Сергей Ним, я автор этого сайта, а также книг, курсов, видеоуроков по английскому языку.
Подпишитесь на мой Телеграм-канал, чтобы узнавать о новых видео, материалах по английскому языку.
У меня также есть канал на YouTube, где я регулярно публикую свои видео.
В этой статье мы подробно разберем модальные глаголы will, would и shall. Узнаем, как с их помощью выразить вероятность события, просьбу, сожаление и ваши предпочтения.
Содержание:
- 1. Построение предложений с модальными глаголами will, would и shall
- 2. Модальный глагол will
- 3. Модальный глагол would
- 4. Модальный глагол shall
Модальные глаголы отличаются от простых глаголов тем, что не употребляются самостоятельно и не обозначают какое-то действие. Они показывают отношение говорящего к этому действию, и у них есть свои особенности в построении предложений. Перед тем как перейти к изучению случаев употребления модальных глаголов will, would и shall, предлагаем узнать, как их правильно использовать в разных типах предложений.
Построение предложений с модальными глаголами will, would и shall
Давайте посмотрим на примеры предложений с модальными глаголами will, would и shall.
Примеры утвердительных предложений:
I will love you no matter what! — Я буду любить тебя несмотря ни на что!
It would be nice to talk to him. — Было бы здорово с ним поговорить.
Примеры отрицательных предложений:
I will not tell anyone. — Я никому не расскажу.
They wouldn’t help us. — Они бы нам не помогли.
Примеры вопросительных предложений:
Will you help me tonight? — Поможешь мне сегодня вечером?
Would you fix it? — Ты починишь это?
Shall we go out tonight? — Может, пойдем погуляем вечером?
Модальный глагол will
Наверняка вам знаком глагол will как вспомогательный — он используется для образования времени Future Simple.
He will come tomorrow. — Он завтра придет.
I will not work that day. — Я не буду работать в этот день.
Will the train arrive on time? — Поезд прибудет вовремя?
Давайте рассмотрим, в каких случаях will употребляется как модальный глагол.
- Готовность сделать что-то
Мы используем will, когда нужно сказать, что кто-то готов выполнить какое-то действие сейчас или в ближайшем будущем.
I will cook dinner for you. — Я приготовлю тебе ужин.
He will redecorate the room for his son. — Он сделает косметический ремонт в комнате для сына.Используйте won’t, когда человек отказывается делать что-то или когда что-то (например, техника) не работает. На русский язык такие предложения переводятся в настоящем времени.
The car won’t start! — Машина не заводится!
I ask her out every day but she won’t agree! — Я каждый день зову ее на свидание, но она не соглашается! - Просьба, предложение
Если вам нужно о чем-то спросить или попросить, употребляйте will. Чаще всего такие вопросы адресованы второму лицу (you — ты, вы).
Will you take children to school? — Отвезешь детей в школу?
Will you stay and have lunch with us? — Останешься пообедать с нами? - Вероятность или уверенность
С помощью will можно говорить о событиях, которые вероятнее всего произойдут. Часто в подобных ситуациях используют слова probably (вероятно), certainly/definitely (точно).
He will certainly pass his math exam. — Он точно сдаст экзамен по математике.
We definitely will not invite him to our housewarming party! — Мы точно не будем приглашать его на наше новоселье! - Приказ
Еще один случай использования will — приказы, распоряжения, команды.
You will go upstairs and clean your room! — Ты поднимешься наверх и уберешь свою комнату!
I don’t care what he wants! He will not quit his job! — Мне все равно, чего он хочет! Он не уволится с работы! - Обещание, предупреждение
Если вам нужно что-то пообещать или предупредить о чем-то, вам поможет глагол will.
I will give you a ride, don’t worry. — Я тебя подвезу, не переживай.
It is raining outside. You will get wet! — На улице дождь. Ты промокнешь!
Модальный глагол would
Модальный глагол would — это прошедшая форма глагола will. Рассмотрим случаи употребления would:
- Вежливая просьба или предложение
С глаголом would ваши просьбы и предложения будут звучать более вежливо, чем с глаголом will.
Would you please bring me the report? — Ты не могла бы принести мне отчет?
Would you show me around? — Вы не могли бы показать мне город? - Готовность делать что-то в прошлом
Используйте would для описания ситуаций, в которых вы готовы были делать какие-то вещи.
She would eagerly wash the dishes and iron clothes, but she didn’t like sweeping the floor. — Она охотно мыла посуду и гладила вещи, но не любила подметать пол.
Используем would not, когда человек отказался что-то делать или когда что-то не работало в прошлом.
I know he was at home but he would not answer the phone. — Я знаю, что он был дома, но на телефон он не отвечал.
I was late because the elevator wouldn’t go this morning! I got stuck! — Я опоздал, потому что лифт никак не хотел ехать этим утром! Я застрял! - Гипотетическая ситуация
Употребляем would вместе с глаголом в инфинитивной форме без частицы to, когда не уверены в чем-то или описываем нереальную ситуацию в настоящем.
I don’t like this coffee. It would taste much better with some cream. — Мне не нравится этот кофе. Он был бы вкуснее со сливками.
Также гипотетическую ситуацию о настоящем или будущем можно выразить с помощью условных предложений второго типа.
He would travel to Asia if he had more money. — Он бы поехал в Азию, если бы у него было больше денег.
Teachers would be more motivated to work if they were paid more. — Учителя были бы более мотивированы работать, если бы им платили больше.Когда описываем нереальную ситуацию в прошлом, используем would have вместе с глаголом в третьей форме.
It is a pity you could not join us at the bar. You would have loved the place! — Жаль, что ты не смог присоединиться к нам в баре. Тебе бы очень понравилось это место!
Также гипотетическую ситуацию о прошлом можно описать с помощью условных предложений третьего типа.
I would have driven you home if you had asked me to. — Я бы подвез тебя домой, если бы ты меня попросила.
If he had spent less time playing video games and more time studying, he would have passed the exam! — Если бы он тратил меньше времени на игры и больше на учебу, он бы сдал экзамен! - Прошлые привычки
Модальный глагол would нужен для описания действий, которые кто-то регулярно выполнял в прошлом, но больше этого не делает.
Every winter we would go skiing in the Alps. — Каждую зиму мы ездили кататься на лыжах в Альпы.
He would come to play with me every evening when we were kids. — Он приходил поиграть со мной каждый вечер, когда мы были детьми. - Предпочтения
Сказать о своих предпочтениях можно с помощью выражений would like (хотел бы), would love (был бы очень рад) и would prefer (предпочел бы). Обратите внимание, если после этих выражений следует глагол, то перед ним нужно поставить частицу to.
I would like to find out more about this palace. The guidebook says it’s haunted. — Я бы хотел узнать больше об этом дворце. В путеводителе сказано, что там живут привидения.
They would love to come, but Michael works on Saturday, so it is impossible. — Они бы с радостью приехали, но Майкл работает в субботу, поэтому это невозможно.
He would prefer a room overlooking the sea. — Он бы предпочел номер с видом на море. - Сожаление, раздражение, недовольство
Когда мы сожалеем о том, что не в силах изменить, используем конструкцию I wish. Говоря о настоящем, используем конструкцию I wish I did (Past Simple), а говоря о прошлом — I wish I had done (Past Perfect). Если же мы выражаем недовольство сложившимся положением дел и при этом надеемся на изменения, употребляем I wish smb would do или if only smb would do. Сравните:
I wish I had not dropped out of university. — Жаль, что я ушел из университета. (сожаление о прошлом, которое мы не в силах изменить)
I wish I lived in London. — Жаль, что я не живу в Лондоне. (сожаление о настоящем, которое мы не в силах изменить)
I wish she would stop complaining all the time! — Мне бы очень хотелось, чтобы она перестала постоянно жаловаться! (недовольство и надежда на изменения)
If only he would stop making so much trouble. — Если бы только он перестал создавать столько неприятностей! (недовольство и надежда на изменения)
Модальный глагол shall
Раньше модальный глагол shall наравне с will служил вспомогательным глаголом для построения будущего времени и использовался с местоимениями I (я) и we (мы). Но в современном английском эта форма считается устаревшей. Для чего же нужен модальный глагол shall сейчас? У него осталась одна функция — используем shall с местоимениями I (я) и we (мы), когда предлагаем что-то или просим совет.
Shall we invite your parents for dinner? — Может, пригласим твоих родителей на ужин?
When shall we start? — Когда можем начать?
What time shall I come? — Во сколько мне прийти?
Shall I или Shall we также ставят в конце разделительных вопросов (tag questions), которые начинаются с let’s (давай/давайте), чтобы что-то предложить.
Let’s dance, shall we? — Потанцуем, хорошо?
Let’s order a pizza, shall we? — Давай закажем пиццу, хорошо?
Потренироваться в употреблении модальных глаголов will, would и shall вы можете на занятиях курса «Практическая грамматика».
Теперь вы знаете больше о функциях модальных глаголов will, would и shall в английском языке. Пройдите тест, чтобы закрепить знания на практике.
Тест по теме «Модальные глаголы will, would, shall в английском языке»
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.
Although we can use “will” in English to talk about the future, we normally use “will” to make predictions, talk about spontaneous decisions, and to make promises, offers, requests and threats. In this article, we explain how to use “will” in English with plenty of examples and links to songs that contain “will” in the lyrics.
Grammar rules for using “will” in English
“Will” is a modal auxiliary verb, meaning that there is no “s” on the third person singular conjugations. The main verb in the sentence is in the infinitive form (without “to”). The negative form is “will not” which is usually contracted in spoken English and we say “won’t”. Similarly “will” is sometimes contracted to “‘ll” when speaking.
Examples:
I’ll bring a bottle of wine.
You’ll enjoy the club!
He won’t sign the document.
She will find it difficult.
We will do our homework!
They’ll probably stay the night.
We make yes/no questions by changing the word order, “will” comes first:
Will he sign the contract?
Will they stay the night?
Won’t she find it difficult?
And we can ask open questions by placing a question word in front of the modal verb “will”:
Why won’t he sign the contract?
Where will they stay the night?
When will we do our homework?
How will she find it difficult?
When to use “will” in English:
- to express beliefs and predictions
- Spontaneous decisions
- to talk about willingness (what people want to do or are happy to do) – offers
- to make promises, requests and threats
Using “will” to express beliefs about the present or future
Although we don’t generally use “will” to talk about plans for the future, we can use it to talk about beliefs or predictions.
Examples:
(Doorbell rings) “That will be Jeremy, I invited him for coffee.” (belief – present)
I think it’ll rain this weekend. (prediction)
I’m sure she’ll be a highly acclaimed lawyer one day. (belief and prediction)
I don’t think you will like him. (negative prediction)
Notice that for negative predictions, we make the “think” negative, not the “will”.
Song: Gloria Gaynor’s I will survive uses “will” in this sense. A more modern song with “will” to express beliefs and predictions is “Can’t feel my face” by The Weekend.
We use “will” when we are making spontaneous decisions
We use “will” when we are making spontaneous decisions
In a restaurant when the waiter or waitress asks you what you would like, you normally make a decision at more or less the time of speaking, for this reason we use the expression “I’ll have…” For example:
I’ll have the fish please,
I’ll just have a coffee, I’m not hungry.
We’ll share the starter selection
I’ll have what Phill’s having (a TV show about food)
Of course, we can make spontaneous decisions in other situations such as:
Someone is calling on the other line, I’ll have to call you back.
I’m not sure when I’m free, I’ll let you know by tomorrow.
I’m cold, I think I’ll turn the heating on.
How to use “will” to express willingness – offers
The question form “Will you…” is asking about willingness.
Willingness is a complicated word to explain, however, it is clear that it is derived from the word “will”. If I want to do something, if I am happy to volunteer to do something, I am willing to help. So when I speak to express that I am willing to help or to offer to do something I use “will”.
Examples:
Don’t worry, I’ll go shopping tomorrow.
I’ll help you make dinner!
(Doorbell rings) “ I’ll get it!”
I’ll talk to him if you like
David will finish painting the garage for you.
All of the above examples are offers to help, even the last sentence, where David is being volunteered by someone else.
“Will not” or “won’t” mean to refuse to do something
In the same way that we can show willingness by using “will”, we can show the opposite attitude, a refusal to help with “will not” or “won’t”. Interestingly, this applies to animals and inanimate objects too.
I can’t go with you on the trip today, my car won’t start.
The donkey won’t budge.
She won’t tell you her secrets.
I won’t allow this to continue.
The governors will not permit smoking on school property.
Why won’t you come with me?
The question form “Will you…” is asking about willingness
The famous “Will you marry me?” is a question that asks if you want to marry me. Here are some other examples:
Will you take your dog on holiday?
Will they put their house on the market?
Will Gail teach business English?
Song: Lana Del Rey’s Young and Beautiful uses “Will you” in this sense.
We use “will” to make promises
We use “will” to make promises
We often use words like “I promise, I swear, I assure you… ” to emphasise a promise about the future with will. Here are some examples:
I swear I’ll never cheat on you again.
I assure you we will do our best to get to the bottom of this.
I promise, my dog won’t pee in your garden again
Songs: Calvin Harris, Sam Smith’s – Promises uses “will” in the chorus – “I’ll give you everything”. Additionally, Jess Glynne promises “You’ll never be alone, I’ll be there for you”.
We use “Will you … ?” to make requests:
With this type of question, we are asking if someone is willing to carry out the request.
Examples:
Will you help me on this project, please?
Will you sign this petition?
In reality, we use “Will you…” and “Would you…” to express that we are annoyed and we want someone to behave in a certain way:
Will you please be quiet!
Would you not eat my pants! (hilarious video!)
Will you please just sign the form so that we can all go home!
Would you please get your dog to stop barking!
Song: Will you be there by Michael Jackson is a simple request.
Using “will” to make a threat or give a warning
Admittedly, Peaky Blinders is not the best Netflix show to learn English with, but this clip where Grace warns Thomas Shelby that her song will break his heart is worth watching!
“OK, but I warn you, it’ll break your heart”
Meat Loaf threatens in one of his blasting ballads:
“In every way, I want you out of my life, but I’ll kill you if you don’t come back!”
Hypotheses and conditionals
We use will in first conditional sentences to say what will happen depending on the first clause:
If it rains tomorrow I’ll cancel the trip to the beach.
We’ll never finish the project if Charlotte doesn’t jump on board.
You won’t get promoted unless you stick to the rules.
So we have gone through all the main points you need to know about how to use “will” in English, one final song: Will you by Hazel O’Connor has many examples of “will” in it! In fact, so many that if you can figure out which use of “Will” in English each example is – you will be a champion of this subject! You can find more examples of this grammar topic in our Business English post: 5 ways to stop employees procrastinating in the workplace
WILL – English Grammar Lesson
In general, WILL is used to talk about the future.
- I will help you tomorrow. (Tomorrow is in the future)
- I think we will win on Saturday. (Saturday is a day in the future)
- We will see more uses of the word WILL in a moment. (It is coming in the near future)
Let’s look at how to create sentences and questions with WILL.
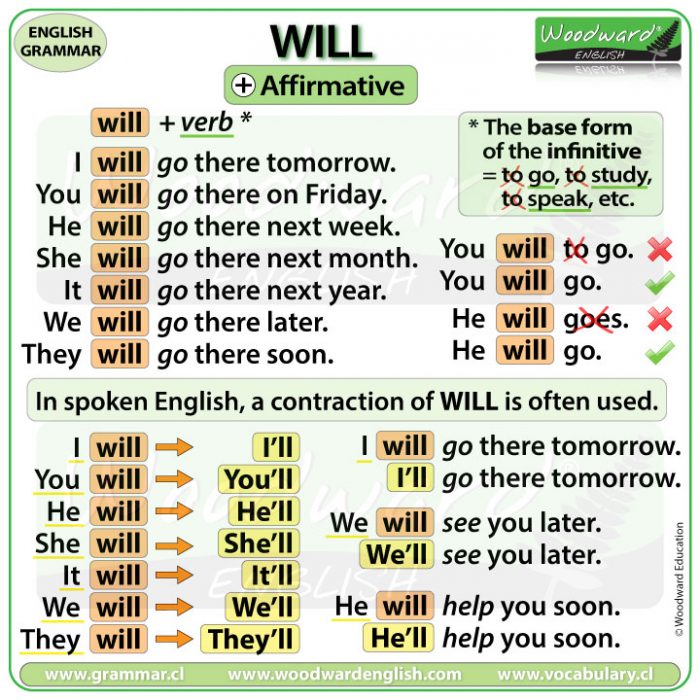
Affirmative Sentences with WILL
WILL is a modal verb. This means it follows the same rules as the other modal verbs.
It only has one form for each subject:
- I will
- You will
- He will
- She will
- It will
- We will
- They will
The word WILL doesn’t change.
You cannot say: He wills … ❌ or She wills … ❌
No! … There is no S at the end of WILL.
He will … ✅ She will … ✅
After WILL we have the base form of the infinitive.
This is the Infinitive without TO at the beginning.
Instead of TO GO, just GO.
Instead of TO STUDY, just STUDY.
Instead of TO SPEAK, just SPEAK is used.
We don’t say: I will TO go. ❌
No, this is NOT correct.
We use the base form of TO GO which is without TO.
You say: You will go. ✅
We don’t say: He will goes. ❌
No, this is NOT correct.
We have the infinitive (TO GO) without TO at the beginning.
You say: He will go. ✅
Let’s look at some example sentences:
- I will go there tomorrow.
- You will go there on Friday.
- He will go there next week.
- She will go there next month.
- It will go there next year.
- We will go there later.
- They will go there soon.
You can see that in these sentences GO is used after WILL for all subjects.
Contractions with WILL
In spoken English, a contraction of WILL is often used.
- I will ➡️ I’ll
- you will ➡️ you’ll
- he will ➡️ he’ll
- she will ➡️ she’ll
- it will ➡️ it’ll
- we will ➡️ we’ll
- they will ➡️ they’ll
Example sentences with contractions:
- I will go there tomorrow. ➡️ I’ll go there tomorrow.
- We will see you later. ➡️ We’ll see you later.
- He will help you soon. ➡️ He’ll help you soon.
Negative Sentences with WILL
To create a negative sentence with WILL, we just add NOT directly after it.
I will (affirmative) becomes I will not (negative)
Let’s look at the rest of the subjects.
Affirmative ➡️ Negative
- I will ➡️ I will not
- You will ➡️ You will not
- He will ➡️ He will not
- She will ➡️ She will not
- It will ➡️ It will not
- We will ➡️ We will not
- They will ➡️ They will not
BUT, in spoken English, the contraction WON’T is used more than WILL NOT.
- I will not = I won’t
- You will not = You won’t
- He will not = He won’t
- She will not = She won’t
- It will not = It won’t
- We will not = We won’t
- They will not = They won’t
Compare these sentences:
- I will be ready in five minutes. (affirmative)
- I will not be ready in five minutes. (negative)
- I won’t be ready in five minutes. (negative – more in spoken English)
- She will arrive on time. (affirmative)
- She will not arrive on time. (negative)
- She won’t arrive on time. (negative – more in spoken English)
See our lesson about the difference between ON TIME and IN TIME.
More examples of negative sentences using WON’T
- He won’t listen to me.
- She won’t find it funny.
- I’m sorry I won’t be at your party.
- It won’t hurt if you stay calm.
- We won’t finish this by the end of the day.
- They won’t accept the offer.
- Don’t worry, I won’t tell anyone.
Questions with WILL
Just like with other modal verbs, we change the order of the SUBJECT and WILL to make it a question.
- You will go there tomorrow.
This is an affirmative sentence.
In order to make it a question, we change the order of the subject (YOU) and WILL. It becomes:
- Will you go there tomorrow?
More examples:
- They will be busy. (affirmative)
- Will they be busy? (question)
- He will visit us. (affirmative)
- Will he visit us? (question)
- You will tell us the truth. (affirmative)
- Will you tell us the truth? (question)
How can you answer a question with WILL?
For short answers, you can use: Yes, I will … OR … No, I won’t.
BUT, we don’t use a contraction with affirmative short answers.
- Will you tell us the truth?
- Yes, I’ll. ❌ (This is NOT correct)
- Yes, I will. ✅ (This is correct)
Another example:
- Will you come with me? Yes, I will. / No, I won’t.
(You cannot say: Yes, I’ll. ❌ – We don’t use a contraction with affirmative short answers.)
Look at this question:
- Will he visit us?
A possible answer is: Yes, he will
BUT, if we want to know the time it will happen, then we can use the question word WHEN at the beginning:
- When will he visit us?
Since this is not a yes/no question, our answer needs to be different.
One possible response is: On Friday.
This means: He will visit us on Friday.
We don’t need to say the whole sentence and it would sound repetitive.
Now look at this question:
- Do you think she will get angry?
Notice the order of subject + will. (Do you think SHE WILL get angry?)
That is because the first part of the sentence “Do you…?” makes it a question so we don’t change the order of the subject and will.
You can answer: Yes, I do … or No, I don’t
BUT, our short answer can also contain WILL if you want to use SHE as the subject:
Yes, she will / No, she won’t.
Question Tags with WILL
WILL and WON’T can also be used in question tags.
- You won’t tell Mum, will you?
- He will arrive on time, won’t he?
See our lesson about Question Tags in English.
In our next lesson, we will look at the different uses of WILL and will also compare WILL vs. GOING TO. (Coming next week)
I hope you found this grammar lesson about WILL useful. If you did, please let other people know about it.