Noun
Elm trees have shallow roots.
Pull weeds up by the roots so that they don’t grow back.
You can tell that she dyes her hair blonde because her dark roots are showing.
Recent Examples on the Web
Controlling Callery pears is difficult because their sturdy, extensive root system makes the trees almost impossible to kill with herbicides.
—
The root cause of that discrepancy is that the Diamondbacks have a lefty-heavy lineup.
—
While a myriad of factors contribute to the condition, poor judgment on the part of select injectors is, no doubt, a root cause.
—
Deep planting will spur a larger, more expansive root system than if the transplant was situated at ground level.
—
In addition, their long root systems prevent soil erosion.
—
The INEOS Facility is currently shut down while officials investigate to determine the incident’s root cause.
—
Smart manufacturing helps identify the waste, track the sources, analyze the data, determine the root causes and then eliminate those causes, which in turn eliminates the waste.
—
As Tim Carney writes in the Washington Examiner, debating the root cause of the problem is secondary to fixing it, and the Texas Department of Health could render the lawsuit moot by clarifying the law for hospitals.
—
For the first time, we’re made to root against him.
—
The aims were to figure out which groups still existed within the department, assess whether existing department policies had been effective in combating them and make recommendations on how to root them out.
—
The encampment of protesters once numbered about 2,000, but police efforts to root them out have dwindled their numbers to around 200 as of Wednesday.
—
This kind of attitude is why many college football fans root against Michigan.
—
After three years of traveling through the lowest part of your chart—your fourth house of home, family, and ancestry—you’ve likely spent a lot of time and energy finding a place to root yourself.
—
We are left with an awkward question: for whom, exactly, are we supposed to root?
—
Inflation eased for a seventh month straight in January, but interest rates will keep rising as the Fed works harder to root stubbornly high prices out of the economy.
—
In my house, Friday is officially Fridge Forage Day, a time to root around the fridge (and pantry) like a truffle-hunting piglet, hoping to unearth a treasure.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘root.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
English[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- enPR: ro͞ot, IPA(key): /ɹuːt/
- (Midwestern US) IPA(key): /ɹʊt/
-
Audio (Midwestern US) (file) - Rhymes: -uːt, -ʊt
- Homophones: route (some pronunciations), rute
Etymology 1[edit]
From Middle English rote, root, roote (“the underground part of a plant”), from late Old English rōt, from Old Norse rót (Icelandic rót), from Proto-Germanic *wrōts, from Proto-Indo-European *wréh₂ds (“root”); cognate with wort, radish, and radix.
Noun[edit]
root (countable and uncountable, plural roots)
- The part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors and supports the plant body, absorbs and stores water and nutrients, and in some plants is able to perform vegetative reproduction.
- Hyponym: taproot
-
This tree’s roots can go as deep as twenty metres underground.
- A root vegetable.
-
- […] two fields which should have been sown with roots in the early summer were not sown because the ploughing had not been completed early enough.
-
- The part of a tooth extending into the bone holding the tooth in place.
-
Root damage is a common problem of overbrushing.
-
- The part of a hair under the skin that holds the hair in place.
-
The root is the only part of the hair that is alive.
-
- The part of a hair near the skin that has not been dyed, permed, or otherwise treated.
-
He dyed his hair black last month, so the grey roots can be seen.
-
- (figurative) The primary source; origin.
- Synonyms: basis, origin, source
-
The love of money is the root of all evil.
- , Book 1
- They were the roots out of which sprang two distinct people.
-
1936, Rollo Ahmed, The Black Art, London: Long, page 160:
-
Phallicism was, therefore, at the root of all religion, and was definitely the opponent of evil and darkness.
-
- (aviation) The section of a wing immediately adjacent to the fuselage.
- (engineering) The bottom of the thread of a threaded object.
- Antonym: crest
-
The root diameter is the minor diameter of an external thread and the major diameter of an internal one.
- (arithmetic) Of a number or expression, a number which, when raised to a specified power, yields the specified number or expression.
- Hyponyms: cube root, functional root, square root
-
The cube root of 27 is 3.
- (arithmetic) A square root (understood if no power is specified; in which case, «the root of» is often abbreviated to «root»).
-
Multiply by root 2.
- 1899, Dante Gabriel Rossetti (transl.), The New Life (La Vita Nuova) of Dante Alighieri, Siddall edition, page 122.
- The number three is the root of the number nine; […] being multiplied merely by itself, it produceth nine, as we manifestly perceive that three times three are nine.
-
- (mathematical analysis) A zero (of an equation).
- Synonym: zero
- Antonym: pole
- Holonym: kernel
- (graph theory, computing) The single node of a tree that has no parent.
- (linguistic morphology) The primary lexical unit of a word, which carries the most significant aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Inflectional stems often derive from roots.
- Coordinate term: stem
-
1530 July 18, Iohan Palſgrave, “The Introduction”, in Leſclarciſſement de la langue francoyſe […] [2], London: Richard Pynſon, Iohan Haukyns, →OCLC, page 32; reprinted as Lesclarcissement de la langue françoyse, Genève: Slatkine Reprints, 1972:
-
In ſo moche that if any verbe be of the thyꝛde coniugation / I ſet out all his rotes and tenſes […]
-
-
2006, Donald Ringe, From Proto-Indo-European to Proto-Germanic (A Linguistic History of English; 1)[3], Oxford: Oxford University Press, →ISBN, page 12:
-
A considerable number of derived nominals, especially thematic nouns, also exhibited o-grade roots.
-
- (linguistics) A word from which another word or words are derived.
- Synonym: etymon
- (music) The fundamental tone of any chord; the tone from whose harmonics, or overtones, a chord is composed[1].
- The lowest place, position, or part.
- 1812, Robert Southey, Omniana
- the roots of the mountains
- 1812, Robert Southey, Omniana
- (computing) In UNIX terminology, the first user account with complete access to the operating system and its configuration, found at the root of the directory structure; the person who manages accounts on a UNIX system.
- Synonyms: superuser, root account, root user
-
I have to log in as root before I do that.
- (computing) The highest directory of a directory structure which may contain both files and subdirectories.
-
I installed the files in the root directory.
-
- (slang) A penis, especially the base of a penis.
Derived terms[edit]
- arrowroot
- deep-rooted
- dick root
- put down roots
- root canal
- root cause
- root gap
- root mean square
- rootkit
- rootless
- roots
- roots music
- rootsy
- strictly roots
- take root
- taproot
- uproot
Translations[edit]
part of a plant
- Acehnese: ukheue
- Afar: rimid
- Afrikaans: wortel (af)
- Aiton: please add this translation if you can
- Aklanon: gamot
- Albanian: rrënjë (sq) f
- Arabic: جَذْر (ar) m (jaḏr)
- Egyptian Arabic: جدر m (gedr)
- North Levantine Arabic: شرش m (šereš)
- Mesopotamian Arabic: عرگ m (ʕereg)
- Moroccan Arabic: جدر m (ždər) ((plural) جدور m pl (ždur))
- South Levantine Arabic: شرش m (šorš)
- Aragonese: radiz (an)
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Aromanian: arãdãtsinã f, zãrãtsinã f, rãdãtsinã f
- Asi: gamot
- Assamese: শিয়া (xia), শিপা (xipa)
- Asturian: raíz (ast) f
- Azerbaijani: kök (az)
- Bakung: lakat
- Balinese: akah
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Basque: sustrai, zuztar, erro
- Belarusian: ко́рань (be) m (kóranʹ)
- Bengali: মূল (bn) (mul)
- Berber:
- Tashelhit: azɣwr m
- Bhojpuri: please add this translation if you can
- Bilba: oka
- Bintulu: waka
- Bulgarian: ко́рен (bg) m (kóren)
- Burmese: အမြစ် (my) (a.mrac)
- Catalan: arrel (ca) f
- Cebuano: gamot
- Central Melanau: akah
- Chakma: please add this translation if you can
- Chamicuro: ijtishi
- Chechen: орам (oram)
- Cherokee: ᎤᎿᏍᏕᏜ (uhnasdedla)
- Chichewa: muzu
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 根 (zh) (gēn)
- Choctaw: akshish
- Classical Nahuatl: nelhuatl
- Czech: kořen (cs) m
- Dalmatian: radaica f
- Danish: rod (da) c
- Dhivehi: please add this translation if you can
- Drung: vng’reu, shing’reu
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m
- Dzongkha: please add this translation if you can
- Eastern Arrernte: artekerre
- Eastern Cham: ꨀꨉꨩ (agha’), ꨉꨩ (gha’), ꨂꨉꨩ (ưgha’)
- Egyptian: (wꜣb m)
- Elfdalian: ruota f
- Esperanto: radiko (eo)
- Estonian: juur (et)
- Evenki: ңиңтэ
- Extremaduran: please add this translation if you can
- Faroese: rót (fo) f
- Finnish: juuri (fi), puunjuuri (of a tree)
- Franco-Provençal: please add this translation if you can
- French: racine (fr) f
- Friulian: lidrîs
- Galician: raíz (gl) f
- Ge’ez: ሥርው (śərw)
- Georgian: ფესვი (pesvi), ძირი (ʒiri)
- German: Wurzel (de) f, Wurzeln (de) pl
- Gothic: 𐍅𐌰𐌿𐍂𐍄𐍃 f (waurts)
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Ancient: ῥίζα f (rhíza)
- Greenlandic: sorlak
- Guaraní: tapo
- Haitian Creole: rasin
- Hawaiian: aʻa
- Hebrew: שורש (he) m (shóresh)
- Higaonon: gamot
- Hindi: जड़ (hi) (jaṛ)
- Hungarian: gyökér (hu)
- Icelandic: rót (is) f
- Indonesian: akar (id)
- Ingrian: juuri
- Iranun: waged
- Irish: fréamh f
- Isnag: xamut
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Iu Mien: nzungh
- Japanese: 根 (ja) (ね, ne)
- Javanese: oyot
- Kamarian: waar
- Kambera: amu
- Kannada: ಬೇರು (kn) (bēru)
- Kashubian: kòrzéń
- Kazakh: тамыр (tamyr), түбір (tübır)
- Khamti: please add this translation if you can
- Khmer: ឫស (km) (rɨh)
- Kilivila: uula
- Komi-Zyrian: вуж (vuž)
- Kongo: mwanzi
- Korean: 뿌리 (ko) (ppuri)
- Kurdish:
- Central Kurdish: ڕەگ (ckb) (reg)
- Northern Kurdish: reg (ku) m, reh (ku) m, kok (ku) f
- Kyrgyz: тамыр (ky) (tamır)
- Ladin: please add this translation if you can
- Lak: бакӏ (bakʼ), бакӏру (bakʼru)
- Lao: ຮາກ (hāk)
- Latgalian: sakne f, saknis f pl
- Latin: rādīx f
- Latvian: sakne (lv) f, saknes f pl
- Lezgi: пун (pun)
- Ligurian: radiccia f, reixe f
- Lithuanian: šaknis (lt)
- Livonian: jūŗ
- Lombard: radis (lmo) f
- Low German: Wortel f
- Luhya: kumuzizi
- Luxembourgish: Wuerzel f
- Lü: ᦣᦱᧅ (haak)
- Macedonian: корен m (koren)
- Magahi: please add this translation if you can
- Maguindanao: dalig, bekaw
- Maithili: please add this translation if you can
- Malay:
- Jawi: اکر
- Rumi: akar (ms)
- Malayalam: വേര് (ml) (vērŭ)
- Maltese: għerq m
- Manchu: ᡩᠠ (da)
- Maori: aka, akaaka (refers to fibrous roots)
- Maranao: bekaw
- Mari:
- Eastern Mari: вож (vož)
- Western Mari: please add this translation if you can
- Middle English: rote, more
- Minangkabau: ure’
- Mirandese: please add this translation if you can
- Mon: ရိုဟ် (mnw)
- Mongolian: үндэс (mn) (ündes)
- Nahuatl: nelhuatl
- Nanai: дачан
- Navajo: akétłʼóól
- Neapolitan: ràdeca f
- Nepali: जरा (ne) (jarā)
- Nias: wa’a
- Norman: raichinne, réchinne
- Northern Sami: ruohtas
- Northern Thai: ᩁᩣ᩠ᨠ
- Norwegian:
- Bokmål: rot (no) m or f
- Nynorsk: rot (nn) f
- Occitan: raiç (oc) f, rasic (oc) f
- Ojibwe: ojiibik
- Okinawan: 根 (にー, nī)
- Old Church Slavonic:
- Cyrillic: корєнь m (korenĭ)
- Old English: wyrttruma m
- Oriya: ଜଡି (jôḍi)
- Oromo: hidda, hundee
- Pacoh: reaih, riêih
- Palu’e: waka
- Papiamentu: rais
- Pashto: جذر (ps) m (ǰazr), جرړه (ps) f (ǰárṛa)
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše)
- Phake: please add this translation if you can
- Piedmontese: rèis f, radis f
- Pipil: nelwat
- Polish: korzeń (pl) m
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Quechua: machu (qu), saphi, sapi (qu)
- Rakhine: please add this translation if you can
- Rapa Nui: aka
- Rohingya: cém
- Romagnol: radìșa f, ràdga f
- Romanian: rădăcină (ro) f
- Romansch: ragisch f, risch f, rieisch f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni), (roots for cooking) коре́нья (ru) pl (korénʹja)
- Saek: ร̄าก
- Sardinian: radichina f, arraighina, raichina
- Sasak: akah
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: ко̏ре̄н m, ко̏рије̄н m
- Roman: kȍrēn (sh) m, kȍrijēn (sh) m
- S’gaw Karen: အဂံၢ် (ʼa ghee̱)
- Shan: ႁၢၵ်ႈ (shn) (hāak)
- Sichuan Yi: ꐴ (njip)
- Sicilian: ràdica (scn) f, ràdiga (scn) f, ràrica (scn) f
- Sinhalese: please add this translation if you can
- Slovak: koreň m
- Slovene: korenina (sl) f
- Somali: xiddid (so)
- Sorbian:
- Lower Sorbian: kórjeń m
- Upper Sorbian: korjeń m
- Southern Kam: sangp
- Southern Thai: please add this translation if you can
- Spanish: raíz (es) f
- Swahili: mzizi (sw)
- Swedish: rot (sv) c
- Sylheti: please add this translation if you can
- Tagal Murut: bakat
- Tagalog: urat, ugat (tl)
- Tahitian: aʻa
- Tai Dam: please add this translation if you can
- Tai Nüa: please add this translation if you can
- Tajik: реша (tg) (reša)
- Tamil: வேர் (ta) (vēr)
- Tatar: тамыр (tt) (tamır)
- Tausug: gamut
- Telugu: వేరు (te) (vēru)
- Ternate: utu
- Tetum: abut
- Thai: ราก (th) (râak)
- Tibetan: རྩ་བ (rtsa ba)
- Tocharian B: witsako
- Tokelauan: aka
- Tongan: aka
- Turkish: kök (tr)
- Turkmen: kök
- Udi: тум (tum)
- Udmurt: выжы (vyžy)
- Ugaritic: 𐎌𐎗𐎌 (šrš)
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ), корі́ння n (korínnja)
- Urdu: جڑ (jaṛ)
- Uyghur: يىلتىز (yiltiz)
- Uzbek: ildiz (uz)
- Venetian: raixa (vec) f, rais
- Vietnamese: rễ (vi) (𣠲)
- Volapük: vul (vo)
- Walloon: raecene (wa) f
- Welsh: gwraidd (cy) m
- West Frisian: woartel (fy)
- Western Cham: please add this translation if you can
- White Hmong: cag
- ǃKung: daŋ
- ǃXóõ: ǃkʻqái
- Yagnobi: риша (riša)
- Yakan: gamut
- Yakut: силис (silis)
- Yamdena: wakar
- Yiddish: וואָרצל m (vortsl)
- Zealandic: wortel m
- Zhuang: rag
- Zulu: impande class 9/10
of a tooth
- Afrikaans: wortel (af)
- Arabic: جَذْر (ar) m (jaḏr) ((plural) جُذُور m pl (juḏūr))
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Berber:
- Tashelhit: azɣwr m
- Bulgarian: корен (bg) m (koren)
- Catalan: arrel (ca) f
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 根 (zh) (gēn)
- Czech: kořen (cs) m
- Danish: rod (da) c
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m
- Finnish: juuri (fi), hampaanjuuri (fi)
- French: racine (fr) f
- Galician: raíz (gl) f, raigoto m
- German: Wurzel (de) f, Wurzeln (de) pl, Zahnwurzel (de) f
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Hebrew: שורש (he) m (shoresh)
- Hungarian: gyökér (hu), foggyökér (hu)
- Icelandic: rót (is) f, rætur pl
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Japanese: 歯根 (しこん, shikon)
- Korean: 뿌리 (ko) (ppuri)
- Latin: radix f, radicis pl
- Latvian: sakne (lv) f
- Norwegian:
- Bokmål: rot (no) m or f
- Nynorsk: rot (nn) f
- Occitan: raiç (oc) f
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše)
- Polish: korzeń (pl) m
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Romanian: rădăcină de dinte f, rădăcină dentară f, rădăcină dentală f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: ко̏ре̄н m, ко̏рије̄н m
- Roman: kȍrēn (sh) m, kȍrijēn (sh) m
- Slovak: koreň m
- Spanish: raíz (es) f, raíces (es) pl
- Swahili: mzizi (sw)
- Swedish: rot (sv), tandrot (sv)
- Turkish: kök (tr)
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ)
- Vietnamese: chân răng
- Zulu: umsuka class 3/4
part of a hair under the skin
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Bulgarian: корен (bg) m (koren)
- Czech: kořen (cs), kořínek (cs)
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m
- Finnish: juuri (fi), hiusjuuri
- French: racine (fr) f
- German: Haarwurzel f, Wurzel (de) f
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Ancient: ἴονθος m (íonthos)
- Hebrew: שורש (he) m (shóresh)
- Hungarian: hajgyökér (hu)
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Norwegian:
- Bokmål: rot (no) m or f
- Nynorsk: rot (nn) f
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše), پیاز (fa) (piyâz)
- Polish: cebulka (pl) f
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Romanian: rădăcină de păr f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: ко̏ре̄н m, ко̏рије̄н m
- Roman: kȍrēn (sh) m, kȍrijēn (sh) m
- Slovak: korienok m
- Spanish: raíz (es) f
- Swedish: hårrot c
- Turkish: kök (tr)
- Vietnamese: chân tóc
- Welsh: gwreiddyn (cy) m
- Zulu: umsuka class 3/4
primary source
- Afrikaans: wortel (af)
- Arabic: أَصْل m (ʔaṣl) ((plural) أُصُول (ar) m pl (ʔuṣūl))
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Bulgarian: ко́рен (bg) m (kóren)
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 根源 (zh) (gēnyuán)
- Czech: kořen (cs) m
- Danish: rod (da) c
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m
- Finnish: lähde (fi), juuri (fi)
- French: racine (fr) f, origine (fr) f
- Galician: raíz (gl) f
- German: Quelle (de) f, Quellen (de) pl
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Ancient: ῥίζα f (rhíza)
- Hebrew: מקור (he) m (makór)
- Hungarian: gyökér (hu), forrás (hu), alap (hu), kiindulópont (hu), eredet (hu), okozó (hu)
- Icelandic: rót (is) f
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Japanese: 起源 (ja) (きげん, kigen), 元 (ja) (もと, moto), 根源 (ja) (こんげん, kongen)
- Korean: 근원 (ko) (geunwon)
- Latin: radix f
- Latvian: sakne (lv) f
- Norwegian:
- Bokmål: rot (no) m or f
- Nynorsk: rot (nn) f
- Occitan: raiç (oc) f
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše), سرچشمه (fa) (sarčašme)
- Polish: źródło (pl) n
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: ко̏ре̄н m, ко̏рије̄н m
- Roman: kȍrēn (sh) m, kȍrijēn (sh) m
- Slovak: koreň m
- Slovene: koren (sl) m
- Spanish: raíz (es) f, raíces (es) pl
- Swedish: källa (sv) c
- Telugu: మూలము (te) (mūlamu)
- Turkish: kaynak (tr)
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ)
- Welsh: gwraidd (cy) m
- Zulu: umsuka class 3/4
arithmetic: number or expression which when raised to a power gives the specified number or expression
- Afrikaans: wortel (af)
- Arabic: جَذْر (ar) m (jaḏr) ((plural) جُذُور m pl (juḏūr))
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Bulgarian: корен (bg) m (koren)
- Catalan: arrel (ca) f
- Czech: odmocnina (cs) f
- Danish: rod (da) n
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m, machtswortel m
- Esperanto: radiko (eo)
- Finnish: juuri (fi)
- French: racine (fr) f
- German: Wurzel (de) f
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Ancient: δύναμις f (dúnamis)
- Hebrew: שורש (he) m (shóresh)
- Hungarian: gyök (hu)
- Icelandic: rót (is) f
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Japanese: 根 (ja) (こん, kon)
- Korean: 거듭제곱근 (ko) (geodeupjegopgeun)
- Latvian: sakne (lv) f
- Mongolian: язгуур (mn) (jazguur)
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše)
- Polish: pierwiastek (pl) m
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: ко̏ре̄н m, ко̏рије̄н m
- Roman: kȍrēn (sh) m, kȍrijēn (sh) m
- Slovak: odmocnina
- Slovene: koren (sl) m
- Spanish: raíz (es) f
- Swahili: kipeuo
- Swedish: rot (sv)
- Tagalog: ugat (tl)
- Telugu: మూలము (te) (mūlamu)
- Turkish: kök (tr)
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ)
- Vietnamese: căn số
- Welsh: isradd f
analysis: zero of a function
- Afrikaans: wortel (af)
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Danish: rod (da) c
- Dutch: nulpunt (nl) n, wortel (nl) m
- Finnish: juuri (fi), nollakohta (fi)
- Hungarian: gyök (hu)
- Japanese: 解 (ja) (かい, kai)
- Korean: 근 (ko) (geun)
- Mongolian: язгуур (mn) (jazguur)
- Polish: pierwiastek (pl) m, miejsce zerowe n
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Slovak: koreň m
- Spanish: raíz (es)
- Swedish: nollställe (sv), rot (sv) c
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ)
linguistic morphology: primary lexical unit of a word
- Arabic: جَذْر (ar) m (jaḏr)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Bulgarian: ко́рен (bg) m (kóren)
- Catalan: arrel (ca) f
- Chinese:
- Cantonese: 語根/语根 (jyu5 gan1)
- Mandarin: 语根 (zh) (yǔgēn), 語根/语根 (zh) (yǔgēn)
- Czech: kořen (cs) m
- Dutch: wortel (nl) m
- Finnish: juuri (fi)
- French: racine (fr), radical (fr)
- Georgian: ფუძე (puʒe)
- German: Grundwort (de) n
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Hungarian: szótő (hu), tő (hu)
- Italian: radice (it) f
- Japanese: 語根 (ごこん, gokon)
- Korean: 어근(語根) (ko) (eogeun)
- Kyrgyz: уңгу (ky) (uŋgu)
- Polish: podstawa słowotwórcza f, rdzeń (pl) m
- Portuguese: radical (pt) m, raiz (pt) f
- Romanian: rădăcină (ro) f, radical (ro) n
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Slovak: koreň
- Spanish: raíz (es) f, lexema (es) f
- Tagalog: salitang ugat
- Turkish: please add this translation if you can
- Ukrainian: ко́рінь (uk) m (kórinʹ)
- Vietnamese: gốc từ (vi)
- Welsh: gwreiddyn (cy) m
- Zulu: umsuka class 3/4
philology: word from which another word or words are derived
- Arabic: أَصْل m (ʔaṣl) ((plural) أُصُول (ar) m pl (ʔuṣūl))
- Armenian: արմատ (hy) (armat)
- Bashkir: тамыр (tamır)
- Bulgarian: корен (bg) m (koren)
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 詞根/词根 (zh) (cígēn)
- Dutch: stam (nl) m
- Finnish: juuri (fi), kantasana (fi), kanta (fi)
- French: racine (fr) f, mot souche m
- German: Stamm (de) m
- Greek: ρίζα (el) f (ríza)
- Hebrew: שורש (he) m (shóresh)
- Hungarian: szógyök (hu), szógyökér, gyök (hu), gyökér (hu), ősszó, gyökérszó, tőszó (hu), tő (hu)
- Irish: stoc m
- Persian: ریشه (fa) (riše)
- Portuguese: raiz (pt) f
- Russian: ко́рень (ru) m (kórenʹ), ко́рни (ru) m pl (kórni)
- Scottish Gaelic: freumh m
- Slovene: koren (sl) m
- Spanish: raíz (es) f
- Swedish: rot (sv), ordrot
- Turkish: köken (tr)
- Welsh: gwreiddyn (cy) m
- Yiddish: שורש m (shoyresh), וואָרצל m (vortsl)
person who manages accounts on a UNIX system
computing: highest directory of a directory structure
See also[edit]
Other terms used in arithmetic operations:
- successor
- addition, summation:
- (augend) + (addend) = (total)
- (summand) + (summand) + (summand)… = (sum)
- subtraction:
- (minuend) − (subtrahend) = (difference)
- multiplication, factorization:
- (multiplier) × (multiplicand) = (product)
- (factor) × (factor) × (factor)… = (product)
- division:
- (dividend) ÷ (divisor) = (quotient)
- (numerator) / (denominator) = (quotient)
- Or sometimes = (quotient) with (remainder) remaining
- exponentiation:
- (base) (exponent) = (power)
- root extraction:
- (degree) √ (radicand) = (root)
- logarithmization:
- log(base) (antilogarithm) = (logarithm)
Advanced hyperoperations: tetration, pentation, hexation
Verb[edit]
root (third-person singular simple present roots, present participle rooting, simple past and past participle rooted)
- To grow roots; to enter the earth, as roots; to take root and begin to grow.
-
The cuttings are starting to root.
-
1707, J[ohn] Mortimer, The Whole Art of Husbandry; or, The Way of Managing and Improving of Land. […], 2nd edition, London: […] J[ohn] H[umphreys] for H[enry] Mortlock […], and J[onathan] Robinson […], published 1708, →OCLC:
- In deep grounds the weeds root the deeper.
-
2014 October 26, Jeff Howell, “Is the Japanese knotweed threat exaggerated? Our troubleshooter calls for calm about Japanese knotweed in the garden – and moss on the roof [print version: Don’t panic about an overhyped invasion, 25 October 2014, p. P13]”, in The Daily Telegraph (Property)[4]:
-
Some old, underfired clay pantiles might be damaged by button mosses rooting in cracks and fissures. But most post-war tiles are hard enough to withstand a bit of moss growth.
-
-
- To prepare, oversee, or otherwise cause the rooting of cuttings.
-
We rooted some cuttings last summer.
-
- To be firmly fixed; to be established.
- 1823, Gilbert Burnet, The Life of Sir Matthew Hale, Knt., Sometime Lord Chief Justice of His Majesty’s Court of King’s-Bench
- If any irregularity chanced to intervene and to cause misapprehensions, he gave them not leave to root and fasten by concealment.
-
2020 October 15, Frank Pasquale, “‘Machines set loose to slaughter’: the dangerous rise of military AI”, in The Guardian[5]:
-
Massacres that take place during war often seem to be rooted in irrational emotion.
-
- 1823, Gilbert Burnet, The Life of Sir Matthew Hale, Knt., Sometime Lord Chief Justice of His Majesty’s Court of King’s-Bench
- (computing slang, transitive) To get root or privileged access on a computer system or mobile phone, often through bypassing some security mechanism.
- Synonym: (mobile phone) jailbreak
-
We rooted his box and planted a virus on it.
-
I want to root my Android phone so I can remove the preinstalled crapware.
Translations[edit]
Etymology 2[edit]
From Middle English wrōten (“to dig with the snout”), from Old English wrōtan, from Proto-Germanic *wrōtaną (“to dig out, to root”). Related to Old English wrōt (“snout; trunk”). Loss of initial w- probably due to influence from the related noun (Etymology 1).
Verb[edit]
root (third-person singular simple present roots, present participle rooting, simple past and past participle rooted)
- (transitive, intransitive) To turn up or dig with the snout.
-
A pig roots the earth for truffles.
- c. 1515–1516, published 1568, John Skelton, Againſt venemous tongues enpoyſoned with ſclaunder and falſe detractions &c.:
- Such tunges ſhuld be torne out by the harde rootes,
Hoyning like hogges that groynis and wrotes.
- Such tunges ſhuld be torne out by the harde rootes,
-
- (by extension) To seek favour or advancement by low arts or grovelling servility; to fawn.
-
c. 1593 (date written), William Shakespeare, “The Tragedy of Richard the Third: […]”, in Mr. William Shakespeares Comedies, Histories, & Tragedies […] (First Folio), London: […] Isaac Iaggard, and Ed[ward] Blount, published 1623, →OCLC, [Act I, scene iii]:
-
Thou elvish-marked, abortive, rooting hog!
-
-
- (intransitive) To rummage; to search as if by digging in soil.
- Synonyms: dig out, root out, rummage
-
rooting about in a junk-filled drawer
- (intransitive) Of a baby: to turn the head and open the mouth in search of food.
- 2016, Rachel Waddilove, The Baby Book: How to enjoy year one: revised and updated (page 179)
- When your baby is rooting, his head will turn to the side and he will open and close his mouth. If you put your finger in your baby’s hand, she has a grasping reflex that makes her curl her fingers around yours and hold on.
- 2016, Rachel Waddilove, The Baby Book: How to enjoy year one: revised and updated (page 179)
- (transitive) To root out; to abolish.
-
1595 December 9 (first known performance), William Shakespeare, “The life and death of King Richard the Second”, in Mr. William Shakespeares Comedies, Histories, & Tragedies: Published According to the True Originall Copies (First Folio), London: […] Isaac Iaggard, and Ed[ward] Blount, published 1623, →OCLC, [Act IV, scene iv]:
-
I will go root away the noisome weeds.
-
-
- (Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, vulgar, slang) To sexually penetrate.
- Synonyms: screw, bang, (US) drill, (British) shag; see also Thesaurus:copulate with
Usage notes[edit]
- The Australian/New Zealand sexual sense is somewhat milder than fuck but still quite coarse, and certainly not for polite conversation. The sexual sense will often be understood, unless care is taken with the context to make the rummage sense clear, or root through or root around is used. The past participle rooted is equivalent to fucked in the figurative sense of broken or tired, but rooting has only the direct verbal sense; it is not an all-purpose intensive like fucking.
Derived terms[edit]
- root about
- rooted
- root for
- root out
- root up
- underroot
Translations[edit]
to seek favour or advancement by servility
coarse slang: to have sexual intercourse
to grow roots
- Ancient Greek: ῥιζόομαι (rhizóomai)
- Bulgarian: пускам корени (puskam koreni)
- Finnish: juurtua (fi)
- Portuguese: enraizar (pt), arraigar (pt), radicar
- Slovak: zakoreniť sa, zapustiť korene
Noun[edit]
root (plural roots)
- (Australia, New Zealand, vulgar, slang) An act of sexual intercourse.
- Synonyms: (UK, US) screw, (UK) shag; see also Thesaurus:copulation
-
Fancy a root?
- (Australia, New Zealand, vulgar, slang) A sexual partner.
- Synonym: (US) screw
Usage notes[edit]
- The Australian/New Zealand sexual sense of root is somewhat milder than fuck but still quite coarse, certainly not for polite conversation. The normal usage is to have a root or similar.
Translations[edit]
coarse slang: sexual partner
- Finnish: pano (fi)
Etymology 3[edit]
Possibly an alteration of rout (“to make a loud noise”), influenced by hoot.
Verb[edit]
root (third-person singular simple present roots, present participle rooting, simple past and past participle rooted)
- (intransitive, with «for» or «on», US) To cheer (on); to show support (for) and hope for the success of. (See root for.) [late 19th century]
- Synonyms: (Australia, New Zealand) barrack, cheer on
- 1908, Jack Norworth, Take Me Out to the Ball Game
- Let me root, root, root for the home team,
-
I’m rooting for you, don’t let me down!
Translations[edit]
cheer
- Dutch: juichen (nl), aanvuren (nl), supporteren (nl)
- Finnish: kannustaa (fi)
- Hungarian: szurkol (hu), drukkol (hu)
- Portuguese: torcer (pt)
- Russian: болеть (ru) (boletʹ), топи́ть (ru) (topítʹ)
- Slovak: držať palce
- Swedish: heja (sv) (followed by preposition på)
- Thai: เอาใจช่วย (ao-jai-chûai)
References[edit]
- ^ 1817, Thomas Busby, A Dictionary of Music, Theoretical and Practical
Anagrams[edit]
- Toor, Toro, roto, roto-, toro, troo
Chinese[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Borrowed from English root.
Verb[edit]
root
- (computing slang) to root (an Android device) (to get root or privileged access)
-
- 這部手機root後不保修。 [MSC, trad.]
- Zhè bù shǒujī root hòu bù bǎoxiū. [Pinyin]
- This mobile phone will not be guaranteed if it is rooted.
这部手机root后不保修。 [MSC, simp.]
-
See also[edit]
- 越獄/越狱 (yuèyù, “to jailbreak”)
French[edit]
Noun[edit]
root m (plural roots)
- (computing) root
German Low German[edit]
Alternative forms[edit]
- raud
- rauth
- rod, rood
- rot, roth
Etymology[edit]
From Old Saxon rōd, from Proto-Germanic *raudaz, from Proto-Indo-European *h₁rowdʰós < *h₁rewdʰ-. Compare Dutch rood, German rot, West Frisian read, English red, Danish rød.
Adjective[edit]
root (comparative röder, superlative röödst)
- red
Declension[edit]
Positive forms of root
| gender | singular | plural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| masculine | feminine | neuter | all genders | ||
| predicative | he is root | se is root | dat is root | se sünd root | |
| partitive | een Roods | een Roods | wat Roods | allens Rood | |
| strong declension (without article) |
nominative | rode | rode | root | rode |
| oblique | roden | rode | root | rode | |
| weak declension (with definite article) |
nominative | de rode | de rode | dat rode | de roden |
| oblique | den roden | de rode | dat rode | de roden | |
| mixed declension (with indefinite article) |
nominative | en rode | en rode | en root/rodet | (keen) roden |
| oblique | en roden | en rode | en root/rodet | (keen) roden |
Comparative forms of root
| gender | singular | plural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| masculine | feminine | neuter | all genders | ||
| predicative | he is röder | se is röder | dat is röder | se sünd röder | |
| partitive | een röders | een röders | wat röders | allens röder | |
| strong declension (without article) |
nominative | rödere | rödere | röder | rödere |
| oblique | rödern | rödere | röder | rödere | |
| weak declension (with definite article) |
nominative | de rödere | de rödere | dat rödere | de rödern |
| oblique | den rödern | de rödere | dat rödere | de rödern | |
| mixed declension (with indefinite article) |
nominative | en rödere | en rödere | en röder | (keen) rödern |
| oblique | en rödern | en rödere | en röder | (keen) rödern |
Superlative forms of root
| gender | singular | plural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| masculine | feminine | neuter | all genders | ||
| predicative | he is de Röödste | se is de Röödste | dat is dat Röödste | se sünd de Röödsten | |
| strong declension (without article) |
nominative | röödste | röödste | röödst | röödste |
| oblique | röödsten | röödste | röödst | röödste | |
| weak declension (with definite article) |
nominative | de röödste | de röödste | dat röödste | de röödsten |
| oblique | den röödsten | de röödste | dat röödste | de röödsten | |
| mixed declension (with indefinite article) |
nominative | en röödste | en röödste | en röödst | (keen) röödsten |
| oblique | en röödsten | en röödste | en röödst | (keen) röödsten |
| Note: This declension is one of many; neither its grammar nor spelling apply to all dialects. |
|---|
Middle Dutch[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Old Dutch rōt, from Proto-Germanic *raudaz, from Proto-Indo-European *h₁rowdʰós, from the root *h₁rewdʰ-.
Adjective[edit]
rôot
- red
Inflection[edit]
This adjective needs an inflection-table template.
Descendants[edit]
- Dutch: rood
- Afrikaans: rooi
- Jersey Dutch: rôi
- Negerhollands: rooi, ro, roo, rood
- Skepi Creole Dutch: aro
- Limburgish: roead
Further reading[edit]
- “root”, in Vroegmiddelnederlands Woordenboek, 2000
- Verwijs, E.; Verdam, J. (1885–1929), “root (I)”, in Middelnederlandsch Woordenboek, The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff, →ISBN, page I
Middle English[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
Noun[edit]
root
- Alternative form of rote (“root”)
Etymology 2[edit]
Noun[edit]
root
- Alternative form of rote (“habit”)
Etymology 3[edit]
Noun[edit]
root
- Alternative form of rot
Plautdietsch[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Middle Low German rōt, from Old Saxon rōd.
Adjective[edit]
root
- red
Portuguese[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Unadapted borrowing from English root.
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Brazil) IPA(key): /ˈʁut͡ʃ/ [ˈhut͡ʃ], /ˈʁu.t͡ʃi/ [ˈhu.t͡ʃi]
- (Rio de Janeiro) IPA(key): /ˈʁut͡ʃ/ [ˈχut͡ʃ], /ˈʁu.t͡ʃi/ [ˈχu.t͡ʃi]
- (Southern Brazil) IPA(key): /ˈʁut͡ʃ/ [ˈhut͡ʃ]
- (Portugal) IPA(key): /ˈʁut/
Noun[edit]
root m (plural roots)
- (computing) root (user with complete access to the operating system)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A root (or root word) is the core of a word that is irreducible into more meaningful elements.[1] In morphology, a root is a morphologically simple unit which can be left bare or to which a prefix or a suffix can attach.[2][3] The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family (this root is then called the base word), which carries aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents.
Content words in nearly all languages contain, and may consist only of, root morphemes. However, sometimes the term «root» is also used to describe the word without its inflectional endings, but with its lexical endings in place. For example, chatters has the inflectional root or lemma chatter, but the lexical root chat. Inflectional roots are often called stems, and a root in the stricter sense, a root morpheme, may be thought of as a monomorphemic stem.
The traditional definition allows roots to be either free morphemes or bound morphemes. Root morphemes are the building blocks for affixation and compounds. However, in polysynthetic languages with very high levels of inflectional morphology, the term «root» is generally synonymous with «free morpheme». Many such languages have a very restricted number of morphemes that can stand alone as a word: Yup’ik, for instance, has no more than two thousand.
The root is conventionally indicated using the mathematical symbol √; for instance, the Sanskrit root «√bhū-» means the root «bhū-«.
Examples[edit]
The root of a word is a unit of meaning (morpheme) and, as such, it is an abstraction, though it can usually be represented alphabetically as a word. For example, it can be said that the root of the English verb form running is run, or the root of the Spanish superlative adjective amplísimo is ampli-, since those words are derived from the root forms by simple suffixes that do not alter the roots in any way. In particular, English has very little inflection and a tendency to have words that are identical to their roots. But more complicated inflection, as well as other processes, can obscure the root; for example, the root of mice is mouse (still a valid word), and the root of interrupt is, arguably, rupt, which is not a word in English and only appears in derivational forms (such as disrupt, corrupt, rupture, etc.). The root rupt can be written as if it were a word, but it is not.
This distinction between the word as a unit of speech and the root as a unit of meaning is even more important in the case of languages where roots have many different forms when used in actual words, as is the case in Semitic languages. In these, roots (semitic roots) are formed by consonants alone, and speakers elaborate different words (belonging potentially to different parts of speech) from the root by inserting different vowels. For example, in Hebrew, the root ג-ד-ל g-d-l represents the idea of largeness, and from it we have gadol and gdola (masculine and feminine forms of the adjective «big»), gadal «he grew», higdil «he magnified» and magdelet «magnifier», along with many other words such as godel «size» and migdal «tower».
Roots and reconstructed roots can become the tools of etymology.[4]
Secondary roots[edit]
Secondary roots are roots with changes in them, producing a new word with a slightly different meaning. In English, a rough equivalent would be to see conductor as a secondary root formed from the root to conduct. In abjad languages, the most familiar of which are Arabic and Hebrew, in which families of secondary roots are fundamental to the language, secondary roots are created by changes in the roots’ vowels, by adding or removing the long vowels a, i, u, e and o. (Notice that Arabic does not have the vowels e and o.) In addition, secondary roots can be created by prefixing (m−, t−), infixing (−t−), or suffixing (−i, and several others). There is no rule in these languages on how many secondary roots can be derived from a single root; some roots have few, but other roots have many, not all of which are necessarily in current use.
Consider the Arabic language:
- مركز [mrkz] or [markaza] meaning ‘centralized (masculine, singular)’, from [markaz] ‘centre’, from [rakaza] ‘plant into the earth, stick up (a lance)’ ( ر-ك-ز | r-k-z). This in turn has derived words مركزي [markaziy], meaning ‘central’, مركزية [markaziy:ah], meaning ‘centralism’ or ‘centralization’, and لامركزية, [la:markaziy:ah] ‘decentralization’[5]
- أرجح [rjh] or [ta’arjaħa] meaning ‘oscillated (masculine, singular)’, from [‘urju:ħa] ‘swing (n)’, from [rajaħa] ‘weighed down, preponderated (masculine, singular)’ ( ر-ج-ح | r-j-ħ).
- محور [mhwr] or [tamaħwara] meaning ‘centred, focused (masculine, singular)’, from [mihwar] meaning ‘axis’, from [ħa:ra] ‘turned (masculine, singular)’ (ح-و-ر | h-w-r).
- مسخر [msxr], تمسخر [tamasxara] meaning ‘mocked, made fun (masculine, singular)’, from مسخرة [masxara] meaning ‘mockery’, from سخر [saxira] ‘mocked (masculine, singular)’ (derived from س-خ-ر[s-x-r]).»[6] Similar cases may be found in other Semitic languages such as Hebrew, Syriac, Aramaic, Maltese language and to a lesser extent Amharic.
Similar cases occur in Hebrew, for example Israeli Hebrew מ-ק-מ √m-q-m ‘locate’, which derives from Biblical Hebrew מקום måqom ‘place’, whose root is ק-ו-מ √q-w-m ‘stand’. A recent example introduced by the Academy of the Hebrew Language is מדרוג midrúg ‘rating’, from מדרג midrág, whose root is ד-ר-ג √d-r-g ‘grade’.»[6]
According to Ghil’ad Zuckermann, «this process is morphologically similar to the production of frequentative (iterative) verbs in Latin, for example:
- iactito ‘to toss about’ derives from iacto ‘to boast of, keep bringing up, harass, disturb, throw, cast, fling away’, which in turn derives from iacio ‘to throw, cast’ (from its past participle iactum).[6]
Consider also Rabbinic Hebrew ת-ר-מ √t-r-m ‘donate, contribute’ (Mishnah: T’rumoth 1:2: ‘separate priestly dues’), which derives from Biblical Hebrew תרומה t’rūmå ‘contribution’, whose root is ר-ו-מ √r-w-m ‘raise’; cf. Rabbinic Hebrew ת-ר-ע √t-r-‘ ‘sound the trumpet, blow the horn’, from Biblical Hebrew תרועה t’rū`å ‘shout, cry, loud sound, trumpet-call’, in turn from ר-ו-ע √r-w-`.»[6]
and it describes the suffix.
Category-neutral roots[edit]
Decompositional generative frameworks suggest that roots hold little grammatical information and can be considered «category-neutral».[7] Category-neutral roots are roots without any inherent lexical category but with some conceptual content that becomes evident depending on the syntactic environment.[7] The ways in which these roots gain lexical category are discussed in Distributed Morphology and the Exoskeletal Model.
Theories adopting a category-neutral approach have not, as of 2020, reached a consensus about whether these roots contain a semantic type but no argument structure,[8] neither semantic type nor argument structure,[9] or both semantic type and argument structure.[10]
In support of the category-neutral approach, data from English indicates that the same underlying root appears as a noun and a verb — with or without overt morphology.[7]
-
English Examples — Overt[7]
Root Noun Verb advertise an advertisement to advertise character a character to characterize employ an employment to employ alphabet an alphabet to alphabetize -
English Examples — Covert[7]
Root Noun Verb dance a dance to dance walk a walk to walk chair a chair to chair wardrobe a wardrobe to wardrobe
In Hebrew, the majority of roots consist of segmental consonants √CCC. Arad (2003) describes that the consonantal root is turned into a word due to pattern morphology. Thereby, the root is turned into a verb when put into a verbal environment where the head bears the «v» feature (the pattern).[11]
Consider the root √š-m-n (ש-מ-נ).
| Pattern | Pronounced word | Gloss |
|---|---|---|
| CeCeC (n) | šemen | oil, grease |
| CaCCeCet (n) | šamenet | cream |
| CuCaC (n) | šuman | fat |
| CaCeC (adj) | šamen | fat |
| hiCCiC (v) | hišmin | grow fat/fatten |
| CiCCeC (n) | šimen | grease |
Although all words vary semantically, the general meaning of a greasy, fatty material can be attributed to the root.
Furthermore, Arad states that there are two types of languages in terms of root interpretation. In languages like English, the root is assigned one interpretation whereas in languages like Hebrew, the root can form multiple interpretations depending on its environment. This occurrence suggests a difference in language acquisition between these two languages. English speakers would need to learn two roots in order to understand two different words whereas Hebrew speakers would learn one root for two or more words.[11]
| English Root | English Word | Hebrew Root | Hebrew Word | Gloss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| √CREAM | cream | √š-m-n ש-מ-נ | šamenet | ‘cream’ |
| √FAT | fat | √š-m-n ש-מ-נ | šuman | ‘fat’ |
Alexiadou and Lohndal (2017) advance the claim that languages have a typological scale when it comes to roots and their meanings and state that Greek lies in between Hebrew and English.[12]
See also[edit]
- Lemma (morphology)
- Lexeme
- Morphological typology
- Morphology (linguistics)
- Phono-semantic matching
- Principal parts
- Proto-Indo-European root
- Radical (Chinese character) (this is more based upon a writing system than a spoken language)
- Semitic root
- Word family
- Word stem
References[edit]
- ^ Katamba, Francis (2006). Morphology (2nd ed.). Houndsmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 42. ISBN 9781403916440.
- ^ «Root». Glossary of Linguistic Terms. 3 December 2015.
- ^ Kemmer, Suzanne. «Words in English: Structure». Words in English. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^
Compare:
Durkin, Philip (2009). «8: Semantic change». The Oxford Guide to Etymology. Oxford: Oxford University Press (published 2011). p. xciv. ISBN 9780191618789. Retrieved 2017-11-10.In etymological reconstruction at the level of proto-languages, it is customary to reconstruct roots, which are assigned glosses, reflecting what is taken to be the common meaning shown by the words derived from this root.
- ^ Wehr, Hans (1976). Cowan, J Milton (ed.). Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic (PDF) (3rd ed.). Ithaca, N.Y.: Spoken Language Services. p. 358. ISBN 0-87950-001-8. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d Zuckermann, Ghil’ad 2003, Language Contact and Lexical Enrichment in Israeli Hebrew, Houndmills: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 1-4039-1723-X. pp 65–66.
- ^ a b c d e f Lohndal, Terje (28 February 2020). «Syntactic Categorization of Roots». Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Linguistics. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199384655.013.257. ISBN 978-0-19-938465-5.
- ^ Levinson, Lisa (27 November 2014). «The ontology of roots and verbs». The Syntax of Roots and the Roots of Syntax: 208–229. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199665266.003.0010. ISBN 978-0199665273.
- ^ Acquaviva, Paolo (May 2009). «Roots and Lexicality in Distributed Morphology». York Papers in Linguistics. University of York. Department of Language and Linguistic Science. 2 (10). hdl:10197/4148.
- ^ Coon, Jessica (1 February 2019). «Building verbs in Chuj: Consequences for the nature of roots». Journal of Linguistics. 55 (1): 35–81. doi:10.1017/S0022226718000087. S2CID 149423392.
- ^ a b c Arad, Maya (2003). «Locality Constraints on the Interpretation of Roots: The Case of Hebrew Denominal Verbs». Natural Language and Linguistic Theory. 21 (4): 737–778. doi:10.1023/A:1025533719905. S2CID 35715020.
- ^ Alexiadou, Artemis; Lohndal, Terje (18 May 2017). «On the division of labor between roots and functional structure». The Verbal Domain. 1. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198767886.003.0004. hdl:10037/19837.
External links[edit]
- Virtual Salt Root words and prefixes
- Espindle — Greek and Latin Root Words
Britannica Dictionary definition of ROOT
1
[count]
:
the part of a plant that grows underground, gets water from the ground, and holds the plant in place
-
Elm trees have shallow roots.
-
Pull weeds up by the roots so that they don’t grow back.
—
see color picture on this page
2
[count]
:
the part of a tooth, hair, fingernail, etc., that is attached to the body
-
You can tell that she dyes her hair blonde because her dark roots are showing.
3
[count]
a
:
the cause or source of something
— usually singular
-
He believes that money is the root of all evil. [=money causes people to do bad things]
-
We need to get to the root of the problem. = We need to get to the root cause of the problem.
-
Simple greed was at the root of the robbery. [=was the reason for the robbery]
b
:
the origin of something
— usually plural
-
Rock-and-roll music has its roots in blues music. [=rock-and-roll music originated/developed from blues music]
4
a
:
the family history of a person or a group of people
-
They have traced their roots [=ancestry] back several generations.
b
:
a special connection to something
— + in
-
She’s a dedicated teacher with roots in the community.
-
His family has roots in the New York theater scene.
-
a novelist with roots deep in Southern life
—
see also grass roots
5
[count]
mathematics
:
a number that is multiplied by itself a certain number of times to produce another number
-
2 is the 4th root of 16. [=2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16]
—
see also cube root, square root
6
[count]
:
a word from which other words are formed
-
“Butler” and “bottle” come from the same Latin root.
-
“Hold” is the root of “holder.”
put down roots
:
to become a member of a community and begin to feel that it is your home
:
to settle and live in one place
-
The family put down roots in New England. [=they made New England their home]
root and branch
chiefly British
1
:
complete or thorough
-
a root and branch overhaul of local schools
2
:
completely or thoroughly
-
The laws were reformed root and branch.
take root
1
of a plant
:
to grow and develop roots
-
There isn’t enough time for the grass to take root before winter.
2
:
to begin to develop
-
The classroom should be a place where creativity can take root and flourish.
-
It was years before democratic ideals took root in that part of the world.
Britannica Dictionary definition of ROOT
1
of a plant
a
[no object]
:
to grow and develop roots
-
The plants had difficulty rooting in the poor soil.
b
[+ object]
:
to make (a plant) grow and develop roots
-
She rooted the seedlings in pots before planting them in the garden.
-
The lichen rooted itself to the rock.
-
The lichen was rooted to the rock.
2
[+ object]
:
to make (someone) unable to move
-
Fear rooted me to my chair.
— usually used as (be) rooted
-
I was rooted to my chair by/with fear.
root (something) in (something)
:
to form, make, or develop (something) by using (something) as a basis
-
He roots his art in reality. [=bases his art on the real world]
— usually used as (be) rooted in
-
His art is rooted in reality.
-
Her opinions are deeply rooted in her faith.
-
a dance rooted in African tradition
Britannica Dictionary definition of ROOT
[no object]
1
always followed by an adverb or preposition
:
to search for something by moving around or by turning things over
-
We rooted through the desk drawers for the phone bill.
-
She rooted around in her purse to find her keys.
-
I think I’ll root around for some leftovers in the fridge.
2
of animals
:
to look for food under the ground by digging with the nose
:
grub
-
a rooting pig
1
root (something or someone) out
or
root out (something or someone)
:
to find and remove (something or someone)
-
The mayor was determined to root out corruption in city government.
2
:
to find (something or someone) after searching for a long time
-
He finally rooted out the cause of the problem.
Britannica Dictionary definition of ROOT
root for (someone or something)
:
to express or show support for (a person, a team, etc.)
-
They always root for the home team.
-
We’re rooting for the underdog.
:
to hope for the success of (someone or something)
-
Remember that we’re all rooting for you. [=we all want to see you succeed]
root (someone or something) on
US
:
to help (someone or something) to win or succeed by expressing or showing strong support
-
The team is playing for the championship tomorrow, and thousands of fans will be there to root them on.
-
Her friends and family were there to root her on to victory.
— rooter
/ˈruːtɚ/
noun,
plural
rooters
[count]
Other forms: roots; rooted; rooting
The root is the part of the plant that’s underground. Dig up a potato, and you will unearth its roots. Just pull them off before you cook the potato.
Root comes from the Latin word radix, which means «starting point,» and you can think of the root of something as the place it starts from, whether that’s the root of a tree, or the root of a problem. The root of your fear of swimming might have been a scary shark attack movie. If your ancestors come from Guatemala, you have Guatemalan roots. If you dig through a pile of junk, you’re «rooting around.»
Definitions of root
-
noun
(botany) the usually underground organ that lacks buds or leaves or nodes; absorbs water and mineral salts; usually it anchors the plant to the ground
see moresee less-
types:
- show 22 types…
- hide 22 types…
-
calamus
the aromatic root of the sweet flag used medicinally
-
cocoyam, dasheen, eddo, taro
edible starchy tuberous root of taro plants
-
ginseng
aromatic root of ginseng plants
-
horseradish, horseradish root
the root of the horseradish plant; it is grated or ground and used for seasoning
-
radish
pungent edible root of any of various cultivated radish plants
-
chicory, chicory root
the dried root of the chicory plant: used as a coffee substitute
-
oyster plant, salsify
edible root of the salsify plant
-
Hottentot bread, Hottentot’s bread
thick edible rootstock of elephant’s-foot
-
briarroot
hard woody root of the briar Erica arborea
-
orris, orrisroot
fragrant rootstock of various irises especially Florentine iris; used in perfumes and medicines
-
sarsaparilla root
dried root of any of various plants of the genus Smilax used as a flavoring agent
-
licorice root
root of licorice used in flavoring e.g. candy and liqueurs and medicines
-
senega
dried root of two plants of the genus Polygala containing an irritating saponin
-
mandrake, mandrake root
the root of the mandrake plant; used medicinally or as a narcotic
-
cassava, manioc
cassava root eaten as a staple food after drying and leaching; source of tapioca
-
carrot
deep orange edible root of the cultivated carrot plant
-
parsnip
the whitish root of cultivated parsnip
-
pneumatophore
an air-filled root (submerged or exposed) that can function as a respiratory organ of a marsh or swamp plant
-
taproot
(botany) main root of a plant growing straight downward from the stem
-
adventitious root
root growing in an unusual location e.g. from a stem
-
rootlet
small root or division of a root
-
prop root
a root that grows from and supports the stem above the ground in plants such as mangroves
-
type of:
-
plant organ
a functional and structural unit of a plant or fungus
-
noun
the part of a tooth that is embedded in the jaw and serves as support
-
verb
take root and begin to grow
“this plant
roots quickly” -
verb
become settled or established and stable in one’s residence or life style
-
noun
the place where something begins, where it springs into being
“communism’s Russian
root”-
synonyms:
beginning, origin, rootage, source
-
noun
someone from whom you are descended (but usually more remote than a grandparent)
-
noun
a simple form inferred as the common basis from which related words in several languages can be derived by linguistic processes
-
noun
(linguistics) the form of a word after all affixes are removed
-
verb
come into existence, originate
“The problem
roots in her depression” -
noun
a number that, when multiplied by itself some number of times, equals a given number
see moresee less-
types:
-
square root
a number that when multiplied by itself equals a given number
-
cube root
a number that when multiplied three times equals a given number
-
type of:
-
number
a concept of quantity involving zero and units
-
square root
-
noun
the set of values that give a true statement when substituted into an equation
-
“the pig was
rooting for truffles”-
synonyms:
rootle, rout
DISCLAIMER: These example sentences appear in various news sources and books to reflect the usage of the word ‘root’.
Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Vocabulary.com or its editors.
Send us feedback
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Look up root for the last time
Close your vocabulary gaps with personalized learning that focuses on teaching the
words you need to know.
Sign up now (it’s free!)
Whether you’re a teacher or a learner, Vocabulary.com can put you or your class on the path to systematic vocabulary improvement.
Get started
root
part of a plant normally below the ground; basic cause, source, or origin: the root of the problem
Not to be confused with:
route – a way or course taken: the shortest route to your destination; a round traveled in delivering, selling, or collecting goods: a newspaper route
Abused, Confused, & Misused Words by Mary Embree Copyright © 2007, 2013 by Mary Embree
root 1
(ro͞ot, ro͝ot)
n.
1.
a. The usually underground portion of a plant that lacks buds, leaves, or nodes and serves as support, draws minerals and water from the surrounding soil, and sometimes stores food.
b. Any of various other underground plant parts, especially an underground stem such as a rhizome, corm, or tuber.
2.
a. The embedded part of an organ or structure such as a hair, tooth, or nerve, that serves as a base or support.
b. The bottom or supporting part of something: We snipped the wires at the roots.
3. The essential part or element; the basic core: I finally got to the root of the problem.
4. A primary source; an origin. See Synonyms at origin.
5. A progenitor or ancestor from which a person or family is descended.
6.
a. often roots The condition of being settled and of belonging to a particular place or society: Our roots in this town go back a long way.
b. roots The state of having or establishing an indigenous relationship with or a personal affinity for a particular culture, society, or environment: music with unmistakable African roots.
7. Linguistics
a. The element that carries the main component of meaning in a word and provides the basis from which a word is derived by adding affixes or inflectional endings or by phonetic change.
b. Such an element reconstructed for a protolanguage. Also called radical.
8. Mathematics
a. A number that when multiplied by itself an indicated number of times forms a product equal to a specified number. For example, a fourth root of 4 is √2. Also called nth root.
b. A number that reduces a polynomial equation in one variable to an identity when it is substituted for the variable.
c. A number at which a polynomial has the value zero.
9. Music
a. The note from which a chord is built.
b. Such a note occurring as the lowest note of a triad or other chord.
v. root·ed, root·ing, roots
v.intr.
1. To grow roots or a root: Carrot tops will root in water.
2. To become firmly established or settled: The idea of tolerance has rooted in our culture.
v.tr.
1. To plant and fix the roots of (a plant) in soil or the ground.
2. To establish or settle firmly: Our love of the ocean has rooted us here.
3. To be the source or origin of: «Much of [the team’s] success was rooted in the bullpen» (Dan Shaughnessy).
4.
a. To dig or pull out by the roots. Often used with up or out: We rooted out the tree stumps with a tractor.
b. To remove or get rid of. Often used with out: «declared that waste and fraud will be vigorously rooted out of Government» (New York Times).
Idiom:
root and branch
Utterly; completely: The organization has been transformed root and branch by its new leaders.
root′er n.
root 2
(ro͞ot, ro͝ot)
v. root·ed, root·ing, roots
v.tr.
1. To turn up by digging with the snout or nose: hogs that rooted up acorns.
2. To cause to appear or be known. Used with out: an investigation that rooted out the source of the problem.
v.intr.
1. To turn over the earth with the snout or nose.
2. To search or rummage for something: rooted around for a pencil in his cluttered office.
[Middle English wroten, from Old English wrōtan.]
root′er n.
root 3
(ro͞ot, ro͝ot)
intr.v. root·ed, root·ing, roots
1. To give audible encouragement or applause to a contestant or team; cheer. See Synonyms at applaud.
2. To give moral support to someone; hope for a favorable outcome for someone: We’ll be rooting for you when you take the exam.
[Possibly alteration of rout.]
root′er n.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
root
(ruːt)
n
1. (Botany)
a. the organ of a higher plant that anchors the rest of the plant in the ground, absorbs water and mineral salts from the soil, and does not bear leaves or buds
b. (loosely) any of the branches of such an organ
2. (Botany) any plant part, such as a rhizome or tuber, that is similar to a root in structure, function, or appearance
3.
a. the essential, fundamental, or primary part or nature of something: your analysis strikes at the root of the problem.
b. (as modifier): the root cause of the problem.
4. (Anatomy) anatomy the embedded portion of a tooth, nail, hair, etc
5. origin or derivation, esp as a source of growth, vitality, or existence
6. (plural) a person’s sense of belonging in a community, place, etc, esp the one in which he was born or brought up
7. an ancestor or antecedent
8. (Bible) Bible a descendant
9. (Linguistics) the form of a word that remains after removal of all affixes; a morpheme with lexical meaning that is not further subdivisible into other morphemes with lexical meaning. Compare stem19
10. (Mathematics) maths a number or quantity that when multiplied by itself a certain number of times equals a given number or quantity: 3 is a cube root of 27.
11. (Mathematics) maths Also called: solution a number that when substituted for the variable satisfies a given equation: 2 is a root of x3 – 2x – 4 = 0.
12. (Music, other) music (in harmony) the note forming the foundation of a chord
13. slang Austral and NZ sexual intercourse
14. root and branch
a. (adverb) entirely; completely; utterly
b. (adjective) thorough; radical; complete
vb
15. (Botany) (intr) Also: take root to put forth or establish a root and begin to grow
16. (intr) Also: take root to become established, embedded, or effective
17. (tr) to fix or embed with or as if with a root or roots
18. slang Austral and NZ to have sexual intercourse (with)
[Old English rōt, from Old Norse; related to Old English wyrt wort]
ˈrooter n
ˈrootˌlike adj
ˈrooty adj
ˈrootiness n
root
(ruːt)
vb (intr)
1. (Zoology) (of a pig) to burrow in or dig up the earth in search of food, using the snout
2. informal (foll by: about, around, in, etc) to search vigorously but unsystematically
[C16: changed (through influence of root1) from earlier wroot, from Old English wrōtan; related to Old English wrōt snout, Middle Dutch wrōte mole]
ˈrooter n
root
vb
(General Sporting Terms) informal (usually foll by: for) to give support to (a contestant, team, etc), as by cheering
[C19: perhaps a variant of Scottish rout to make a loud noise, from Old Norse rauta to roar]
ˈrooter n
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
root1
(rut, rʊt)
n.
1. a part of the body of a plant that develops, typically, from the radicle and grows downward into the soil, anchoring the plant and absorbing nutriment and moisture.
2. any underground part of a plant, as a rhizome.
3. something resembling or suggesting the root of a plant in position or function.
4. the embedded or basal portion of a hair, tooth, nail, nerve, etc.
5. the fundamental or essential part.
6. the source or origin of a thing: the root of all evil.
7. a person or family as the source of offspring or descendants.
8. roots,
a. a person’s original or ancestral home, environment, and culture.
b. the personal relationships, affinity for a place, habits, etc., that make a locale one’s true home.
9.
a. a quantity that, when multiplied by itself a certain number of times, produces a given quantity: 2 is the square root of 4, the cube root of 8, and the fourth root of 16.
b. r th root, the quantity raised to the power 1/r: 2 is the ? root of 8.
c. a value of the argument of a function for which the function takes the value zero.
10.
a. a morpheme that underlies an inflectional or derivational paradigm, as dance, the root in danced, dancer or tend-, the root of Latin tendere “to stretch.”
b. such a form reconstructed for a parent language, as *sed-, the hypothetical proto-Indo-European root meaning “sit.”
11.
a. the fundamental tone of a compound musical tone of a series of harmonies.
b. the lowest tone of a chord when arranged as a series of thirds; fundamental.
12.
a. (in a screw or other threaded object) the narrow inner surface between threads.
b. (in a gear) the narrow inner surface between teeth.
v.i.
13. to become fixed or established.
v.t.
14. to fix by or as if by roots: We were rooted to the spot in amazement.
15. to implant or establish deeply.
16. to pull, tear, or dig up by the roots (often fol. by up or out).
17. to extirpate; remove completely (often fol. by up or out): to root out crime.
Idioms:
take root,
a. to send out roots; begin to grow.
b. to become established.
[before 1150; Middle English; late Old English rōt < Old Norse rōt, akin to Old English wyrt plant, wort2]
root2
(rut, rʊt)
v.i.
1. to turn up the soil with the snout, as swine.
2. to poke or search: to root around in a drawer for a cuff link.
v.t.
3. to turn over with the snout (often fol. by up).
4. to unearth (often fol. by up).
[1530–40; variant of wroot (now obsolete), Middle English wroten, Old English wrōtan, c. Old High German ruozzen; akin to Old English wrōt a snout]
root3
(rut or, sometimes, rʊt)
v.i.
1. to encourage a team or contestant by cheering or applauding enthusiastically.
2. to lend moral support.
[1885–90, Amer.; perhaps variant of rout3]
root′er, n.
Root
(rut)
n.
Elihu, 1845–1937, U.S. statesman: Nobel peace prize 1912.
Random House Kernerman Webster’s College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
root
(ro͞ot)
1. A plant part that usually grows underground, secures the plant in place, absorbs minerals and water, and stores food manufactured by leaves and other plant parts. In certain plants, additional roots grow out from the stem above ground, bending down into the soil, to provide more support.
2. Any of various other plant parts that grow underground, especially an underground stem such as a corm, rhizome, or tuber.
3. The part of a tooth that is embedded in the jaw and not covered by enamel.
4. Mathematics
a. A number that, when multiplied by itself a given number of times, produces a specified number. For example, since 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 16, 2 is a fourth root of 16.
b. A solution to an equation. For example, a root of the equation x2 — 4 = 0 is 2, since 22 — 4 = 0.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
root
Past participle: rooted
Gerund: rooting
| Imperative |
|---|
| root |
| root |
| Present |
|---|
| I root |
| you root |
| he/she/it roots |
| we root |
| you root |
| they root |
| Preterite |
|---|
| I rooted |
| you rooted |
| he/she/it rooted |
| we rooted |
| you rooted |
| they rooted |
| Present Continuous |
|---|
| I am rooting |
| you are rooting |
| he/she/it is rooting |
| we are rooting |
| you are rooting |
| they are rooting |
| Present Perfect |
|---|
| I have rooted |
| you have rooted |
| he/she/it has rooted |
| we have rooted |
| you have rooted |
| they have rooted |
| Past Continuous |
|---|
| I was rooting |
| you were rooting |
| he/she/it was rooting |
| we were rooting |
| you were rooting |
| they were rooting |
| Past Perfect |
|---|
| I had rooted |
| you had rooted |
| he/she/it had rooted |
| we had rooted |
| you had rooted |
| they had rooted |
| Future |
|---|
| I will root |
| you will root |
| he/she/it will root |
| we will root |
| you will root |
| they will root |
| Future Perfect |
|---|
| I will have rooted |
| you will have rooted |
| he/she/it will have rooted |
| we will have rooted |
| you will have rooted |
| they will have rooted |
| Future Continuous |
|---|
| I will be rooting |
| you will be rooting |
| he/she/it will be rooting |
| we will be rooting |
| you will be rooting |
| they will be rooting |
| Present Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I have been rooting |
| you have been rooting |
| he/she/it has been rooting |
| we have been rooting |
| you have been rooting |
| they have been rooting |
| Future Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I will have been rooting |
| you will have been rooting |
| he/she/it will have been rooting |
| we will have been rooting |
| you will have been rooting |
| they will have been rooting |
| Past Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I had been rooting |
| you had been rooting |
| he/she/it had been rooting |
| we had been rooting |
| you had been rooting |
| they had been rooting |
| Conditional |
|---|
| I would root |
| you would root |
| he/she/it would root |
| we would root |
| you would root |
| they would root |
| Past Conditional |
|---|
| I would have rooted |
| you would have rooted |
| he/she/it would have rooted |
| we would have rooted |
| you would have rooted |
| they would have rooted |
Collins English Verb Tables © HarperCollins Publishers 2011
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. |  root — (botany) the usually underground organ that lacks buds or leaves or nodes; absorbs water and mineral salts; usually it anchors the plant to the ground root — (botany) the usually underground organ that lacks buds or leaves or nodes; absorbs water and mineral salts; usually it anchors the plant to the ground
phytology, botany — the branch of biology that studies plants calamus — the aromatic root of the sweet flag used medicinally cocoyam, dasheen, eddo, taro — edible starchy tuberous root of taro plants ginseng — aromatic root of ginseng plants horseradish, horseradish root — the root of the horseradish plant; it is grated or ground and used for seasoning radish — pungent edible root of any of various cultivated radish plants chicory, chicory root — the dried root of the chicory plant: used as a coffee substitute oyster plant, salsify — edible root of the salsify plant Hottentot bread, Hottentot’s bread — thick edible rootstock of elephant’s-foot briarroot — hard woody root of the briar Erica arborea orrisroot, orris — fragrant rootstock of various irises especially Florentine iris; used in perfumes and medicines sarsaparilla root — dried root of any of various plants of the genus Smilax used as a flavoring agent licorice root — root of licorice used in flavoring e.g. candy and liqueurs and medicines senega — dried root of two plants of the genus Polygala containing an irritating saponin mandrake, mandrake root — the root of the mandrake plant; used medicinally or as a narcotic cassava, manioc — cassava root eaten as a staple food after drying and leaching; source of tapioca carrot — deep orange edible root of the cultivated carrot plant parsnip — the whitish root of cultivated parsnip plant organ — a functional and structural unit of a plant or fungus parenchyma — the primary tissue of higher plants composed of thin-walled cells that remain capable of cell division even when mature; constitutes the greater part of leaves, roots, the pulp of fruits, and the pith of stems root system, rootage — a developed system of roots pneumatophore — an air-filled root (submerged or exposed) that can function as a respiratory organ of a marsh or swamp plant taproot — (botany) main root of a plant growing straight downward from the stem adventitious root — root growing in an unusual location e.g. from a stem root cap — thimble-shaped mass of cells covering and protecting the growing tip of a root rootlet — small root or division of a root root hair — thin hairlike outgrowth of an epidermal cell just behind the tip; absorbs nutrients from the soil prop root — a root that grows from and supports the stem above the ground in plants such as mangroves bark — tough protective covering of the woody stems and roots of trees and other woody plants |
| 2. |  root — the place where something begins, where it springs into being; «the Italian beginning of the Renaissance»; «Jupiter was the origin of the radiation»; «Pittsburgh is the source of the Ohio River»; «communism’s Russian root» root — the place where something begins, where it springs into being; «the Italian beginning of the Renaissance»; «Jupiter was the origin of the radiation»; «Pittsburgh is the source of the Ohio River»; «communism’s Russian root»
origin, source, rootage, beginning derivation — the source or origin from which something derives (i.e. comes or issues); «he prefers shoes of Italian derivation»; «music of Turkish derivation» spring — a point at which water issues forth headspring, fountainhead, head — the source of water from which a stream arises; «they tracked him back toward the head of the stream» headwater — the source of a river; «the headwaters of the Nile» wellhead, wellspring — the source of water for a well jumping-off place, point of departure — a place from which an enterprise or expedition is launched; «one day when I was at a suitable jumping-off place I decided to see if I could find him»; «my point of departure was San Francisco» place of origin, provenance, provenience, birthplace, cradle — where something originated or was nurtured in its early existence; «the birthplace of civilization» home — place where something began and flourished; «the United States is the home of basketball» point source — a concentrated source (especially of radiation or pollution) that is spatially constricted trail head, trailhead — the beginning of a trail point — the precise location of something; a spatially limited location; «she walked to a point where she could survey the whole street» |
|
| 3. | root — (linguistics) the form of a word after all affixes are removed; «thematic vowels are part of the stem»
root word, stem, theme, radical, base linguistics — the scientific study of language descriptor, form, signifier, word form — the phonological or orthographic sound or appearance of a word that can be used to describe or identify something; «the inflected forms of a word can be represented by a stem and a list of inflections to be attached» |
|
| 4. | root — a number that, when multiplied by itself some number of times, equals a given number
number — a concept of quantity involving zero and units; «every number has a unique position in the sequence» square root — a number that when multiplied by itself equals a given number cube root — a number that when multiplied three times equals a given number |
|
| 5. | root — the set of values that give a true statement when substituted into an equation
solution set — (mathematics) an abstract collection of numbers or symbols; «the set of prime numbers is infinite» |
|
| 6. | 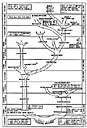 root — someone from whom you are descended (but usually more remote than a grandparent) root — someone from whom you are descended (but usually more remote than a grandparent)
ancestor, antecedent, ascendant, ascendent ancestress — a woman ancestor forbear, forebear — a person from whom you are descended forefather, sire, father — the founder of a family; «keep the faith of our forefathers» foremother — a woman ancestor primogenitor, progenitor — an ancestor in the direct line relative, relation — a person related by blood or marriage; «police are searching for relatives of the deceased»; «he has distant relations back in New Jersey» |
|
| 7. | root — a simple form inferred as the common basis from which related words in several languages can be derived by linguistic processes
etymon descriptor, form, signifier, word form — the phonological or orthographic sound or appearance of a word that can be used to describe or identify something; «the inflected forms of a word can be represented by a stem and a list of inflections to be attached» |
|
| 8. | 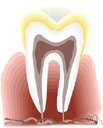 root — the part of a tooth that is embedded in the jaw and serves as support root — the part of a tooth that is embedded in the jaw and serves as support
tooth root anatomical structure, bodily structure, body structure, complex body part, structure — a particular complex anatomical part of a living thing; «he has good bone structure» tooth — hard bonelike structures in the jaws of vertebrates; used for biting and chewing or for attack and defense cementum, cement — a specialized bony substance covering the root of a tooth |
|
| Verb | 1. | root — take root and begin to grow; «this plant roots quickly»
grow — become larger, greater, or bigger; expand or gain; «The problem grew too large for me»; «Her business grew fast» root — cause to take roots |
| 2. | root — come into existence, originate; «The problem roots in her depression»
become — come into existence; «What becomes has duration» |
|
| 3. | root — plant by the roots
plant, set — put or set (seeds, seedlings, or plants) into the ground; «Let’s plant flowers in the garden» |
|
| 4. | root — dig with the snout; «the pig was rooting for truffles»
rootle, rout cut into, delve, dig, turn over — turn up, loosen, or remove earth; «Dig we must»; «turn over the soil for aeration» |
|
| 5. | root — become settled or established and stable in one’s residence or life style; «He finally settled down»
steady down, take root, settle down, settle stabilise, stabilize — become stable or more stable; «The economy stabilized» roost — settle down or stay, as if on a roost |
|
| 6. | root — cause to take roots
grow — cause to grow or develop; «He grows vegetables in his backyard» root — take root and begin to grow; «this plant roots quickly» |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
root
1
noun
2. source, cause, heart, bottom, beginnings, base, seat, occasion, seed, foundation, origin, core, fundamental, essence, nucleus, starting point, germ, crux, nub, derivation, fountainhead, mainspring We got to the root of the problem.
put down roots settle, set up home, get established, make your home, establish yourself They put down roots in India.
root and branch
root something or someone out
1. get rid of, remove, destroy, eliminate, abolish, cut out, erase, eradicate, do away with, uproot, weed out, efface, exterminate, extirpate, wipe from the face of the earth The generals have to root out traitors.
take root
2. germinate, take, establish, become established, begin to sprout Cover the bulbs with chicken wire, removing it when they take root.
Related words
adjective radical
root
2
verb dig, hunt, nose, poke, burrow, delve, ferret, pry, rummage, forage, rootle She rooted through the bag.
Collins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
root 1
noun
1. The most central and material part:
core, essence, gist, heart, kernel, marrow, meat, nub, pith, quintessence, soul, spirit, stuff, substance.
2. A fundamental principle or underlying concept:
3. A point of origination:
beginning, derivation, fount, fountain, fountainhead, mother, origin, parent, provenance, provenience, rootstock, source, spring, well.
4. A point of origin from which ideas or influences, for example, originate:
5. The main part of a word to which affixes are attached:
verb
1. To implant so deeply as to make change nearly impossible:
2. To provide a basis for:
3. To destroy all traces of.Out or up:
abolish, annihilate, blot out, clear, eradicate, erase, exterminate, extinguish, extirpate, kill, liquidate, obliterate, remove, rub out, snuff out, stamp out, uproot, wipe out.
root 2
verb
To express approval, especially by clapping:
Idiom: give someone a hand.
The American Heritage® Roget’s Thesaurus. Copyright © 2013, 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Translations
wortel
أصْل، شُرشجذرجَذْرجِذْرجُذور العائِلَه، أُصول
корен
arrel
kořenkořenykořínekodmocninarýt
rodrodeplante
juurilähdepääkäyttäjä
korijen
gyökgyökérok
akar
rótrót, orsökrótaróta ískjóta rótum
根歯根起源元
뿌리근원
radicisradix
saknesaknesvandītiesapsakņotcēlonis
koreňkorienok
koreninakoren
korenкорен
rotröttertandrotkällanollställe
mizizimzizi
ราก
коренікорінь
chân răngchân tócrễrễ cây
root
[ruːt]
A. N
2. (Bio) [of hair, tooth] → raíz f
root through VI + PREP
Collins Spanish Dictionary — Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
root
[ˈruːt]
n
[plant, tree] → racine f
to take root [plant, idea] → prendre racine
root and branch adv → entièrement; adj [review, reform] → complet/ète
to put down roots (= settle down) [person] → s’enraciner
[hair, tooth] → racine f
They pulled her hair out by the roots → Ils lui ont arraché les cheveux avec leurs racines. root canal treatment
(= origin) [problem, disease] → racine f
to have its roots in sth → avoir ses racines dans qch
modif
[system, growth] → racinaire; [ball] → de racines root crop, root stock
npl (= origins) [person] → racines fpl
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
root
n
(fig: = source: of evil, of trouble etc) → Wurzel f; the root of the matter → der Kern der Sache; to get to the root(s) of the problem → dem Problem auf den Grund gehen; that is or lies at the root of his behaviour (Brit) or behavior (US) → das ist der eigentliche Grund für sein Benehmen
root
in cpds → Wurzel-;
root beer
n (US) Art Limonade
root-canal work, root-canal therapy
n (Dentistry) → Wurzelkanalbehandlung f, → Zahnwurzelbehandlung f
root directory
n (Comput) → Stammverzeichnis nt
root
:
root word
n (Ling) → Wortwurzel f; (= base form) → Wortstamm m
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
root
[ruːt]
root for vi + prep (Am) (fam) → fare il tifo per
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
root1
(ruːt) noun
1. the part of a plant that grows under the ground and draws food and water from the soil. Trees often have deep roots; Carrots and turnips are edible roots.
2. the base of something growing in the body. the roots of one’s hair/teeth.
3. cause; origin. Love of money is the root of all evil; We must get at the root of the trouble.
4. (in plural) family origins. Our roots are in Scotland.
verb
to (make something) grow roots. These plants aren’t rooting very well; He rooted the plants in compost.
root beer
a kind of non-alcoholic drink made from the roots of certain plants.
root crop
plants with roots that are grown for food. The farm has three fields of root crops.
root out
1. to pull up or tear out by the roots. The gardener began to root out the weeds.
2. to get rid of completely. We must do our best to root out poverty.
take root
to grow firmly; to become established. The plants soon took root.
root2
(ruːt) verb
1. to poke about in the ground. The pigs were rooting about for food.
2. to search by turning things over etc. She rooted about in the cupboard.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
root
→ جِذْر kořen rod Wurzel ρίζα raíz juuri racine korijen radice 根 뿌리 wortel rot korzeń raiz корень rot ราก kök rễ cây 根
Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
root
n raíz f; hair — raíz del pelo or cabello; nerve — raíz nerviosa; — canal (fam, root canal therapy) endodoncia, tratamiento de conducto; tooth — o— of a tooth raíz dental, raíz de un diente
English-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What do we mean by root?
The usually underground portion of a plant that lacks buds, leaves, or nodes and serves as support, draws minerals and water from the surrounding soil, and sometimes stores food. noun
Any of various other underground plant parts, especially an underground stem such as a rhizome, corm, or tuber. noun
The embedded part of an organ or structure such as a hair, tooth, or nerve, that serves as a base or support. noun
The bottom or supporting part of something. noun
The essential part or element; the basic core. noun
A primary source; an origin. synonym: origin. noun
A progenitor or ancestor from which a person or family is descended. noun
The condition of being settled and of belonging to a particular place or society. noun
The state of having or establishing an indigenous relationship with or a personal affinity for a particular culture, society, or environment. noun
The element that carries the main component of meaning in a word and provides the basis from which a word is derived by adding affixes or inflectional endings or by phonetic change. noun
Such an element reconstructed for a protolanguage. noun
A number that when multiplied by itself an indicated number of times forms a product equal to a specified number. For example, a fourth root of 4 is √2. noun
A number that reduces a polynomial equation in one variable to an identity when it is substituted for the variable. noun
A number at which a polynomial has the value zero. noun
The part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors and supports the plant body, absorbs and stores water and nutrients, and in some plants is able to perform vegetative reproduction.
A root vegetable.
The part of a tooth extending into the bone holding the tooth in place.
The part of a hair under the skin that holds the hair in place.
The part of a hair near the skin that has not been dyed, permed, or otherwise treated.
The primary source; origin.
Of a number or expression, a number which, when raised to a specified power, yields the specified number or expression.
A square root (understood if no power is specified; in which case, “the root of” is often abbreviated to “root”).
A zero (of an equation).
The single node of a tree that has no parent.
The primary lexical unit of a word, which carries the most significant aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Inflectional stems often derive from roots.
(philology) A word from which another word or words are derived.
The fundamental tone of any chord; the tone from whose harmonics, or overtones, a chord is composed.
The lowest place, position, or part.
In UNIX terminology, the first user account with complete access to the operating system and its configuration, found at the root of the directory structure; the person who manages accounts on a UNIX system.
The highest directory of a directory structure which may contain both files and subdirectories.
A penis, especially the base of a penis.
1. A Kiwi/Australian slang that is used in place of the more commonly used term «fuck.» Urban Dictionary
The administrator user in Unix (e.g. GNU/Linux) systems with the highest level of permissions. Urban Dictionary
1. An Australian substitute for the more crass equivalent, fuck.
2. An American substitute for the more correct, support or barrack.
3. Somewhat confusing for those moving between these countries
4. Found under trees, shrubs, bushes etc. Draws nutrients from the soil. Easily tripped over. Urban Dictionary
A term for a penis, nothing more. Urban Dictionary
Male sexual organ used to reproduce. Urban Dictionary
Another term for a stiffy. Urban Dictionary
This is a slang word for a penis. Urban Dictionary
A very large penis, usually refered to when erect. Urban Dictionary
Whoever posted the example below forgot to include the all-important comma: Urban Dictionary
What a plant uses to extract water and nutrients from the soil. Urban Dictionary
|
WordReference Random House Learner’s Dictionary of American English © 2023 root1 /rut, rʊt/USA pronunciation
v.
Idioms
root•less, adj.
root2 /rut, rʊt/USA pronunciation
root3 /rut/USA pronunciation
root•er, n. [countable] WordReference Random House Unabridged Dictionary of American English © 2023 root1
v.i.
v.t.
root′like′, adj.
v.t.
root3 (ro̅o̅t or, sometimes, rŏŏt),USA pronunciation
(el′ə hyo̅o̅′),USA pronunciation 1845–1937, U.S. lawyer and statesman: Nobel peace prize 1912. John Well•born (wel′bərn),USA pronunciation 1851–91, U.S. architect. Collins Concise English Dictionary © HarperCollins Publishers:: root /ruːt/ n
Related adjective(s): radical vb
ˈrooter n ˈrootˌlike adj ˈrooty adj ˈrootiness n root /ruːt/ vb (intransitive)
Etymology: 16th Century: changed (through influence of root1) from earlier wroot, from Old English wrōtan; related to Old English wrōt snout, Middle Dutch wrōte mole ˈrooter n root vb
Etymology: 19th Century: perhaps a variant of Scottish rout to make a loud noise, from Old Norse rauta to roar ‘root‘ also found in these entries (note: many are not synonyms or translations): |
|
Search also in:
Web
News
Encyclopedia
Images
root
[
1]
n
a the organ of a higher plant that anchors the rest of the plant in the ground, absorbs water and mineral salts from the soil, and does not bear leaves or buds
b (loosely) any of the branches of such an organ
2 any plant part, such as a rhizome or tuber, that is similar to a root in structure, function, or appearance
a the essential, fundamental, or primary part or nature of something
your analysis strikes at the root of the problem
b (as modifier)
the root cause of the problem
4 (Anatomy) the embedded portion of a tooth, nail, hair, etc.
5 origin or derivation, esp. as a source of growth, vitality, or existence
6 pl a person’s sense of belonging in a community, place, etc., esp. the one in which he was born or brought up
7 an ancestor or antecedent
9 the form of a word that remains after removal of all affixes; a morpheme with lexical meaning that is not further subdivisible into other morphemes with lexical meaning
Compare →
stem 1 →
9
10 (Maths) a number or quantity that when multiplied by itself a certain number of times equals a given number or quantity
3 is a cube root of 27
11 (Also called)
solution (Maths) a number that when substituted for the variable satisfies a given equation
2 is a root of x3 — 2x — 4 = 0
12 (Music) (in harmony) the note forming the foundation of a chord
13 (Austral. and N.Z.)
slang sexual intercourse
14 ♦
root and branch adv entirely; completely; utterly, (Related adj)
→
radical
vb
15 intr (Also)
take root to put forth or establish a root and begin to grow
16 intr (Also)
take root to become established, embedded, or effective
17 tr to fix or embed with or as if with a root or roots
18 (Austral. and N.Z.)
slang to have sexual intercourse (with), (See also)
→
root out →
root up
(Old English rot, from Old Norse; related to Old English wyrt wort)
♦
rooter n
♦
rootlike adj
♦
rooty adj
♦
rootiness n
English Collins Dictionary — English Definition & Thesaurus
root [2]
vb intr
1 (of a pig) to burrow in or dig up the earth in search of food, using the snout
2 foll by: about, around, in etc
Informal to search vigorously but unsystematically
(C16: changed (through influence of root1) from earlier wroot, from Old English wrotan; related to Old English wrot snout, Middle Dutch wrote mole)
♦
rooter n
English Collins Dictionary — English Definition & Thesaurus
root [3]
vb intr; usually foll by: for
Informal to give support to (a contestant, team, etc.), as by cheering
(C19: perhaps a variant of Scottish rout to make a loud noise, from Old Norse rauta to roar)
♦
rooter n
English Collins Dictionary — English Definition & Thesaurus
root
[
1]
n
1 radicle, radix, rhizome, stem, tuber
2 base, beginnings, bottom, cause, core, crux, derivation, essence, foundation, fountainhead, fundamental, germ, heart, mainspring, nub, nucleus, occasion, origin, seat, seed, source, starting point
3 (plural)
birthplace, cradle, family, heritage, home, origins, sense of belonging
4 root and branch completely, entirely, finally, radically, thoroughly, totally, to the last man, utterly, wholly, without exception
vb
5 anchor, become established, become settled, embed, entrench, establish, fasten, fix, ground, implant, moor, set, stick, take root
English Collins Dictionary — English synonyms & Thesaurus
root [2]
vb burrow, delve, dig, ferret, forage, hunt, nose, poke, pry, rootle, rummage
English Collins Dictionary — English synonyms & Thesaurus
To add entries to your own vocabulary, become a member of Reverso community or login if you are already a member.
It’s easy and only takes a few seconds:
Educalingo cookies are used to personalize ads and get web traffic statistics. We also share information about the use of the site with our social media, advertising and analytics partners.
Download the app
educalingo

I’ve always liked TV shows that have slightly unlikable leads, where you root for them in spite of a lot of things. I know it’s not common with shows with young people; they have to be so likable. But, I mean, teenagers just generally aren’t very likable. I know I wasn’t as a teenager.
Bo Burnham
ETYMOLOGY OF THE WORD ROOT
Old English rōt, from Old Norse; related to Old English wyrtwort.
Etymology is the study of the origin of words and their changes in structure and significance.
PRONUNCIATION OF ROOT
GRAMMATICAL CATEGORY OF ROOT
Root is a verb and can also act as a noun.
A noun is a type of word the meaning of which determines reality. Nouns provide the names for all things: people, objects, sensations, feelings, etc.
The verb is the part of the sentence that is conjugated and expresses action and state of being.
See the conjugation of the verb root in English.
WHAT DOES ROOT MEAN IN ENGLISH?
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. However, roots can also be aerial or aerating. Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either.Therefore, the root is best defined as the non-leaf, non-nodes bearing parts of the plant’s body. However, important internal structural differences between stems and roots exist. The first root that comes from a plant is called the radicle. The four major functions of roots are 1) absorption of water and inorganic nutrients, 2) anchoring of the plant body to the ground, and supporting it, 3) storage of food and nutrients, 4) vegetative reproduction. In response to the concentration of nutrients, roots also synthesise cytokinin, which acts as a signal as to how fast the shoots can grow. Roots often function in storage of food and nutrients. The roots of most vascular plant species enter into symbiosis with certain fungi to form mycorrhizae, and a large range of other organisms including bacteria also closely associate with roots. Large, mature tree roots above the soil…
Definition of root in the English dictionary
The first definition of root in the dictionary is the organ of a higher plant that anchors the rest of the plant in the ground, absorbs water and mineral salts from the soil, and does not bear leaves or buds. Other definition of root is any of the branches of such an organ. Root is also any plant part, such as a rhizome or tuber, that is similar to a root in structure, function, or appearance.
CONJUGATION OF THE VERB TO ROOT
PRESENT
Present
I root
you root
he/she/it roots
we root
you root
they root
Present continuous
I am rooting
you are rooting
he/she/it is rooting
we are rooting
you are rooting
they are rooting
Present perfect
I have rooted
you have rooted
he/she/it has rooted
we have rooted
you have rooted
they have rooted
Present perfect continuous
I have been rooting
you have been rooting
he/she/it has been rooting
we have been rooting
you have been rooting
they have been rooting
Present tense is used to refer to circumstances that exist at the present time or over a period that includes the present time. The present perfect refers to past events, although it can be considered to denote primarily the resulting present situation rather than the events themselves.
PAST
Past
I rooted
you rooted
he/she/it rooted
we rooted
you rooted
they rooted
Past continuous
I was rooting
you were rooting
he/she/it was rooting
we were rooting
you were rooting
they were rooting
Past perfect
I had rooted
you had rooted
he/she/it had rooted
we had rooted
you had rooted
they had rooted
Past perfect continuous
I had been rooting
you had been rooting
he/she/it had been rooting
we had been rooting
you had been rooting
they had been rooting
Past tense forms express circumstances existing at some time in the past,
FUTURE
Future
I will root
you will root
he/she/it will root
we will root
you will root
they will root
Future continuous
I will be rooting
you will be rooting
he/she/it will be rooting
we will be rooting
you will be rooting
they will be rooting
Future perfect
I will have rooted
you will have rooted
he/she/it will have rooted
we will have rooted
you will have rooted
they will have rooted
Future perfect continuous
I will have been rooting
you will have been rooting
he/she/it will have been rooting
we will have been rooting
you will have been rooting
they will have been rooting
The future is used to express circumstances that will occur at a later time.
CONDITIONAL
Conditional
I would root
you would root
he/she/it would root
we would root
you would root
they would root
Conditional continuous
I would be rooting
you would be rooting
he/she/it would be rooting
we would be rooting
you would be rooting
they would be rooting
Conditional perfect
I would have root
you would have root
he/she/it would have root
we would have root
you would have root
they would have root
Conditional perfect continuous
I would have been rooting
you would have been rooting
he/she/it would have been rooting
we would have been rooting
you would have been rooting
they would have been rooting
Conditional or «future-in-the-past» tense refers to hypothetical or possible actions.
IMPERATIVE
Imperative
you root
we let´s root
you root
The imperative is used to form commands or requests.
NONFINITE VERB FORMS
Present Participle
rooting
Infinitive shows the action beyond temporal perspective. The present participle or gerund shows the action during the session. The past participle shows the action after completion.
WORDS THAT RHYME WITH ROOT
Synonyms and antonyms of root in the English dictionary of synonyms
SYNONYMS OF «ROOT»
The following words have a similar or identical meaning as «root» and belong to the same grammatical category.
Translation of «root» into 25 languages

TRANSLATION OF ROOT
Find out the translation of root to 25 languages with our English multilingual translator.
The translations of root from English to other languages presented in this section have been obtained through automatic statistical translation; where the essential translation unit is the word «root» in English.
Translator English — Chinese
根
1,325 millions of speakers
Translator English — Spanish
raíz
570 millions of speakers
English
root
510 millions of speakers
Translator English — Hindi
जड़
380 millions of speakers
Translator English — Arabic
جِذْر
280 millions of speakers
Translator English — Russian
корень
278 millions of speakers
Translator English — Portuguese
raiz
270 millions of speakers
Translator English — Bengali
মূল
260 millions of speakers
Translator English — French
racine
220 millions of speakers
Translator English — Malay
Akar
190 millions of speakers
Translator English — German
Wurzel
180 millions of speakers
Translator English — Japanese
根
130 millions of speakers
Translator English — Korean
뿌리
85 millions of speakers
Translator English — Javanese
ROOT
85 millions of speakers
Translator English — Vietnamese
rễ cây
80 millions of speakers
Translator English — Tamil
ரூட்
75 millions of speakers
Translator English — Marathi
मूळ
75 millions of speakers
Translator English — Turkish
kök
70 millions of speakers
Translator English — Italian
radice
65 millions of speakers
Translator English — Polish
korzeń
50 millions of speakers
Translator English — Ukrainian
корінь
40 millions of speakers
Translator English — Romanian
rădăcină
30 millions of speakers
Translator English — Greek
ρίζα
15 millions of speakers
Translator English — Afrikaans
wortel
14 millions of speakers
Translator English — Swedish
rot
10 millions of speakers
Translator English — Norwegian
rot
5 millions of speakers
Trends of use of root
TENDENCIES OF USE OF THE TERM «ROOT»
The term «root» is very widely used and occupies the 4.616 position in our list of most widely used terms in the English dictionary.

FREQUENCY
Very widely used
The map shown above gives the frequency of use of the term «root» in the different countries.
Principal search tendencies and common uses of root
List of principal searches undertaken by users to access our English online dictionary and most widely used expressions with the word «root».
FREQUENCY OF USE OF THE TERM «ROOT» OVER TIME
The graph expresses the annual evolution of the frequency of use of the word «root» during the past 500 years. Its implementation is based on analysing how often the term «root» appears in digitalised printed sources in English between the year 1500 and the present day.
Examples of use in the English literature, quotes and news about root
10 QUOTES WITH «ROOT»
Famous quotes and sentences with the word root.
Money is the root of all evil, and yet it is such a useful root that we cannot get on without it any more than we can without potatoes.
The main ingredient of the first quantum revolution, wave-particle duality, has led to inventions such as the transistor and the laser that are at the root of the information society.
During my lifetime, I realized that discrimination was not accidental, that there were structural roots and causes to it. So if we wanted to change women’s lives, we need to deal with those root causes.
The mind is the root from which all things grow if you can understand the mind, everything else is included.
I’ve always liked TV shows that have slightly unlikable leads, where you root for them in spite of a lot of things. I know it’s not common with shows with young people; they have to be so likable. But, I mean, teenagers just generally aren’t very likable. I know I wasn’t as a teenager.
Good science fiction is intelligent. It asks big questions that are on people’s minds. It’s not impossible. It has some sort of root in the abstract.
Video games are a special kind of play, but at root, they’re about the same things as other games: embracing particular rules and restrictions in order to develop skills and experience rewards. When a game is well-designed, it’s the balance between these factors that engages people on a fundamental level.
A disruptive innovation is a technologically simple innovation in the form of a product, service, or business model that takes root in a tier of the market that is unattractive to the established leaders in an industry.
Conscience is the root of all true courage; if a man would be brave let him obey his conscience.
When we read dystopia, we root for these people to break free because we are these people; hoping and fighting against things that are bigger than ourselves.
10 ENGLISH BOOKS RELATING TO «ROOT»
Discover the use of root in the following bibliographical selection. Books relating to root and brief extracts from same to provide context of its use in English literature.
It is important to include Tuber and Root Crops in the Handbook of Plant Breeding.
2
An Imaginary Tale: The Story of «i» [the square root of …
This book can be read as an engaging history, almost a biography, of one of the most evasive and pervasive «numbers» in all of mathematics.
3
Ruling the Root: Internet Governance and the Taming of …
In Ruling the Root, Milton Mueller uses the theoretical framework of institutional economics to analyse the global policy and governance problems created by the assignment of Internet domain names and addresses.
4
Root Cause Analysis: A Tool for Total Quality Management
This book describes the methods and tools used to develop and implement an effective TQM program. it provides a practical explanation of root cause analysis and discusses the proactive use of analysis techniques for the prediction and …
5
Root Methods: A Handbook
Plant root research, root distribution, root dynamics.
6
Tropical Root and Tuber Crops: Cassava, Sweet Potato, Yams …
This book compiles information on the origin, genetics, physiology, agronomy, pests and diseases and post harvest processing of these crops, while providing ideas for further research and development.
7
Root Cause Analysis Handbook: A Guide to Efficient and …
Understanding and applying the processes outlined in this book increases your businessa ability to recover from and prevent incidents with financial and health/safety implications.
Donald K. Lorenzo, Walter E. Hanson, 2008
8
Root of Bitterness: Documents of the Social History of …
A thoroughly revised edition of the classic text in American women’s social history.
9
Root Cause Failure Analysis
Root Cause Failure Analysis provides the concepts for performing industrial troubleshooting investigations. It describes the methodology to perform Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA), a topic in maintenance engineering.
10
Root Cause Analysis, Second Edition: Simplified Tools and …
The book is suited for employees and managers at any organizational level in any type of industry, including service, manufacturing, and the public sector.
Bjørn Andersen, Tom Fagerhaug, 2006
10 NEWS ITEMS WHICH INCLUDE THE TERM «ROOT»
Find out what the national and international press are talking about and how the term root is used in the context of the following news items.
Ashes 2015: Joe Root leaves Australia’s bowlers with no margin for …
Joe Root hit a clinical first-innings hundred in the first Ashes Test, taking the attacking option whenever Australia’s bowlers strayed. Photograph: Andrew … «The Guardian, Jul 15»
David Warner lifts lid on Walkabout bar run-in with Joe Root
In the incident the Australia opener punched Root, offended by the … Now, though, Warner tells the full story, confirming he thought Root’s placement of the wig … «The Guardian, Jul 15»
Joe Root shines in T20 to hand England pre-Ashes boost against …
Joe Root continued his impressive ODI form in the one-off T20 international to help England to a 56-run win at Old Trafford. Photograph: Shaun Botterill/Getty … «The Guardian, Jun 15»
England’s Morgan and Root pulverise New Zealand with fine centuries
Eoin Morgan celebrates with Joe Root after the England captain reached his century in the victory over New Zealand at Trent Bridge. Photograph: Gareth … «The Guardian, Jun 15»
Joe Root and Jos Buttler star as England set ODI record on way to …
Indeed the star turns for England were not the new boys, but players who were part of the World Cup fiasco. Joe Root hit a century in 71 balls, Jos Buttler in 66, … «Daily Mail, Jun 15»
Joe Root: England vice-captain adds mischief and might in new role
Joe Root, right, and Alastair Cook put on 158 in 43 overs on the fourth day of the first Test against New Zealand at Lord’s. Photograph: Kirsty Wigglesworth/AP. «The Guardian, May 15»
Joe Root: I was called ‘craptain’ at Yorkshire
Just as the eye is caught by the blossoming flower in Maytime rather than the hardy perennial, Joe Root was chosen as England’s player of the year at their … «Telegraph.co.uk, May 15»
Joe Root left fuming after being denied double century by England …
Joe Root was denied the chance of scoring 200 runs against the West Indies as he was left stranded at the middle of the wicket due to an error by James … «Daily Mail, Apr 15»
Dentist’s Office Manager Allegedly Thought Root Canals Were Part …
If you’ve seen «Dr. Val» in the Bronx lately, there’s a good chance the woman pulling your teeth and performing your root canals (!!) was actually just «Val,» short … «Gothamist, Apr 15»
Joe Root century not enough as Sri Lanka crush England in World …
They scored 300 for the second successive match, the first time that has happened for four years, a young batsman in Joe Root made a composed coming of … «Telegraph.co.uk, Mar 15»
REFERENCE
« EDUCALINGO. Root [online]. Available <https://educalingo.com/en/dic-en/root>. Apr 2023 ».
Download the educalingo app


Discover all that is hidden in the words on