Asked by: Ruben Marquardt
Score: 4.1/5
(16 votes)
Definitions of polysemantic word. a word having more than one meaning. synonyms: polysemant, polysemous word. type of: word. a unit of language that native speakers can identify.
What is polysemy and it Examples?
polysemy Add to list Share. When a symbol, word, or phrase means many different things, that’s called polysemy. The verb «get» is a good example of polysemy — it can mean «procure,» «become,» or «understand.»
How do you use Polysemantic in a sentence?
RhymeZone: Use polysemantic in a sentence. Significant mentions of polysemantic: His paintings have been noted for being polysemantic . …is explained as a misdirected and irrelevant SA as an outcome of the functional deficiency of the polysemantic right-hemispheric way of thinking.
When a word has multiple meanings?
Homonyms, or multiple-meaning words, are words that have the same spelling and usually sound alike, but have different meanings (e.g. dog bark, tree bark).
What are made words examples?
Made-up Words
- autoised.
- billocked.
- bloatware.
- custodied.
- impactful.
- incentivizing.
- jointery.
- mentee.
40 related questions found
What are some aesthetic words?
- elegant,
- exquisite,
- glorious,
- Junoesque,
- magnificent,
- resplendent,
- splendid,
- statuesque,
What are some fake words?
7 Fake Words That Ended Up in the Dictionary
- Dord. Dord is perhaps the most famous of the ghost words. …
- Abacot. Abacot made its debut in the second edition of Holinshed’s Chronicles, edited by Abraham Fleming and published in 1587. …
- 3. Morse. …
- Phantomnation. …
- Momblishness. …
- Cairbow. …
- Esquivalience.
What words have the most meanings?
According to Guinness World Records, the word that has the most meanings in the English language is the verb “set.” “Set” has 430 senses listed in the second edition of the Oxford English Dictionary, which was published in 1989.
When a sentence has two meanings?
A double entendre is a phrase or figure of speech that could have two meanings or that could be understood in two different ways.
What is the meaning of Polysemous?
: having multiple meanings. Other Words from polysemous Example Sentences Learn More About polysemous.
What is a word with two meanings called?
When words are spelled the same and sound the same but have different meanings, then they are called homonyms.
What is Homonymy and examples?
The word Homonymy (from the Greek—homos: same, onoma: name) is the relation between words with identical forms but different meanings—that is, the condition of being homonyms. A stock example is the word bank as it appears in «river bank» and «savings bank.»
What are the types of polysemy?
Types of polysemy
Linear polysemy accounts for a specialization-generalization relation between senses and, in turn, is divided into four types: autohyponymy, automeronymy, autosuperordination and autoholonymy.
What is the most complex word?
Why ‘Run’ Is The Most Complex Word in the English Language. English can be hard for other language speakers to learn. To use just one example, there are at least eight different ways of expressing events in the future, and conditional tenses are another matter entirely.
What 3 letter word has the most meanings?
So Far One three-letter word does much of the heavy lifting in the English language. The little word «run» — in its verb form alone — has 645 distinct meanings.
What is the longest word in English language?
The longest word in any of the major English language dictionaries is pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis, a word that refers to a lung disease contracted from the inhalation of very fine silica particles, specifically from a volcano; medically, it is the same as silicosis.
What are 20 Homographs examples?
20 example of homograph
- Bear — To endure ; Bear — Animal.
- Close — Connected ; Close — Lock.
- Lean — Thin ; Lean — Rest against.
- Bow — Bend forward ; Bow — Front of a ship.
- Lead — Metal ; Lead — Start off in front.
- Skip — Jump ; Skip — Miss out.
- Fair — Appearance ; Fair — Reasonable.
How do you describe a fake person?
Phony is something or someone that is not as it seems, or a person who pretends to be something he is not. Counterfeit is defined as an imitation or forgery. … Counterfeit or fake; not genuine.
What are words that aren’t words?
5 Common Words That Aren’t Words At All
- Alot. “The alot is better than you at everything,” says online humor blog Hyperbole and a Half. …
- Sherbert. …
- Irregardless. …
- Misunderestimate. …
- Definately.
Is Wisdomous a real word?
When a person has more wisdom than a wise person.
What is unique word?
—used to say that something or someone is unlike anything or anyone else. : very special or unusual. : belonging to or connected with only one particular thing, place, or person. See the full definition for unique in the English Language Learners Dictionary. unique.
What are some cute aesthetic words?
cute
- adorable.
- beautiful.
- charming.
- delightful.
- pleasant.
- pretty.
- dainty.
Most words convey several
concepts and thus possess the corresponding number of meanings. A
word having several meanings is called
polysemantic,
and the
ability of words to have more than one meaning is described by the
term polysemy.
Most English words are
polysemantic.
It should be noted that the wealth of expressive resources of a
language largely depends on the degree to which polysemy has
developed in the language.
The number of sound
combinations that human speech organs can produce is limited.
Therefore at a certain stage of language development the production
of new words by morphological means becomes limited, and polysemy
becomes increasingly important in providing the means for enriching
the vocabulary. The process of
enriching the vocabulary does not consist merely in adding new words
to it, but, also, in the constant development of polysemy.
The system of meanings of
any polysemantic word develops gradually, mostly over the centuries,
as more and more new meanings are either added to old ones, or oust
some of them.
So the
complicated processes of polysemy
development involve both the appearance of new meanings and the loss
of old ones. Yet,
the general tendency with English vocabulary at the modern stage of
its history is to increase the total number of its meanings and in
this way to provide for a quantitative and qualitative growth of the
language’s expressive resources.
Thus, stone
has the
following meanings:
1)
hard compact
nonmetallic material of which rocks are made, a small lump of rock;
2)
pebble;
3)
the woody
central part of such fruits as the peach and plum, that contains the
seed;
4)
Jewellery,
short for gemstone;
5)
a unit of
weight, used esp. to Brit, a unit of weight, used esp. to express
human body weight, equal to 14
pounds or
6.350
kilograms;
6)
a calculous
concretion in the body, as in the kidney, gallbladder, or urinary
bladder; a disease arising from such a concretion.
My brother-in-law, he says
gallstones hurt worse than anything. Except maybe kidney stones.
(King)
The bank became low again,
and Miro crossed the brook by running lightly on the moss-covered
stones.
(Card)
“Here,” she said, and
took off a slim silver necklace with an intricately carved pale jade
stone the
size of a grape. (Hamilton)
Smoke curled lazily from the
brown and gray rock chimney made of rounded river stones.
(Foster)
Ukrainian
земля
is also
polysemantic:
1) третя від Сонця планета;
2) верхній шар земної кори;
3) речовина темно-бурого кольору, що
входить до складу земної кори;
4) суша (на відміну від водного простору);
5) країна, край, держава.
Polysemy
is very characteristic of the English vocabulary due to the
monosyllabic character of English words and the predominance of root
words. The greater the frequency of the word, the greater the number
of meanings that constitute its semantic structure. Frequency −
combinability
− polysemy
are closely connected. A special formula known as Zipf’s
law has
been worked out to express the correlation between frequency, word
length and polysemy: the shorter the word, the higher its frequency
of use; the higher the frequency, the wider its combinability,
i.e. the more
word combinations it enters; the wider its combinability, the more
meanings are realized in these contexts.
The word in one of its
meanings is termed a lexico-semantic
variant of
this word. The problem in polysemy is that of interrelation of
different lexico-semantic variants. There may be no single semantic
component common to all lexico-semantic variants but every variant
has something in common with at least one of the others.
All the lexico-semantic
variants of a word taken together form its semantic
structure
or semantic
paradigm.
The word
face, for
example, according to the dictionary data has the following semantic
structure:
1. The
front part of the head: He
fell on his face.
2. Look,
expression: a
sad face, smiling faces, she is a good judge of faces.
3. Surface,
facade: face
of a
clock, face of a building, He laid his cards face down.
4. Impudence,
boldness, courage: put
a good/brave/boldface on smth, put a new face on smth, the face of
it, have the face to do,
save one’s
face.
5. Style
of typecast for printing: bold-face
type.
Meaning is direct
when it nominates the referent without the help of a context, in
isolation; meaning is figurative
when the referent is named and at the same time characterized through
its similarity with other objects, Cf.
-
direct meaning
figurative meaning
tough
meathead
foot
face
tough
politicianhead
of a cabbagefoot
of a mountainput a new face on smth.
Differentiation between the
terms primary/secondary
main/derived
meanings
is connected with two approaches to polysemy: diachrpnic
and synchronic.
If viewed diachronically,
polysemy is understood as the growth and development (or change) in
the semantic structure of the word.
primary meaning
→
secondary
meanings
table
―
Old Eng “a flat slab of stone or wood”.→
derived
from the primary meaning
Synchronically
polysemy is understood as the coexistence of various meanings of the
same word at a certain historical period of the development of the
English language. In that case the problem of interrelation and
interdependence of individual meanings making up the semantic
structure of the word must be investigated from different points of
view, that of main/derived, central/peripheric meanings.
An objective criterion of
determining the main or central meaning is the frequency of its
occurance in speech. Thus, the main meaning of the word table
in Modern
English is “a piece of furniture”.
Polysemy is a phenomenon of
language, not of speech. As a rule the contextual meaning represents
only one of the possible lexico-semantic variants of the word. So
polysemy does not interfere with the communicative function of the
language because the situation and the context cancel all the
unwanted meanings, as in the following sentences:
The steak is tough.
This is a tough problem.
Prof. Holborn is a tough examiner.
When analysing the semantic
structure of a polysemantic word, it is necessary to
distinguish between two levels of analysis.
On the first level, the
semantic structure of a word is treated as a system of meanings.
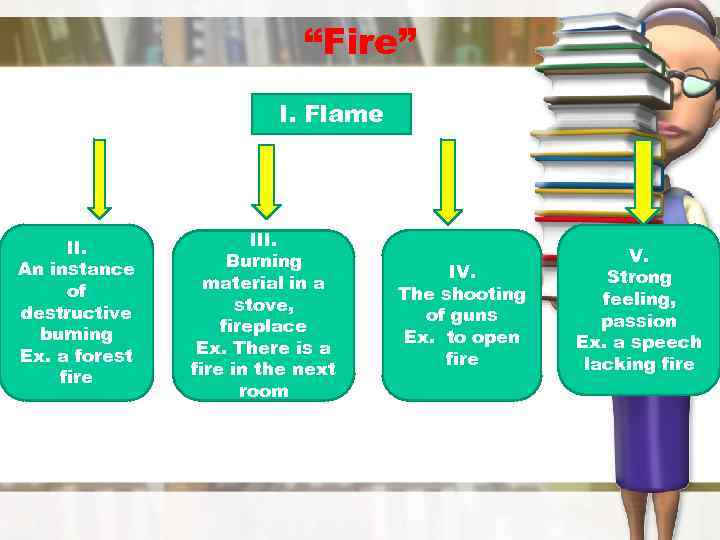
For example, the semantic structure of the noun fire
could be
roughly presented by this scheme (only the most frequent meanings are
given):
Figure 2
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
One example of polysemy is the word ‘sound’. This word has a very large number of meanings. It has 19 noun meanings, 12 adjective meanings, 12 verb meanings, 4 meanings in verb phrases, and 2 adverb meanings. A word with an even greater number of meanings is another example, ‘set’.
- Which one is an example of Polysemous words?
- What are Polysemous words?
- What are Polysemantic words?
- What is Homonymy and examples?
- What are homonyms give 5 examples?
- How do you use polysemy in a sentence?
- What is Oronyms?
- What are words with two meanings called?
- What is a word with two meanings called?
- What predetermines the meaning of a Polysemantic word?
- How does polysemy gain importance in enriching the vocabulary?
Which one is an example of Polysemous words?
English has many polysemous words. For example, the verb «to get» can mean «procure» (I’ll get the drinks), «become» (she got scared), «understand» (I get it) etc. In linear or vertical polysemy, one sense of a word is a subset of the other.
What are Polysemous words?
A polysemous word is a word that has different meanings that derive from a common origin; a homograph is a word that has different meanings with unrelated origins. Polysemous words and homographs constitute a known problem for language learners.
What are Polysemantic words?
Definitions of polysemantic word. noun. a word having more than one meaning.
What is Homonymy and examples?
A homonym is a word that is said or spelled the same way as another word but has a different meaning. «Write” and “right” is a good example of a pair of homonyms.
What are homonyms give 5 examples?
Homonym Examples
- Address — to speak to / location.
- Air — oxygen / a lilting tune.
- Arm — body part / division of a company.
- Band — a musical group / a ring.
- Bark — a tree’s out layer / the sound a dog makes.
- Bat — an implement used to hit a ball / a nocturnal flying mammal.
How do you use polysemy in a sentence?
4. As a pervasive semantic phenomenon across languages, polysemy has been given a systematic and extensive study, but there is not much attention shown to spatial polysemous words. 5. Its polysemy makes it a key concept articulating different fields such as new media technology, popular culture and media economy.
What is Oronyms?
A sequence of words (for example, «ice cream») that sounds the same as a different sequence of words («I scream»). The term oronym was coined by Gyles Brandreth in The Joy of Lex (1980).
What are words with two meanings called?
Homonyms, or multiple-meaning words, are words that have the same spelling and usually sound alike, but have different meanings (e.g. dog bark, tree bark).
What is a word with two meanings called?
A double entendre (plural double entendres) is a figure of speech or a particular way of wording that is devised to have a double meaning, of which one is typically obvious, whereas the other often conveys a message that would be too socially awkward, sexually suggestive, or offensive to state directly.
What predetermines the meaning of a Polysemantic word?
1. polysemantic word — a word having more than one meaning.
How does polysemy gain importance in enriching the vocabulary?
A well-developed polysemy is not a drawback but a great advantage in a language. … Therefore at a certain stage of language development the production of new words by morphological means becomes limited, and polysemy becomes increasingly important in providing the means for enriching the vocabulary.
In order to convey this or that information,a person uses words, each of which has its own lexical meaning. That is, a kind of idea that is in the mind of the speaker. Thanks to him, one person understands or does not understand (if he makes another sense) of another.
All the variety of vocabulary can be divided into single-valued and polysemantic words. Examples in the Russian language of the latter are the subject of the proposed article.
A bit of theory
There are fewer single-valued words. These include:
- various terms — colon, gastritis, kilogram;
- proper names — Volga, Elena, Penza;
- newly appeared in the language — briefing, pizzeria, gadget;
- possessing a narrowly subject meaning nouns — binoculars, trolley bus, melon.
Having more than one meaning is many-valued words of the Russian language, exampleswhich we will discuss in more detail. They are much more and understand what meaning the speaker puts in them, it is possible only in the context of the phrase. If you open an explanatory dictionary, you can see that the same concept belongs to several descriptions or articles numbered in numbers. For example, the word «take» can detect 14 values, and «go» — 26.
Any part can be multivaluedspeech: verbs, nouns, adjectives. The only exception is numerals. Acquaintance with the named theme children begin in 4-th class where they learn to distinguish homonyms and polysemantic words in Russian.
Examples (4th grade)
Acquaintance of children with a new topic is organized on the example of a specific word. So, if you consider the noun «button», then it can find three values:
- A stationery pins the paper against a table or wall.
- The bell button serves to click on it. Then a melody or beep will be heard.
- The button on the dress or other clothes serves as a buckle.
What is important here? What distinguishes polysemantic words? Examples in Russian clearly demonstrate that they must have a similarity on some basis. And the truth, the button in all cases is a small round object that serves to connect things with each other.
Homonyms are words that have similarities inwriting, but have a completely different meaning. For example, «braid». A noun can mean an agricultural implement and, at the same time, a female hairdress.
Let us consider other examples with different parts of speech. Nouns:
- Sleeve — a piece of clothing; the water flow separating from the main channel; pipe for the removal of gases or liquids, for example, a fireman.
- Comb — cocking; comb; the top of the mountain.
- Brush — part of the hand; an accessory of the artist; fruits of mountain ash; the end of the shawl.
Verbs:
- Shut up — hide in a pillow; immerse oneself in reading.
- Collect — thoughts, harvest, things, evidence.
- Was born — idea, daughter, thought.
Adjectives:
- Heavy — character, period, suitcase.
- Sour — facial expression, apple.
- Gold — earrings, words, hands.
Many-valued words: examples in Russian, Grade 5
At an older age, students comprehend thatsuch a direct, as well as portable meaning of the word. The thing, the phenomenon or its sign, most often associated with a specific concept and used in different contexts, is the first option. Widely used values can also be more than one. For example, the word «bread». It is considered in two aspects:
- Like a grain. This year will be an excellent harvest of bread.
- As an article. The store was closed, so at the table yesterday’s bread was eaten.
With a portable particle of direct valuepasses on to another object or phenomenon on the basis of some similarity. For example, the word «father». Means a person who brings up a son or daughter. When the father is called the father of the unit commander, it is assumed that he is surrounded by parental soldiers by parental care. And in this case we are dealing with a portable value.
Let’s consider other examples in the proposed table:
| Direct value | Figurative meaning | |
| 1. Silver | Silver ring | Silver medalist |
| 2. Deep | Deep lake | Deep feeling |
| 3. The Cloud | Rain cloud | Cloud of dust |
| 4. Wind | Strong wind | Wind in the head |
| 5. Wasting | Spend money | Spending the nerves |
| 6. Sneeze | Sneezing with a cold | Sneezing at people |
Nominative and characterizing significance
What else are complex words for understanding? Examples in the Russian language show that it is required to distinguish a nominative and characterizing their meaning. Otherwise, it is difficult to understand the information transmitted by the author of the phrase.
According to VV Vinogradov, the nominative meaning is associated with the reflection of reality and freely (easily) combined with other words. Consider this with the example of the word «father»:
- My father returned from work. We have a direct nominal value.
It will be nominative in the following version:
- The father of a hydrogen bomb. Only in a figurative sense, as before.
But in the phrase, which has already been considered in the text, the meaning will be not only portable, but also characterizing:
- Commander — father of the native. The word seems to transfer certain features to the concept of «commander.» Which ones? Caring, attentive, understanding.
Extended value
This is another importantmany-valued words (examples in Russian will be given below). In this case, a certain characteristic is vested in a whole concept or a large number of people or objects. For example, the title of the book «Fathers and Sons» implies that the word «father» hides a whole generation of people united on the basis of age.
More examples of multi-valued words with extended meaning in sentences:
- Bread — the whole head (head).
- Ice cream — shine (shine).
- Always need to beat first (beat).
- To be, not to seem (to be, to seem).
- People who have a hard life.
So, the studied words can always be found inexplanatory dictionary. The latter confirms that there are more than single-valued ones, and they attach special colors to the presentation of thoughts. They are actively used by writers, where much is built on the play of words and attentive attitude to the context of the phrase.
</ p>>
Polysemy. The semantic structure of a polysemantic word
Polysemy is the universal phenomenon, the essence of which consists in the fact that several related meanings are associated with the same group of sounds within one part of speech. Thus, polysemantic words denote a whole set of related concepts, grouped according to the national peculiarities of a given language.
Meanings of the word «model» : 1) a copy of something usually smaller than the original; 2) a particular design or type of product; 3) a simple description of a system, used for explaining how something works, or calculating what might happen; 4) a system that can be copied by other people; 5) a person or thing that is considered to be an excellent example of something.
Polysemy is a result of: 1. Shifts in application Ex. : adj. red ink (is really red) red hair red deer red cabbage red Indian 2. Specialization Ex. : partner Basic meaning: a type of relationship between 2 or more people. — business partner — marriage partner — partner in crime 3. Metaphorical extension Ex. : leaf of a tree – leaf of a book hands of a person – hands of a clock
One of the most important characteristics of polysemy is the presence of significance of a particular word. Polysemy is a condition of one word which has the possibility to increase more aspects of the same referent. Polysemantic words are those that have more than one meaning.
The problem of distinguishing polysemy from homonymy E. Hatch, and I. R. Galperin consider polysemy to be the source of the rise of homonymy, appearing in result of growing weak in its meaningful relationship, on the base of which a new additional meaning appears. E. Hatch claims that polysemy and homonymy are of special interest, and only the context can determine where polysemy or homonymy is
R. O. Yakobson asserts that in polysemy and homonymy there is some invariant that links even some separate entries. I. R. Galperin asserts that a polysemantic word breaks its semantic ties with the head word and becomes a homonym for the word it is derived from.
R. S. Ginsburg mentions that words, identical in their sound form, but different in meaning, are traditionally termed homonyms, and tries to show the difference between various meanings of one word, and the meaning of two homonymous words.
In case when words which sound the same retain a remote, but still the same meaning, and are united by the same shape meaning, we have an example of polysemy. When two different words sound the same, but have no relationship in meaning, homonymy appears. Homonyms are the result of disintegration, or split of polysemy, and represent the case when two words sound the same way, but have nothing in common, in spite of the same spelling.
The semantic structure of a polysemantic word Two levels of analysis. On the first level, the semantic structure of a word is treated as a system of meanings.
“Fire” I. Flame II. An instance of destructive burning Ex. a forest fire III. Burning material in a stove, fireplace Ex. There is a fire in the next room IV. The shooting of guns Ex. to open fire V. Strong feeling, passion Ex. a speech lacking fire
Dull, adj. A dull book, a dull film — uninteresting, monotonous, boring. A dull student — slow in understanding, stupid. Dull weather, a dull day, a dull colour not clear or bright. A dull sound — not loud or distinct. A dull knife — not sharp. Trade is dull — not active. Dull eyes — seeing badly. Dull ears — hearing badly.
Dull Uninteresting — deficient in interest or excitement. Stupid — deficient in intellect. Not bright — deficient in light or colour. Not loud — deficient in sound. Not sharp — deficient in sharpness. Not active — deficient in activity. Seeing badly — deficient in eyesight. Hearing badly — deficient in hearing.
Semantic structure of a word should be investigated at both these levels: 1) of different meanings, 2) of semantic components within each separate meaning.



![many-valued words in Russian examples 4 class [1]](https://stuklopechat.com/images/obrazovanie/chto-takoe-mnogoznachnie-slova-primeri-v-russkom-yazike_3.jpg)