Английский глагол read [riːd], переводится как: читать.
Входит в группы:
неправильные глаголы,
глаголы 3-й класс,
глаголы 4-й класс,
глаголы 5-й класс.
3 формы глагола read: Infinitive (read), Past Simple — (read), Past Participle — (read).
📚 Глагол read имеет значения: читать, зачитывать, оглашать, прочитать, расшифровывать, толковать, изучать, разгадывать.
👉 Формы глагола read в настоящем и прошедшем времени 2-я и 3-я форма.
❓ Как будет read в прошедшем времени past simple.
Три формы глагола read
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle | Перевод |
|---|---|---|---|
| read [riːd] |
read [red] |
read [red] |
читать |
Как поставить read во 2-ю и 3-ю форму?
🎓 Как поставить глагол read в Past Simple, Future Simple, Present Perfect, Past Perfect, Future Perfect?
👉 Всё очень просто, в этих временах прошедшего, будущего и совершённого времени, в английском используются 2я и 3я форма глагола:
- First form (V1) — read. (Present simple, Future Simple)
- Second form (V2) —
read.(Past simple)
- Third form (V3) —
read.(Present perfect, Past perfect)
Как поставить read в past simple?
Если вы не совсем поняли какую форму для read нужно использовать в прошедшем времени, будет:
read в past simple — read.
What is the past tense of read?
The past tense of read is read.
The past participle of read is read.
Временные формы глагола — Verb Tenses
Past simple — read в past simple, будет read.
(V2)
Future simple — read в future simple будет read. (will + V1)
Present Perfect — read в present perfect будет
read.
(havehas + V3)
Past Perfect — read в past perfect будет
read.
(had + V3)
Правильный или неправильный глагол read?
👉 Правильный это глагол ли нет? Глагол read это неправильный глагол.
Примеры применения глагола read
-
It must be comfortable to read materials — Читать материалы должно быть приятно для глаз.
(Present Simple) -
Then why did articles I read yesterday said that it couldn’t be true — Тогда почему в статьях, которые я читал вчера говорится, что это не может быть правдой.
(Past Simple) -
She has read all about that thing — Она прочитала все об этом.
(Present Perfect) -
Never read anything as interesting as this book — Никогда не читал ничего интереснее, чем эта книга.
(Past Simple) -
She rarely reads in the mornings, doesn’t have time — Она редко читает по утрам, нет времени.
(Present Simple) -
Aren’t they reading in the bedroom right now? — Разве они не читают в спальне сейчас?
(Present Continuous) -
Can he read music? — Он может читать ноты?
(Present Simple) -
Look, a policeman is reading her her rights — Смотри, полицейский зачитывает ему его права.
(Present Continuous) -
Could you read the article out? — Не могли бы вы зачитать статью вслух?
(Present Simple) -
I won’t read a letter if you are against that — Я не буду читать письмо, если ты против.
(Future Simple)
Вместе с read, часто смотрят глаголы
ride
and be.
Глаголы на букву:
r,
d,
u,
c,
m,
p,
b,
w,
h,
a,
e,
g,
s,
q,
j,
l,
t,
f,
o,
n,
k,
i,
v,
y,
z.
First Question: Do you like to read?
Second Question: What’s the best book you’ve ever read?
Third Question: Notice anything about the last words in the first and second questions?
Most likely you noticed they are spelled the same and both relate to the same activity: reading. They are, however, pronounced differently. The read at the end of the first question rhymes with seed, while the read in the second question rhymes with bed.
So how do you know which pronunciation to use? Read (like seed) more to find out!
What Does «Read» Mean?
Read most often takes the form of a verb and, like many words in the English language, has several related but distinct definitions.
The most used definitions for the verb “to read” are:
- To look at, interpret, and comprehend the meaning of written material
- To verbalize written material, usually to another person who is listening
What Is the Past Tense of «Read»?
For most regular verbs, if you want to write in the past tense, you just add -ed (e.g. played, jumped, shouted). Unfortunately, the irregular verb read doesn’t work like that. There’s no such word as readed.
Instead, there are a few different ways to write read in the past tense, depending on who was doing the reading and when it happened.
When it comes to pronunciation, there are two general rules you can follow for «read» in the past tense:
- Any form with the ing ending has the long e sound (like «weeding»).
- Any form that includes has/have/had before read (without the ing) has the short e sound (like «red»).
How Do I Conjugate the Verb «To Read»?
If you’re studying English grammar, you might have heard of verb conjugation before. This sounds complicated, but all it means is changing a verb to make it make sense in your sentence.
There are several different ways you can talk about the past in English, and each of them has its own rules. We’ll break them down and give you examples so you can get it right every time.
What Is the Simple Past Form of «To Read»?
We use the simple past tense to describe an action that was completed before now.
- I read the instructions before I built the wardrobe.
Pronunciation: «Read» sounds like «red».
What Is the Past Perfect Form of «To Read»?
Now we get a bit more specific. If you had finished reading something before a specific point in the past, use «had read».
- I had read Moby Dick three times by the time I was ten years old.
Pronunciation: «Read» sounds like «red»—and remember to include «had» before «read».
What Is the Past Continuous Form of “To Read”?
If someone began reading in the past, and was still reading when another event occurred, use «was reading,» like this:
- He was reading when the telephone rang.
- They were reading when the alarm sounded.
Pronunciation: «Reading» rhymes with «weeding».
What Is the Past Perfect Continuous Form of «To Read»?
If you want to describe a continuing action that occurred before a particular time in the past, use «had been reading».
- She had been reading romance novels for years before she decided to write a novel herself.
- I had been reading about space travel, so I decided to become an astronaut.
As you can see from these examples, we use «had been reading» to describe actions that have taken place continuously over a longer period of time (e.g. for years) that directly relate to the moment you want to reference (e.g. she decided to write a novel herself).
Pronunciation: «Reading» rhymes with «weeding».
What Is the Past Participle of «Read»?
Time for a bonus round! The past participle is not actually a tense. Instead, it is the form of a verb that we use to make the past perfect tense.
That’s a lot of grammar jargon. All you really need to know is that the past participle of «to read» is «read» (rhymes with «red»).
While this is spelled the same as the simple past version, it is used differently.
Simple Past:
- I read the book yesterday.
- I read the reviews before I made my decision.
- I read to her to help her fall asleep.
Past Participle:
- My students had read the book, but I don’t think they understood it.
- I had read about it in a book, but seeing the sunrise over Mount Fuji in person was so much better.
- The book had been read by millions of people before the movie came out.
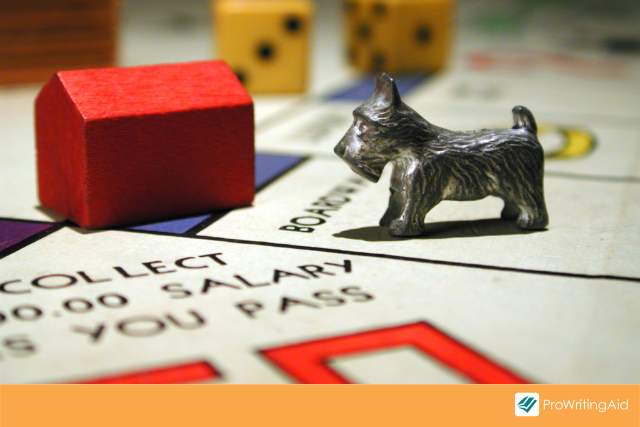
Does «Reading» Ever Rhyme with «Bedding»?
The only instance I know of where «reading» rhymes with «bedding» is when it’s referring to a city in the state of Pennsylvania, the town near London, or the (no longer in existence) Reading Co., which was a railroad in Southeast Philadelphia, PA. If you’ve ever played the board game Monopoly (the American version) you may have heard of the Reading Railroad.
If you know other examples of «reading» rhyming with «bedding» let me know!
What Are Some Homophones for «Read»?
Now that you know the past tense of read, let’s check your spelling.
Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings, spellings, or origins.
For example, the past tense of «to read», which is read, shares the same sound as red—but not the same meaning.
The present tense to read (rhymes with deed) sounds like reed, but as with the past tense of read and the word red, that similar sound is all the words have in common.
- Red is an adjective that identifies color. It’s the color of blood, marinara sauce, and the most popular roses and sports cars. Red is not an action. It’s not a verb. Read (past tense) is a verb. It means that in the past, you (or another subject) looked at, interpreted, and comprehended some written text.
- Reed is not a verb either. In its noun form, a reed is a long, grassy plant that grows in a marsh or a thin blade of cane or metal that is used to play certain instruments.
As an adjective, reed describes instruments that require reeds (the noun) to make sound: a clarinet is a reed instrument.
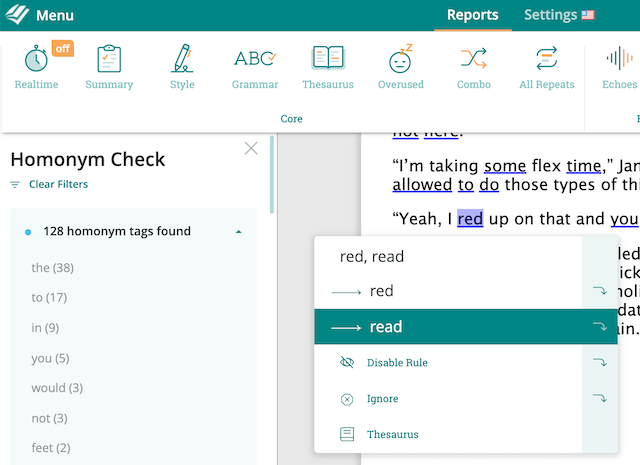
ProWritingAid’s Homonym Report can help you recognize any possible homophone errors in your work. Be sure to try it out!
What Does It Mean to «Read Up On» Something?
There are lots of phrases in English that contain the word «read» (in both the past and present tense). Many of these phrases are idioms, which means that the meaning of the phrase differs from the meaning of its individual words. For example, to call off an event means to cancel that event even though neither «call» nor «off» means «to cancel».
Most of the phrases below can be presented in either the past (where read rhymes with red) or present (where read rhymes with reed) tense.
-
Read over: to read through something quickly; get an overview.
-
Read off: to read out loud from a list.
-
Read back: to read, out loud, information someone has just dictated or given.
-
Read up on: to learn about something by reading about it.
-
Read one’s mind: to know what someone is thinking.
-
Do you read me?: the speaker is saying, “Do you understand me?”. This one can only be used in the present tense.
-
Read between the lines: to recognize the real meaning behind the surface or apparent meaning.
-
Read like a book: to understand someone completely—their emotions or intentions.
-
Read my lips: the speaker is saying “Pay attention!” or “Listen closely!”. This one can only be used in the present tense.
-
Read one’s rights: law enforcement must recite the perpetrator’s legal rights upon arrest.
-
Read the room: to assess/analyze the mood of people in a particular setting and act appropriately in response.
-
Read the fine print: to make certain you are aware of and understand the specific rules/regulations.
-
Read ’em and weep: to show results that make you the victor! This idiom is often used in card games. This one can only be used in the present tense.
-
Read the riot act: to scold harshly.
-
It reads well: this means a work is written well and pleasing to read. (Past tense: It read well, rhyming with «red».)
-
Read music: to understand the symbols used in written musical scores.
For even more read idioms, check out TheFreeDictionary.
How Does «Read» Function as a Noun?
Because the English language loves to keep its readers, writers, speakers, and learners on their toes, read has another function as a noun.
If you give something a read, that means you’ve read through it.
If you enjoy a book or article, you might say, «that was a great read!»
If you have a read on something, that means you understand how it works.
When used as a noun, read has the long e sound and is preceded by an article (usually «a»).
Quiz: How Do You Pronounce «Read»?
Which «read» is it? Long e or short e? Test yourself. Pay attention to the tense!
-
I cannot read very fast.
-
She read that entire book yesterday!
-
You will need to read those instructions carefully.
-
I would have read it, but I was so tired I fell asleep.
-
Keep reading! You’ll love the ending.
-
Please don’t disturb me while I’m reading.
-
I was reading that last night.
-
I read it, but I didn’t enjoy it.
-
He reads aloud to the children every night.
-
He read aloud to the children every night when they were small.
-
You can find the answer if you read carefully.
-
If you had read more carefully, you would have found the answer.
-
At school, teachers help students learn to read.
-
They have not read the newspaper yet.
-
The teacher read to the class.
-
I read books.
Answers: 1. Long 2. Short 3. Long 4. Short 5. Long 6. Long 7. Long 8. Short 9. Long 10. Short 11. Long 12. Short 13. Long 14. Short 15. Short 16. It depends!
In 16., we need more information to determine the correct answer to this «trick» question. If the speaker is making a present-tense statement, then it’s the long e. If they are answering a question about what they did last week (or some other time in the past), then it’s the short e.
FREE quiz PDF download: Which «read» is it?
Example of past tense:
-
«What did you do while you were sitting on the beach?»
-
«I read books.»
(short e, rhymes with «red»)
Example of present tense:
-
«What do you do for a hobby?»
-
«I read books.»
(long e, rhymes with «weed»)
Read: A Review
Now you’ve read through this post you should have a solid read on when to pronounce read with the long e or short e sound.
If you need a review, read through it again and let the sounds sink in.
Before you go, I’d love to recommend a book I just read (short e). I’m a fan of thoughtful suspense (and rich psychological thrillers) and The Searcher by Tana French was a great read (long e)—I hope you enjoy it!
Take your writing to the next level:
20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas.
This guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers.

The English verb ‘read’ is pronounced as [riːd].
Related to:
irregular verbs.
3 forms of verb read: Infinitive (read), Past Simple — (read), Past Participle — (read).
Here are the past tense forms of the verb read
👉 Forms of verb read in future and past simple and past participle.
❓ What is the past tense of read.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| read [riːd] |
read [red] |
read [red] |
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb read?
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ‘read‘?
Learn the three forms of the English verb ‘read’
- the first form (V1) is ‘read’ used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is ‘read’
used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is
‘read’used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of read?
The past tense and past participle of read are:
read in past simple is
read,
and past participle is
read.
What is the past tense of read?
The past tense of the verb «read» is «read»,
and the past participle is
«read».
Verb Tenses
Past simple — read in past simple read
(V2).
Future simple — read in future simple is read (will + V1).
Present Perfect — read in present perfect tense is
read
(have/has + V3).
Past Perfect — read in past perfect tense is
read
(had + V3).
read regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is ‘read’ a regular or irregular verb? The verb ‘read’ is irregular verb.
Examples of Verb read in Sentences
-
It must be comfortable to read materials(Present Simple)
-
Then why did articles I read yesterday said that it couldn’t be true(Past Simple)
-
She has read all about that thing(Present Perfect)
-
Never read anything as interesting as this book(Past Simple)
-
She rarely reads in the mornings, doesn’t have time(Present Simple)
-
Aren’t they reading in the bedroom right now?(Present Continuous)
-
Can he read music?(Present Simple)
-
Look, a policeman is reading her her rights(Present Continuous)
-
Could you read the article out?(Present Simple)
-
I won’t read a letter if you are against that(Future Simple)
Along with read, words are popular
buy
Verbs by letter:
r,
d,
u,
c,
m,
p,
b,
w,
h,
a,
e,
g,
s,
q,
j,
l,
t,
f,
o,
n,
k,
i,
v,
y,
z.
Why Is the Past Tense of Read Read?
To first understand a word, its history, and how to use it properly, it is important to first define what it actually means. According to the Merriam Webster Dictionary, the English verb read can be defined as “to receive or take in the sense of (letters, symbols, etc.), especially by sight or touch, to study the movements of with mental formulation of the communication expressed.”. A secondary definition is to become acquainted with or look over the contents of (something, such as a book), e.g., to read over a piece of documentation. Overall, there are more than forty definitions listed for the verb “to read” in both transitive and intransitive forms.
The correct simple past tense of the verb to read is just “read.” According to WordHippo, while the present tense of the verb is “to read” (with the third person plural being “reads”), the past tense is also read, but it is pronounced “red” rather than “reed”. The confusion inherent in the grammar does pretty much come down to the pronunciation at the end of the day with this irregular verb. So, in short, the past tense of read is also read in pretty much any context. Past tense verbs can be tricky like this. We will discuss context later on in this article.
What Are the 3 Forms of Read?
There are actually three different forms of the word “read,” and they all work in different contexts. Here they are:
- Read: sounds like need, and is the simple present tense of the verb.
- Read: sounds like red, and is the past tense of the verb.
- Read: sounds like red, but is the past participle of the verb, and is used in the context of things that have happened in your life. For example, “I have read that book in the past.”
What Is the Past and Past Participle of Read?
The correct past tense of read is also spelled “read,” but it is pronounced like the color red rather than the plant, a reed. The past participle, which is the third form of the verb, is always preceded by the word “have,” and it conveys a completed action in someone’s past (e.g., I have read, I have done, I have been, etc.). Both “read” and “have read” are past tense, but usually, the past participle is used for when people are describing an action in their past that is completed.
As a side note, if you’re curious about any other verb forms, the present participle, or gerund, of read is reading— for example, you would say “I am reading.” In the future tense, in both American English and British English, we say “will read,” as in “they will read, he/she will read.” The past perfect tense would be “have/has been reading.”
The word “read” also has a noun form, but it is not used often, and because it is a noun, it has no tense or conjugation (past, present, or future).
The History and Origin of the Word
One of the best ways to understand a word is to learn where it came from. A word’s etymology can reveal a lot about the changes a word has gone through to get to where it is today in modern English. According to EtymOnline.com, the word “to read” first entered modern English from the Old English word “raedan,” which came from the Anglian word “redan,” which was translated “to advise, counsel, persuade, discuss, deliberate, rule, or guide.” Words from most of this root in most modern languages still mean counsel or advise, but also mean “to understand the meaning of written symbols.”
The word came from the Latin word “legere,” which means to read as well. Much of the vocabulary in modern English actually comes from ancient Latin or Greek by way of other modern European languages such as Italian, Spanish, or French.
Examples of the Word in Context
Another great way to learn how to use a word is to explore the word being used correctly. Either reading the word in its proper context or hearing someone else use it in conversation. Here are some common examples of the word “to read” (and its past tense, also read) in context:
- “Are you going to read the assignment for this week? Or are you just planning on looking over the Sparknotes?”
- “Have you read the most recent news article about the earthquakes on the west coast? Things seem to be getting pretty rough.”
- “He read the lyrics and got really emotional. It seemed like the song really hit close to home.”
Synonyms for Read
Finally, to really solidify a word into your vocabulary, it is useful to explore words with similar or same definitions. The more words you know that can fit into a specific context, the easier it will be to remember which ones to use. Here are some synonyms for the verb “to read”:
- To peruse means to read quickly, to glance over
- To devour means to read deeply and often
- To scrutinize means to read with very specific intent and focus
Sources:
- https://thewordcounter.com/blog-common-grammar-mistakes/
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/read
- https://www.wordhippo.com/what-is/the-past-tense-of/read.html
- https://www.etymonline.com/word/read#etymonline_v_7319
- https://thewordcounter.com/midnight-and-noon/
- https://thewordcounter.com/is-vs-are/
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do’s and don’ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
Let’s find out with English tivi in the article below.
See more at: Verbs
Read of Definition and Meaning
Read is a verb that means to occupy oneself with reading.
It can also mean to read something attentively or care about it.
| Base Form (V1) | read |
| Past Form (V2) | read |
| Past Participle Form (V3) | read |
| s / es/ es (V4) | reads |
| ‘ing’ form (V5) |
reading |
Read of Past Simple V2
The verb read is also employed in its V2 form as “read”. It is used to indicate the past tense in sentences.
Read of Past Participle V3
This verb’s V3 form is ‘read‘. In the case of past perfect tense or present perfect tense, the word ‘read‘ is used.
+ In the present perfect tense, the word read is used ‘have +’read’ or ‘has +’read.’
- I, you, and we are used as ‘have + ‘read‘ subjects.
- He, she, and it are used as ‘has +’read’ subjects.
+ If you need to use the past perfect tense, use ‘had +’read‘ regardless of the subject.
You might also like: ALL the English Grammar Basics You Need
Conjugation of Read V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
| Conjugation table: Read | |||
| Number | Singular | ||
| Present Simple of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| read | read | reads | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| read | read | read | |
| Present Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| am reading | are reading | is reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| are reading | are reading | are reading | |
| Present Perfect of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| have read | have read | has read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| have read | have read | have read | |
| Present Perfect Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| have been reading | have been reading | has been reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| have been reading | have been reading | have been reading | |
| Past Simple of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| read | read | read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| read | read | read | |
| Past Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| was reading | were reading | was reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| were reading | were reading | were reading | |
| Past Perfect of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| had read | had read | had read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had read | had read | had read | |
| Past Perfect Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| had been reading | had been reading | had been reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had been reading | had been reading | had been reading | |
| Future Simple of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall read | will/shall read | will/shall read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall read | will/shall read | will/shall read | |
| Future Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall be reading | will/shall be reading | will/shall be reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall be reading | will/shall be reading | will/shall be reading | |
| Future Perfect of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall have read | will/shall have read | will/shall have read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall have read | will/shall have read | will/shall have read | |
| Future Perfect Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall have been reading | will/shall have been reading | will/shall have been reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall have been reading | will/shall have been reading | will/shall have been reading | |
| Conditional Present of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| would read | would read | would read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would read | would read | would read | |
| Conditional Perfect of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| would have read | would have read | would have read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would have read | would have read | would have read | |
| Conditional Present Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| would be reading | would be reading | would be reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would be reading | would be reading | would be reading | |
| Conditional Perfect Continuous of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| would have been reading | would have been reading | would have been reading | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would have been reading | would have been reading | would have been reading | |
| Present Subjunctive of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| read | read | read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| read | read | read | |
| Past Subjunctive of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| read | read | read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| read | read | read | |
| Past Perfect Subjunctive of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| had read | had read | had read | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had read | had read | had read | |
| Imperative of read | I | You | She/He/It |
| read | |||
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| Let’s read | read |
See more at: Vocabulary
Example Sentences with Read V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
In this section, we will learn about read sentence examples:
+ They read this article
+ They read this book a month ago
+ My sister has read English well
+ He reads book about the love romantic
+ I’m reading news
Synonym Words For Read
Synonym of read word list. Here are a variety of words whose meaning is nearly the synonym of read:
- peruse
- study
- scan
- browse
- examine
- inspect
- skim
- view
- follow
- con
- devour
- glance
- through
- go over
- go through
- look at
- look over
- look through
- pore over
- browse through
- flick through
- flip through
- leaf through
- refer to
- thumb through
- bury oneself in
Opposite Words For Read
The antonym of read word list. Here are some words that have nearly the opposite meaning as read:
- ignore
- overlook
- bypass
- dismiss
- skip
- miss
- omit
- overpass
- discount
- misheed
- neglect
- unheed
- avoid
- evade
- misinterpret
- misunderstand
- forget
- brush
- aside
- dispense with
- pass over
- pay no attention to
- pay no heed to
- pay no mind to
You might also like: Best List of Irregular Verbs in English
Some Frequently Asked Questions About Read(Verb)
What is the V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 of read?
The past tense of read is read . The third-person singular simple present indicative form of read is reads. The present participle of read is reading. The past participle of read is read.
| Base Form (V1) | read |
| Past Form (V2) | read |
| Past Participle Form (V3) | read |
| s / es/ ies (V4) | reads |
| ‘ing’ form (V5) | reading |
What is the V2 and V3 form of read ?
+ The V2 and V3 form of read is “ read “ and “read ”.
What is the sentence of read ?
What is the past tense V2 of read ?
+ The past tense of read is “ read “.
What is the past participle V3 of read?
+ The past participle of read is “ read “.
What is the present participle V5 of read ?
+ The present participle of read is “ reading“.
Conclusion
Let’s learn with Englishtivi.com the structure of the verb Read V1 V2 V3 V4 V5: Base Form, Past Simple, Present Continuous and Present Continuous and Present Continuous and Present Continuous forms. We wish you all the best of luck.
You should subscribe to the English TV YouTube channel if you want to learn more about the English language and improve your proficiency.
Here are other verbs V1 V2 V3 List
| Base Form V1 | Past Form V2 | Past Participle Form V3 |
| abide | abode/abided | abode/abided |
| arise | arose | arisen |
| awake | awoke | awoken |
| backslide | backslid | backslidden/backslid |
| be | was/were | been |
| bear | bore | borne |
| beat | beat | beaten/beat |
| become | became | become |
| befall | befell | befallen |
| begin | began | begun |
| behold | beheld | beheld |
| bend | bent | bent |
| beset | beset | beset |
| bespeak | bespoke | bespoken |
| bet | bet/betted | bet/betted |
| bid | bid | bid |
| bind | bound | bound |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| bleed | bled | bled |
| blow | blew | blown |
| break | broke | broken |
| breed | bred | bred |
| bring | brought | brought |
| broadcast | broadcast | broadcast |
| browbeat | browbeat | browbeaten/browbeat |
| build | built | built |
| burn | burnt/burned | burnt/burned |
| burst | burst | burst |
| bust | busted/bust | busted/bust |
| buy | bought | bought |
| cast | cast | cast |
| catch | caught | caught |
| chide | chid/chided | chid/chidden/chided |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| cleave | clove/cleft/cleaved | cloven/cleft/cleaved |
| cleave | clave | cleaved |
| cling | clung | clung |
| clothe | clothed/clad | clothed/clad |
| come | came | come |
| cost | cost | cost |
| creep | crept | crept |
| crossbreed | crossbred | crossbred |
| crow | crew/crewed | crowed |
| cut | cut | cut |
| daydream | daydreamed daydreamt |
daydreamed daydreamt |
| deal | dealt | dealt |
| dig | dug | dug |
| disprove | disproved | disproved/disproven |
| dive | dove/dived | dived |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| dream | dreamt/dreamed | dreamt/dreamed |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| drive | drove | driven |
| dwell | dwelt | dwelt |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feed | fed | fed |
| feel | felt | felt |
| fight | fought | fought |
| find | found | found |
| fit | fitted/fit | fitted/fit |
| flee | fled | fled |
| fling | flung | flung |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forbear | forbore | forborne |
| forbid | forbade/forbad | forbidden |
| forecast | forecast/forecasted | forecast/forecasted |
| forego (also forgo) | forewent | foregone |
| foresee | foresaw | foreseen |
| foretell | foretold | foretold |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven |
| forsake | forsook | forsaken |
| freeze | froze | frozen |
| frostbite | frostbit | frostbitten |
| get | got | got/gotten |
| gild | gilt/gilded | gilt/gilded |
| gird | girt/girded | girt/girded |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| grind | ground | ground |
| grow | grew | grown |
| hand-feed | hand-fed | hand-fed |
| handwrite | handwrote | handwritten |
| hang | hung | hung |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| heave | hove/heaved | hove/heaved |
| hew | hewed | hewn/hewed |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| inbreed | inbred | inbred |
| inlay | inlaid | inlaid |
| input | input | input |
| inset | inset | inset |
| interbreed | interbred | interbred |
| interweave | interwove interweaved |
interwoven interweaved |
| interwind | interwound | interwound |
| jerry-build | jerry-built | jerry-built |
| keep | kept | kept |
| kneel | knelt/kneeled | knelt/kneeled |
| knit | knit/knitted | knit/knitted |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| lean | leaned/leant | leaned/leant |
| leap | leapt /leaped | leapt /leaped |
| learn | learnt/learned | learnt/learned |
| leave | left | left |
| lend | lent | lent |
| let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain |
| light | lit/lighted | lit/lighted |
| lip-read | lip-read | lip-read |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| mean | meant | meant |
| meet | met | met |
| miscast | miscast | miscast |
| misdeal | misdealt | misdealt |
| misdo | misdid | misdone |
| mishear | misheard | misheard |
| mislay | mislaid | mislaid |
| mislead | misled | misled |
| mislearn | mislearned mislearnt |
mislearned mislearnt |
| misread | misread | misread |
| misset | misset | misset |
| misspeak | misspoke | misspoken |
| misspell | misspelt | misspelt |
| misspend | misspent | misspent |
| mistake | mistook | mistaken |
| misteach | mistaught | mistaught |
| misunderstand | misunderstood | misunderstood |
| miswrite | miswrote | miswritten |
| mow | mowed | mown/mowed |
| offset | offset | offset |
| outbid | outbid | outbid |
| outbreed | outbred | outbred |
| outdo | outdid | outdone |
| outdraw | outdrew | outdrawn |
| outdrink | outdrank | outdrunk |
| outdrive | outdrove | outdriven |
| outfight | outfought | outfought |
| outfly | outflew | outflown |
| outgrow | outgrew | outgrown |
| outleap | outleaped/outleapt | outleaped/outleapt |
| outlie | outlied | outlied |
| output | output | output |
| outride | outrode | outridden |
| outrun | outran | outrun |
| outsell | outsold | outsold |
| outshine | outshined/outshone | outshined/outshone |
| outshoot | outshot | outshot |
| outsing | outsang | outsung |
| outsit | outsat | outsat |
| outsleep | outslept | outslept |
| outsmell | outsmelled/outsmelt | outsmelled/outsmelt |
| outspeak | outspoke | outspoken |
| outspeed | outsped | outsped |
| outspend | outspent | outspent |
| outswear | outswore | outsworn |
| outswim | outswam | outswum |
| outthink | outthought | outthought |
| outthrow | outthrew | outthrown |
| outwrite | outwrote | outwritten |
| overbid | overbid | overbid |
| overbreed | overbred | overbred |
| overbuild | overbuilt | overbuilt |
| overbuy | overbought | overbought |
| overcome | overcame | overcome |
| overdo | overdid | overdone |
| overdraw | overdrew | overdrawn |
| overdrink | overdrank | overdrunk |
| overeat | overate | overeaten |
| overfeed | overfed | overfed |
| overfly | overflew | overflown |
| overhang | overhung | overhung |
| overhear | overheard | overheard |
| overlay | overlaid | overlaid |
| overpay | overpaid | overpaid |
| override | overrode | overridden |
| overrun | overran | overrun |
| oversee | oversaw | overseen |
| oversell | oversold | oversold |
| oversew | oversewed | oversewn/oversewed |
| overshoot | overshot | overshot |
| oversleep | overslept | overslept |
| overspeak | overspoke | overspoken |
| overspend | overspent | overspent |
| overspill | overspilled/overspilt | overspilled/overspilt |
| overtake | overtook | overtaken |
| overthink | overthought | overthought |
| overthrow | overthrew | overthrown |
| overwind | overwound | overwound |
| overwrite | overwrote | overwritten |
| partake | partook | partaken |
| pay | paid | paid |
| plead | pleaded/pled | pleaded/pled |
| prebuild | prebuilt | prebuilt |
| premake | premade | premade |
| prepay | prepaid | prepaid |
| presell | presold | presold |
| preset | preset | preset |
| preshrink | preshrank | preshrunk |
| proofread | proofread | proofread |
| prove | proved | proven/proved |
| put | put | put |
| quick-freeze | quick-froze | quick-frozen |
| quit | quit/quitted | quit/quitted |
| read | read | read |
| reawake | reawoke | reawaken |
| rebid | rebid | rebid |
| rebind | rebound | rebound |
| rebroadcast | rebroadcast rebroadcasted |
rebroadcast rebroadcasted |
| rebuild | rebuilt | rebuilt |
| recast | recast | recast |
| recut | recut | recut |
| redeal | redealt | redealt |
| redo | redid | redone |
| redraw | redrew | redrawn |
| refit | refitted/refit | refitted/refit |
| regrind | reground | reground |
| regrow | regrew | regrown |
| rehang | rehung | rehung |
| rehear | reheard | reheard |
| reknit | reknitted/reknit | reknitted/reknit |
| relay | relaid | relaid |
| relearn | relearned/relearnt | relearned/relearnt |
| relight | relit/relighted | relit/relighted |
| remake | remade | remade |
| rend | rent | rent |
| repay | repaid | repaid |
| reread | reread | reread |
| rerun | reran | rerun |
| resell | resold | resold |
| resend | resent | resent |
| reset | reset | reset |
| resew | resewed | resewn/resewed |
| retake | retook | retaken |
| reteach | retaught | retaught |
| retear | retore | retorn |
| retell | retold | retold |
| rethink | rethought | rethought |
| retread | retread | retread |
| retrofit | retrofitted/retrofit | retrofitted/retrofit |
| rewake | rewoke/rewaked | rewaken/rewaked |
| rewear | rewore | reworn |
| reweave | rewove/reweaved | rewoven/reweaved |
| rewed | rewed/rewedded | rewed/rewedded |
| rewet | rewet/rewetted | rewet/rewetted |
| rewin | rewon | rewon |
| rewind | rewound | rewound |
| rewrite | rewrote | rewritten |
| rid | rid | rid |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| rise | rose | risen |
| roughcast | roughcast | roughcast |
| run | ran | run |
| sand-cast | sand-cast | sand-cast |
| saw | sawed | sawn |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| seek | sought | sought |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| set | set | set |
| sew | sewed | sewn/sewed |
| shake | shook | shaken |
| shave | shaved | shaved/shaven |
| shear | sheared | shorn |
| shed | shed | shed |
| shine | shone | shone |
| shit | shit/shat/shitted | shit/shat/shitted |
| shoot | shot | shot |
| show | showed | shown/showed |
| shrink | shrank | shrunk |
| shut | shut | shut |
| sight-read | sight-read | sight-read |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sink | sank | sunk |
| sit | sat | sat |
| slay | slew | slain |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| slide | slid | slid |
| sling | slung | slung |
| slink | slunk | slunk |
| slit | slit | slit |
| smell | smelt | smelt |
| smite | smote | smitten |
| sneak | sneaked/snuck | sneaked/snuck |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| speed | sped/speeded | sped/speeded |
| spell | spelt/spelled | spelt/spelled |
| spend | spent | spent |
| spill | spilt/spilled | spilt/spilled |
| spin | spun/span | spun |
| spoil | spoilt/spoiled | spoilt/spoiled |
| spread | spread | spread |
| stand | stood | stood |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| stick | stuck | stuck |
| sting | stung | stung |
| stink | stunk/stank | stunk |
| stride | strode | stridden |
| strike | struck | struck |
| string | strung | strung |
| sunburn | sunburned/sunburnt | sunburned/sunburnt |
| swear | swore | sworn |
| sweat | sweat/sweated | sweat/sweated |
| sweep | swept | swept |
| swell | swelled | swollen/swelled |
| swim | swam | swum |
| swing | swung | swung |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| tear | tore | torn |
| telecast | telecast | telecast |
| tell | told | told |
| think | thought | thought |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| thrust | thrust | thrust |
| tread | trod | trodden/trod |
| typewrite | typewrote | typewritten |
| unbend | unbent | unbent |
| unbind | unbound | unbound |
| unclothe | unclothed/unclad | unclothed/unclad |
| undercut | undercut | undercut |
| underfeed | underfed | underfed |
| undergo | underwent | undergone |
| underlie | underlay | underlain |
| understand | understood | understood |
| undertake | undertook | undertaken |
| underwrite | underwrote | underwritten |
| undo | undid | undone |
| unfreeze | unfroze | unfrozen |
| unhang | unhung | unhung |
| unhide | unhid | unhidden |
| unlearn | unlearned/unlearnt | unlearned/unlearnt |
| unspin | unspun | unspun |
| unwind | unwound | unwound |
| uphold | upheld | upheld |
| upset | upset | upset |
| wake | woke/waked | woken/waked |
| wear | wore | worn |
| wed | wed/wedded | wed/wedded |
| weep | wept | wept |
| wet | wet/wetted | wet/wetted |
| win | won | won |
| wind | wound | wound |
| withdraw | withdrew | withdrawn |
| withhold | withheld | withheld |
| withstand | withstood | withstood |
| work | worked | worked |
| wring | wrung | wrung |
| write | wrote | written |
Post Views: 4,961