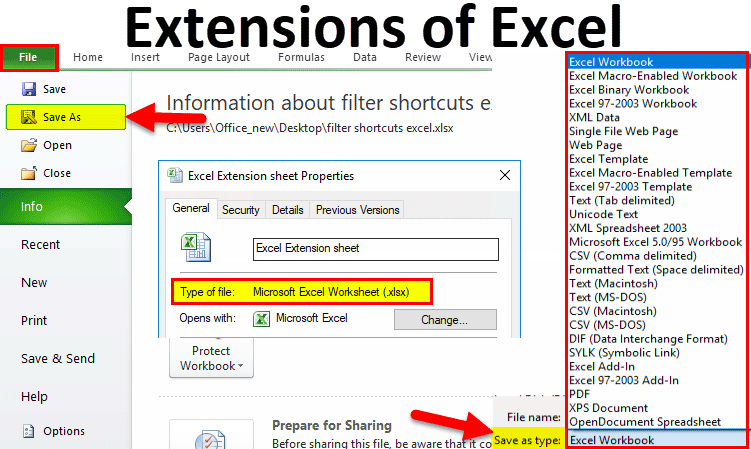
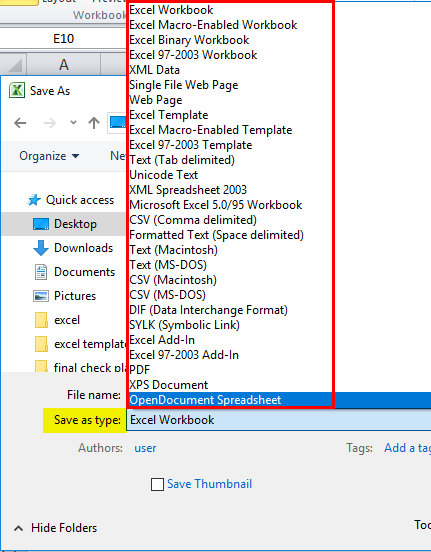
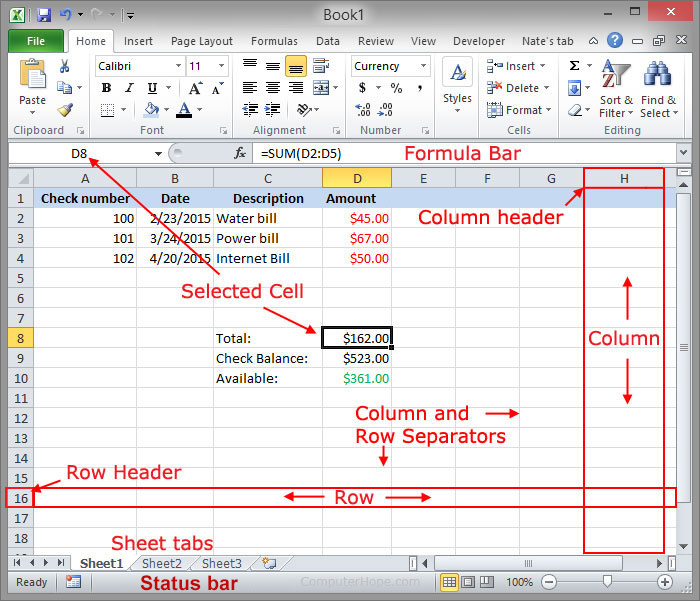
You can save an Excel file in another file format by clicking the File > Save As. The file formats that are available in the Save As dialog box vary, depending on what type of sheet is active (a worksheet, chart sheet, or other type of sheet).
Note: Whenever you save a file in another file format, some of its formatting, data, and features might not be transferred.
To open a file that was created in another file format, either in an earlier version of Excel or in another program, click File > Open. If you open an Excel 97-2003 workbook, it automatically opens in Compatibility Mode. To take advantage of the new features of Excel 2010, you can save the workbook to an Excel 2010 file format. However, you also have the option to continue to work in Compatibility Mode, which retains the original file format for backward compatibility.
Excel file formats
|
Format |
Extension |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Excel Workbook |
.xlsx |
The default XML-based file format for Excel 2010 and Excel 2007. Cannot store Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macro code or Microsoft Office Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
|
Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (code) |
.xlsm |
The XML-based and macro-enabled file format for Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, and Excel 2007. Stores VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
|
Excel Binary Workbook |
.xlsb |
The binary file format (BIFF12) for Excel 2010 and Excel 2007. |
|
Template |
.xltx |
The default file format for an Excel template for Excel 2010 and Excel 2007. Cannot store VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
|
Template (code) |
.xltm |
The macro-enabled file format for an Excel template Excel 2010 and Excel 2007. Stores VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
|
Excel 97- Excel 2003 Workbook |
.xls |
The Excel 97 — Excel 2003 Binary file format (BIFF8). |
|
Excel 97- Excel 2003 Template |
.xlt |
The Excel 97 — Excel 2003 Binary file format (BIFF8) for an Excel template. |
|
Microsoft Excel 5.0/95 Workbook |
.xls |
The Excel 5.0/95 Binary file format (BIFF5). |
|
XML Spreadsheet 2003 |
.xml |
XML Spreadsheet 2003 file format (XMLSS). |
|
XML Data |
.xml |
XML Data format. |
|
Excel Add-In |
.xlam |
The XML-based and macro-enabled Add-In format for Excel 2010 and Excel 2007. An Add-In is a supplemental program that is designed to run additional code. Supports the use of VBA projects and Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
|
Excel 97-2003 Add-In |
.xla |
The Excel 97-2003 Add-In, a supplemental program that is designed to run additional code. Supports the use of VBA projects. |
|
Excel 4.0 Workbook |
.xlw |
An Excel 4.0 file format that saves only worksheets, chart sheets, and macro sheets. You can open a workbook in this file format in Excel 2010, but you cannot save an Excel file to this file format. |
|
Works 6.0-9.0 spreadsheet |
.xlr |
Spreadsheet saved in Microsoft Works 6.0-9.0. Note: This format is supported in Excel Starter only. |
Text file formats
|
Format |
Extension |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Formatted Text (Space-delimited) |
.prn |
Lotus space-delimited format. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
Text (Tab-delimited) |
.txt |
Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on another Microsoft Windows operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
Text (Macintosh) |
.txt |
Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on the Macintosh operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
Text (MS-DOS) |
.txt |
Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
Unicode Text |
.txt |
Saves a workbook as Unicode text, a character encoding standard that was developed by the Unicode Consortium. |
|
CSV (comma delimited) |
.csv |
Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on another Windows operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
CSV (Macintosh) |
.csv |
Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on the Macintosh operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
CSV (MS-DOS) |
.csv |
Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
DIF |
.dif |
Data Interchange Format. Saves only the active sheet. |
|
SYLK |
.slk |
Symbolic Link Format. Saves only the active sheet. |
Note: If you save a workbook in any text format, all formatting is lost.
Other file formats
|
Format |
Extension |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
DBF 3, DBF 4 |
.dbf |
dBase III and IV. You can open these files formats in Excel, but you cannot save an Excel file to dBase format. |
|
OpenDocument Spreadsheet |
.ods |
OpenDocument Spreadsheet. You can save Excel 2010 files so they can be opened in spreadsheet applications that use the OpenDocument Spreadsheet format, such as Google Docs and OpenOffice.org Calc. You can also open spreadsheets in the .ods format in Excel 2010. Formatting might be lost when saving and opening .ods files. |
|
|
|
Portable Document Format (PDF). This file format preserves document formatting and enables file sharing. When the PDF format file is viewed online or printed, it retains the format that you intended. Data in the file cannot be easily changed. The PDF format is also useful for documents that will be reproduced by using commercial printing methods. Note: This format is not supported in Excel 2007. |
|
XPS Document |
.xps |
XML Paper Specification (XPS). This file format preserves document formatting and enables file sharing. When the XPS file is viewed online or printed, it retains exactly the format that you intended, and the data in the file cannot be easily changed. Note: This format is not supported in Excel 2007. |
File formats that use the Clipboard
You can paste data from the Microsoft Office Clipboard into Excel by using the Paste or Paste Special command (Home tab, Clipboard group, Paste button) if the Office Clipboard data is in one of the following formats.
|
Format |
Extension |
Clipboard type identifiers |
|---|---|---|
|
Picture |
.wmf or .emf |
Pictures in Windows Metafile Format (WMF) or Windows Enhanced Metafile Format (EMF). Note If you copy a Windows metafile picture from another program, Excel pastes the picture as an enhanced metafile. |
|
Bitmap |
.bmp |
Pictures stored in Bitmap format (BMP). |
|
Microsoft Excel file formats |
.xls |
Binary file formats for Excel versions 5.0/95 (BIFF5), Excel 97-2003 (BIFF8), and Excel 2010 (BIFF12). |
|
SYLK |
.slk |
Symbolic Link Format. |
|
DIF |
.dif |
Data Interchange Format. |
|
Text (tab-delimited) |
.txt |
Tab-separated text format. |
|
CSV (Comma-delimited) |
.csv |
Comma-separated values format. |
|
Formatted text (Space-delimited) |
.rtf |
Rich Text Format (RTF). Only from Excel. |
|
Embedded object |
.gif, .jpg, .doc, .xls, or .bmp |
Microsoft Excel objects, objects from properly registered programs that support OLE 2.0 (OwnerLink), and Picture or another presentation format. |
|
Linked object |
.gif, .jpg, .doc, .xls, or .bmp |
OwnerLink, ObjectLink, Link, Picture, or other format. |
|
Office drawing object |
.emf |
Office drawing object format or Picture (Windows enhanced metafile format, EMF). |
|
Text |
.txt |
Display Text, OEM Text. |
|
Single File Web Page |
.mht, .mhtml |
Single File Web Page (MHT or MHTML). This file format integrates inline graphics, applets, linked documents, and other supporting items referenced in the document. Note: This format is not supported in Excel 2007. |
|
Web Page |
.htm, .html |
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Note: When you copy text from another program, Excel pastes the text in HTML format, regardless of the format of the original text. |
File formats that are not supported in Excel
The following file formats are no longer supported in Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel Starter, and Excel 2007. You cannot open or save files in these file formats.
|
Format |
Extension |
Clipboard type identifiers |
|---|---|---|
|
Excel Chart |
.xlc |
Excel 2.0, 3.0, and 2.x file formats |
|
WK1, FMT, WK2, WK3, FM3, WK4 |
.wk1, .wk2, .wk3, .wk4, .wks |
Lotus 1-2-3 file formats (all versions) |
|
Microsoft Works |
.wks |
Microsoft Works file format (all versions) |
|
DBF 2 |
.dbf |
DBASE II file format |
|
WQ1 |
.wq1 |
Quattro Pro for MS-DOS file format |
|
WB1, WB3 |
.wb1, .wb3 |
Quattro Pro 5.0 and 7.0 for Windows. |
File formats that are not supported in Excel Starter
Additionally, the following file formats are no longer supported in Excel Starter. You cannot open or save files in these file formats.
|
Format |
Extension |
|---|---|
|
Excel 97-2003 Add-In |
.xla |
|
Excel Add-In |
.xlam |
|
Data source name |
.dsn |
|
Access MDE database |
.mde |
|
Office Data Connection |
.odc |
|
Data Link File |
.udl |
Opening or viewing unsupported file formats
If a file format that you want to use is not supported in Excel, you can try the following:
-
Search the Internet for a company that makes file format converters for file formats that are not supported in Excel.
-
Save to a file format that another program supports and then export from that program into a file format that Excel supports.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Related Topics
Excel formatting and features that are not transferred to other file formats
 |
|
A simple bar graph being created in Excel, running on Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | November 19, 1987; 35 years ago |
| Stable release |
2103 (16.0.13901.20400) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end)[2] |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Trialware[3] |
| Website | microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/excel |
Excel for Mac (version 16.67), running on macOS Big Sur 11.5.2 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | September 30, 1985; 37 years ago |
| Stable release |
16.70 (Build 23021201) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end), Objective-C (API/UI)[2] |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/mac |

Excel for Android running on Android 13 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
16.0.14729.20146 |
| Operating system | Android Oreo and later |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/en-us/excel |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
2.70.1 |
| Operating system | iOS 15 or later iPadOS 15 or later |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/en-us/excel |
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft 365 suite of software.
Features
Basic operation
Microsoft Excel has the basic features of all spreadsheets,[7] using a grid of cells arranged in numbered rows and letter-named columns to organize data manipulations like arithmetic operations. It has a battery of supplied functions to answer statistical, engineering, and financial needs. In addition, it can display data as line graphs, histograms and charts, and with a very limited three-dimensional graphical display. It allows sectioning of data to view its dependencies on various factors for different perspectives (using pivot tables and the scenario manager).[8] A PivotTable is a tool for data analysis. It does this by simplifying large data sets via PivotTable fields. It has a programming aspect, Visual Basic for Applications, allowing the user to employ a wide variety of numerical methods, for example, for solving differential equations of mathematical physics,[9][10] and then reporting the results back to the spreadsheet. It also has a variety of interactive features allowing user interfaces that can completely hide the spreadsheet from the user, so the spreadsheet presents itself as a so-called application, or decision support system (DSS), via a custom-designed user interface, for example, a stock analyzer,[11] or in general, as a design tool that asks the user questions and provides answers and reports.[12][13] In a more elaborate realization, an Excel application can automatically poll external databases and measuring instruments using an update schedule,[14] analyze the results, make a Word report or PowerPoint slide show, and e-mail these presentations on a regular basis to a list of participants. Excel was not designed to be used as a database.[citation needed]
Microsoft allows for a number of optional command-line switches to control the manner in which Excel starts.[15]
Functions
Excel 2016 has 484 functions.[16] Of these, 360 existed prior to Excel 2010. Microsoft classifies these functions in 14 categories. Of the 484 current functions, 386 may be called from VBA as methods of the object «WorksheetFunction»[17] and 44 have the same names as VBA functions.[18]
With the introduction of LAMBDA, Excel will become Turing complete.[19]
Macro programming
VBA programming
Use of a user-defined function sq(x) in Microsoft Excel. The named variables x & y are identified in the Name Manager. The function sq is introduced using the Visual Basic editor supplied with Excel.
Subroutine in Excel calculates the square of named column variable x read from the spreadsheet, and writes it into the named column variable y.
The Windows version of Excel supports programming through Microsoft’s Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), which is a dialect of Visual Basic. Programming with VBA allows spreadsheet manipulation that is awkward or impossible with standard spreadsheet techniques. Programmers may write code directly using the Visual Basic Editor (VBE), which includes a window for writing code, debugging code, and code module organization environment. The user can implement numerical methods as well as automating tasks such as formatting or data organization in VBA[20] and guide the calculation using any desired intermediate results reported back to the spreadsheet.
VBA was removed from Mac Excel 2008, as the developers did not believe that a timely release would allow porting the VBA engine natively to Mac OS X. VBA was restored in the next version, Mac Excel 2011,[21] although the build lacks support for ActiveX objects, impacting some high level developer tools.[22]
A common and easy way to generate VBA code is by using the Macro Recorder.[23] The Macro Recorder records actions of the user and generates VBA code in the form of a macro. These actions can then be repeated automatically by running the macro. The macros can also be linked to different trigger types like keyboard shortcuts, a command button or a graphic. The actions in the macro can be executed from these trigger types or from the generic toolbar options. The VBA code of the macro can also be edited in the VBE. Certain features such as loop functions and screen prompt by their own properties, and some graphical display items, cannot be recorded but must be entered into the VBA module directly by the programmer. Advanced users can employ user prompts to create an interactive program, or react to events such as sheets being loaded or changed.
Macro Recorded code may not be compatible with Excel versions. Some code that is used in Excel 2010 cannot be used in Excel 2003. Making a Macro that changes the cell colors and making changes to other aspects of cells may not be backward compatible.
VBA code interacts with the spreadsheet through the Excel Object Model,[24] a vocabulary identifying spreadsheet objects, and a set of supplied functions or methods that enable reading and writing to the spreadsheet and interaction with its users (for example, through custom toolbars or command bars and message boxes). User-created VBA subroutines execute these actions and operate like macros generated using the macro recorder, but are more flexible and efficient.
History
From its first version Excel supported end-user programming of macros (automation of repetitive tasks) and user-defined functions (extension of Excel’s built-in function library). In early versions of Excel, these programs were written in a macro language whose statements had formula syntax and resided in the cells of special-purpose macro sheets (stored with file extension .XLM in Windows.) XLM was the default macro language for Excel through Excel 4.0.[25] Beginning with version 5.0 Excel recorded macros in VBA by default but with version 5.0 XLM recording was still allowed as an option. After version 5.0 that option was discontinued. All versions of Excel, including Excel 2021 are capable of running an XLM macro, though Microsoft discourages their use.[26]
Charts
Graph made using Microsoft Excel
Excel supports charts, graphs, or histograms generated from specified groups of cells. It also supports Pivot Charts that allow for a chart to be linked directly to a Pivot table. This allows the chart to be refreshed with the Pivot Table. The generated graphic component can either be embedded within the current sheet or added as a separate object.
These displays are dynamically updated if the content of cells changes. For example, suppose that the important design requirements are displayed visually; then, in response to a user’s change in trial values for parameters, the curves describing the design change shape, and their points of intersection shift, assisting the selection of the best design.
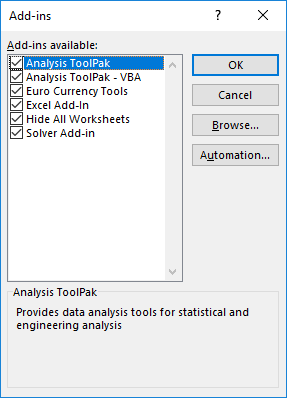
Add-ins
Additional features are available using add-ins. Several are provided with Excel, including:
- Analysis ToolPak: Provides data analysis tools for statistical and engineering analysis (includes analysis of variance and regression analysis)
- Analysis ToolPak VBA: VBA functions for Analysis ToolPak
- Euro Currency Tools: Conversion and formatting for euro currency
- Solver Add-In: Tools for optimization and equation solving
Data storage and communication
Number of rows and columns
Versions of Excel up to 7.0 had a limitation in the size of their data sets of 16K (214 = 16384) rows. Versions 8.0 through 11.0 could handle 64K (216 = 65536) rows and 256 columns (28 as label ‘IV’). Version 12.0 onwards, including the current Version 16.x, can handle over 1M (220 = 1048576) rows, and 16384 (214, labeled as column ‘XFD’) columns.[27]
File formats
| Filename extension |
.xls, (.xlsx, .xlsm, .xlsb — Excel 2007) |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
application/vnd.ms-excel |
| Uniform Type Identifier (UTI) | com.microsoft.excel.xls |
| Developed by | Microsoft |
| Type of format | Spreadsheet |
Microsoft Excel up until 2007 version used a proprietary binary file format called Excel Binary File Format (.XLS) as its primary format.[28] Excel 2007 uses Office Open XML as its primary file format, an XML-based format that followed after a previous XML-based format called «XML Spreadsheet» («XMLSS»), first introduced in Excel 2002.[29]
Although supporting and encouraging the use of new XML-based formats as replacements, Excel 2007 remained backwards-compatible with the traditional, binary formats. In addition, most versions of Microsoft Excel can read CSV, DBF, SYLK, DIF, and other legacy formats. Support for some older file formats was removed in Excel 2007.[30] The file formats were mainly from DOS-based programs.
Binary
OpenOffice.org has created documentation of the Excel format. Two epochs of the format exist: the 97-2003 OLE format, and the older stream format.[31] Microsoft has made the Excel binary format specification available to freely download.[32]
XML Spreadsheet
The XML Spreadsheet format introduced in Excel 2002[29] is a simple, XML based format missing some more advanced features like storage of VBA macros. Though the intended file extension for this format is .xml, the program also correctly handles XML files with .xls extension. This feature is widely used by third-party applications (e.g. MySQL Query Browser) to offer «export to Excel» capabilities without implementing binary file format. The following example will be correctly opened by Excel if saved either as Book1.xml or Book1.xls:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <Workbook xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:o="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" xmlns:x="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:excel" xmlns:ss="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40"> <Worksheet ss:Name="Sheet1"> <Table ss:ExpandedColumnCount="2" ss:ExpandedRowCount="2" x:FullColumns="1" x:FullRows="1"> <Row> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Name</Data></Cell> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Example</Data></Cell> </Row> <Row> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Value</Data></Cell> <Cell><Data ss:Type="Number">123</Data></Cell> </Row> </Table> </Worksheet> </Workbook>
Current file extensions
Microsoft Excel 2007, along with the other products in the Microsoft Office 2007 suite, introduced new file formats. The first of these (.xlsx) is defined in the Office Open XML (OOXML) specification.
| Format | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Excel Workbook | .xlsx
|
The default Excel 2007 and later workbook format. In reality, a ZIP compressed archive with a directory structure of XML text documents. Functions as the primary replacement for the former binary .xls format, although it does not support Excel macros for security reasons. Saving as .xlsx offers file size reduction over .xls[33] |
| Excel Macro-enabled Workbook | .xlsm
|
As Excel Workbook, but with macro support. |
| Excel Binary Workbook | .xlsb
|
As Excel Macro-enabled Workbook, but storing information in binary form rather than XML documents for opening and saving documents more quickly and efficiently. Intended especially for very large documents with tens of thousands of rows, and/or several hundreds of columns. This format is very useful for shrinking large Excel files as is often the case when doing data analysis. |
| Excel Macro-enabled Template | .xltm
|
A template document that forms a basis for actual workbooks, with macro support. The replacement for the old .xlt format. |
| Excel Add-in | .xlam
|
Excel add-in to add extra functionality and tools. Inherent macro support because of the file purpose. |
Old file extensions
| Format | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet | .xls
|
Main spreadsheet format which holds data in worksheets, charts, and macros |
| Add-in (VBA) | .xla
|
Adds custom functionality; written in VBA |
| Toolbar | .xlb
|
The file extension where Microsoft Excel custom toolbar settings are stored. |
| Chart | .xlc
|
A chart created with data from a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that only saves the chart. To save the chart and spreadsheet save as .XLS. XLC is not supported in Excel 2007 or in any newer versions of Excel. |
| Dialog | .xld
|
Used in older versions of Excel. |
| Archive | .xlk
|
A backup of an Excel Spreadsheet |
| Add-in (DLL) | .xll
|
Adds custom functionality; written in C++/C, Fortran, etc. and compiled in to a special dynamic-link library |
| Macro | .xlm
|
A macro is created by the user or pre-installed with Excel. |
| Template | .xlt
|
A pre-formatted spreadsheet created by the user or by Microsoft Excel. |
| Module | .xlv
|
A module is written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) for Microsoft Excel |
| Library | .DLL
|
Code written in VBA may access functions in a DLL, typically this is used to access the Windows API |
| Workspace | .xlw
|
Arrangement of the windows of multiple Workbooks |
Using other Windows applications
Windows applications such as Microsoft Access and Microsoft Word, as well as Excel can communicate with each other and use each other’s capabilities. The most common are Dynamic Data Exchange: although strongly deprecated by Microsoft, this is a common method to send data between applications running on Windows, with official MS publications referring to it as «the protocol from hell».[34] As the name suggests, it allows applications to supply data to others for calculation and display. It is very common in financial markets, being used to connect to important financial data services such as Bloomberg and Reuters.
OLE Object Linking and Embedding allows a Windows application to control another to enable it to format or calculate data. This may take on the form of «embedding» where an application uses another to handle a task that it is more suited to, for example a PowerPoint presentation may be embedded in an Excel spreadsheet or vice versa.[35][36][37][38]
Using external data
Excel users can access external data sources via Microsoft Office features such as (for example) .odc connections built with the Office Data Connection file format. Excel files themselves may be updated using a Microsoft supplied ODBC driver.
Excel can accept data in real-time through several programming interfaces, which allow it to communicate with many data sources such as Bloomberg and Reuters (through addins such as Power Plus Pro).
- DDE: «Dynamic Data Exchange» uses the message passing mechanism in Windows to allow data to flow between Excel and other applications. Although it is easy for users to create such links, programming such links reliably is so difficult that Microsoft, the creators of the system, officially refer to it as «the protocol from hell».[34] In spite of its many issues DDE remains the most common way for data to reach traders in financial markets.
- Network DDE Extended the protocol to allow spreadsheets on different computers to exchange data. Starting with Windows Vista, Microsoft no longer supports the facility.[39]
- Real Time Data: RTD although in many ways technically superior to DDE, has been slow to gain acceptance, since it requires non-trivial programming skills, and when first released was neither adequately documented nor supported by the major data vendors.[40][41]
Alternatively, Microsoft Query provides ODBC-based browsing within Microsoft Excel.[42][43][44]
Export and migration of spreadsheets
Programmers have produced APIs to open Excel spreadsheets in a variety of applications and environments other than Microsoft Excel. These include opening Excel documents on the web using either ActiveX controls, or plugins like the Adobe Flash Player. The Apache POI opensource project provides Java libraries for reading and writing Excel spreadsheet files.
Password protection
Microsoft Excel protection offers several types of passwords:
- Password to open a document[45]
- Password to modify a document[46]
- Password to unprotect the worksheet
- Password to protect workbook
- Password to protect the sharing workbook[47]
All passwords except password to open a document can be removed instantly regardless of the Microsoft Excel version used to create the document. These types of passwords are used primarily for shared work on a document. Such password-protected documents are not encrypted, and a data sources from a set password is saved in a document’s header. Password to protect workbook is an exception – when it is set, a document is encrypted with the standard password «VelvetSweatshop», but since it is known to the public, it actually does not add any extra protection to the document. The only type of password that can prevent a trespasser from gaining access to a document is password to open a document. The cryptographic strength of this kind of protection depends strongly on the Microsoft Excel version that was used to create the document.
In Microsoft Excel 95 and earlier versions, the password to open is converted to a 16-bit key that can be instantly cracked. In Excel 97/2000 the password is converted to a 40-bit key, which can also be cracked very quickly using modern equipment. As regards services that use rainbow tables (e.g. Password-Find), it takes up to several seconds to remove protection. In addition, password-cracking programs can brute-force attack passwords at a rate of hundreds of thousands of passwords a second, which not only lets them decrypt a document but also find the original password.
In Excel 2003/XP the encryption is slightly better – a user can choose any encryption algorithm that is available in the system (see Cryptographic Service Provider). Due to the CSP, an Excel file cannot be decrypted, and thus the password to open cannot be removed, though the brute-force attack speed remains quite high. Nevertheless, the older Excel 97/2000 algorithm is set by the default. Therefore, users who do not change the default settings lack reliable protection of their documents.
The situation changed fundamentally in Excel 2007, where the modern AES algorithm with a key of 128 bits started being used for decryption, and a 50,000-fold use of the hash function SHA1 reduced the speed of brute-force attacks down to hundreds of passwords per second. In Excel 2010, the strength of the protection by the default was increased two times due to the use of a 100,000-fold SHA1 to convert a password to a key.
Other platforms
Excel for mobile
Excel Mobile is a spreadsheet program that can edit XLSX files. It can edit and format text in cells, calculate formulas, search within the spreadsheet, sort rows and columns, freeze panes, filter the columns, add comments, and create charts. It cannot add columns or rows except at the edge of the document, rearrange columns or rows, delete rows or columns, or add spreadsheet tabs.[48][49][50][51][52][53] The 2007 version has the ability to use a full-screen mode to deal with limited screen resolution, as well as split panes to view different parts of a worksheet at one time.[51] Protection settings, zoom settings, autofilter settings, certain chart formatting, hidden sheets, and other features are not supported on Excel Mobile, and will be modified upon opening and saving a workbook.[52] In 2015, Excel Mobile became available for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile on Windows Store.[54][55]
Excel for the web
Excel for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft Excel available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Word and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Excel for the web can display most of the features available in the desktop versions of Excel, although it may not be able to insert or edit them. Certain data connections are not accessible on Excel for the web, including with charts that may use these external connections. Excel for the web also cannot display legacy features, such as Excel 4.0 macros or Excel 5.0 dialog sheets. There are also small differences between how some of the Excel functions work.[56]
Microsoft Excel Viewer
Microsoft Excel Viewer was a freeware program for Microsoft Windows for viewing and printing spreadsheet documents created by Excel.[57] Microsoft retired the viewer in April 2018 with the last security update released in February 2019 for Excel Viewer 2007 (SP3).[58][59]
The first version released by Microsoft was Excel 97 Viewer.[60][61] Excel 97 Viewer was supported in Windows CE for Handheld PCs.[62] In October 2004, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2003.[63] In September 2007, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2003 Service Pack 3 (SP3).[64] In January 2008, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 (featuring a non-collapsible Ribbon interface).[65] In April 2009, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 2 (SP2).[66] In October 2011, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 3 (SP3).[67]
Microsoft advises to view and print Excel files for free to use the Excel Mobile application for Windows 10 and for Windows 7 and Windows 8 to upload the file to OneDrive and use Excel for the web with a Microsoft account to open them in a browser.[58][68]
Quirks
In addition to issues with spreadsheets in general, other problems specific to Excel include numeric precision, misleading statistics functions, mod function errors, date limitations and more.
Numeric precision
Excel maintains 15 figures in its numbers, but they are not always accurate: the bottom line should be the same as the top line.
Despite the use of 15-figure precision, Excel can display many more figures (up to thirty) upon user request. But the displayed figures are not those actually used in its computations, and so, for example, the difference of two numbers may differ from the difference of their displayed values. Although such departures are usually beyond the 15th decimal, exceptions do occur, especially for very large or very small numbers. Serious errors can occur if decisions are made based upon automated comparisons of numbers (for example, using the Excel If function), as equality of two numbers can be unpredictable.[citation needed]
In the figure, the fraction 1/9000 is displayed in Excel. Although this number has a decimal representation that is an infinite string of ones, Excel displays only the leading 15 figures. In the second line, the number one is added to the fraction, and again Excel displays only 15 figures. In the third line, one is subtracted from the sum using Excel. Because the sum in the second line has only eleven 1’s after the decimal, the difference when 1 is subtracted from this displayed value is three 0’s followed by a string of eleven 1’s. However, the difference reported by Excel in the third line is three 0’s followed by a string of thirteen 1’s and two extra erroneous digits. This is because Excel calculates with about half a digit more than it displays.
Excel works with a modified 1985 version of the IEEE 754 specification.[69] Excel’s implementation involves conversions between binary and decimal representations, leading to accuracy that is on average better than one would expect from simple fifteen digit precision, but that can be worse. See the main article for details.
Besides accuracy in user computations, the question of accuracy in Excel-provided functions may be raised. Particularly in the arena of statistical functions, Excel has been criticized for sacrificing accuracy for speed of calculation.[70][71]
As many calculations in Excel are executed using VBA, an additional issue is the accuracy of VBA, which varies with variable type and user-requested precision.[72]
Statistical functions
The accuracy and convenience of statistical tools in Excel has been criticized,[73][74][75][76][77] as mishandling missing data, as returning incorrect values due to inept handling of round-off and large numbers, as only selectively updating calculations on a spreadsheet when some cell values are changed, and as having a limited set of statistical tools. Microsoft has announced some of these issues are addressed in Excel 2010.[78]
Excel MOD function error
Excel has issues with modulo operations. In the case of excessively large results, Excel will return the error warning #NUM! instead of an answer.[79]
Fictional leap day in the year 1900
Excel includes February 29, 1900, incorrectly treating 1900 as a leap year, even though e.g. 2100 is correctly treated as a non-leap year.[80][81] The bug originated from Lotus 1-2-3 (deliberately implemented to save computer memory), and was also purposely implemented in Excel, for the purpose of bug compatibility.[82] This legacy has later been carried over into Office Open XML file format.[83]
Thus a (not necessarily whole) number greater than or equal to 61 interpreted as a date and time are the (real) number of days after December 30, 1899, 0:00, a non-negative number less than 60 is the number of days after December 31, 1899, 0:00, and numbers with whole part 60 represent the fictional day.
Date range
Excel supports dates with years in the range 1900–9999, except that December 31, 1899, can be entered as 0 and is displayed as 0-jan-1900.
Converting a fraction of a day into hours, minutes and days by treating it as a moment on the day January 1, 1900, does not work for a negative fraction.[84]
Conversion problems
Entering text that happens to be in a form that is interpreted as a date, the text can be unintentionally changed to a standard date format. A similar problem occurs when a text happens to be in the form of a floating-point notation of a number. In these cases the original exact text cannot be recovered from the result. Formatting the cell as TEXT before entering ambiguous text prevents Excel from converting to a date.
This issue has caused a well known problem in the analysis of DNA, for example in bioinformatics. As first reported in 2004,[85] genetic scientists found that Excel automatically and incorrectly converts certain gene names into dates. A follow-up study in 2016 found many peer reviewed scientific journal papers had been affected and that «Of the selected journals, the proportion of published articles with Excel files containing gene lists that are affected by gene name errors is 19.6 %.»[86] Excel parses the copied and pasted data and sometimes changes them depending on what it thinks they are. For example, MARCH1 (Membrane Associated Ring-CH-type finger 1) gets converted to the date March 1 (1-Mar) and SEPT2 (Septin 2) is converted into September 2 (2-Sep) etc.[87] While some secondary news sources[88] reported this as a fault with Excel, the original authors of the 2016 paper placed the blame with the researchers misusing Excel.[86][89]
In August 2020 the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) published new guidelines in the journal Nature regarding gene naming in order to avoid issues with «symbols that affect data handling and retrieval.» So far 27 genes have been renamed, including changing MARCH1 to MARCHF1 and SEPT1 to SEPTIN1 in order to avoid accidental conversion of the gene names into dates.[90]
Errors with large strings
The following functions return incorrect results when passed a string longer than 255 characters:[91]
type()incorrectly returns 16, meaning «Error value»IsText(), when called as a method of the VBA objectWorksheetFunction(i.e.,WorksheetFunction.IsText()in VBA), incorrectly returns «false».
Filenames
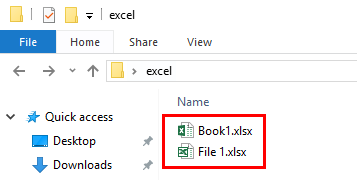
Microsoft Excel will not open two documents with the same name and instead will display the following error:
- A document with the name ‘%s’ is already open. You cannot open two documents with the same name, even if the documents are in different folders. To open the second document, either close the document that is currently open, or rename one of the documents.[92]
The reason is for calculation ambiguity with linked cells. If there is a cell ='[Book1.xlsx]Sheet1'!$G$33, and there are two books named «Book1» open, there is no way to tell which one the user means.[93]
Versions
Early history
Microsoft originally marketed a spreadsheet program called Multiplan in 1982. Multiplan became very popular on CP/M systems, but on MS-DOS systems it lost popularity to Lotus 1-2-3. Microsoft released the first version of Excel for the Macintosh on September 30, 1985, and the first Windows version was 2.05 (to synchronize with the Macintosh version 2.2) on November 19, 1987.[94][95] Lotus was slow to bring 1-2-3 to Windows and by the early 1990s, Excel had started to outsell 1-2-3 and helped Microsoft achieve its position as a leading PC software developer. This accomplishment solidified Microsoft as a valid competitor and showed its future of developing GUI software. Microsoft maintained its advantage with regular new releases, every two years or so.
Microsoft Windows
Excel 2.0 is the first version of Excel for the Intel platform. Versions prior to 2.0 were only available on the Apple Macintosh.
Excel 2.0 (1987)
The first Windows version was labeled «2» to correspond to the Mac version. It was announced on October 6, 1987, and released on November 19.[96] This included a run-time version of Windows.[97]
BYTE in 1989 listed Excel for Windows as among the «Distinction» winners of the BYTE Awards. The magazine stated that the port of the «extraordinary» Macintosh version «shines», with a user interface as good as or better than the original.
Excel 3.0 (1990)
Included toolbars, drawing capabilities, outlining, add-in support, 3D charts, and many more new features.[97]
Excel 4.0 (1992)
Introduced auto-fill.[98]
Also, an easter egg in Excel 4.0 reveals a hidden animation of a dancing set of numbers 1 through 3, representing Lotus 1-2-3, which is then crushed by an Excel logo.[99]
Excel 5.0 (1993)
With version 5.0, Excel has included Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), a programming language based on Visual Basic which adds the ability to automate tasks in Excel and to provide user-defined functions (UDF) for use in worksheets. VBA includes a fully featured integrated development environment (IDE). Macro recording can produce VBA code replicating user actions, thus allowing simple automation of regular tasks. VBA allows the creation of forms and in‑worksheet controls to communicate with the user. The language supports use (but not creation) of ActiveX (COM) DLL’s; later versions add support for class modules allowing the use of basic object-oriented programming techniques.
The automation functionality provided by VBA made Excel a target for macro viruses. This caused serious problems until antivirus products began to detect these viruses. Microsoft belatedly took steps to prevent the misuse by adding the ability to disable macros completely, to enable macros when opening a workbook or to trust all macros signed using a trusted certificate.
Versions 5.0 to 9.0 of Excel contain various Easter eggs, including a «Hall of Tortured Souls», a Doom-like minigame, although since version 10 Microsoft has taken measures to eliminate such undocumented features from their products.[100]
5.0 was released in a 16-bit x86 version for Windows 3.1 and later in a 32-bit version for NT 3.51 (x86/Alpha/PowerPC)
Excel 95 (v7.0)
Released in 1995 with Microsoft Office for Windows 95, this is the first major version after Excel 5.0, as there is no Excel 6.0 with all of the Office applications standardizing on the same major version number.
Internal rewrite to 32-bits. Almost no external changes, but faster and more stable.
Excel 95 contained a hidden Doom-like mini-game called «The Hall of Tortured Souls», a series of rooms featuring the names and faces of the developers as an easter egg.[101]
Excel 97 (v8.0)
Included in Office 97 (for x86 and Alpha). This was a major upgrade that introduced the paper clip office assistant and featured standard VBA used instead of internal Excel Basic. It introduced the now-removed Natural Language labels.
This version of Excel includes a flight simulator as an Easter Egg.
Excel 2000 (v9.0)
Included in Office 2000. This was a minor upgrade but introduced an upgrade to the clipboard where it can hold multiple objects at once. The Office Assistant, whose frequent unsolicited appearance in Excel 97 had annoyed many users, became less intrusive.
A small 3-D game called «Dev Hunter» (inspired by Spy Hunter) was included as an easter egg.[102][103]
Excel 2002 (v10.0)
Included in Office XP. Very minor enhancements.
Excel 2003 (v11.0)
Included in Office 2003. Minor enhancements.
Excel 2007 (v12.0)
Included in Office 2007. This release was a major upgrade from the previous version. Similar to other updated Office products, Excel in 2007 used the new Ribbon menu system. This was different from what users were used to, and was met with mixed reactions. One study reported fairly good acceptance by users except highly experienced users and users of word processing applications with a classical WIMP interface, but was less convinced in terms of efficiency and organization.[104] However, an online survey reported that a majority of respondents had a negative opinion of the change, with advanced users being «somewhat more negative» than intermediate users, and users reporting a self-estimated reduction in productivity.
Added functionality included Tables,[105] and the SmartArt set of editable business diagrams. Also added was an improved management of named variables through the Name Manager, and much-improved flexibility in formatting graphs, which allow (x, y) coordinate labeling and lines of arbitrary weight. Several improvements to pivot tables were introduced.
Also like other office products, the Office Open XML file formats were introduced, including .xlsm for a workbook with macros and .xlsx for a workbook without macros.[106]
Specifically, many of the size limitations of previous versions were greatly increased. To illustrate, the number of rows was now 1,048,576 (220) and columns was 16,384 (214; the far-right column is XFD). This changes what is a valid A1 reference versus a named range. This version made more extensive use of multiple cores for the calculation of spreadsheets; however, VBA macros are not handled in parallel and XLL add‑ins were only executed in parallel if they were thread-safe and this was indicated at registration.
Excel 2010 (v14.0)
Microsoft Excel 2010 running on Windows 7
Included in Office 2010, this is the next major version after v12.0, as version number 13 was skipped.
Minor enhancements and 64-bit support,[107] including the following:
- Multi-threading recalculation (MTR) for commonly used functions
- Improved pivot tables
- More conditional formatting options
- Additional image editing capabilities
- In-cell charts called sparklines
- Ability to preview before pasting
- Office 2010 backstage feature for document-related tasks
- Ability to customize the Ribbon
- Many new formulas, most highly specialized to improve accuracy[108]
Excel 2013 (v15.0)
Included in Office 2013, along with a lot of new tools included in this release:
- Improved Multi-threading and Memory Contention
- FlashFill[109]
- Power View[110]
- Power Pivot[111]
- Timeline Slicer
- Windows App
- Inquire[112]
- 50 new functions[113]
Excel 2016 (v16.0)
Included in Office 2016, along with a lot of new tools included in this release:
- Power Query integration
- Read-only mode for Excel
- Keyboard access for Pivot Tables and Slicers in Excel
- New Chart Types
- Quick data linking in Visio
- Excel forecasting functions
- Support for multiselection of Slicer items using touch
- Time grouping and Pivot Chart Drill Down
- Excel data cards[114]
Excel 2019, Excel 2021, Office 365 and subsequent (v16.0)
Microsoft no longer releases Office or Excel in discrete versions. Instead, features are introduced automatically over time using Windows Update. The version number remains 16.0. Thereafter only the approximate dates when features appear can now be given.
- Dynamic Arrays. These are essentially Array Formulas but they «Spill» automatically into neighboring cells and does not need the ctrl-shift-enter to create them. Further, dynamic arrays are the default format, with new «@» and «#» operators to provide compatibility with previous versions. This is perhaps the biggest structural change since 2007, and is in response to a similar feature in Google Sheets. Dynamic arrays started appearing in pre-releases about 2018, and as of March 2020 are available in published versions of Office 365 provided a user selected «Office Insiders».
Apple Macintosh
Microsoft Excel for Mac 2011
- 1985 Excel 1.0
- 1988 Excel 1.5
- 1989 Excel 2.2
- 1990 Excel 3.0
- 1992 Excel 4.0
- 1993 Excel 5.0 (part of Office 4.x—Final Motorola 680×0 version[115] and first PowerPC version)
- 1998 Excel 8.0 (part of Office 98)
- 2000 Excel 9.0 (part of Office 2001)
- 2001 Excel 10.0 (part of Office v. X)
- 2004 Excel 11.0 (part of Office 2004)
- 2008 Excel 12.0 (part of Office 2008)
- 2010 Excel 14.0 (part of Office 2011)
- 2015 Excel 15.0 (part of Office 2016—Office 2016 for Mac brings the Mac version much closer to parity with its Windows cousin, harmonizing many of the reporting and high-level developer functions, while bringing the ribbon and styling into line with its PC counterpart.)[116]
OS/2
- 1989 Excel 2.2
- 1990 Excel 2.3
- 1991 Excel 3.0
Summary
| Legend: | Old version, not maintained | Older version, still maintained | Current stable version |
|---|
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | Excel 2 | 2.0 | Renumbered to 2 to correspond with contemporary Macintosh version. Supported macros (later known as Excel 4 macros). |
| 1990 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | Added 3D graphing capabilities |
| 1992 | Excel 4 | 4.0 | Introduced auto-fill feature |
| 1993 | Excel 5 | 5.0 | Included Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) and various object-oriented options |
| 1995 | Excel 95 | 7.0 | Renumbered for contemporary Word version. Both programs were packaged in Microsoft Office by this time. |
| 1997 | Excel 97 | 8.0 | |
| 2000 | Excel 2000 | 9.0 | Part of Microsoft Office 2000, which was itself part of Windows Millennium (also known as «Windows ME»). |
| 2002 | Excel 2002 | 10.0 | |
| 2003 | Excel 2003 | 11.0 | Released only 1 year later to correspond better with the rest of Microsoft Office (Word, PowerPoint, etc.). |
| 2007 | Excel 2007 | 12.0 | |
| 2010 | Excel 2010 | 14.0 | Due to superstitions surrounding the number 13, Excel 13 was skipped in version counting. |
| 2013 | Excel 2013 | 15.0 | Introduced 50 more mathematical functions (available as pre-packaged commands, rather than typing the formula manually). |
| 2016 | Excel 2016 | 16.0 | Part of Microsoft Office 2016 |
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | Excel 1 | 1.0 | Initial version of Excel. Supported macros (later known as Excel 4 macros). |
| 1988 | Excel 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 1989 | Excel 2 | 2.2 | |
| 1990 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1992 | Excel 4 | 4.0 | |
| 1993 | Excel 5 | 5.0 | Only available on PowerPC-based Macs. First PowerPC version. |
| 1998 | Excel 98 | 8.0 | Excel 6 and Excel 7 were skipped to correspond with the rest of Microsoft Office at the time. |
| 2000 | Excel 2000 | 9.0 | |
| 2001 | Excel 2001 | 10.0 | |
| 2004 | Excel 2004 | 11.0 | |
| 2008 | Excel 2008 | 12.0 | |
| 2011 | Excel 2011 | 14.0 | As with the Windows version, version 13 was skipped for superstitious reasons. |
| 2016 | Excel 2016 | 16.0 | As with the rest of Microsoft Office, so it is for Excel: Future release dates for the Macintosh version are intended to correspond better to those for the Windows version, from 2016 onward. |
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Excel 2.2 | 2.2 | Numbered in between Windows versions at the time |
| 1990 | Excel 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| 1991 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | Last OS/2 version. Discontinued subseries of Microsoft Excel, which is otherwise still an actively developed program. |
Impact
Excel offers many user interface tweaks over the earliest electronic spreadsheets; however, the essence remains the same as in the original spreadsheet software, VisiCalc: the program displays cells organized in rows and columns, and each cell may contain data or a formula, with relative or absolute references to other cells.
Excel 2.0 for Windows, which was modeled after its Mac GUI-based counterpart, indirectly expanded the installed base of the then-nascent Windows environment. Excel 2.0 was released a month before Windows 2.0, and the installed base of Windows was so low at that point in 1987 that Microsoft had to bundle a runtime version of Windows 1.0 with Excel 2.0.[117] Unlike Microsoft Word, there never was a DOS version of Excel.
Excel became the first spreadsheet to allow the user to define the appearance of spreadsheets (fonts, character attributes, and cell appearance). It also introduced intelligent cell re-computation, where only cells dependent on the cell being modified are updated (previous spreadsheet programs recomputed everything all the time or waited for a specific user command). Excel introduced auto-fill, the ability to drag and expand the selection box to automatically copy a cell or row contents to adjacent cells or rows, adjusting the copies intelligently by automatically incrementing cell references or contents. Excel also introduced extensive graphing capabilities.
Security
Because Excel is widely used, it has been attacked by hackers. While Excel is not directly exposed to the Internet, if an attacker can get a victim to open a file in Excel, and there is an appropriate security bug in Excel, then the attacker can gain control of the victim’s computer.[118] UK’s GCHQ has a tool named TORNADO ALLEY with this purpose.[119][120]
Games
Besides the easter eggs, numerous games have been created or recreated in Excel, such as Tetris, 2048, Scrabble, Yahtzee, Angry Birds, Pac-Man, Civilization, Monopoly, Battleship, Blackjack, Space Invaders, and others.[121][122][123][124][125]
In 2020, Excel became an esport with the advent of the Financial Modeling World Cup.[126]
See also
- Comparison of spreadsheet software
- Numbers (spreadsheet)—the iWork equivalent
- Spreadmart
- Financial Modeling World Cup, online esport financial modelling competition using Excel
References
- ^ «Update history for Microsoft Office 2019». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ a b «C++ in MS Office». cppcon. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- ^ «Microsoft Office Excel 365». Microsoft.com. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ «Update history for Office for Mac». Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel APKs». APKMirror.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel». App Store.
- ^
Harvey, Greg (2006). Excel 2007 For Dummies (1st ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-03737-9. - ^
Harvey, Greg (2007). Excel 2007 Workbook for Dummies (2nd ed.). Wiley. p. 296 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-16937-7. - ^
de Levie, Robert (2004). Advanced Excel for scientific data analysis. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515275-3. - ^
Bourg, David M. (2006). Excel scientific and engineering cookbook. O’Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00879-6. - ^
Şeref, Michelle M. H. & Ahuja, Ravindra K. (2008). «§4.2 A portfolio management and optimization spreadsheet DSS». In Burstein, Frad & Holsapple, Clyde W. (eds.). Handbook on Decision Support Systems 1: Basic Themes. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-48712-8. - ^
Wells, Eric & Harshbarger, Steve (1997). Microsoft Excel 97 Developer’s Handbook. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-1-57231-359-0. Excellent examples are developed that show just how applications can be designed. - ^
Harnett, Donald L. & Horrell, James F. (1998). Data, statistics, and decision models with Excel. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-13398-8. - ^
Some form of data acquisition hardware is required. See, for example, Austerlitz, Howard (2003). Data acquisition techniques using PCs (2nd ed.). Academic Press. p. 281 ff. ISBN 978-0-12-068377-2. - ^
«Description of the startup switches for Excel». Microsoft Help and Support. Microsoft Support. May 7, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2010.Microsoft Excel accepts a number of optional switches that you can use to control how the program starts. This article lists the switches and provides a description of each switch.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Excel functions (alphabetical)». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «WorksheetFunction Object (Excel)». Office VBA Reference. Microsoft. March 30, 2022. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Functions (Visual Basic for Applications)». Office VBA Reference. Microsoft. September 13, 2021. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Gordon, Andy (January 25, 2021). «LAMBDA: The ultimate Excel worksheet function». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^
For example, by converting to Visual Basic the recipes in Press, William H. Press; Teukolsky, Saul A.; Vetterling, William T. & Flannery, Brian P. (2007). Numerical recipes: the art of scientific computing (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88068-8. Code conversion to Basic from Fortran probably is easier than from C++, so the 2nd edition (ISBN 0521437210) may be easier to use, or the Basic code implementation of the first edition: Sprott, Julien C. (1991). Numerical recipes: routines and examples in BASIC. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-40689-5. - ^ «Excel». Office for Mac. OfficeforMacHelp.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- ^ «Using Excel — PC or Mac? | Excel Lemon». www.excellemon.com. Archived from the original on September 21, 2016. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ However an increasing proportion of Excel functionality is not captured by the Macro Recorder leading to largely useless macros. Compatibility among multiple versions of Excel is also a downfall of this method. A macro recorder in Excel 2010 may not work in Excel 2003 or older. This is most common when changing colors and formatting of cells.
Walkenbach, John (2007). «Chapter 6: Using the Excel macro recorder». Excel 2007 VBA Programming for Dummies (Revised by Jan Karel Pieterse ed.). Wiley. p. 79 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-04674-6. - ^ Walkenbach, John (February 2, 2007). «Chapter 4: Introducing the Excel object model». cited work. p. 53 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-04674-6.
- ^ «The Spreadsheet Page for Excel Users and Developers». spreadsheetpage.com. J-Walk & Associates, Inc. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ^ «Working with Excel 4.0 macros». microsoft.com. Microsoft Office Support. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ^ «The «Big Grid» and Increased Limits in Excel 2007″. microsoft.com. May 23, 2014. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «How to extract information from Office files by using Office file formats and schemas». microsoft.com. Microsoft. February 26, 2008. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b «XML Spreadsheet Reference». Microsoft Excel 2002 Technical Articles. MSDN. August 2001. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Deprecated features for Excel 2007». Microsoft—David Gainer. August 24, 2006. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
- ^ «OpenOffice.org’s documentation of the Microsoft Excel File Format» (PDF). August 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Office Excel 97 — 2007 Binary File Format Specification (*.xls 97-2007 format)». Microsoft Corporation. 2007.
- ^ Fairhurst, Danielle Stein (March 17, 2015). Using Excel for Business Analysis: A Guide to Financial Modelling Fundamentals. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-06245-5.
- ^ a b Newcomer, Joseph M. «Faking DDE with Private Servers». Dr. Dobb’s.
- ^ Schmalz, Michael (2006). «Chapter 5: Using Access VBA to automate Excel». Integrating Excel and Access. O’Reilly Media, Inc. ISBN 978-0-596-00973-1.Schmalz, Michael (2006). «Chapter 5: Using Access VBA to automate Excel». Integrating Excel and Access. O’Reilly Media, Inc. ISBN 978-0-596-00973-1.
- ^ Cornell, Paul (2007). «Chapter 5: Connect to other databases». Excel as Your Database. Apress. p. 117 ff. ISBN 978-1-59059-751-4.
- ^ DeMarco, Jim (2008). «Excel’s data import tools». Pro Excel 2007 VBA. Apress. p. 43 ff. ISBN 978-1-59059-957-0.
- ^
Harts, Doug (2007). «Importing Access data into Excel 2007». Microsoft Office 2007 Business Intelligence: Reporting, Analysis, and Measurement from the Desktop. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-149424-3. - ^ «About Network DDE — Win32 apps». learn.microsoft.com.
- ^ «How to set up and use the RTD function in Excel — Office». learn.microsoft.com.
- ^
DeMarco, Jim (2008). Pro Excel 2007 VBA. Berkeley, CA: Apress. p. 225. ISBN 978-1-59059-957-0.External data is accessed through a connection file, such as an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc)
- ^
Bullen, Stephen; Bovey, Rob & Green, John (2009). Professional Excel Development (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Addison-Wesley. p. 665. ISBN 978-0-321-50879-9.To create a robust solution, we always have to include some VBA code …
- ^ William, Wehrs (2000). «An Applied DSS Course Using Excel and VBA: IS and/or MS?» (PDF). The Proceedings of ISECON (Information System Educator Conference). p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 21, 2010. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
Microsoft Query is a data retrieval tool (i.e. ODBC browser) that can be employed within Excel 97. It allows a user to create and save queries on external relational databases for which an ODBC driver is available.
- ^ Use Microsoft Query to retrieve external data Archived March 12, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations — Word — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations — Word — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «Password protect worksheet or workbook elements — Excel — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2013. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Ralph, Nate. «Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide». TechHive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Wollman, Dana. «Microsoft Office Mobile for iPhone hands-on». Engadget. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Pogue, David. «Microsoft Adds Office for iPhone. Yawn». The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ a b Ogasawara, Todd. «What’s New in Excel Mobile». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 8, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2007.
- ^ a b «Unsupported features in Excel Mobile». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 20, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Use Excel Mobile Archived October 20, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «Excel Mobile». Windows Store. Microsoft. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ «PowerPoint Mobile». Windows Store. Microsoft. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ «Differences between using a workbook in the browser and in Excel — Office Support». support.office.com. Archived from the original on 8 February 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Excel Viewer». Microsoft. February 17, 2012. Archived from the original on April 6, 2013.
- ^ a b «How to obtain the latest Excel Viewer». Microsoft Docs. May 22, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Description of the security update for Excel Viewer 2007: February 12, 2019». Microsoft. April 16, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel Viewer». Microsoft. 1997. Archived from the original on January 20, 1998.
- ^ «Excel 97/2000 Viewer: Spreadsheet Files». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 13, 2004.
- ^ «New Features in Windows CE .NET 4.1». Microsoft Docs. June 30, 2006. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2003». Microsoft. October 12, 2004. Archived from the original on January 15, 2005.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2003 Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. September 17, 2007. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007.
- ^ «Excel Viewer». Microsoft. January 14, 2008. Archived from the original on September 26, 2010.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Microsoft. April 24, 2009. Archived from the original on April 28, 2012.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. October 25, 2011. Archived from the original on December 29, 2011.
- ^ «Supported versions of the Office viewers». Microsoft. April 16, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^
Microsoft’s overview is found at: «Floating-point arithmetic may give inaccurate results in Excel». Revision 8.2 ; article ID: 78113. Microsoft support. June 30, 2010. Retrieved July 2, 2010. - ^
Altman, Micah; Gill, Jeff; McDonald, Michael (2004). «§2.1.1 Revealing example: Computing the coefficient standard deviation». Numerical issues in statistical computing for the social scientist. Wiley-IEEE. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-471-23633-7. - ^ de Levie, Robert (2004). cited work. pp. 45–46. ISBN 978-0-19-515275-3.
- ^
Walkenbach, John (2010). «Defining data types». Excel 2010 Power Programming with VBA. Wiley. pp. 198 ff and Table 8–1. ISBN 978-0-470-47535-5. - ^ McCullough, Bruce D.; Wilson, Berry (2002). «On the accuracy of statistical procedures in Microsoft Excel 2000 and Excel XP». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 40 (4): 713–721. doi:10.1016/S0167-9473(02)00095-6.
- ^ McCullough, Bruce D.; Heiser, David A. (2008). «On the accuracy of statistical procedures in Microsoft Excel 2007». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 52 (10): 4570–4578. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.455.5508. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.004.
- ^ Yalta, A. Talha (2008). «The accuracy of statistical distributions in Microsoft Excel 2007». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 52 (10): 4579–4586. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.005.
- ^ Goldwater, Eva. «Using Excel for Statistical Data Analysis—Caveats». University of Massachusetts School of Public Health. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^
Heiser, David A. (2008). «Microsoft Excel 2000, 2003 and 2007 faults, problems, workarounds and fixes». Archived from the original on April 18, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2010. - ^
Function improvements in Excel 2010 Archived April 6, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Comments are provided from readers that may illuminate some remaining problems. - ^ «The MOD bug». Byg Software. Archived from the original on January 11, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Days of the week before March 1, 1900 are incorrect in Excel». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 14, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Excel incorrectly assumes that the year 1900 is a leap year». Microsoft. Retrieved May 1, 2019.
- ^ Spolsky, Joel (June 16, 2006). «My First BillG Review». Joel on Software. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «The Contradictory Nature of OOXML». ConsortiumInfo.org. January 17, 2007.
- ^ «Negative date and time value are displayed as pound signs (###) in Excel». Microsoft. Retrieved March 26, 2012.
- ^ Zeeberg, Barry R; Riss, Joseph; Kane, David W; Bussey, Kimberly J; Uchio, Edward; Linehan, W Marston; Barrett, J Carl; Weinstein, John N (2004). «Mistaken Identifiers: Gene name errors can be introduced inadvertently when using Excel in bioinformatics». BMC Bioinformatics. 5 (1): 80. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-5-80. PMC 459209. PMID 15214961.
- ^ a b Ziemann, Mark; Eren, Yotam; El-Osta, Assam (2016). «Gene name errors are widespread in the scientific literature». Genome Biology. 17 (1): 177. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-1044-7. PMC 4994289. PMID 27552985.
- ^ Anon (2016). «Microsoft Excel blamed for gene study errors». bbc.co.uk. London: BBC News.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (August 24, 2016). «One in Five Scientific Papers on Genes Contains Errors Because of Excel». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ Ziemann, Mark (2016). «Genome Spot: My personal thoughts on gene name errors». genomespot.blogspot.co.uk. Archived from the original on August 30, 2016.
- ^ Vincent, James (August 6, 2020). «Scientists rename human genes to stop Microsoft Excel from misreading them as dates». The Verge. Retrieved October 9, 2020.
- ^ «Excel: type() and
WorksheetFunction.IsText()fail for long strings». Stack Overflow. November 3, 2018. - ^ Rajah, Gary (August 2, 2004). «Trouble with macros». The Hindu Business Line. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Chirilov, Joseph (January 8, 2009). «Microsoft Excel — Why Can’t I Open Two Files With the Same Name?». MSDN Blogs. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on July 29, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Infoworld Media Group, Inc. (July 7, 1986). InfoWorld First Look: Supercalc 4 challenging 1-2-3 with new tactic.
- ^ «The History of Microsoft — 1987». channel9.msdn.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2010. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «The History of Microsoft — 1987». learn.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ a b Walkenbach, John (December 4, 2013). «Excel Version History». The Spreadsheet Page. John Walkenbach. Retrieved July 12, 2020.
- ^ Lewallen, Dale (1992). PC/Computing guide to Excel 4.0 for Windows. Ziff Davis. p. 13. ISBN 9781562760489. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ Lake, Matt (April 6, 2009). «Easter Eggs we have loved: Excel 4». crashreboot.blogspot.com. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ Osterman, Larry (October 21, 2005). «Why no Easter Eggs?». Larry Osterman’s WebLog. MSDN Blogs. Retrieved July 29, 2006.
- ^ «Excel 95 Hall of Tortured Souls». Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ «Excel Oddities: Easter Eggs». Archived from the original on August 21, 2006. Retrieved August 10, 2006.
- ^ «Car Game In Ms Excel». Totalchoicehosting.com. September 6, 2005. Retrieved January 28, 2014.
- ^ Dostál, M (December 9, 2010). User Acceptance of the Microsoft Ribbon User Interface (PDF). Palacký University of Olomouc. ISBN 978-960-474-245-5. ISSN 1792-6157. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
- ^ [Using Excel Tables to
Manipulate Billing Data https://mooresolutionsinc.com/downloads/Billing_MJ12.pdf] - ^ Dodge, Mark; Stinson, Craig (2007). «Chapter 1: What’s new in Microsoft Office Excel 2007». Microsoft Office Excel 2007 inside out. Microsoft Press. p. 1 ff. ISBN 978-0-7356-2321-7.
- ^ «What’s New in Excel 2010 — Excel». Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2010.
- ^ Walkenbach, John (2010). «Some Essential Background». Excel 2010 Power Programming with VBA. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. p. 20. ISBN 9780470475355.
- ^ Harris, Steven (October 1, 2013). «Excel 2013 — Flash Fill». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «What’s new in Excel 2013». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- ^ K., Gasper (October 10, 2013). «Does a PowerPivot Pivot Table beat a regular Pivot Table». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ K., Gasper (May 20, 2013). «Inquire Add-In for Excel 2013». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «New functions in Excel 2013». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «What’s new in Office 2016». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved August 16, 2015.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces March Availability of Office 98 Macintosh Edition». Microsoft. January 6, 1998. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ «Office for Mac Is Finally a ‘First-Class Citizen’«. Re/code. July 16, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ Perton, Marc (November 20, 2005). «Windows at 20: 20 things you didn’t know about Windows 1.0». switched.com. Archived from the original on April 11, 2013. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (February 24, 2009). «Attackers exploit unpatched Excel vulnerability». Computerworld. IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ «JTRIG Tools and Techniques». The Intercept. First Look Productions, Inc. July 14, 2014. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Cook, John. «JTRIG Tools and Techniques». The Intercept. p. 4. Retrieved March 19, 2019 – via DocumentCloud.
- ^ Phillips, Gavin (December 11, 2015). «8 Legendary Games Recreated in Microsoft Excel». MUO.
- ^ «Excel Games – Fun Things to Do With Spreadsheets». November 10, 2021.
- ^ «Unusual Uses of Excel». techcommunity.microsoft.com. August 5, 2022.
- ^ «Someone made a version of ‘Civilization’ that runs in Microsoft Excel». Engadget.
- ^ Dalgleish, Debra. «Have Fun Playing Games in Excel». Contextures Excel Tips.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel esports is real and it already has an international tournament». ONE Esports. June 9, 2021.
References
- Bullen, Stephen; Bovey, Rob; Green, John (2009). Professional Excel Development: The Definitive Guide to Developing Applications Using Microsoft Excel and VBA (2nd ed.). Boston: Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-321-50879-9.
- Dodge, Mark; Stinson, Craig (2007). Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Inside Out. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2321-7.
- Billo, E. Joseph (2011). Excel for Chemists: A Comprehensive Guide (3rd ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-38123-6.
- Gordon, Andy (January 25, 2021). «LAMBDA: The ultimate Excel worksheet function». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
External links
Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Excel
- Microsoft Excel – official site
Excel File Extensions and Their Uses
XLS, XLSX, XLSM, XLTX and XLTM
A file extension is the group of letters that appear after the last period in a file name. File extensions are usually 2 to 4 characters long, although they can be of any length. Excel uses a handful of standard extensions to disambiguate certain kinds of spreadsheet files.
The information in this article applies to Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel Online, and Excel for Mac.
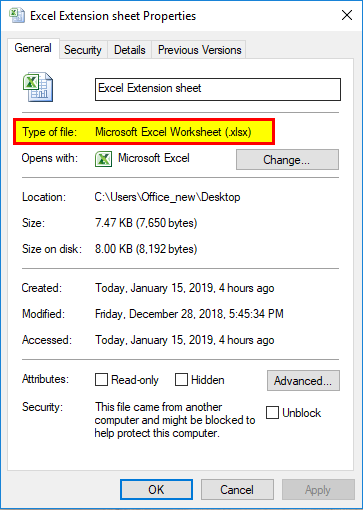
XLS vs. XLSX
The current default file extension for an Excel file is XLSX. Prior to Excel 2007, the default file extension was XLS. The main difference between the two is that XLSX is an XML-based open file format and XLS is a proprietary Microsoft format. But, the newer versions of Excel save and open XLS files for the sake of compatibility with earlier versions of the program.
Determine if a file contains macros before you open it. Macros contain code that could damage files and compromise computer security if they come from untrusted sources. Excel files containing VBA and XLM macros use the XLSM extension.
XML and HTML
XML stands for extensible markup language. XML is related to HTML, the extension used for web pages. Advantages of this file format include:
- Smaller file sizes for storage and transfer.
- Better recovery of information from damaged files.
- Easier detection of files containing macros.
XLTX and XLTM
If an Excel file has either an XLTX or an XLTM extension, it is saved as a template file. Template files are used as starter files for new workbooks. Templates contain saved settings such as the default number of sheets per workbook, formatting, formulas, graphics, and custom toolbars. The difference between the two extensions is that the XLTM format can store VBA and XML macro code.
Macintosh computers do not rely on file extensions to determine which program to use when opening a file. However, for the sake of compatibility with the Windows version of the program, Excel for Mac uses the XLSX file extension.
Excel files created in one operating system can be opened the other. One exception to this is Excel 2008 for the Mac, which does not support VBA macros. As a result, it cannot open XLMX or XMLT files created by Windows or later Mac versions that support VBA macros.
Change File Formats With Save As
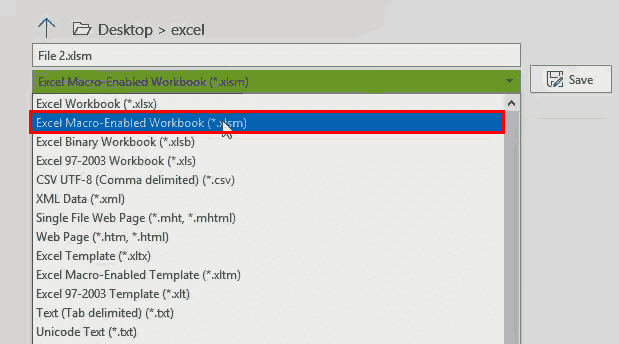
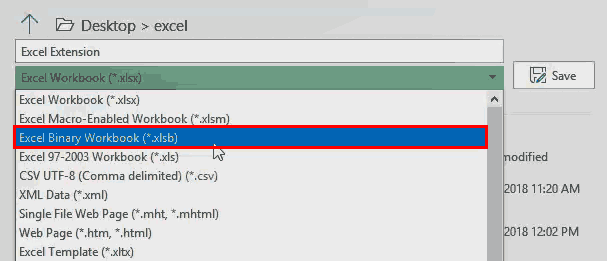
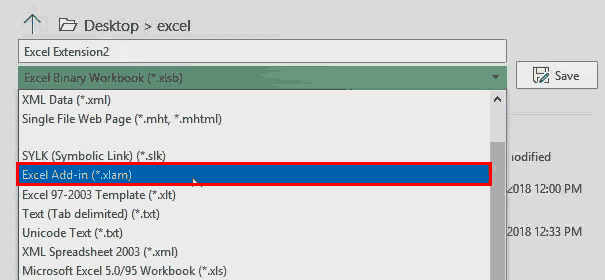
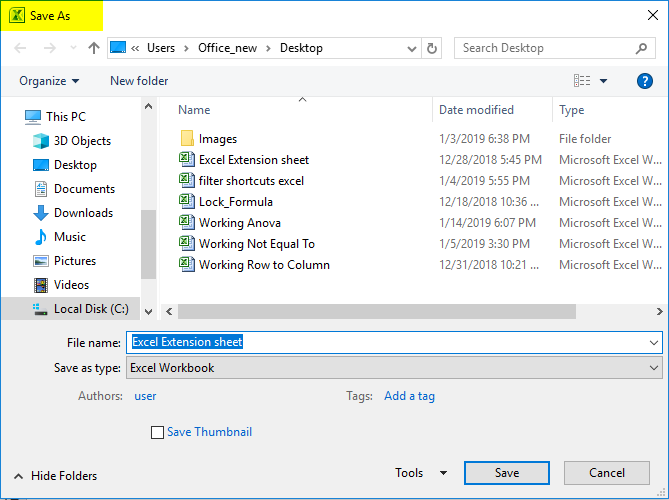
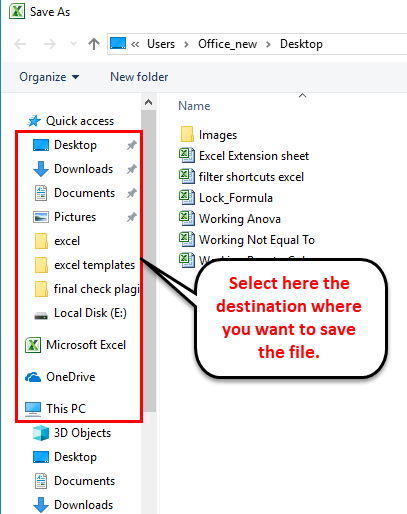
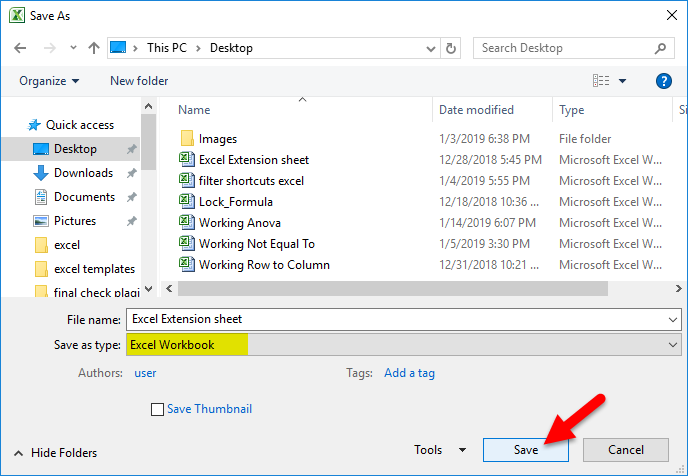
To change an Excel format (and its extension), follow these steps:
-
Open the workbook and select File > Save As. In Excel 2019, select Save a Copy instead.
-
In the dialog box, accept the suggested file name or type a new name for the workbook.
-
In the Save as type or File Format list, choose the format for the resulting file.
-
Select Save to save the file in the new format and return to the current worksheet.
If a file is saved in a format that does not support all the features of the current format, such as formatting or formulas, an alert message box appears prompting you to continue or to cancel.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Microsoft created and released the spreadsheet program known as Excel. It comes from the Microsoft Office family of productivity programs. Excel groups data into columns and rows as opposed to a word processor like Microsoft Word. A cell is a location where rows and columns cross. Data, such as text, a number, or a formula, are contained in each cell. They might not be able to display every feature of a file, programs that are compatible with a file format can present an overview of a file. When we want to save our files, we will have numerous file formats including Excel workbooks, templates, etc. These file formats are divided into various types, including Excel, Word, and PowerPoint presentations.
File formats in Excel are of various types, but to determine how many formats exist in Excel, we must follow the procedure outlined below:
Step 1: Click on the file option at the top of the ribbon.
Step 2: Select the Save As option. The Workbook can be saved on local devices (like a computer) and the internet (e.g. OneDrive).
Step 3: Click on the option Browse and save as the dialog box opens.
Step 4: Choose the Save As option and you will see a list of file formats. Depending on the type of active Worksheet in your Workbook, several file types will be displayed (Data Worksheet, Chart Worksheet, or another type of Worksheet).
Step 5: Select the desired file format by clicking.
Excel File Formats
Excel Workbook
Extension: .xlsx
Spreadsheet files were created using Excel version 2007 and later have this extension. Currently, the default file extension for Excel files is XLSX. XML is the foundation of the file format XSLX. With the aid of this technology, XSLX files are significantly lighter and smaller than XLS files, which immediately results in space savings. Excel documents may be downloaded or uploaded more quickly. The only drawback of this XSLX extension is that it cannot open files created before Excel 2007.
Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook
Extension: .xlsm
With Excel 2007 and later, including Excel macros, the spreadsheet produces files with this suffix. It’s simple to deduce that a file contains a macro with the aid of an extension. This version was created for security purposes to prevent computer viruses, harmful macros, infecting machines, etc. from accessing a file. When it comes to security and macros, this file extension is quite dependable.
Excel Binary Workbook
Extension: .xlsb
When it comes to compressing, storing, opening, etc., this file extension type completely supports excel files that include a lot of data or information. It takes a lot of time to open and process an excel file with a lot of data. It occasionally hangs while opening and regularly crashes.
Template
Extension: .xltx
A template made by the spreadsheet program Microsoft Excel, part of the Microsoft Office family, is known as an XLTX file. It has predetermined layout options that may be used to produce several Excel spreadsheets (typically.XLSX files) with the same formatting and characteristics. XLTX files that give you a head start when making spreadsheets like bills, calendars, and budget plans. Additionally, you may make unique templates using your spreadsheets.
Template (code)
Extension: .xltm
A Microsoft Excel spreadsheet template with macro support is known as an XLTM file. It may also keep settings, spreadsheet data, and information about the layout in addition to one or more macros. When looking to generate several spreadsheets (primarily. XLSM) with the same data and style, Excel users save spreadsheets as XLTM files.
XLTX files and XLTM files are related. XLTM files, on the other hand, enable macros, which are collections of instructions that a user has organized so they may swiftly carry out a time-consuming or difficult operation, including formatting a document, inputting data, or conducting computations.
Excel Add-In
Extension: .xlam
The spreadsheet program Microsoft Excel, part of the Microsoft Office family, uses XLAM files, and add-ins that support macros. It is used in Excel to add new features and instructions. While some XLAM files are produced by Microsoft, others are produced by Excel users and third-party developers. Microsoft Excel users can add more features since different users use the program for various, specialized purposes. Users must install an XLAM file-based Excel add-in to add this functionality.
XML Spreadsheet 2003
Extension: .xml
A plain text document is an XML file, and to distinguish them, they are saved with the.xml file extension. The XML file format was created to convey data over the internet and can hold hundreds of entries in the computation. Either humans or machines can read it.. The majority of programming languages make use of XML libraries to do the parsing. Down-converting is the process of converting XML files to other required forms.
XML Data
Extension: .xml
Other description languages like RSS, DOCX format, XSL, and Microsoft don’t employ XML as a format. The text editor notepad++ can open this XML file natively. We need to have a few interactions with the various file organizations to manage the different file formats. The only organization that is required for data and web pages is XML. Next, you could double-click the browser—the file’s default viewer—on occasion to examine a file.
Microsoft Excel 5.0/95 Workbook
Extension: .xls
A spreadsheet file, known as an XLS file, can be produced by Microsoft Excel or exported by another spreadsheet application, like OpenOffice Calc or Apple Numbers. It includes one or more worksheets that store and present data as tables. The Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet (XLS) binary format was introduced together with the initial 1987 version of Excel. Up to the introduction of Excel 2007, XLS files became one of the most used file formats for preserving spreadsheets. Microsoft replaced XLS files with the Microsoft Excel Open XML Spreadsheet (XLSX) format with this version. Excel spreadsheets are often saved in XLSX files.
Excel 4.0 Workbook
Extension: .xlw
Workspace files, which are saved in the well-known spreadsheet program Microsoft Excel, have the .xlw file extension. Workbook file references and screen locations are stored in files with the .xlw extension. When .xlw files are opened, the program can move them back to the spot on the screen where they were stored. .xlw files are essential for restoring layouts when a user is working on many workbooks at once. .xlw files only refer to workbook layouts on the screen, therefore they should not be mistaken for files that contain workbook data. These files are primarily utilized by Microsoft Excel 2010 and 2011, and users need to have all workbook files to correctly reopen these files.
Works 6.0-9.0 spreadsheet
Extension: .xlr
The file format specifications for XLR files were not made publicly available and were instead kept as binary files. Developers are consequently unable to examine the file system and create programs that read from and write to these files programmatically. The Works Spreadsheet saves data to.xlr files using the same Excel file format.
Text File Formats
Formatted Text (Space-delimited)
Extension: .prn
A PRN file is one that was made using the Print to File checkbox that may be found in several Windows Print dialogue boxes. A printer, fax machine, or other device utilizes it to print a document because it contains a set of device-specific instructions. Depending on the device the file was produced for, PRN files may include text or binary information.
Text (Tab-delimited)
Extension: .txt
An ordinary text document with simple text is known as a TXT file. Any text-editing or word-processing application may open and edit it. The most widely used text editors for producing TXT files are Apple TextEdit and Microsoft Notepad, which come pre-installed with Windows and macOS, respectively. TXT files are plain text files with very little to no formatting. They are utilized to manage manuscripts, detailed instructions, notes, and other text-based information.
When a user of TextEdit saves a document as a TXT file, those applications remove the document’s formatting (bolding, italicization, font style, alignment, etc.). Most users don’t store more complex text documents, including flyers, reports, letters, or resumes, as TXT files. Instead, they save them as other types of files.
Text (Macintosh)
Extension: .txt
This function guarantees that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are properly understood when a workbook is saved as a tab-delimited text file for usage on the Macintosh operating system. only saves the active sheet.
Text (MS-DOS)
Extension: .txt
Ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are properly understood when saving a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system. only saves the active sheet.
DIF
Extension: .dif
Data interchange format, or DIF for short, is a widely accepted standard for exporting spreadsheets. Users can export data from a spreadsheet in a format that can be loaded by several other programs using DIF files. The format has the drawback of not supporting numerous spreadsheets. This indicates that just one spreadsheet may be stored in a DIF file. As a result, you will need to make numerous DIF files if you wish to export many spreadsheets in the DIF format.
Unicode Text
Extension: .txt
The workbook can be saved as Unicode text, a character encoding standard created by the Unicode Consortium.
SYLK
Extension: .slk
A file stored in the Symbolic Link (SYLK) format, developed by Microsoft to transmit data between spreadsheet applications and other databases, is referred to as an SLK file. It has semicolons between lines of text that describe the cell row, column, layout, and content. An ANSI text file format is used to hold SLK files. SYLK (Symbolic Link) codes, such “E,” which stands for an expression within a cell, are used to record complex formulae.
CSV (comma delimited)
Extension: .csv
The Comma Separated Value (CSV) file extension is frequently used to identify files in this format. An easy text format for a database table is a comma-separated values file. A row in the table is represented by one line in the CSV file. Fields from different table columns are separated inside the line by commas. The CSV file format is straightforward and is accepted by a wide range of software. Moving tabular data between two separate computer applications sometimes involves the usage of csv files.
CSV (Macintosh)
Extension: .csv
Ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are properly understood when saving a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for usage on the Macintosh operating system. Only saves the active sheet.
CSV (MS-DOS)
Extension: .csv
Ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are properly understood when saving a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system. only saves the active sheet.
Other File Formats
Extension: .pdf
Format for Portable Documents (PDF). This file format allows file sharing and maintains document layout. The format that you intended is kept when the PDF file is printed or read online. The file’s data cannot be readily altered. For papers that will be printed using professional printing techniques, the PDF format is also beneficial. Note: Excel 2007 does not support this format.
Open document spreadsheet
Extension: .ods
The spreadsheet in OpenDocument. You can save Excel 2010 files so they can be opened in spreadsheet software like Google Docs and OpenOffice.org Calc which supports the OpenDocument Spreadsheet format. Additionally, Excel 2010 supports opening spreadsheets in the. ods format. When. ods, files are opened and saved, and formatting could be lost.
DBF 3, DBF 4
Extension: .dbf
The database management system program dBASE uses a standard database file called a DBF. It divides the information into several records with fields kept in an array data type. Due to the ubiquity of the file format, other “xBase” database tools are also compatible with DBF files. DBF files have been extensively embraced as a standard storage format for structured data in business applications due to their early adoption in the database community and a very simple file layout.
XPS Document
Extension: .xps
XML paper specification files are the ones with the .XPS suffix. These files have a predefined layout and are used to safeguard the accuracy of the data they contain. The sole distinction between them and the well-known PDF file format is the .XPS format’s usage of XML standards for its file structure. The data in your file may be read, shared, and modified using XPS files, which are simple to distribute online. It has become a well-liked substitute for the PDF file format as a result. Any software that runs on Windows and has printing capabilities may produce XPS files.
A file with XLSX, XLSM, XLS, XLTX or XLTM extension is a Microsoft Excel file that uses specific standard file format. You can show or display file extension on Windows OS from Folder Options. MS Excel lets you save files in any of these file formats using the Save As option. These Excel file formats serve different purposes for working with Spreadsheet files as explained in this article.
In addition to standard file formats, Excel indirectly uses other file formats as well for a set of different operations. For example, it uses Windows Metafile Format (WMF) or Windows Enhanced Metafile Format (EMF) when a windows metafile picture is copied and paste into Excel Worksheet.

What is XLSX file?
An XLSX file is the default file format for Microsoft Excel that was introduced with Office 2007. It is based on Office Open XML standard that can be opened by a number of applications as well as APIs. The contents inside an XLSX file can be viewed by renaming XLSX extension to ZIP and opening it with any archiving software.
What is XLS file?
An XLS file is a spreadsheet file that is created in Excel Binary Interchange File Format (BIFF) and is proprietary to Microsoft. It can be created with Excel 2003 and earlier versions. An XLS file can be opened in the latest version of Microsoft Excel and can be saved as the latest version of spreadsheet file format i.e. XLSX. Microsoft Excel viewer provides the capability to open these files in read-only mode for reading purpose.
What is XLSM file?
An XLSM file is a Macro-enabled spreadsheet file that can store instructions to record the steps that are performed repeatedly. Macros are programmed in Microsoft Visual Basic for Application (VBA) from within the Excel Workbook. The Visual Basic editor is used to record and run macros in Excel.
XLSM files are similar to XLM file formats but are based on the Open XML format introduced in Microsoft Office 2007. In other words, XLSM are XLSX files but with support of macros. By default, Excel itself provides several macros for common use. However, you can also record your own macros with required functions.
What is XLTX file?
An XLTX file is an Excel Template file that preserves user defined settings. Excel 2007 and above can open XLTX files for creating new XLSX files that retain the settings from template. XLTX file format is based on the Office Open XML standard and can be viewed by remaining its extension to ZIP. Excel comes with predefined templates as well that can be opened and populated with spreadsheet data.
What is XLTM File?
An XLTM file is a Macro-Enabled template file that is created with Microsoft Excel. These are similar to XLTX but with additional feature of macros. Such template files are used to generate and set the layout, formatting, and other settings along with the macros to facilitate creating similar XLSX files then.
Probably 99% of all Excel workbooks are saved in the XLSX file type these days. But there are various other file extensions available: For example XLSM, XLSB or “older” Excel users might still remember the XLS file type. What are the differences of these file types? And even more important: Which one should you use?
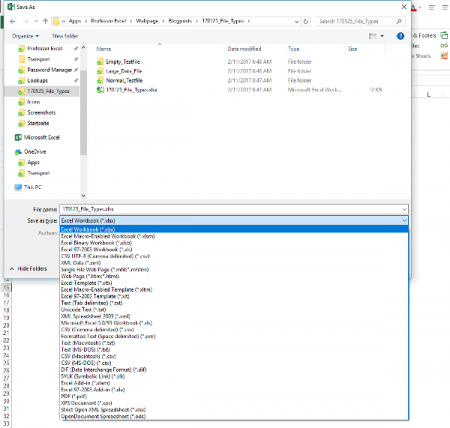
When you save an Excel workbook for the first time or use the “Save As” function, you are asked for a folder, file name as well as the file type. By default, Excel suggests the XLSX file type (unless your file has VBA macros). The window looks similar to the screenshot on the right side.
So which file type are you going to use? The answer – like so often: It depends. Before we conclude in a decision tree, we we take a look at the most important file extensions in Excel with their advantages and disadvantages first.
XLSX
The “default” file extension is XLSX. The large majority of Excel workbooks uses this format these days. Microsoft says in the Excel help text about the XLSX file format:
The default XML-based file format for Excel 2007-2013. Cannot store Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macro code […].
Most of the time you use the XLSX format: It’s save (can’t store malicious code), has the maximum number of rows and columns and is best known. XLSX is available since Excel 2007 and replaces the old XLS file type. It uses the open XML standard so which is documented well.
Knowing these quick facts, there are the following advantages and disadvantages for the XLSX file format:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
XLS

The XLS file type has been the default Excel file extension and format before Excel 2007. In Excel 2007, XLSX replaced the XLS format. Therefore, XLS is kind of outdated right now. In the daily life you won’t find it often any more. But some data base tools still export data as XLS files.
The XLS file type has some disadvantages towards the newer file types XLSX or XLSM: It’s rather unsafe as it can contain VBA macros with malicious code. Also, it needs more disk space than the other file types and at the same time has less rows and columns.
On the other side the only advantage: You can easily open XLS files with older versions of Excel.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
XLSM
If you include VBA macros in your XLSX file, you will be asked to change the file extension to XLSM. Only that way you can save your macro within the Excel file (there are other file types possible, e.g. XLSB – but you can’t use XLSX for VBA macros). Therefore, it has most of the advantages and disadvantages of the XLSX file type. Positive: You can immediately identify Excel files with VBA macros.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
XLSB

Many people don’t know that there is an actual alternative to the XLSX and XLSM file type: The XLSB file extension. XLSB files store the data a little bit different than the XLSX or XLSM file types: They don’t use the XLM file structure. Instead, XLSB files try to save disk space because the data is stored in the binary structure. The main difference: Binary files are computer- but not human-readable. For more information on binary files in general, please refer to this Wikipedia entry.
The main disadvantage: Binary Excel files can contain VBA macros. So unless you don’t know the origin of a file, please consider well before opening them. Besides that: All the other disadvantages seem minor.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Do you want to boost your productivity in Excel?
Get the Professor Excel ribbon!
Add more than 120 great features to Excel!
CSV

CSV stands for comma separated values. These files are basically plain text – so there are no formulas or formatting. CSV is often used for data exchange. Excel provides the functionality to import or even directly open CSV files.
The basic application for CSV files: Import or export data. Data base programs often export data as CSV files. Also if you want to transport Excel data into a database program, often the CSV file type works.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
ODS
ODS stands for Open Document Spreadsheet. The file type is designed to work on both Excel and other applications, e.g. LibreOffice. From the Excel point of view, ODS doesn’t support all the features. Text and data is usually saved well though. But formatting and many other features (for example charts, tables, conditional formatting) might run into problems.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
XLSX (Strict)
Besides the regular XLSX format, Excel offers to save your Excel workbook as “Strict Open XML Spreadsheet”. So what is the difference between those two? Basically, the two file types use the same structure. But:
The Strict variant has less support for backwards compatibility when converting documents from older formats.
Furthermore:
The Strict variant of XLSX disallows a variety of elements and attributes that are permitted in the more common Transitional variant […]
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|

As you’ve probably heard of PDF files, we won’t go much into detail here. PDF stands for portable document format and has the reputation of not easily being manipulated. Also, it’s quite save to say that how a PDF file looks on your computer, it will most probably look like this on most other computers.
And that’s it for the advantages. I recommend using it when you present your final results in the following cases:
- The recipient of your file should not edit it any more.
- Formatting should be exactly preserved.
- There is no database included, just the summarized results.
That could be the case if somebody wants to check your results on an iPad or a similar device. But: In many cases it would be professional (and nice) to also send at least parts of your Excel file. That way, your recipient could at least take a look at the calculation process.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
XLAM
XLAM is the file extension for Excel add-ins. Also our add-ins (for example the popular “Professor Excel Tools“) are XLAM files. They can contain VBA macros, worksheets as well as forms, images and individual ribbons. If you double click on such file, it will open in Excel and you can use the funcationality of the add-in. But next time you open Excel again, it won’t be available any longer. You rather have to enable the add-in within the options (File –> Options –> Add-Ins).
As the XLAM file type is not really an alternative for all the other file extensions above, we skip the advantages and disadvantages.
Comparison of file types
So if we put all the advantages, disadvantages and facts from above together, we come to the following comparison:
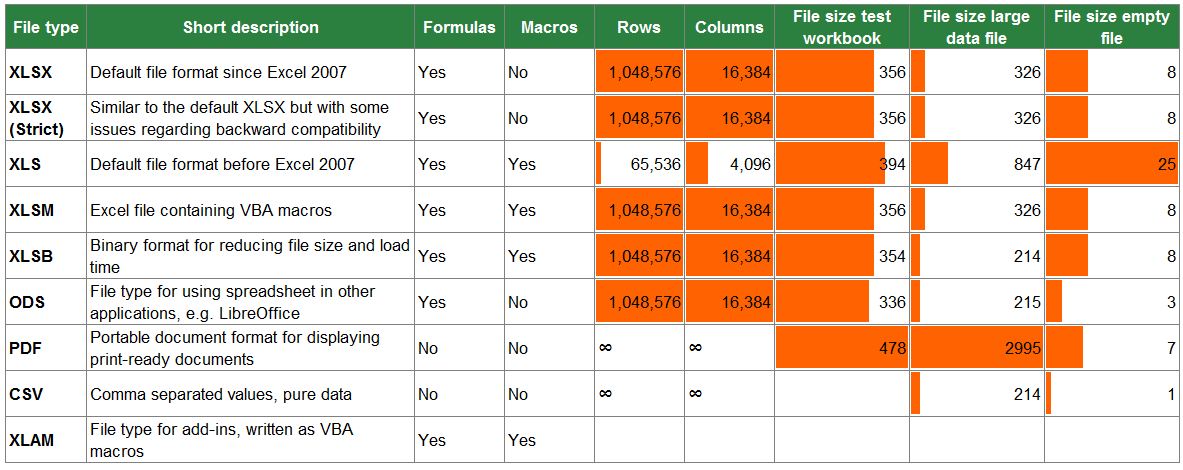
Which file type should you use?
Decision Tree
In order to define the best file type for your Excel workbook, please follow the decision tree.
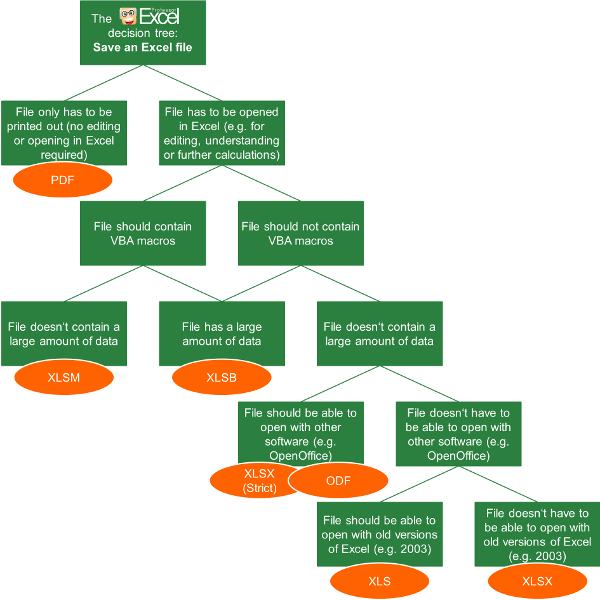
- The first question: Do you just want to display your results only? Then you could also consider the PDF format. But if the recipient of your work wants to edit or follow up your calculations, you shouldn’t use PDF.
- Does your file contain VBA macros?
- If yes, choose XLSB if you have a large file. Choose XLSM for a file size smaller than app. 10 MB.
- If no and you got a large file (larger than app. 10 MB), also choose XLSB.
- If no (you don’t have macros) and your file small, follow the tree on the right hand side.
- The lower two levels of the decision tree are just about compatibility: If you want to open and edit your workbook with another software, choose the strict XLSX or ODF format.
- If you want to make sure that you can open it with versions of Excel 2003 or earlier, go for XLS.
Summary
In conclusion, you can distill a quite short table (if you don’t need to consider old file types and other applications as LibreOffice). You just have to answer two questions: Do you need VBA macros and do you work with a large amount of data?
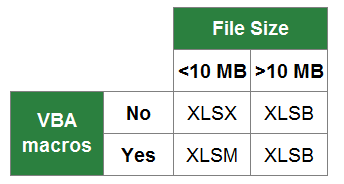
Excel file extensions are there to identify the file format. For example, in computer operating systems, file extensions are to identify the file type for the operating system so that it runs and opens the file with the specified format.
If you observe at the end of the file name, you will see the extension of that file.
The above image, includes XLSX, XLSM, XLSB, XLS, and XLAM.
I am sure you know about Excel but not about their formats. If you have no idea about Excel file extensions, this is a tailor-made article. In a general case scenario, you must have seen the xlsx file format in Excel. When you try to save the unsaved workbook Excel automatically saves it as an “xlsx” file.
Note: When we save the existing file with a different Excel file format (extension), some of the features of the current file might not be transferred to the new file extension.
Table of contents
- Extensions in Excel
- Where to Find File Extensions in Excel?
- Top 5 Excel file Formats
- #1 – XLSX
- #2 – XLSM
- #3 – XLSB
- #4 – XLS
- #5 – XLAM
- Other Additional Excel File Formats
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Where to Find File Extensions in Excel?
You must be thinking about where these file formats are. These file formats are available when we see the save dialog box. Under the “Save as type,” we can see many of the accessible file formats in the computer system.
If you look at the above image, the first extension the operating system recognizes is Excel Workbook (*.xlsx) format, and all the other remaining forms follow after.
Top 5 Excel file Formats
Below are some of the top file formats for Excel. You may follow this article to explore some of them.
#1 – XLSX
The default Excel format is “XLSX.” However, when we press the “Save As” option, Excel, by default, recognizes this extension. It is the replacement of the earlier extension called XLS. It is the most popular Excel file extension for non-macro files.
Below is the image which shows how the file is saved under this method.
#2 – XLSM
This Excel file format is used for a VBA Macro file. If we are working with macro in Excel, we need to change the Excel extension to enable the smooth flow of macro running. It is the default extension type for a macro containing a workbook.
XLSX does not support the macro code. Therefore, we need to save the workbook as a macro-enabled workbook to run the macros.
While saving the workbook, we need to select the file type as “Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook.”
#3 – XLSB
Often in Excel, we face the issue of too much data, and the Excel file slows down. In addition, if Excel is saved in the form of “XLSX” or “XLSM” Excel, the workbook tends to slow down.
“XLSB” means “Excel Binary Workbook.” If we save the workbook as a binary workbook, it will reduce the weight of the workbook.
Look at the below image, an Excel workbook saved in the form of “XLSX,” and the total workbook weight is 63.4 KB.
Now, we will save this file as “Excel Binary Workbook.”
Now, look at the size of the workbook.
So, Excel binary workbook reduces the workbook size to 59.4 KB. In the case of a large file, it reduces the size of the workbook by 50%.
#4 – XLS
Probably, we may not see this kind of Excel file format these days. However, this file is saved for the binary workbook of Excel 97 to Excel 2003 binary format.
#5 – XLAM
It is the Excel Add-in. Excel Add-insAn add-in is an extension that adds more features and options to the existing Microsoft Excel.read more are extra features we add to the Excel workbook. Excel has many built-in features. On top of these available features, we can create some macros and make Excel talk according to our wishes.
Once the macro is created, we need to save the file as “Excel Add-ins.” Once the workbook is saved as “Add-in,” click on Developer TabEnabling the developer tab in excel can help the user perform various functions for VBA, Macros and Add-ins like importing and exporting XML, designing forms, etc. This tab is disabled by default on excel; thus, the user needs to enable it first from the options menu.read more >Excel Add-ins and select the additional feature created by a User Defined Function (UDF).
Other Additional Excel File Formats
We have seen the top five file formats. On top of these, there are many other additional extensions available.
- XLC: Excel Chart Type
- XLT: Excel Template
- XLD: Excel DataBase
- XLK: Excel Back up
Things to Remember
- For macros, we need to select the “XLSM” type extension.
- We cannot use the workbook of the Excel “Add-in” extension, but we can use that as an add-in in other workbooks.
- If the Excel is saved as “CSV,” it will not be an Excel workbook. It is to store the data, but it is not very easy to work on it. It will reduce the size of the workbook.
- “Excel Binary Workbook” can reduce the workbook size by 50%.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Excel Extensions. We discussed the top file formats, including XLSX, XLSM, XLSB, XLS, and XLAM, their key features, and applications. You may also look at these useful Excel tools below: –
- Equations in Excel ExamplesIn Excel, equations are the formulas we type into cells. We begin by writing an equation with an equals to symbol (=), which Excel knows as calculate.read more
- AutoFill in ExcelAutoFill in excel can fill a range in a specific direction by using the fill handle.read more
- Excel vs. Google SheetsIn Google Sheets, we may share a link with other users to permit them to read or edit the sheet at the same time, however in Excel, only one person can edit the file at a time.read more
- How to use Array Formulas in Excel?Array formulas are extremely helpful and powerful formulas that are used in Excel to execute some of the most complex calculations. There are two types of array formulas: one that returns a single result and the other that returns multiple results.read more
- LINEST Excel FunctionThe built-in LINEST Function in Excel calculates statistics for a line by the least-squares regression method & returns an array that defines the line proving to be well-suited for the given data. read more
Extension File (Table of Contents)
- Extensions of Excel
- How to Change the Excel file format or Extension?
- How do you know the file type of saved file?
Extensions of Excel
Excel is one the tool which has a variety of extension in which we can save the file. A commonly used extension in Excel is .xlsx, which is used for storing a simple type of data. XLS is another type of default extension which was used until MS Office 2007. For storing a VBA code, we have XLSM. This is purely made for macros. Another extension, CSV (Comma Separated Values), delimits the data, which is separated by commas. XLSB extension is used for compression, saving, opening etc.
For example, the filename “XYZ.doc” has an extension of “.doc, ” a file extension associated with the document file.
Excel file extensions can be of various types. Here we will cover the most common file type:
- XLS – Excel file extension
This extension is the most common and default type in the spreadsheet generated by Microsoft office. Prior to Excel 2007, the file extension was XLS. This extension refers to a file which contains all type of information including data, formats, graphics etc. The operating system recognizes the file type with the help of an extension and operates this file using the Excel application.
The XLS is the default file type for Excel version 2.0 to Excel 2003.
- XLSX – Excel file extension
This extension is used by the spreadsheet files generated with the Excel version 2007 onwards. For an Excel file, the current default file extension is XLSX.
XSLX is an XML based file format. With the use of this technology, the file with XSLX format is very less in weight or size, and as compared to the XLS file format, this leads directly to saving space. It requires less time to download or upload excel documents.
Only one disadvantage of this XSLX extension is that this version is incompatible to run the files prior to Excel 2007.
- XLSM – Excel file extension
This extension file type is generated by the spreadsheet with the excel version 2007 onwards, including Excel macros.
With the help of an extension, it’s easy to understand that the file contains a macro. Because of security reasons and for protecting a file with computer viruses, malicious macros, infecting computers, etc., this version comes into existence.
This file extension is very reliable in terms of macros and for security reasons.
- XLSB – Excel file extension
If excel files contain a large amount of data or information, this file extension type fully supports in the compression process, saving, opening, etc.
An excel file that contains a large amount of data takes a lot of time in the opening in processing that file. Sometimes while opening, it gets hanged and frequently crashes.
How to Change the Excel file format or Extension?
For changing the file extension, follow the below steps:
- Open the workbook for which you want to change the format.
- Go to the FILE tab.
- It will open a left pane window. There are a lot of options available in this pane. Refer to the below screenshot.
- Click on Save As option as shown below.
- It will open a dialog box, as shown below.
- Now you need to select where you want to save the file in the system. Refer to the below screenshot.
- I have selected the Desktop for saving this file as a destination.
- Under the File name field, give the file name for the workbook.
- Under Save as type field, we need to choose the file format.
- Click on Save as type filed; it will open a list of formats as shown in the below screenshot.
- Choose the file format and click on the Save button for saving the file.
- It will save the file with the extension.
How do you know the file type of saved file?
For this, follow below steps:
- Select the file for which you want to know the file format.
- Right-click on that file.
- It will open a drop-down list of options.
- Click on the Properties option from the list. Refer to the below screenshot.
- It will open a Properties window.
- Under the Type of file option, you can see the file type or extension of the file. Refer to the below screenshot.
Things to Remember about Excel File Formats
- Any file format doesn’t support all the features of excel like formulas etc.; then it will display an alert message box.
- Then you can change the file format again.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Extensions of Excel. Here we discuss how to Change the Excel file format or Extension along with its practical examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Cheat Sheet of Excel Formulas
- CSV Files into Excel
- Sort Columns in Excel
- Data Table in Excel
Updated: 11/06/2021 by
Excel is a spreadsheet application developed and published by Microsoft. It is part of the Microsoft Office suite of productivity software.
Unlike a word processor, such as Microsoft Word, Excel organizes data in columns and rows. Rows and columns intersect at a space called a cell. Each cell contains data, such as text, a numerical value, or a formula.
Excel was originally code-named Odyssey during development. It was first released on September 30, 1985.
Excel overview
Excel is a tool for organizing and performing calculations on data. It can analyze data, calculate statistics, generate pivot tables, and represent data as charts or graphs.
For example, you could create an Excel spreadsheet that calculates a monthly budget, tracks associated expenses, and interactively sorts the data by criteria.
Below is an example of Microsoft Excel with each of its major sections highlighted. See the formula bar, cell, column, row, or sheet tab links for further information about each section.
Where do you find or start Excel?
If you have Excel or the entire Microsoft Office package installed on your Windows computer, you can find Excel in the Start menu.
Keep in mind that new computers do not include Excel. It must be purchased and installed before running it on your computer. If you do not want (or cannot afford) to purchase Excel, you can use a limited version for free at the Microsoft Office website.
If Excel is installed on your computer but isn’t in your Start menu, use the following steps to launch Excel manually.
- Open My Computer or File Explorer.
- Click or select the C: drive. If Microsoft Office is installed on a drive other than the C: drive, select that drive instead.
- Find and open the Program Files (x86) or Program Files folder.
- Open the Microsoft Office folder.
- In the Microsoft Office folder, open the root folder. Then open the OfficeXX folder, where XX is the version of Microsoft Office (e.g., Office16 for Microsoft Office 2016) installed on your computer.
Tip
If there is no root folder, look for and open the folder with Office in the folder name.
- Find and double-click the file named EXCEL.EXE to start the Excel program.
How to open Microsoft Excel without using a mouse
- Press the Windows key.
- Type Excel and select the Microsoft Excel entry in the search results.
- If Excel does not open after selecting it in the search results, press Enter to launch it.
How can Excel be formatted?
Each of the rows, columns, and cells can be modified in many ways, including the background color, number or date format, size, text font, layout, etc. In our example above, you can see that the first row (row 1) has a blue background, bold text, and each cell has its text centered.
- How to format a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Download an example of a spreadsheet file
We created a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that you can download and open in any spreadsheet program, including Microsoft Excel. This spreadsheet illustrates some capabilities of a spreadsheet, formulas, and functions, and lets you experiment more with a spreadsheet.
- Download example.xls
Why do people use Excel?
There are many reasons people use Excel. For example, someone might use Excel and a spreadsheet to keep track of their expenses. See our spreadsheet definition for a complete list of reasons and examples of how people use a spreadsheet.
Why would someone use Excel over another spreadsheet program?
Today, there are many free spreadsheet programs that someone could use instead of Excel. However, even with the available free options, Excel remains the most-used spreadsheet because of all its available options, features, and because many businesses still use the program.
- Where can I get a free spreadsheet program?
Tip
Even with all Excel’s options, a free spreadsheet program like Google Sheets is often all most users need.
Note
If you want to get Excel because it’s a job requirement, it’s still okay to learn all the basics in a free spreadsheet program. However, there are still many differences between Excel and a free spreadsheet program.
Excel file extensions
Microsoft Excel supports the following file extensions. The default format for saving a Microsoft Excel workbook is .xlsx in all modern versions and .xls in early versions.
| Extension | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| .csv | CSV (Comma-separated values) | A minimal format compatible with many spreadsheet applications. Rows of data are represented as lines in the text file, with columnar breaks delimited by a single character, usually a comma. |
| .dbf | DBF 3, DBF 4 | The native database file format of DBASE III and IV. |
| .dif | Data interchange format | A feature-limited, widely-supported file format. Supports saving a single-page spreadsheet only. |
| .htm, .html | HTML | Contains data formatted in HTML. When exported by Excel, supporting files such as images and sounds are stored in a folder. |
| .mht, .mhtml | Single-page HTML | HTML-formatted single-page data. |
| .ods | OpenDocument Spreadsheet | An open-source file format supported by word processors including OpenOffice and LibreOffice. |
| PDF (Portable Data Format) | An industry-standard document format created by Adobe. | |
| .prn | Space-delimited formatted text | A format similar to CSV that supports text formatting, created by Lotus. Supports only a single sheet. |
| .slk | SYLK Symbolic Link Format. | Supports only a single sheet. |
| .txt | Tab-delimited text | A text file format similar to CSV, using tab as the delimiter character. Also, stores Unicode-encoded single-page spreadsheets. |
| .xla | Excel Add-in | Supporting file for Visual Basic VBA projects, compatible with Excel 95-2003. |
| .xlam | Excel Add-in with Macros | XML-based format compatible with Excel 2007 and 2013-2019, supporting VBA projects and Excel 4.0 macros. |
| .xls | Excel Workbook (deprecated) | The native Excel file format for Excel versions 97-2003. |
| .xlsb | Excel Binary Workbook | A fast load-and-save format compatible with Excel 2007-2019. Supports VBA projects and Excel 4.0 macros. |
| .xlsm | Excel Workbook with Macros | XML-based format compatible with Excel 2007-2019, supporting VBA and Excel 4.0 macros. |
| .xlsx | Excel Workbook | The native Excel file format for Excel versions 2007-2019. Supports «ISO Strict» formatting. Does not support macros. |
| .xlt | Excel Template (deprecated) | Excel template file format, Excel 97-2003. |
| .xltx | Excel Template | Excel template file format, Excel 2007-2019. |
| .xlw | Excel Workbook Only | Saves only worksheets, chart sheets, and macro sheets but does not save spreadsheets. Compatible with Excel 2013-2019. |
| .xml | XML Data | Spreadsheet data exported as XML. |
| .xps | OpenXML Paper Specification | An open-source document format similar to PDF. |
What are the different versions of Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel has had many versions throughout its history. The different releases with their release dates are listed below.
Windows versions
- Excel 2019, released in 2018
- Office 365 and Excel 2016, released in 2016
- Excel 2013, released in 2013
- Excel 2010, released in 2010
- Excel 2007, released in 2007
- Excel 2003, released in 2003
- Excel 2002, released in 2002
- Excel 2000, released in 2000
- Excel 97, released in 1997
- Excel 95, released in 1995
- Excel 5.0, released in 1993
- Excel 4.0, released in 1992
- Excel 3.0, released in 1990
- Excel 2.0, released in 1987
Mac versions
- Excel 2019, released in 2018
- Excel 2016, released in 2016
- Excel 2011, released in 2011
- Excel 2008, released in 2008
- Excel 2004, released in 2004
- Excel 2001, released in 2001
- Excel 2000, released in 2000
- Excel 98, released in 1998
- Excel 5.0, released in 1993
- Excel 4.0, released in 1992
- Excel 3.0, released in 1990
- Excel 2.2, released in 1989
- Excel 1.5, released in 1988
- Excel 1, released in 1985
What came before Excel?
Microsoft Excel was not the first spreadsheet program. Lotus 1-2-3 and VisiCalc were popular spreadsheet programs released before Excel.
Conditional formatting, Formula, Function, Google Docs, Lookup, Multiplan, Office, Office 365, Office Online, Spreadsheet, Spreadsheet terms