Population vs Sample – the difference
The concept of population vs sample is important for every researcher to comprehend.
Understanding the difference between a given population and a sample is easy. You must remember one fundamental law of statistics: A sample is always a smaller group (subset) within the population.
In market research and statistics, every study has an essential inquiry at hand. Observation and experiment of a population sample size determine this inquiry’s result. It is done to derive insights that explain a phenomenon within the whole population.
What is the ‘population’ in market research?
Definition: Population in research is a complete set of elements with a standard parameter between them.
We are all aware of what the word ‘population’ means daily. Frequently it is used to describe the human population or the total number of people living in a geographic area of our country or state.
The ‘population’ in research doesn’t necessarily have to be human. It can be any parameter of data that possesses a common trait.
Example: The total number of ‘Pet’ Stores on Sunset Boulevard in Los Angeles, California.
What is a sample in market research?
Definition: A sample is a smaller part of the whole, i.e., a subset of the entire population. It is representative of the population in a study. When conducting surveys, the sample is the members of the population who are invited to participate in the survey. Hence said, a sample is a subgroup or subset within the population. This sample can be studied to investigate the characteristics or behavior of the entire population data.
Data samples are created using various research methods like probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Sampling methods vary according to research types, based on the kind of inquiry and the quality of information required.
Example: A cat food company would like to know all the pet stores where it can sell its canned fish. The company has population data on the total number of pet stores on Sunset Boulevard.
This pet food manufacturer can now create an online research sample by only selecting the pet stores that sell cat food. The data characteristics are studied. The results are displayed in statistics and reports analyzed for business insights. Using data from the sample, the company can uncover ways to grow its business into the total population of pet stores.
Here are the most common sampling techniques:
Sampling techniques are broadly classified into two types:
Probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
-
Probability sampling
Samples were chosen based on probability theory.
a. Simple random sampling
b. Cluster sampling
c. Systematic sampling
d. Stratified random sampling -
Non-Probability sampling
Samples were chosen based on the researcher’s subjective judgment.
a. Convenience sampling
b. Judgemental or Purposive sampling
c. Snowball sampling
d. Quota sampling
How to choose high-quality samples:
Although we ensure that all the population members have an equal chance to be included in the sample, it does not mean that the samples derived from a particular population satisfying the criterion will be alike. They will still vary from one another. This variation can be slight or substantial.
For example, a set of samples of healthy people’s body temperatures will show less difference. But the difference in these people’s systolic blood pressure would be sizeable.
It is also observed that the data’s accuracy depends on the sample size. The accuracy is much lesser with a smaller sample size than using a larger study sample. Thus, if two, three, or more samples are derived from a population, the bigger they are, the more they resemble each other.
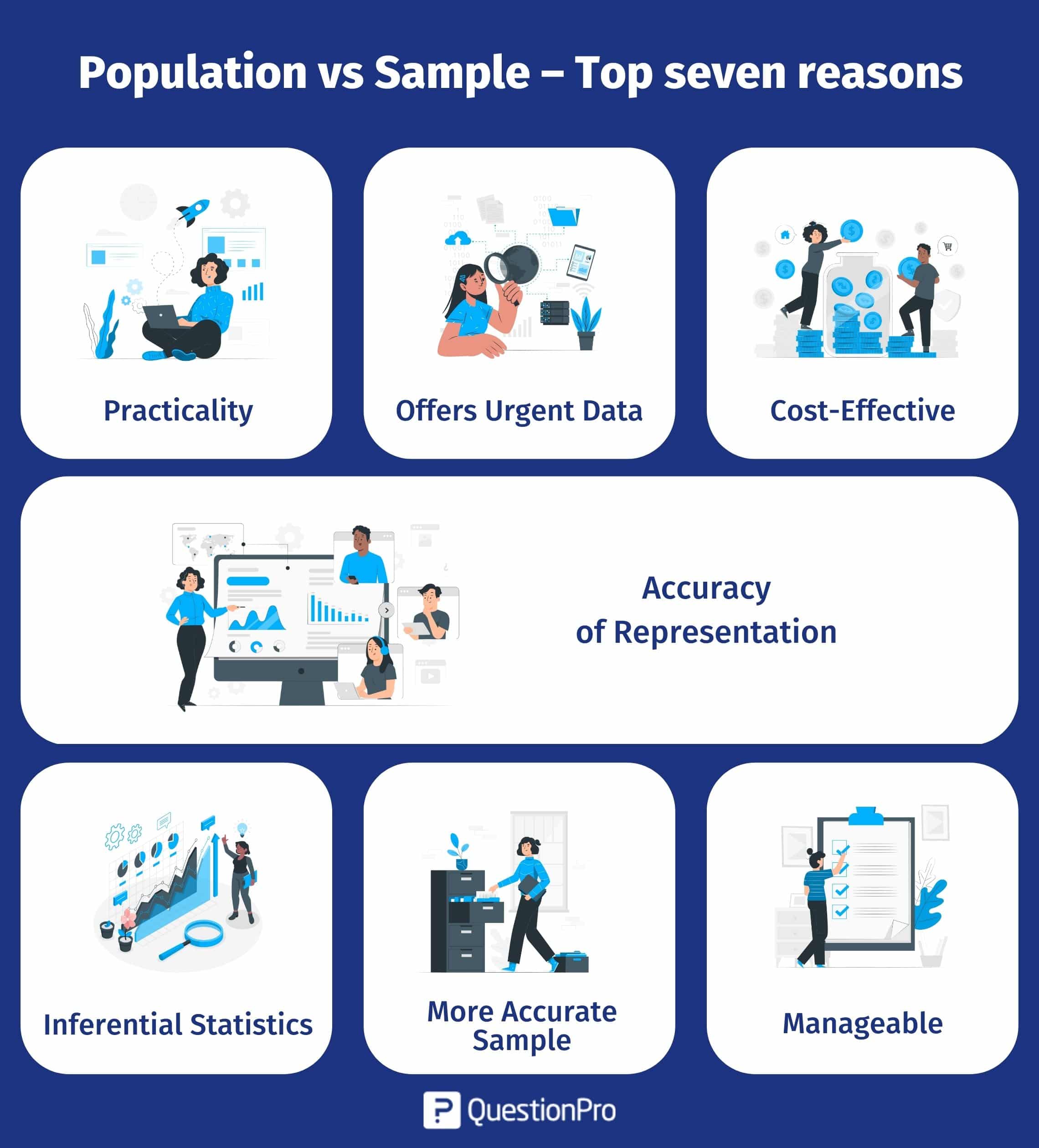
Population vs Sample – top seven reasons to choose a sample from a given population
Sampling is a must to conduct any research study. Here are the top seven reasons to use a sample:
- Practicality: In most cases, a population can be too large to collect accurate data – which is not practical. Samples allow researchers to collect data that can be analyzed to provide insights into the entire population. Samples offer a representation of the whole population if sampled accordingly.
- Offers urgent data: When it comes to research, the amount of time available can be a defining factor for a study. A sample provides a smaller set of the population for review, delivering data useful to represent the whole population. Surveying a smaller sample, as opposed to the entire population, can save precious time for researchers and offer urgent data.
- Cost-effective: The cost of conducting research is often a parameter for the study. Researchers must do their best with the resources they have to conduct a survey and gain accurate insights. Surveying a representative population sample is cost-effective as it requires fewer resources – like computers, researchers, interviewers, servers, and data collection centers.
- Accuracy of representation: Depending on the sampling method, research conducted on a sample can be accurate with lesser non-response bias than if performed by the census. A sample that is selected using the non-probability method is an accurate representation of the population. This data collected can be used to gather insight into the whole community.
- Inferential statistics: Inferential statistics is a process by which representative data is used to infer insights about the entire population. Inferential statistics can only be obtained using data samples. Data collected from a sample represents the whole population.
- A sample is more accurate than a census: A census of an entire population only sometimes offers accurate data due to errors such as inconsistent responses or non-response bias. A carefully obtained sample, however, does away with this sampling bias and provides more accurate data – that adequately represents the population.
- Manageable: Sometimes, collecting an entire data population is near impossible as some populations are too challenging to come by. In this case, a sample can represent the study as it is feasible, manageable, and accessible.
Select your respondents
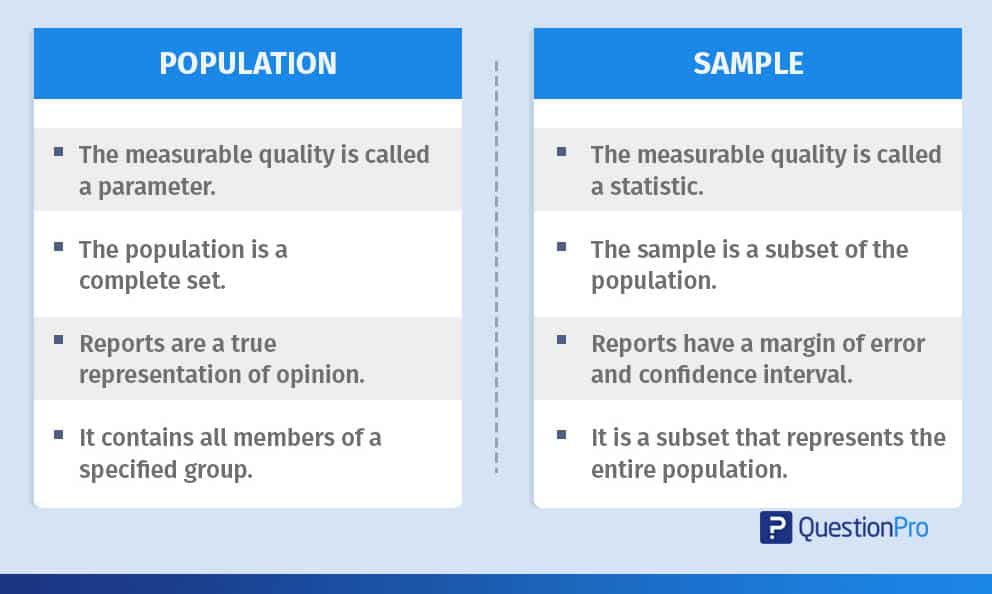
Population vs Sample – What is the difference?
Usually, a population sample is used in research, as it is easier and cost-effective to process a smaller subset of the population rather than the entire group.
In this table, we can take a closer look at the difference between the sample and population:
|
Population |
Sample |
| The measurable characteristic of the population, like the mean or standard deviation, is known as the parameter. | The measurable characteristic of the sample is called a statistic. |
| Population data is a whole and complete set. | The sample is a subset of the population that is derived using sampling. |
| A survey of an entire population is accurate and more precise with no margin of error except human inaccuracy in responses. However, this may only sometimes be possible. | A population sample survey bears accurate results only after further factoring in the margin of error and confidence interval. |
| The parameter of the population is a numerical or measurable element that defines the system of the set. | The statistic is the descriptive component of the sample found by using sample mean or sample proportion. |
Conclusion
Although Population and Sample are two different terms, they both are related to each other. The population is used to draw samples. Making statistical inferences about the population is the primary purpose of the sample. Without the population, samples can’t exist. The better the quality of the sample, the higher the level of accuracy of generalization.
Right sampling is essential to conduct insightful market research. Explore quality samples with QuestionPro Audience.
Asked by: Mrs. Clarabelle Ebert IV
Score: 4.2/5
(74 votes)
Population typically refers the number of people in a single area whether it be a city or town, region, country, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction by a process called a census.
What does the word population mean?
A population is a distinct group of individuals, whether that group comprises a nation or a group of people with a common characteristic. In statistics, a population is the pool of individuals from which a statistical sample is drawn for a study. … Only an analysis of an entire population would have no standard error.
What does population mean example?
The population mean is an average of a group characteristic. The group could be a person, item, or thing, like “all the people living in the United States” or “all dog owners in Georgia”. A characteristic is just an item of interest. For example: … Dogs seen in a certain veterinary practice weigh, on average, 38 pounds.
What is a population simple definition?
1a : the whole number of people or inhabitants in a country or region. b : the total of individuals occupying an area or making up a whole.
What does population mean in science?
A population is defined as a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. … Scientists study a population by examining how individuals in that population interact with each other and how the population as a whole interacts with its environment.
20 related questions found
What are the types of population?
There are different types of population.
…
Population
- Finite Population.
- Infinite Population.
- Existent Population.
- Hypothetical Population.
What is the world population as of 2020?
By contrast, the trend is towards a graying population in Europe. The 2020 World Population Data Sheet indicates that world population is projected to increase from 7.8 billion in 2020 to 9.9 billion by 2050.
What is population and their types?
A discrete assemblage of entities with identifiable characteristics such as people, animals with the objective of analysis and data collection is called a population. … A metapopulation is when individuals in local populations scatter between other local populations.
What is the root word of population?
Population means the number of people in a geographic area. … The word population––and also the word populace––derive from the Latin populus, «people.» To remember that population is connected to people, think about the words popular, populist, pop culture, pop music.
What are characteristics of population?
Demography is the study of a population, the total number of people or organisms in a given area. Understanding how population characteristics such as size, spatial distribution, age structure, or the birth and death rates change over time can help scientists or governments make decisions.
What is the difference between a population mean and a sample mean?
Sample mean is the arithmetic mean of random sample values drawn from the population. Population mean represents the actual mean of the whole population.
Which of these is an example of a population?
All of the students in your classroom would be an example of a population. A population can be defined as a specific species within a determined…
What is the difference between a sample mean and the population mean called?
The absolute value of the difference between the sample mean, x̄, and the population mean, μ, written |x̄ − μ|, is called the sampling error. … The standard deviation of a sampling distribution is called the standard error.
Is Quad Greek or Latin?
The root -quad- comes from Latin, where it has the meaning «four, fourth.» This meaning is found in such words as: quad, quadrangle, quadrant, quadruped, quadruplet.
What is another name for population groups?
Another name for population groups is target groups. Human services organizations typically fall under one of two financial structures: for-profit and nonprofit.
What is the important of population?
The population is one of the important factors which helps to balance the environment, the population should in a balance with the means and resources. If the population will be balanced, then all the needs and demand of the people can be easily fulfilled, which helps to preserve the environment of the country.
How does overpopulation happen?
Overpopulation or overabundance occurs when a species’ population becomes so large that it is deemed exceeding the carrying capacity and must be actively intervened. It can result from an increase in births (fertility rate), a decline in the mortality rate, an increase in immigration, or a depletion of resources.
How is population important to a country?
Population data is essential for planning purposes. Any country needs to know the size and composition of its population – around age and sex structure, among other factors. … That helps to plan how many schools, clinics, hospitals and jobs a country needs.
What is the largest race in the world?
The world’s largest ethnic group is Han Chinese, with Mandarin being the world’s most spoken language in terms of native speakers. The world’s population is predominantly urban and suburban, and there has been significant migration toward cities and urban centres.
How Many People Can Earth Support?
The average American uses about 9.7 hectares. These data alone suggest the Earth can support at most one-fifth of the present population, 1.5 billion people, at an American standard of living. Water is vital.
How many females are in the world 2020?
Gender ratio in the World
The population of females in the world is estimated at 3,904,727,342 or 3,905 million or 3.905 billion, representing 49.58% of the world population.
What are the 5 stages of population pyramid?
There are five stages of population pyramids: high fluctuating, early expanding, late expanding, low fluctuating, and natural decrease.
How do you control a population?
The recommendations are: 1) coordinate employment, food rationing, salaries, bonuses, health treatment, age and condition of retirement, preschool care and education with family planning programs, maintain the elderly’s living standard, and give preference to childless and single child families; 2) educate people about …
What defines overpopulation?
Overpopulation is the state whereby the human population rises to an extent exceeding the carrying capacity of the ecological setting. In an overpopulated environment, the numbers of people might be more than the available essential materials for survival such as transport, water, shelter, food or social amenities.
What does the sample mean tell us?
The sample mean from a group of observations is an estimate of the population mean . … Each of these variables has the distribution of the population, with mean and standard deviation . The sample mean is defined to be .
- W
- Population
- World Population
Current World Population
retrieving data…
Today
Population Growth today
…
This year
Population Growth this year
…
World Population: Past, Present, and Future
(move and expand the bar at the bottom of the chart to navigate through time)
The chart above illustrates how world population has changed throughout history. View the full tabulated data.
At the dawn of agriculture, about 8000 B.C., the population of the world was approximately 5 million. Over the 8,000-year period up to 1 A.D. it grew to 200 million (some estimate 300 million or even 600, suggesting how imprecise population estimates of early historical periods can be), with a growth rate of under 0.05% per year.
A tremendous change occurred with the industrial revolution: whereas it had taken all of human history until around 1800 for world population to reach one billion, the second billion was achieved in only 130 years (1930), the third billion in 30 years (1960), the fourth billion in 15 years (1974), and the fifth billion in only 13 years (1987).
- During the 20th century alone, the population in the world has grown from 1.65 billion to 6 billion.
- In 1970, there were roughly half as many people in the world as there are now.
- Because of declining growth rates, it will now take over 200 years to double again.
Wonder how big was the world’s population when you were born?
Check out this simple wizard or this more elaborated one to find out.
Sources:
- World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision — United Nations Population Division
- The World at Six Billion, World Population, Year 0 to near stabilization [Pdf file] — United Nations Population Division
Growth Rate
Population in the world is, as of 2022, growing at a rate of around 0.84% per year (down from 1.05% in 2020, 1.08% in 2019, 1.10% in 2018, and 1.12% in 2017). The current population increase is estimated at 67 million people per year.
Annual growth rate reached its peak in the late 1960s, when it was at around 2%. The rate of increase has nearly halved since then, and will continue to decline in the coming years.
World population will therefore continue to grow in the 21st century, but at a much slower rate compared to the recent past. World population has doubled (100% increase) in 40 years from 1959 (3 billion) to 1999 (6 billion). It is now estimated that it will take another nearly 40 years to increase by another 50% to become 9 billion by 2037.
The latest world population projections indicate that world population will reach 10 billion persons in the year 2057.
World Population (2020 and historical)
View the complete population historical table
| Year (July 1) |
Population | Yearly % Change |
Yearly Change |
Median Age |
Fertility Rate |
Density (P/Km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 7,794,798,739 | 1.05 % | 81,330,639 | 30.9 | 2.47 | 52 |
| 2019 | 7,713,468,100 | 1.08 % | 82,377,060 | 29.8 | 2.51 | 52 |
| 2018 | 7,631,091,040 | 1.10 % | 83,232,115 | 29.8 | 2.51 | 51 |
| 2017 | 7,547,858,925 | 1.12 % | 83,836,876 | 29.8 | 2.51 | 51 |
| 2016 | 7,464,022,049 | 1.14 % | 84,224,910 | 29.8 | 2.51 | 50 |
| 2015 | 7,379,797,139 | 1.19 % | 84,594,707 | 30 | 2.52 | 50 |
| 2010 | 6,956,823,603 | 1.24 % | 82,983,315 | 28 | 2.58 | 47 |
| 2005 | 6,541,907,027 | 1.26 % | 79,682,641 | 27 | 2.65 | 44 |
| 2000 | 6,143,493,823 | 1.35 % | 79,856,169 | 26 | 2.78 | 41 |
| 1995 | 5,744,212,979 | 1.52 % | 83,396,384 | 25 | 3.01 | 39 |
| 1990 | 5,327,231,061 | 1.81 % | 91,261,864 | 24 | 3.44 | 36 |
| 1985 | 4,870,921,740 | 1.79 % | 82,583,645 | 23 | 3.59 | 33 |
| 1980 | 4,458,003,514 | 1.79 % | 75,704,582 | 23 | 3.86 | 30 |
| 1975 | 4,079,480,606 | 1.97 % | 75,808,712 | 22 | 4.47 | 27 |
| 1970 | 3,700,437,046 | 2.07 % | 72,170,690 | 22 | 4.93 | 25 |
| 1965 | 3,339,583,597 | 1.93 % | 60,926,770 | 22 | 5.02 | 22 |
| 1960 | 3,034,949,748 | 1.82 % | 52,385,962 | 23 | 4.90 | 20 |
| 1955 | 2,773,019,936 | 1.80 % | 47,317,757 | 23 | 4.97 | 19 |
World Population Forecast (2020-2050)
View population projections for all years (up to 2100)
| Year (July 1) |
Population | Yearly % Change |
Yearly Change |
Median Age |
Fertility Rate |
Density (P/Km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 7,794,798,739 | 1.10 % | 83,000,320 | 31 | 2.47 | 52 |
| 2025 | 8,184,437,460 | 0.98 % | 77,927,744 | 32 | 2.54 | 55 |
| 2030 | 8,548,487,400 | 0.87 % | 72,809,988 | 33 | 2.62 | 57 |
| 2035 | 8,887,524,213 | 0.78 % | 67,807,363 | 34 | 2.70 | 60 |
| 2040 | 9,198,847,240 | 0.69 % | 62,264,605 | 35 | 2.77 | 62 |
| 2045 | 9,481,803,274 | 0.61 % | 56,591,207 | 35 | 2.85 | 64 |
| 2050 | 9,735,033,990 | 0.53 % | 50,646,143 | 36 | 2.95 | 65 |
World Population Milestones
10 Billion (2058)
The United Nations projects world population to reach 10 billion in the year 2058.
9 Billion (2037)
World population is expected to reach 9 billion in the year 2037.
8 Billion (2022)
World population has reached 8 billion people on November 15, 2022 according to the United Nations.
7 Billion (2010)
According to the latest revision by the United Nations (released in 2022), world population reached 7 Billion in late 2010 (this was previously estimated as occurring on October 31, 2011). The US Census Bureau made a lower estimate, for which the 7 billion mark was only reached on March 12, 2012.
6 Billion (1998)
According to the latest revision by the United Nations (released in 2022), the 6 billion figure was reached towards the end of 1998 (this was previously estimated as occurring on October 12, 1999, celebrated as the Day of 6 Billion). According to the U.S. Census Bureau instead, the six billion milestone was reached on July 22, 1999, at about 3:49 AM GMT. Yet, according to the U.S. Census, the date and time of when 6 billion was reached will probably change because the already uncertain estimates are constantly being updated.
Previous Milestones
- 5 Billion: 1987
- 4 Billion: 1974
- 3 Billion: 1960
- 2 Billion: 1930
- 1 Billion: 1804
Summary Table
1 — 1804 (1803 years): 0.2 to 1 bil.
1804 — 2022 (218 years): from 1 billion to 8 billion
| Year |
1 |
1000 |
1500 |
1650 |
1750 |
1804 |
1850 |
1900 |
1930 |
1950 |
1960 |
1974 |
1980 |
1987 |
1998 |
2010 |
2022 |
2029 |
2037 |
2046 |
2058 |
2100 |
| Population |
0.2 |
0.275 |
0.45 |
0.5 |
0.7 |
1 |
1.2 |
1.6 |
2 |
2.55 |
3 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
8.5 |
9 |
9.5 |
10 |
10.3 |
World Population by Region
| # | Region | Population (2020) |
Yearly Change |
Net Change |
Density (P/Km²) |
Land Area (Km²) |
Migrants (net) |
Fert. Rate |
Med. Age |
Urban Pop % |
World Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asia | 4,641,054,775 | 0.86 % | 39,683,577 | 150 | 31,033,131 | -1,729,112 | 2.2 | 32 | 0 % | 59.5 % |
| 2 | Africa | 1,340,598,147 | 2.49 % | 32,533,952 | 45 | 29,648,481 | -463,024 | 4.4 | 20 | 0 % | 17.2 % |
| 3 | Europe | 747,636,026 | 0.06 % | 453,275 | 34 | 22,134,900 | 1,361,011 | 1.6 | 43 | 0 % | 9.6 % |
| 4 | Latin America and the Caribbean | 653,962,331 | 0.9 % | 5,841,374 | 32 | 20,139,378 | -521,499 | 2 | 31 | 0 % | 8.4 % |
| 5 | Northern America | 368,869,647 | 0.62 % | 2,268,683 | 20 | 18,651,660 | 1,196,400 | 1.8 | 39 | 0 % | 4.7 % |
| 6 | Oceania | 42,677,813 | 1.31 % | 549,778 | 5 | 8,486,460 | 156,226 | 2.4 | 33 | 0 % | 0.5 % |
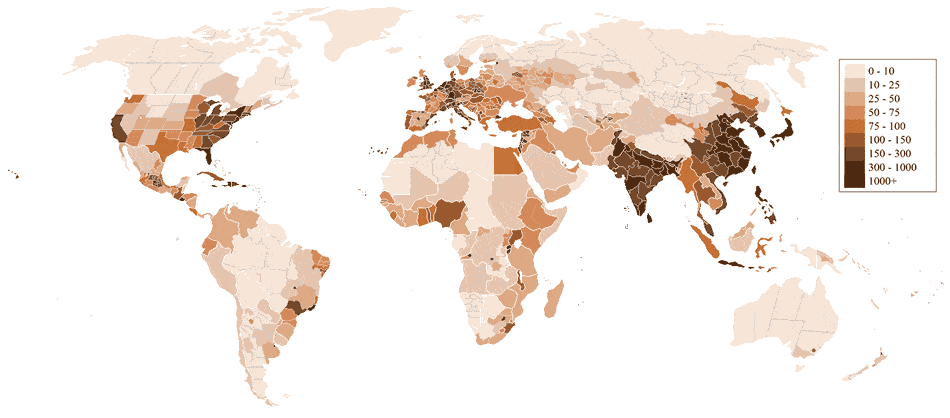
World Population Density (people/km2)
Population density map of the world showing not only countries but also many subdivisions (regions, states, provinces). See also: World Map
Courtesy of Junuxx at en.wikipedia [CC-BY-SA-3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons
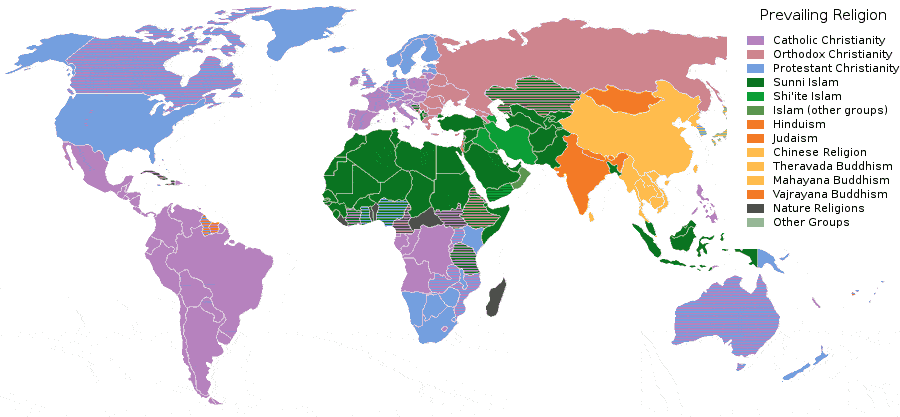
World Population by Religion
According to a recent study (based on the 2010 world population of 6.9 billion) by The Pew Forum, there are:
- 2,173,180,000 Christians (31% of world population), of which 50% are Catholic, 37% Protestant, 12% Orthodox, and 1% other.
- 1,598,510,000 Muslims (23%), of which 87-90% are Sunnis, 10-13% Shia.
- 1,126,500,000 No Religion affiliation (16%): atheists, agnostics and people who
do not identify with any particular religion. One-in-five people (20%) in the United States are religiously unaffiliated. - 1,033,080,000 Hindus (15%), the overwhelming majority (94%) of which live in India.
- 487,540,000 Buddhists (7%), of which half live in China.
- 405,120,000 Folk Religionists (6%): faiths that are closely associated with a particular
group of people, ethnicity or tribe. - 58,110,000 Other Religions (1%): Baha’i faith, Taoism,
Jainism, Shintoism, Sikhism, Tenrikyo, Wicca, Zoroastrianism and many others. - 13,850,000 Jews (0.2%), four-fifths of which live in two countries: United States (41%) and Israel (41%).
World Population by Country
| # | Country (or dependency) | Population (2020) |
Yearly Change |
Net Change |
Density (P/Km²) |
Land Area (Km²) |
Migrants (net) |
Fert. Rate |
Med. Age |
Urban Pop % |
World Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 1,439,323,776 | 0.39 % | 5,540,090 | 153 | 9,388,211 | -348,399 | 1.69 | 38 | 60.8 % | 18.5 % |
| 2 | India | 1,380,004,385 | 0.99 % | 13,586,631 | 464 | 2,973,190 | -532,687 | 2.2402 | 28 | 35 % | 17.7 % |
| 3 | United States | 331,002,651 | 0.59 % | 1,937,734 | 36 | 9,147,420 | 954,806 | 1.7764 | 38 | 82.8 % | 4.2 % |
| 4 | Indonesia | 273,523,615 | 1.07 % | 2,898,047 | 151 | 1,811,570 | -98,955 | 2.3195 | 30 | 56.4 % | 3.5 % |
| 5 | Pakistan | 220,892,340 | 2 % | 4,327,022 | 287 | 770,880 | -233,379 | 3.55 | 23 | 35.1 % | 2.8 % |
| 6 | Brazil | 212,559,417 | 0.72 % | 1,509,890 | 25 | 8,358,140 | 21,200 | 1.74 | 33 | 87.6 % | 2.7 % |
| 7 | Nigeria | 206,139,589 | 2.58 % | 5,175,990 | 226 | 910,770 | -60,000 | 5.4168 | 18 | 52 % | 2.6 % |
| 8 | Bangladesh | 164,689,383 | 1.01 % | 1,643,222 | 1,265 | 130,170 | -369,501 | 2.052 | 28 | 39.4 % | 2.1 % |
| 9 | Russia | 145,934,462 | 0.04 % | 62,206 | 9 | 16,376,870 | 182,456 | 1.8205 | 40 | 73.7 % | 1.9 % |
| 10 | Mexico | 128,932,753 | 1.06 % | 1,357,224 | 66 | 1,943,950 | -60,000 | 2.14 | 29 | 83.8 % | 1.7 % |
| 11 | Japan | 126,476,461 | -0.3 % | -383,840 | 347 | 364,555 | 71,560 | 1.3697 | 48 | 91.8 % | 1.6 % |
| 12 | Ethiopia | 114,963,588 | 2.57 % | 2,884,858 | 115 | 1,000,000 | 30,000 | 4.3 | 19 | 21.3 % | 1.5 % |
| 13 | Philippines | 109,581,078 | 1.35 % | 1,464,463 | 368 | 298,170 | -67,152 | 2.58 | 26 | 47.5 % | 1.4 % |
| 14 | Egypt | 102,334,404 | 1.94 % | 1,946,331 | 103 | 995,450 | -38,033 | 3.33 | 25 | 43 % | 1.3 % |
| 15 | Vietnam | 97,338,579 | 0.91 % | 876,473 | 314 | 310,070 | -80,000 | 2.0556 | 32 | 37.7 % | 1.2 % |
| 16 | DR Congo | 89,561,403 | 3.19 % | 2,770,836 | 40 | 2,267,050 | 23,861 | 5.9635 | 17 | 45.6 % | 1.1 % |
| 17 | Turkey | 84,339,067 | 1.09 % | 909,452 | 110 | 769,630 | 283,922 | 2.08 | 32 | 75.7 % | 1.1 % |
| 18 | Iran | 83,992,949 | 1.3 % | 1,079,043 | 52 | 1,628,550 | -55,000 | 2.15 | 32 | 75.5 % | 1.1 % |
| 19 | Germany | 83,783,942 | 0.32 % | 266,897 | 240 | 348,560 | 543,822 | 1.586 | 46 | 76.3 % | 1.1 % |
| 20 | Thailand | 69,799,978 | 0.25 % | 174,396 | 137 | 510,890 | 19,444 | 1.5346 | 40 | 51.1 % | 0.9 % |
| 21 | United Kingdom | 67,886,011 | 0.53 % | 355,839 | 281 | 241,930 | 260,650 | 1.75 | 40 | 83.2 % | 0.9 % |
| 22 | France | 65,273,511 | 0.22 % | 143,783 | 119 | 547,557 | 36,527 | 1.8523 | 42 | 81.5 % | 0.8 % |
| 23 | Italy | 60,461,826 | -0.15 % | -88,249 | 206 | 294,140 | 148,943 | 1.33 | 47 | 69.5 % | 0.8 % |
| 24 | Tanzania | 59,734,218 | 2.98 % | 1,728,755 | 67 | 885,800 | -40,076 | 4.9237 | 18 | 37 % | 0.8 % |
| 25 | South Africa | 59,308,690 | 1.28 % | 750,420 | 49 | 1,213,090 | 145,405 | 2.4139 | 28 | 66.7 % | 0.8 % |
| 26 | Myanmar | 54,409,800 | 0.67 % | 364,380 | 83 | 653,290 | -163,313 | 2.17 | 29 | 31.4 % | 0.7 % |
| 27 | Kenya | 53,771,296 | 2.28 % | 1,197,323 | 94 | 569,140 | -10,000 | 3.52 | 20 | 27.8 % | 0.7 % |
| 28 | South Korea | 51,269,185 | 0.09 % | 43,877 | 527 | 97,230 | 11,731 | 1.11 | 44 | 81.8 % | 0.7 % |
| 29 | Colombia | 50,882,891 | 1.08 % | 543,448 | 46 | 1,109,500 | 204,796 | 1.82 | 31 | 80.4 % | 0.7 % |
| 30 | Spain | 46,754,778 | 0.04 % | 18,002 | 94 | 498,800 | 40,000 | 1.33 | 45 | 80.3 % | 0.6 % |
| 31 | Uganda | 45,741,007 | 3.32 % | 1,471,413 | 229 | 199,810 | 168,694 | 5.01 | 17 | 25.7 % | 0.6 % |
| 32 | Argentina | 45,195,774 | 0.93 % | 415,097 | 17 | 2,736,690 | 4,800 | 2.268 | 32 | 92.8 % | 0.6 % |
| 33 | Algeria | 43,851,044 | 1.85 % | 797,990 | 18 | 2,381,740 | -10,000 | 3.05 | 29 | 72.9 % | 0.6 % |
| 34 | Sudan | 43,849,260 | 2.42 % | 1,036,022 | 25 | 1,765,048 | -50,000 | 4.4345 | 20 | 35 % | 0.6 % |
| 35 | Ukraine | 43,733,762 | -0.59 % | -259,876 | 75 | 579,320 | 10,000 | 1.4435 | 41 | 69.4 % | 0.6 % |
| 36 | Iraq | 40,222,493 | 2.32 % | 912,710 | 93 | 434,320 | 7,834 | 3.682 | 21 | 73.1 % | 0.5 % |
| 37 | Afghanistan | 38,928,346 | 2.33 % | 886,592 | 60 | 652,860 | -62,920 | 4.5552 | 18 | 25.4 % | 0.5 % |
| 38 | Poland | 37,846,611 | -0.11 % | -41,157 | 124 | 306,230 | -29,395 | 1.4202 | 42 | 60.2 % | 0.5 % |
| 39 | Canada | 37,742,154 | 0.89 % | 331,107 | 4 | 9,093,510 | 242,032 | 1.525 | 41 | 81.3 % | 0.5 % |
| 40 | Morocco | 36,910,560 | 1.2 % | 438,791 | 83 | 446,300 | -51,419 | 2.42 | 30 | 63.8 % | 0.5 % |
| 41 | Saudi Arabia | 34,813,871 | 1.59 % | 545,343 | 16 | 2,149,690 | 134,979 | 2.34 | 32 | 84 % | 0.4 % |
| 42 | Uzbekistan | 33,469,203 | 1.48 % | 487,487 | 79 | 425,400 | -8,863 | 2.43 | 28 | 50.1 % | 0.4 % |
| 43 | Peru | 32,971,854 | 1.42 % | 461,401 | 26 | 1,280,000 | 99,069 | 2.27 | 31 | 79.1 % | 0.4 % |
| 44 | Angola | 32,866,272 | 3.27 % | 1,040,977 | 26 | 1,246,700 | 6,413 | 5.55 | 17 | 66.7 % | 0.4 % |
| 45 | Malaysia | 32,365,999 | 1.3 % | 416,222 | 99 | 328,550 | 50,000 | 2.0105 | 30 | 78.4 % | 0.4 % |
| 46 | Mozambique | 31,255,435 | 2.93 % | 889,399 | 40 | 786,380 | -5,000 | 4.8858 | 18 | 38.3 % | 0.4 % |
| 47 | Ghana | 31,072,940 | 2.15 % | 655,084 | 137 | 227,540 | -10,000 | 3.8928 | 22 | 56.7 % | 0.4 % |
| 48 | Yemen | 29,825,964 | 2.28 % | 664,042 | 56 | 527,970 | -30,000 | 3.8372 | 20 | 38.4 % | 0.4 % |
| 49 | Nepal | 29,136,808 | 1.85 % | 528,098 | 203 | 143,350 | 41,710 | 1.934 | 25 | 21.4 % | 0.4 % |
| 50 | Venezuela | 28,435,940 | -0.28 % | -79,889 | 32 | 882,050 | -653,249 | 2.283 | 30 | N.A. | 0.4 % |
| 51 | Madagascar | 27,691,018 | 2.68 % | 721,711 | 48 | 581,795 | -1,500 | 4.1085 | 20 | 38.5 % | 0.4 % |
| 52 | Cameroon | 26,545,863 | 2.59 % | 669,483 | 56 | 472,710 | -4,800 | 4.603 | 19 | 56.3 % | 0.3 % |
| 53 | Côte d’Ivoire | 26,378,274 | 2.57 % | 661,730 | 83 | 318,000 | -8,000 | 4.68 | 19 | 51.3 % | 0.3 % |
| 54 | North Korea | 25,778,816 | 0.44 % | 112,655 | 214 | 120,410 | -5,403 | 1.91 | 35 | 62.5 % | 0.3 % |
| 55 | Australia | 25,499,884 | 1.18 % | 296,686 | 3 | 7,682,300 | 158,246 | 1.8316 | 38 | 85.9 % | 0.3 % |
| 56 | Niger | 24,206,644 | 3.84 % | 895,929 | 19 | 1,266,700 | 4,000 | 6.95 | 15 | 16.5 % | 0.3 % |
| 57 | Taiwan | 23,816,775 | 0.18 % | 42,899 | 673 | 35,410 | 30,001 | 1.15 | 42 | 78.9 % | 0.3 % |
| 58 | Sri Lanka | 21,413,249 | 0.42 % | 89,516 | 341 | 62,710 | -97,986 | 2.2102 | 34 | 18.4 % | 0.3 % |
| 59 | Burkina Faso | 20,903,273 | 2.86 % | 581,895 | 76 | 273,600 | -25,000 | 5.2315 | 18 | 30.6 % | 0.3 % |
| 60 | Mali | 20,250,833 | 3.02 % | 592,802 | 17 | 1,220,190 | -40,000 | 5.9215 | 16 | 44 % | 0.3 % |
| 61 | Romania | 19,237,691 | -0.66 % | -126,866 | 84 | 230,170 | -73,999 | 1.6198 | 43 | 54.6 % | 0.2 % |
| 62 | Malawi | 19,129,952 | 2.69 % | 501,205 | 203 | 94,280 | -16,053 | 4.25 | 18 | 18.5 % | 0.2 % |
| 63 | Chile | 19,116,201 | 0.87 % | 164,163 | 26 | 743,532 | 111,708 | 1.65 | 35 | 84.8 % | 0.2 % |
| 64 | Kazakhstan | 18,776,707 | 1.21 % | 225,280 | 7 | 2,699,700 | -18,000 | 2.7638 | 31 | 57.7 % | 0.2 % |
| 65 | Zambia | 18,383,955 | 2.93 % | 522,925 | 25 | 743,390 | -8,000 | 4.6555 | 18 | 45.3 % | 0.2 % |
| 66 | Guatemala | 17,915,568 | 1.9 % | 334,096 | 167 | 107,160 | -9,215 | 2.8989 | 23 | 51.8 % | 0.2 % |
| 67 | Ecuador | 17,643,054 | 1.55 % | 269,392 | 71 | 248,360 | 36,400 | 2.44 | 28 | 63 % | 0.2 % |
| 68 | Syria | 17,500,658 | 2.52 % | 430,523 | 95 | 183,630 | -427,391 | 2.8398 | 26 | 60 % | 0.2 % |
| 69 | Netherlands | 17,134,872 | 0.22 % | 37,742 | 508 | 33,720 | 16,000 | 1.66 | 43 | 92.5 % | 0.2 % |
| 70 | Senegal | 16,743,927 | 2.75 % | 447,563 | 87 | 192,530 | -20,000 | 4.65 | 19 | 49.4 % | 0.2 % |
| 71 | Cambodia | 16,718,965 | 1.41 % | 232,423 | 95 | 176,520 | -30,000 | 2.5238 | 26 | 24.2 % | 0.2 % |
| 72 | Chad | 16,425,864 | 3 % | 478,988 | 13 | 1,259,200 | 2,000 | 5.7973 | 17 | 23.3 % | 0.2 % |
| 73 | Somalia | 15,893,222 | 2.92 % | 450,317 | 25 | 627,340 | -40,000 | 6.12 | 17 | 46.8 % | 0.2 % |
| 74 | Zimbabwe | 14,862,924 | 1.48 % | 217,456 | 38 | 386,850 | -116,858 | 3.6255 | 19 | 38.4 % | 0.2 % |
| 75 | Guinea | 13,132,795 | 2.83 % | 361,549 | 53 | 245,720 | -4,000 | 4.7384 | 18 | 38.6 % | 0.2 % |
| 76 | Rwanda | 12,952,218 | 2.58 % | 325,268 | 525 | 24,670 | -9,000 | 4.1 | 20 | 17.6 % | 0.2 % |
| 77 | Benin | 12,123,200 | 2.73 % | 322,049 | 108 | 112,760 | -2,000 | 4.8675 | 19 | 48.4 % | 0.2 % |
| 78 | Burundi | 11,890,784 | 3.12 % | 360,204 | 463 | 25,680 | 2,001 | 5.45 | 17 | 13.8 % | 0.2 % |
| 79 | Tunisia | 11,818,619 | 1.06 % | 123,900 | 76 | 155,360 | -4,000 | 2.2 | 33 | 70.1 % | 0.2 % |
| 80 | Bolivia | 11,673,021 | 1.39 % | 159,921 | 11 | 1,083,300 | -9,504 | 2.75 | 26 | 69.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 81 | Belgium | 11,589,623 | 0.44 % | 50,295 | 383 | 30,280 | 48,000 | 1.7148 | 42 | 98.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 82 | Haiti | 11,402,528 | 1.24 % | 139,451 | 414 | 27,560 | -35,000 | 2.96 | 24 | 56.9 % | 0.1 % |
| 83 | Cuba | 11,326,616 | -0.06 % | -6,867 | 106 | 106,440 | -14,400 | 1.6166 | 42 | 78.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 84 | South Sudan | 11,193,725 | 1.19 % | 131,612 | 18 | 610,952 | -174,200 | 4.7359 | 19 | 24.6 % | 0.1 % |
| 85 | Dominican Republic | 10,847,910 | 1.01 % | 108,952 | 225 | 48,320 | -30,000 | 2.36 | 28 | 84.5 % | 0.1 % |
| 86 | Czech Republic (Czechia) | 10,708,981 | 0.18 % | 19,772 | 139 | 77,240 | 22,011 | 1.6413 | 43 | 73.5 % | 0.1 % |
| 87 | Greece | 10,423,054 | -0.48 % | -50,401 | 81 | 128,900 | -16,000 | 1.3024 | 46 | 84.9 % | 0.1 % |
| 88 | Jordan | 10,203,134 | 1 % | 101,440 | 115 | 88,780 | 10,220 | 2.7723 | 24 | 91.5 % | 0.1 % |
| 89 | Portugal | 10,196,709 | -0.29 % | -29,478 | 111 | 91,590 | -6,000 | 1.288 | 46 | 66.5 % | 0.1 % |
| 90 | Azerbaijan | 10,139,177 | 0.91 % | 91,459 | 123 | 82,658 | 1,200 | 2.0835 | 32 | 56.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 91 | Sweden | 10,099,265 | 0.63 % | 62,886 | 25 | 410,340 | 40,000 | 1.85 | 41 | 88.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 92 | Honduras | 9,904,607 | 1.63 % | 158,490 | 89 | 111,890 | -6,800 | 2.4872 | 24 | 57.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 93 | United Arab Emirates | 9,890,402 | 1.23 % | 119,873 | 118 | 83,600 | 40,000 | 1.42 | 33 | 86.4 % | 0.1 % |
| 94 | Hungary | 9,660,351 | -0.25 % | -24,328 | 107 | 90,530 | 6,000 | 1.4911 | 43 | 71.7 % | 0.1 % |
| 95 | Tajikistan | 9,537,645 | 2.32 % | 216,627 | 68 | 139,960 | -20,000 | 3.6075 | 22 | 27.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 96 | Belarus | 9,449,323 | -0.03 % | -3,088 | 47 | 202,910 | 8,730 | 1.7099 | 40 | 79.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 97 | Austria | 9,006,398 | 0.57 % | 51,296 | 109 | 82,409 | 65,000 | 1.5292 | 43 | 57.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 98 | Papua New Guinea | 8,947,024 | 1.95 % | 170,915 | 20 | 452,860 | -800 | 3.5883 | 22 | 13.1 % | 0.1 % |
| 99 | Serbia | 8,737,371 | -0.4 % | -34,864 | 100 | 87,460 | 4,000 | 1.4612 | 42 | 56.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 100 | Israel | 8,655,535 | 1.6 % | 136,158 | 400 | 21,640 | 10,000 | 3.044 | 30 | 93.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 101 | Switzerland | 8,654,622 | 0.74 % | 63,257 | 219 | 39,516 | 52,000 | 1.535 | 43 | 74.1 % | 0.1 % |
| 102 | Togo | 8,278,724 | 2.43 % | 196,358 | 152 | 54,390 | -2,000 | 4.3515 | 19 | 43.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 103 | Sierra Leone | 7,976,983 | 2.1 % | 163,768 | 111 | 72,180 | -4,200 | 4.319 | 19 | 43.3 % | 0.1 % |
| 104 | Hong Kong | 7,496,981 | 0.82 % | 60,827 | 7,140 | 1,050 | 29,308 | 1.3262 | 45 | N.A. | 0.1 % |
| 105 | Laos | 7,275,560 | 1.48 % | 106,105 | 32 | 230,800 | -14,704 | 2.7 | 24 | 35.7 % | 0.1 % |
| 106 | Paraguay | 7,132,538 | 1.25 % | 87,902 | 18 | 397,300 | -16,556 | 2.4455 | 26 | 61.6 % | 0.1 % |
| 107 | Bulgaria | 6,948,445 | -0.74 % | -51,674 | 64 | 108,560 | -4,800 | 1.5584 | 45 | 75.6 % | 0.1 % |
| 108 | Libya | 6,871,292 | 1.38 % | 93,840 | 4 | 1,759,540 | -1,999 | 2.25 | 29 | 78.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 109 | Lebanon | 6,825,445 | -0.44 % | -30,268 | 667 | 10,230 | -30,012 | 2.09 | 30 | 78.4 % | 0.1 % |
| 110 | Nicaragua | 6,624,554 | 1.21 % | 79,052 | 55 | 120,340 | -21,272 | 2.42 | 26 | 57.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 111 | Kyrgyzstan | 6,524,195 | 1.69 % | 108,345 | 34 | 191,800 | -4,000 | 3 | 26 | 35.6 % | 0.1 % |
| 112 | El Salvador | 6,486,205 | 0.51 % | 32,652 | 313 | 20,720 | -40,539 | 2.0529 | 28 | 73.4 % | 0.1 % |
| 113 | Turkmenistan | 6,031,200 | 1.5 % | 89,111 | 13 | 469,930 | -5,000 | 2.785 | 27 | 52.5 % | 0.1 % |
| 114 | Singapore | 5,850,342 | 0.79 % | 46,005 | 8,358 | 700 | 27,028 | 1.209 | 42 | N.A. | 0.1 % |
| 115 | Denmark | 5,792,202 | 0.35 % | 20,326 | 137 | 42,430 | 15,200 | 1.7621 | 42 | 88.2 % | 0.1 % |
| 116 | Finland | 5,540,720 | 0.15 % | 8,564 | 18 | 303,890 | 14,000 | 1.53 | 43 | 86.1 % | 0.1 % |
| 117 | Congo | 5,518,087 | 2.56 % | 137,579 | 16 | 341,500 | -4,000 | 4.45 | 19 | 69.9 % | 0.1 % |
| 118 | Slovakia | 5,459,642 | 0.05 % | 2,629 | 114 | 48,088 | 1,485 | 1.502 | 41 | 53.7 % | 0.1 % |
| 119 | Norway | 5,421,241 | 0.79 % | 42,384 | 15 | 365,268 | 28,000 | 1.68 | 40 | 83.4 % | 0.1 % |
| 120 | Oman | 5,106,626 | 2.65 % | 131,640 | 16 | 309,500 | 87,400 | 2.93 | 31 | 87 % | 0.1 % |
| 121 | State of Palestine | 5,101,414 | 2.41 % | 119,994 | 847 | 6,020 | -10,563 | 3.6677 | 21 | 80 % | 0.1 % |
| 122 | Costa Rica | 5,094,118 | 0.92 % | 46,557 | 100 | 51,060 | 4,200 | 1.7639 | 33 | 80 % | 0.1 % |
| 123 | Liberia | 5,057,681 | 2.44 % | 120,307 | 53 | 96,320 | -5,000 | 4.35 | 19 | 52.6 % | 0.1 % |
| 124 | Ireland | 4,937,786 | 1.13 % | 55,291 | 72 | 68,890 | 23,604 | 1.8409 | 38 | 63 % | 0.1 % |
| 125 | Central African Republic | 4,829,767 | 1.78 % | 84,582 | 8 | 622,980 | -40,000 | 4.7541 | 18 | 43 % | 0.1 % |
| 126 | New Zealand | 4,822,233 | 0.82 % | 39,170 | 18 | 263,310 | 14,881 | 1.9 | 38 | 86.9 % | 0.1 % |
| 127 | Mauritania | 4,649,658 | 2.74 % | 123,962 | 5 | 1,030,700 | 5,000 | 4.585 | 20 | 56.9 % | 0.1 % |
| 128 | Panama | 4,314,767 | 1.61 % | 68,328 | 58 | 74,340 | 11,200 | 2.4688 | 30 | 68 % | 0.1 % |
| 129 | Kuwait | 4,270,571 | 1.51 % | 63,488 | 240 | 17,820 | 39,520 | 2.1 | 37 | N.A. | 0.1 % |
| 130 | Croatia | 4,105,267 | -0.61 % | -25,037 | 73 | 55,960 | -8,001 | 1.4461 | 44 | 57.7 % | 0.1 % |
| 131 | Moldova | 4,033,963 | -0.23 % | -9,300 | 123 | 32,850 | -1,387 | 1.2552 | 38 | 42.7 % | 0.1 % |
| 132 | Georgia | 3,989,167 | -0.19 % | -7,598 | 57 | 69,490 | -10,000 | 2.0615 | 38 | 58.1 % | 0.1 % |
| 133 | Eritrea | 3,546,421 | 1.41 % | 49,304 | 35 | 101,000 | -39,858 | 4.1 | 19 | 63.3 % | 0 % |
| 134 | Uruguay | 3,473,730 | 0.35 % | 11,996 | 20 | 175,020 | -3,000 | 1.98 | 36 | 96.1 % | 0 % |
| 135 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 3,280,819 | -0.61 % | -20,181 | 64 | 51,000 | -21,585 | 1.27 | 43 | 52.3 % | 0 % |
| 136 | Mongolia | 3,278,290 | 1.65 % | 53,123 | 2 | 1,553,560 | -852 | 2.9023 | 28 | 67.2 % | 0 % |
| 137 | Armenia | 2,963,243 | 0.19 % | 5,512 | 104 | 28,470 | -4,998 | 1.7559 | 35 | 62.8 % | 0 % |
| 138 | Jamaica | 2,961,167 | 0.44 % | 12,888 | 273 | 10,830 | -11,332 | 1.991 | 31 | 55.4 % | 0 % |
| 139 | Qatar | 2,881,053 | 1.73 % | 48,986 | 248 | 11,610 | 40,000 | 1.8805 | 32 | 96.2 % | 0 % |
| 140 | Albania | 2,877,797 | -0.11 % | -3,120 | 105 | 27,400 | -14,000 | 1.62 | 36 | 63.5 % | 0 % |
| 141 | Puerto Rico | 2,860,853 | -2.47 % | -72,555 | 323 | 8,870 | -97,986 | 1.22 | 44 | N.A. | 0 % |
| 142 | Lithuania | 2,722,289 | -1.35 % | -37,338 | 43 | 62,674 | -32,780 | 1.6698 | 45 | 71.3 % | 0 % |
| 143 | Namibia | 2,540,905 | 1.86 % | 46,375 | 3 | 823,290 | -4,806 | 3.4153 | 22 | 55.2 % | 0 % |
| 144 | Gambia | 2,416,668 | 2.94 % | 68,962 | 239 | 10,120 | -3,087 | 5.25 | 18 | 59.4 % | 0 % |
| 145 | Botswana | 2,351,627 | 2.08 % | 47,930 | 4 | 566,730 | 3,000 | 2.8944 | 24 | 72.8 % | 0 % |
| 146 | Gabon | 2,225,734 | 2.45 % | 53,155 | 9 | 257,670 | 3,260 | 4 | 23 | 87.1 % | 0 % |
| 147 | Lesotho | 2,142,249 | 0.8 % | 16,981 | 71 | 30,360 | -10,047 | 3.1641 | 24 | 31.5 % | 0 % |
| 148 | North Macedonia | 2,083,374 | -0 % | -85 | 83 | 25,220 | -1,000 | 1.5 | 39 | 58.6 % | 0 % |
| 149 | Slovenia | 2,078,938 | 0.01 % | 284 | 103 | 20,140 | 2,000 | 1.6 | 45 | 55.2 % | 0 % |
| 150 | Guinea-Bissau | 1,968,001 | 2.45 % | 47,079 | 70 | 28,120 | -1,399 | 4.51 | 19 | 44.9 % | 0 % |
| 151 | Latvia | 1,886,198 | -1.08 % | -20,545 | 30 | 62,200 | -14,837 | 1.7167 | 44 | 68.6 % | 0 % |
| 152 | Bahrain | 1,701,575 | 3.68 % | 60,403 | 2,239 | 760 | 47,800 | 1.9982 | 32 | 89.3 % | 0 % |
| 153 | Equatorial Guinea | 1,402,985 | 3.47 % | 46,999 | 50 | 28,050 | 16,000 | 4.5543 | 22 | 73.3 % | 0 % |
| 154 | Trinidad and Tobago | 1,399,488 | 0.32 % | 4,515 | 273 | 5,130 | -800 | 1.7299 | 36 | 52.4 % | 0 % |
| 155 | Estonia | 1,326,535 | 0.07 % | 887 | 31 | 42,390 | 3,911 | 1.5878 | 42 | 67.9 % | 0 % |
| 156 | Timor-Leste | 1,318,445 | 1.96 % | 25,326 | 89 | 14,870 | -5,385 | 4.1 | 21 | 32.8 % | 0 % |
| 157 | Mauritius | 1,271,768 | 0.17 % | 2,100 | 626 | 2,030 | 0 | 1.3885 | 37 | 40.8 % | 0 % |
| 158 | Cyprus | 1,207,359 | 0.73 % | 8,784 | 131 | 9,240 | 5,000 | 1.3375 | 37 | 66.8 % | 0 % |
| 159 | Eswatini | 1,160,164 | 1.05 % | 12,034 | 67 | 17,200 | -8,353 | 3.0257 | 21 | 30 % | 0 % |
| 160 | Djibouti | 988,000 | 1.48 % | 14,440 | 43 | 23,180 | 900 | 2.7577 | 27 | 79 % | 0 % |
| 161 | Fiji | 896,445 | 0.73 % | 6,492 | 49 | 18,270 | -6,202 | 2.7874 | 28 | 59.1 % | 0 % |
| 162 | Réunion | 895,312 | 0.72 % | 6,385 | 358 | 2,500 | -1,256 | 2.2735 | 36 | 99.8 % | 0 % |
| 163 | Comoros | 869,601 | 2.2 % | 18,715 | 467 | 1,861 | -2,000 | 4.2365 | 20 | 29.4 % | 0 % |
| 164 | Guyana | 786,552 | 0.48 % | 3,786 | 4 | 196,850 | -6,000 | 2.4728 | 27 | 26.9 % | 0 % |
| 165 | Bhutan | 771,608 | 1.12 % | 8,516 | 20 | 38,117 | 320 | 2 | 28 | 45.8 % | 0 % |
| 166 | Solomon Islands | 686,884 | 2.55 % | 17,061 | 25 | 27,990 | -1,600 | 4.435 | 20 | 23.2 % | 0 % |
| 167 | Macao | 649,335 | 1.39 % | 8,890 | 21,645 | 30 | 5,000 | 1.2 | 39 | N.A. | 0 % |
| 168 | Montenegro | 628,066 | 0.01 % | 79 | 47 | 13,450 | -480 | 1.7506 | 39 | 67.6 % | 0 % |
| 169 | Luxembourg | 625,978 | 1.66 % | 10,249 | 242 | 2,590 | 9,741 | 1.45 | 40 | 88.2 % | 0 % |
| 170 | Western Sahara | 597,339 | 2.55 % | 14,876 | 2 | 266,000 | 5,582 | 2.4149 | 28 | 86.8 % | 0 % |
| 171 | Suriname | 586,632 | 0.9 % | 5,260 | 4 | 156,000 | -1,000 | 2.4298 | 29 | 65.1 % | 0 % |
| 172 | Cabo Verde | 555,987 | 1.1 % | 6,052 | 138 | 4,030 | -1,342 | 2.2885 | 28 | 68 % | 0 % |
| 173 | Micronesia | 548,914 | 1 % | 5,428 | 784 | 700 | -2,957 | 2.858000189 | 27 | 68.2 % | 0 % |
| 174 | Maldives | 540,544 | 1.81 % | 9,591 | 1,802 | 300 | 11,370 | 1.88 | 30 | 34.5 % | 0 % |
| 175 | Malta | 441,543 | 0.27 % | 1,171 | 1,380 | 320 | 900 | 1.45 | 43 | 93.2 % | 0 % |
| 176 | Brunei | 437,479 | 0.97 % | 4,194 | 83 | 5,270 | 0 | 1.8482 | 32 | 79.5 % | 0 % |
| 177 | Guadeloupe | 400,124 | 0.02 % | 68 | 237 | 1,690 | -1,440 | 2.17 | 44 | N.A. | 0 % |
| 178 | Belize | 397,628 | 1.86 % | 7,275 | 17 | 22,810 | 1,200 | 2.32 | 25 | 46.1 % | 0 % |
| 179 | Bahamas | 393,244 | 0.97 % | 3,762 | 39 | 10,010 | 1,000 | 1.76 | 32 | 86.1 % | 0 % |
| 180 | Martinique | 375,265 | -0.08 % | -289 | 354 | 1,060 | -960 | 1.88 | 47 | 91.6 % | 0 % |
| 181 | Iceland | 341,243 | 0.65 % | 2,212 | 3 | 100,250 | 380 | 1.77 | 37 | 94.4 % | 0 % |
| 182 | Vanuatu | 307,145 | 2.42 % | 7,263 | 25 | 12,190 | 120 | 3.8 | 21 | 24.4 % | 0 % |
| 183 | French Guiana | 298,682 | 2.7 % | 7,850 | 4 | 82,200 | 1,200 | 3.36 | 25 | 87.3 % | 0 % |
| 184 | Barbados | 287,375 | 0.12 % | 350 | 668 | 430 | -79 | 1.62 | 40 | 31.2 % | 0 % |
| 185 | New Caledonia | 285,498 | 0.97 % | 2,748 | 16 | 18,280 | 502 | 1.97 | 34 | 71.9 % | 0 % |
| 186 | French Polynesia | 280,908 | 0.58 % | 1,621 | 77 | 3,660 | -1,000 | 1.95 | 34 | 64.1 % | 0 % |
| 187 | Mayotte | 272,815 | 2.5 % | 6,665 | 728 | 375 | 0 | 3.7289 | 20 | 45.8 % | 0 % |
| 188 | Sao Tome & Principe | 219,159 | 1.91 % | 4,103 | 228 | 960 | -1,680 | 4.35 | 19 | 74 % | 0 % |
| 189 | Samoa | 198,414 | 0.67 % | 1,317 | 70 | 2,830 | -2,803 | 3.9029 | 22 | 18 % | 0 % |
| 190 | Saint Lucia | 183,627 | 0.46 % | 837 | 301 | 610 | 0 | 1.4442 | 34 | 18.6 % | 0 % |
| 191 | Channel Islands | 173,863 | 0.93 % | 1,604 | 915 | 190 | 1,351 | 1.502 | 43 | 29.8 % | 0 % |
| 192 | Guam | 168,775 | 0.89 % | 1,481 | 313 | 540 | -506 | 2.3193 | 31 | 94.9 % | 0 % |
| 193 | Curaçao | 164,093 | 0.41 % | 669 | 370 | 444 | 515 | 1.76 | 42 | 88.7 % | 0 % |
| 194 | Kiribati | 119,449 | 1.57 % | 1,843 | 147 | 810 | -800 | 3.5836 | 23 | 57 % | 0 % |
| 195 | Grenada | 112,523 | 0.46 % | 520 | 331 | 340 | -200 | 2.0732 | 32 | 35.5 % | 0 % |
| 196 | St. Vincent & Grenadines | 110,940 | 0.32 % | 351 | 284 | 390 | -200 | 1.9019 | 33 | 52.9 % | 0 % |
| 197 | Aruba | 106,766 | 0.43 % | 452 | 593 | 180 | 201 | 1.9 | 41 | 43.6 % | 0 % |
| 198 | Tonga | 105,695 | 1.15 % | 1,201 | 147 | 720 | -800 | 3.5763 | 22 | 24.3 % | 0 % |
| 199 | U.S. Virgin Islands | 104,425 | -0.15 % | -153 | 298 | 350 | -451 | 2.0458 | 43 | 96.3 % | 0 % |
| 200 | Seychelles | 98,347 | 0.62 % | 608 | 214 | 460 | -200 | 2.46 | 34 | 56.2 % | 0 % |
| 201 | Antigua and Barbuda | 97,929 | 0.84 % | 811 | 223 | 440 | 0 | 2 | 34 | 26.2 % | 0 % |
| 202 | Isle of Man | 85,033 | 0.53 % | 449 | 149 | 570 | N.A. | N.A. | 53.4 % | 0 % | |
| 203 | Andorra | 77,265 | 0.16 % | 123 | 164 | 470 | N.A. | N.A. | 87.8 % | 0 % | |
| 204 | Dominica | 71,986 | 0.25 % | 178 | 96 | 750 | N.A. | N.A. | 74.1 % | 0 % | |
| 205 | Cayman Islands | 65,722 | 1.19 % | 774 | 274 | 240 | N.A. | N.A. | 97.2 % | 0 % | |
| 206 | Bermuda | 62,278 | -0.36 % | -228 | 1,246 | 50 | N.A. | N.A. | 97.4 % | 0 % | |
| 207 | Marshall Islands | 59,190 | 0.68 % | 399 | 329 | 180 | N.A. | N.A. | 70 % | 0 % | |
| 208 | Northern Mariana Islands | 57,559 | 0.6 % | 343 | 125 | 460 | N.A. | N.A. | 88.3 % | 0 % | |
| 209 | Greenland | 56,770 | 0.17 % | 98 | 0 | 410,450 | N.A. | N.A. | 87.3 % | 0 % | |
| 210 | American Samoa | 55,191 | -0.22 % | -121 | 276 | 200 | N.A. | N.A. | 88.1 % | 0 % | |
| 211 | Saint Kitts & Nevis | 53,199 | 0.71 % | 376 | 205 | 260 | N.A. | N.A. | 32.9 % | 0 % | |
| 212 | Faeroe Islands | 48,863 | 0.38 % | 185 | 35 | 1,396 | N.A. | N.A. | 43.3 % | 0 % | |
| 213 | Sint Maarten | 42,876 | 1.15 % | 488 | 1,261 | 34 | N.A. | N.A. | 96.5 % | 0 % | |
| 214 | Monaco | 39,242 | 0.71 % | 278 | 26,337 | 1 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | |
| 215 | Turks and Caicos | 38,717 | 1.38 % | 526 | 41 | 950 | N.A. | N.A. | 89.3 % | 0 % | |
| 216 | Saint Martin | 38,666 | 1.75 % | 664 | 730 | 53 | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | 0 % | |
| 217 | Liechtenstein | 38,128 | 0.29 % | 109 | 238 | 160 | N.A. | N.A. | 14.6 % | 0 % | |
| 218 | San Marino | 33,931 | 0.21 % | 71 | 566 | 60 | N.A. | N.A. | 97.1 % | 0 % | |
| 219 | Gibraltar | 33,691 | -0.03 % | -10 | 3,369 | 10 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | |
| 220 | British Virgin Islands | 30,231 | 0.67 % | 201 | 202 | 150 | N.A. | N.A. | 52.4 % | 0 % | |
| 221 | Caribbean Netherlands | 26,223 | 0.94 % | 244 | 80 | 328 | N.A. | N.A. | 75 % | 0 % | |
| 222 | Palau | 18,094 | 0.48 % | 86 | 39 | 460 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | |
| 223 | Cook Islands | 17,564 | 0.09 % | 16 | 73 | 240 | N.A. | N.A. | 75.3 % | 0 % | |
| 224 | Anguilla | 15,003 | 0.9 % | 134 | 167 | 90 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | |
| 225 | Tuvalu | 11,792 | 1.25 % | 146 | 393 | 30 | N.A. | N.A. | 62.4 % | 0 % | |
| 226 | Wallis & Futuna | 11,239 | -1.69 % | -193 | 80 | 140 | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | 0 % | |
| 227 | Nauru | 10,824 | 0.63 % | 68 | 541 | 20 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | |
| 228 | Saint Barthelemy | 9,877 | 0.3 % | 30 | 470 | 21 | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | 0 % | |
| 229 | Saint Helena | 6,077 | 0.3 % | 18 | 16 | 390 | N.A. | N.A. | 27.2 % | 0 % | |
| 230 | Saint Pierre & Miquelon | 5,794 | -0.48 % | -28 | 25 | 230 | N.A. | N.A. | 99.8 % | 0 % | |
| 231 | Montserrat | 4,992 | 0.06 % | 3 | 50 | 100 | N.A. | N.A. | 9.6 % | 0 % | |
| 232 | Falkland Islands | 3,480 | 3.05 % | 103 | 0 | 12,170 | N.A. | N.A. | 66 % | 0 % | |
| 233 | Niue | 1,626 | 0.68 % | 11 | 6 | 260 | N.A. | N.A. | 46.4 % | 0 % | |
| 234 | Tokelau | 1,357 | 1.27 % | 17 | 136 | 10 | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % | 0 % | |
| 235 | Holy See | 801 | 0.25 % | 2 | 2,003 | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 % |
How many people have ever lived on earth?
It was written during the 1970s that 75% of the people who had ever been born were alive at that moment. This was grossly false.
Assuming that we start counting from about 50,000 B.C., the time when modern Homo sapiens appeared on the earth (and not from 700,000 B.C. when the ancestors of Homo sapiens appeared, or several million years ago when hominids were present), taking into account that all population data are a rough estimate, and assuming a constant growth rate applied to each period up to modern times, it has been estimated that a total of approximately 106 billion people have been born since the dawn of the human species, making the population currently alive roughly 6% of all people who have ever lived on planet Earth.
Others have estimated the number of human beings who have ever lived to be anywhere from 45 billion to 125 billion, with most estimates falling into the range of 90 to 110 billion humans.
World Population clock: sources and methodology
The world population counter displayed on Worldometer takes into consideration data from two major sources: the United Nations and the U.S. Census Bureau.
- The United Nations Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs every two years calculates, updates, and publishes estimates of total population in its World Population Prospects series. These population estimates and projections provide the standard and consistent set of population figures that are used throughout the United Nations system.
The World Population Prospect: the 2022 Revision provides the most recent data available (released in July of 2022). Estimates and projected world population and country specific populations are given from 1950 through 2100 and are released every two years. Worldometer, as it is common practice, utilizes the medium fertility estimates.
Data underlying the population estimates are national and sub national census data and data on births, deaths, and migrants available from national sources and publications, as well as from questionnaires. For all countries, census and registration data are evaluated and, if necessary, adjusted for incompleteness by the Population Division as part of its preparations of the official United Nations population estimates and projections.
- The International Programs Center at the U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division also develops estimates and projections based on analysis of available data (based on census, survey, and administrative information) on population, fertility, mortality, and migration for each country or area of the world. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, world population reached 7 billion on March 12, 2012.
For most countries adjustment of the data is necessary to correct for errors, omissions, and inconsistencies in the data. Finally, since most recent data for a single country is often at least two years old, the current world population figure is necessarily a projection of past data based on assumed trends. As new data become available, assumptions and data are reevaluated and past conclusions and current figures may be modified.
For information about how these estimates and projections are made by the U.S. Census Bureau, see the Population Estimates and Projections Methodology.
Why Worldometer’s Population Clock is the most accurate
The above world population clock is based on the latest estimates released in July of 2022 by the United Nations. It will show the same number wherever you are in the world and whatever time you set on your PC.
Visitors around the world visiting a PC clock based counter, instead, will see different numbers depending on where they are located. This is the case with other world population clocks — such as the one hosted on a United Nations website, reaching 8 billion in 24 different instances (one per hour) on November 15, 2022, when each local time zone reached 12:10:08. Similarly, in 2011, the clocks on a UN website and on National Geographic — showed 7 billion whenever the visitor’s locally set PC clocks reached 4:21:10 AM on October 31, 2011.
Obviously, the UN data is based on estimates and can’t be 100% accurate, so in all honesty nobody can possibly say with any degree of certainty on which day world population reached 7 billion (or any other exact number), let alone at what time. But once an estimate is made (based on the best data and analysis available), the world population clock should be showing the same number at any given time anywhere around the world.
I’ve seen the word population most commonly used in the context of the magnitude of a community or group e.g. «The population of the United States is 320 million«. I have also seen it used to simply refer to the collective e.g. «The immigrant population of X experience low levels of racism.«
Which is the primary or original meaning: magnitude or collective noun?
Edit: So, etymology suggests that the collective noun is the original meaning. When did it change in popular use?
asked Nov 9, 2015 at 6:29
GyanGyan
1055 bronze badges
According to the OED, neither one is the original meaning in English. The first citation is from 1544, and is:
- A populated or inhabited place. Obs.
And their clearest citation for this sense is:
1578 T. Nicholas tr. F. Lopez de Gómara Pleasant Hist. Conquest W. India They received their advise that neere at hand were great populations [Sp. poblaciones], and soone after he came to Zimpanzinco.
The next citation not in this sense is:
1612 Bacon Ess. Not the hundredth poll will be fit for a helmet, and so great population and little strength.
and most of the early citations after this are in the sense of the magnitude of a group.
answered Nov 9, 2015 at 10:10
Peter Shor Peter Shor
84.4k8 gold badges171 silver badges291 bronze badges
Given that the word population is derived from the Latin populus, which translates as people, I believe that it was originally meant to be a collective noun.
answered Nov 9, 2015 at 6:59
What Is Population?
A population is the complete set group of individuals, whether that group comprises a nation or a group of people with a common characteristic.
In statistics, a population is the pool of individuals from which a statistical sample is drawn for a study. Thus, any selection of individuals grouped by a common feature can be said to be a population. A sample may also refer to a statistically significant portion of a population, not an entire population. For this reason, a statistical analysis of a sample must report the approximate standard deviation, or standard error, of its results from the entire population. Only an analysis of an entire population would have no standard error.
Key Takeaways
- In ordinary usage, a population is a distinct group of individuals with shared citizenship, identity, or characteristics.
- In statistics, a population is a representative sample of a larger group of people (or even things) with one or more characteristics in common.
- The members of a sample population must be randomly selected for the results of the study to accurately reflect the whole.
- The U.S. Census is perhaps the most ambitious survey in existence, given that it entails a door-to-door canvas of the entire population rather than a sample group study.
- Population surveys large and small inform many if not most decisions by government and business.
Understanding Populations
In most everyday uses, the word population implies a group of people or at least a group of living beings. However, statisticians refer to whatever group they are studying as a population. The population of a study might be babies born in North America in 2021, the total number of tech startups in Asia since the year 2000, the average height of all accounting examination candidates, or the mean weight of U.S. taxpayers.
Statisticians and researchers prefer to know the characteristics of every entity in a population to draw the most precise conclusions possible. This is impossible or impractical most of the time, however, since population sets tend to be quite large.
For example, if a company wanted to know whether most of its 50,000 customers were satisfied with the company’s service last year, it would be impractical to call every client on the phone to conduct a survey. A sample of the population must be taken since the characteristics of every individual in a population cannot be measured due to constraints of time, resources, and accessibility.
How to Calculate a Population
A population can be defined narrowly, such as the number of newborn babies in North America with brown eyes, the number of startups in Asia that failed in less than three years, the average height of all female accounting examination candidates, or the mean weight of all U.S. taxpayers over age 30.
The science of political polling offers a good example of the difficulty of selecting a random sampling of the population. One of the reasons why many of the last two presidential election polls have been wrong could be that the type of people who willingly answer poll questions may not constitute a random sample of the population of likely voters.
Nonetheless, surveys and polls may be the only efficient way to identify and validate issues and trends that affect the wider population. For example, growing concerns have been expressed about harassment online, but how common is it? A study by Pew Research indicates that 41% of American adults have experienced online harassment, with 11% reporting they had been outright stalked, and 14% saying they had been physically threatened.
Population vs. Samples
A sample is a random selection of members of a population. It is a smaller group drawn from the population that has the characteristics of the entire population. The observations and conclusions made against the sample data are attributed to the population as a whole.
The information obtained from the statistical sample allows statisticians to develop hypotheses about the larger population. In statistical equations, the population is usually denoted with an uppercase N while the sample is usually denoted with a lowercase n.
There are several ways to obtain samples (known as sampling) from a population. These include a simple random sample, stratified sampling, representative sampling, and convenience sampling. Researchers and analysts employ a range of statistical techniques to infer information about the broader population using just the smaller sample chosen. Note that sample size is an important issue when conducting such inference — if the sample is too small it may be biased and not trustworthy, while larger samples may be overly expensive and time-consuming to collect and analyze.
As an illustration, assume that the population being studied is all of the zeroes depicted in the image below. The red circles form a sample of the population of all circles on the page.
The red circles form a sample of the population of all circles on the page.
C.K.Taylor
Population Parameters
A parameter is data based on an entire population. Statistics such as averages (means) and standard deviations, when taken from populations, are referred to as population parameters. The population mean and population standard deviation are represented by the Greek letters µ and σ, respectively.
A valid statistic may be drawn from either a population sample or a study of an entire population. The objective of a random sample is to avoid bias in the results. A sample is random if every member of the whole population has an equal chance to be selected to participate.
While a parameter is a characteristic of a population, a statistic is a characteristic of a sample. Inferential statistics enables you to make an educated guess about a population parameter based on a statistic computed from a sample randomly drawn from that population.
The standard deviation, for example, is the variation of some variable in the population, which can be inferred from the variation observed in the sample. But, because this is being inferred from a sample, there will always be some sort of error term describing how likely it is that the analysis from the sample does not reflect the true standard deviation (or mean, etc.). Various statistical tools like confidence intervals, the t-test, and p-values can inform an analyst of how confident they might be in making such inferences.
If you have the data for the entire population being studied, you do not need to use statistical inference from a sample, since you already know the population’s parameters.
The Demographic Meaning of Population
While population can refer to any complete set of data in the statistical sense, population takes on another meaning when we talk about the demographic or geopolitical context. Here, a population refers to the entirety of the people inhabiting a particular region, country, or even the entire planet. Census counts keep track of the number of citizens that populate different counties along with their characteristics such as age, race, gender, income, occupation, and so on. Population counts are important for governments in order to collect taxes and allocate the proper amount of funding to various infrastructure and social programs.
Demography is the study of populations and their characteristics, and how these change over time and from place to place. Population statistics and demographics inform public policy and business decisions. Some examples:
- The World Bank is an international organization that aims to reduce global poverty by lending money to poor nations for projects that improve their economies and raise their overall standard of living. To pinpoint where help is most needed, the Bank conducts an authoritative, country-by-country headcount based on local data of people living in extreme poverty. The numbers fell steadily from over 40% of the global population in 1981 to as low as 8.7% in 2018, according to the Bank. However, in 2020, the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic was expected to cause the first yearly increase in extreme poverty in more than 20 years.
- The U.S. Census, mandated once a decade by the U.S. Constitution, is probably the most ambitious population study in existence, given that it is not a sample but an actual door-to-door count. It is used to determine how many congressional seats each state gets and how federal funds are distributed. The data also is used by many other entities, private and public, to decide where hospitals and schools are built, where businesses locate, and what types of homes are built.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been conducting a National Health Interview Survey since 1957 to identify and track health issues and problems. Its recent reports include studies of chronic conditions among military veterans, opioid-related visits to emergency wards, and the quality of care for Americans suffering from dementia.
9.7 billion
The world’s population by the middle of the 21st century, according to the United Nations.
What Is Population in Research?
The entire set of units (the universe of things) being studied is referred to collectively as the population. This can be a group of people, companies, organisms, government bonds, or anything else. What matters is that the population includes every one of those things.
If randomly selected, a sample taken from the population can be used to study associations or attributes that may be representative of the larger population. For example, in a recent Gallup Poll, 57% of randomly selected 1,015 retirees said Social Security was a «major» source of their income. It can be concluded that most American retirees rely on Social Security, based on the responses of the population surveyed, but with a margin of error.
What Will the World Population Be in 2050?
The world population is expected to grow from 7.7 billion in 2019 to 9.7 billion in 2050, according to a projection by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. The greatest growth is expected in sub-Sarahan Africa, where the population may double, while Europe and North America are expected to have the least growth, at just 2%.
What Is 1% of the World’s Population?
The world’s current population is estimated at 7.7 billion by the United Nations, so 1% of that would be 77 million.
What Are the 10 Countries with the Largest Populations?
China and India have by far the largest populations in the world, as of 2021, according to the World Bank. Here are the top 10 nations and their estimated populations:
- China, 1.41 billion
- India, 1.39 billion
- United States, 331.89 million
- Indonesia, 276.36 million
- Pakistan, 225.20 million
- Brazil, 213.99 million
- Nigeria, 211.40 million
- Bangladesh, 166.30 million
- Russia, 143.45 million
- Mexico, 130.26 million
Is Earth Overpopulated?
The issue of overpopulation has been debated since at least 1786 when economist Thomas Malthus published his theory that the growth of the population will always outpace the growth in the food supply. This theory is known as Malthusianism.
Malthus viewed the problem as an over-stretching of resources. Today’s thinkers tend to give greater importance to the ethical and efficient distribution of resources.
In any case, population trends are complex and their results are subject to debate. The population of the Earth has indisputably risen dramatically in the past 70 years, from under three billion in 1950 to nearly eight billion now. But birth rates have declined sharply in developed nations during the same period.
The Bottom Line
Each of us is an individual component of many populations. In addition to being members of the human population of Earth and citizens of a nation, we are members of many sub-populations based on age, gender, income, health status, and many other factors.
When statisticians attempt to ascertain a fact or facts about any of those sub-populations, they typically rely on a sample population. These test subjects, selected at random, yield conclusions that are extended to the general population being studied.