From Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Environment means anything that surrounds us. It can be living (biotic) or non-living (abiotic) things. It includes physical, chemical and other natural forces. Living things live in their environment. They constantly interact with it and adapt themselves to conditions in their environment. In the environment there are different interactions between animals, plants, soil, water, and other living and non-living things.
Since everything is part of the environment of something else, the word environment is used to talk about many things. People in different fields of knowledge use the word environment differently. Electromagnetic environment is radio waves and other electromagnetic radiation and magnetic fields. The environment of galaxy refers to conditions of interstellar medium.
In psychology and medicine, a person’s environment is the people, physical things and places that the person lives with. The environment affects the growth and development of the person. It affects the person’s behavior, body, mind and heart.
The living conditions of living organisms in an environment are affected by the weather or climate changes in the environment.
Natural environment[change | change source]
In biology and ecology, the environment is all of the natural materials and living things, If those things are natural, it is a natural environment.
Environment includes the living and non-living things that an organism interacts with, or has an effect on it. Living elements that an organism interacts with are known as biotic elements: animals, plants, etc., abiotic elements are non living things which include air, water, sunlight etc. Studying the environment means studying the relationships among these various things. An example of interactions between non-living and living things is plants getting their minerals from the soil and making food using sunlight. Predation, an organism eating another, is an example of interaction between living things.
Some people call themselves environmentalists. They think we must protect the natural environment, to keep it safe. Things in the natural environment that we value are called natural resources. For example; fish, insects, and forests. These are renewable resources because they come back naturally when we use them. Non-renewable resources are important things in the environment that are limited for example, ores and fossil fuels after a few thousand years. Some things in the natural environment can kill people, such as lightning.
- Ecological units which are natural systems without much human interference. These include all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural events.
- Universal natural resources and physical phenomenon which lack clear-cut boundaries. These include climate, air, water, energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism.
[change | change source]
- Environmental chemistry
- Environmental factor
- Environmental revitalization
- Environmentalism
- Ecology
The environment infers to all living and non-living beings in their physical and biological surrounding that affect an organism during its lifetime. The word environment is taken from the old French verb “environner” which means to encircle or surround. Hence all the things that surround us in the form of living or non-living are a component of our environment.
It includes the air we breathe, the water we use for our needs, the soil we cultivate, flora and fauna. In other words, the environment is collectively the total of water, air and land interrelationships among themselves and also with the human being and other living organisms.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Environment?
- 2 Environment Definition
- 3 Components of Environment
- 3.1 Lithosphere
- 3.2 Hydrosphere
- 3.3 Atmosphere
- 3.4 Biosphere
- 4 Importance of Environment
- 4.1 Environment protects the ecosystem
- 4.2 Provides healthy living
- 4.3 Biodiversity is an important part of the environment
- 4.4 Environment is necessary for generating the Food Chain
- 4.5 Regulation of Climatic Conditions
- 4.6 Protecting the environment for future generations
- 5 Need of Environmental Education
- 6 Environmental Degradation
- 6.1 Effective Methods of Conserving the Environment
The physical environment refers to non-living attributes such as air, water, soil, climate, heat, light, noise, housing, and radiations. On the other hand, the biological environment refers to all types of flora, fauna and micro-organisms.
The physical and the biological environments are interdependent on each other and the external conditions consist of both physical and biological conditions. It has been witnessed that deforestation leads to a decline in wildlife population from the biological environment and it also increases the atmospheric temperature within the physical environment.
Environment Definition
According to E. J. Ross. “Environment is an external force which influences us.”
The study of the environment helps us to understand the issues related to the loss of global biodiversity, global warming, dwindling forests, depletion of the ozone layer, and energy resources. It is the approach that helps us to study the global environment by analysing the processes involved in water, air, land, soil, and organisms that lead to pollution or degradation of the environment.
In the words of Herbert L. Mason and Jean H. Langenheim, environment is “The sum of all substances and forces external to an organism which determines its existence and regulates its process”.
According to A.G. Tansley “An ecosystem is an ecological unit consisting of Biotic factors or Living things and Abiotic factors or Non-Living things in a specific area.”
Components of Environment
On a broader note, the environment is an integration of different interdependent components. Broadly classified, into four components:
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the upper part of the earth that consists of a mantle of rocks called the crust. There are dense rocks that form the crust of the earth. The rocks get converted to a smaller loose material called soil by the process of weathering due to the elements of weather, temperature, humidity, and rainfall. The components of the lithosphere are:
- Mineral matter
- Soil organic matter or humus
- Soil water
- Soil atmosphere
- Biological system
- Micronutrients and macronutrients
Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is that part of the earth that contains water in either liquid or solid form. Water is covered through three fourth of the total area of the earth, which includes surface water as well as underground water.
Water is an important contributor in the sustenance of life and acts as the life-supporting module for the earth. Water helps to control the atmospheric temperature, functions as an air purifier, and also works as a waste assimilator.
Atmosphere
The mixture of gases that envelop the earth is called the atmosphere. Due to the gravitational pull, it holds close to the earth and it covers the earth’s area comprising of water and landmass to a height of many kilometres. The mixture of gases consists of:
- Nitrogen 78.05%
- Oxygen 20.95%
- Argon 0.94%
- Carbon dioxide 0.03%
- Hydrogen, nitrous oxides, and ozone in small quantities
The atmosphere helps to sustain life on earth and the atmosphere can be divided into five zones which are as follows:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Ionosphere or Thermosphere
- Exosphere
Biosphere
The Biosphere is that part of Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere where life exists. It consists of the domain of living organisms where they interact with each other in the physical environment of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
The physical environment and the biosphere are influenced by each other in the manner where the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere depend entirely on the plant kingdom, which involves the processes of respiration and photosynthesis.
Importance of Environment
The environment is important for the existence of life on planet earth and it plays a crucial role in the sustenance of life. People must protect the environment since it is a home for different living organisms and each one is dependent on the environment for food, air, water, and other needs.
According to P. Gisbert, “Environment is anything immediately surrounding an object and exerting a direct influence on it.”
Any form of life on earth will not be possible without the presence of the Environment. The importance of the environment can be explained through the following reasons:
Environment protects the ecosystem
Any changes in the ecosystem affect the organisms and put them in danger of extinction. Hence, it is necessary to protect our environment since the various aspects of the ecosystems are connected.
Provides healthy living
It is important to protect the environment for leading a healthy life with fresh air, clean water, and safe surroundings. If the environment gets polluted then water and air gets polluted the most and it leads to health problems for all living organisms on this planet hence it is necessary to protect the environment from different types of pollution.
Biodiversity is an important part of the environment
The environment consists of fauna and flora like grasslands, forests etc. which are necessary for maintaining the lifecycle of the ecosystem. The forests are necessary since they provide the habitat for various animals living in the forests. Forests also provide the people with various raw materials like food, medicines, rubber, timber, essential oils and more. The destruction of forests leads to destroying the ecosystem as a whole.
Environment is necessary for generating the Food Chain
The environment helps in generating the food chain and hence the complex establishment of food web occurs. Plants absorb sunlight and through the process of photosynthesis convert the light energy into chemical energy that is then released and used by the living organisms for their activities.
Plants are food for herbivorous animals which in turn gets eaten by other carnivorous animals, and these carnivorous animals are in turn again eaten by higher order carnivorous animals. Hence, destroying environment would lead to the destruction of the food chain.
Regulation of Climatic Conditions
Various trees and plants help to maintain the weather pattern resulting in various forms of micro-climates. The forests absorb carbon dioxide and other harmful impurities generated by various anthropogenic activities.
Carbon dioxide is one of the major gas responsible for global warming. The forest trees play an important role in blocking the winds and prevent soil erosion. They are also responsible for the rainfall patterns in the area and subsequently recharge groundwater.
Protecting the environment for future generations
The environment is prerequisite for continued existence of living organisms and non-living things, hence people must take care of the environment. It is a moral duty of the present generation to safeguard it so that it can also benefit future generations.
Hence, the environment plays an important role in the healthy living of human beings and it provides air, food, shelter, and also fulfils other basic needs. The sustenance of humanity depends on the well-being of all the factors of the environment.
The need for a clean and safe environment is necessary:
- To ensure existence of life on the earth
- To preserve source of natural beauty
- To provide safe habitat for the flora and fauna present here
- To promote various food webs and food chains
- To control the important ecological processes
- To help in recycling of nutrients between biotic and abiotic components
- To facilitate and maintain the flow of energy in an ecosystem with the help of carbon dioxide cycle, nitrogen cycle, oxygen cycle, water cycle and energy cycle.
Need of Environmental Education
Environmental education is required for environmental protection that takes into account the moral and ethical relationship of human beings with the environment. It is the process of conserving the environment and it became a necessity because of the fast-growing population and their impact on the environment.
Environmental education is needed for people to conserve and explore environmental issues, and work at problem solving and actions for improving the environment. Bringing awareness of environmental issues makes people develop a better understanding of the environment and work towards making responsible decisions.
Environmental education makes a human being aware of their moral and ethical obligations towards the environment. It involves the decisions that people need to make in regard to the environment and it takes into account the ethical relationship between people, the environmental conditions, and its ecological biodiversity.
Environmental education is an important tool for the conservation of the environment and its sustainable development. It teaches us to be friendly with the environment for developing a healthy lifestyle. It gives awareness regarding the responsibility of the people, environmental rights, knowledge on conservation and protection of the environment, and the traditional knowledge that has been passed to us from our ancestors.
It deals with the philosophical issues which deal with the conservation and development of the environment for the welfare of human beings. This is because the changes in the environment have led to several natural disasters that have been happening in different countries across the globe with severe consequences. The activities of human beings have resulted in adding to pollution, desertification, extinction of certain animals and birds, deforestation, and several reasons which add to the impact on the environment.
It is the responsibility of the people to protect their environment and providing environmental education gives them the opportunity to understand the environment and the factors that lead to degrading of the environment. Environmental education gives information on how simple changes in daily life can make a huge difference to the environment. Hence, environmental education is required by every individual through a continuous and lifelong process for saving the environment. It must be a continuous and lifelong process.
The various components of environmental education are:
- To understand and gain knowledge of the environment and environmental challenges.
- To raise concern for the environment and motivate people to improve or maintain environmental quality.
- To identify skills required to resolve environmental challenges.
- To engage in activities that lead to the resolution of environmental challenges.
Environmental education does not get confined to teaching or advocating a specific viewpoint or course of action, rather it teaches people how to understand the environment better through critical thinking and it helps in enhancing their own problem-solving and decision-making skills.
For promoting environmental awareness across the country, the Centre for Environment Education (CEE) was established in August 1984 with support from the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India. The main responsibility of the Centre for Environmental Education is to provide the people of the country with knowledge on environmental issues through effective educational programs.
Environmental Degradation
The degradation of ecosystems and the changes in the global climate has resulted in the initiation of environmental ethics. Environmental ethics outlines the moral responsibilities of human beings and their respect towards the environment.
Human activities are the major cause of environmental pollution along with the increase in population that results in demand for food and shelter which lead to the more utilisation of resources. The needs and requirements of the people disturb the natural balance of the environment that results in the exploitation of the environment and depletion of the resources.
The deterioration of the physical aspects of the environment takes place due to human activities to the extent that it gets degraded and it cannot be put back or set right by any form of mechanism. The depletion of natural resources from the earth takes place in the form of pollution of air, water, and soil, extinction of species, and the activities involved with the economic and technological development processes of human beings.
It results in forms of pollution, depletion of forest cover, over-dependence on energy-consuming technologies, and exponential growth of population that damage the ecology. The degradation of ecology takes place when the environment has been destroyed or the important assets or components are depleted.
The different kinds of environmental degradation are in form of atmospheric degradation, soil degradation, water degradation, noise pollution, light pollution, overpopulation, deforestation, etc. The degradation of the environment leads to the loss of biodiversity, affects human health, depletes ozone layer, loss for the tourism industry, and financial implications.
Effective Methods of Conserving the Environment
Effective methods of conserving the environment and finding ways for maintaining the quality of environmental standard are:
- To conserve and protest biodiversity
- To ensure effective measures for population control.
- To ensure optimum use of natural resources.
- To create public awareness for conserving the environment.
- Prioritising the need for environmental protection.
- To develop eco-friendly technological processes.
- To promote sustainable agriculture through methods that are not harmful to the environment.
- To use bio-fertiliser or eco-friendly fertilisers.
- To use a minimum amount of pesticides and insecticides.
- To adopt afforestation programs and developing wasteland
- To ensure effective clean-up of hazardous wastes from the environment.
- To determine a suitable technique to treat the pollutants before their discharge into the environment.

Environment
n., plural: environments
[ɪnˈvaɪɚ(n)mənt]
Definition: The totality of the surrounding conditions and elements in an individual
What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding conditions and elements with which a living thing interacts with. However, apart from the physical, there are other types of elements that make up an environment. They are the chemical and biological attributes. Thus, an environment contains all biotic and abiotic factors that have a role in the survival, evolution, and development of the organism occupying it. A related term “environ” is defined as “to surround” or “to enclose”. The scope of the environment varies — from the tiniest, “micro” scale to the largest, global scale.
The terms “ecosystem” and “surroundings” are the common synonyms for the word “environment”. However, they differ in such a way that the term “ecosystem” includes the interaction between the organism and its surroundings. The surroundings, in turn, refer to that which surrounds an organism or a population. In this regard, the environment is a rather vast concept whereas the term “surrounding” is relatively more specific.
Another related term is nature. What’s the difference between environment and nature? Similarly, the definition of nature includes all living and nonliving things on Earth but what characterizes nature is that it is a natural entity as opposed to the artificial that implicates an attribute that is not occurring naturally, and by that it is man-made or “built”.
Different branches of science are interested in studying the environment, its components, and the interaction between living organisms and their environment. For example, environmental science is interested in studying and investigating the interaction of organisms with their environment and its outcomes. A branch of environmental science is ecology, which deals with the ecological interactions within ecosystems.
Biology definition:
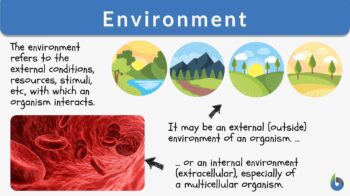
The environment is the external conditions, resources, stimuli, etc., with which an organism interacts. It may also refer to the external surroundings including all of the biotic and abiotic factors that surround and affect the survival and development of an organism or population, It may also be defined as the totality of the surrounding conditions and elements in an individual.But a simple ecological definition would be is that an environment is essentially the place over a particular time where organisms live or that which is occupied by a living thing. It includes all the physicochemical and biological components of the ecosystem.
Etymology: Middle English “envirounen”, from Old French “environner”, “environ”, meaning “round about” + -“ment”.
Types of Environments
The environment differs from one perspective to another. Let’s take a look at the following ways to group or classify environments.
Internal and external
In physiology, the environment may be internal or external. An internal environment would be the internal milieu of a multicellular organism. Maintaining the internal environment of an organism through homeostasis is crucial to the organism’s survival. An external environment refers to the environment outside of the organism. The next sections focus on the external environment.
Natural and Built
Environments may be natural or built. A natural environment is a type of environment found in nature. It includes all naturally occurring things, both living and nonliving. It, therefore, involves the complex relationships of weather, climate, living species, and natural resources.
Built environments, unlike natural environments, are made by humans, such as agricultural conversions or urban settings. With the current breadth of human interventions and conversions, many natural environments have acquired some degree or level of being “built”.
It is clear that man is a part of the environment; however, the intervention of a man produces a built environment. Humans have developed advanced tools to change components of the environment to meet their needs. Some animal species are also capable of using tools such as raw material to build nests, mounds, dams, and dwellings. However, their tools are relatively primitive and often the impact is not as extensive as that of human tools and technology. Human technology became widely distributed all over the world affecting all aspects of the environment either directly or indirectly.
Aquatic, terrestrial, and atmospheric
Based on the components, the environment may also be classified into (1) aquatic environment (marine, such as oceans and seas, and freshwaters, such as lakes and rivers), (2) terrestrial environment (land), and (3) atmospheric environment (air).
Marine environments are the largest known environments, they are characterized by the presence of water with great salt content. On the other hand, freshwater environments have less salt content. Marine environments represent about 97% of the water on Earth. Organisms within marine environments communicate with each other and with their physical surrounding. These environments are of great importance to humans because it is an important source of nutrition and resources. Marine pollution, acidification, and warming are threats to the marine environment as a result of human activities.
Read: Freshwater Ecology – Biology Online Tutorial
Terrestrial environments are environments found on land only. It represents the land of islands and continents and organisms living on them. Unlike aquatic or marine environments, terrestrial environments are not abundant in water; therefore, the presence of water in terrestrial environments is important. Due to the relatively lower availability of water, the temperature of terrestrial environments fluctuates daily and seasonally. There are six terrestrial ecosystems: taiga, rainforests, temperate forests, tundra, deserts, and grassland.
The atmospheric environment refers to the atmospheric component of an environment. The atmosphere (air) is a part of the Earth that has a huge impact on the thriving and survival of many organisms. Solar radiation, air components, climate, and air pollution are just some of the physicochemical attributes that can define an environment.
Living organisms have adapted to living in a particular environment with its specific conditions, such as humidity, temperature, light, and so on. All these factors affect the species in the environment. Therefore, living organisms have to adapt and modify through time to survive and tolerate different environmental conditions. Nevertheless, the environment itself also ‘evolves’. For example, oxygen eventually became incorporated into the Earth’s atmosphere after being released by photosynthetic organisms (such as algae) when producing sugar as food. Oxygen, eventually, became indispensable to the thriving of aerobic organisms, such as animals, including humans.
Different environments are found around us — from the natural to the artificial. Artificial (or “built”) environments are affected fully or partially by human technology. They include urban settings, parks, buildings, and neighborhoods containing all water, energy, and roads where people can live and work. The meaning of the natural environment is that this type of environment occurs in nature and not made by man. In a natural environment, vegetation, for instance, would grow by itself without being introduced or cultivated artificially.
External Environment Components
The external environment includes all biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) things. They are as follows:
Air, land, water
The Earth’s crust is the solid surface of the Earth and is also referred to as the lithosphere. The lithosphere is part of the environment. One natural source of the lithosphere is the solidification of magma.
Water (hydrosphere) is one of the main constituents of the environment. It covers about 71% of the Earth’s surface. It is found in oceans, rivers, seas, and lakes. Oceans cover a great area of the Earth’s surface. They contain saline water in a continuous ocean body and small seas.
Unlike oceans and seas, rivers contain freshwater and they flow toward a sea, a lake, an ocean, or another river. Few rivers flow toward the ground without reaching another water body and dry up. Rivers flow in a channel. They complete the water cycle since the river water is collected from glaciers, recharge of groundwater, and springs. Small rivers are known as streams. They are important in the environment because they connect different habitats and maintain biodiversity.
A lake is a body of water in part of the land and not connected to an ocean, the lake is deeper and larger than a pond. Natural lakes are usually present in areas with recent glacier formations or mountain areas. Ponds are small bodies of standing water, they are either naturally formed or man-made, they are smaller than lakes. Man-made ponds include fish ponds and solar ponds.
Water in built environments is affected by humans in various ways such as deforestation, urbanization, building dams, and channels to modify rivers as well as streams. Dams are designed to keep water to keep water and change its direction. Even though dams are useful in generating electricity and creating water reservoirs, they have a negative impact on natural environments by stopping the movement of fish and organisms through rivers and streams. Moreover, they affect the water supplying the forests. This eventually leads to the deterioration of trees and a decrease in the food supply for different biotic factors in the environment.
The atmosphere is the main factor in maintaining the balance of an ecosystem. The atmosphere is composed of a thin layer of gases that covers the Earth. The atmosphere is maintained in its position by the gravitational force. The atmosphere is composed of different gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, and inert gases. Moreover, the atmosphere includes water vapor and ice crystals forming clouds. One of the atmosphere layers is the ozone which reduces the intensity of ultraviolet rays reaching the Earth’s surface. Ultraviolet radiation damages the DNA of living organisms. Thus, the atmosphere as a component of the environment is important for the survival of living organisms including humans, and for maintaining the environmental balance by preventing temperature extremes.
Global warming is one of the major challenges affecting our environment nowadays. It refers to the recent increase in the Earth’s average atmospheric temperature due to an increase in the levels of greenhouse gas (e.g., carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and fluorocarbon). These gases keep the heat within the atmosphere. The rise in their levels in the atmosphere is caused by human activities such as deforestation, carbon dioxide combustion, etc. Because of that, the Earth’s surface temperature became warmer, thus, the name. Global warming is said to increase the average temperature of the Earth’s surface that is enough to cause climatic change. Accordingly, the global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18 °C (1.33 ± 0.32 °F) during the last century.
The climate is the state of wind, humidity, rain, atmospheric pressure, and temperature in a given area over a long period of time. It is classified in relation to different variables such as precipitation and temperature. Conversely, weather represents the condition of these elements but in the short term only. Both are important components of the environment. Weather is the sum of all phenomena taking place at a given time in a given area. Generally, the weather describes daily temperature values, while the climate describes the average condition of the atmosphere over a long time.
Weather describes differences between places in their moisture and temperature. These differences are due to several factors such as the sun angle on a given area. Surface pressure differs due to differences in temperature from one region to another. Humans developed systems that can predict the future state of the atmosphere, moreover, they tried to control the weather by different methods. There is evidence that activities of humans such as industry and agriculture have modified the weather since it is affected by any small change in the atmosphere.
Biosphere
The biotic components represent all living things on Earth, such as bacteria, protists, algae, fungi, plants, and animals. Life existed on Earth for more than 3.7 billion years. It is generally characterized by metabolism, growth, organization, adaptation, response, and reproduction. It includes all living organisms in the environment. The part of the Earth where living organisms occupy is referred to as the biosphere. Different living organisms are found within the biosphere. Living organisms have distinct features and traits that make them adapt to specific environments.
Biomes are ecological communities of different organisms that are able to adapt to the environmental conditions and climate in a certain geographic area; therefore, biomes are large environments characterized by biotic and abiotic factors such as light, temperature, precipitation, and other factors. Biomes are classified into 6 regions, which may either be land or aquatic. Land biomes are grassland, forest, tundra, and desert whereas aquatic biomes are freshwater and marine biomes. Biomes are useful in ecological studies and ecosystem changes as they provide information about the environments and how they change, adapt, evolve, and function.
Ecological Role
The ecosystem is the external environment wherein all organisms function together along with all non-living things in the environment. Living organisms within the ecosystem form complex relationships with abiotic factors in their environment to support their development and survival.
Energy flow
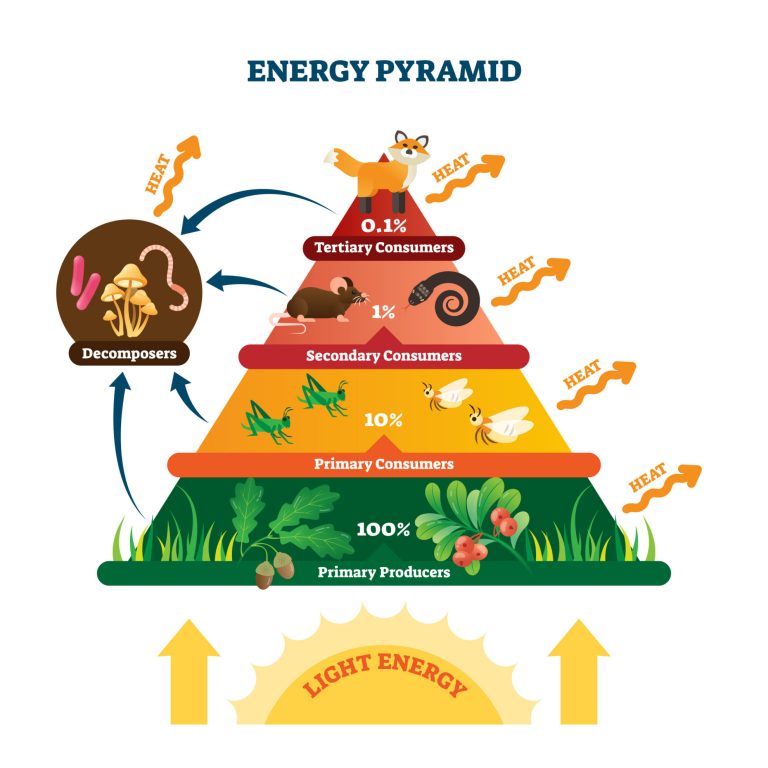
Energy flows between biotic and abiotic parts of the environment in cycles within the system of the ecosystem. Consequently, all components of the ecosystem are integrated with each other in harmony. In the chart below, notice how energy flows in an ecosystem. The energy from the sun (light energy) flows through the various trophic levels (from producers to consumers and decomposers) as it is converted into chemical energy that drives various metabolic activities and ultimately dissipated, e.g. as heat, into the environment.
Biogeochemical cycles
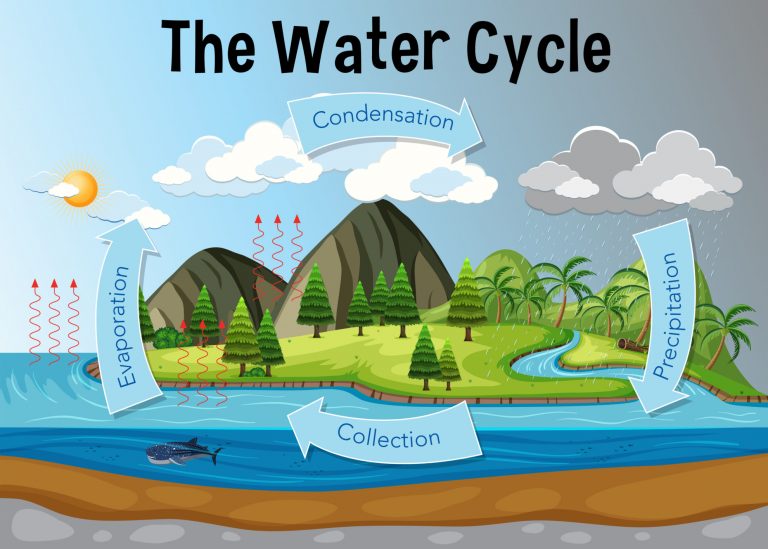
Biogeochemical cycles are pathways that allow different chemical substances to move through biotic and abiotic factors on Earth. Biogeochemical cycles are essential for different environments, especially those of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and water. For example, the water moves continuously in the water cycle through different parts of the Earth in different forms such as liquid, ice, or vapor in various places. Although water moves continuously in this cycle, its balance remains constant over time. Similarly, the carbon and oxygen cycle maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon on Earth to maintain the life and the atmosphere of Earth.
Challenges
The environment is facing many challenges due to human technologies. Environmentalism is a social movement that aims to eliminate or minimize the harmful effect of humans on the environment. environmentalism is mainly concerned with natural environments and issues they are facing such as the extinction of species, change in climate, loss of old forests, and pollution.
Wildlife is generally the natural environment that has not been affected or modified by man. Wildlife represents regions that are not controlled or developed by human industrial activity. Wilderness areas are mainly used to protect some animal species from extinction, it can also be used in ecological studies and recreation. Wildlife is greatly valued for its environmental, cultural, and spiritual importance.
Because wildlife, uncultivated grassland, unchanged forests, and wildflowers are slowly becoming fewer, the goal of environmentalism is to conserve and protect them. It aims to preserve and protect species, especially those that are at risk of extinction. It also takes effort in maintaining biodiversity in the natural environment. Sustainable and conserved use of water, air, raw material, land, energy, and other natural resources is ideal to help protect the environment. The use of renewable energy to generate electricity, cooling, heating, and in means of transportation instead of using fossil fuel to decrease pollution, minimize global warming, and ensure sustainability is highly encouraged.
How do we define “environment”? In biology, the definition of environment is the place where organisms live or occupy. Thus, the environment includes all the elements surrounding the organism. Living organisms constantly interact with their environment and adapt to all environmental conditions in order to survive. In psychology, the environmental definition refers to the person’s surroundings and that includes people apart from physical elements. The environment affects a person’s development, growth, behavior, mind, body, and heart.
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about the environment.
References
- Built Environment. Built Environment – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/built-environment.
- Johnson, D. L., Ambrose, S. H., Bassett, T. J., Bowen, M. L., Crummey, D. E., Isaacson, J. S., … & Winter‐Nelson, A. E. (1997). Meanings of environmental terms. Journal of environmental quality, 26(3), 581-589.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Environment most often refers to:
- Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
- Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or a group of organisms
Other physical and cultural environments[edit]
- Ecology, the branch of ethology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings
- Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or other properties
- Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic surroundings to the personal places
- Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact
- Market environment, business term
Arts, entertainment and publishing[edit]
- Environment (magazine), a peer-reviewed, popular environmental science publication founded in 1958
- Environment (1917 film), 1917 American silent film
- Environment (1922 film), 1922 American silent film
- Environment (1927 film), 1927 Australian silent film
- Environments (album series), a series of LPs, cassettes and CDs depicting natural sounds
- Environments (album), a 2007 album by The Future Sound of London
- «Environment», a song by Dave from Psychodrama
- Environments (journal), a scientific journal
In computing[edit]
- Environment (type theory), the association between variable names and data types in type theory
- Deployment environment, in software deployment, a computer system in which a computer program or software component is deployed and executed
- Runtime environment, a virtual machine state which provides software services for processes or programs while a computer is running
See also[edit]
- Environmentalism, a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection
- Environmental science
- Environment variable
I have to admit that some of the insights had a “Well, Duh!” quality when I first read them ie that a phenotype which enjoys a reproductive advantage in one environment may be selected against in another environment*. ❋ Unknown (2006)
That is, a non-mammalian is a fertilized egg _plus_ its parental (or extra-parental) environment; but a mammalian individual is a fertilized egg, _plus its intra-maternal environment_, plus its non-parental environment. ❋ Melvin Moses Knight (1934)
A Goldman spokesman said: «The firm produced very good results for 2009, but the environment is very difficult and the board was mindful of that difficult environment in making decisions about executive compensation.» ❋ Unknown (2010)
However, I use the term environment in a different way than most are accustomed to. ❋ Unknown (2007)
The term environment is used in this statement broadly to also include health, safety, and the conservation of natural resources. ❋ ITY National Archives (1999)
The term environment of evolutionary adaptedness attachment theory. ❋ Unknown (2009)
«Trying to influence people’s behaviour towards the environment is admirable, not political,» maintained everchanging. ❋ Phil Daoust (2010)
The impact on the environment is the same or worse. ❋ Nick Joy (2010)
“The job of ensuring energy companies are following the law and protecting the safety of their workers and the environment is a big one,” Mr. Salazar said, “and should be independent from other missions of the agency.” ❋ Unknown (2010)
«It’s nowhere near the glory days, particularly in places like the U.S., and I don’t think the environment is all that golden in Australia either, with interest rates rising sharply.» ❋ Ross Kelly (2010)
Whether or not they are subject to their environment is a matter of the worldscape that they inhabit, the alethic quirks that construct it. ❋ Hal Duncan (2009)
Attempts by Europe’s far right to couch their anti-immigrant arguments in the language of the environment is another thing that surprised me. ❋ Unknown (2010)
The ephemera throughout the environment is as detailed as I’ve seen anywhere. ❋ Ben Abraham (2009)
But first, let’s take a look at the political, social and economic causes, and foreign influences as well, because we can’t forget that the environment is a single, coherent unit. ❋ Beverly Bell (2010)
«[The environment] is being [ruined] by all this polution the world is [creating]» ❋ Sarah (2003)
Bush claims to care about [the environment] but has tried [to roll] back every major [environmental] protectoin law that has ever existed ❋ Middle America (2004)
Hevick of the [Bahamas] didn’t care about [the environment], and he also thought it was foolish to and thought «why care about the environment?» Hevick’s country was hit by global warming along with severe [floods]. Then he realized for not caring about the environment, he wasn’t the only fool that caused global warming, he also realized why to care about the environment. He now has common sense. ❋ Caitlin13579 (2008)
«I heard [the environment] used to be all over this place. [Hard to believe] this air used to be breathable, and this place was filled with more than just the color [grey].» ❋ Achet3 (2011)
I was living the other day in the environment just like all humans do and [realized] that the [U.S]. President doesn’t [give a fuck] about it. ❋ Von Groovy (2017)
[My mother] be [gettin’] [all up] in my environs.
Yea dude she was cleaning. ❋ Little Thunder (2020)
So for example, [product of the environment] implies that if one grows up in a home full of [domestic violence], one of the children in that home may become violent as well when they have a family of their own. If someone grows up in the hood, that person may become a gangster. If somebody grows up in a descent home that is filled with good resources (computer, good books, television, radio, etc.), then they are more likely to become successful. If somebody grows up in a Christian home, they will most likely become a Christian. If somebody grows up in [the Middle East] or in a home with Muslim parents, they are more likely to be Muslim. ❋ Dancing With Fire (2011)
Kids who [grow up] in excessively controlled environments often fall behind in college, having all that freedom to [cut loose] but [not knowing] how to manage it. ❋ D.S. Credito (2015)
“You hear it in the strength of my voice and in my rhythm, Now you know, how I was livin, It happened to me, like it happened to Serch, Prime Minister Pete Nice`ll kick the verse, in Bed-Stuy with my boy, [Kiwai] Height, The K to A Kingston, Wednesday night, To the Empire, show slammin, Open for Dana, crew flammin, Mouth open wide, or listening, Dumb dope with a forty in my system, Unprotected but respected for [my own self], Cause of talent, no shade, or nothin else, A time of tension, racially fenced in, I came off (and all the brothers blessed him), I left more than a mark, I left a dent, Cause I’m a [product of the environment].” – Pete Nice of 3rd Bass (Hip Hop Group) ❋ ♫ Highway To Hell ♫ (2009)
Girl, I gave that dude [my number] the other day and he called me at [2am] for a booty call! I don’t know who he thinks he is, but this is a [corporate environment]! ❋ DANNIP (2009)