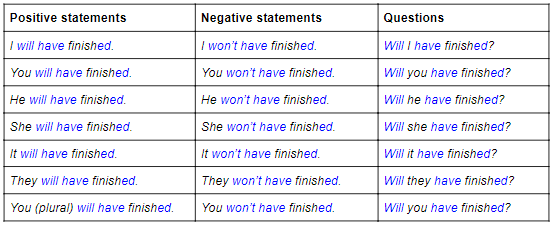
The future tense of the verb «to have» is «will have» or «shall
have»
More answers
Will have. I will have a sandwich thanks.
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: What is the future tense of ‘have’?
Write your answer…
Made with 💙 in St. Louis
Copyright ©2023 Infospace Holdings LLC, A System1 Company. All Rights Reserved. The material on this site can not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with prior written permission of Answers.
Future Perfect образуется с помощью вспомогательного глагола have в форме будущего времени (will have) и формы причастия прошедшего времени глагола (Past Participle). Способы образования предложений с правильными и неправильными глаголами разные.
— С правильными глаголами.
К форме инфинитива прибавляется окончание -ed.
— С неправильными глаголами.
Используется форма Past Participle (третья колонка таблицы неправильных глаголов).
|
Тип предложения |
Действительный залог |
Страдательный залог |
|
Утвердительное |
I (he, she, it, we, you, they) will have asked. (I (we) shall have asked.) |
I (he, she, it, we, you, they) will have been asked. (I (we) shall have been asked.) |
|
Вопросительное |
Will I (he, she, it, we, you, they) have asked? (Shall I (we) have asked?) |
Will I (he, she, it, we, you, they) have been asked? (Shall I (we) have been asked?) |
|
Отрицательное |
I (he, she, it, we, you, they) will not have asked. (I (we) shall not have asked.) |
I (he, she, it, we, you, they) will not have been asked. (I (we) shall not have been asked.) |
Случаи употребления The Future Perfect Tense
|
Действие, которое будет завершено до определенного момента в будущем, который определяется обстоятельством времени с предлогом by к, до |
I’ll have translated this text by 2 o’clock tomorrow. Я переведу этот текст завтра до 2 часов. |
|
Действие, которое завершится до другого действия в будущем, выраженного глаголом в Present Simple (c предлогом by к, до) |
I’ll have written my composition by the time you ring me up. Я напишу сочинение до того, как ты мне позвонишь. |
пройти тест на «Будущее совершенное время»
продолжить с «Временами»
вернуться к выбору в разделе «Грамматика»
Курсы английского языка по уровням
Beginner
Экспресс-курс
«I LOVE ENGLISH»
Elementary
Космический квест
«БЫСТРЫЙ СТАРТ»
Intermediate
Обычная жизнь
КЕВИНА БРАУНА
В разработке
Advanced
Продвинутый курс
«ПРОРЫВ»
Практичные советы по изучению английского языка
“Your future is whatever you make it, so make it a good one.” – Doc Brown, Back to the future.
Just like the past and present tenses, there is more than one future tense in English. These change depending on the function and what we want to say.
Today we’re going to look at four future tenses: the future simple, the future continuous, the future perfect and the future perfect continuous. We’ll show you how and when to use them. We’ll also share with you some fun videos and activities to help you understand them better.
Ready to learn? Let’s go!
The future tenses
Take a look at the four future tenses in English and how they’re used in a sentence:
1. Future Simple
Let’s start with the basics. The future simple is used to talk about a time later than now and can be used in lots of different ways.
Form
- It is made up of the verb will/won’t + base infinitive (infinitive without to).
- Because will is a modal verb it doesn’t change depending on the person doing the action.
- We can use contractions e.g. I will = I’ll.
- In the negative, we can also use will not for more emphasis.
- Won’t is more common in speech.
- In short answers we say: yes X will or no X won’t.
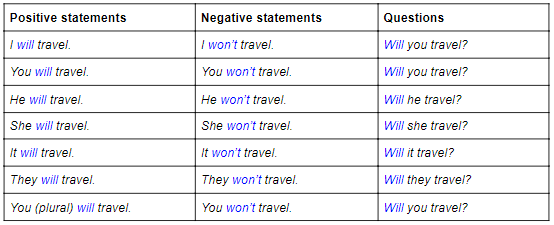
Here’s a look at the future simple in positive and negative statements and questions.
Uses and examples
- Instant or spontaneous decisions – I’m hungry. I think I’ll make a sandwich.
- Future predictions based on a belief – I’m sure you’ll pass the test.
- Promises – I won’t tell anyone your secret.
- Offers – I’ll carry your bags for you.
- Requests – Will you tell Henry I called?
- Threats – If you do that again, I’ll tell Mum.
- Future facts – I’ll be back later tonight.
Shall
We can use shall instead of will for future time references with I and we. However, it is slightly more formal.
E.g. We shall never forget this beautiful day.
It is also common to use shall in questions to make offers, suggestions or ask for advice.
E.g. Shall I carry these bags for you?
Shall I open the window?
What shall I tell Mary about the broken vase?
Be going to vs will
It’s important to note that for predictions based on evidence and for future plans we use be going to not will.
E.g. Look at those grey clouds. It’s definitely going to rain!
– What are you doing after work?
– I’m going to the gym.
Activity One
For more about the differences between will and be going to to talk about the future, watch this video from Learn English with TV Series:
2. Future continuous
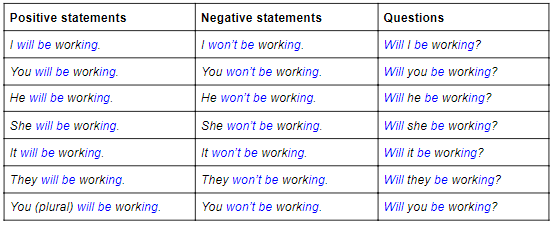
Now let’s move on to the future continuous. Generally, we use this tense to talk about things in progress at a particular time in the future. Take a look at the form:
Form
The structure of the future continuous is as follows: will/won’t + be + ing form
Uses and examples
- An action in progress at a specific time in the future (at 5pm, this time tomorrow, in two weeks, in five years time etc.). This time tomorrow, I’ll be flying to Barbados.
- An action we see as new or temporary. I’ll be working for my Dad until I find a new job.
- Predictions or guesses about future events. He’ll be coming to the party, I guess.
- Predictions about the present. She’ll be getting married right now, I imagine.
- Polite enquiries. Will you be joining us for dinner?
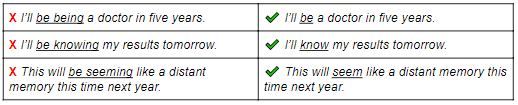
Stative verbs
It’s important to remember that some verbs cannot be used in the continuous tense. These are called stative verbs. Stative verbs describe states, feelings, thoughts and opinions. Instead of the future continuous, we use the future simple tense for these verbs. Here are some examples:
Activity two
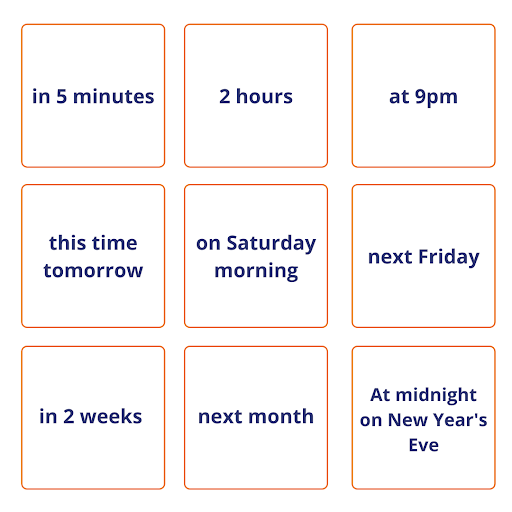
Here’s a fun activity to practise what you’ve learnt about the future continuous. All you have to do is talk about what you’ll be doing at these different points in time. Try saying them out loud or write down your answers on a piece of paper. We’ll post some possible answers at the end of this blog post.
What will you be doing…?
3. Future perfect
Once you’ve mastered the future continuous, it’s time to learn the future perfect. The future perfect is used to talk about a completed action in the future. Here’s a look at the form:
Form
- The form of the future perfect is will/won’t + have + past participle.
- Regular past participles end in -ed.
- Irregular past participles don’t follow the common conjugation pattern.
Uses and examples
- An action that will be completed before a specific time in the future. Next September, we’ll have been married for 50 years.
- Use by or by the time to mean some time before. I’ll have finished this report by the time you’re home.
- Use in, in a day’s time, in two weeks’ time, in three months’ time etc. to mean at the end of this period. In three years’ time, I’ll have completed my degree.
Activity three
Should you use has instead of have for third person in the future perfect? Here’s BBC Learn English with the answer.
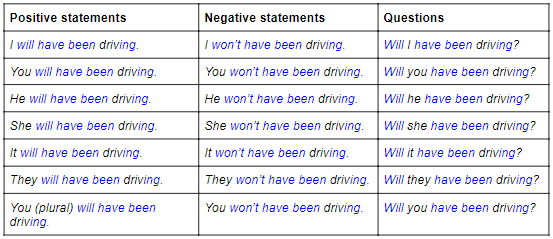
4. Future perfect continuous
We use the future perfect continuous to show that something will continue up until a particular event in the future. We normally use it to emphasise how long something will have been happening for.
Form
The form of the future perfect continuous is will/won’t + have + been + ing (present participle)
Uses and examples
- To show that something will continue up until a particular event in the future. In October, I’ll have been working here for ten years.
- To show something finished just before another time action (cause and effect). When I arrive, I’ll have been working all day, so I’ll be tired.
- With time expressions (by + then / tomorrow / next year etc., by the time, when). By the time we arrive, we’ll have been travelling for fifteen hours.
Activity four
Look at these five photos of people with different professions. Write down sentences using the future perfect continuous to describe what they will have been doing four hours into their work shift. E.g. They will have been cooking for four hours. We’ll write some examples at the end of the blog post.
Suggested Answers
Activity two
- In five minutes I’ll still be reading this blog post.
- In two hours I’ll be at home watching the TV on the sofa.
- At 9pm I’ll be cooking dinner.
- This time tomorrow I’ll be doing my English exam.
- I’ll probably be playing football on Saturday morning.
- I’ll be having dinner with friends next Friday.
- I’ll be having my operation in 2 weeks.
- I’m not sure what I’ll be doing next month.
- I’ll be saying goodbye to 2021 at midnight on New Year’s Eve.
Activity four
- A) Police officer – He’ll have been catching criminals for four hours.
- B) Doctor – She’ll have been saving lives for four hours.
- C) English Teacher – He’ll have been teaching grammar for four hours.
- D) Chefs – They’ll have been cooking for four hours.
- E) Footballer – She’ll have been kicking a ball around for four hours.
So there you have it. You’ve officially learnt the future tenses. Well done you! If you’d like to learn more grammar, check out the following blog posts:
- 4 Present tenses and how to use them
- 4 Past tenses and when to use them
And if you’d like some extra help, why not join one of our General English Courses, to practise using these tenses in conversation?
Glossary for Language Learners
Find the following words in the article and then write down any new ones you didn’t know.
to be made up of sth. (pv): to be comprised up of something.
out loud (exp): audibly.
to master sth. (v): to become an expert at something.
work shift (n): a period of time that you work.
Key
pv = phrasal verb
exp = expression
n = noun
v = verb
Study English at Oxford House Barcelona
Interested in taking an English course at Oxford House Barcelona? Check all the different English classes we can offer you or contact us for more information.
Study English at Oxford House Barcelona
Interested in taking an English course at Oxford House Barcelona? Check all the different English classes we can offer you or contact us for more information.
What Type of Word Is “Have” and What Are Its Forms?
powered by
LanguageTool
We’ll be covering the verb “to have” and its different conjugated forms. Plus, we’re also going to provide example sentences to help you better understand this irregular verb.
Quick Summary on Forms of “To Have”
- To have is an irregular verb that can be used as a main or auxiliary verb. Its forms are have, has, had, and having.
- ○ I have a lot to do tomorrow.
- ○ He has to win three games to make it to the finals.
- ○ Luis had to arrive at the airport at 3:00 PM.
- ○ We’re having a party tomorrow.
Have you ever wondered what type of word have is? Or maybe you’re here because you know it’s a verb, but want to know what type. We’ll be going over this, plus we’re also going to show you the conjugation of to have and example sentences.
What Type of Verb Is “To Have”?
To have can function as a main verb, but it can also be a helping verb (also known as an auxiliary verb). Whether you’re using it as a main verb or helping verb, the forms of to have are have, has, had, and having.
Please note that had is both the past tense and past participle, as you can see in the following table.
Conjugated Forms of “To Have”
|
Person |
Present |
Past |
Past Participle |
Present Participle |
|
I |
have |
had |
(have) had |
(am) having |
|
You |
(are) having |
|||
|
He/She/It |
has |
(has) had |
(is) having |
|
|
We |
have |
(have) had |
(are) having |
|
|
You |
||||
|
They |
“To Have” as a Main Verb
As a main verb, to have has several different uses, but it’s most commonly used to indicate possession or “to stand in a certain relationship to.”
Do you have a pencil I can borrow?
I have three brothers and one sister.
To have can also mean “to experience something.”
We had a great time.
Here are a few more uses of to have as a main verb:
1. “Consist of”
The car has many innovative features.
2. “Demonstrate a quality or feature”
They have an unusual sense of humor.
3. “Should” or “must” (just when preceding “to”)
I have to help.
4. “To show or ask if something is available”
Do you have time?
5. “To entertain in the mind” or “express a feeling”
I had a feeling something bad was going to happen.
6. “Put or keep in a position”
I had my back to her.
7. “To organize or hold an event or activity”
Let’s have a reunion soon.
“To Have” as an Auxiliary Verb
To have is one of English’s three auxiliary verbs (along with to be and to do). An auxiliary verb adds more information (such as tense, mood, and voice) to the main verb.
As an auxiliary verb, to have is used with a past participle to form future present perfect and past perfect.
The structure for using to have as an auxiliary verb that indicates present perfect tense is [“have” or “has”] + [past participle].
I have scrubbed the walls.
She has supported me all throughout my career.
The structure that indicates past perfect tense is [“had”] + [“past participle”].
Clarence had betted against the team.
To form the future perfect, follow this structure: [will “have”] + [past participle]
I will have eaten too many desserts.
Having is the continuous form of to have and can be used as either the main verb or auxiliary verb.
The children were having a playful competition.
(Main verb)
Having said that, the parents enjoyed themselves too.
(Auxiliary verb)
It’s important to note that have can function as a main verb and auxiliary verb within the same sentence. For example:
I have had several meals at that restaurant.
In this example, have is the auxiliary verb and had is the main verb. In the following example, had is also both the main verb and auxiliary.
Thomas had had a difficult time before he enrolled in the school.
Using “To Have” Correctly
As you can see, have has a plethora of uses. Therefore, it’s a word that is used quite frequently in the English language. If you find yourself overwhelmed trying to use the correct form of to have, you should use LanguageTool as your spelling and grammar checker. This multilingual writing assistant can ensure proper usage of the verb to have and check for all types of errors.
Verb tenses can be confusing! So, we’ve created this guide to help you learn the 12 basic types of verb tenses in English, their grammatical structure, and how we use them. Scroll down for paperless worksheets designed for shaping the digital classroom.
What Are The 12 Verb Tenses In English?
Tenses are vital in English for constructing sentences and phrases. There are 12 basic tenses in English, which help us figure out how an action (verb) relates to time.
English tenses are split into three broad time-related categories.
- Past
- Present
- Future
Tenses can be broken down even further. Tap on the links below and see further information about each type of verb tense.
- Present: Simple Present Tense, Present Continuous, Present Perfect, and Present Perfect Continuous.
- Past: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect Tense, and Past Perfect Continuous.
- Future: Future Simple, Future Continuous Tense, Future Perfect, and Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
Types of Tenses in English
Flip the flashcards to get a simple definition of each type of verb tense in English.
Present Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
Learning about the different present tense forms in English is important. Present tenses can be in the simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous. Read about them and then scroll down to take the present tense forms quiz. Here we have focused on the different types of present tenses in the affirmative. For a more in-depth study of each type of present tense, click the links below.
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Present Simple Tense
The simple present tense refers to an action (verb) that occurs in the present— the simple present tense deals with facts and repeated activities.
We use English personal pronouns followed by present tense verbs to form the simple present tense with regular verbs. Note: Singular third-person verbs often change, and an -s is placed at the end of the verb.
- She plays the piano.
- Sarah loves burgers.
- She speaks Spanish.
- Do you speak Spanish?
Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense or present progressive tense refers to an action or state of being. They deal with temporary actions or states and things that are happening now.
In the affirmative, we form the present continuous tense with the subject + am/ is/ are + verb-ing for regular verbs.
- I am working on the report.
- You are playing in the yard.
- What are you doing? I’m eating my dinner.
- My parents are traveling.
Present Perfect Tense
Next up is the present perfect tense! We use it to talk about present experiences that relate to the past. They can refer to present situations that will continue or new information.
In the affirmative, we form the present perfect tense with the subject + have/ has + past participle verb. To form a past participle with regular verbs, we usually add -ed as a suffix.
- The euro has decreased in value lately.
- I haven’t seen her since February.
- I haven’t played football for ages.
- She has forgotten to switch off the light again!
- Have you been to China?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous is an exciting type of tense in English. It refers to a non-specific time that began in the near past but is usually unfinished.
To form this tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + have/has + been + verb-ing.
- I have been living in France since 2018.
- He has been playing football since he was five.
- Our teacher has been talking for too long.
Present Tenses Quiz
Are you a present-tense expert? This present tense paperless worksheet will test your knowledge. Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of present tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
I have ______ living in France since 2018.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She _____ piano.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
___ you been to China?
Choose the best answer from the choices below
Past Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
The past tense generally functions to place an action or situation in the past. They are the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous. Here are some examples suitable for ESL and Grades 3-6 learners. We have focused solely on the past tense in the affirmative. For more examples in interrogative and negative, click on each type of tense below.
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
Past Simple Tense
The past simple tense or preterite refers to a completed action before now.
To form the past simple tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + verb + -ed for regular verbs. For irregular verbs like «sing,» you have to learn the past participle.
- They played soccer.
- She sang songs at our Christmas concert.
Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense or past progressive refers to an action that is ongoing or continues. It is often used to describe something that happened in the past.
To form the past continuous English tense, add the subject + was/were + verb-ing. This is for affirmative sentences, for negative, and for interrogative check out our past continuous page.
- I was making lunch when they arrived.
- I was singing when the doorbell rang.
- She was laughing when she fell over.
Past Perfect Tense
We refer to the past perfect tense when discussing an action completed at a particular time in the past.
To form the past perfect tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + had + past participle + object. Sometimes adverbs are used to give even more information, like ‘just.’
- He had just broken up with her.
- If only I had known how to solve the equation.
- She had almost finished.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
We use the past perfect continuous tense to talk about actions or events that began before a specific time in the past and were ongoing up to that time. It can also be used to describe the cause of a past event.
To form the past perfect continuous tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + had + been + verb-ing
- She had been studying when her mom called her.
- They had been traveling when the doctor called them.
- He was tired because he had been running.
Past Tenses Quiz
Want to test your knowledge of the different past tenses? Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of past tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She had been ______ when her mom called her.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She ____ almost finished.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She _____ laughing when she fell over.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
Future Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
A future tense expresses an action that hasn’t happened yet, but might in the future. Here we will talk about future tenses in the affirmative. If you want to learn more about future tenses in the interrogative or negative, check out the future tense guides using the links below.
- Future Simple
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
Future Simple Tense
The future simple tense is one of 5 future tenses. We used it to talk about events that haven’t come about yet.
We use the subject + will / shall + the base verb
- This year, we will go to Disneyland.
- We will come.
- I will go to Japan.
You can also form this tense with «going to,» but this is for more informal language.
Future Continuous Tense
We use the future continuous tense or future progressive when discussing an action that will start in the future and continue for a specific amount of time.
To form the future continuous tense, we use will + be + the present participle of the verb + ing as the suffix.
- We will be buying a house next year.
- We will be going to college.
- They will be starting school next year.
We use the future continuous tense with action verbs and a few stative verbs.
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used when discussing something that will be finished by a specific time in the future. We add expressions of time to help the sentence.
To form the future perfect in the affirmative, we use the subject + will / shall + have + past participle.
- By the year 2050, we will have tackled climate change.
- He will have completed his homework by next week.
- By next year, she will have graduated.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense or future progressive is used to talk about an action or event that will continue up to a specific time in the future. Think of it like projecting yourself to some time in the future.
To form this tense, we use the subject + will / shall + have + been + verb-ing. You can also add an expression of time.
- In January, I will have been studying for 10 years.
- I will have been living in my parent’s house for eighteen years by the time I graduate.
Future Tenses Quiz
Taken it all in? Try our future tenses quiz. Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of future tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct future tense for the sentence?
By next year she ____ have graduated.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
We will be _____ to college.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
I _____ to Japan.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
See? Studying the tenses in English doesn’t have to be a headache. To explore more on these topics in detail, click on ELA-related content suitable for grades 4-6+ and ESL learners. We’ve got flashcards, quizzes, and much more to bring inspiration to homeschooling, online tutoring, and for students and your classrooms.