Filters
Filter synonyms by Letter
C D E G H I N O S V W
Filter by Part of speech
phrase
noun
adjective
Suggest
If you know synonyms for Internet, then you can share it or put your rating in listed similar words.
Suggest synonym
Menu
Internet Thesaurus
Definitions of Internet
Nearby Words
intern, interne, internetwork, internetting
External Links
Other usefull sources with synonyms of this word:
Synonym.tech
Thesaurus.com
Collinsdictionary.com
Wiktionary.org
Photo search results for Internet






Image search results for Internet






Cite this Source
- APA
- MLA
- CMS
Synonyms for Internet. (2016). Retrieved 2023, April 12, from https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/internet
Synonyms for Internet. N.p., 2016. Web. 12 Apr. 2023. <https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/internet>.
Synonyms for Internet. 2016. Accessed April 12, 2023. https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/internet.
What is another word for internet?
What is another word for internet?
| World Wide Web | cyberspace |
|---|---|
| interweb | WWW |
What is another word for connected to the Internet?
wired
Is Web another name of Internet?
The terms internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably; it is common to speak of “going on the Internet” when using a web browser to view web pages.
What are the disadvantages of Internet?
What are the disadvantages of the Internet?
- Addiction, time-waster, and causes distractions.
- Bullying, trolls, stalkers, and crime.
- Spam and advertising.
- Pornographic and violent images.
- Never being able to disconnect from work.
- Identity theft, hacking, viruses, and cheating.
- Affects focus and patience.
What is the three disadvantage of Internet?
1) Hacking is the most common disadvantage of the internet. 2) Personal information in social media is very much vulnerable to hackers. 3) Virus threats on the internet can damage your data and information. 4) Too much addiction to internet leads to time wastage, affecting our productivity and health.
What is the disadvantage of internet to students?
Addiction The internet can also be extremely addictive to students. The students could spend too much time wasting on internet neglecting their studies. There are so much of entertainment options on internet that can make a student distracted from their studies.
What is the positive and negative effect of Internet?
The positive impacts of the internet include the following: It provides effective communication using emailing and instant messaging services to any part of the world. It improves business interactions and transactions, saving on vital time. Banking and shopping online have made life less complicated.
Is Internet a good thing?
Roughly 70 percent of American adults who use the internet believe it’s mostly good for society, down from 76 percent in 2014, Pew found. The internet is great for many things, like helping people stay in touch, spreading vital information and easing the burden of everyday tasks, like shopping or paying the bills.
How internet affect our daily life?
The Internet has changed business, education, government, healthcare, and even the ways in which we interact with our loved ones—it has become one of the key drivers of social evolution. The changes in social communication are of particular significance. The Internet has removed all communication barriers.
How can we use the Internet in a positive way?
10 ways to use the internet positively
- Building friendships. Digital communication is now a fact of life for many young people.
- Keeping in touch.
- Making a difference.
- Exploring the world (virtually)
- Choosing a job or career.
- Following the news.
- Learning new skills.
- Getting published.
How can I be a good person on the Internet?
- Take a deep breath. You should take a deep breath before you do anything, ever.
- Think about your goal.
- Remember that words have meaning.
- Remember that all actions have consequences.
- Don’t like or retweet mean comments.
- If you make a mistake, apologize.
- Don’t put other people’s crap in your mouth.
What are the different ways to use the Internet?
Top 10 uses of the Internet
- Electronic mail. At least 85% of the inhabitants of cyberspace send and receive e-mail.
- Research.
- Downloading files.
- Discussion groups.
- Interactive games.
- Education and self-improvement.
- Friendship and dating.
- Electronic newspapers and magazines.
Why the Internet is bad?
And that’s not all: Extensive Internet use has been linked with eyestrain, bad posture, ADHD, sleep deprivation, bullying, relationship stress and more. The majority of Americans – 85 percent of adults and 95 percent of teens – use the Internet, and up to 5-10 percent of Internet users are addicted.
Is the Internet good or bad for your brain?
Recent research suggests that excess use of the internet over prolonged periods of time may negatively affect some cognitive functions, particularly attention and short-term memory.
How the Internet affects your mental health?
Excessive Internet use may create a heightened level of psychological arousal, resulting in little sleep, failure to eat for long periods, and limited physical activity, possibly leading to the user experiencing physical and mental health problems such as depression, OCD, low family relationships and anxiety.
What is the most dangerous technology?
Here are seven of the most dangerous technology trends:
- Drone Swarms.
- Spying Smart Home Devices.
- Facial Recognition.
- AI Cloning.
- Ransomware, AI and Bot-enabled Blackmailing and Hacking.
What does technology do to your brain?
Potential harmful effects of extensive screen time and technology use include heightened attention-deficit symptoms, impaired emotional and social intelligence, technology addiction, social isolation, impaired brain development, and disrupted sleep.
How technology affect our life?
Technology affects the way individuals communicate, learn, and think. It helps society and determines how people interact with each other on a daily basis. We are living in an era where technological advances are common. The internet and cell phones are some examples.
Can you live a life without technology?
Yes, for most people, tech is not something we give a second thought to, but some people literally can’t live without technology – and we aren’t being dramatic. For some people, the existence of technology is the difference between silence and laughter, loneliness and interaction, and even life and death.
What are the positive effects of technology?
These are just a few of the ways in which technology may positively affect our physical and mental health:
- health apps to track chronic illnesses and communicate vital information to doctors.
- health apps that help you track diet, exercise, and mental health information.
Is technology positive or negative?
Overall, views about the effects of technology are also largely positive, if a bit less so in comparison with science. About half of adults (52%) say technology has had mostly positive effects, compared with 38% who say there have been an equal mix of positive and negative effects of technology.
What are the positive effects of medical technology?
Appropriate and widespread use of medical technology has the potential to improve health outcomes via earlier and more accurate diagnosis and safer, more effective and appropriate treatment. This is especially clear when one considers the impact of advances in diagnostic technologies and devices.
How is technology affecting the learning process?
Technology can help students by making learning more engaging and collaborative. Rather than memorizing facts, students learn by doing and through critical thinking. This could be as simple as taking an interactive quiz in class or participating in tech-enabled group discussions.
What are the positive effects of technology in education?
Effects of Technology on Classrooms and Students
- Change in Student and Teacher Roles.
- Increased Motivation and Self Esteem.
- Technical Skills.
- Accomplishment of More Complex Tasks.
- More Collaboration with Peers.
- Increased Use of Outside Resources.
- Improved Design Skills/Attention to Audience.
How technology enhances teaching and learning?
Technology in education enables children to adjust to their own pace of learning. Students who need extra time can spend more time going over exercises until they understand, whilst students who need less support can continue ahead. It also frees up the teacher to help kids who need more support on an individual level.
How beneficial technology is used in teaching and learning process?
Technology, when integrated into the curriculum, revolutionizes the learning process. More and more studies show that technology integration in the curriculum improves students’ learning processes and outcomes. Teachers who recognize computers as problem-solving tools change the way they teach.
This article is about the worldwide computer network. For the global system of pages accessed via URLs, see World Wide Web. For other uses, see Internet (disambiguation).
The Internet (or internet)[a] is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP)[b] to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the late 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers.[2] The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the 1970s to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, led to worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies, and the merger of many networks.[3] The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet,[4] and generated a sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, commercialization incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life.
Most traditional communication media, including telephone, radio, television, paper mail, and newspapers, are reshaped, redefined, or even bypassed by the Internet, giving birth to new services such as email, Internet telephone, Internet television, online music, digital newspapers, and video streaming websites. Newspaper, book, and other print publishing have adapted to website technology or have been reshaped into blogging, web feeds, and online news aggregators. The Internet has enabled and accelerated new forms of personal interaction through instant messaging, Internet forums, and social networking services. Online shopping has grown exponentially for major retailers, small businesses, and entrepreneurs, as it enables firms to extend their «brick and mortar» presence to serve a larger market or even sell goods and services entirely online. Business-to-business and financial services on the Internet affect supply chains across entire industries.
The Internet has no single centralized governance in either technological implementation or policies for access and usage; each constituent network sets its own policies.[5] The overarching definitions of the two principal name spaces on the Internet, the Internet Protocol address (IP address) space and the Domain Name System (DNS), are directed by a maintainer organization, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). The technical underpinning and standardization of the core protocols is an activity of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), a non-profit organization of loosely affiliated international participants that anyone may associate with by contributing technical expertise.[6] In November 2006, the Internet was included on USA Today‘s list of New Seven Wonders.[7]
Terminology
The word internetted was used as early as 1849, meaning interconnected or interwoven.[8] The word Internet was used in 1945 by the United States War Department in a radio operator’s manual,[9] and 1974 as the shorthand form of Internetwork.[10] Today, the term Internet most commonly refers to the global system of interconnected computer networks, though it may also refer to any group of smaller networks.[11]
When it came into common use, most publications treated the word Internet as a capitalized proper noun; this has become less common.[11] This reflects the tendency in English to capitalize new terms and move to lowercase as they become familiar.[11][12] The word is sometimes still capitalized to distinguish the global internet from smaller networks, though many publications, including the AP Stylebook since 2016, recommend the lowercase form in every case.[11][12] In 2016, the Oxford English Dictionary found that, based on a study of around 2.5 billion printed and online sources, «Internet» was capitalized in 54% of cases.[13]
The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably; it is common to speak of «going on the Internet» when using a web browser to view web pages. However, the World Wide Web or the Web is only one of a large number of Internet services,[14] a collection of documents (web pages) and other web resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs.[15]
History
In the 1960s, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) funded research into time-sharing of computers.[16][17][18] J. C. R. Licklider proposed the idea of a universal network while leading the Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO) at ARPA. Research into packet switching, one of the fundamental Internet technologies, started in the work of Paul Baran in the early 1960s and, independently, Donald Davies in 1965.[2][19] After the Symposium on Operating Systems Principles in 1967, packet switching from the proposed NPL network was incorporated into the design for the ARPANET and other resource sharing networks such as the Merit Network and CYCLADES, which were developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s.[20]
ARPANET development began with two network nodes which were interconnected between the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and SRI International (SRI) on 29 October 1969.[21] The third site was at the University of California, Santa Barbara, followed by the University of Utah. In a sign of future growth, 15 sites were connected to the young ARPANET by the end of 1971.[22][23] These early years were documented in the 1972 film Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing.[24] Thereafter, the ARPANET gradually developed into a decentralized communications network, connecting remote centers and military bases in the United States.[25]
Early international collaborations for the ARPANET were rare. Connections were made in 1973 to the Norwegian Seismic Array (NORSAR),[26] and to University College London which provided a gateway to British academic networks forming the first international resource sharing network.[27] ARPA projects, international working groups and commercial initiatives led to the development of various protocols and standards by which multiple separate networks could become a single network or «a network of networks».[28] In 1974, Bob Kahn at DARPA and Vint Cerf at Stanford University published their ideas for «A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication».[29] They used the term internet as a shorthand for internetwork in RFC 675,[10] and later RFCs repeated this use.[30] Kahn and Cerf credit Louis Pouzin with important influences on the resulting TCP/IP design.[31] National PTTs and commercial providers developed the X.25 standard and deployed it on public data networks.[32]
Access to the ARPANET was expanded in 1981 when the National Science Foundation (NSF) funded the Computer Science Network (CSNET). In 1982, the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) was standardized, which permitted worldwide proliferation of interconnected networks. TCP/IP network access expanded again in 1986 when the National Science Foundation Network (NSFNet) provided access to supercomputer sites in the United States for researchers, first at speeds of 56 kbit/s and later at 1.5 Mbit/s and 45 Mbit/s.[33] The NSFNet expanded into academic and research organizations in Europe, Australia, New Zealand and Japan in 1988–89.[34][35][36][37] Although other network protocols such as UUCP and PTT public data networks had global reach well before this time, this marked the beginning of the Internet as an intercontinental network. Commercial Internet service providers (ISPs) emerged in 1989 in the United States and Australia.[38] The ARPANET was decommissioned in 1990.[39]
Steady advances in semiconductor technology and optical networking created new economic opportunities for commercial involvement in the expansion of the network in its core and for delivering services to the public. In mid-1989, MCI Mail and Compuserve established connections to the Internet, delivering email and public access products to the half million users of the Internet.[40] Just months later, on 1 January 1990, PSInet launched an alternate Internet backbone for commercial use; one of the networks that added to the core of the commercial Internet of later years. In March 1990, the first high-speed T1 (1.5 Mbit/s) link between the NSFNET and Europe was installed between Cornell University and CERN, allowing much more robust communications than were capable with satellites.[41] Six months later Tim Berners-Lee would begin writing WorldWideWeb, the first web browser, after two years of lobbying CERN management. By Christmas 1990, Berners-Lee had built all the tools necessary for a working Web: the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 0.9,[42] the HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the first Web browser (which was also an HTML editor and could access Usenet newsgroups and FTP files), the first HTTP server software (later known as CERN httpd), the first web server,[43] and the first Web pages that described the project itself. In 1991 the Commercial Internet eXchange was founded, allowing PSInet to communicate with the other commercial networks CERFnet and Alternet. Stanford Federal Credit Union was the first financial institution to offer online Internet banking services to all of its members in October 1994.[44] In 1996, OP Financial Group, also a cooperative bank, became the second online bank in the world and the first in Europe.[45] By 1995, the Internet was fully commercialized in the U.S. when the NSFNet was decommissioned, removing the last restrictions on use of the Internet to carry commercial traffic.[46]
| Users | 2005 | 2010 | 2017 | 2019 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World population[48] | 6.5 billion | 6.9 billion | 7.4 billion | 7.75 billion | 7.9 billion |
| Worldwide | 16% | 30% | 48% | 53.6% | 63% |
| In developing world | 8% | 21% | 41.3% | 47% | 57% |
| In developed world | 51% | 67% | 81% | 86.6% | 90% |
As technology advanced and commercial opportunities fueled reciprocal growth, the volume of Internet traffic started experiencing similar characteristics as that of the scaling of MOS transistors, exemplified by Moore’s law, doubling every 18 months. This growth, formalized as Edholm’s law, was catalyzed by advances in MOS technology, laser light wave systems, and noise performance.[49]
Since 1995, the Internet has tremendously impacted culture and commerce, including the rise of near instant communication by email, instant messaging, telephony (Voice over Internet Protocol or VoIP), two-way interactive video calls, and the World Wide Web[50] with its discussion forums, blogs, social networking services, and online shopping sites. Increasing amounts of data are transmitted at higher and higher speeds over fiber optic networks operating at 1 Gbit/s, 10 Gbit/s, or more. The Internet continues to grow, driven by ever greater amounts of online information and knowledge, commerce, entertainment and social networking services.[51] During the late 1990s, it was estimated that traffic on the public Internet grew by 100 percent per year, while the mean annual growth in the number of Internet users was thought to be between 20% and 50%.[52] This growth is often attributed to the lack of central administration, which allows organic growth of the network, as well as the non-proprietary nature of the Internet protocols, which encourages vendor interoperability and prevents any one company from exerting too much control over the network.[53] As of 31 March 2011, the estimated total number of Internet users was 2.095 billion (30.2% of world population).[54] It is estimated that in 1993 the Internet carried only 1% of the information flowing through two-way telecommunication. By 2000 this figure had grown to 51%, and by 2007 more than 97% of all telecommunicated information was carried over the Internet.[55]
Governance
The Internet is a global network that comprises many voluntarily interconnected autonomous networks. It operates without a central governing body. The technical underpinning and standardization of the core protocols (IPv4 and IPv6) is an activity of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), a non-profit organization of loosely affiliated international participants that anyone may associate with by contributing technical expertise. To maintain interoperability, the principal name spaces of the Internet are administered by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). ICANN is governed by an international board of directors drawn from across the Internet technical, business, academic, and other non-commercial communities. ICANN coordinates the assignment of unique identifiers for use on the Internet, including domain names, IP addresses, application port numbers in the transport protocols, and many other parameters. Globally unified name spaces are essential for maintaining the global reach of the Internet. This role of ICANN distinguishes it as perhaps the only central coordinating body for the global Internet.[56]
Regional Internet registries (RIRs) were established for five regions of the world. The African Network Information Center (AfriNIC) for Africa, the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) for North America, the Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) for Asia and the Pacific region, the Latin American and Caribbean Internet Addresses Registry (LACNIC) for Latin America and the Caribbean region, and the Réseaux IP Européens – Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC) for Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia were delegated to assign IP address blocks and other Internet parameters to local registries, such as Internet service providers, from a designated pool of addresses set aside for each region.
The National Telecommunications and Information Administration, an agency of the United States Department of Commerce, had final approval over changes to the DNS root zone until the IANA stewardship transition on 1 October 2016.[57][58][59][60] The Internet Society (ISOC) was founded in 1992 with a mission to «assure the open development, evolution and use of the Internet for the benefit of all people throughout the world».[61] Its members include individuals (anyone may join) as well as corporations, organizations, governments, and universities. Among other activities ISOC provides an administrative home for a number of less formally organized groups that are involved in developing and managing the Internet, including: the IETF, Internet Architecture Board (IAB), Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG), Internet Research Task Force (IRTF), and Internet Research Steering Group (IRSG). On 16 November 2005, the United Nations-sponsored World Summit on the Information Society in Tunis established the Internet Governance Forum (IGF) to discuss Internet-related issues.
Infrastructure
2007 map showing submarine fiberoptic telecommunication cables around the world
The communications infrastructure of the Internet consists of its hardware components and a system of software layers that control various aspects of the architecture. As with any computer network, the Internet physically consists of routers, media (such as cabling and radio links), repeaters, modems etc. However, as an example of internetworking, many of the network nodes are not necessarily internet equipment per se, the internet packets are carried by other full-fledged networking protocols with the Internet acting as a homogeneous networking standard, running across heterogeneous hardware, with the packets guided to their destinations by IP routers.
Service tiers
Packet routing across the Internet involves several tiers of Internet service providers.
Internet service providers (ISPs) establish the worldwide connectivity between individual networks at various levels of scope. End-users who only access the Internet when needed to perform a function or obtain information, represent the bottom of the routing hierarchy. At the top of the routing hierarchy are the tier 1 networks, large telecommunication companies that exchange traffic directly with each other via very high speed fibre optic cables and governed by peering agreements. Tier 2 and lower-level networks buy Internet transit from other providers to reach at least some parties on the global Internet, though they may also engage in peering. An ISP may use a single upstream provider for connectivity, or implement multihoming to achieve redundancy and load balancing. Internet exchange points are major traffic exchanges with physical connections to multiple ISPs. Large organizations, such as academic institutions, large enterprises, and governments, may perform the same function as ISPs, engaging in peering and purchasing transit on behalf of their internal networks. Research networks tend to interconnect with large subnetworks such as GEANT, GLORIAD, Internet2, and the UK’s national research and education network, JANET.
Access
Common methods of Internet access by users include dial-up with a computer modem via telephone circuits, broadband over coaxial cable, fiber optics or copper wires, Wi-Fi, satellite, and cellular telephone technology (e.g. 3G, 4G). The Internet may often be accessed from computers in libraries and Internet cafes. Internet access points exist in many public places such as airport halls and coffee shops. Various terms are used, such as public Internet kiosk, public access terminal, and Web payphone. Many hotels also have public terminals that are usually fee-based. These terminals are widely accessed for various usages, such as ticket booking, bank deposit, or online payment. Wi-Fi provides wireless access to the Internet via local computer networks. Hotspots providing such access include Wi-Fi cafes, where users need to bring their own wireless devices such as a laptop or PDA. These services may be free to all, free to customers only, or fee-based.
Grassroots efforts have led to wireless community networks. Commercial Wi-Fi services that cover large areas are available in many cities, such as New York, London, Vienna, Toronto, San Francisco, Philadelphia, Chicago and Pittsburgh, where the Internet can then be accessed from places such as a park bench.[62] Experiments have also been conducted with proprietary mobile wireless networks like Ricochet, various high-speed data services over cellular networks, and fixed wireless services. Modern smartphones can also access the Internet through the cellular carrier network. For Web browsing, these devices provide applications such as Google Chrome, Safari, and Firefox and a wide variety of other Internet software may be installed from app-stores. Internet usage by mobile and tablet devices exceeded desktop worldwide for the first time in October 2016.[63]
Mobile communication
Number of mobile cellular subscriptions 2012–2016
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) estimated that, by the end of 2017, 48% of individual users regularly connect to the Internet, up from 34% in 2012.[64] Mobile Internet connectivity has played an important role in expanding access in recent years especially in Asia and the Pacific and in Africa.[65] The number of unique mobile cellular subscriptions increased from 3.89 billion in 2012 to 4.83 billion in 2016, two-thirds of the world’s population, with more than half of subscriptions located in Asia and the Pacific. The number of subscriptions is predicted to rise to 5.69 billion users in 2020.[66] As of 2016, almost 60% of the world’s population had access to a 4G broadband cellular network, up from almost 50% in 2015 and 11% in 2012.[disputed – discuss][66] The limits that users face on accessing information via mobile applications coincide with a broader process of fragmentation of the Internet. Fragmentation restricts access to media content and tends to affect poorest users the most.[65]
Zero-rating, the practice of Internet service providers allowing users free connectivity to access specific content or applications without cost, has offered opportunities to surmount economic hurdles, but has also been accused by its critics as creating a two-tiered Internet. To address the issues with zero-rating, an alternative model has emerged in the concept of ‘equal rating’ and is being tested in experiments by Mozilla and Orange in Africa. Equal rating prevents prioritization of one type of content and zero-rates all content up to a specified data cap. A study published by Chatham House, 15 out of 19 countries researched in Latin America had some kind of hybrid or zero-rated product offered. Some countries in the region had a handful of plans to choose from (across all mobile network operators) while others, such as Colombia, offered as many as 30 pre-paid and 34 post-paid plans.[67]
A study of eight countries in the Global South found that zero-rated data plans exist in every country, although there is a great range in the frequency with which they are offered and actually used in each.[68] The study looked at the top three to five carriers by market share in Bangladesh, Colombia, Ghana, India, Kenya, Nigeria, Peru and Philippines. Across the 181 plans examined, 13 per cent were offering zero-rated services. Another study, covering Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa, found Facebook’s Free Basics and Wikipedia Zero to be the most commonly zero-rated content.[69]
Internet Protocol Suite
The Internet standards describe a framework known as the Internet protocol suite (also called TCP/IP, based on the first two components.) This is a suite of protocols that are ordered into a set of four conceptional layers by the scope of their operation, originally documented in RFC 1122 and RFC 1123. At the top is the application layer, where communication is described in terms of the objects or data structures most appropriate for each application. For example, a web browser operates in a client–server application model and exchanges information with the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and an application-germane data structure, such as the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML).
Below this top layer, the transport layer connects applications on different hosts with a logical channel through the network. It provides this service with a variety of possible characteristics, such as ordered, reliable delivery (TCP), and an unreliable datagram service (UDP).
Underlying these layers are the networking technologies that interconnect networks at their borders and exchange traffic across them. The Internet layer implements the Internet Protocol (IP) which enables computers to identify and locate each other by IP address, and route their traffic via intermediate (transit) networks.[70] The internet protocol layer code is independent of the type of network that it is physically running over.
At the bottom of the architecture is the link layer, which connects nodes on the same physical link, and contains protocols that do not require routers for traversal to other links. The protocol suite does not explicitly specify hardware methods to transfer bits, or protocols to manage such hardware, but assumes that appropriate technology is available. Examples of that technology include Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and DSL.
As user data is processed through the protocol stack, each abstraction layer adds encapsulation information at the sending host. Data is transmitted over the wire at the link level between hosts and routers. Encapsulation is removed by the receiving host. Intermediate relays update link encapsulation at each hop, and inspect the IP layer for routing purposes.
Internet protocol
Conceptual data flow in a simple network topology of two hosts (A and B) connected by a link between their respective routers. The application on each host executes read and write operations as if the processes were directly connected to each other by some kind of data pipe. After the establishment of this pipe, most details of the communication are hidden from each process, as the underlying principles of communication are implemented in the lower protocol layers. In analogy, at the transport layer the communication appears as host-to-host, without knowledge of the application data structures and the connecting routers, while at the internetworking layer, individual network boundaries are traversed at each router.
The most prominent component of the Internet model is the Internet Protocol (IP). IP enables internetworking and, in essence, establishes the Internet itself. Two versions of the Internet Protocol exist, IPv4 and IPv6.
IP Addresses
A DNS resolver consults three name servers to resolve the domain name user-visible «www.wikipedia.org» to determine the IPv4 Address 207.142.131.234.
For locating individual computers on the network, the Internet provides IP addresses. IP addresses are used by the Internet infrastructure to direct internet packets to their destinations. They consist of fixed-length numbers, which are found within the packet. IP addresses are generally assigned to equipment either automatically via DHCP, or are configured.
However, the network also supports other addressing systems. Users generally enter domain names (e.g. «en.wikipedia.org») instead of IP addresses because they are easier to remember, they are converted by the Domain Name System (DNS) into IP addresses which are more efficient for routing purposes.
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) defines an IP address as a 32-bit number.[70] IPv4 is the initial version used on the first generation of the Internet and is still in dominant use. It was designed to address up to ≈4.3 billion (109) hosts. However, the explosive growth of the Internet has led to IPv4 address exhaustion, which entered its final stage in 2011,[71] when the global IPv4 address allocation pool was exhausted.
IPv6
Because of the growth of the Internet and the depletion of available IPv4 addresses, a new version of IP IPv6, was developed in the mid-1990s, which provides vastly larger addressing capabilities and more efficient routing of Internet traffic. IPv6 uses 128 bits for the IP address and was standardized in 1998.[72][73][74] IPv6 deployment has been ongoing since the mid-2000s and is currently in growing deployment around the world, since Internet address registries (RIRs) began to urge all resource managers to plan rapid adoption and conversion.[75]
IPv6 is not directly interoperable by design with IPv4. In essence, it establishes a parallel version of the Internet not directly accessible with IPv4 software. Thus, translation facilities must exist for internetworking or nodes must have duplicate networking software for both networks. Essentially all modern computer operating systems support both versions of the Internet Protocol. Network infrastructure, however, has been lagging in this development. Aside from the complex array of physical connections that make up its infrastructure, the Internet is facilitated by bi- or multi-lateral commercial contracts, e.g., peering agreements, and by technical specifications or protocols that describe the exchange of data over the network. Indeed, the Internet is defined by its interconnections and routing policies.
Subnetwork
Creating a subnet by dividing the host identifier
A subnetwork or subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network.[76]: 1, 16 The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting.
Computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with an identical most-significant bit-group in their IP addresses. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, the network number or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
The routing prefix may be expressed in Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation written as the first address of a network, followed by a slash character (/), and ending with the bit-length of the prefix. For example, 198.51.100.0/24 is the prefix of the Internet Protocol version 4 network starting at the given address, having 24 bits allocated for the network prefix, and the remaining 8 bits reserved for host addressing. Addresses in the range 198.51.100.0 to 198.51.100.255 belong to this network. The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/32 is a large address block with 296 addresses, having a 32-bit routing prefix.
For IPv4, a network may also be characterized by its subnet mask or netmask, which is the bitmask that when applied by a bitwise AND operation to any IP address in the network, yields the routing prefix. Subnet masks are also expressed in dot-decimal notation like an address. For example, 255.255.255.0 is the subnet mask for the prefix 198.51.100.0/24.
Traffic is exchanged between subnetworks through routers when the routing prefixes of the source address and the destination address differ. A router serves as a logical or physical boundary between the subnets.
The benefits of subnetting an existing network vary with each deployment scenario. In the address allocation architecture of the Internet using CIDR and in large organizations, it is necessary to allocate address space efficiently. Subnetting may also enhance routing efficiency, or have advantages in network management when subnetworks are administratively controlled by different entities in a larger organization. Subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning an organization’s network address space into a tree-like routing structure.
Routing
Computers and routers use routing tables in their operating system to direct IP packets to reach a node on a different subnetwork. Routing tables are maintained by manual configuration or automatically by routing protocols. End-nodes typically use a default route that points toward an ISP providing transit, while ISP routers use the Border Gateway Protocol to establish the most efficient routing across the complex connections of the global Internet. The default gateway is the node that serves as the forwarding host (router) to other networks when no other route specification matches the destination IP address of a packet.[77][78]
IETF
While the hardware components in the Internet infrastructure can often be used to support other software systems, it is the design and the standardization process of the software that characterizes the Internet and provides the foundation for its scalability and success. The responsibility for the architectural design of the Internet software systems has been assumed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).[79] The IETF conducts standard-setting work groups, open to any individual, about the various aspects of Internet architecture. The resulting contributions and standards are published as Request for Comments (RFC) documents on the IETF web site. The principal methods of networking that enable the Internet are contained in specially designated RFCs that constitute the Internet Standards. Other less rigorous documents are simply informative, experimental, or historical, or document the best current practices (BCP) when implementing Internet technologies.
Applications and services
The Internet carries many applications and services, most prominently the World Wide Web, including social media, electronic mail, mobile applications, multiplayer online games, Internet telephony, file sharing, and streaming media services.
Most servers that provide these services are today hosted in data centers, and content is often accessed through high-performance content delivery networks.
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a global collection of documents, images, multimedia, applications, and other resources, logically interrelated by hyperlinks and referenced with Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs), which provide a global system of named references. URIs symbolically identify services, web servers, databases, and the documents and resources that they can provide. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the main access protocol of the World Wide Web. Web services also use HTTP for communication between software systems for information transfer, sharing and exchanging business data and logistic and is one of many languages or protocols that can be used for communication on the Internet.[80]
World Wide Web browser software, such as Microsoft’s Internet Explorer/Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Apple’s Safari, and Google Chrome, lets users navigate from one web page to another via the hyperlinks embedded in the documents. These documents may also contain any combination of computer data, including graphics, sounds, text, video, multimedia and interactive content that runs while the user is interacting with the page. Client-side software can include animations, games, office applications and scientific demonstrations. Through keyword-driven Internet research using search engines like Yahoo!, Bing and Google, users worldwide have easy, instant access to a vast and diverse amount of online information. Compared to printed media, books, encyclopedias and traditional libraries, the World Wide Web has enabled the decentralization of information on a large scale.
The Web has enabled individuals and organizations to publish ideas and information to a potentially large audience online at greatly reduced expense and time delay. Publishing a web page, a blog, or building a website involves little initial cost and many cost-free services are available. However, publishing and maintaining large, professional web sites with attractive, diverse and up-to-date information is still a difficult and expensive proposition. Many individuals and some companies and groups use web logs or blogs, which are largely used as easily updatable online diaries. Some commercial organizations encourage staff to communicate advice in their areas of specialization in the hope that visitors will be impressed by the expert knowledge and free information, and be attracted to the corporation as a result.
Advertising on popular web pages can be lucrative, and e-commerce, which is the sale of products and services directly via the Web, continues to grow. Online advertising is a form of marketing and advertising which uses the Internet to deliver promotional marketing messages to consumers. It includes email marketing, search engine marketing (SEM), social media marketing, many types of display advertising (including web banner advertising), and mobile advertising. In 2011, Internet advertising revenues in the United States surpassed those of cable television and nearly exceeded those of broadcast television.[81]: 19 Many common online advertising practices are controversial and increasingly subject to regulation.
When the Web developed in the 1990s, a typical web page was stored in completed form on a web server, formatted in HTML, complete for transmission to a web browser in response to a request. Over time, the process of creating and serving web pages has become dynamic, creating a flexible design, layout, and content. Websites are often created using content management software with, initially, very little content. Contributors to these systems, who may be paid staff, members of an organization or the public, fill underlying databases with content using editing pages designed for that purpose while casual visitors view and read this content in HTML form. There may or may not be editorial, approval and security systems built into the process of taking newly entered content and making it available to the target visitors.
Communication
Email is an important communications service available via the Internet. The concept of sending electronic text messages between parties, analogous to mailing letters or memos, predates the creation of the Internet.[82][83] Pictures, documents, and other files are sent as email attachments. Email messages can be cc-ed to multiple email addresses.
Internet telephony is a common communications service realized with the Internet. The name of the principle internetworking protocol, the Internet Protocol, lends its name to voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). The idea began in the early 1990s with walkie-talkie-like voice applications for personal computers. VoIP systems now dominate many markets, and are as easy to use and as convenient as a traditional telephone. The benefit has been substantial cost savings over traditional telephone calls, especially over long distances. Cable, ADSL, and mobile data networks provide Internet access in customer premises[84] and inexpensive VoIP network adapters provide the connection for traditional analog telephone sets. The voice quality of VoIP often exceeds that of traditional calls. Remaining problems for VoIP include the situation that emergency services may not be universally available, and that devices rely on a local power supply, while older traditional phones are powered from the local loop, and typically operate during a power failure.
Data transfer
File sharing is an example of transferring large amounts of data across the Internet. A computer file can be emailed to customers, colleagues and friends as an attachment. It can be uploaded to a website or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server for easy download by others. It can be put into a «shared location» or onto a file server for instant use by colleagues. The load of bulk downloads to many users can be eased by the use of «mirror» servers or peer-to-peer networks. In any of these cases, access to the file may be controlled by user authentication, the transit of the file over the Internet may be obscured by encryption, and money may change hands for access to the file. The price can be paid by the remote charging of funds from, for example, a credit card whose details are also passed—usually fully encrypted—across the Internet. The origin and authenticity of the file received may be checked by digital signatures or by MD5 or other message digests. These simple features of the Internet, over a worldwide basis, are changing the production, sale, and distribution of anything that can be reduced to a computer file for transmission. This includes all manner of print publications, software products, news, music, film, video, photography, graphics and the other arts. This in turn has caused seismic shifts in each of the existing industries that previously controlled the production and distribution of these products.
Streaming media is the real-time delivery of digital media for the immediate consumption or enjoyment by end users. Many radio and television broadcasters provide Internet feeds of their live audio and video productions. They may also allow time-shift viewing or listening such as Preview, Classic Clips and Listen Again features. These providers have been joined by a range of pure Internet «broadcasters» who never had on-air licenses. This means that an Internet-connected device, such as a computer or something more specific, can be used to access online media in much the same way as was previously possible only with a television or radio receiver. The range of available types of content is much wider, from specialized technical webcasts to on-demand popular multimedia services. Podcasting is a variation on this theme, where—usually audio—material is downloaded and played back on a computer or shifted to a portable media player to be listened to on the move. These techniques using simple equipment allow anybody, with little censorship or licensing control, to broadcast audio-visual material worldwide.
Digital media streaming increases the demand for network bandwidth. For example, standard image quality needs 1 Mbit/s link speed for SD 480p, HD 720p quality requires 2.5 Mbit/s, and the top-of-the-line HDX quality needs 4.5 Mbit/s for 1080p.[85]
Webcams are a low-cost extension of this phenomenon. While some webcams can give full-frame-rate video, the picture either is usually small or updates slowly. Internet users can watch animals around an African waterhole, ships in the Panama Canal, traffic at a local roundabout or monitor their own premises, live and in real time. Video chat rooms and video conferencing are also popular with many uses being found for personal webcams, with and without two-way sound. YouTube was founded on 15 February 2005 and is now the leading website for free streaming video with more than two billion users.[86] It uses an HTML5 based web player by default to stream and show video files.[87] Registered users may upload an unlimited amount of video and build their own personal profile. YouTube claims that its users watch hundreds of millions, and upload hundreds of thousands of videos daily.
The Internet has enabled new forms of social interaction, activities, and social associations. This phenomenon has given rise to the scholarly study of the sociology of the Internet.
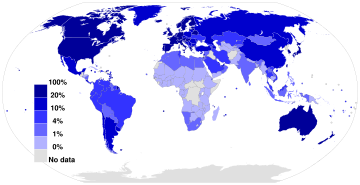
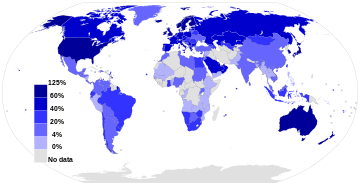
Users
Share of population using the Internet.[88] See or edit source data.
Internet users per 100 population members and GDP per capita for selected countries
From 2000 to 2009, the number of Internet users globally rose from 394 million to 1.858 billion.[91] By 2010, 22 percent of the world’s population had access to computers with 1 billion Google searches every day, 300 million Internet users reading blogs, and 2 billion videos viewed daily on YouTube.[92] In 2014 the world’s Internet users surpassed 3 billion or 43.6 percent of world population, but two-thirds of the users came from richest countries, with 78.0 percent of Europe countries population using the Internet, followed by 57.4 percent of the Americas.[93] However, by 2018, Asia alone accounted for 51% of all Internet users, with 2.2 billion out of the 4.3 billion Internet users in the world coming from that region. The number of China’s Internet users surpassed a major milestone in 2018, when the country’s Internet regulatory authority, China Internet Network Information Centre, announced that China had 802 million Internet users.[94] By 2019, China was the world’s leading country in terms of Internet users, with more than 800 million users, followed closely by India, with some 700 million users, with the United States a distant third with 275 million users. However, in terms of penetration, China has[when?] a 38.4% penetration rate compared to India’s 40% and the United States’s 80%.[95] As of 2020, it was estimated that 4.5 billion people use the Internet, more than half of the world’s population.[96][97]
The prevalent language for communication via the Internet has always been English. This may be a result of the origin of the Internet, as well as the language’s role as a lingua franca and as a world language. Early computer systems were limited to the characters in the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII), a subset of the Latin alphabet.
After English (27%), the most requested languages on the World Wide Web are Chinese (25%), Spanish (8%), Japanese (5%), Portuguese and German (4% each), Arabic, French and Russian (3% each), and Korean (2%).[98] By region, 42% of the world’s Internet users are based in Asia, 24% in Europe, 14% in North America, 10% in Latin America and the Caribbean taken together, 6% in Africa, 3% in the Middle East and 1% in Australia/Oceania.[99] The Internet’s technologies have developed enough in recent years, especially in the use of Unicode, that good facilities are available for development and communication in the world’s widely used languages. However, some glitches such as mojibake (incorrect display of some languages’ characters) still remain.
In an American study in 2005, the percentage of men using the Internet was very slightly ahead of the percentage of women, although this difference reversed in those under 30. Men logged on more often, spent more time online, and were more likely to be broadband users, whereas women tended to make more use of opportunities to communicate (such as email). Men were more likely to use the Internet to pay bills, participate in auctions, and for recreation such as downloading music and videos. Men and women were equally likely to use the Internet for shopping and banking.[100]
More recent studies indicate that in 2008, women significantly outnumbered men on most social networking services, such as Facebook and Myspace, although the ratios varied with age.[101] In addition, women watched more streaming content, whereas men downloaded more.[102] In terms of blogs, men were more likely to blog in the first place; among those who blog, men were more likely to have a professional blog, whereas women were more likely to have a personal blog.[103]
Splitting by country, in 2012 Iceland, Norway, Sweden, the Netherlands, and Denmark had the highest Internet penetration by the number of users, with 93% or more of the population with access.[104]
Several neologisms exist that refer to Internet users: Netizen (as in «citizen of the net»)[105] refers to those actively involved in improving online communities, the Internet in general or surrounding political affairs and rights such as free speech,[106][107] Internaut refers to operators or technically highly capable users of the Internet,[108][109] digital citizen refers to a person using the Internet in order to engage in society, politics, and government participation.[110]
Usage
The Internet allows greater flexibility in working hours and location, especially with the spread of unmetered high-speed connections. The Internet can be accessed almost anywhere by numerous means, including through mobile Internet devices. Mobile phones, datacards, handheld game consoles and cellular routers allow users to connect to the Internet wirelessly. Within the limitations imposed by small screens and other limited facilities of such pocket-sized devices, the services of the Internet, including email and the web, may be available. Service providers may restrict the services offered and mobile data charges may be significantly higher than other access methods.
Educational material at all levels from pre-school to post-doctoral is available from websites. Examples range from CBeebies, through school and high-school revision guides and virtual universities, to access to top-end scholarly literature through the likes of Google Scholar. For distance education, help with homework and other assignments, self-guided learning, whiling away spare time or just looking up more detail on an interesting fact, it has never been easier for people to access educational information at any level from anywhere. The Internet in general and the World Wide Web in particular are important enablers of both formal and informal education. Further, the Internet allows researchers (especially those from the social and behavioral sciences) to conduct research remotely via virtual laboratories, with profound changes in reach and generalizability of findings as well as in communication between scientists and in the publication of results.[114]
The low cost and nearly instantaneous sharing of ideas, knowledge, and skills have made collaborative work dramatically easier, with the help of collaborative software. Not only can a group cheaply communicate and share ideas but the wide reach of the Internet allows such groups more easily to form. An example of this is the free software movement, which has produced, among other things, Linux, Mozilla Firefox, and OpenOffice.org (later forked into LibreOffice). Internet chat, whether using an IRC chat room, an instant messaging system, or a social networking service, allows colleagues to stay in touch in a very convenient way while working at their computers during the day. Messages can be exchanged even more quickly and conveniently than via email. These systems may allow files to be exchanged, drawings and images to be shared, or voice and video contact between team members.
Content management systems allow collaborating teams to work on shared sets of documents simultaneously without accidentally destroying each other’s work. Business and project teams can share calendars as well as documents and other information. Such collaboration occurs in a wide variety of areas including scientific research, software development, conference planning, political activism and creative writing. Social and political collaboration is also becoming more widespread as both Internet access and computer literacy spread.
The Internet allows computer users to remotely access other computers and information stores easily from any access point. Access may be with computer security, i.e. authentication and encryption technologies, depending on the requirements. This is encouraging new ways of remote work, collaboration and information sharing in many industries. An accountant sitting at home can audit the books of a company based in another country, on a server situated in a third country that is remotely maintained by IT specialists in a fourth. These accounts could have been created by home-working bookkeepers, in other remote locations, based on information emailed to them from offices all over the world. Some of these things were possible before the widespread use of the Internet, but the cost of private leased lines would have made many of them infeasible in practice. An office worker away from their desk, perhaps on the other side of the world on a business trip or a holiday, can access their emails, access their data using cloud computing, or open a remote desktop session into their office PC using a secure virtual private network (VPN) connection on the Internet. This can give the worker complete access to all of their normal files and data, including email and other applications, while away from the office. It has been referred to among system administrators as the Virtual Private Nightmare,[115] because it extends the secure perimeter of a corporate network into remote locations and its employees’ homes.
By late 2010s Internet has been described as «the main source of scientific information «for the majority of the global North population».[116]: 111
Social networking and entertainment
Many people use the World Wide Web to access news, weather and sports reports, to plan and book vacations and to pursue their personal interests. People use chat, messaging and email to make and stay in touch with friends worldwide, sometimes in the same way as some previously had pen pals. Social networking services such as Facebook have created new ways to socialize and interact. Users of these sites are able to add a wide variety of information to pages, pursue common interests, and connect with others. It is also possible to find existing acquaintances, to allow communication among existing groups of people. Sites like LinkedIn foster commercial and business connections. YouTube and Flickr specialize in users’ videos and photographs. Social networking services are also widely used by businesses and other organizations to promote their brands, to market to their customers and to encourage posts to «go viral». «Black hat» social media techniques are also employed by some organizations, such as spam accounts and astroturfing.
A risk for both individuals and organizations writing posts (especially public posts) on social networking services, is that especially foolish or controversial posts occasionally lead to an unexpected and possibly large-scale backlash on social media from other Internet users. This is also a risk in relation to controversial offline behavior, if it is widely made known. The nature of this backlash can range widely from counter-arguments and public mockery, through insults and hate speech, to, in extreme cases, rape and death threats. The online disinhibition effect describes the tendency of many individuals to behave more stridently or offensively online than they would in person. A significant number of feminist women have been the target of various forms of harassment in response to posts they have made on social media, and Twitter in particular has been criticised in the past for not doing enough to aid victims of online abuse.[117]
For organizations, such a backlash can cause overall brand damage, especially if reported by the media. However, this is not always the case, as any brand damage in the eyes of people with an opposing opinion to that presented by the organization could sometimes be outweighed by strengthening the brand in the eyes of others. Furthermore, if an organization or individual gives in to demands that others perceive as wrong-headed, that can then provoke a counter-backlash.
Some websites, such as Reddit, have rules forbidding the posting of personal information of individuals (also known as doxxing), due to concerns about such postings leading to mobs of large numbers of Internet users directing harassment at the specific individuals thereby identified. In particular, the Reddit rule forbidding the posting of personal information is widely understood to imply that all identifying photos and names must be censored in Facebook screenshots posted to Reddit. However, the interpretation of this rule in relation to public Twitter posts is less clear, and in any case, like-minded people online have many other ways they can use to direct each other’s attention to public social media posts they disagree with.
Children also face dangers online such as cyberbullying and approaches by sexual predators, who sometimes pose as children themselves. Children may also encounter material which they may find upsetting, or material that their parents consider to be not age-appropriate. Due to naivety, they may also post personal information about themselves online, which could put them or their families at risk unless warned not to do so. Many parents choose to enable Internet filtering or supervise their children’s online activities in an attempt to protect their children from inappropriate material on the Internet. The most popular social networking services, such as Facebook and Twitter, commonly forbid users under the age of 13. However, these policies are typically trivial to circumvent by registering an account with a false birth date, and a significant number of children aged under 13 join such sites anyway. Social networking services for younger children, which claim to provide better levels of protection for children, also exist.[118]
The Internet has been a major outlet for leisure activity since its inception, with entertaining social experiments such as MUDs and MOOs being conducted on university servers, and humor-related Usenet groups receiving much traffic.[citation needed] Many Internet forums have sections devoted to games and funny videos.[citation needed] The Internet pornography and online gambling industries have taken advantage of the World Wide Web. Although many governments have attempted to restrict both industries’ use of the Internet, in general, this has failed to stop their widespread popularity.[119]
Another area of leisure activity on the Internet is multiplayer gaming.[120] This form of recreation creates communities, where people of all ages and origins enjoy the fast-paced world of multiplayer games. These range from MMORPG to first-person shooters, from role-playing video games to online gambling. While online gaming has been around since the 1970s, modern modes of online gaming began with subscription services such as GameSpy and MPlayer.[121] Non-subscribers were limited to certain types of game play or certain games. Many people use the Internet to access and download music, movies and other works for their enjoyment and relaxation. Free and fee-based services exist for all of these activities, using centralized servers and distributed peer-to-peer technologies. Some of these sources exercise more care with respect to the original artists’ copyrights than others.
Internet usage has been correlated to users’ loneliness.[122] Lonely people tend to use the Internet as an outlet for their feelings and to share their stories with others, such as in the «I am lonely will anyone speak to me» thread.
A 2017 book claimed that the Internet consolidates most aspects of human endeavor into singular arenas of which all of humanity are potential members and competitors, with fundamentally negative impacts on mental health as a result. While successes in each field of activity are pervasively visible and trumpeted, they are reserved for an extremely thin sliver of the world’s most exceptional, leaving everyone else behind. Whereas, before the Internet, expectations of success in any field were supported by reasonable probabilities of achievement at the village, suburb, city or even state level, the same expectations in the Internet world are virtually certain to bring disappointment today: there is always someone else, somewhere on the planet, who can do better and take the now one-and-only top spot.[123]
Cybersectarianism is a new organizational form which involves: «highly dispersed small groups of practitioners that may remain largely anonymous within the larger social context and operate in relative secrecy, while still linked remotely to a larger network of believers who share a set of practices and texts, and often a common devotion to a particular leader. Overseas supporters provide funding and support; domestic practitioners distribute tracts, participate in acts of resistance, and share information on the internal situation with outsiders. Collectively, members and practitioners of such sects construct viable virtual communities of faith, exchanging personal testimonies and engaging in the collective study via email, online chat rooms, and web-based message boards.»[124] In particular, the British government has raised concerns about the prospect of young British Muslims being indoctrinated into Islamic extremism by material on the Internet, being persuaded to join terrorist groups such as the so-called «Islamic State», and then potentially committing acts of terrorism on returning to Britain after fighting in Syria or Iraq.
Cyberslacking can become a drain on corporate resources; the average UK employee spent 57 minutes a day surfing the Web while at work, according to a 2003 study by Peninsula Business Services.[125] Internet addiction disorder is excessive computer use that interferes with daily life. Nicholas G. Carr believes that Internet use has other effects on individuals, for instance improving skills of scan-reading and interfering with the deep thinking that leads to true creativity.[126]
Electronic business
Electronic business (e-business) encompasses business processes spanning the entire value chain: purchasing, supply chain management, marketing, sales, customer service, and business relationship. E-commerce seeks to add revenue streams using the Internet to build and enhance relationships with clients and partners. According to International Data Corporation, the size of worldwide e-commerce, when global business-to-business and -consumer transactions are combined, equate to $16 trillion for 2013. A report by Oxford Economics added those two together to estimate the total size of the digital economy at $20.4 trillion, equivalent to roughly 13.8% of global sales.[127]
While much has been written of the economic advantages of Internet-enabled commerce, there is also evidence that some aspects of the Internet such as maps and location-aware services may serve to reinforce economic inequality and the digital divide.[128] Electronic commerce may be responsible for consolidation and the decline of mom-and-pop, brick and mortar businesses resulting in increases in income inequality.[129][130][131]
Author Andrew Keen, a long-time critic of the social transformations caused by the Internet, has focused on the economic effects of consolidation from Internet businesses. Keen cites a 2013 Institute for Local Self-Reliance report saying brick-and-mortar retailers employ 47 people for every $10 million in sales while Amazon employs only 14. Similarly, the 700-employee room rental start-up Airbnb was valued at $10 billion in 2014, about half as much as Hilton Worldwide, which employs 152,000 people. At that time, Uber employed 1,000 full-time employees and was valued at $18.2 billion, about the same valuation as Avis Rent a Car and The Hertz Corporation combined, which together employed almost 60,000 people.[132]
Remote work
Remote work is facilitated by tools such as groupware, virtual private networks, conference calling, videotelephony, and VoIP so that work may be performed from any location, most conveniently the worker’s home. It can be efficient and useful for companies as it allows workers to communicate over long distances, saving significant amounts of travel time and cost. More workers have adequate bandwidth at home to use these tools to link their home to their corporate intranet and internal communication networks.
Collaborative publishing
Wikis have also been used in the academic community for sharing and dissemination of information across institutional and international boundaries.[133] In those settings, they have been found useful for collaboration on grant writing, strategic planning, departmental documentation, and committee work.[134] The United States Patent and Trademark Office uses a wiki to allow the public to collaborate on finding prior art relevant to examination of pending patent applications. Queens, New York has used a wiki to allow citizens to collaborate on the design and planning of a local park.[135] The English Wikipedia has the largest user base among wikis on the World Wide Web[136] and ranks in the top 10 among all Web sites in terms of traffic.[137]
Politics and political revolutions
Banner in Bangkok during the 2014 Thai coup d’état, informing the Thai public that ‘like’ or ‘share’ activities on social media could result in imprisonment (observed 30 June 2014)
The Internet has achieved new relevance as a political tool. The presidential campaign of Howard Dean in 2004 in the United States was notable for its success in soliciting donation via the Internet. Many political groups use the Internet to achieve a new method of organizing for carrying out their mission, having given rise to Internet activism, most notably practiced by rebels in the Arab Spring.[138][139] The New York Times suggested that social media websites, such as Facebook and Twitter, helped people organize the political revolutions in Egypt, by helping activists organize protests, communicate grievances, and disseminate information.[140]
Many have understood the Internet as an extension of the Habermasian notion of the public sphere, observing how network communication technologies provide something like a global civic forum. However, incidents of politically motivated Internet censorship have now been recorded in many countries, including western democracies.[141][142]
Philanthropy
The spread of low-cost Internet access in developing countries has opened up new possibilities for peer-to-peer charities, which allow individuals to contribute small amounts to charitable projects for other individuals. Websites, such as DonorsChoose and GlobalGiving, allow small-scale donors to direct funds to individual projects of their choice. A popular twist on Internet-based philanthropy is the use of peer-to-peer lending for charitable purposes. Kiva pioneered this concept in 2005, offering the first web-based service to publish individual loan profiles for funding. Kiva raises funds for local intermediary microfinance organizations that post stories and updates on behalf of the borrowers. Lenders can contribute as little as $25 to loans of their choice, and receive their money back as borrowers repay. Kiva falls short of being a pure peer-to-peer charity, in that loans are disbursed before being funded by lenders and borrowers do not communicate with lenders themselves.[143][144]
Security
Internet resources, hardware, and software components are the target of criminal or malicious attempts to gain unauthorized control to cause interruptions, commit fraud, engage in blackmail or access private information.
Malware
Malware is malicious software used and distributed via the Internet. It includes computer viruses which are copied with the help of humans, computer worms which copy themselves automatically, software for denial of service attacks, ransomware, botnets, and spyware that reports on the activity and typing of users. Usually, these activities constitute cybercrime. Defense theorists have also speculated about the possibilities of hackers using cyber warfare using similar methods on a large scale.[145]
Surveillance
The vast majority of computer surveillance involves the monitoring of data and traffic on the Internet.[146] In the United States for example, under the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act, all phone calls and broadband Internet traffic (emails, web traffic, instant messaging, etc.) are required to be available for unimpeded real-time monitoring by Federal law enforcement agencies.[147][148][149] Packet capture is the monitoring of data traffic on a computer network. Computers communicate over the Internet by breaking up messages (emails, images, videos, web pages, files, etc.) into small chunks called «packets», which are routed through a network of computers, until they reach their destination, where they are assembled back into a complete «message» again. Packet Capture Appliance intercepts these packets as they are traveling through the network, in order to examine their contents using other programs. A packet capture is an information gathering tool, but not an analysis tool. That is it gathers «messages» but it does not analyze them and figure out what they mean. Other programs are needed to perform traffic analysis and sift through intercepted data looking for important/useful information. Under the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act all U.S. telecommunications providers are required to install packet sniffing technology to allow Federal law enforcement and intelligence agencies to intercept all of their customers’ broadband Internet and VoIP traffic.[150]
The large amount of data gathered from packet capturing requires surveillance software that filters and reports relevant information, such as the use of certain words or phrases, the access of certain types of web sites, or communicating via email or chat with certain parties.[151] Agencies, such as the Information Awareness Office, NSA, GCHQ and the FBI, spend billions of dollars per year to develop, purchase, implement, and operate systems for interception and analysis of data.[152] Similar systems are operated by Iranian secret police to identify and suppress dissidents. The required hardware and software was allegedly installed by German Siemens AG and Finnish Nokia.[153]
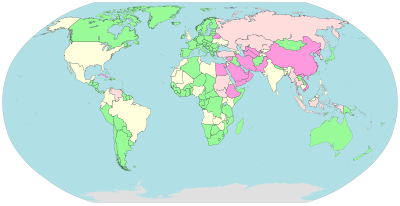
Censorship
Pervasive
Substantial
Selective
Little or none
Some governments, such as those of Burma, Iran, North Korea, Mainland China, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, restrict access to content on the Internet within their territories, especially to political and religious content, with domain name and keyword filters.[159]
In Norway, Denmark, Finland, and Sweden, major Internet service providers have voluntarily agreed to restrict access to sites listed by authorities. While this list of forbidden resources is supposed to contain only known child pornography sites, the content of the list is secret.[160] Many countries, including the United States, have enacted laws against the possession or distribution of certain material, such as child pornography, via the Internet, but do not mandate filter software. Many free or commercially available software programs, called content-control software are available to users to block offensive websites on individual computers or networks, in order to limit access by children to pornographic material or depiction of violence.
Performance
As the Internet is a heterogeneous network, the physical characteristics, including for example the data transfer rates of connections, vary widely. It exhibits emergent phenomena that depend on its large-scale organization.[161]
Traffic volume
Global Internet Traffic as of 2018
The volume of Internet traffic is difficult to measure, because no single point of measurement exists in the multi-tiered, non-hierarchical topology. Traffic data may be estimated from the aggregate volume through the peering points of the Tier 1 network providers, but traffic that stays local in large provider networks may not be accounted for.
Outages
An Internet blackout or outage can be caused by local signalling interruptions. Disruptions of submarine communications cables may cause blackouts or slowdowns to large areas, such as in the 2008 submarine cable disruption. Less-developed countries are more vulnerable due to a small number of high-capacity links. Land cables are also vulnerable, as in 2011 when a woman digging for scrap metal severed most connectivity for the nation of Armenia.[162] Internet blackouts affecting almost entire countries can be achieved by governments as a form of Internet censorship, as in the blockage of the Internet in Egypt, whereby approximately 93%[163] of networks were without access in 2011 in an attempt to stop mobilization for anti-government protests.[164]
Energy use
Estimates of the Internet’s electricity usage have been the subject of controversy, according to a 2014 peer-reviewed research paper that found claims differing by a factor of 20,000 published in the literature during the preceding decade, ranging from 0.0064 kilowatt hours per gigabyte transferred (kWh/GB) to 136 kWh/GB.[165] The researchers attributed these discrepancies mainly to the year of reference (i.e. whether efficiency gains over time had been taken into account) and to whether «end devices such as personal computers and servers are included» in the analysis.[165]
In 2011, academic researchers estimated the overall energy used by the Internet to be between 170 and 307 GW, less than two percent of the energy used by humanity. This estimate included the energy needed to build, operate, and periodically replace the estimated 750 million laptops, a billion smart phones and 100 million servers worldwide as well as the energy that routers, cell towers, optical switches, Wi-Fi transmitters and cloud storage devices use when transmitting Internet traffic.[166][167] According to a non-peer reviewed study published in 2018 by The Shift Project (a French think tank funded by corporate sponsors), nearly 4% of global CO2 emissions could be attributed to global data transfer and the necessary infrastructure.[168] The study also said that online video streaming alone accounted for 60% of this data transfer and therefore contributed to over 300 million tons of CO2 emission per year, and argued for new «digital sobriety» regulations restricting the use and size of video files.[169]
See also
- Crowdfunding
- Crowdsourcing
- Darknet
- Deep web
- Freenet
- Internet industry jargon
- Index of Internet-related articles
- Internet metaphors
- Internet video
- «Internets»
- Open Systems Interconnection
- Outline of the Internet
Notes
- ^ See Capitalization of Internet.
- ^ Despite the name, TCP/IP also includes UDP traffic, which is significant.[1]
References
- ^ Amogh Dhamdhere. «Internet Traffic Characterization». Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ a b «A Flaw in the Design». The Washington Post. 30 May 2015. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
The Internet was born of a big idea: Messages could be chopped into chunks, sent through a network in a series of transmissions, then reassembled by destination computers quickly and efficiently. Historians credit seminal insights to Welsh scientist Donald W. Davies and American engineer Paul Baran. … The most important institutional force … was the Pentagon’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) … as ARPA began work on a groundbreaking computer network, the agency recruited scientists affiliated with the nation’s top universities.
- ^ Stewart, Bill (January 2000). «Internet History – One Page Summary». The Living Internet. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014.
- ^ «#3 1982: the ARPANET community grows» in 40 maps that explain the internet Archived 6 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Timothy B. Lee, Vox Conversations, 2 June 2014. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ Strickland, Jonathan (3 March 2008). «How Stuff Works: Who owns the Internet?». Archived from the original on 19 June 2014. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ Hoffman, P.; Harris, S. (September 2006). The Tao of IETF: A Novice’s Guide to Internet Engineering Task Force. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4677. RFC 4677.
- ^ «New Seven Wonders panel». USA Today. 27 October 2006. Archived from the original on 15 July 2010. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- ^ «Internetted». Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.) nineteenth-century use as an adjective.
- ^ «United States Army Field Manual FM 24-6 Radio Operator’s Manual Army Ground Forces June 1945». United States War Department.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Cerf, Vint; Dalal, Yogen; Sunshine, Carl (December 1974). Specification of Internet Transmission Control Protocol. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC0675. RFC 675.
- ^ a b c d Corbett, Philip B. (1 June 2016). «It’s Official: The ‘Internet’ Is Over». The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 14 October 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ a b Herring, Susan C. (19 October 2015). «Should You Be Capitalizing the Word ‘Internet’?». Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ Coren, Michael J. (2 June 2016). «One of the internet’s inventors thinks it should still be capitalized». Quartz. Archived from the original on 27 September 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- ^ «World Wide Web Timeline». Pews Research Center. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 29 July 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ «HTML 4.01 Specification». World Wide Web Consortium. Archived from the original on 6 October 2008. Retrieved 13 August 2008.
[T]he link (or hyperlink, or Web link) [is] the basic hypertext construct. A link is a connection from one Web resource to another. Although a simple concept, the link has been one of the primary forces driving the success of the Web.
- ^ Hauben, Michael; Hauben, Ronda (1997). «5 The Vision of Interactive Computing And the Future». Netizens: On the History and Impact of Usenet and the Internet (PDF). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-8186-7706-9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 January 2021. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ Zelnick, Bob; Zelnick, Eva (1 September 2013). The Illusion of Net Neutrality: Political Alarmism, Regulatory Creep and the Real Threat to Internet Freedom. Hoover Press. ISBN 978-0-8179-1596-4. Archived from the original on 10 January 2021. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ Peter, Ian (2004). «So, who really did invent the Internet?». The Internet History Project. Archived from the original on 3 September 2011. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ «Inductee Details — Paul Baran». National Inventors Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2017; «Inductee Details — Donald Watts Davies». National Inventors Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- ^ Kim, Byung-Keun (2005). Internationalising the Internet the Co-evolution of Influence and Technology. Edward Elgar. pp. 51–55. ISBN 978-1-84542-675-0.
- ^ Gromov, Gregory (1995). «Roads and Crossroads of Internet History». Archived from the original on 27 January 2016.
- ^ Hafner, Katie (1998). Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins of the Internet. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-684-83267-8.
- ^ Hauben, Ronda (2001). «From the ARPANET to the Internet». Archived from the original on 21 July 2009. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- ^ «Internet Pioneers Discuss the Future of Money, Books, and Paper in 1972». Paleofuture. 23 July 2013. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 31 August 2020.
- ^ Townsend, Anthony (2001). «The Internet and the Rise of the New Network Cities, 1969–1999». Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design. 28 (1): 39–58. doi:10.1068/b2688. ISSN 0265-8135. S2CID 11574572.
- ^ «NORSAR and the Internet». NORSAR. Archived from the original on 21 January 2013.
- ^ Kirstein, P.T. (1999). «Early experiences with the Arpanet and Internet in the United Kingdom» (PDF). IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 21 (1): 38–44. doi:10.1109/85.759368. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 1558618. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 February 2020.
- ^ Leiner, Barry M. «Brief History of the Internet: The Initial Internetting Concepts». Internet Society. Archived from the original on 9 April 2016. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ Cerf, V.; Kahn, R. (1974). «A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication» (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Communications. 22 (5): 637–648. doi:10.1109/TCOM.1974.1092259. ISSN 1558-0857. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 September 2006.
The authors wish to thank a number of colleagues for helpful comments during early discussions of international network protocols, especially R. Metcalfe, R. Scantlebury, D. Walden, and H. Zimmerman; D. Davies and L. Pouzin who constructively commented on the fragmentation and accounting issues; and S. Crocker who commented on the creation and destruction of associations.
- ^ Leiner, Barry M.; Cerf, Vinton G.; Clark, David D.; Kahn, Robert E.; Kleinrock, Leonard; Lynch, Daniel C.; Postel, Jon; Roberts, Larry G.; Wolff, Stephen (2003). «A Brief History of Internet». Internet Society. p. 1011. arXiv:cs/9901011. Bibcode:1999cs……..1011L. Archived from the original on 4 June 2007. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- ^ «The internet’s fifth man». The Economist. 30 November 2013. ISSN 0013-0613. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
In the early 1970s Mr Pouzin created an innovative data network that linked locations in France, Italy and Britain. Its simplicity and efficiency pointed the way to a network that could connect not just dozens of machines, but millions of them. It captured the imagination of Dr Cerf and Dr Kahn, who included aspects of its design in the protocols that now power the internet.
- ^ Schatt, Stan (1991). Linking LANs: A Micro Manager’s Guide. McGraw-Hill. p. 200. ISBN 0-8306-3755-9.
- ^ Frazer, Karen D. (1995). «NSFNET: A Partnership for High-Speed Networking, Final Report 1987–1995» (PDF). Merit Network, Inc. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 February 2015.
- ^ Ben Segal (1995). «A Short History of Internet Protocols at CERN». Archived from the original on 19 June 2020. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- ^ Réseaux IP Européens (RIPE)
- ^ «Internet History in Asia». 16th APAN Meetings/Advanced Network Conference in Busan. Archived from the original on 1 February 2006. Retrieved 25 December 2005.
- ^ «The History of NORDUnet» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
- ^ Clarke, Roger. «Origins and Nature of the Internet in Australia». Archived from the original on 9 February 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ Zakon, Robert (November 1997). RFC 2235. IETF. p. 8. doi:10.17487/RFC2235. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Inc, InfoWorld Media Group (25 September 1989). «InfoWorld». Archived from the original on 29 January 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ «INTERNET MONTHLY REPORTS». February 1990. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim. «The Original HTTP as defined in 1991». W3C.org. Archived from the original on 5 June 1997.
- ^ «The website of the world’s first-ever web server». info.cern.ch. Archived from the original on 5 January 2010.
- ^ «Stanford Federal Credit Union Pioneers Online Financial Services» (Press release). 21 June 1995. Archived from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ «History — About us — OP Group». Archived from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ Harris, Susan R.; Gerich, Elise (April 1996). «Retiring the NSFNET Backbone Service: Chronicling the End of an Era». ConneXions. 10 (4). Archived from the original on 17 August 2013.
- ^ «Measuring digital development: Facts and figures 2021». Telecommunication Development Bureau, International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ «Total Midyear Population for the World: 1950-2050»«. International Programs Center for Demographic and Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 17 April 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Jindal, R. P. (2009). «From millibits to terabits per second and beyond — Over 60 years of innovation». 2009 2nd International Workshop on Electron Devices and Semiconductor Technology: 1–6. doi:10.1109/EDST.2009.5166093. ISBN 978-1-4244-3831-0. S2CID 25112828. Archived from the original on 23 August 2019. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (3 August 2006). «How the web went world wide». Technology Correspondent. BBC News. Archived from the original on 21 November 2011. Retrieved 24 January 2011.
- ^ «Brazil, Russia, India and China to Lead Internet Growth Through 2011». Clickz.com. Archived from the original on 4 October 2008. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- ^ Coffman, K.G; Odlyzko, A.M. (2 October 1998). «The size and growth rate of the Internet» (PDF). AT&T Labs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2007.
- ^ Comer, Douglas (2006). The Internet book. Prentice Hall. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-13-233553-9.
- ^ «World Internet Users and Population Stats». Internet World Stats. Miniwatts Marketing Group. 22 June 2011. Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ Hilbert, Martin; López, Priscila (April 2011). «The World’s Technological Capacity to Store, Communicate, and Compute Information». Science. 332 (6025): 60–65. Bibcode:2011Sci…332…60H. doi:10.1126/science.1200970. PMID 21310967. S2CID 206531385. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 May 2011.
- ^ Klein, Hans (2004). «ICANN and Non-Territorial Sovereignty: Government Without the Nation State». Internet and Public Policy Project. Georgia Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on 24 May 2013.
- ^ Packard, Ashley (2010). Digital Media Law. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-4051-8169-3.
- ^ McCarthy, Kieren (1 July 2005). «Bush administration annexes internet». The Register. Archived from the original on 19 September 2011.
- ^ Mueller, Milton L. (2010). Networks and States: The Global Politics of Internet Governance. MIT Press. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-262-01459-5.
- ^ «ICG Applauds Transfer of IANA Stewardship». IANA Stewardship Transition Coordination Group (ICG). Archived from the original on 12 July 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ «Internet Society (ISOC) All About The Internet: History of the Internet». ISOC. Archived from the original on 27 November 2011. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ^ Pasternak, Sean B. (7 March 2006). «Toronto Hydro to Install Wireless Network in Downtown Toronto». Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 10 April 2006. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Mobile and Tablet Internet Usage Exceeds Desktop for First Time Worldwide». StatCounter: Global Stats, Press Release. 1 November 2016. Archived from the original on 1 November 2016.
StatCounter Global Stats finds that mobile and tablet devices accounted for 51.3% of Internet usage worldwide in October compared to 48.7% by desktop.
- ^ «World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators Database 2020 (24th Edition/July 2020)». International Telecommunication Union (ITU). 2017a. Archived from the original on 21 April 2019.
Key ICT indicators for developed and developing countries and the world (totals and penetration rates). World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators database
- ^ a b World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development Global Report 2017/2018 (PDF). UNESCO. 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ a b «GSMA The Mobile Economy 2019 — The Mobile Economy». 11 March 2019. Archived from the original on 11 March 2019. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ Galpaya, Helani (12 April 2019). «Zero-rating in Emerging Economies» (PDF). Global Commission on Internet Governance. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ «Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI). 2015. Models of Mobile Data Services in Developing Countries. Research brief. The Impacts of Emerging Mobile Data Services in Developing Countries».[dead link]
- ^ Alison GillwAld, ChenAi ChAir, Ariel Futter, KweKu KorAntenG, FolA oduFuwA, John wAlubenGo (12 September 2016). «Much Ado About Nothing? Zero Rating in the African Context» (PDF). Researchictafrica. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b J. Postel, ed. (September 1981). Internet Protocol, DARPA Internet Program Protocol Specification. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC0791. RFC 791. Updated by RFC 1349, 2474, 6864
- ^ Huston, Geoff. «IPv4 Address Report, daily generated». Archived from the original on 1 April 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ S. Deering; R. Hinden (December 1995). Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC1883. RFC 1883.
- ^ S. Deering; R. Hinden (December 1998). Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC2460. RFC 2460.
- ^ S. Deering; R. Hinden (July 2017). Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8200. RFC 8200.
- ^ «Notice of Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) Address Depletion» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2010. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- ^ Jeffrey Mogul; Jon Postel (August 1985). Internet Standard Subnetting Procedure. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC0950. RFC 950. Updated by RFC 6918.
- ^ Fisher, Tim. «How to Find Your Default Gateway IP Address». Lifewire. Archived from the original on 25 February 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- ^ «Default Gateway». techopedia.com. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020.
- ^ «IETF Home Page». Ietf.org. Archived from the original on 18 June 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2009.
- ^ «The Difference Between the Internet and the World Wide Web». Webopedia.com. QuinStreet Inc. 24 June 2010. Archived from the original on 2 May 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- ^ «IAB Internet advertising revenue report: 2012 full year results» (PDF). PricewaterhouseCoopers, Internet Advertising Bureau. April 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2014. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ^ Brown, Ron (26 October 1972). «Fax invades the mail market». New Scientist. 56 (817): 218–221.
- ^ Luckett, Herbert P. (March 1973). «What’s News: Electronic-mail delivery gets started». Popular Science. 202 (3): 85.
- ^ Booth, C (2010). «Chapter 2: IP Phones, Software VoIP, and Integrated and Mobile VoIP». Library Technology Reports. 46 (5): 11–19.
- ^ Morrison, Geoff (18 November 2010). «What to know before buying a ‘connected’ TV – Technology & science – Tech and gadgets – Tech Holiday Guide». NBC News. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Press — YouTube». www.youtube.com. Archived from the original on 11 November 2017. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ «YouTube now defaults to HTML5 <video>». YouTube Engineering and Developers Blog. Archived from the original on 10 September 2018. Retrieved 10 September 2018.
- ^ Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max (2 October 2017). «Technology Adoption». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 12 October 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- ^ «Individuals using the Internet 2005 to 2014» Archived 28 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Key ICT indicators for developed and developing countries and the world (totals and penetration rates), International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Retrieved 25 May 2015.
- ^ «Internet users per 100 inhabitants 1997 to 2007» Archived 17 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine, ICT Data and Statistics (IDS), International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Retrieved 25 May 2015.
- ^ Internet users graphs Archived 9 May 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Market Information and Statistics, International Telecommunication Union
- ^ «Google Earth demonstrates how technology benefits RI’s civil society, govt». Antara News. 26 May 2011. Archived from the original on 29 October 2012. Retrieved 19 November 2012.
- ^ Steve Dent. «There are now 3 billion Internet users, mostly in rich countries». Archived from the original on 28 November 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ «Statistical Report on Internet Development in China» (PDF). Cnnic.com. January 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 April 2019.
- ^ «World Internet Users Statistics and 2019 World Population Stats». internetworldstats.com. Archived from the original on 24 November 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ «Digital 2020: 3.8 billion people use social media». 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ «Internet». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 21 March 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ a b «Number of Internet Users by Language». Internet World Stats, Miniwatts Marketing Group. 31 May 2011. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ «World Internet Usage Statistics News and Population Stats». 30 June 2010. Archived from the original on 19 March 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ^ How men and women use the Internet Pew Research Center 28 December 2005
- ^ «Rapleaf Study on Social Network Users». Archived from the original on 20 March 2009.
- ^ «Women Ahead of Men in Online Tv, Dvr, Games, And Social Media». Entrepreneur.com. 1 May 2008. Archived from the original on 16 September 2008. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ «Technorati’s State of the Blogosphere». Technorati. Archived from the original on 2 October 2009. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ a b «Percentage of Individuals using the Internet 2000–2012» Archived 9 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine, International Telecommunication Union (Geneva), June 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Seese, Michael (2009). Scrappy Information Security. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-60005-132-6. Archived from the original on 5 September 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ netizen Archived 21 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Dictionary.com
- ^ Hauben, Michael. «The Net and Netizens». Columbia University. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «A Brief History of the Internet». the Internet Society. Archived from the original on 4 June 2007.
- ^ «Oxford Dictionaries – internaut». oxforddictionaries.com. Archived from the original on 13 June 2015. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Mossberger, Karen; Tolbert, Caroline J.; McNeal, Ramona S. (23 November 2011). Digital Citizenship – The Internet, Society and Participation. ISBN 978-0-8194-5606-9.
- ^ «Usage of content languages for websites». W3Techs.com. Archived from the original on 31 March 2012. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- ^ «Fixed (wired)-broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants 2012» Archived 26 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine, Dynamic Report, ITU ITC EYE, International Telecommunication Union. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ^ «Active mobile-broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants 2012» Archived 26 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine, Dynamic Report, ITU ITC EYE, International Telecommunication Union. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ^ Reips, U.-D. (2008). «How Internet-mediated research changes science». Psychological aspects of cyberspace: Theory, research, applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 268–294. ISBN 9780521694643. Archived from the original on 9 August 2014.
- ^ «The Virtual Private Nightmare: VPN». Librenix. 4 August 2004. Archived from the original on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ Dariusz Jemielniak; Aleksandra Przegalinska (18 February 2020). Collaborative Society. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-35645-9. Archived from the original on 23 November 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- ^ Moore, Keith (27 July 2013). «Twitter ‘report abuse’ button calls after rape threats». BBC News. Archived from the original on 4 September 2014. Retrieved 7 December 2014.
- ^ Kessler, Sarah (11 October 2010). «5 Fun and Safe Social Networks for Children». Mashable. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 7 December 2014.
- ^ Goldman, Russell (22 January 2008). «Do It Yourself! Amateur Porn Stars Make Bank». ABC News. Archived from the original on 30 December 2011.
- ^ Spohn, Dave (15 December 2009). «Top Online Game Trends of the Decade». About.com. Archived from the original on 29 September 2011.
- ^ Spohn, Dave (2 June 2011). «Internet Game Timeline: 1963 – 2004». About.com. Archived from the original on 25 April 2006.
- ^ Carole Hughes; Boston College. «The Relationship Between Internet Use and Loneliness Among College Students». Boston College. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ Barker, Eric (2017). Barking Up the Wrong Tree. HarperCollins. pp. 235–6. ISBN 9780062416049.
- ^ Thornton, Patricia M. (2003). «The New Cybersects: Resistance and Repression in the Reform era». In Perry, Elizabeth; Selden, Mark (eds.). Chinese Society: Change, Conflict and Resistance (2 ed.). London and New York: Routledge. pp. 149–150. ISBN 9780415560740.
- ^ «Net abuse hits small city firms». The Scotsman. Edinburgh. 11 September 2003. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- ^ Carr, Nicholas G. (7 June 2010). The Shallows: What the Internet Is Doing to Our Brains. W.W. Norton. p. 276. ISBN 978-0393072228.
- ^ «The New Digital Economy: How it will transform business» (PDF). Oxford Economics. 2 July 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2014.
- ^ Badger, Emily (6 February 2013). «How the Internet Reinforces Inequality in the Real World». The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 11 February 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- ^ «E-commerce will make the shopping mall a retail wasteland». ZDNet. 17 January 2013. Archived from the original on 19 February 2013.
- ^ «‘Free Shipping Day’ Promotion Spurs Late-Season Online Spending Surge, Improving Season-to-Date Growth Rate to 16 Percent vs. Year Ago». Comscore. 23 December 2012. Archived from the original on 28 January 2013.
- ^ «The Death of the American Shopping Mall». The Atlantic – Cities. 26 December 2012. Archived from the original on 15 February 2013.
- ^ Harris, Michael (2 January 2015). «Book review: ‘The Internet Is Not the Answer’ by Andrew Keen». The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 20 January 2015. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ MM Wanderley; D Birnbaum; J Malloch (2006). New Interfaces For Musical Expression. IRCAM – Centre Pompidou. p. 180. ISBN 978-2-84426-314-8.
- ^ Nancy T. Lombardo (June 2008). «Putting Wikis to Work in Libraries». Medical Reference Services Quarterly. 27 (2): 129–145. doi:10.1080/02763860802114223. PMID 18844087. S2CID 11552140.
- ^ Noveck, Beth Simone (March 2007). «Wikipedia and the Future of Legal Education». Journal of Legal Education. 57 (1). Archived from the original on 3 July 2014.(subscription required)
- ^ «WikiStats by S23». S23Wiki. 3 April 2008. Archived from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 7 April 2007.
- ^ «Alexa Web Search – Top 500». Alexa Internet. Archived from the original on 2 March 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ^ «The Arab Uprising’s Cascading Effects». Miller-mccune.com. 23 February 2011. Archived from the original on 27 February 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ^ «The Role of the Internet in Democratic Transition: Case Study of the Arab Spring» (PDF). 5 July 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2012., Davit Chokoshvili, Master’s Thesis, June 2011
- ^ Kirkpatrick, David D. (9 February 2011). «Wired and Shrewd, Young Egyptians Guide Revolt». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 29 January 2017.
- ^ Ronald Deibert; John Palfrey; Rafal Rohozinski; Jonathan Zittrain (25 January 2008). Access Denied: The Practice and Policy of Global Internet Filtering. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-29072-2.
- ^ Larry Diamond; Marc F. Plattner (30 July 2012). Liberation Technology: Social Media and the Struggle for Democracy. JHU Press. ISBN 978-1-4214-0568-1.
- ^ Roodman, David (2 October 2009). «Kiva Is Not Quite What It Seems». Center for Global Development. Archived from the original on 10 February 2010. Retrieved 16 January 2010.
- ^ Strom, Stephanie (9 November 2009). «Confusion on Where Money Lent via Kiva Goes». The New York Times. p. 6. Archived from the original on 29 January 2017.
- ^ Andriole, Steve. «Cyberwarfare Will Explode In 2020 (Because It’s Cheap, Easy And Effective)». Forbes. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ Diffie, Whitfield; Susan Landau (August 2008). «Internet Eavesdropping: A Brave New World of Wiretapping». Scientific American. Archived from the original on 13 November 2008. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- ^ «CALEA Archive». Electronic Frontier Foundation (website). Archived from the original on 25 October 2008. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ «CALEA: The Perils of Wiretapping the Internet». Electronic Frontier Foundation (website). Archived from the original on 16 March 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ «CALEA: Frequently Asked Questions». Electronic Frontier Foundation (website). 20 September 2007. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ «American Council on Education vs. FCC, Decision, United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit» (PDF). 9 June 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ Hill, Michael (11 October 2004). «Government funds chat room surveillance research». USA Today. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 11 May 2010. Retrieved 19 March 2009.
- ^ McCullagh, Declan (30 January 2007). «FBI turns to broad new wiretap method». ZDNet News. Archived from the original on 7 April 2010. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- ^ «First round in Internet war goes to Iranian intelligence». Debkafile. 28 June 2009. Archived from the original on 21 December 2013.
- ^ «Freedom on the Net 2018» (PDF). Freedom House. November 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 November 2018. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- ^ OpenNet Initiative «Summarized global Internet filtering data spreadsheet» Archived 10 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 8 November 2011 and «Country Profiles» Archived 26 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine, the OpenNet Initiative is a collaborative partnership of the Citizen Lab at the Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto; the Berkman Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University; and the SecDev Group, Ottawa
- ^ Due to legal concerns the OpenNet Initiative does not check for filtering of child pornography and because their classifications focus on technical filtering, they do not include other types of censorship.
- ^ «Enemies of the Internet 2014: Entities at the heart of censorship and surveillance». Reporters Without Borders. Paris. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 12 March 2014.
- ^ «Internet Enemies» (PDF). Reporters Without Borders. Paris. 12 March 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 July 2017.
- ^ Deibert, Ronald J.; Palfrey, John G.; Rohozinski, Rafal; Zittrain, Jonathan (April 2010). Access Controlled: The Shaping of Power, Rights, and Rule in Cyberspace. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262514354. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «Finland censors anti-censorship site». The Register. 18 February 2008. Archived from the original on 20 February 2008. Retrieved 19 February 2008.
- ^ Albert, Réka; Jeong, Hawoong; Barabási, Albert-László (9 September 1999). «Diameter of the World-Wide Web». Nature. 401 (6749): 130–131. arXiv:cond-mat/9907038. Bibcode:1999Natur.401..130A. doi:10.1038/43601. S2CID 4419938.
- ^ «Georgian woman cuts off web access to whole of Armenia». The Guardian. 6 April 2011. Archived from the original on 25 August 2013. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ^ Cowie, James. «Egypt Leaves the Internet». Renesys. Archived from the original on 28 January 2011. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ «Egypt severs internet connection amid growing unrest». BBC News. 28 January 2011. Archived from the original on 23 January 2012.
- ^ a b Coroama, Vlad C.; Hilty, Lorenz M. (February 2014). «Assessing Internet energy intensity: A review of methods and results» (PDF). Environmental Impact Assessment Review. 45: 63–68. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2013.12.004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ^ Giles, Jim (26 October 2011). «Internet responsible for 2 per cent of global energy usage». New Scientist. Archived from the original on 1 October 2014.,
- ^ Raghavan, Barath; Ma, Justin (14 November 2011). «The Energy and Emergy of the Internet» (PDF). Proceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks. Cambridge, MA.: ACM SIGCOMM: 1–6. doi:10.1145/2070562.2070571. ISBN 9781450310598. S2CID 6125953. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 August 2014.
- ^ Cwienk, Jeannette (11 July 2019). «Is Netflix bad for the environment? How streaming video contributes to climate change | DW | 11.07.2019». Deutsche Welle. Archived from the original on 12 July 2019. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ^ ««Climate crisis: The Unsustainable Use of Online Video» : Our new report». The Shift Project. 10 July 2019. Archived from the original on 21 July 2019. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
Sources
This article incorporates text from a free content work. . Text taken from World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development Global Report 2017/2018, 202, UNESCO. To learn how to add open license text to Wikipedia articles, please see this how-to page. For information on reusing text from Wikipedia, please see the terms of use.
Further reading
- First Monday, a peer-reviewed journal on the Internet by the University Library of the University of Illinois at Chicago, ISSN 1396-0466
- The Internet Explained, Vincent Zegna & Mike Pepper, Sonet Digital, November 2005, pp. 1–7.
- Abram, Cleo (8 January 2020). «How Does the Internet Work?». YouTube. Vox Media. Archived from the original on 27 October 2021. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- Castells, Manuel (2010). The Rise of the Network Society. Wiley. ISBN 9781405196864.
External links
- The Internet Society
- Living Internet, Internet history and related information, including information from many creators of the Internet
Here’s what the Internet full form stands for:
Internet doesn’t stand for International Network or Interconnected Network—neither is correct.
The word Internet is a combination of the prefix inter-, from the Latin word inter meaning between or among, and net which is short for network.
So Internet simply stands for among or between networks.
So if you want to learn all about what the Internet stands for exactly, then this article is for you.
Without further ado, let’s do this!
What Does Internet Stand For?
The Internet is one of the most important technological advances in the history of man.
As a result, people often wonder where the word came from and what it means.
In fact, there are a number of myths about the word’s origins.
Some people think that it is an abbreviation for “International Network,” and others claim that it is short for “Interconnected network.” The reality is that it is neither.
The word “Internet” is a combination of the prefix “inter-,“ from the Latin word “inter” meaning “between” or “among,” and “net” which is short for “network.”
So Internet simply means, “among or between networks.”
How Did the Concept of the Internet Start & Evolve?
The concept that later became the Internet was born in August of 1962, in memos by J.C.R Licklider of MIT.
He discussed his vision of the concept whereby a set of computers could be interconnected on a global level, thereby providing access to programs and data to people in different locations.
In October of the same year, he became the head of the computer research program at the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and he convinced his successors, including Lawrence G. Roberts, that the Internet was an important concept.
In 1967, Roberts published a plan for the “ARPANET,” the predecessor to the Internet, and in 1968, Roberts and his team began to develop one of the most important components: the packet switches that would be used in place of circuits to allow communication between remote computers.
In 1969, the first computer-to-computer message was successfully sent, and the following years saw more and more computers added to the ARPANET.
By 1972, network users were able to develop applications to use on ARPANET, and in this same year, “electronic mail” was introduced. It took off, and people began to see the possibilities ahead.
The Beginning of the Internet
The original ARPANET system was a closed architecture network, so one method joined networks together, and there was a computer-to-computer connection where bits of information could be shared.
Bob Kahn played a huge role in designing this system, and he introduced the concept of “internetting,” which is an open network architecture that allows networks that are designed and developed separately.
The concept of “internetting” was that different networks with unique designs and functions could communicate and share applications.
The design of ARPANET was not sufficient for this open-architecture network, so Kahn decided to create a new protocol that could meet its needs.
This protocol is the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
It would function more similarly to a communications protocol than a device driver.
In 1973, he invited Stanford researcher Vincent Cerf to help him design the protocol.
They published a paper for the International Network Working Group (INWG) in 1973, and the term “Internet” was born.
Growth of the Internet
As researchers explored ways to improve and further develop the Internet, other technologies including LANs, PCs, and workstations were developed.
TCPs were improved to accommodate different application suites and performance objectives of different devices, which showed that workstations and personal computers could be a part of the Internet.
As the Internet grew, the number of hosts grew along with it, and there was a need to allow networks to be independently managed.
The Domain Name System (DNS) was created by Paul Mockapetris. With this change, the routers had trouble keeping up, so the system of routing was replaced by the Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), which tied different regions together.
By 1985, the Internet was a well-established technology that connected a number of developers and researchers, and it was being used in various communities for email and other communications.
During this time, other computer researchers were working on other networking, but they were mostly closed within their respective communities.
In fact, universities that received funding were required to make the Internet available to all qualified users on their campuses.
Since then, the amount of Internet users has grown at a steady rate in all regions of the world.
In 2009, Internet penetration in Africa was the worldwide lowest at 7.6% but it eventually grew to 28.2% in 2019.
As of 2019, Europe had the highest Internet penetration worldwide with 82.5% of its population having access to the Internet.
The Internet Is Defined
The Internet began to grow and experience technological advances for the next 10 years, and more and more communities became connected.
On October 24, 1995, the FNC (Federal networking Council) passed a resolution that defined the term Internet:
- RESOLUTION: The Federal Networking Council (FNC) agrees that the following language reflects our definition of the term “Internet.”
- “Internet” refers to the global information system that:
- (i) is logically linked together by a globally unique address space based on the Internet Protocol (IP) or its subsequent extensions/follow-ons;
- (ii) is able to support communications using the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) suite or its subsequent extensions/follow-ons, and/or other IP-compatible protocols, and;
- (iii) provides, uses, or makes accessible, either publicly or privately, high-level services layered on the communications and related infrastructure described herein.
- “Internet” refers to the global information system that:
The Internet Today
The Internet today has grown beyond email, web pages, and discussion boards to incorporate places where people collaborate, engage in commerce, and share.
Social media has transformed all aspects of society in terms of marketing, political campaigns, the news, and more.
If you want to see just how widespread use of the Internet is, check out Internet Live Stats, a website that shows live counters of Internet users in the world and on websites, email, and more.
At this moment, there are 4,467,484,737 Internet users according to the site.
What Is the Internet Today?

The Internet has evolved from a concept of connecting remote computers to a huge global network system that links millions of computers.
These networks serve government, business, academic, private, and public purposes, and data is exchanged worldwide through these connections.
The Internet is no longer limited to computer connections; many devices—including smartphones, tablets, video consoles, TVs, and more—can use an Internet connection to access and share information.
People can send emails, access websites, make purchases, collaborate, watch movies, play games, and so much more.
In fact, businesses have even utilized the Internet for their marketing strategies through social media marketing.
There are various social networking sites available but Facebook remains at the top as the most commonly used social media platform worldwide, with 94% of social media marketers using the said network to promote their business.
The Internet has transformed the way people live.
Politicians offer live streams via the Internet, and people Tweet their opinions.
So much information is readily available within seconds, and people can communicate with friends and family anywhere in the world at no cost.
People can collaborate from remote locations, making the world even more accessible.
What Are the Important Features of the Internet? (3 Applications)
The Internet is a carrier for many of the applications that people use in everyday life including e-commerce, email, online chat, file sharing, file transfer, text and multimedia data, online gaming, and more.
The Internet is the means by which the following applications are shared.
Take a look:
#1 Email
The email was created around the same time as the Internet.
Today, almost everyone on the planet has an email address, and there are many choices for getting one.
Email addresses can be free from providers such as Google or Yahoo, or they can be self-hosted with someone’s specific web address.
#2 E-Commerce
E-commerce has been revolutionary for businesses and consumers alike.
E-commerce sites allow consumers to shop from home which can drastically reduce businesses’ operating costs or supplement their brick-and-mortar presence.
Small businesses worldwide have become more successful because of the Internet since they can reach a wide audience.
#3 File Transfer and File Sharing
The Internet was created for the purpose of file transfer and file sharing, and today it is easier than ever before.
Large files can be uploaded for recipients, and email attachments can be sent with ease.
It is easier and more reliable to keep records and collaborate.
Is the Internet the Same as the WWW?
The WWW is an acronym for the World Wide Web. The WWW is not the same thing as the Internet.
The Internet is the protocol that allows for the interconnectivity of networks, and the WWW is an application that uses the Internet.
The WWW is basically an information system that identifies links with URLs (Uniform Resource Locators), and they are accessible over the Internet.
Each website has a distinct URL.
Why Do People Think That Internet Means “Interconnected Network”?
Some people claim that the Internet’s full form is “Interconnected Network.”
This is a logical explanation for the term, as the Internet is made up of many different networks that can access and share information.
However, it is a common misconception because the term was first coined from “Internetting,” which referred to connecting different networks.
Why Do People Think That Internet Means “International Network”?
In 1973, Bob Kahn and Vincent Cerf published a paper on the concept of internetting on an open architecture network by way of a TCP/IP.
They presented this paper to the International Network Working Group (INWG), and this was truly the beginning of the Internet that we know today.
As a result, some people mistakenly think that the term Internet came from the first two words in the group’s name, International network.
However, this is not the case. Kahn and Cerf had already referred to their new open-architecture process as “internetting,” and Internet was simply the noun form of that term.
Internet is a combination of the Latin prefix, “inter-“ and the shortened form of the word network, “net.”
Together, it means among or between networks, and the idea was that different network systems could communicate and share information.
What Are Other Vital Tech Words and Their Meanings?
Here’s a list of particularly interesting tech acronyms—or maybe they’re not even acronyms?
Learn what these stand for:
- GOOGLE full form: what does it stand for?
- COMPUTER full form: what does it stand for?
- WI-FI full form: what does it stand for?
Visualization of the various routes through a portion of the Internet.
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that are set up to exchange various types of data. This «network of networks» connects millions of computers, including those in academic, business, and government networks, transcending geographic and national boundaries. It is made possible through the merging of computer technology with technologies used by the media and telecommunications industries.
The Internet connects information resources and provides various services, such as electronic mail, online chat, file transfer and file sharing, online gaming, and the inter-linked hypertext documents and other resources of the World Wide Web (WWW).
Terminology
The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used in every-day speech without much distinction. However, the Internet and the World Wide Web are not one and the same. The Internet is a global data communications system. It is a hardware and software infrastructure that provides connectivity between computers. In contrast, the Web is one of the services communicated via the Internet. It is a collection of interconnected documents and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs: «The link (or hyperlink, or Web link) [is] the basic hypertext construct. A link is a connection from one Web resource to another. Although a simple concept, the link has been one of the primary forces driving the success of the Web.»[1]
History
Creation
Did you know?
The internet was first conceived of in the 1946 science fiction short story, «A Logic Named Joe»
A 1946 science fiction short story, A Logic Named Joe, by Murray Leinster laid out the Internet and many of its strengths and weaknesses. However, it took more than a decade before reality began to catch up with this vision.
The USSR’s launch of Sputnik spurred the United States to create the Advanced Research Projects Agency, known as ARPA, in February 1958 to regain a technological lead.[2] ARPA created the Information Processing Technology Office (IPTO) to further the research of the Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) program, which had networked country-wide radar systems together for the first time. J. C. R. Licklider was selected to head the IPTO, and saw universal networking as a potential unifying human revolution.
Licklider moved from the Psycho-Acoustic Laboratory at Harvard University to MIT in 1950, after becoming interested in information technology. At MIT, he served on a committee that established Lincoln Laboratory and worked on the SAGE project. In 1957 he became a Vice President at BBN, where he bought the first production PDP-1 computer and conducted the first public demonstration of time-sharing.
At the IPTO, Licklider recruited Lawrence Roberts to head a project to implement a network, and Roberts based the technology on the work of Paul Baran, who had written an exhaustive study for the U.S. Air Force that recommended packet switching (as opposed to circuit switching) to make a network highly robust and survivable. After much work, the first two nodes of what would become the ARPANET were interconnected between UCLA and SRI International in Menlo Park, California, on October 29, 1969. The ARPANET was one of the «eve» networks of today’s Internet. Following on from the demonstration that packet switching worked on the ARPANET, the British Post Office, Telenet, DATAPAC and TRANSPAC collaborated to create the first international packet-switched network service. In the UK, this was referred to as the International Packet Switched Service (IPSS), in 1978. The collection of X.25-based networks grew from Europe and the US to cover Canada, Hong Kong and Australia by 1981. The X.25 packet switching standard was developed in the CCITT (now called ITU-T) around 1976. X.25 was independent of the TCP/IP protocols that arose from the experimental work of DARPA on the ARPANET, Packet Radio Net and Packet Satellite Net during the same time period. Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn developed the first description of the TCP protocols during 1973 and published a paper on the subject in May 1974. Use of the term «Internet» to describe a single global TCP/IP network originated in December 1974 with the publication of RFC 675, the first full specification of TCP that was written by Vinton Cerf, Yogen Dalal and Carl Sunshine, then at Stanford University. During the next nine years, work proceeded to refine the protocols and to implement them on a wide range of operating systems.
The first TCP/IP-based wide-area network was operational by January 1, 1983 when all hosts on the ARPANET were switched over from the older NCP protocols. In 1985, the United States’ National Science Foundation (NSF) commissioned the construction of the NSFNET, a university 56 kilobit/second network backbone using computers called «fuzzballs» by their inventor, David L. Mills. The following year, NSF sponsored the conversion to a higher-speed 1.5 megabit/second network. A key decision to use the DARPA TCP/IP protocols was made by Dennis Jennings, then in charge of the Supercomputer program at NSF.
The opening of the network to commercial interests began in 1988. The United States Federal Networking Council approved the interconnection of the NSFNET to the commercial MCI Mail system in that year and the link was made in the summer of 1989. Other commercial electronic e-mail services were soon connected, including OnTyme, Telemail and Compuserve. In that same year, three commercial Internet service providers (ISP) were created: UUNET, PSINET and CERFNET. Important, separate networks that offered gateways into, then later merged with, the Internet include Usenet and BITNET. Various other commercial and educational networks, such as Telenet, Tymnet, Compuserve and JANET were interconnected with the growing Internet. Telenet (later called Sprintnet) was a large privately funded national computer network with free dial-up access in cities throughout the United States that had been in operation since the 1970s. This network was eventually interconnected with the others in the 1980s as the TCP/IP protocol became increasingly popular. The ability of TCP/IP to work over virtually any pre-existing communication networks allowed for a great ease of growth, although the rapid growth of the Internet was due primarily to the availability of commercial routers from companies such as Cisco Systems, Proteon and Juniper, the availability of commercial Ethernet equipment for local-area networking and the widespread implementation of TCP/IP on the UNIX operating system.
Growth
Although the basic applications and guidelines that make the Internet possible had existed for almost a decade, the network did not gain a public face until the 1990s. On August 6, 1991, CERN, which straddles the border between France and Switzerland, publicized the new World Wide Web project. The Web was invented by English scientist Tim Berners-Lee in 1989.
An early popular web browser was ViolaWWW, patterned after HyperCard and built using the X Window System. It was eventually replaced in popularity by the Mosaic web browser. In 1993, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois released version 1.0 of Mosaic, and by late 1994 there was growing public interest in the previously academic, technical Internet. By 1996 usage of the word Internet had become commonplace, and consequently, so had its use as a synecdoche in reference to the World Wide Web.
Meanwhile, over the course of the decade, the Internet successfully accommodated the majority of previously existing public computer networks (although some networks, such as FidoNet, have remained separate). During the 1990s, it was estimated that the Internet grew by 100 percent per year, with a brief period of explosive growth in 1996 and 1997. This growth is often attributed to the lack of central administration, which allows organic growth of the network, as well as the non-proprietary open nature of the Internet protocols, which encourages vendor interoperability and prevents any one company from exerting too much control over the network.
University students’ appreciation and contributions
New findings in the field of communications during the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s were quickly adopted by universities across North America.
Graduate students played a huge part in the creation of ARPANET. In the 1960s, the network working group, which did most of the design for ARPANET’s protocols, was composed mainly of graduate students.
Today’s Internet
The My Opera Community server rack. From the top, user file storage (content of files.myopera.com), «bigma» (the master MySQL database server), and two IBM blade centers containing multi-purpose machines (Apache front ends, Apache back ends, slave MySQL database servers, load balancers, file servers, cache servers and sync masters).
Aside from the complex physical connections that make up its infrastructure, the Internet is facilitated by bi- or multi-lateral commercial contracts (e.g., peering agreements), and by technical specifications or protocols that describe how to exchange data over the network. Indeed, the Internet is defined by its interconnections and routing policies.
Internet protocols
The complex communications infrastructure of the Internet consists of its hardware components and a system of software layers that control various aspects of the architecture. While the hardware can often be used to support other software systems, it is the design and the rigorous standardization process of the software architecture that characterizes the Internet.
The responsibility for the architectural design of the Internet software systems has been delegated to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).[3] The IETF conducts standard-setting work groups, open to any individual, about the various aspects of Internet architecture. Resulting discussions and final standards are published in Request for Comments (RFCs), freely available on the IETF web site.
The principal methods of networking that enable the Internet are contained in a series of RFCs that constitute the Internet Standards. These standards describe a system known as the Internet Protocol Suite. This is a model architecture that divides methods into a layered system of protocols (RFC 1122, RFC 1123). The layers correspond to the environment or scope in which their services operate. At the top is the space (Application Layer) of the software application, e.g., a web browser application, and just below it is the Transport Layer which connects applications on different hosts via the network (e.g., client-server model). The underlying network consists of two layers: the Internet Layer which enables computers to connect to one-another via intermediate (transit) networks and thus is the layer that establishes internetworking and the Internet, and lastly, at the bottom, is a software layer that provides connectivity between hosts on the same local link (therefore called Link Layer), e.g., a local area network (LAN) or a dial-up connection. This model is also known as the TCP/IP model of networking. While other models have been developed, such as the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, they are not compatible in the details of description, nor implementation.
The most prominent component of the Internet model is the Internet Protocol (IP) which provides addressing systems for computers on the Internet and facilitates the internetworking of networks. IP Version 4 (IPv4) is the initial version used on the first generation of the today’s Internet and is still in dominant use. It was designed to address up to ~4.3 billion (109) Internet hosts. However, the explosive growth of the Internet has led to IPv4 address exhaustion. A new protocol version, IPv6, was developed which provides vastly larger addressing capabilities and more efficient routing of data traffic. IPv6 is currently in commercial deployment phase around the world.
IPv6 is not interoperable with IPv4. It essentially establishes a «parallel» version of the Internet not accessible with IPv4 software. This means software upgrades are necessary for every networking device that needs to communicate on the IPv6 Internet. Most modern computer operating systems are already converted to operate with both version of the Internet Protocol. Network infrastructures, however, are still lagging in this development.
Internet structure
There have been many analyses of the Internet and its structure. For example, it has been determined that the Internet IP routing structure and hypertext links of the World Wide Web are examples of scale-free networks.
Similar to the way the commercial Internet providers connect via Internet exchange points, research networks tend to interconnect into large subnetworks such as the following:
- GEANT
- GLORIAD
- The Internet2 Network (formally known as the Abilene Network)
- JANET (the UK’s national research and education network)
These in turn are built around relatively smaller networks. See also the list of academic computer network organizations.
In computer network diagrams, the Internet is often represented by a cloud symbol, into and out of which network communications can pass.
ICANN
ICANN former headquarters in Marina Del Rey, California, United States
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the authority that coordinates the assignment of unique identifiers on the Internet, including domain names, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, and protocol port and parameter numbers. A globally unified namespace (i.e., a system of names in which there is at most one holder for each possible name) is essential for the Internet to function. ICANN is headquartered in Los Angeles, California, but is overseen by an international board of directors drawn from across the Internet technical, business, academic, and non-commercial communities.[4] Because the Internet is a distributed network comprising many voluntarily interconnected networks, the Internet has no governing body. ICANN’s role in coordinating the assignment of unique identifiers distinguishes it as perhaps the only central coordinating body on the global Internet, but the scope of its authority extends only to the Internet’s systems of domain names, IP addresses, protocol ports and parameter numbers.
On November 16, 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society, held in Tunis, established the Internet Governance Forum (IGF) to discuss Internet-related issues.
Language
The prevalent language for communication on the Internet is English. This may be a result of the Internet’s origins, as well as English’s role as a lingua franca. It may also be related to the poor capability of early computers, largely originating in the United States, to handle characters other than those in the English variant of the Latin alphabet.
After English (25 percent of Web visitors) the most requested languages on the World Wide Web are Chinese (19 percent), Spanish (8 percent), Arabic (5 percent), Portuguese (4 percent), Indonesian/Malaysian (4 percent), Japanese (3 percent), French (3 percent), Russian (2 percent), and German (2 percent).[5]
By region, 50 percent of the world’s Internet users are based in Asia, 16 percent in Europe, 8 percent in North America, 10 percent in Latin America and the Caribbean, 11 percent in Africa, 4 percent in the Middle East and 1 percent in Australia.[6]
The Internet’s technologies have developed enough in recent years, especially in the use of Unicode, that good facilities are available for development and communication in most widely used languages. However, some glitches such as mojibake (incorrect display of foreign language characters, also known as kryakozyabry) still remain.
Internet and the workplace
The Internet is allowing greater flexibility in working hours and location, especially with the spread of unmetered high-speed connections and Web applications.
The Internet viewed on mobile devices
The Internet can now be accessed virtually anywhere by numerous means. Mobile phones, datacards, handheld game consoles and cellular routers allow users to connect to the Internet from anywhere there is a cellular network supporting that device’s technology.
Within the limitations imposed by the small screen and other limited facilities of such a pocket-sized device, all the services of the Internet, including email and web browsing, may be available in this way. Service providers may restrict the range of these services and charges for data access may be significant, compared to home usage.
Common uses
The concept of sending electronic text messages between parties in a way analogous to mailing letters or memos predates the creation of the Internet. Even today it can be important to distinguish between Internet and internal e-mail systems. Internet e-mail may travel and be stored unencrypted on many other networks and machines out of both the sender’s and the recipient’s control. During this time it is quite possible for the content to be read and even tampered with by third parties, if anyone considers it important enough. Purely internal or intranet mail systems, where the information never leaves the corporate or organization’s network, are much more secure, although in any organization there will be IT and other personnel whose job may involve monitoring, and occasionally accessing, the e-mail of other employees not addressed to them.
The World Wide Web
Graphic representation of a minute fraction of the WWW, demonstrating hyperlinks
Many people use the terms Internet and World Wide Web (or just the Web) interchangeably, but, as discussed above, the two terms are not synonymous.
The World Wide Web is a huge set of interlinked documents, images and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs. These hyperlinks and URLs allow the web servers and other machines that store originals, and cached copies, of these resources to deliver them as required using HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). HTTP is only one of the communication protocols used on the Internet.
Web services also use HTTP to allow software systems to communicate in order to share and exchange business logic and data.
Software products that can access the resources of the Web are correctly termed user agents. In normal use, web browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox and Apple Safari, access web pages and allow users to navigate from one to another via hyperlinks. Web documents may contain almost any combination of computer data including graphics, sounds, text, video, multimedia and interactive content including games, office applications and scientific demonstrations.
Through keyword-driven Internet research using search engines like Yahoo! and Google, millions of people worldwide have easy, instant access to a vast and diverse amount of online information. Compared to encyclopedias and traditional libraries, the World Wide Web has enabled a sudden and extreme decentralization of information and data.
Using the Web, it is also easier than ever before for individuals and organizations to publish ideas and information to an extremely large audience. Anyone can find ways to publish a web page, a blog or build a website for very little initial cost. Publishing and maintaining large, professional websites full of attractive, diverse and up-to-date information is still a difficult and expensive proposition, however.
Many individuals and some companies and groups use «web logs» or blogs, which are largely used as easily updatable online diaries. Some commercial organizations encourage staff to fill them with advice on their areas of specialization in the hope that visitors will be impressed by the expert knowledge and free information, and be attracted to the corporation as a result. One example of this practice is Microsoft, whose product developers publish their personal blogs in order to pique the public’s interest in their work.
Collections of personal web pages published by large service providers remain popular, and have become increasingly sophisticated. Whereas operations such as Angelfire and GeoCities have existed since the early days of the Web, newer offerings from, for example, Facebook and MySpace currently have large followings. These operations often brand themselves as social network services rather than simply as web page hosts.
Advertising on popular web pages can be lucrative, and e-commerce or the sale of products and services directly via the Web continues to grow.
In the early days, web pages were usually created as sets of complete and isolated HTML text files stored on a web server. More recently, websites are more often created using content management system (CMS) or wiki software with, initially, very little content. Contributors to these systems, who may be paid staff, members of a club or other organization or members of the public, fill underlying databases with content using editing pages designed for that purpose, while casual visitors view and read this content in its final HTML form. There may or may not be editorial, approval and security systems built into the process of taking newly entered content and making it available to the target visitors.
Remote access
The Internet allows computer users to connect to other computers and information stores easily, wherever they may be across the world. They may do this with or without the use of security, authentication and encryption technologies, depending on the requirements.
There are encouraging new ways of working from home, collaboration and information-sharing in many industries. An accountant sitting at home can audit the books of a company based in another country, on a server situated in a third country that is remotely maintained by IT specialists in a fourth. These accounts could have been created by home-working bookkeepers, in other remote locations, based on information e-mailed to them from offices all over the world. Some of these things were possible before the widespread use of the Internet, but the cost of private leased lines would have made many of them infeasible in practice.
An office worker away from his desk, perhaps on the other side of the world on a business trip or a holiday, can open a remote desktop session into his normal office PC using a secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection via the Internet. This gives the worker complete access to all of his or her normal files and data, including e-mail and other applications, while away from the office.
This concept is also referred to by some network security people as the Virtual Private Nightmare, because it extends the secure perimeter of a corporate network into its employees’ homes; this has been the source of some notable security breaches, but also provides security for the workers.
Collaboration
The low cost and nearly instantaneous sharing of ideas, knowledge, and skills has made collaborative work dramatically easier. Not only can a group cheaply communicate and test, but the wide reach of the Internet allows such groups to easily form in the first place, even among niche interests. An example of this is the free software movement in software development, which produced GNU and Linux from scratch and has taken over development of Mozilla and OpenOffice.org (formerly known as Netscape Communicator and StarOffice).
Internet «chat,» whether in the form of IRC «chat rooms» or channels, or via instant messaging systems, allow colleagues to stay in touch in a very convenient way when working at their computers during the day. Messages can be sent and viewed even more quickly and conveniently than via e-mail. Extension to these systems may allow files to be exchanged, «whiteboard» drawings to be shared as well as voice and video contact between team members.
Version control systems allow collaborating teams to work on shared sets of documents without either accidentally overwriting each other’s work or having members wait until they get «sent» documents to be able to add their thoughts and changes.
File sharing
A computer file can be e-mailed to customers, colleagues and friends as an attachment. It can be uploaded to a website or FTP server for easy download by others. It can be put into a «shared location» or onto a file server for instant use by colleagues. The load of bulk downloads to many users can be eased by the use of «mirror» servers or peer-to-peer networks.
In any of these cases, access to the file may be controlled by user authentication; the transit of the file over the Internet may be obscured by encryption, and money may change hands before or after access to the file is given. The price can be paid by the remote charging of funds from, for example, a credit card whose details are also passed—hopefully fully encrypted—across the Internet. The origin and authenticity of the file received may be checked by digital signatures or by MD5 or other message digests.
These simple features of the Internet, over a worldwide basis, are changing the basis for the production, sale, and distribution of anything that can be reduced to a computer file for transmission. This includes all manner of print publications, software products, news, music, film, video, photography, graphics and the other arts. This in turn has caused seismic shifts in each of the existing industries that previously controlled the production and distribution of these products.
Internet collaboration technology enables business and project teams to share documents, calendars and other information. Such collaboration occurs in a wide variety of areas including scientific research, software development, conference planning, political activism and creative writing.
Streaming media
Many existing radio and television broadcasters provide Internet «feeds» of their live audio and video streams (for example, the BBC). They may also allow time-shift viewing or listening such as Preview, Classic Clips and Listen Again features. These providers have been joined by a range of pure Internet «broadcasters» who never had on-air licenses. This means that an Internet-connected device, such as a computer or something more specific, can be used to access on-line media in much the same way as was previously possible only with a television or radio receiver. The range of material is much wider, from pornography to highly specialized, technical webcasts. Podcasting is a variation on this theme, where—usually audio—material is first downloaded in full and then may be played back on a computer or shifted to a digital audio player to be listened to on the move. These techniques using simple equipment allow anybody, with little censorship or licensing control, to broadcast audio-visual material on a worldwide basis.
Webcams can be seen as an even lower-budget extension of this phenomenon. While some webcams can give full-frame-rate video, the picture is usually either small or updates slowly. Internet users can watch animals around an African waterhole, ships in the Panama Canal, the traffic at a local roundabout or their own premises, live and in real time. Video chat rooms, video conferencing, and remote controllable webcams are also popular. Many uses can be found for personal webcams in and around the home, with and without two-way sound.
YouTube, sometimes described as an Internet phenomenon because of the vast amount of users and how rapidly the site’s popularity has grown, was founded on February 15, 2005. It is now the leading website for free streaming video. It uses a flash-based web player which streams video files in the format FLV. Users are able to watch videos without signing up; however, if users do sign up they are able to upload an unlimited amount of videos and they are given their own personal profile. It is currently estimated that there are 64,000,000 videos on YouTube, and it is also currently estimated that 825,000 new videos are uploaded every day.
Voice telephony (VoIP)
VoIP stands for Voice over IP, where IP refers to the Internet Protocol that underlies all Internet communication. This phenomenon began as an optional two-way voice extension to some of the instant messaging systems that took off around the year 2000. In recent years many VoIP systems have become as easy to use and as convenient as a normal telephone. The benefit is that, as the Internet carries the actual voice traffic, VoIP can be free or cost much less than a normal telephone call, especially over long distances and especially for those with always-on Internet connections such as cable or ADSL.
Thus, VoIP is maturing into a viable alternative to traditional telephones. Interoperability between different providers has improved and the ability to call or receive a call from a traditional telephone is available. Simple, inexpensive VoIP modems are now available that eliminate the need for a PC.
Voice quality can still vary from call to call but is often equal to and can even exceed that of traditional calls.
Remaining problems for VoIP include emergency telephone number dialing and reliability. Currently, a few VoIP providers provide an emergency service, but it is not universally available. Traditional phones are line-powered and operate during a power failure; VoIP does not do so without a backup power source for the electronics.
Most VoIP providers offer unlimited national calling, but the direction in VoIP is clearly toward global coverage with unlimited minutes for a low monthly fee.
VoIP has also become increasingly popular within the gaming world, as a form of communication between players. Popular gaming VoIP clients include Ventrilo and Teamspeak, and there are others available also. The PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360 also offer VoIP chat features.
Internet access
Common methods of home access include dial-up, landline broadband (over coaxial cable, fiber optic or copper wires), Wi-Fi, satellite and 3G technology cell phones.
Public places to use the Internet include libraries and Internet cafes, where computers with Internet connections are available. There are also Internet access points in many public places such as airport halls and coffee shops, in some cases just for brief use while standing. Various terms are used, such as «public Internet kiosk,» «public access terminal,» and «Web payphone.» Many hotels now also have public terminals, though these are usually fee-based.
These terminals are widely accessed for various usage like ticket booking, bank deposit, online payment etc. Wi-Fi provides wireless access to computer networks, and therefore can do so to the Internet itself. Hotspots providing such access include Wi-Fi cafes, where would-be users need to bring their own wireless-enabled devices such as a laptop or PDA. These services may be free to all, free to customers only, or fee-based. A hotspot need not be limited to a confined location. A whole campus or park, or even an entire city can be enabled. Grassroots efforts have led to wireless community networks. Commercial Wi-Fi services covering large city areas are in place in London, Vienna, Toronto, San Francisco, Philadelphia, Chicago and Pittsburgh. The Internet can then be accessed from such places as a park bench.
Apart from Wi-Fi, there have been experiments with proprietary mobile wireless networks like Ricochet, various high-speed data services over cellular phone networks, and fixed wireless services.
High-end mobile phones such as smartphones generally come with Internet access through the phone network. Web browsers such as Opera are available on these advanced handsets, which can also run a wide variety of other Internet software. More mobile phones have Internet access than PCs, though this is not as widely used. An Internet access provider and protocol matrix differentiates the methods used to get online.
The Internet has made possible entirely new forms of social interaction, activities and organizing, thanks to its basic features such as widespread usability and access.
Social networking websites such as Facebook and MySpace have created a new form of socialization and interaction. Users of these sites are able to add a wide variety of items to their personal pages, to indicate common interests, and to connect with others. It is also possible to find a large circle of existing acquaintances, especially if a site allows users to utilize their real names, and to allow communication among large existing groups of people.
Sites like meetup.com exist to allow wider announcement of groups which may exist mainly for face-to-face meetings, but which may have a variety of minor interactions over their group’s site at meetup.org, or other similar sites.
Political organization and censorship
In democratic societies, the Internet has achieved new relevance as a political tool. The presidential campaign of Howard Dean in 2004 in the United States became famous for its ability to generate donations via the Internet. Many political groups use the Internet to achieve a whole new method of organizing, in order to carry out Internet activism.
Some governments, such as those of Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Myanmar, the People’s Republic of China, and Saudi Arabia, restrict what people in their countries can access on the Internet, especially political and religious content. This is accomplished through software that filters domains and content so that they may not be easily accessed or obtained without elaborate circumvention.
In Norway, Denmark, Finland[7] and Sweden, major Internet service providers have voluntarily (possibly to avoid such an arrangement being turned into law) agreed to restrict access to sites listed by police. While this list of forbidden URLs is only supposed to contain addresses of known child pornography sites, the content of the list is secret.
Many countries, including the United States, have enacted laws making the possession or distribution of certain material, such as child pornography, illegal, but do not use filtering software.
There are many free and commercially available software programs with which a user can choose to block offensive websites on individual computers or networks, such as to limit a child’s access to pornography or violence. See Content-control software.
Leisure activities
The Internet has been a major source of leisure since before the World Wide Web, with entertaining social experiments such as MUDs and MOOs being conducted on university servers, and humor-related Usenet groups receiving much of the main traffic. Today, many Internet forums have sections devoted to games and funny videos; short cartoons in the form of Flash movies are also popular. Over 6 million people use blogs or message boards as a means of communication and for the sharing of ideas.
The pornography and gambling industries have both taken full advantage of the World Wide Web, and often provide a significant source of advertising revenue for other websites. Although many governments have attempted to put restrictions on both industries’ use of the Internet, this has generally failed to stop their widespread popularity.
One main area of leisure on the Internet is multiplayer gaming. This form of leisure creates communities, bringing people of all ages and origins to enjoy the fast-paced world of multiplayer games. These range from MMORPG to first-person shooters, from role-playing games to online gambling. This has revolutionized the way many people interact and spend their free time on the Internet.
While online gaming has been around since the 1970s, modern modes of online gaming began with services such as GameSpy and MPlayer, to which players of games would typically subscribe. Non-subscribers were limited to certain types of gameplay or certain games.
Many use the Internet to access and download music, movies and other works for their enjoyment and relaxation. As discussed above, there are paid and unpaid sources for all of these, using centralized servers and distributed peer-to-peer technologies. Some of these sources take more care over the original artists’ rights and over copyright laws than others.
Many use the World Wide Web to access news, weather and sports reports, to plan and book holidays and to find out more about their random ideas and casual interests.
People use chat, messaging and e-mail to make and stay in touch with friends worldwide, sometimes in the same way as some previously had pen pals. Social networking websites like MySpace, Facebook and many others like them also put and keep people in contact for their enjoyment.
The Internet has seen a growing number of Web desktops, where users can access their files, folders, and settings via the Internet.
Complex architecture
Many computer scientists see the Internet as a «prime example of a large-scale, highly engineered, yet highly complex system.»[8] The Internet is extremely heterogeneous. (For instance, data transfer rates and physical characteristics of connections vary widely.) The Internet exhibits «emergent phenomena» that depend on its large-scale organization. For example, data transfer rates exhibit temporal self-similarity. Further adding to the complexity of the Internet is the ability of more than one computer to use the Internet through only one node, thus creating the possibility for a very deep and hierarchal sub-network that can theoretically be extended infinitely (disregarding the programmatic limitations of the IPv4 protocol). However, since principles of this architecture date back to the 1960s, it might not be a solution best suited to modern needs, and thus the possibility of developing alternative structures is currently being looked into.[9]
According to a June 2007 article in Discover magazine, the combined weight of all the electrons moved within the Internet in a day is 0.2 millionths of an ounce.[10] Others have estimated this at nearer 2 ounces (50 grams).[11]
Marketing
The Internet has also become a large market for companies; some of the biggest companies today have grown by taking advantage of the efficient nature of low-cost advertising and commerce through the Internet, also known as e-commerce. It is the fastest way to spread information to a vast number of people simultaneously. The Internet has also subsequently revolutionized shopping—for example; a person can order a CD online and receive it in the mail within a couple of days, or download it directly in some cases. The Internet has also greatly facilitated personalized marketing which allows a company to market a product to a specific person or a specific group of people more so than any other advertising medium.
Examples of personalized marketing include online communities such as MySpace, Friendster, Orkut, Facebook and others which thousands of Internet users join to advertise themselves and make friends online. Many of these users are young teens and adolescents ranging from 13- to 25-years-old. In turn, when they advertise themselves they advertise interests and hobbies, which online marketing companies can use as information as to what those users will purchase online, and advertise their own companies’ products to those users.
The terms “internet” and “Internet”
The term internet is written both with capital and without capital, and is used both with and without article. This can be explained from the various ways in which the term has come to be used over time.
The term originated as a determiner, a shorthand for internetworking, and is mostly used in this way in RFCs, the documentation for the evolving Internet Protocol (IP) standards for internetworking between ARPANET and other computer networks in the 1970s. As the impetus behind IP grew, it became more common to regard the results of internetworking as entities of their own, and internet became a noun, used both in a generic sense (any collection of computer networks connected through internetworking) and in a specific sense (the collection of computer networks that internetworked with ARPANET, and later NSFNET, using the IP standards, and that grew into the connectivity service we know today).
In its generic sense, internet is a common noun, a synonym for internetwork; therefore, it has a plural form (first appearing in RFC 870 and RFC 872), and is not to be capitalized.
In its specific sense, it is a proper noun, and therefore, with article, without a plural form, and with capitalization.[12]
A sentence that uses both meanings:
-
- «The Internet is an internet based on the Internet Protocol suite.»
The proper noun can again be used as a determiner, which will then carry a capital (e.g. «Internet mail»).
The Internet Society, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), and several other Internet-related organizations use this convention in their publications, including the RFCs.
As Internet connectivity grew more popular, it became known as a service, similar to television, radio, and telephone, and the word came to be used in this way (e.g. «I have Internet at home» and «I saw it on (the) Internet»). For this type of use, English spelling and grammar do not prescribe whether the article or capitalization are to be used, which explains the inconsistency that exists in practice.
Many newspapers, newswires, periodicals, and technical journals capitalize the term (Internet). Examples include The Dhaka Daily Star, The New York Times, the Associated Press, Time, The Times of India, Hindustan Times, and Communications of the ACM.
Other publications do not capitalize the term, including The Economist, the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, the Financial Times, The Guardian, The Times, The Sydney Morning Herald, and Wired News; this appears to be more popular outside North America.
Notes
- ↑ Introduction to links and anchors World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Where the Future Becomes Now Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Home page Internet Engineering Task Force. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ ICANN. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ https://www.internetworldstats.com/stats7.htm Internet world users by language.] Internet World Stats. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Internet usage statistics; The Internet Big Picture World Internet Stats. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Dan Goodin, Finland censors anti-censorship site. The Register, 2008. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Walter Willinger, Ramesh Govindan, Sugih Jamin, Vern Paxson, and Scott Shenker, Scaling phenomena in the Internet. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99, S1 (2002):2573–2580. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Anick Jesanun, Internet Makeover? Some argue it’s time. The Seattle Times, April 16, 2007. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Doug Bonderud, How Much Does The Internet Weigh? Progress. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ Russell Seitz, Weighing The Web Adamant, June 1, 2007. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- ↑ What is the Internet? What-is-what?.com. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Castells, M. Rise of the Network Society. 3 vols. Vol. 1. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 1996. ISBN 978-1557866165
- Castells, M. The Internet Galaxy. Ch. 1. Oxford, UK; New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2001. ISBN 978-0199241538
- Levine, John R., and Margaret Levine Young. The Internet For Dummies. For Dummies, 2015. ISBN 1118967690
External links
All links retrieved November 30, 2022.
- «10 Years that changed the world» Wired looks back at the evolution of the Internet.
- Berkman Klein Center for Internet and Society at Harvard.
- Global Internet Traffic Report.
- Brief History of the Internet Internet Society.
- «Warriors of the net» A movie about the Internet.
- 43+ Insightful Domain Facts (Infographic).
- Informationalism, Networks, and the Network Society: A Theoretical Blueprint by Manuel Castells
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Internet history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
- History of «Internet»
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.






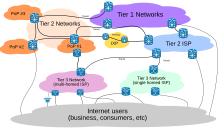






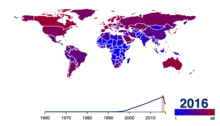


![Internet users by language[98]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e0/InternetUsersByLanguagePieChart.svg/562px-InternetUsersByLanguagePieChart.svg.png)
![Website content languages[111]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/88/WebsitesByLanguagePieChart.svg/562px-WebsitesByLanguagePieChart.svg.png)