|
|

Microsoft Office 2007 applications shown on Windows Vista – clockwise from top left: Word, Excel, OneNote and PowerPoint. These four programs make up the Home and Student edition. |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 30, 2007; 16 years ago[1] |
| Final release |
Service Pack 3 (12.0.6612.1000)[2] |
| Operating system |
[3] |
| Platform | IA-32[3] |
| Predecessor | Microsoft Office 2003 (2003) |
| Successor | Microsoft Office 2010 (2010) |
| Available in | English, Arabic, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Lithuanian, Norwegian (Bokmål), Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Turkish, and Ukrainian.[4] |
| Type | Office suite |
| License | Trialware |
| Website | products.office.com/download-office-2007 |
Microsoft Office 2007 (codenamed Office 12[5]) is an office suite for Windows, developed and published by Microsoft. It was officially revealed on March 9, 2006 and was the 12th version of Microsoft Office. It was released to manufacturing on November 3, 2006;[6] it was subsequently made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006,[7][8] and later to retail on January 30, 2007,[1] shortly after the completion of Windows Vista. The ninth major release of Office for Windows, Office 2007 was preceded by Office 2003 and succeeded by Office 2010. The Mac OS X equivalent, Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac, was released on January 15, 2008.
Office 2007 introduced a new graphical user interface called the Fluent User Interface, which uses ribbons and an Office menu instead of menu bars and toolbars.[9] Office 2007 also introduced Office Open XML file formats as the default file formats in Excel, PowerPoint, and Word. The new formats are intended to facilitate the sharing of information between programs, improve security, reduce the size of documents, and enable new recovery scenarios.[10]
Office 2007 is incompatible with Windows 2000 and earlier versions of Windows. Office 2007 is compatible with Windows XP SP2 or later, Windows Server 2003 SP1 or later, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 10.[3] It is the last version of Microsoft Office to support the 64-bit versions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, the 32-bit versions of Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP1, and Windows Vista RTM as the following version, Microsoft Office 2010 only supports Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003 SP2, and Windows Vista SP1 or later.[11]
Office 2007 includes new applications and server-side tools, including Microsoft Office Groove, a collaboration and communication suite for smaller businesses, which was originally developed by Groove Networks before being acquired by Microsoft in 2005. Also included is SharePoint Server 2007, a major revision to the server platform for Office applications, which supports Excel Services, a client-server architecture for supporting Excel workbooks that are shared in real time between multiple machines, and are also viewable and editable through a web page.
With Microsoft FrontPage discontinued, Microsoft SharePoint Designer, which is aimed towards development of SharePoint portals, becomes part of the Office 2007 family. Its designer-oriented counterpart, Microsoft Expression Web, is targeted for general web development. However, neither application has been included in Office 2007 software suites.
Speech recognition functionality has been removed from the individual programs in the Office 2007 suite, as Windows Speech Recognition was integrated into Windows Vista. Windows XP users must install a previous version of Office to use speech recognition features.[12]
According to Forrester Research, as of May 2010, Microsoft Office 2007 is used in 81% of enterprises it surveyed (its sample comprising 115 North American and European enterprise and SMB decision makers).[13]
Mainstream support for Office 2007 ended on October 9, 2012, and extended support ended on October 10, 2017.[14] On August 27, 2021, Microsoft announced that Outlook 2007 and Outlook 2010 would be cut off from connecting to Microsoft 365 Exchange servers on November 1, 2021.[15]
Development[edit]
Microsoft announced Beta 1 of Office 2007 with the revelation of the ribbon user interface on March 9, 2006, at CeBIT in Germany.[16]
Beta 2 was announced by Bill Gates at WinHEC 2006, and was initially released to the public at no cost from Microsoft’s web site. However, because of an unprecedented number of downloads, a fee of $1.50 was introduced for each product downloaded after August 2, 2006, The beta was updated on September 14, 2006, in Beta 2 Technical Refresh (Beta2TR). It included an updated user interface, better accessibility support, improvements in the robustness of the platform, and greater functionality.
Office 2007 was released to volume licensing customers on November 30, 2006, and to the general public on January 30, 2007.[1] Mainstream support ended on October 9, 2012.[17] Extended support ended on October 10, 2017.[17]
Service packs[edit]
Since the initial release of Microsoft Office 2007, three service packs containing updates as well as additional features have been released. Microsoft Office 2007 Service Packs are cumulative, so previous Service Packs are not a prerequisite for installation.[18]
Microsoft Office 2007 Service Pack 1 was released on December 11, 2007.[19] Official documentation claims that SP1 is not simply a rollup of publicly released patches, but that it also contains fixes for a total of 481 issues throughout the entire Office suite.[20] Microsoft Office 2007 Service Pack 2 was released on April 28, 2009.[21] It added improved support for ODF, XPS and PDF standards, and included several bug fixes.[21][22] Microsoft Office 2007 Service Pack 3 was released on October 25, 2011.[23]
Editions[edit]
| Programs and Features | Basic | Home and Student | Standard | Small Business | Professional | Professional Plus | Enterprise | Ultimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Licensing scheme | OEM | Retail and OEM | Retail and volume | Retail, OEM and volume | Retail and OEM | Volume | Volume | Retail |
| Word 2007 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Excel 2007 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PowerPoint 2007 | Viewer only | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Outlook 2007 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| OneNote 2007 | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Picture Manager 2007 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Publisher 2007 | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Access 2007 | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| InfoPath 2007 | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Communicator 2007 R2 | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Groove 2007 | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Project 2007 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| SharePoint Designer 2007 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Visio 2007 | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only | Viewer only |
| Office Customization Tool (OCT) 2007 | No | No | Volume licensing only[26] | Volume licensing only[26] | No | Yes[26] | Yes[26] | No |
| Upgrade MSRP | ? | — | $239.95[25] | $279.95[25] | $329.95[25] | ? | ? | $539.95[25] |
| Full MSRP | ? | $149.95[25] | $399.95[25] | $449.95[25] | $499.95[25] | ? | ? | $679.95[25] |
- 1 Office Customization Tool is used to customize the installation of Office 2007 by creating a Windows Installer patch file (.MSP) and replacing the Custom Installation Wizard and Custom Deployment Wizard included in earlier versions of the Office Resource Kit that created a Windows Installer Transform (.MST).[26]
Volume licensing[edit]
Eligible employees of companies with volume license agreements for Microsoft Office receive additional tools, including enterprise content management, electronic forms, Information Rights Management capabilities and copies for use on a home computer.[27]
New features[edit]
User interface[edit]
The new user interface (UI), officially known as Fluent User Interface,[28][29] has been implemented in the core Microsoft Office applications: Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Access, and in the item inspector used to create or edit individual items in Outlook. These applications have been selected for the UI overhaul because they center around document authoring.[30] The rest of the applications in the suite changed to the new UI in subsequent versions.[31] The default font used in this edition is Calibri. Original prototypes of the new user interface were revealed at MIX 2008 in Las Vegas.[32]
Office button[edit]
The Office 2007 button, located on the top-left of the window, replaces the File menu and provides access to functionality common across all Office applications, including opening, saving, printing, and sharing a file. It can also close the application. Users can also choose color schemes for the interface. A notable accessibility improvement is that the Office button follows Fitts’s law.[33]
Ribbon [edit]
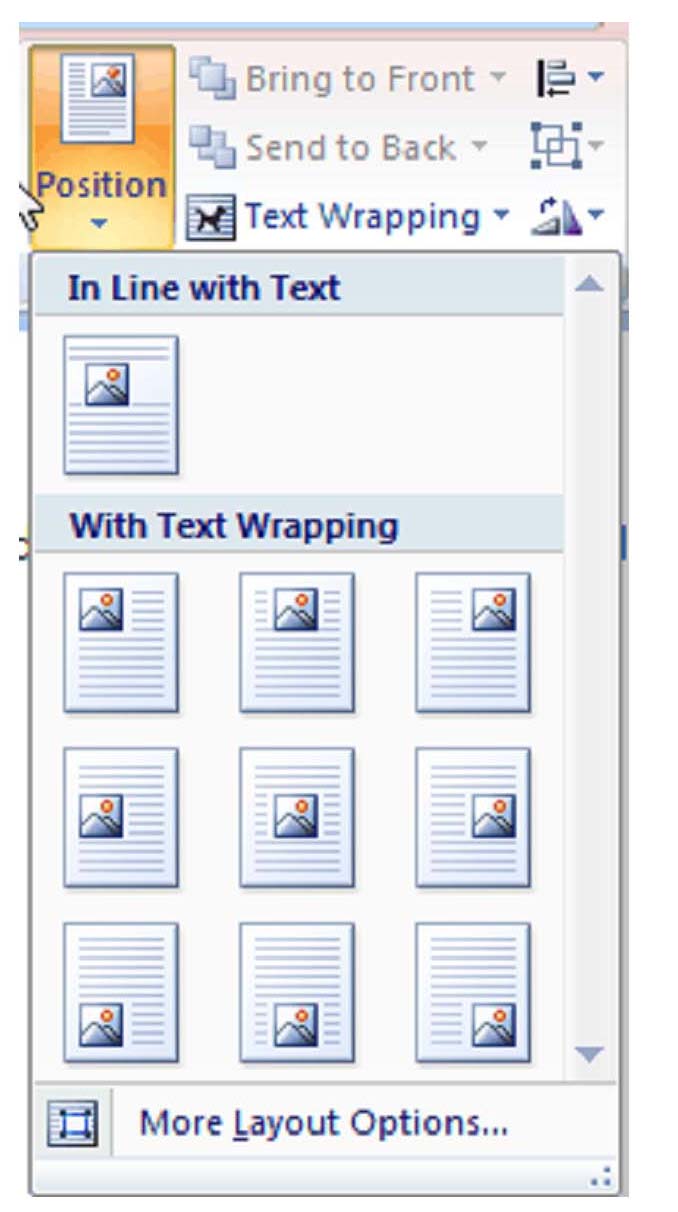
The ribbon, a panel that houses a fixed arrangement of command buttons and icons, organizes commands as a set of tabs, each grouping relevant commands. The ribbon is present in Microsoft Word 2007, Excel 2007, PowerPoint 2007, Access 2007 and some Outlook 2007 windows. The ribbon is not user customizable in Office 2007. Each application has a different set of tabs that exposes functions that the application offers. For example, while Excel has a tab for the graphing capabilities, Word does not; instead it has tabs to control the formatting of a text document. Within each tab, various related options may be grouped together. The ribbon is designed to make the features of the application more discoverable and accessible with fewer mouse clicks[34] as compared to the menu-based UI used prior to Office 2007. Moving the mouse scroll wheel while on any of the tabs on the ribbon cycles—through the tabs. The ribbon can be minimized by double clicking the active section’s title, such as the Home text in the picture below.[35] Office 2007 does not natively support removing, modifying or replacing ribbon. Third party add-ins, however, can bring menus and toolbars back to Office 2007 or customize the ribbon commands. Add-ins that restore menus and toolbars include Classic Menu for Office,[36] ToolbarToggle,[37][38] and Ubitmenu.[39] Others like RibbonCustomizer enable the customization of ribbons.[38] Office 2010 does allow user customization of the ribbon out of the box.
The ribbon in Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 running on Windows Vista
Contextual Tabs[edit]
Some tabs, called Contextual Tabs, appear only when certain objects are selected. Contextual Tabs expose functionality specific only to the object with focus. For example, selecting a picture brings up the Pictures tab, which presents options for dealing with the picture. Similarly, focusing on a table exposes table-related options in a specific tab. Contextual Tabs remain hidden except when an applicable object is an selected.
Live Preview[edit]
Microsoft Office 2007 also introduces a feature called Live Preview, which temporarily applies formatting on the focused text or object when any formatting button is moused-over. The temporary formatting is removed when the mouse pointer is moved from the button. This allows users to have a preview of how the option would affect the appearance of the object, without actually applying it.
Mini Toolbar[edit]
The new Mini Toolbar is a small toolbar with basic formatting commands that appears within the document editing area, much like a context menu. When the mouse selects part of the text, Mini Toolbar appears close to selected text. It remains semi-transparent until the mouse pointer is hovered on it, to avoid obstructing what is underneath. Mini Toolbar can also be made to appear by right-clicking in the editing area or via ≣ Menu key on keyboard, in which case it appears near the cursor, above or below the traditional context menu. Mini Toolbar is not customizable in Office 2007, but can be turned off.
Quick Access Toolbar[edit]
The Quick Access toolbar (by default) sits in the title bar and serves as a repository of most used functions, such as save, undo/redo and print. It is customizable, although this feature is limited, compared to toolbars in previous Office versions. Any command available in the entire Office application can be added to the Quick Access toolbar, including commands not available on the ribbon as well as macros. Keyboard shortcuts for any of the commands on the toolbar are also fully customizable, similar to previous Office versions.
Other UI features[edit]
- Super-tooltips, or screentips, that can house formatted text and even images, are used to provide detailed descriptions of what most buttons do.
- A zoom slider present in the bottom-right corner, allowing for dynamic and rapid magnification of documents.
- The status bar is fully customizable. Users can right click the status bar and add or remove what they want the status bar to display.[40]
SmartArt[edit]
SmartArt flowchart in PowerPoint
SmartArt, found under the Insert tab in the ribbon in PowerPoint, Word, Excel, and Outlook, is a new group of editable and formatted diagrams. There are 115 preset SmartArt graphics layout templates in categories such as list, process, cycle, and hierarchy. When an instance of a SmartArt is inserted, a Text Pane appears next to it to guide the user through entering text in the hierarchical levels. Each SmartArt graphic, based on its design, maps the text outline, automatically resized for best fit, onto the graphic. There are a number of «quick styles» for each graphic that apply largely different 3D effects to the graphic, and the graphic’s shapes and text can be formatted through shape styles and WordArt styles. In addition, SmartArt graphics change their colors, fonts, and effects to match the document’s theme.
File formats[edit]
Office Open XML[edit]
Microsoft Office 2007 introduced a new file format, called Office Open XML, as the default file format. Such files are saved using an extra X letter in their extension (.docx/xlsx/pptx/etc.). However, it can still save documents in the old format, which is compatible with previous versions. Alternatively, Microsoft has made available a free add-on known as the Microsoft Office Compatibility Pack that lets Office 2000, XP, and 2003 open, edit, and save documents created under the newer 2007 format.[41]
Office Open XML is based on XML and uses the ZIP file container. According to Microsoft, documents created in this format are up to 75% smaller than the same documents saved with previous Microsoft Office file formats, owing to the ZIP data compression.[42]
Files containing macros are saved with an extra M letter in their extension instead (.docm/xlsm/pptm/etc.).
PDF[edit]
Initially, Microsoft promised to support exporting to Portable Document Format (PDF) in Office 2007. However, due to legal objections from Adobe Systems, Office 2007 originally did not offer PDF support out of the box, but rather as a separate free download.[43][44][45] However, starting with Service Pack 2, Office allows users to natively export PDF files.[46]
XPS[edit]
Office 2007 documents can also be exported as XPS documents. This is part of Service Pack 2 and prior to that, was available as a free plug-in in a separate download.[46]
[47]
OpenDocument[edit]
Microsoft backs an open-source effort to support OpenDocument in Office 2007, as well as earlier versions (up to Office 2000), through a converter add-in for Word, Excel and PowerPoint, and also a command-line utility.[48] As of 2008, the project supports conversion between ODF and Office Open XML file formats for all three applications.[49] According to ODF Alliance this support falls short and substantial improvements are still needed for interoperability in real-world situations.[50][51]
Third-party plugins able to read from and write to the ISO-standard Open Document Format (ODF) are available as a separate download.[52][53]
Office 2007 Service Pack 2 adds native support for the OpenDocument Format.[54] The ODF Alliance has released test results on ODF support of Office 2007 SP2,[55] concluding that Office ODF support, both SP2 and other add-ons, have «serious shortcomings that, left unaddressed, would break the open standards based interoperability that the marketplace, especially governments, is demanding». Particularly, SP2 has no support for encrypted ODF files and has limited interoperability with other ODF spreadsheet implementations.
The ISO/IEC 26300 OpenDocument standard specifies encryption of files, which is based on sha1, Blowfish, and RFC 2898.
Microsoft Office 2007 SP2 does not support reading and writing encrypted (password protected) ODF files.[55][56][57] Users are presented with a message: “cannot use password protection using the ODF format.”[55][57]
The ISO/IEC 26300 OpenDocument standard has no spreadsheet formula language included (or referenced) in the standard specification. Office 2007 SP2 uses the spreadsheet formula language specified in the ISO/IEC 29500 Office Open XML open standard when creating ODF documents. According to the ODF Alliance report «ODF spreadsheets created in Excel 2007 SP2 do not in fact conform to ODF 1.1 because Excel 2007 incorrectly encodes formulas with cell addresses. Section 8.3.1 of ODF 1.1 says that addresses in formulas «start with a «[» and end with a «]».» In Excel 2007 cell addresses were not enclosed with the necessary square brackets.»[55] The ISO/IEC 26300 specification states that the semantics and the syntax depends on the used namespace, which is implementation dependent, leaving the syntax implementation defined as well.[58]
Microsoft stated that they consider adding support for an official ODF formula language (OpenFormula), once a future version of the ISO/IEC 26300 standard specification includes one.[59]
Microsoft’s ODF spreadsheet support in SP2 is not fully inter-operable with other implementations of OpenDocument, such as the IBM Symphony, which use the non-standardized OpenOffice.org 2.x formula language, and OpenOffice.org 3.x, which uses a draft of OpenFormula.[60] The company had previously reportedly stated that «where ODF 1.1 is ambiguous or incomplete, the Office implementation can be guided by current practice in OpenOffice.org, mainly, and other implementations including KOffice and AbiWord. Peter Amstein and the Microsoft Office team are reluctant to make liberal use of extension mechanisms, even though provided in ODF 1.1. They want to avoid all appearance of an embrace-extend attempt.»[61]
The EU investigated Microsoft Office OpenDocument Format support to see if it provided consumers greater choice.[62]
Metadata[edit]
In Office 2007, Microsoft introduced the Document Inspector, an integral metadata removal tool that strips Word, Excel, and PowerPoint documents of information such as author name and comments and other «metadata».
User assistance system[edit]
In Microsoft Office 2007, the Office Assistants were eliminated in favour of a new online help system. One of its features is the extensive use of Super Tooltips, which explain in about one paragraph what each function performs. Some of them also use diagrams or pictures. These appear and disappear like normal tooltips, and replace normal tooltips in many areas. The Help content also directly integrates searching and viewing Office Online articles.
Collaboration features[edit]
SharePoint[edit]
Microsoft Office 2007 includes features geared towards collaboration and data sharing. As such, Microsoft Office 2007 features server components for applications such as Excel, which work in conjunction with SharePoint Services, to provide a collaboration platform. SharePoint works with Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007, which is used to host a SharePoint site, and uses IIS and ASP.NET 2.0. Excel server exposes Excel Services, which allows any worksheet to be created, edited and maintained via web browsers. It features Excel Web Access, the client-side component which is used to render the worksheet on a browser, Excel Calculation Service which is the server side component which populates the worksheet with data and perform calculations, and Excel Web Services that extends Excel functionalities into individual web services. SharePoint can also be used to host Word documents for collaborative editing, by sharing a document. SharePoint can also be used to hold PowerPoint slides in a Slide Library, from which the slides can be used as a formatting template. It also notifies users of a slide automatically in case the source slide is modified. Also by using SharePoint, PowerPoint can manage shared review of presentations. Any SharePoint hosted document can be accessed from the application which created the document or from other applications such as a browser or Microsoft Office Outlook.
Groove[edit]
Microsoft Office 2007 also includes Groove, which brings collaborative features to a peer-to-peer paradigm. Groove can host documents, including presentations, workbooks and others, created in Microsoft Office 2007 application in a shared workspace, which can then be used in collaborative editing of documents. Groove can also be used in managing workspace sessions, including access control of the workspace. To collaborate on one or more documents, a Workspace must be created, and then those who are to work on it must be invited. Any file shared on the workspace are automatically shared among all participants. The application also provides real-time messaging, including one-to-one as well as group messaging, and presence features, as well as monitoring workspace activities with alerts, which are raised when pre-defined set of activities are detected. Groove also provides features for conflict resolution for conflicting edits. Schedules for a collaboration can also be decided by using a built-in shared calendar, which can also be used to keep track of the progress of a project. However, the calendar is not compatible with Microsoft Outlook.
Themes and Quick Styles[edit]
Microsoft Office 2007 places more emphasis on Document Themes and Quick Styles. The Document Theme defines the colors, fonts and graphic effects for a document. Almost everything that can be inserted into a document is automatically styled to match the overall document theme creating a consistent document design. The new Office Theme file format (.THMX) is shared between Word, Excel, PowerPoint and Outlook email messages. Similar themes are also available for data reports in Access and Project or shapes in Visio.
Quick Styles are galleries with a range of styles based on the current theme. There are quick styles galleries for text, tables, charts, SmartArt, WordArt and more. The style range goes from simple/light to more graphical/darker.
Application-specific changes[edit]
Word[edit]
- New style sheets (quick styles) and ability to switch easily among them.
- Default font now Calibri instead of Times New Roman, as featured in previous versions of Microsoft Office.
- Word count listed by default in the status bar. The word count dynamically updates as you type.
- New contextual spell checker, signified by a wavy blue underline to the traditional wavy red underline for misspellings and wavy green underline for grammar errors, sometimes catches incorrect usage of correctly spelled words, such as in «I think we will loose this battle».
- Translation tool tip option available for English (U.S.), French (France), and Spanish (International Sort). When selected, hovering the mouse cursor over a word displays its translation in the particular language. Non-English versions have different sets of languages. Other languages can be added by using a separate multilingual pack.
- Automated generation of citations and bibliographies according to defined style rules, including APA, Chicago, and MLA. Changing style updates all references automatically. Connect to web services to access online reference databases.
- Redesigned native mathematical equation support with TeX-like linear input/edit language or GUI. Also supports the Unicode Plain Text Encoding of Mathematics.[63]
- Preset gallery of cover pages with fields for Author, Title, Date, Abstract, etc. Cover pages follow the theme of the document (found under the Page Layout tab).
- Document comparison engine updated to support moves, differences in tables, and also easy to follow tri-pane view of original document, new document, and differences.
- Full screen reading layout that shows two pages at a time with maximal screen usage, plus a few critical tools for reviewing.
- Building Blocks, which lets one save frequently used content, so that they are easily accessible for further use. Building blocks can have data mapped controls in them to allow for form building or structured document authoring.
- The ability to save multiple versions of a document (which had existed since Word 97) has been removed.[64]
- Blog entries[65] can be authored in Word itself and uploaded directly to a blog. Supported blogging sites include Windows Live Spaces, WordPress, SharePoint, Blogger, Telligent Community etc.
- Drops function for Insert/Picture/From Scanner or Camera. Can be added manually.[66]
- Drops the «Bullets and Numbering» dialog boxes and rich, easily controlled range of options for formatting Outline Numbered lists
- For Indian languages, proofing tools were introduced in Office for Bengali, Malayalam, Odia, Konkani and Assamese[67][68]
Outlook[edit]
- As a major change in Outlook 2007, Exchange 5.5 support has been dropped. Like Evolution, Outlook Express and Entourage, Outlook now works only with Exchange 2000 and above.
- Word becomes the default text editor for this and all subsequent versions.
- Outlook now indexes (using the Windows Search APIs) the e-mails, contacts, tasks, calendar entries, RSS feeds and other items, to speed up searches. As such, it features word-wheeled search, which displays results as characters are typed.[69][70]
- Search folders, which are saved searches, have been updated to include RSS feeds as well. Search folders can be created with a specific search criteria, specifying the subject, type and other attributes of the information being searched. When a search folder is opened, all matching items for the search are automatically retrieved and grouped up.
- Outlook now supports text-messages and SMSs, when used in conjunction with Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging.
- Outlook includes a reader for RSS feeds, which use the Windows Common Feeds Store. RSS subscription URLs can be shared via e-mails; updates can also be pushed to a mobile device.
- Outlook can now support multiple calendars being worked with simultaneously. It also includes a side-by-side view for calendars, where each calendar is displayed in a different tab, and allows easy comparison of them. Outlook also supports web calendars. Calendars can be shared with other users, and also exported as a HTML file for viewing by others who do not have Outlook installed.
- Calendar view shows which tasks are due.
- Flagged e-mails and notes can also be converted to Task items.
- Outlook includes a To Do Bar, which consolidates appointment, calendar, and task items in a single view.[70]
- Outlook includes a Windows SideShow Calendar Gadget[71]
- Online or offline editing of all Microsoft Office 2007 documents via a SharePoint site. All edits are automatically synchronized.
- Contacts can be shared among users, via e-mail, Exchange Server or a SharePoint site.
- Attachment preview allows users to view Office e-mail attachments in the reading pane rather than having to open another program.[70]
- HTML in e-mails is now rendered using the Microsoft Word rendering engine which disallows several HTML tags like object, script, iframe etc. along with several CSS properties.
Microsoft Office Outlook can also include an optional Business Contact Manager (included on a separate installation disc in Office 2007 Small Business and above) which allows management of business contacts and their sales and marketing activities. Phone calls, e-mails, appointments, notes and other business metrics can be managed for each contact. It can also keep a track of billable time for each contact on the Outlook Calendar. Based on these data, a consolidated report view can be generated by Microsoft Office Outlook with Business Contact Manager. The data can be further analyzed using Microsoft Office Excel. This data can also be shared using SharePoint Services.
Excel[edit]
- Support up to 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns (XFD) in a single worksheet, with 32,767 characters in a single cell (17,179,869,184 cells in a worksheet, 562,932,773,552,128 characters in a worksheet)[72]
- Conditional Formatting introduces support for three new features — Color Scales, Icon Sets and Data Bars
- Color Scales, which automatically color the background of a group of cells with different colors according to the values.
- Icon sets, which precede the text in a cell with an icon that represent some aspect of the value of the cell with respect to other values in a group of cells, can also be applied. Icons can be conditionally applied to show up only when certain criteria are met, such as a cross showing up on an invalid value, where the condition for invalidity can be specified by the user.
- Data Bars show as a gradient bar in the background of a cell the contribution of the cell value in the group.
- Column titles can optionally show options to control the layout of the column.
- Multithreaded calculation of formulae, to speed up large calculations, especially on multi-core/multi-processor systems.
- User Defined Functions (UDF), which are custom functions written to supplement Excel’s set of built-in functions, supports the increased number of cells and columns. UDFs now can also be multithreaded. Server side UDFs are based on the .NET Managed code.
- Importing data from external sources, such as a database, has been upgraded. Data can also be imported from formatted tables and reports, which do not have a regular grid structure
- Formula Autocomplete, automatically suggests function names, arguments and named ranges, and automatically completing them if desired, based on the characters entered. Formulae can refer to a table as well
- CUBE functions which allow importing data, including set aggregated data, from data analysis services, such as SQL Server Analysis Services
- Page Layout view, to author spreadsheets in a way that mirrors the formatting of the printed document
- PivotTables, which are used to create analysis reports out of sets of data, can now support hierarchical data by displaying a row in the table with a «+» icon, which, when clicked, shows more rows regarding it, which can also be hierarchical. PivotTables can also be sorted and filtered independently, and conditional formatting used to highlight trends in the data.
- Filters, now includes a Quick filter option allowing the selection of multiple items from a drop down list of items in the column. The option to filter based on color has been added to the choices available.
- Excel features a new charting engine, which supports advanced formatting, including 3D rendering, transparencies and shadows. Chart layouts can also be customized to highlight various trends in the data.
PowerPoint[edit]
- Improvements to text rendering to support text based graphics.
- Rendering of 3D graphics.
- Support for many more sound file formats such as .mp3 and .wma.
- Support for tables and enhanced support for table pasting from Excel.[73]
- Slide Library, which lets you reuse any slide or presentation as a template. Any presentation or slide can be published to the Slide Library.
- Any custom-designed slide library can be saved.
- Presentations can be digitally signed.
- Improved Presenter View.[74]
- Added support for widescreen slides.[75]
- Allows addition of custom placeholders.
- Drops function for Insert/Picture/From Scanner or Camera.
- Allows for duplication of a slide through right-clicking it without having to go through Copy and Paste
OneNote[edit]
- OneNote now supports multiple notebooks.[76]
- Notebooks can be shared across multiple computers. Anyone can edit even while not connected and changes are merged automatically across machines when a connection is made. Changes are labeled with author and change time/date.[76][77][78]
- Notebooks can be synchronized between two or more machines without an Internet connection when stored on removable media such as an SD card or USB flash drive; changes made to a notebook on a machine when removable media is disconnected will be synced with the notebook when the media is reinserted to that machine. To prevent potential synchronization issues associated with drive mapping during reinsertion, OneNote 2007 associates notebooks with unique device identifiers rather than drive letters to ensure that changes are successfully synced.[79]
- Notebook templates.[76]
- Word-wheeled search is also present in OneNote, which also indexes notes.[76]
- Synchronization of Tasks with Outlook 2007. Also Outlook can send mails to OneNote, or open pages in OneNote that are linked to tasks, contacts, appointments/meetings.[76][80]
- Support for tables. Using tabs to create tabular structure automatically converts it to a table.[76]
- Optical character recognition is performed on images (e.g., brochures, photos, prints, scans, screen clips) so that any text that appears in them is searchable.[76][81] Handwritten text on a tablet PC is also searchable.[81]
- Words that are included in audio and video recordings are also tagged and indexed, so that they can be searched.[81]
- Notes can have hyperlinks among themselves, or from outside OneNote to a specific point on a page.[76]
- Embedding documents in notes.[76]
- Extensibility support for add-ins.
- Drawing tools for creating diagrams in OneNote.[76]
- Typing any arithmetic expression, followed by «=» results in the result of the calculation being displayed.[76]
- OneNote Import Printer Driver, where any application can print to a virtual printer for OneNote and the «printed» document is imported to the notebook; OCR is performed on the text that appears in the printed document to facilitate searches.[80][81]
- OneNote Mobile is included for Smartphones and some PocketPC devices. Syncs notes two-way with OneNote. Takes text, voice, and photo notes.
Access[edit]
- Access now includes support for a broader range of data types, including documents and images.
- Whenever any table is updated, all reports referencing the table are also updated.
- Dropdown lists for a table can be modified in place.
- Lookup Fields, which get their values by «looking up» some value in a table, have been updated to support multi valued lookups.
- Many new preset schemata are included.
- Access can synchronize with Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 and Office SharePoint Server 2007. This feature enables a user to use Access reports while using a server-based, backed-up, IT managed version of the data.
Publisher[edit]
- Templates automatically fill out with information such as company name, logo etc., wherever applicable.
- Frequently used content can be stored in Content Store for quick access.
- A document can be automatically converted from one publication type, such as a newsletter, to another publication type, say a web page.
- Save as PDF supports commercial printing quality PDF.
- Catalog Merge can create publication content automatically by retrieving data, including text, images and other supported types, from an external data source.
- Design Checker, which is used to find design inconsistencies, has been updated.
InfoPath[edit]
- InfoPath designed forms can now be used from a browser, provided the server is running InfoPath Forms Services in SharePoint 2007 or Office Forms Server.
- A form can be sent out to people via e-mail. Such forms can be filled out from Outlook 2007 itself.
- Automatic conversion of forms in Word and Excel to InfoPath forms. Forms can also be exported to Excel.
- Forms can be published to a network share or to SharePoint Server.
- Adding data validation, using validation formulae, and conditional formatting features without manually writing code.
- Print Layout view for designing forms in a view that mirror the printed layout. Such forms can be opened using Word as well.
- Ability to use Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Office Access, or other databases as back-end data repository.
- Multiple views for the same forms, to expose different features to different class of users.
- Template Parts, used to group Office InfoPath controls for use later. Template parts retain its XML schema.
Visio[edit]
- PivotDiagrams, which are used to visualize data, show data groups and hierarchical relationships.[82]
- Visual modification of PivotDiagrams by dragging data around levels, to restructure the data relationships.
- PivotDiagrams can show aggregate statistical summaries for the data and show them.
- Shapes can be linked with external data sources. Doing so, the shapes are formatted according to the data. The data, and hence the shapes, are updated periodically. Such shapes can also be formatted manually using the Data Graphics feature.
- AutoConnect : Link easily two shapes.[83]
- Data Link : Link data to shapes.[84]
- Data Graphics : Dynamic objects (text and images) linked with external data.[85]
- New Theme behaviour and new shapes.[86]
Project[edit]
- Ability to create custom templates.
- Any change in the project plan or schedule highlights everything else that is affected.
- Analyze changes without actually committing them. Changes can also be done and undone programmatically, to automate analysis of different changes.
- Improved cost resource management and analysis for projects.
- Project data can be used to automatically create charts and diagrams in Microsoft Office Excel and Microsoft Office Visio, respectively.
- The project schedule can be managed as 3D Gantt chart
- Sharing project data with the help of SharePoint Services.
SharePoint Designer[edit]
Microsoft Office SharePoint Designer 2007 is new addition to the Office suite, replacing discontinued FrontPage for users of SharePoint. People who don’t use SharePoint can use Microsoft Expression Web
- Supports features and constructs that expose SharePoint functionality
- Supports ASP.NET 2.0 and Windows Workflow Foundation
- Support for creating workflows and data reports, from external data sources
- Can optionally render XML using XSLT
Server components[edit]
SharePoint Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007 allows sharing and collaborative editing of Office 2007 documents. It allows central storage of documents and management of Office documents, throughout the enterprise. These documents can be accessed either by the applications which created them, Microsoft Office Outlook 2007, or a web browser. Documents can also be managed through pre-defined policies that let users create and publish shared content, through a SharePoint site.
SharePoint Server allows searching of all Office documents which are being managed by it, centrally, thereby making data more accessible. It also provides access control for documents. Specialized server components can plug into the SharePoint Server to extend the functionality of the server, such as Excel Services exposing data analysis services for Excel services. Data from other data sources can also be merged with Office data.
SharePoint also lets users personalize the SharePoint sites, filtering content they are interested in. SharePoint documents can also be locally cached by clients for offline editing; the changes are later merged.
Forms Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft Office Forms Server 2007 allows InfoPath forms to be accessed and filled out using any browser, including mobile phone browsers. Forms Server 2007 also supports using a database or other data source as the back-end for the form. Additionally, it allows centralized deployment and management of forms. Forms Server 2007 hosted forms also support data validation and conditional formatting, as does their InfoPath counterpart. It also supports advanced controls like Repeating section and Repeating table. However, some InfoPath controls cannot be used if it must be hosted on a Forms server.
Groove Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft Office Groove Server 2007 is for centrally managing all deployments of Microsoft Office Groove 2007 in the enterprise. It enables using Active Directory for Groove user accounts, and create Groove Domains, with individual policy settings. It allows Groove workspaces to be hosted at the server, and the files in the workspaces made available for collaborative editing via the Groove client. It also includes the Groove Server Data Bridge component to allow communication between data stored at both Groove clients and servers and external applications.
Project Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft Office Project Server 2007 allows one to centrally manage and coordinate projects. It allows budget and resource tracking, and activity plan management. The project data and reports can also be further analyzed using Cube Building Service. The project management data can be accessed from a browser as well.
Project Portfolio Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft Office Project Portfolio Server 2007 allows creation of a project portfolio, including workflows, hosted centrally, so that the information is available throughout the enterprise, even from a browser. It also aids in centralized data aggregation regarding the project planning and execution, and in visualizing and analyzing the data to optimize the project plan. It can also support multiple portfolios per project, to track different aspects of it. It also includes reporting tools to create consolidated reports out of the project data.
PerformancePoint Server 2007[edit]
Microsoft PerformancePoint Server allows users to monitor, analyze, and plan their business as well as drive alignment, accountability, and actionable insight across the entire organization. It includes features for scorecards, dashboards, reporting, analytics, budgeting and forecasting, among others.
Removed features[edit]
The following Office 2003 features were removed in Office 2007:
- Fully customizable toolbars and menus for all of its applications[87] Quick Access Toolbar and the ribbon have limited customizability.[88] Office 2010 reintroduced ribbon UI customizability.[89]
- Office Assistant[90]
- Speech recognition (included as part of Windows Vista and later)[91][92]
- Handwriting recognition and ink features (included as part of Windows Vista and later)[93][unreliable source?][94]
- Ability to slipstream service packs into the original setup files (administrative installation images)[95]
- Office Web Components[95]
- Save My Settings Wizard[96][unreliable source?]
- Choice of local installation source allowing users to choose whether to keep a locally cached copy of installation source files or remove it. Setup files are now cached locally without user preference and cannot be removed. They are recreated by Office 2007 if removed.[97]
- Several deployment-related utility Resource Kit tools. Some primary deployment tools ship with Office 2007 itself.[98]
- Office FileSearch object and File Search functionality from File menu.[95]
- Chart Wizard
Criticism[edit]
Redesigned user interface[edit]
Even though the ribbon can be hidden, PC World wrote that the new «ribbon» interface crowds the Office work area, especially for notebook users.[99] Others have called its large icons distracting.[100] Essentially, the GUI-type interface of the ribbon contrasts sharply with the older menus that were organized according to the typical functions undertaken in paper-based offices: for instance, the old «File» menu dealt with opening, (re-)naming, saving, and printing a file, and the old «Edit» menu dealt with making changes to the content of the file. As a result, users who were more familiar with the logic of the old menus would be somewhat frustrated with the new, more visually oriented ribbon. The ribbon cannot be moved from the top to the side of the page, as floating toolbars could be.
Some users with experience using previous versions of Microsoft Office have complained about having to find features in the ribbon. Others state that having learnt to use the new interface, it has improved the speed with which «professional-looking» documents can be created.[101] Microsoft has released a series of small programs,[102] help sheets,[103] videos[104] and add-ins[105] to help users learn the new interface more quickly.
Patenting controversy[edit]
Microsoft contractor Mike Gunderloy left Microsoft partially over his disagreement with the company’s «sweeping land grab» including its attempt to patent the ribbon interface. He says «Microsoft itself represents a grave threat to the future of software development through its increasing inclination to stifle competition through legal shenanigans.»[106] He says that by leaving Microsoft, he is «no longer contributing to the eventual death of programming.»[107]
Office Open XML[edit]
The new XML-based document file format in Microsoft Office 2007 is incompatible with previous versions of Microsoft Office unless an add-on is installed for the older version.[108]
PC World has stated that upgrading to Office 2007 presents dangers to certain data, such as templates, macros, and mail messages.[109]
The Microsoft Word 2007 equation editor, which uses a form of MathML called Office MathML (OMML), is also incompatible with that of Microsoft Word 2003 and previous versions.[110] Upon converting Microsoft Word 2007 .docx files to .doc files, equations are rendered as graphics.[111] On June 6, 2007, Inera Inc. revealed that Science and Nature refused to accept manuscripts prepared in Microsoft Word 2007 .docx format; subsequently Inera Inc. informed Microsoft that Microsoft Word 2007’s file format impairs usability for scholarly publishing.[112] As of 25 April 2011 Nature still does not support Office Open XML format;[110] Science however, accepts this format but discourages its use.[113]
Bibliographies[edit]
The new Word 2007 features for bibliographies only support a small number of fixed citation styles. Using XSLT, new styles can be added. Some extra styles, such as the standard Association for Computing Machinery publication format, are made freely available by third parties.[114]
See also[edit]
- Comparison of office suites
- List of office suites
- Microsoft Office 2007 filename extensions
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and Microsoft Office 2007 to Consumers Worldwide». News Center. Microsoft. January 29, 2007. Archived from the original on September 24, 2017. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (October 26, 2011). «Microsoft ships final Office 2007 service pack». Computer World. IDG. Archived from the original on September 25, 2017. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ a b c «Getting started with the 2007 Office system». TechNet. Microsoft. System requirements for the 2007 Office release. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ «Language identifiers in the 2007 Office system». TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Montalbano, Elizabeth (February 15, 2006). «It’s Official: Office ’12’ to Become Office 2007». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Harris, Jensen (November 6, 2006). «Office 2007 Released to Manufacturing». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Hill, Brandon (December 1, 2006). «Vista, Office 2007 Now Available for Volume Licensing». DailyTech. DailyTech, LLC. Archived from the original on March 23, 2007. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Montalbano, Elizabeth (November 30, 2006). «Microsoft Windows Vista, Office 2007 Released to Businesses». CIO Magazine. IDG. Archived from the original on November 10, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ «The Microsoft Office Fluent user interface overview». Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 5, 2010. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Rice, Frank (May 2006). «Introducing the Office (2007) Open XML File Formats». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ «System requirements for Office 2010». Microsoft TechNet. Wasif K Niazi. Retrieved March 10, 2022.
- ^ «What happened to speech recognition?». Office Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (May 11, 2010). «Forrester: Google still a distant Office competitor». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 12, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Office 2007». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017. Retrieved June 17, 2019.
- ^ «New minimum Outlook for Windows version requirements for Microsoft 365». Microsoft. August 27, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ Harris, Jensen (March 9, 2006). «Picture This: A New Look For Office». An Office User Interface Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 4, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Support Lifecycle – Office 2007». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ «Description of the 2007 Office suite SP3 and of Office Language Pack 2007 SP3». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 10, 2015. Retrieved August 13, 2015.
- ^ «Description of the 2007 Microsoft Office suite Service Pack 1». Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ «Office 2007 Service Pack 1 – Changes» (XLSX). Microsoft. 2007. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- ^ a b «Office Service Pack 2 A Significant Stability, Performance and Interoperability Upgrade». News Center. Microsoft. April 28, 2009. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Expands List of Formats Supported in Microsoft Office». News Center. Microsoft. May 21, 2008. Archived from the original on August 5, 2016. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (October 26, 2011). «Microsoft ships final Office 2007 service pack». Computer World. IDG. Archived from the original on September 25, 2017. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ «Office Basic Home Page». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 18, 2010. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j «Microsoft Office 2007 – Compare the 2007 Office suites». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 18, 2010. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e «Office Customization Tool in the 2007 Office system». TechNet. Microsoft. October 22, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ «Software Assurance Home Use Program». Microsoft. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ See «Microsoft Office Fluent User Interface» (DOC). Microsoft. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ «How ‘Fluent’ Are You in Office 2007?». Archived from the original on September 10, 2012. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ «What programs get the new Office UI?». Archived from the original on May 24, 2010. Retrieved May 25, 2006.
- ^ «Office 2007 Beta 2 UI Review». Archived from the original on July 3, 2006. Retrieved May 25, 2006.
- ^ Zheng, Long (March 8, 2008). «Office 2007 interface prototypes». I Started Something. Archived from the original on September 4, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Harris, Jensen (August 22, 2006). «Giving You Fitts». Jensen Harris’ blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 12, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Use the Ribbon instead of toolbars and menus». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on March 7, 2013. Retrieved March 31, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft: Use the Ribbon». Archived from the original on March 5, 2008. Retrieved March 4, 2008.
- ^ http://www.addintools.com Archived February 3, 2021, at the Wayback Machine Classic Menu for Office
- ^ Barrett, Ron (May 7, 2008). «Does the Office Ribbon have you coming «unwound»… Here’s some help». Network World. IDG. Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ a b Ericson, Richard (April 29, 2007). «Hands on: Show Office 2007 who’s the boss». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 15, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Rick Broida. «Editorial Review of UBitMenu». PC World. Archived from the original on November 1, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2011.
- ^ Harris, Jensen (January 5, 2006). «Status Bar Update». Jensen Harris’ blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Office Compatibility Pack for Word, Excel, and PowerPoint File Formats». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 31, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ^ «File formats». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 14, 2006. Retrieved May 25, 2006.
- ^ «Legal issues around PDF support». Archived from the original on February 9, 2010. Retrieved June 3, 2006.
- ^ «Follow-up on PDF legal issues». Archived from the original on December 18, 2009. Retrieved June 3, 2006.
- ^ SaveAsPDFandXPS.exe (November 8, 2006). «SaveasPDFandXPS». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 2, 2021. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ a b Microsoft (April 21, 2009). «Description of 2007 Microsoft Office Suite Service Pack 2 (SP2) and of Microsoft Office Language Pack 2007 SP2». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 29, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2008.
- ^ «Download details: 2007 Microsoft Office Add-in: Microsoft Save as PDF or XPS». Download Center. Microsoft. November 8, 2006. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «OpenDocument to Office Open XML conversion». Archived from the original on February 10, 2007. Retrieved February 11, 2007.
- ^ «OpenXML/ODF Translator Add-in for Office Downloads». Archived from the original on April 20, 2008. Retrieved April 17, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft’s ODF Support Falls Short». Open Document Alliance. ODF Alliance. May 19, 2009. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved May 22, 2009.
- ^ Allison, Jeremy (May 19, 2009). «In Office SP2, Microsoft manages to reduce interoperability». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 3, 2010. Retrieved May 23, 2009.
- ^ «Sun ODF Plugin 1.1 for Microsoft Office: Tech Specs». Sun Microsystems. Archived from the original on January 19, 2008. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ «Sun’s OpenDocument filter for MS Office is finished». Heise Online. July 4, 2006. Archived from the original on July 11, 2007. Retrieved July 6, 2007.
- ^ Worthington, David (May 21, 2008). «Office 2007 won’t support ISO’s OOXML». SD Times. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ^ a b c d MS Office 2007 Service Pack 2 With Support for ODF: How Well Does It Work? Archived June 11, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, OpenDocument Format (ODF) Alliance – www.odfalliance.org
- ^ Stephen Peront (site) (December 14, 2009). «OASIS ODF 1.1 > Specification Outline > 17 Packages > 17.3 Encryption». Document Interop Initiative. Microsoft. Rightmost frame: Implementation Notes List. Archived from the original on April 2, 2021. Retrieved January 10, 2010.
- ^ a b «Microsoft now attempt to fragment ODF». void life (void). May 5, 2009. Archived from the original on May 9, 2009. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1/Subcommittee 34 (December 1, 2006), «Information technology — Open Document Format for Office Applications (OpenDocument) v1.0», International Standard, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization, ISO/IEC 26300:2006, archived from the original on September 18, 2009, retrieved January 10, 2010
- ^ Mahugh, Doug (May 10, 2009). «1 + 2 = 1?». Office Interoperability. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 15, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Weir, Rob (May 7, 2009). «Update on ODF Spreadsheet Interoperability». Rob Weir: An Antic Disposition. Archived from the original on November 30, 2009. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft ODF Interoperability Workshop». Orcmid’s Lair. August 3, 2009. Archived from the original on September 2, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Jones, Huw; Melander, Ingrid (May 22, 2008). «EU says to study Microsoft’s open-source step». Reuters. Archived from the original on January 26, 2010. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ^ See «Unicode Nearly Plain-Text Encoding of Mathematics» (PDF). Unicode, Inc. April 4, 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 6, 2007. Retrieved December 19, 2006.
- ^ «What happened to versioning?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 31, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2007.
- ^ «Blogging from Word 2007». May 12, 2006. Archived from the original on May 21, 2006. Retrieved May 25, 2006.
- ^ Bryntze, John (September 27, 2009). ««Insert – Picture – From Scanner or Camera…» in Word 2007″. Office-kb4. John Bryntze’s Knowledge Base. Archived from the original on November 22, 2009. Retrieved January 10, 2010.
- ^ «Office 2007 Language Interface Packs and spell-checkers for Armenian, Georgian, Telugu, Konkani, Punjabi, Kannada, and Oriya». Archived from the original on April 2, 2021. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ Microsoft Office Language Interface Pack 2007s
- ^ Kennedy, William (December 16, 2005). «Search in Outlook 12 – ‘It changes the way you work’«. MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 2, 2021. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ a b c Lowe, Scott (November 2, 2006). «A look at what is new and different in Outlook 2007». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Review, Part 5: Windows Vista Features: Mobility Features». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on October 9, 2016. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- ^ Frie, Curtis (May 22, 2006). «Preview the Enhanced Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Business Intelligence Capabilities». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 13, 2012. Retrieved July 15, 2006.
- ^ «Introducing: New PowerPoint Tables!». Archived from the original on February 19, 2007. Retrieved July 26, 2006.
- ^ «Re-Presenting PowerPoint’s Presenter View». Archived from the original on December 4, 2007. Retrieved July 26, 2006.
- ^ «Take a Walk on the Wide Slide». Archived from the original on February 19, 2007. Retrieved July 26, 2006.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k «What’s new in Microsoft Office OneNote 2007». Office Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 12, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ Pratley, Chris (June 8, 2006). «Syncing OneNote 2007 notes across your many PCs». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ Pratley, Chris (September 27, 2005). «OneNote 12 – Working as a team with shared notebooks». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ Rasmussen, David (June 29, 2006). «OneNote Notebooks on USB drives and SD cards». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 1, 2018. Retrieved March 31, 2018.
- ^ a b Pratley, Chris (May 24, 2006). «OneNote 2007 and Outlook: Best Buddies». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 14, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Pratley, Chris (September 15, 2005). «Unifying the analog and the digital with OneNote». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ «Create a PivotDiagram». office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 8, 2014. Retrieved December 4, 2013.
- ^ «A brief detour from data: AutoConnect». Archived from the original on June 19, 2006. Retrieved July 27, 2006.
- ^ «Data Link: getting data into your shapes». Archived from the original on April 22, 2006. Retrieved July 27, 2006.
- ^ «Data Graphics: visualizing data on your diagram». Archived from the original on June 21, 2006. Retrieved July 27, 2006.
- ^ «Themes: Great Results in a few clicks». Archived from the original on February 13, 2007. Retrieved July 27, 2006.
- ^ Kantor, Andrew (November 22, 2006). «Microsoft takes a step backward with IE7, Office 2007». USA Today. Gannett Company. Archived from the original on May 13, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Schmid, Patrick (October 18, 2006). «Customizing Office 2007». pschmid.net. Archived from the original on March 17, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «User interface differences in Office 2010 from earlier versions of Microsoft Office». TechNet Library. Microsoft. May 16, 2012. Archived from the original on January 18, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «What happened to the Office Assistant?». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Wojcik, Brian (March 24, 2008). «Getting Speech Recognition Back into MS Office 2007 on Windows XP». At Cubed. Archived from the original on June 15, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Speech Recognition Removed from Office 2007 Archived August 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «How can i set up handwriting recognition in Office 2007?». Forums.techarena.in. Archived from the original on March 28, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Barksdale, Karl (September 13, 2006). «Upgrading Digitools to Windows Vista and Office 2007 and what it may mean for speech and handwriting instruction». Karl Barksdale blog. Archived from the original on July 3, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ a b c «Changes in the 2007 Office system». TechNet Library. Microsoft. January 15, 2009. Archived from the original on October 20, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Save My Settings Wizard wizard removed from Office 2007?». Techtalkz.com. April 3, 2008. Archived from the original on March 9, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Description of the Local Install Source feature in 2007 Office programs». Support. Microsoft. October 15, 2007. Archived from the original on October 26, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «2007 Office Resource Kit». TechNet Library. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 20, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ Lasky, Michael. «Office Beta: Good Looks, Tricky Formats» PC World (August 2006), p. 24
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «MS Office Edges Closer», PC Magazine, Vol. 25, Issue 12 (July 2006) p. 48
- ^ Cummings, Joanne (October 1, 2007). «Word 2007: Not Exactly a Must-Have». Redmondmag.com. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on December 12, 2007. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Download details: Office Labs: Search Commands». Download Center. Microsoft. December 15, 2011. Archived from the original on January 24, 2019. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ «Guides to the Ribbon: Use Office 2003 menus to learn the Office 2007 user interface». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 4, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «The Microsoft Office Fluent user interface video». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 9, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Download details: Word 2007 Add-in: Get Started Tab for Word 2007». Download Center. Microsoft. February 21, 2007. Archived from the original on May 8, 2019. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ Gunderloy, Mike (December 8, 2006). «What’s Going On Here?». A Fresh Cup. Archived from the original on September 11, 2007. Retrieved April 25, 2011.
- ^ Muhajir, Ahmad (July 28, 2008). «Veteran developer ditches Microsoft for open source». OpenWorld2010. WordPress.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2009. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ «How to use earlier versions of Excel, PowerPoint, and Word to open and save files from 2007 Office programs». Microsoft Support (3.1 ed.). December 14, 2006. Archived from the original on January 1, 2007. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ Luhn, Robert. «Get Ready to Work With Office 2007’s New Formats» PC World, Vol. 25, Issue 4 (April 2007) p. 132.
- ^ a b «Initial and revised submissions». Nature Publishing Group. Archived from the original on March 3, 2011. Retrieved April 25, 2011.
Acceptable formats for the manuscript are Microsoft Word (preferred), PostScript (PS, EPS or PRN), PDF, WordPerfect, Rich Text Format (RTF), TeX and plain text (TXT). If using Word 2007, please create the document in Compatibility Mode (i.e. as a Word 97-2003 document; saved as .doc, not .docx).
- ^ «Creating and numbering equations with Microsoft Word 2007». University of Waterloo. October 17, 2013. Archived from the original on November 7, 2014. Retrieved November 6, 2014.
- ^ «Word 2007 DOCX File Format». Inera Inc. June 22, 2007. Archived from the original on March 11, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ^ «Users of Word 2007/DOCX». Information for Authors. American Association for the Advancement of Science. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved April 25, 2011.
Science can now accept manuscripts prepared in Word 2007 and its .docx format, both at submission and revision. However, we strongly discourage the use of the Word 2007 equation editor. Instead please use Mathtype or Word’s legacy equation editor, which can be obtained through the «Insert» ribbon and the «Object menu» on the «text» panel.
- ^ «Microsoft Word 2007 Bibliography styles». Codeplex. Microsoft Corporation. December 9, 2008. Archived from the original on December 19, 2008. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
Microsoft offers a bundle of software programs within MS Office, with each offering a different function. Microsoft Word is a word processing program similar (but better than) the antiquated Word Perfect or the Microsoft Works Word processor. Just like any other word processing program, you use MS Word to view and edit formatted text within a document. A formatted text document is defined as a document that contains text which may be in bold, italics, underlined, a different color, or a different font. All word processing programs can do all of this, but Microsoft Word allows you to do a lot more. For that reason, Microsoft Word is the most used word processing program in existence today.
Remember, even if you’ve never used MS Word before or need to become familiar with the features of Word 2007. For that reason, pay attention even if you think you already know the information. Some features have changed in 2007 and others have been moved. We’ll show you how to use and find everything.
Before we continue and delve into the particulars, it’s important for you to realize that MS Word is not a desktop publishing software program. There are distinct similarities and differences between a word processing program and desktop publishing, so the lines can become blurry. Knowing which software you need to use – and if using MS Word will complete your task for you— will enable you to use MS Word for the correct reasons and not to waste your time trying to get it to do something it simply cannot.
The differences are:
- When you open a new document in MSWord, you see a blank field in which you input text.
- In desktop publishing software, you must create a text frame in which to add text.
Keep in mind that you can insert text frames into MS Word and use it as a desktop publisher, but it is not as easy as using a desktop publishing software.
Starting Microsoft Word 2007
You open Microsoft Word by clicking on the icon on your desktop (if you have one there) or in the program bar. The icon for 
When you click on the icon, a blank document will open. This is a new document for which the default name is Document1. For each additional new document that you open, the name increases by one digit: Document2, Document3, etc. If you start MS Word by clicking on an already existing document on your computer, it will open automatically and your document will be displayed in the MS Word window.
Virtual Tour of MS Word 2007
There are main components of the MS Word 2007 window that you need to be aware of before we even get into features and functions.
As with any software program or web page that you look at, the line allows you to minimize the page, the box allows you to maximize, and the X closes out the page on your computer. Don’t worry. If you should accidentally click the X, MS Word will prompt you to save the document.
Another component of MS Word is the toolbars. Toolbars appear just at the top of your page, right below the title bar. Take a look at the following snapshot. You’ll see the toolbars right below the bar that reads «Home Insert Page Layout…» You will use these toolbars to accomplish specific functions within MS Word. Using the toolbars will make your job quick and easy.
The toolbars in MS Word 2007 change depending on whether you click Home, Insert, etc. Above is the toolbar that appears when you click Home. Below is the toolbar you will see when you click Insert.
We’ll learn the features of these toolbars later, so do not worry about studying them right now. It’s only important that you know what they are and where they are located.
You can also customize your toolbars in MS Word 2007. To do this, click the downward arrow at the very top left of the page. It can be seen in the snapshot below on your far right. This is called the Quick Access Toolbar. You can click on it while using MS Word to preview all you can do with it, including customizing your toolbars. 
Below the toolbars, you have the document area. It takes up the majority of the window and is where you will type or edit text. To type in the document area, just click in it and your cursor will appear.
The Microsoft Office button appears on the left in the picture above. Clicking on it will give you many of the same options as File did in previous versions of MS Windows.
You can create a new document, edit an existing document, save, publish, print, or close.
The Ribbon is an improved feature to MS Word 2007. The Ribbon is tabs you see at the top of the page labeled Home, Insert, Page Layout, etc. There are seven tabs. These tabs are divided into groups which you will see below the tab. These groups are in place to provide the editing features you might need when clicking on that particular tab. The groups are labeled. Those labels are right above your document pane. In the ‘Home’ tab, the groups are Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles, and Editing. The toolbars for these groups are located just above the labels. The groups in MS Word 2007 are the same as the toolbars in previous versions. They are just much more organized, making it easier for you to find what you need and complete the task. To view additional features, click on the arrow at the bottom right of each group beside the label.
In the picture below, you see the Home tab. To see additional features for Font, for example, you’d click on the arrow to the right of Font (located directly above the document area.)
This is what you will see:
Spend some time clicking the tabs and becoming familiar with the groups within each tab. It is recommended that you do this before continuing to familiarize yourself with the layout of MS Word 2007, especially if you’re currently accustomed to previous versions.
Opening a New Document
Opening a new document can be accomplished two ways. The first way is to click on the MS Word 2007 icon on your computer. If you already have MS Word open and wish to start a new document, simply click on the Window Office button and select ‘New’. You will be presented with the screen pictured below.
On the left, you have templates that you may choose from. If you would select ‘Award Certificates,’ you would then see a screen that would allow you to choose a certificate template as your new document.
However, to open just a blank MS Word document, you can simply select ‘blank document’ as highlighted in the former picture, then create. It’s as simple and easy as it can be.
Saving a Document
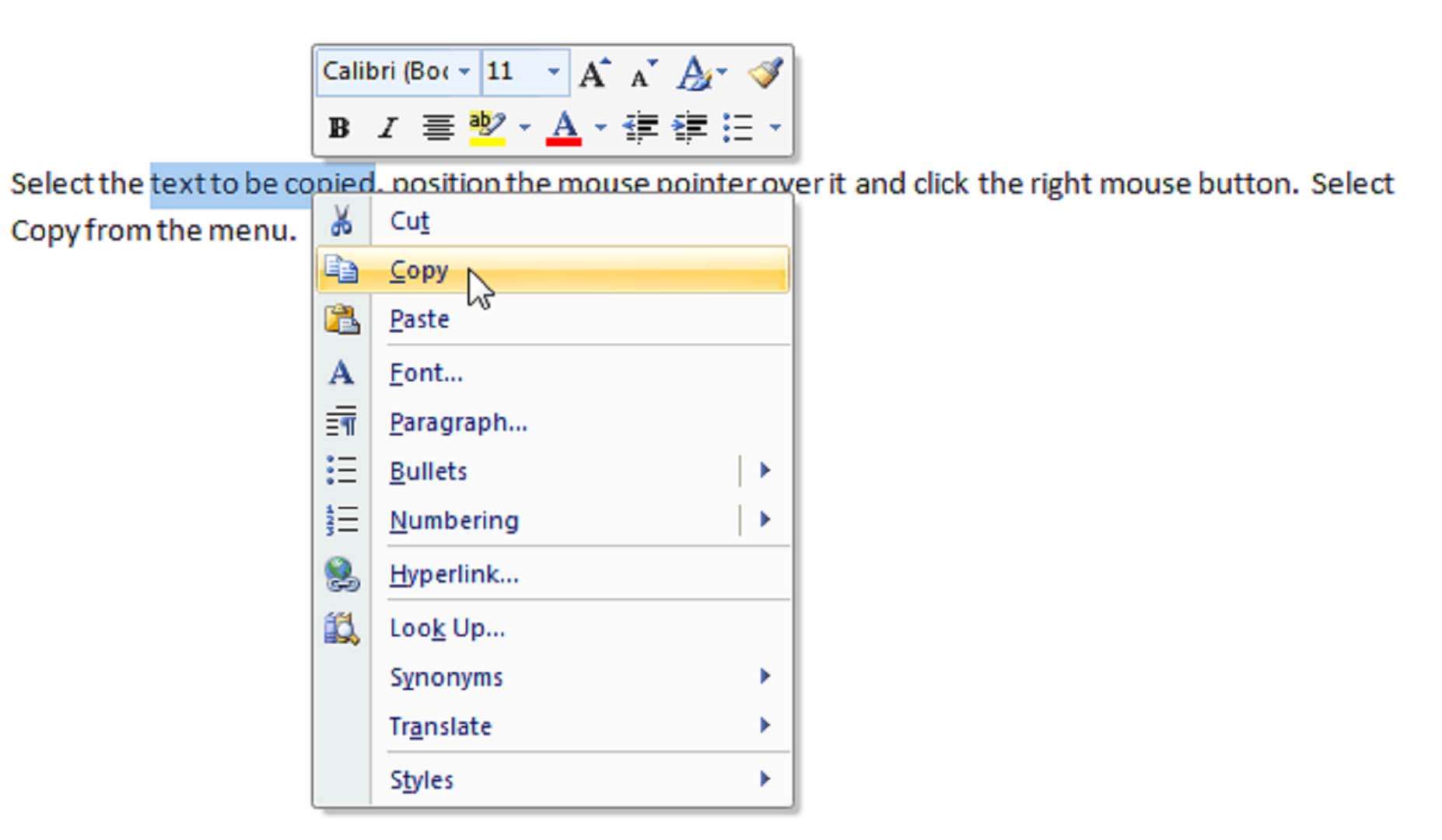
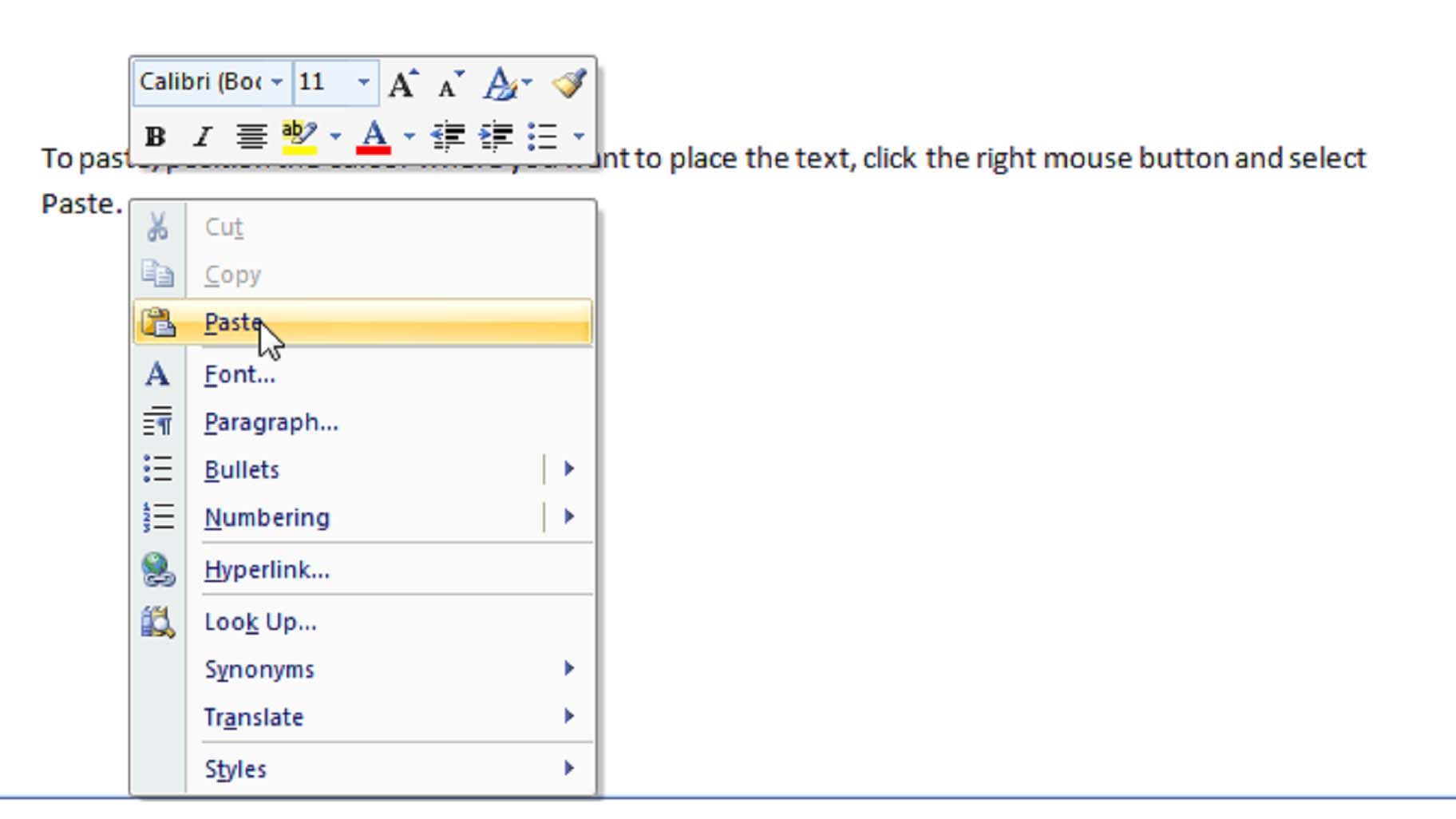
Let’s say that you’ve created a new document and wish to save it to your computer to use again later. You can do this quickly and easily in MS Word 2007 in one of two ways. The first way is to use the Microsoft Office button. Click on it, then scroll down to select either ‘Save’ or ‘Save As’. Clicking ‘Save’ will enable you to save the file under its current name. Keep in mind that if this is a new document, it will save the file by the default name of Document1. When you click ‘Save,’ if another file of the same name exists, MS Word will prompt you to either enter a new file name or to replace the existing copy with the new version you are currently saving.
Clicking ‘Save As’ gives you a lot more options to saving your work. First of all, when you click ‘Save As,’ you must specify a file name. You must also specify the format that you want to save the file in. MS Word’s default file format is .doc or Word Document. This is an acceptable and much-used format that should be satisfactory for most MS Word users, but you can select the format that you need depending on the work you need to save. You can also save your work as a template or in MS Word 97-2003 recognizable format if you’ll be forwarding the file to users who may not have MS Word 2007. When you click on ‘Save As,’ it will present all these options to you in a slide-out window to the right of ‘Save As.’
You can also save a document by clicking the picture of the floppy disk that is located to the left of the Quick Access button. However, this will save the file under the current name. You will not be able to name the file or select the format. It’s a good idea to click this button every so often while working in a document to save it in case of a power outage, computer freeze, or anything else that may cause you to lose your work.
Warning: Do NOT close MS Word without saving your document. You MUST save your document using one of the methods listed above or your work will be lost forever.
Getting Help with MS Word 2007
If at any time you have a question or need to know exactly how to find or accomplish a task, you can also ask MS Word for help.
In the upper right hand corner of the screen, you’ll see a dark blue circle with a question mark inside. This is the help button. You can click on this and a menu will pop up so that you may find the answer to your question. You can also bring up this help window by simply clicking F1 on your keyboard.
You can use MS Word help to remind you how to complete certain tasks or to refresh your memory. It is always there as a reference tool and is free to use.
Conclusion
In this article, you’ve received a virtual tour of MS Word 2007. Again, it is highly recommended that if you aren’t yet familiar with the layout of MS Word 2007 that you take some time now to familiarize yourself with the various aspects we’ve discussed.
Basic Editing
Microsoft Word 2007 is a big step up from the days of old, when we’d roll a sheet of paper into our typewriter and pound away, praying we wouldn’t make a mistake. If we did make a mistake, our options were limited—we could either crank a clean sheet into the carriage and start all over or use white-out. Neither option was particularly inviting. On the one hand, we’d have to type most of it all over again and hope we didn’t make another mistake or we’d have to use white-out, glopping that foul-smelling elixir onto our mistakes, losing our inspiration or our train of thought while we waited for it to dry.
With Microsoft Word 2007, we leave all of that behind. We can go back and fix an error with a mouse-click and a few simple keystrokes. We can delete and insert words, paragraphs or an entire page anywhere in the document, and even move text from one location to another.
In this article, you’ll become familiar with the basic tools Word 2007 uses to edit a document.
The Cursor
If you’ve spent any time at all on the computer, you should be familiar with the cursor. In Word, it is a thick blinking black line. It is the line that lets you know where you are in the document and where characters will appear as you type. You can move the cursor anywhere in a document by using the arrow keys on the keyboard or by moving the mouse pointer to the desired location and clicking the left mouse button.
The cursor moves to the right as you type and to the left as you backspace.
The cursor can be quickly repositioned to certain preprogrammed places in the document by using keyboard shortcuts. To move the cursor to the beginning of a line, use the HOME key. To move it to the end of a line, use the END key. To move the cursor to the beginning of the document, use CTRL + HOME and to move it to the end of the document, use CTRL + END.
Inserting Text
You can insert text anywhere in a document simply by moving the cursor to the desired location and typing.
Word automatically moves all text to the right of the cursor as you type. If, however, you’d rather replace the text as you type, Word 2007 gives you two options:
- Select the text you’d like to replace and start typing. This deletes the highlighted text and positions the cursor in its place.
- Use Overtype Mode. To turn on overtype mode, click the Microsoft Office button
, select Word Options
then Advanced. Check «Use the Insert key to control overtype mode» or the «Use overtype mode» box.
If you select the «Use the Insert key to control overtype mode» box, you can toggle overtype mode on or off by pressing the Insert key. If you select only «Use overtype mode» you must manually turn it off by deselecting it.
You can also insert text by the copy and paste method. To copy and paste text anywhere in your document, you select the text to be copied, position the mouse pointer over it, and click the right mouse button. A menu will appear. Select Copy from the menu by clicking the left mouse button.
To insert the copied text into your document, position the cursor where you want to place the text and click the right mouse buttonagain. Select Paste from the menu.
Selecting Cut rather than Copy, removes the selected text but still allows you to paste it where you want it.
Deleting Text
You can delete text by using the Backspace and Delete keys. But you must remember that Backspace removes characters to the left of the cursor, and Delete removes characters to the right.
To delete blocks of text, select the text to be deleted and press either the Backspace or Delete key.
Moving Text
You can move selected text by holding the left mouse button and moving the cursor to the desired location in the document. When moving text, a small box appears near the mouse pointer and the cursor turns into a broken black line. You position the cursor in the place you want the text and release the left mouse button.
Undo and Redo But let’s say you accidently delete something or deleted it and then decided that you want it back. You grit your teeth and start to grumble, trying to remember the exact wording. It’s a lost cause, right? Wrong. The makers of Word anticipated this problem and supplied an easy solution. The Undo button!
The Undo button can be found in the upper left corner of the program window in what Microsoft calls the «Quick Access Toolbar» The Undo button is the blue arrow shaped like a comma. If you are not sure you’ve got the right button, you can move your mouse over it and wait and a small box that reads «Undo Typing (Ctrl-z)» will appear. Word allows you to undo up to 100 actions.
The Redo button is to the right of the Undo button. 
Wrap Text
Word 2007 can also wrap text around a picture, charts and graphs as in the example below.
To wrap text around a picture or art object, click on the object. The Format tab will appear in the ribbon. In the Arrange group, click Position. A menu will unfurl. Select the desired position.
To wrap text around a table, click the table, then select the Layout tab in the menu. In the table group, select Properties.
This is what you will see:
Under Text Wrapping, select Around. You can change the horizontal and vertical position of the table and other options by clicking Positioning. The dialogue box on the right, is what you will see when you click Positioning. Select the desired options and clickOK.
Описание Microsoft Word 2007
Microsoft Word 2007 — первая версия офисного редактора от ведущего разработчика ПО, выполненная с акцентом на новые функциональные элементы и вызываемых с ленты инструментов и быстрых команд, заменившей собой главное меню программы. В текущей сборке программы Word 2007 был существенно переработан интерфейс приложения и добавлены свежие, концептуальные находки и решения. Также впервые была имплементирована поддержка модуля Windows SharePoint Services, что принесло возможность переноса документов в рабочую среду WSS без установки сторонних модулей и плагинов. Также в этой версии редактора впервые был представлен новый формат DOCX для создания, редактирования и сохранения Word-файлов, основанный на спецификации XML. Как показало время, данная технология стала де-факто стандартом на рынке настольных офисных приложений, и ее поддержкой обзавелись все крупнейшие игроки и компании. Наконец, благодаря интеграции с другими компонентами Microsoft Office 2007, все составляющие офисного бандла тесно связаны между собой и используют одну и ту же спецификацию для обработки информации в пределах нативной оболочки.
Дополнительные новшества и свежие механики Word 2007
В очередной ревизии текстового редактора Word 2007 были реализованы следующие нововведения и инструменты:
- интуитивная, четко продуманная и комфортная смена масштаба отображения страницы документа. За эту функцию отвечает специальный ползунок, расположенный в правом нижнем углу активной страницы Word 2007
- имплементирован новый формат представления данных на основе XML-спецификации — Office Open XML. Файлы, хранимые в формате DOCX, выделяется лучшей защищенностью, скоростью и компактностью. Позднее альтернативные пакеты от сторонних разработчиков также обзавелись его поддержкой
- всплывающая панель форматирования шрифта, которая сопровождает каждое точечное выделение текстового фрагмента на текущей странице
- быстрые стили. Эта функция предоставляет возможность тотчас увидеть результат применения выбранного стиля путем простого наведения курсора мыши на результирующую иконку на ленте
- реализованы продвинутые опции работы с графикой. В Word 2007 были добавлены новые трехмерные эффекты, тени, блики, текстуры и цветовые схемы.
На нашем веб-ресурсе вы можете с легкостью скачать полностью русифицированную последнюю стабильную сборку Word 2007 без регистрации и финансовых микроплатежей. Перед установкой бандла на ПК настоятельно рекомендуем ознакомиться с обзором системных требований пакета, дабы быть уверенным, что утилита без проблем запустится на вашем устройстве без задержек и фризов.
Системные требования Microsoft Word 2007
Для обеспечения продуктивной и качественной работы над текстом, придется обзавестись стационарным компьютером или портативным ноутбуком, удовлетворяющим следующему набору характеристик:
- графика: видеоадаптер должен поддерживать вывод картинки на дисплей в разрешении 1024х768
- оперативная память: минимум 256 МБ ОЗУ
- платформа: Windows XP SP3/Vista SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP2 или более новая модификация системы
- процессор: вычислительное ядро с частотой не менее 500 МГц
- накопитель: 1,5 — 2 ГБ свободного места на физическом носителе.

Обучение MS Office прибавило немало нам подписчиков и читателей, поэтому мы продолжаем рубрику Обучение Word на нашем сайте. И главное, что будем разбирать подробно, это текстовый редактор. Кому-то с ним не впервой работать, а кто-то сталкивается с новым приложением впервые, поэтому для таких пользователей не будет, скорее всего, шокирующим новый интерфейс и новый подход компании Microsoft к MS Office 2007.
До 2007 года компания Microsoft последовательно шла в разработке своих приложений в MS Office, следуя только совершенствованию функций, а начиная с MS Office 2007 все продукты, входящие в Офис 2007 принципиально отличаются от своих предшествующих версий и полностью меняют сознание пользователя. Итак, начнем последовательное изучение программы MS Word 2007 в картинках, шаг за шагом, на практике разбирая вопросы наших читателей.
Хочется предупредить всех наших читателей и учащихся, что Офис 2007 и Офис 2010 (Office 2010) имеют практически один и тот же интерфейс и дополненный функционал, поэтому не удивляйтесь, если в дальнейшем появятся окна и команды Офиса 2010.
После изучения предыдущих версий программы MS Word пользователю, который привык работать в этом текстовом редакторе с первого взгляда вызывает недоумение, а может быть и шок, интерфейс новой версии 2007 года.
Это полностью иной принцип организации интерфейса.
Главное отличие Word 2007 от предыдущих версий Word 2000 — 2003 (XP) — это то, что разработчики изменили принцип списка имеющихся операций на принцип списка контекстных функций, т.е. иными словами, команды мы выбирали в выпадающих сверху меню, а теперь главное меню предлагает режим тех функций, которые мы привыкли видеть в контекстном меню к каждому объекту.
Итак, что же все-таки нового в Office 2007 изложено ниже коротко, а вот в дальнейшем мы начнем разбирать все новшевства и функции более подробно, иллюстрируя их картинками из Word 2007.
Что нового появилось в программе MS Word 2007?
1. Интерфейс программы теперь не содержит привычных меню и списков команд. Все строится на взаимодействии программы и пользователя. То есть, то или иное действие пользователя активирует соответствующие кнопки команд, которые объединены во вкладки и располагаются на ленте (тематический набор команд).
2. Кроме ленты окно программы содержит всего одну привычную панель инструментов, которая называется панель быстрого доступа, так как она никогда не исчезает с экрана и содержит самые востребованные команды для работы с документом. При этом к минимальному составу панели всегда можно добавить кнопки команд сообразно собственному представлению о самом главном.
Таким образом, панель быстрого доступа стала своеобразным мостиком между прежними версиями программы и новыми принципами организации работы.
3. Несколько изменился состав и назначение меню «Файл», которое теперь активируется кнопкой «Office» и носит название меню типичных задач. Оно, как и панель быстрого доступа, формируется на принципе самых необходимых и востребованных операций с документом Word.
4. Порадовала в программе еще одна новинка — быстрая и, главное, удобная смена масштаба отображения страницы документа. Регулятором в правом нижнем углу окна программы в любой момент можно увеличить или уменьшить масштаб.
5. Появился у Word 2007 и новый формат файлов, основанный на Office Open XML. Он призван обеспечить бульшую защищенность документов, снижение вероятности их повреждения, компактность и совместное с рядом систем хранение и обработку данных иных производителей программного обеспечения.
Пожалуй, главное вновшество в программе word 2007, которое удивляет пользователей — это сохранение всех документов в формате с четырехзначными символами: ранние версии документов сохранялись, как *.doc, а сейчас *.docx. Для тех кто все еще использует программу версии ХP или 2003, вам может помочь конвертор, который можно скачать на сайте Microsoft и установить у себя на компьютере, для того чтобы можно было открывать документы Офиса 2007 (например, документы, приходящие от клиентов, которые пользуются Офисом 2007) в более ранних версиях Word. Или же воспользуйтесь конвертором онлайн docx в doc.
6. Еще одна из новинок программы — быстрый стиль. С помощью этой функции можно сразу увидеть, каким будет результат применения того или иного стиля, шрифта или размера, лишь подведя курсор мыши к нужной кнопке.
7. Понравится многим пользователям и всплывающая панель форматирования шрифта, которая будет сопровождать каждое выделение фрагмента текста на странице. На ней размещаются самые востребованные команды, что сокращает время манипуляций с основными вкладками и группами ленты.
8. Расширены и возможности автотекста, который преобразован в понятие экспресс-блок, основанный на блоках готовых данных. Экспресс-блоки стандартной информации достаточно легко используются, обновляются и применяются при групповой работе.
9. Работа с графикой в Word 2007 стала поистине приятным сюрпризом. Новые трехмерные эффекты, тени, блики, текстуры и цветовые схемы делают программу самодостаточной в вопросах оформления документов графикой практически любой сложности.
10. Нельзя не упомянуть и новый, теперь уже встроенный, редактор формул, который позволяет в нужный момент добавлять и редактировать формулы любой сложности и назначения. Редактор дает возможность использовать библиотеку готовых выражений, комплект реальных математических символов и выражений.
11. Следующей новинкой стал инспектор документов, в чью функцию включена возможность находить и удалять из свойств документа личную или конфиденциальную информацию, а также нежелательные комментарии, скрытый текст — словом, все те данные, которые могут представить угрозу безопасности пользователя.
12. Не забыты в программе и блоггеры, для которых в Word появилась поддержка отправки постов в свои дневники прямо из окна приложения. При этом Word автоматически преобразовывает графику в формат PNG и загружает ее на сервер. Теперь создание сайтов становится еще более актуальным и доступным для пользователей.
13. Имеются нововведения и в использовании сочетаний клавиш. Теперь клавише Alt присвоена функция активации карточек с буквами для каждой вкладки, группы и команды ленты. Используя эти обозначения, можно получить быстрый доступ к нужным функциям программы. При этом имеется возможность всегда вернуться к привычному использованию клавиши Alt.
14. И напоследок — темы документов, которые предоставляют собой готовые комплексные решения по оформлению документов с использованием одних и тех же шрифтов, цветов и эффектов в едином стиле.
Microsoft Word 2007
Microsoft Word 2007’s document types, interface, and some features—very nearly every aspect of this word processor—have changed. With this update, Microsoft Word 2007 becomes a more image-conscious application. New picture-editing tools help you deck out documents and play with fancy fonts. Bloggers and researchers may also benefit. It’s easier to get a handle on document security, but those who only need basic typing features may not want to relearn the interface or deal with the new file formats.
The Good
Microsoft Word 2007 adds built-in blogging and live previews of font and image styles; better displays complex features such as those for references and mass mailing; introduces new, smaller file formats; improves document security; integrates with other applications.
The Bad
Word 2007 moves all of its commands; contextual tabs and style galleries can be distracting; new Word file formats require converters in order to be opened in Word 2000 through 2003; no free way to save work to the Web.
The Bottom Line
If you’re ready to let go of old habits from previous versions of Word and want to make sleeker-looking documents, Microsoft Word 2007 is worth the upgrade. However, less-expensive alternatives handle its core features without the clutter.
Our installation of various Office suites on Windows XP computers took between 10 and 20 minutes, which was quicker than prior editions of Office. You’ll have to be online to access services later, such as Help and How-To as well as Clip Art and document templates. Our reviews of Microsoft Office 2007 detail the installation process and the ingredients of each edition.
Word 2007 will operate in Compatibility Mode, shutting off some of the new graphics-rich features, should you, for example, open a Word 2003 DOC file without converting it to the new DOCX format.
Interface
Once you have Word 2007 running, you will notice a completely redesigned toolbar, now known as the Ribbon, with many familiar commands in new places. Instead of the old, gray drop-down menus atop the page, Microsoft’s new and very colorful Ribbon clumps common features into tabs: Home, Insert, Page Layout, References, Mailings, Review, and View. Some tabs don’t show up until you might need them; for example, you must select a picture to bring up its formatting tab. At first, you’ll need to wander around to find what’s moved from prior versions of Word. Clicking the Office 2007 logo in the upper-left corner drops down a menu of staple functions—such as opening, saving, and printing files—that were under Word 2003’s File menu. We had the hardest time locating commands from Word 2003’s Editing and Tools menus. To insert a comment in Word 2007, for instance, you must look under the Review tab instead of the Insert tab. Prepare to relearn Word. Alas, there is no «classic» view to help you make the transition to the 2007 version.
While it’s a challenge to upgrade, those learning Word for the first time may find its features easier to stumble upon than they would have with Word 2003. For instance, the new interface better presents page view options that used to be a hassle to get to. From the View tab, now you can simply check a box to see a ruler or gridlines, or click the Arrange All button to stack various open Word documents atop each other. Although we sometimes mixed up the placement of commands within the Review and References tabs, those features were still easier to find than in Word 2003.
Microsoft placed a lot of emphasis on the wow factor of Office’s galleries of graphics, which share the Aero look of Windows Vista and are found throughout the Office applications. Pull-down menus of fonts, color themes, and images let you preview changes on the page before making them. And thankfully, Microsoft killed Clippy, the cartoonish helper. Now a less-intrusive quick formatting toolbar shows up near your cursor. Keyboard shortcuts remain the same; pressing the Alt key displays the corresponding quick key for each Ribbon command. A running word count is always present in the lower-left corner, and the new slider bar for zooming in and out is a terrific, no-brainer improvement, particularly for the vision impaired.
Features
Aside from the interface, the other radical change in Word 2007 is its new file type. For the first time in a decade, Microsoft foists a new file format upon users, and old Word DOC files make way for the new DOCX type of Word 2007. Microsoft has taken steps to ease this transition, but we anticipate that it will not be smooth for many users.
Word 2007’s new Picture Tools options let you hover over galleries of changes to preview how they’ll look. In the past, you may have applied a change out of curiosity, then hit Undo when it didn’t meet your expectations.
What happens when you’re sharing work with people who use an older version of Word? Word 2003 and 2000 are supposed to detect when you first try to open a DOCX file, then prompt you to download and install an Office 2007 Compatibility Pack. After you’ve done this, the older Word should convert your Word 2007 files and remove incompatible features. When you reopen that same DOCX file again in Word 2007, the file’s original elements are supposed to stay intact. On the other hand, if you open an older DOC file within Word 2007, it will also run in Compatibility Mode, shutting off access to some of the newer program features, which explains why two documents within Word 2007 may display different formatting options.
Among the small tweaks in Word 2007 that make formatting easier, rollover style galleries let you preview the changes. However, the constant shape-shifting of the galleries can be distracting. And some options, such as for adjusting margins, use an older-style dialog box rather than the live preview menus.
Still, it takes just a couple of clicks to insert a JPEG, a GIF, a BMP, a PNG, or another image type. Click the graphic, and the Picture Tools Format tab lets you tweak the brightness, the color mode, and the contrast of a picture. You can also rotate it, crop it, skew its angle, add 3D effects and shadows to its borders, and convert it to all manner of shapes, such as a thought bubble, an arrow, or a star. Options for positioning an image and wrapping text around it are also front and center, which should be helpful for creating professional-looking business documents, as well as casual party invitations. You don’t get nearly the amount of control offered by Microsoft Publisher, QuarkXPress, or Adobe InDesign, but Word 2007 may do the trick for ultrabasic desktop-publishing needs.
For those who don’t need all the formatting choices, we’re glad that Word 2007 doesn’t apply a complex style to our text by default. In Word 2003, we’d have to highlight all the text, and then Clear Formatting to remove unwanted indentations and bold letters. In Word 2007, Calibri, a crisp, default font, replaces the standard Times New Roman from Word 2003. You can choose from galleries of text styles, such as Emphasis, Strong, or Book Title, and easily create your own styles and set them as a default.
The Prepare menu offers choices for inspecting, encrypting, and restricting access to your Word files in addition to checking to see how its elements will appear in older versions of Word.
While Corel WordPerfect has traditionally offered better features for managing longer documents, Microsoft Word 2007 has improved a bit in this regard. For those working on a dissertation or book report, the References tab lets you manage citations and bibliographies in styles from APA to Turabian. Just click Next Footnote, and the cursor takes you there. However, the Table of Contents feature still isn’t easy to figure out.
Editors who collaborate on documents with others can make use of the Review tab. The new Compare pull-down menu lets you look at two versions of the same document side by side, as well as merge changes from several authors and editors into one file. Administrative assistants and those charged with mass-mailing tasks should find those features much easier to access than in Word 2003. Bloggers can now compose and post entries to their Web sites without leaving Word.
If you deal with sensitive information—in a private diary entry, a resume, or a company financial statement, for example—Word 2007 allows more control over buried data, such as the original author’s name or your supervisor’s cursing comments. Office 2007’s Prepare options step you through inspecting that metadata, as well as adding a digital signature and encrypting a file. You’ll also find some of these options under the Review tab’s Protect button. However, should you plan to black out text, you’ll have to turn to Adobe Acrobat 8 to make secure redactions (highlighting the font in black within Word won’t do it).
As integration has improved throughout Office 2007, you can click Send from the Office logo menu to attach a Word document to an e-mail message through Outlook’s composition window. A message recipient using Outlook 2007 can preview that Word document within the e-mail message pane. And if you paste an Excel 2007 chart into a Word 2007 file, just right-click the chart and select Edit Data to launch Excel in split-pane view. When you change the source data within Excel, the chart adjusts in Word.
Unfortunately, Microsoft isn’t providing an option for storing or editing Word files online to most users who buy below the $679 Ultimate edition of Office, and there’s no browser-based version of Word. Need to collaborate on a file with specific people or take work on the road? At this time, you may have to e-mail those documents. Alternately, you could upload a Word file into one of the many free, Web-based word processors served up by other companies, including Zoho Writer, which offers a free upload add-in for Word 2007.
Options for blogging include an editing interface that lets you insert art and charts and lets you post entries without leaving Word.
Service and support
Boxed editions of Microsoft Office 2007 include a decent, 174-page Getting Started guide. During the first 90 days, you can contact tech support for free, and help at any time with any security-related or virus problems also costs nothing. Beyond that, paid support costs a painfully high $49 per telephone or e-mail incident. Luckily, Microsoft’s online help is excellent, although we’re displeased that Microsoft and other software makers are increasingly promoting do-it-yourself assistance. We especially like the Command Reference Guide for Word, which walks you through where commands have moved since Office 2003. You can also pose questions to the large community of Microsoft Office users via free support forums and chats. Microsoft Office Diagnostics tool, included with the Office 2007 suites, is also designed to detect and repair problems if something goes haywire.
Conclusion
Is Word 2007 worth the upgrade? If you primarily work with plain text and don’t need to pretty up reports and newsletters and the like, then it might not be right for you. For our purposes as editors, for instance, Word 2007 doesn’t introduce must-have goodies, although commenting commands are within easier reach. At the same time, Word 2007 handily presents options for footnotes and citations under its References tab, which researchers should appreciate. Mail-merge functions are also easier to reach. Bloggers might use Word’s posting tools in a pinch, but we found Word 2007’s rebuilt HTML to be clunky still. Above all, Microsoft’s new word processor is most upgrade-worthy if you want to play with pictures, charts, and diagrams in addition to text.




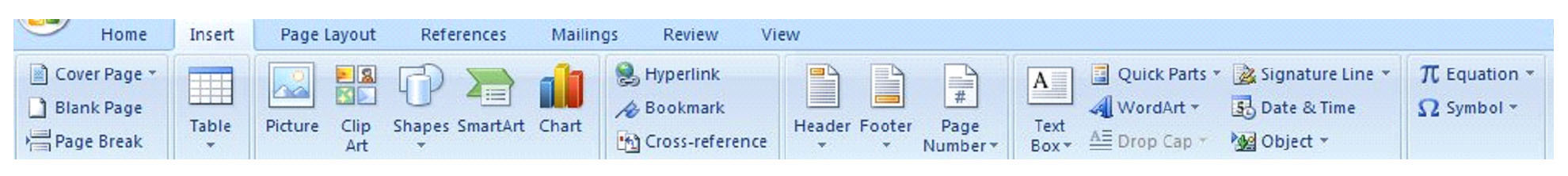
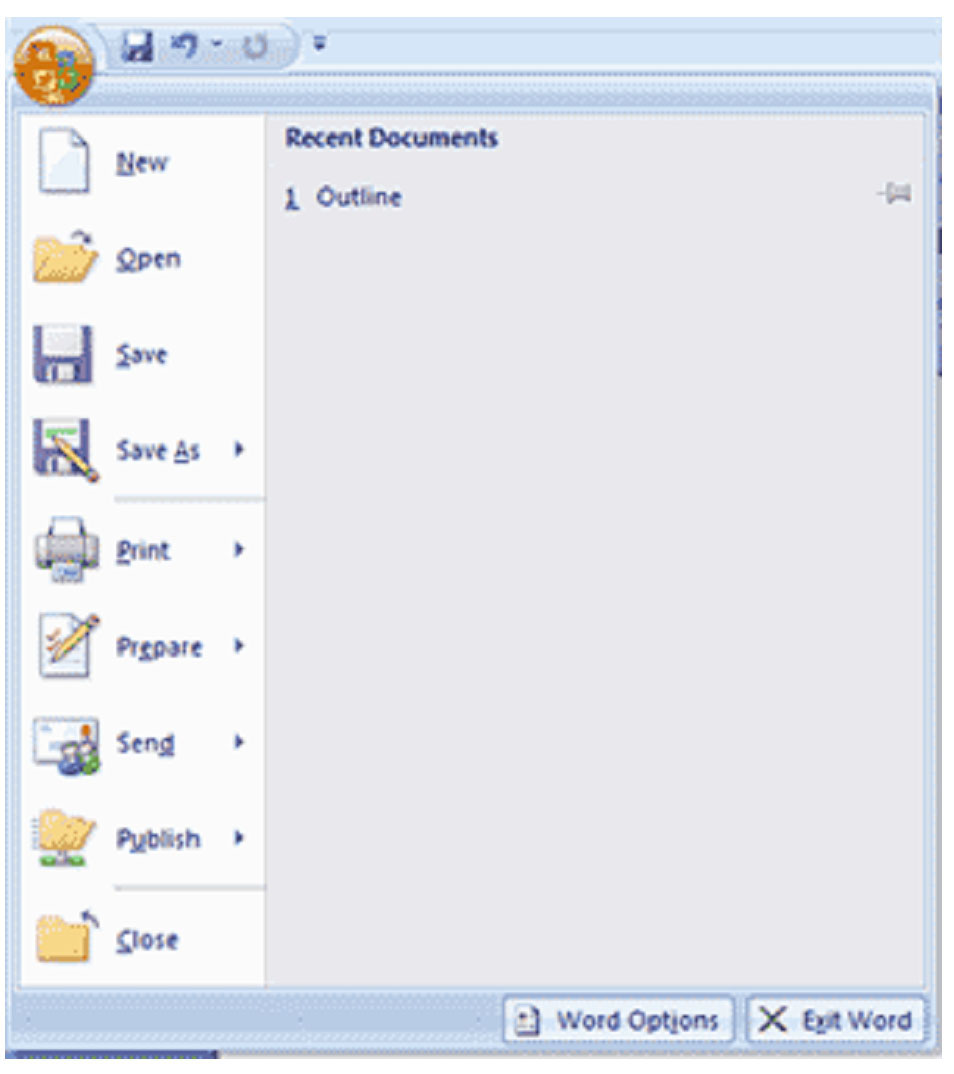
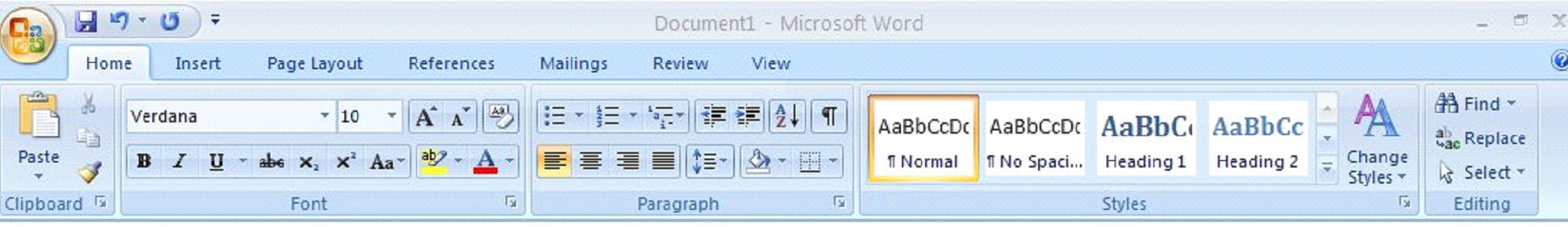
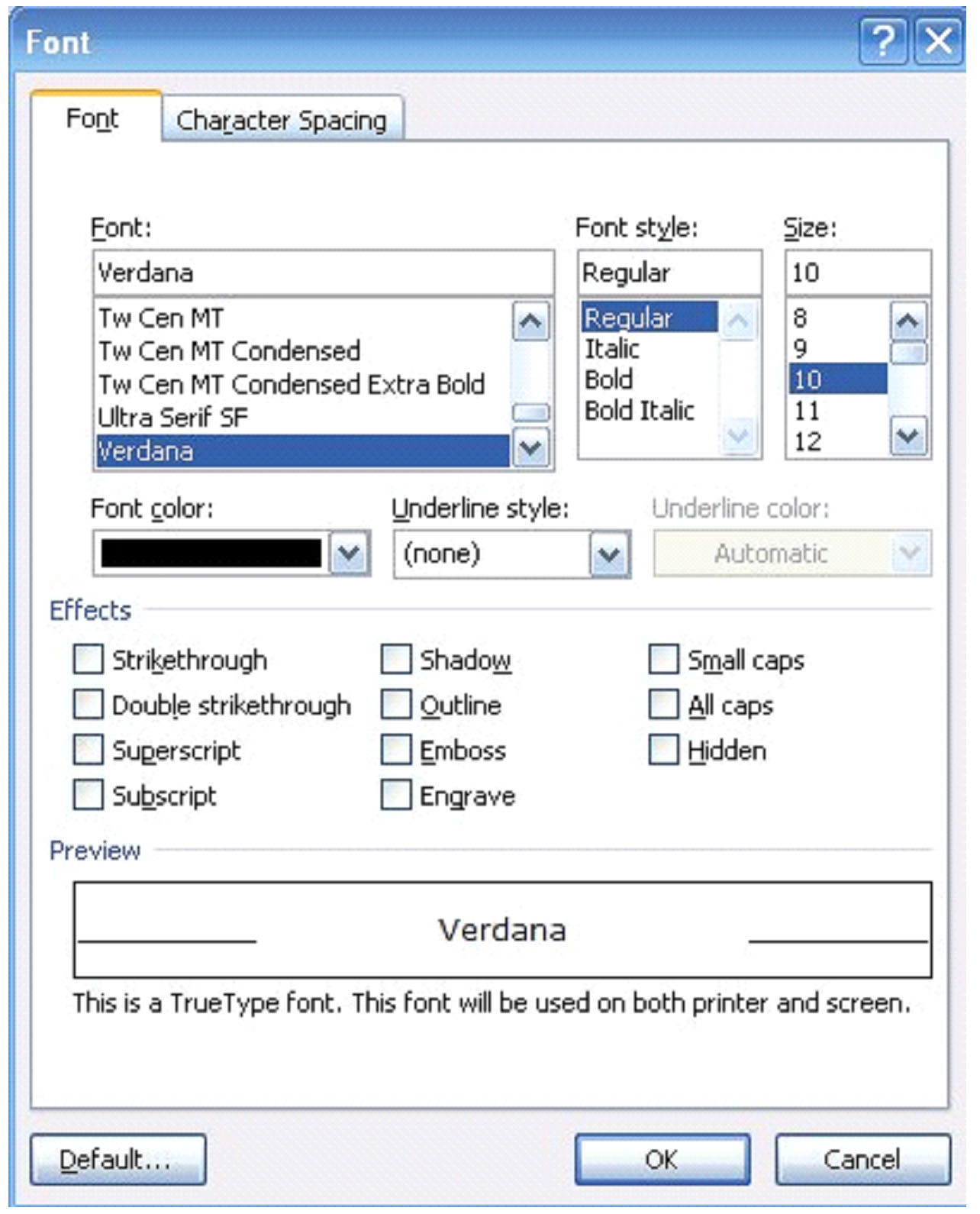
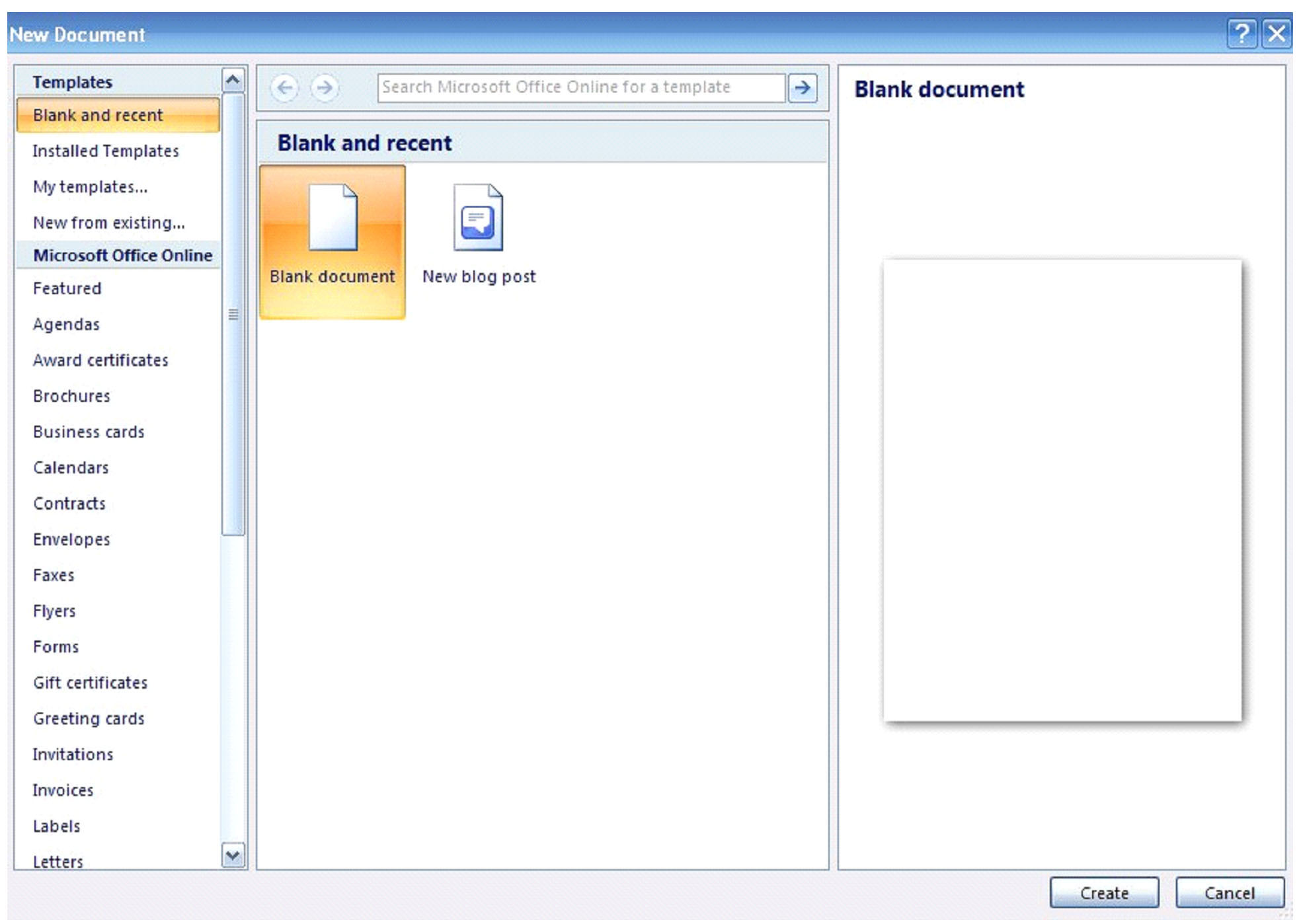
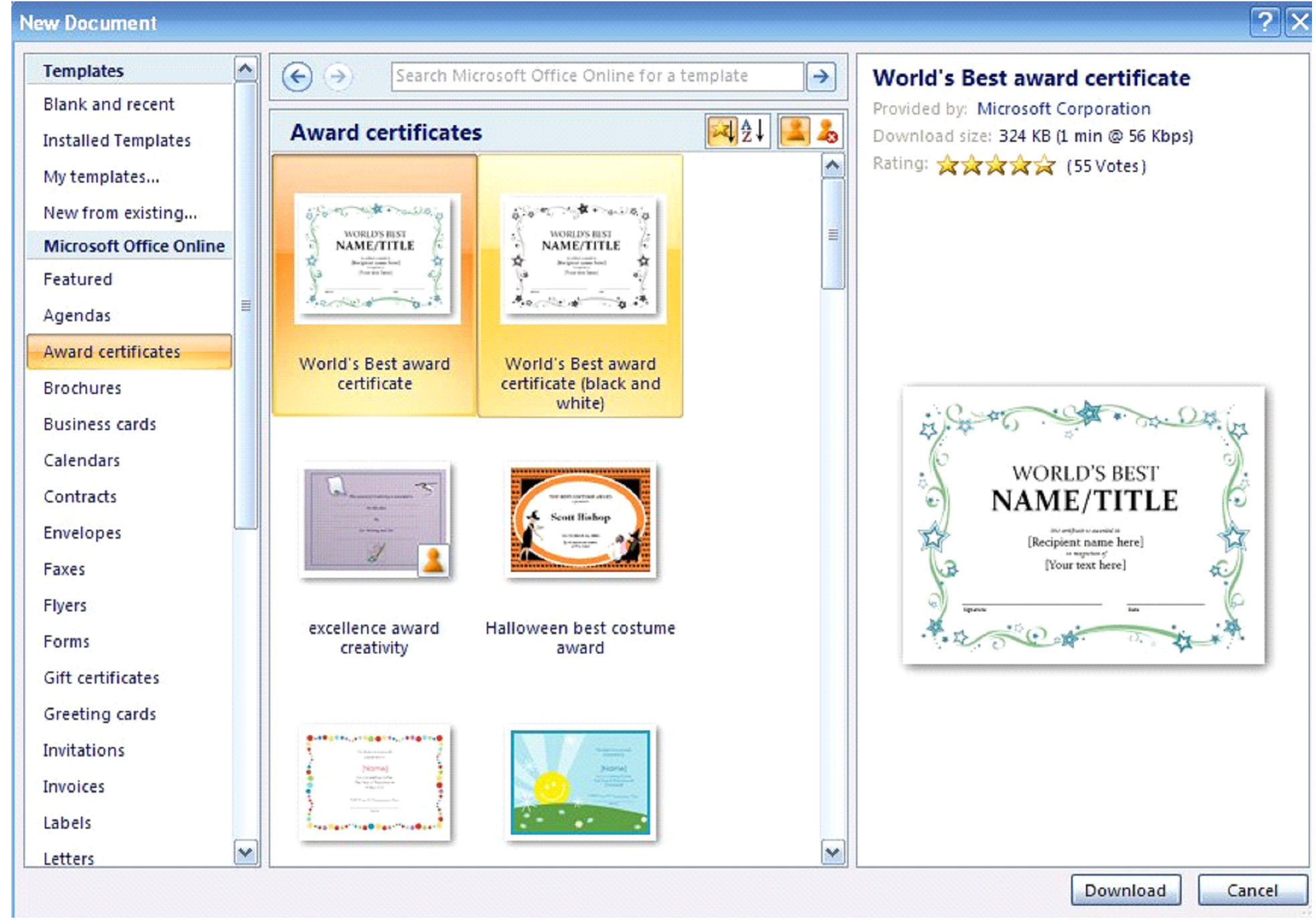
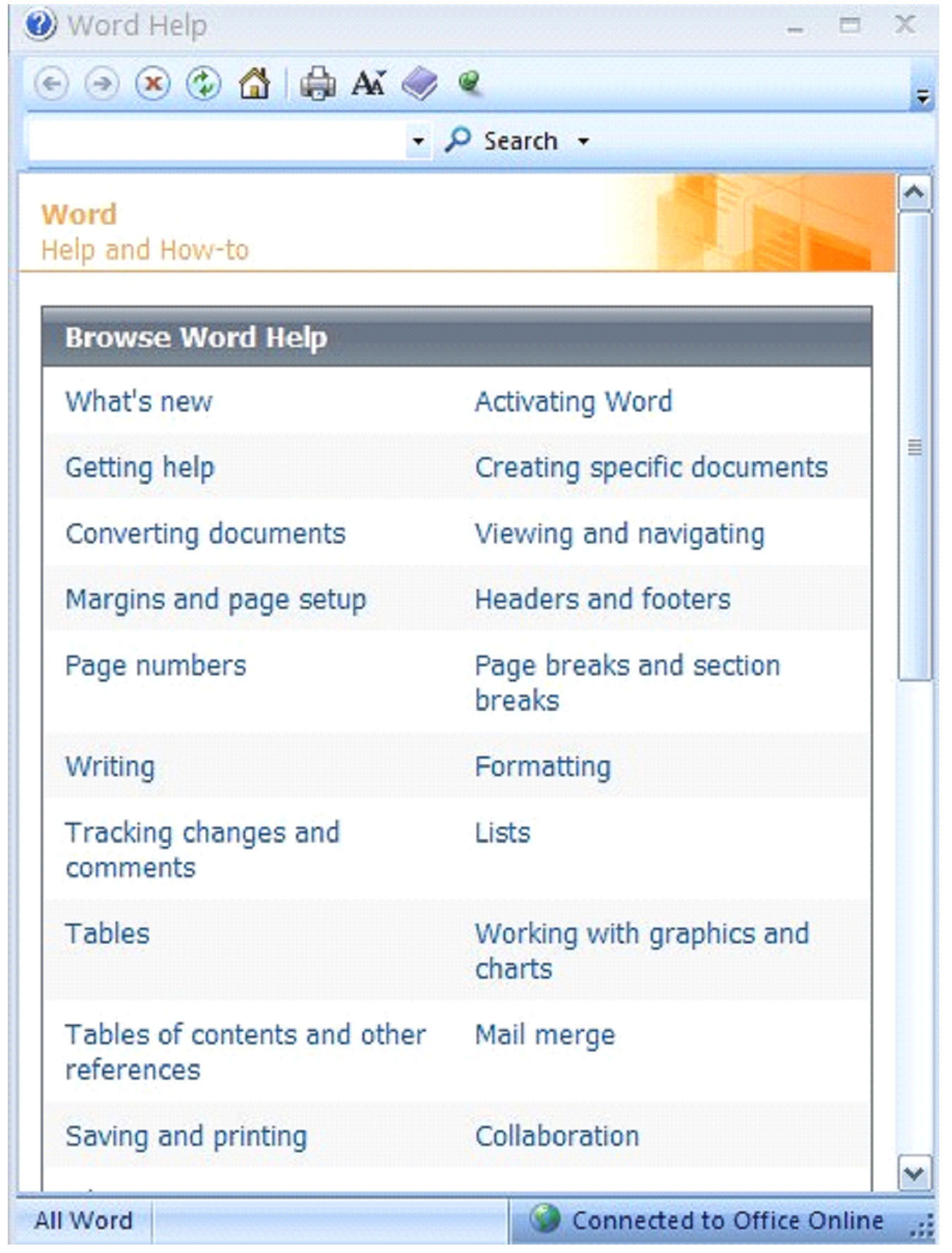
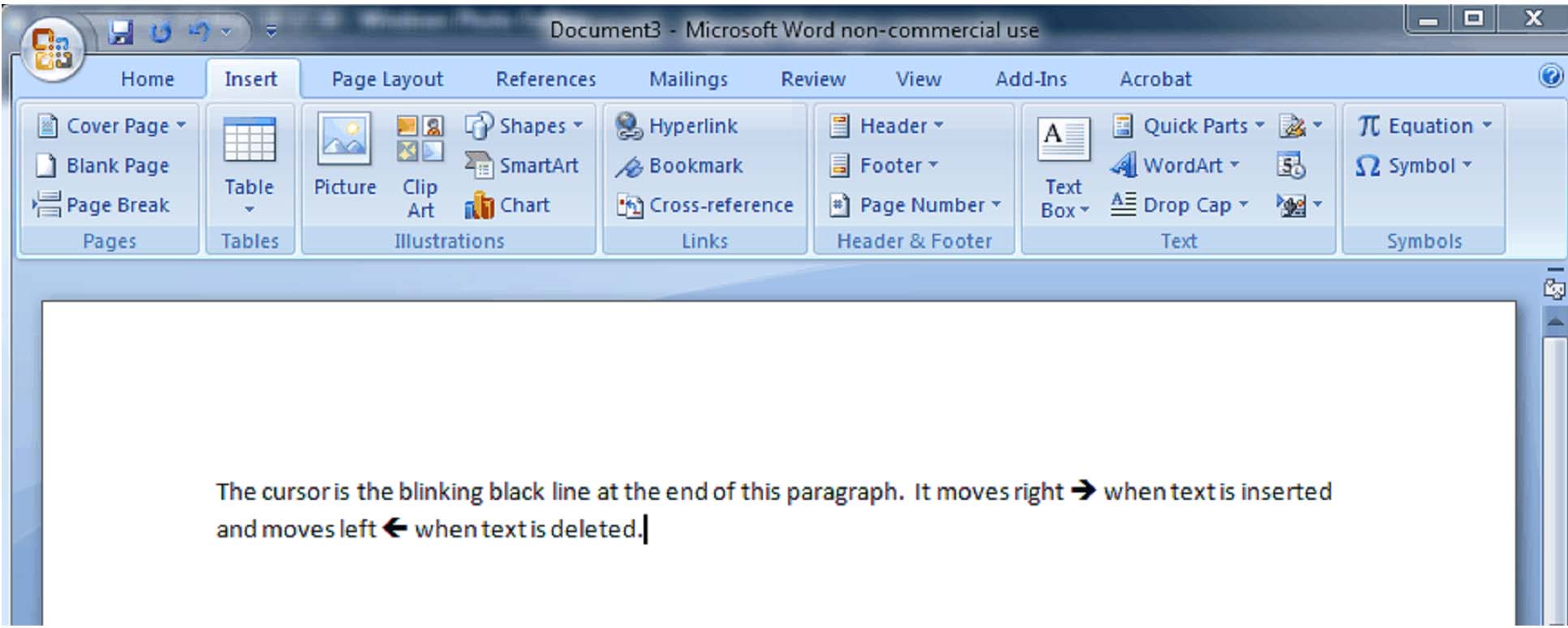
 , select Word Options
, select Word Options  then Advanced. Check «
then Advanced. Check «