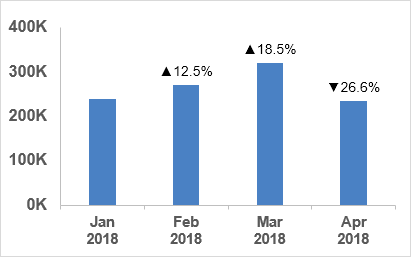Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 for Mac Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
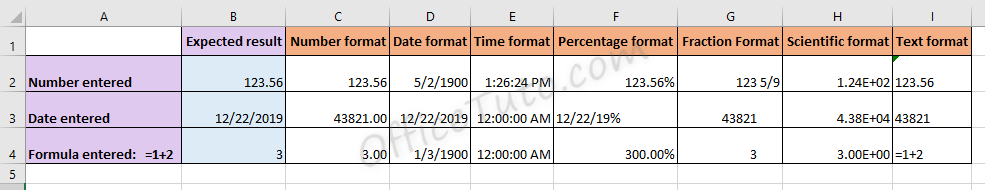
You can use number formats to change the appearance of numbers, including dates and times, without changing the actual number. The number format does not affect the cell value that Excel uses to perform calculations. The actual value is displayed in the formula bar.
Excel provides several built-in number formats. You can use these built-in formats as is, or you can use them as a basis for creating your own custom number formats. When you create custom number formats, you can specify up to four sections of format code. These sections of code define the formats for positive numbers, negative numbers, zero values, and text, in that order. The sections of code must be separated by semicolons (;).
The following example shows the four types of format code sections.
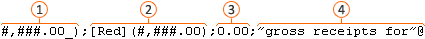
If you specify only one section of format code, the code in that section is used for all numbers. If you specify two sections of format code, the first section of code is used for positive numbers and zeros, and the second section of code is used for negative numbers. When you skip code sections in your number format, you must include a semicolon for each of the missing sections of code. You can use the ampersand (&) text operator to join, or concatenate, two values.
Create a custom format code
-
On the Home tab, click Number Format
, and then click More Number Formats.
-
In the Format Cells dialog box, in the Category box, click Custom.
-
In the Type list, select the number format that you want to customize.
The number format that you select appears in the Type box at the top of the list.
-
In the Type box, make the necessary changes to the selected number format.
Format code guidelines
To display both text and numbers in a cell, enclose the text characters in double quotation marks (» «) or precede a single character with a backslash (). Include the characters in the appropriate section of the format codes. For example, you could type the format $0.00″ Surplus»;$–0.00″ Shortage» to display a positive amount as «$125.74 Surplus» and a negative amount as «$–125.74 Shortage.»
You don’t have to use quotation marks to display the characters listed in the following table:
|
Character |
Name |
|
$ |
Dollar sign |
|
+ |
Plus sign |
|
— |
Minus sign |
|
/ |
Forward slash |
|
( |
Left parenthesis |
|
) |
Right parenthesis |
|
: |
Colon |
|
! |
Exclamation point |
|
^ |
Circumflex accent (caret) |
|
& |
Ampersand |
|
‘ |
Apostrophe |
|
~ |
Tilde |
|
{ |
Left curly bracket |
|
} |
Right curly bracket |
|
< |
Less than sign |
|
> |
Greater than sign |
|
= |
Equal sign |
|
Space character |
To create a number format that includes text that is typed in a cell, insert an «at» sign (@) in the text section of the number format code section at the point where you want the typed text to be displayed in the cell. If the @ character is not included in the text section of the number format, any text that you type in the cell is not displayed; only numbers are displayed. You can also create a number format that combines specific text characters with the text that is typed in the cell. To do this, enter the specific text characters that you want before the @ character, after the @ character, or both. Then, enclose the text characters that you entered in double quotation marks (» «). For example, to include text before the text that’s typed in the cell, enter «gross receipts for «@ in the text section of the number format code.
To create a space that is the width of a character in a number format, insert an underscore (_) followed by the character. For example, if you want positive numbers to line up correctly with negative numbers that are enclosed in parentheses, insert an underscore at the end of the positive number format followed by a right parenthesis character.
To repeat a character in the number format so that the width of the number fills the column, precede the character with an asterisk (*) in the format code. For example, you can type 0*– to include enough dashes after a number to fill the cell, or you can type *0 before any format to include leading zeros.
You can use number format codes to control the display of digits before and after the decimal place. Use the number sign (#) if you want to display only the significant digits in a number. This sign does not allow the display non-significant zeros. Use the numerical character for zero (0) if you want to display non-significant zeros when a number might have fewer digits than have been specified in the format code. Use a question mark (?) if you want to add spaces for non-significant zeros on either side of the decimal point so that the decimal points align when they are formatted with a fixed-width font, such as Courier New. You can also use the question mark (?) to display fractions that have varying numbers of digits in the numerator and denominator.
If a number has more digits to the left of the decimal point than there are placeholders in the format code, the extra digits are displayed in the cell. However, if a number has more digits to the right of the decimal point than there are placeholders in the format code, the number is rounded off to the same number of decimal places as there are placeholders. If the format code contains only number signs (#) to the left of the decimal point, numbers with a value of less than 1 begin with the decimal point, not with a zero followed by a decimal point.
|
To display |
As |
Use this code |
|
1234.59 |
1234.6 |
####.# |
|
8.9 |
8.900 |
#.000 |
|
.631 |
0.6 |
0.# |
|
12 1234.568 |
12.0 1234.57 |
#.0# |
|
Number: 44.398 102.65 2.8 |
Decimal points aligned: 44.398 102.65 2.8 |
???.??? |
|
Number: 5.25 5.3 |
Numerators of fractions aligned: 5 1/4 5 3/10 |
# ???/??? |
To display a comma as a thousands separator or to scale a number by a multiple of 1000, include a comma (,) in the code for the number format.
|
To display |
As |
Use this code |
|
12000 |
12,000 |
#,### |
|
12000 |
12 |
#, |
|
12200000 |
12.2 |
0.0,, |
To display leading and trailing zeros prior to or after a whole number, use the codes in the following table.
|
To display |
As |
Use this code |
|
12 123 |
00012 00123 |
00000 |
|
12 123 |
00012 000123 |
«000»# |
|
123 |
0123 |
«0»# |
To specify the color for a section in the format code, type the name of one of the following eight colors in the code and enclose the name in square brackets as shown. The color code must be the first item in the code section.
[Black] [Blue] [Cyan] [Green] [Magenta] [Red] [White] [Yellow]
To indicate that a number format will be applied only if the number meets a condition that you have specified, enclose the condition in square brackets. The condition consists of a comparison operator and a value. For example, the following number format will display numbers that are less than or equal to 100 in a red font and numbers that are greater than 100 in a blue font.
[Red][<=100];[Blue][>100]
To hide zeros or to hide all values in cells, create a custom format by using the codes below. The hidden values appear only in the formula bar. The values are not printed when you print your sheet. To display the hidden values again, change the format to the General number format or to an appropriate date or time format.
|
To hide |
Use this code |
|
Zero values |
0;–0;;@ |
|
All values |
;;; (three semicolons) |
Use the following keyboard shortcuts to enter the following currency symbols in the Type box.
|
To enter |
Press these keys |
|
¢ (cents) |
OPTION + 4 |
|
£ (pounds) |
OPTION + 3 |
|
¥ (yen) |
OPTION + Y |
|
€ (euro) |
OPTION + SHIFT + 2 |
The regional settings for currency determine the position of the currency symbol (that is, whether the symbol appears before or after the number and whether a space separates the symbol and the number). The regional settings also determine the decimal symbol and the thousands separator. You can control these settings by using the Mac OS X International system preferences.
To display numbers as a percentage of 100 — for example, to display .08 as 8% or 2.8 as 280% — include the percent sign (%) in the number format.
To display numbers in scientific notation, use one of the exponent codes in the number format code — for example, E–, E+, e–, or e+. If a number format code section contains a zero (0) or number sign (#) to the right of an exponent code, Excel displays the number in scientific notation and inserts an «E» or «e». The number of zeros or number signs to the right of a code determines the number of digits in the exponent. The codes «E–» or «e–» place a minus sign (-) by negative exponents. The codes «E+» or «e+» place a minus sign (-) by negative exponents and a plus sign (+) by positive exponents.
To format dates and times, use the following codes.
Important: If you use the «m» or «mm» code immediately after the «h» or «hh» code (for hours) or immediately before the «ss» code (for seconds), Excel displays minutes instead of the month.
|
To display |
As |
Use this code |
|
Years |
00-99 |
yy |
|
Years |
1900-9999 |
yyyy |
|
Months |
1-12 |
m |
|
Months |
01-12 |
mm |
|
Months |
Jan-Dec |
mmm |
|
Months |
January-December |
mmmm |
|
Months |
J-D |
mmmmm |
|
Days |
1-31 |
d |
|
Days |
01-31 |
dd |
|
Days |
Sun-Sat |
ddd |
|
Days |
Sunday-Saturday |
dddd |
|
Hours |
0-23 |
h |
|
Hours |
00-23 |
hh |
|
Minutes |
0-59 |
m |
|
Minutes |
00-59 |
mm |
|
Seconds |
0-59 |
s |
|
Seconds |
00-59 |
ss |
|
Time |
4 AM |
h AM/PM |
|
Time |
4:36 PM |
h:mm AM/PM |
|
Time |
4:36:03 PM |
h:mm:ss A/P |
|
Time |
4:36:03.75 PM |
h:mm:ss.00 |
|
Elapsed time (hours and minutes) |
1:02 |
[h]:mm |
|
Elapsed time (minutes and seconds) |
62:16 |
[mm]:ss |
|
Elapsed time (seconds and hundredths) |
3735.80 |
[ss].00 |
Note: If the format contains AM or PM, the hour is based on the 12-hour clock, where «AM» or «A» indicates times from midnight until noon and «PM» or «P» indicates times from noon until midnight. Otherwise, the hour is based on the 24-hour clock.
See also
Create and apply a custom number format
Display numbers as postal codes, Social Security numbers, or phone numbers
Display dates, times, currency, fractions, or percentages
Highlight patterns and trends with conditional formatting
Display or hide zero values
Need more help?
Преобразование чисел, дат и строк в настраиваемый текстовый формат из кода VBA Excel с помощью функции Format. Синтаксис, параметры, символы, примеры.
Format – это функция, которая преобразует число, дату или строку в текст, отформатированный в соответствии с именованным выражением формата или инструкциями, составленными из специальных символов.
Синтаксис и параметры
Format(Expression, [FormatExpression], [FirstDayOfWeek], [FirstWeekOfYear])
- Expression – любое допустимое выражение (переменная), возвращающее числовое значение или строку (обязательный параметр).
- FormatExpression – выражение формата, именованное или содержащее инструкции из специальных символов (необязательный параметр).
- FirstDayOfWeek – константа, задающая первый день недели (необязательный параметр).
- FirstWeekOfYear – константа, задающая первую неделю года (необязательный параметр).
Именованные выражения форматов
Именные форматы даты и времени
| Имя формата | Описание |
|---|---|
| General Date | Стандартное отображение даты и времени в соответствии с параметрами системы. |
| Long Date | Длинный формат даты. |
| Medium Date | Средний формат даты. |
| Short Date | Краткий формат даты. |
| Long Time | Длинный формат времени. |
| Medium Time | Средний формат времени. |
| Short Time | Краткий формат времени. |
Проверьте отображение даты и времени с использованием именованных форматов на вашем компьютере при помощи следующего кода VBA Excel:
|
Sub FormatDateTime() MsgBox «General Date: « & Format(Now, «General Date») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Long Date: « & Format(Now, «Long Date») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Medium Date: « & Format(Now, «Medium Date») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Short Date: « & Format(Now, «Short Date») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Long Time: « & Format(Now, «Long Time») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Medium Time: « & Format(Now, «Medium Time») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Short Time: « & Format(Now, «Short Time») End Sub |
Скорее всего, результат будет таким:
Именованные форматы чисел
| Имя формата | Описание |
|---|---|
| General Number | Стандартное отображение числа без знака разделителя групп разрядов. |
| Currency | Денежный формат. |
| Fixed | Отображение числа без знака разделителя групп разрядов с двумя цифрами после разделителя целой и дробной части. |
| Standard | Отображение числа со знаком разделителя групп разрядов и с двумя цифрами после разделителя целой и дробной части. |
| Percent | Процентный формат: отображение числа, умноженного на 100, со знаком процента (%), добавленного справа. |
| Scientific | Отображение числа в экспоненциальном виде. |
| Yes/No | Возвращается «Нет», если число равно 0, иначе отображается «Да». |
| True/False | Возвращается «Ложь», если число равно 0, иначе отображается «Истина». |
| On/Off | Возвращается «Выкл», если число равно 0, иначе отображается «Вкл». |
Проверяем работу именованных форматов на числах 2641387.7381962 и 0 с помощью кода VBA Excel:
|
Sub FormatNumber() Dim n As Double n = 2641387.7381962 ‘n = 0 MsgBox «Форматируемое число = « & n & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «General Number: « & Format(n, «General Number») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Currency: « & Format(n, «Currency») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Fixed: « & Format(n, «Fixed») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Standard: « & Format(n, «Standard») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Percent: « & Format(n, «Percent») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Scientific: « & Format(n, «Scientific») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Yes/No: « & Format(n, «Yes/No») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «True/False: « & Format(n, «True/False») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «On/Off: « & Format(n, «On/Off») End Sub |
Получаем следующий результат:

Вместо вопросительного знака в отображении числа в формате Currency, по идее, должен быть знак валюты (₽ или руб.).
Специальные символы для выражений форматов
Символы для форматов даты и времени
| Символ | Описание |
|---|---|
| Точка (.) | Разделитель компонентов даты (день, месяц, год). Используется при отображении месяца в виде числа. |
| Пробел | Разделитель компонентов даты (день, месяц, год). Используется при отображении месяца прописью. |
| Двоеточие (:) | Разделитель компонентов времени (часы, минуты, секунды). |
| d | День в виде числа без нуля в начале (1–31). |
| dd | День в виде числа с нулем в начале (01–31). |
| m | Месяц в виде числа без нуля в начале (1–12). Если (m) следует после (h) или (hh), отображаются минуты (0–59). |
| mm | Месяц в виде числа с нулем в начале (01–12). Если (mm) следует после (h) или (hh), отображаются минуты (00–59). |
| mmm | Месяц прописью в сокращенном виде (янв–дек). |
| mmmm | Полное название месяца (январь–декабрь). |
| y | День года в виде числа (1–366). |
| yy | Год в виде 2-значного числа (00–99). |
| yyyy | Год в виде 4-значного числа (1900–9999). |
| h | Часы в виде числа без нуля в начале (0–23). |
| hh | Часы в виде числа с нулем в начале (00–23). |
| n (m) | Минуты в виде числа без нуля в начале (0–59). |
| nn (mm) | Минуты в виде числа с нулем в начале (00–59). |
| s | Секунды в виде числа без нуля в начале (0–59). |
| ss | Секунды в виде числа с нулем в начале (00–59). |
В этой таблице перечислены далеко не все символы для выражений форматов даты и времени. Вы можете ознакомиться со всеми символами, в том числе и для форматирования чисел, на сайте разработчика.
Примеры отображения даты с помощью разных по количеству наборов символа d:
|
Sub DataIsD() MsgBox «d: « & Format(Now, «d») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «dd: « & Format(Now, «dd») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «ddd: « & Format(Now, «ddd») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «dddd: « & Format(Now, «dddd») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «ddddd: « & Format(Now, «ddddd») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «dddddd: « & Format(Now, «dddddd») End Sub |
Символы для числовых форматов
| Символ | Описание |
|---|---|
| Точка (.) | Десятичный разделитель. |
| Запятая (,) | Разделитель групп разрядов. В отображаемых числах заполняется пробелом. |
| (0) | Заполнитель, который отображает цифру или ноль. Используется, когда нужны ведущие нули или нули в конце числа. |
| (#) | Заполнитель, который отображает цифру или ничего не отображает. Используется, когда не нужны ведущие нули или нули в конце числа. |
| (%) | Заполнитель процента. Выражение умножается на 100, а знак процента (%) вставляется на той позиции, где он указан в строке формата. |
| (E- E+ e- e+) | Экспоненциальный формат. |
Примеры использования символов в выражениях числовых форматов VBA Excel:
|
Sub FormatNumber2() Dim n As Double n = 2641387.7381962 ‘n = 0.2397842 MsgBox «Форматируемое число = « & n & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «0.##: « & Format(n, «0.##») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «000.###: « & Format(n, «000.###») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «#,###.###: « & Format(n, «#,###.###») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «0 %: « & Format(n, «0 %») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «0.### E-: « & Format(n, «0.### E-«) & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «0.### E+: « & Format(n, «0.### E+») End Sub |

Символы для текстовых форматов
| Символ | Описание |
|---|---|
| At-символ (@) | Заполнитель для символов, отображающий знак или пробел. |
| Амперсанд (&) | Заполнитель для символов, отображающий знак или ничего (пустая строка). |
| Меньше (<) | Принудительный перевод всех буквенных символов в нижний регистр. |
| Больше (>) | Принудительный перевод всех буквенных символов в верхний регистр. |
Примеры использования символов в выражениях строковых форматов VBA Excel:
|
Sub FormatString() MsgBox «Номер телефона: « & Format(«1234567890», «+7 (@@@) @@@-@@-@@») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Серия и номер паспорта: « & Format(«1234567890», «&& && &&&&») & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Нижний регистр: « & Format(«Нижний регистр», «<«) & vbNewLine _ & vbNewLine & «Верхний регистр: « & Format(«Верхний регистр», «>») End Sub |
Форматы для различных значений одного выражения
Различные форматы для разных числовых значений
В выражении формата для чисел предусмотрено от одного до четырех разделов, отделяемых друг от друга точкой с запятой. Отображаемая строка зависит от значения, возвращенного параметром Expression функции Format.
| Количество разделов | Результат форматирования |
|---|---|
| Один раздел | Выражение формата применяется ко всем значениям. |
| Два раздела | Первый раздел применяется к положительным значениям и нулям, второй – к отрицательным значениям. |
| Три раздела | Первый раздел применяется к положительным значениям, второй – к отрицательным значениям, третий – к нулям. |
| Четыре раздела | Первый раздел применяется к положительным значениям, второй – к отрицательным значениям, третий – к нулям, четвертый – к значениям Null. |
Пример использования четырех разделов в выражении формата числовых значений:
|
Sub FormatDifferentValues() MsgBox «Число 1234,5678: « & _ Format(1234.5678, «#,##0.00 руб.;Отрицательное число;Ноль рублей;Значение Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Число -25: « & _ Format(—25, «#,##0.00 руб.;Отрицательное число;Ноль рублей;Значение Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Число 0: « & _ Format(0, «#,##0.00 руб.;Отрицательное число;Ноль рублей;Значение Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Null: « & _ Format(Null, «#,##0.00 руб.;Отрицательное число;Ноль рублей;Значение Null») End Sub |
Различные форматы для разных строковых значений
В выражении формата для строк предусмотрено до двух разделов, отделяемых друг от друга точкой с запятой. Отображаемая строка зависит от текста, возвращенного параметром Expression функции Format.
| Количество разделов | Результат форматирования |
|---|---|
| Один раздел | Выражение формата применяется ко всем строковым данным. |
| Два раздела | Первый раздел применяется к строковым данным, второй – к значениям Null и пустым строкам («»). |
Пример использования двух разделов в выражении формата строк:
|
Sub FormatString2() MsgBox «Строка «Белка»: « & _ Format(«Белка», «@;Пустая строка или Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Пустая строка: « & _ Format(«», «@;Пустая строка или Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Строка «Null»: « & _ Format(«Null», «@;Пустая строка или Null») _ & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & «Значение Null: « & _ Format(Null, «@;Пустая строка или Null») End Sub |
This tutorial about cell format types in Excel is an essential part of your learning of Excel and will definitely do a lot of good to you in your future use of this software, as a lot of tasks in Excel sheets are based on cells format, as well as several errors are due to a bad implementation of it.
A good comprehension of the cell format types will build your knowledge on a solid basis to master Excel basics and will considerably save you time and effort when any related issue occurs.
A- Introduction
Excel software formats the cells depending on what type of information they contain.
To update the format of the highlighted cell, go to the “Home” tab of the ribbon and click, in the “Number” group of commands on the “Number Format” drop-down list.
The drop-down list allows the selection to be changed.
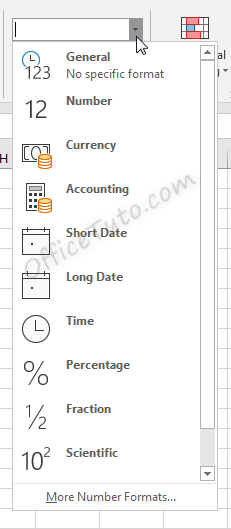
Cell formatting options in the “Number Format” drop-down list are:
- General
- Number
- Currency
- Accounting
- Short Date
- Long Date
- Time
- Percentage
- Fraction
- Scientific
- Text
- And the “More Number Formats” option.
Clicking the “More Number Formats” option brings up additional options for formatting cells, including the ability to do special and custom formatting options.
These options are discussed in detail in the below sections.
Cell format types in Excel are: General, Number, Currency, Accounting, Date, Time, Percentage, Fraction, Scientific, Text, Special (Zip Code, Zip Code + 4, Phone Number, Social Security Number), and Custom. You can get them from the “Number Format” drop-down list in the “Home” tab, or from the launcher arrow below it.
I will detail each one of them in the following sections:
1- General format
By default, cells are formatted as “General”, which could store any type of information. The General format means that no specific format is applied to the selected cell.
When information is typed into a cell, the cell format may change automatically. For example, if I enter “4/4/19” into a cell and press enter, then highlight the cell to view details about it, the cell format will be listed as “Date” instead of “General”.
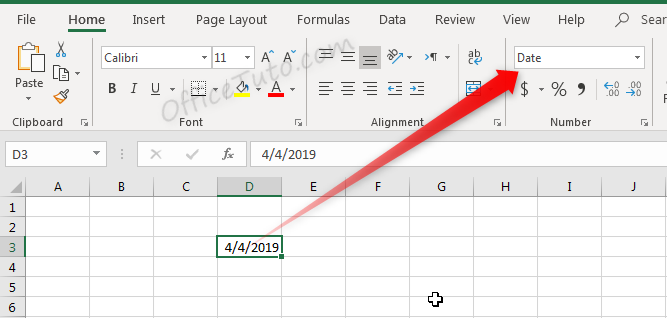
Similarly, we can update a cell’s format before or after entering data to adjust the way the data appears. Changing the format of a cell to “Currency” will make it so information entered is displayed as a dollar amount.
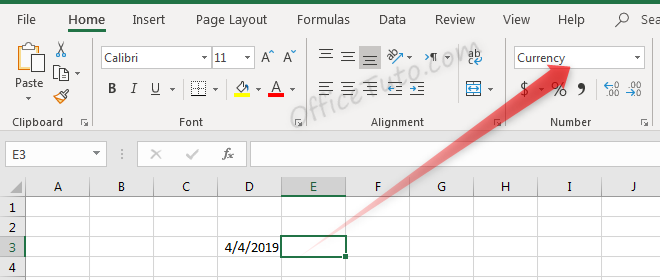
Typing a number into this cell and pressing enter will not just show that number, but will instead format it accordingly.
Before pressing enter, Excel shows the value which was typed: “4”.
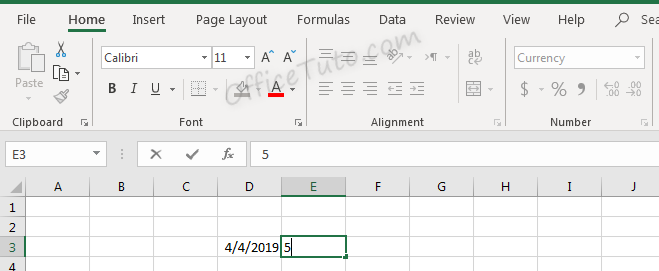
After pressing enter, the value is updated based on the formatting type selected.
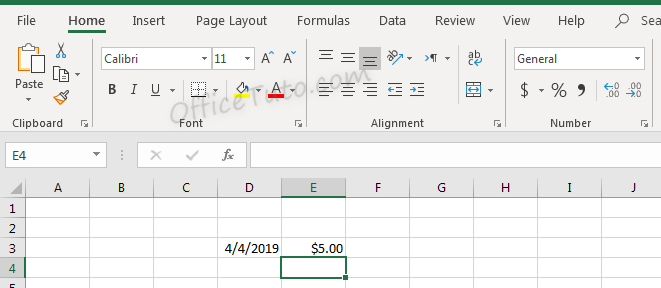
Don’t let the format type showed in the illustration at the drop-down list confusing you; it is reflecting the cell below (i.e. E4), since we validated by an Enter.
2- Number format
Cells formatted as numbers behave differently than general formatted cells. By default, when a number is entered, or when a cell is formatted as a number already, the alignment of the information within the cell will be on the right instead of on the left. This makes it easier to read a list of numbers such as the below.
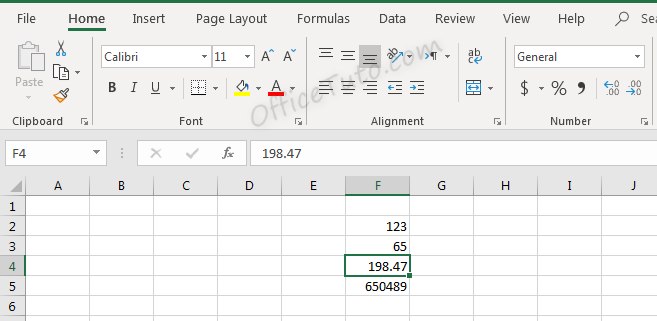
Note in the above screenshot that since we didn’t choose the “Number” format for our cells, they still have a “General” one. They are numbers for Excel (meaning, we can do calculations on them), but they didn’t have yet the number format and its formatting aspects:
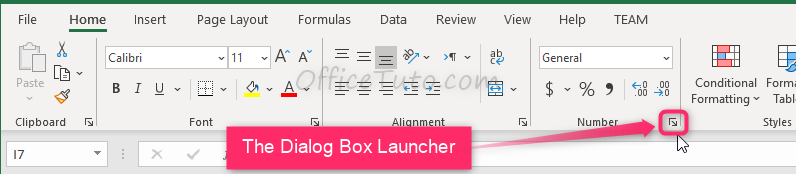
You can set the formatting options for Excel numbers in the “Format Cells” dialog box.
To do that, select the cell or the range of cells you want to set the formatting options for their numbers, and go to the “Home” tab of the ribbon, then in the “Number” group of commands, click on the launcher of the dialog box (the arrow on the right-down side of the group).
Excel opens the “Format Cells” dialog box in its “Number” tab. Click in the “Category” pane on “Number”.
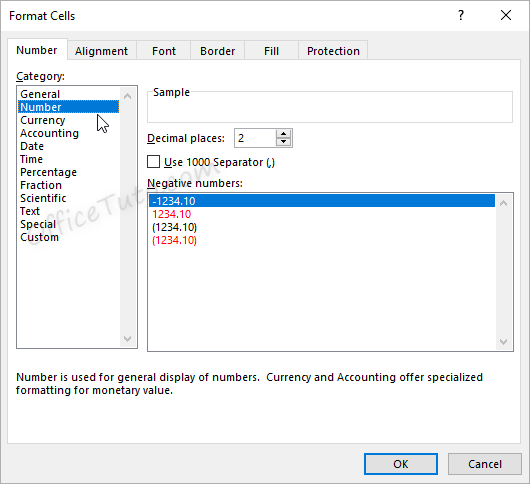
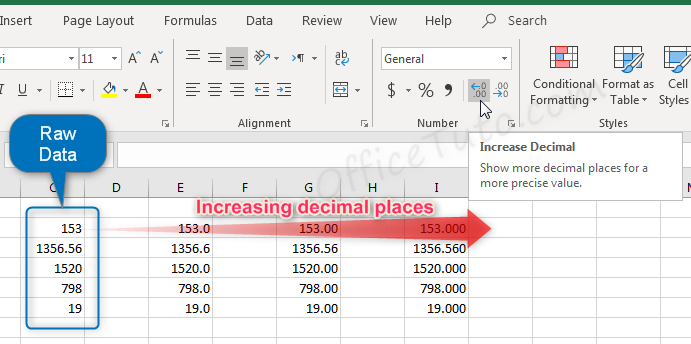
- In this dialog box, you can decide how many decimal places to display by updating options in the “Decimal places” field.
Note that this feature is also available in the “Home” tab of the ribbon where you can go to the “Number” group of commands and click the Increase Decimal or Decrease Decimal
buttons.
Here is the result of consecutive increasing of decimal places on our example of data (1 decimal; 2 decimals; and 3 decimals):
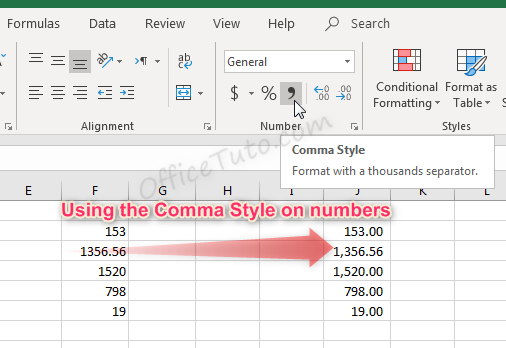
- You can also decide if commas should be shown in the display as a thousand separator, by updating the “Use 1000 Separator (,)” option in the “Format Cells” dialog box.
This feature is also available in the “Home” tab of the ribbon by clicking the “Comma Style” button in the “Number” group of commands.
Note that using the Comma Style button will automatically set the format to Accounting.
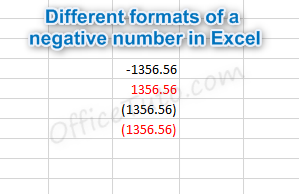
- Another option from the Format Cells dialog box is to decide how negative numbers should display by using the “Negative numbers” field.
There are four options for displaying negative
numbers.
- Display
negative numbers with a negative sign before the number. - Display
negative numbers in red. - Display
negative numbers in parentheses. - Display
negative numbers in red and in parentheses.
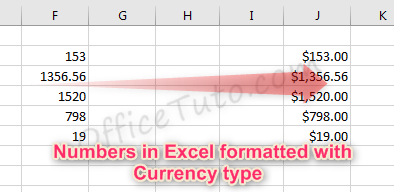
3- Currency format
Cells formatted as currency have a currency symbol such as a dollar sign $ immediately to the left of the number in the cell, and contain two numbers after the decimal by default.
The alignment of numbers in currency formatted cells will be on the right for readability.
Currency formatting options are similar to
number formatting options, apart from the currency symbol display.
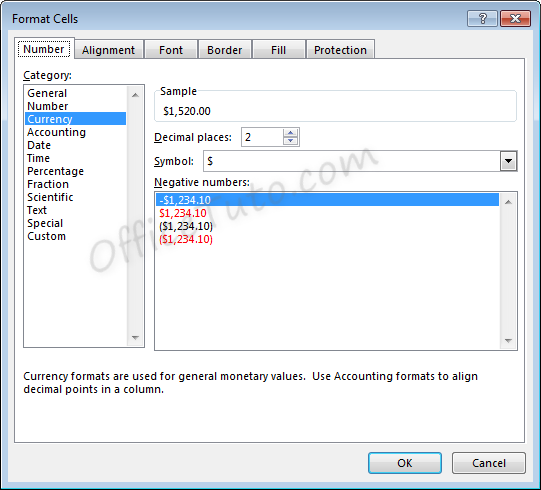
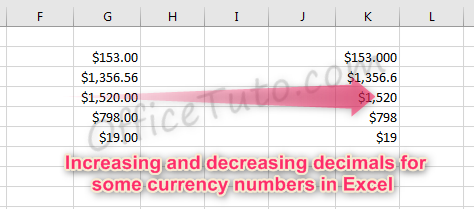
- As with regular number formatting, you can decide, in the “Format Cells” dialog box, how many decimal places to display by updating the field “Decimal places”.
You can also find this feature in the “Home” tab of the ribbon, by going to the “Number” group of commands and clicking the Increase Decimal or Decrease Decimal
.
- You can also decide what currency symbol should be shown in the display by updating the “Symbol” field in the “Format Cells” dialog box.
- As with regular number formatting, you can also decide how negative numbers should display by updating the “Negative numbers” field in the “Format Cells” dialog box.
There are four
options for displaying negative numbers.
- Display
negative numbers with a negative sign before the number. - Display
negative numbers in red. - Display
negative numbers in parentheses. - Display
negative numbers in red and in parentheses.
4- Accounting format
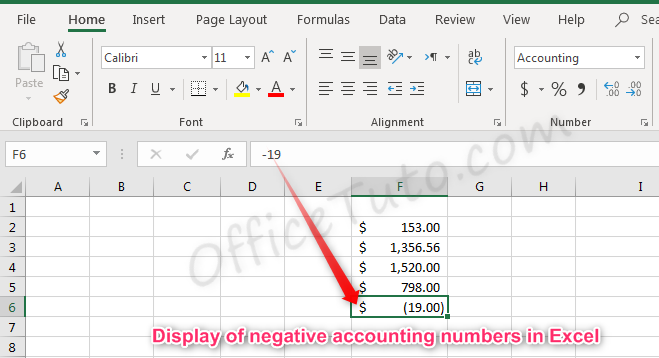
Like with the currency format, cells formatted as accounting have a currency symbol such as a dollar sign $; however, this symbol is to the far left of the cell, while the alignment of numbers in the cell is on the right. Accounting numbers contain two numbers after the decimal by default.
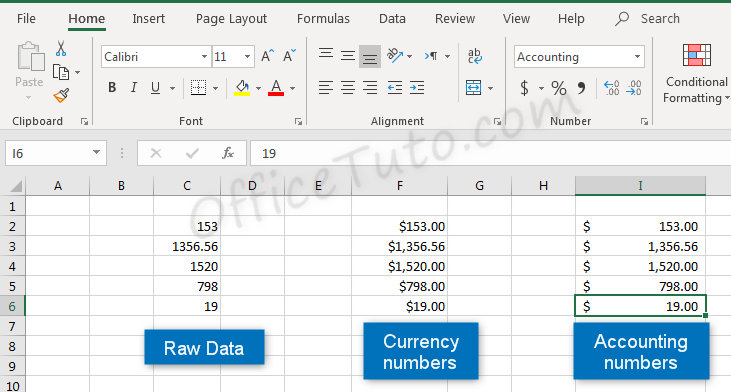
Clicking the “Accounting Number Format” button in the “Number” group of commands of the “Home” tab, will quickly format a cell or cells as Accounting.
The down arrow to the right of the Accounting Number Format button allows selection between common symbols used for accounting, including English (dollar sign), English (pound), Euro, Chinese, and French symbols.
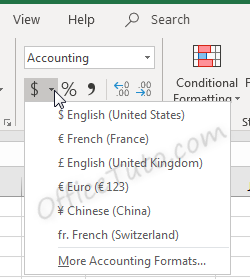
Accounting formatting options in the “Format Cells” dialog box (“Home” tab of the ribbon, in the “Number” group of commands, click on the launcher of the “Number Format” dialog box), are similar to number and currency formatting options.
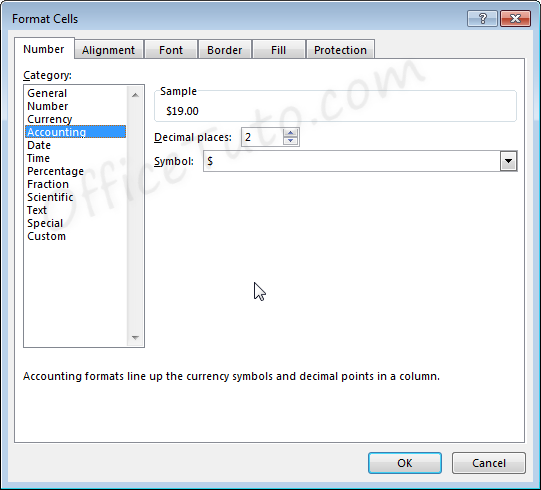
- You can decide how many decimal places to display by updating its option in the “Format Cells” dialog box.
As mentioned before in this tutorial, this feature is also available directly in the “Home” tab of the ribbon by clicking the Increase Decimal or Decrease Decimal
buttons in the “Number” group of commands.
- You can also decide in the “Format Cells” dialog box, what currency symbol should be shown in the display by using the “Symbol” drop-down list.
This dropdown gives a much broader list of options than the “Accounting Number Format” option in the “Home” tab of the ribbon.
Note that with the Accounting formatting option, negative numbers display in parentheses by default. There are not options to change this.
5- Date format
There are options for “Short Date” and “Long Date” in the “Number Format” dropdown list of the “Home” tab.
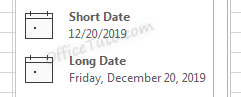
Short date shows the date with slashes separating month, day, and year. The order of the month and day may vary depending on your computer’s location settings.
Long date shows the date with the day of the week, month, day, and year separated by commas.
More options for formatting dates are available in the “Format Cells” dialog box (accessible by clicking in the “Number Format” dropdown list of the “Home” tab and choosing the “More Number Formats” option at the bottom).
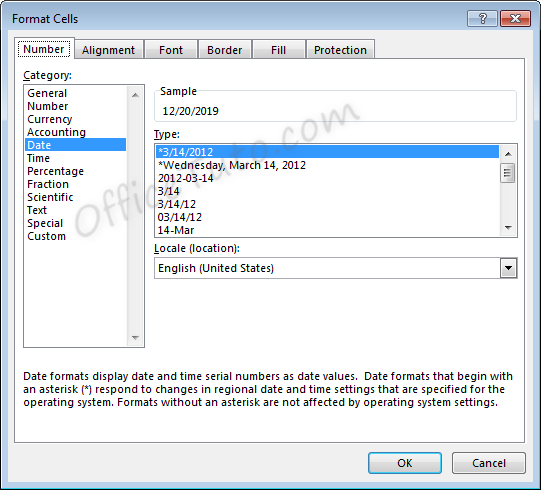
- You can choose from a long list of available date formats.
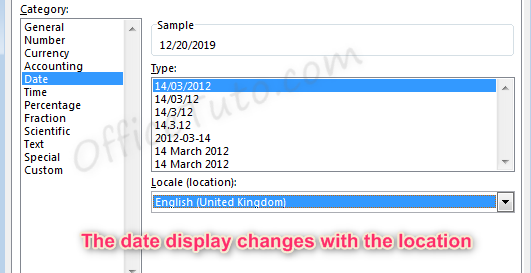
- You can update the location settings used for formatting the date. This will alter the list of format options in the above list and will adjust the display and potentially the order of the elements (day, month, year) within the date.
Note the below example when we switch from English (United States) format to English (United Kingdom) format.
6- Time format
Cells formatted as time display the time of
day. The default time display is based on your computer’s location settings.
Time formatting options are available in the “Format Cells” dialog box (accessible by choosing the “More Number Formats” option at the bottom of the “Number Format” dropdown list in the “Home” tab of the ribbon).
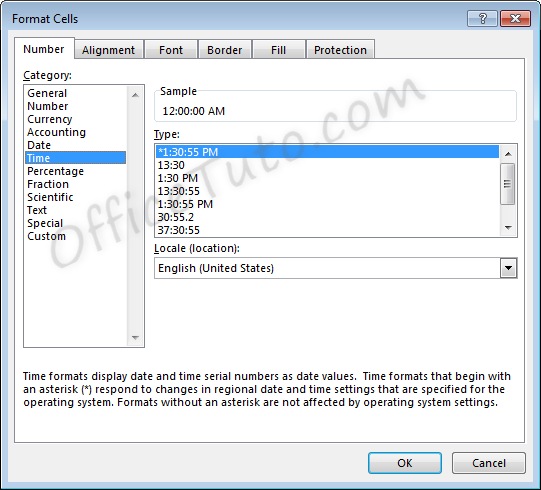
- You can choose from a long list of available time formats.
- You can update the location settings used for formatting the time. This will alter the list of format options in the above list and will adjust the display.
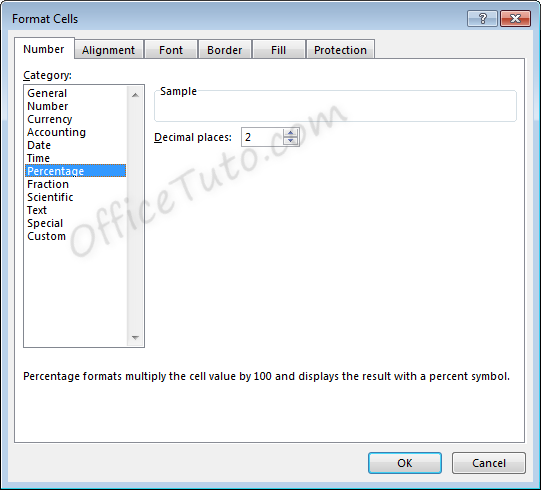
7- Percentage format
Cells formatted as percentage display a percent sign to the right of the number. You can change the format of a cell to a percentage using the “Number Format” dropdown list, or by clicking the “Percent Style” button . Both options are accessible from the “Home” tab of the ribbon, in the “Number” group of commands.
Note that updating a number to a percentage
will expect that the number already contains the decimal. For example:
A cell containing the value 0.08, as a percentage, will show 8%.
A cell containing the value 8, as a percentage, will show 800%.
Percentage formatting options are available in the “Format Cells” dialog box, accessible by clicking on “More Number Formats” of the “Number Format” dropdown list in the “Home” tab of the ribbon.
8- Fraction format
Cells formatted as a fraction display with a slash
symbol separating the numerator and denominator.
Fraction formatting options are available in the “Format Cells” dialog box, accessible by clicking in the “Home” tab of the ribbon, on “More Number Formats” of the “Number Format” dropdown list.
- Note that
when selecting the format to use for a fraction, Excel will round to the
nearest fraction where the formatting criteria can be met.
As an example, if the
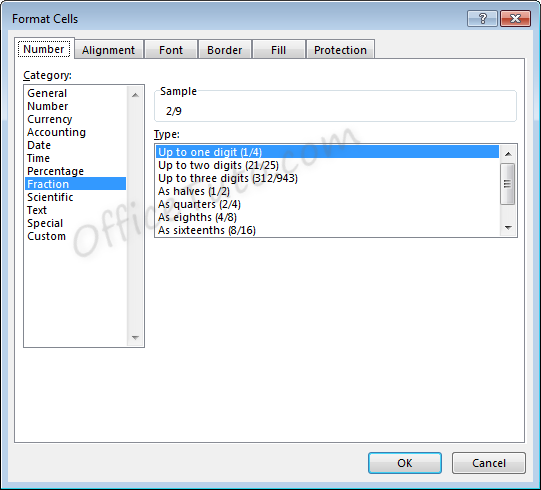
formatting option selected is “Up to one digit”, entering a fraction with two
digits will cause rounding to occur. For example, with the setting of “Up to
one digit”,
If we enter a value of 7/16, the value displayed will be 4/9, as converting to 9ths was the option with only one digit which required the least amount of rounding.
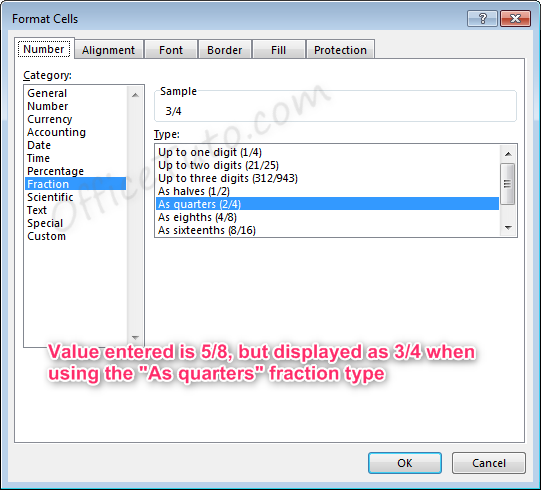
For another example, if the formatting option selected is “As quarters”, entering a fraction that cannot be expressed in quarters (divisible by four) will also cause rounding to occur.
If we enter a value of 5/8, the value displayed will be 3/4. Excel rounded up to 6/8, or 3/4, which was the closest option divisible by four.
- Also note
that for the formatting options with “Up to x digits”, Excel will always round
down to the lowest exact equivalent fraction when possible.
For example, if we enter a value of 2/4 with one of these formatting options active, the value displayed will be 1/2, as this is the mathematical equivalent. This behavior will not take place for formatting options “As…”, since these specifically determine what the denominator should be.
- Fractions listed as more than a whole (meaning the numerator is a higher number than the denominator), such as 7/4 will automatically be adjusted into a whole number and a fraction 13/4, where the fraction follows the formatting rules selected.
9- Scientific format
Scientific format, otherwise known as
Exponential Notation, allows very large and small numbers to be accurately
represented within a cell, even when the size of the cell cannot accommodate
the size of the numbers.
The way exponential notation works is to theoretically place a decimal in a spot that would make the number shorter, then describe where to move that decimal to return to the original number.
Examples with large numbers, where the decimal is moved to the left:
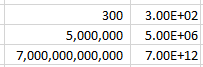
For the number 300 to be expressed in
exponential notation, Excel moves the decimal from after the whole number
300.00 to between the 3 and the 00. This is typed out as E+02 since the decimal
was moved two places to the left. The other examples are similar, where the
decimal was moved 6 and 12 places to the left.
Examples with small numbers, where the decimal is moved to the right:
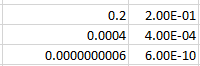
For the number 0.2 to be expressed in
exponential notation, Excel moves the decimal to create a whole number 2. This
is typed out as E-01 since the decimal was moved one place to the right. The
other examples are similar, where the decimal was moved 4 and 10 places to the
right.
Scientific formatting options are listed in the “Format Cells” dialog box, accessible by going to the “Home” tab of the ribbon, and clicking the “More Number Formats” option of the “Number Format” dropdown list.
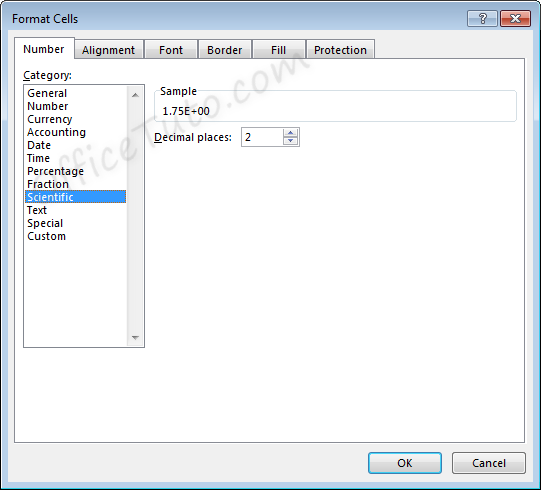
The only option available is to alter the
number of decimal places shown in the number prior to the scientific notation.
For example, for the value 11.43 formatted with the scientific format, if we change the Decimal places from 2 to 1, the display will change as follows.
Two decimals: 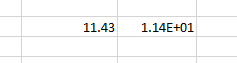
One decimal: 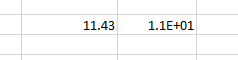
10- Text format
Cells can be formatted as Text through the
“Number Format” dropdown list, in the “Number” group of commands of the “Home”
tab.
Using the Text format in Excel allows values to be entered as they are, without Excel changing them per the above formatting rules.
In general, when entering a text in a cell, you won’t need to set its type to “Text”, as the default format type “General” is sufficient in most cases.
This may be useful when you want to display numbers with leading zeros, want to have spaces before or after numbers or letters, or when you want to display symbols that Excel normally uses for formulas.
Below are examples of some fields formatted as Text.
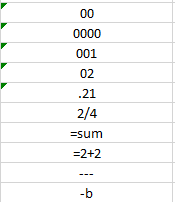
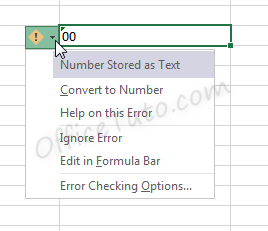
Note that when a number is formatted as Text, Excel will display a symbol showing that there could be a possible error .
Clicking the cell, then clicking the pop-up icon will show what the error may be and offer suggestions for resolution.
11- Special format
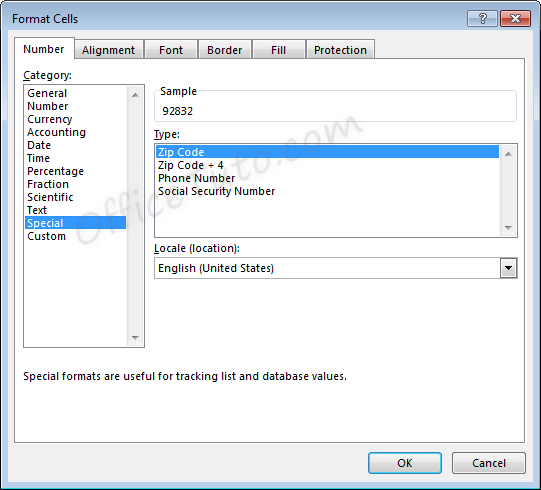
Special format offers four options in the “Format Cells” dialog box, accessible by going to the “Home” tab of the ribbon, and clicking the launcher arrow in the “Number” group of commands.
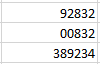
- Zip Code
When less than five numbers are entered in Zip
Code format, leading zeros will be added to bring the total to five numbers.
When more than five numbers are entered in Zip Code format, all numbers will be displayed, even though this does not meet the format criteria.
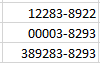
- Zip Code + 4
Zip Code + 4 format automatically creates a
dash symbol – before the last four numbers in the zip code.
When less than nine numbers are entered in Zip
Code + 4 format, leading zeros will be added to bring the total to nine
numbers.
When more than nine numbers are entered in Zip Code + 4 format, extra numbers are displayed prior to the dash symbol –.
- Phone Number
Phone Number format automatically creates a
dash –
before the last four numbers in the phone number. This format also adds
parentheses ( ) around the area code when an area code is entered.
When less than the expected number of digits
are entered in Phone Number format, only the entered digits will be displayed,
starting from the end of the phone number, as shown on the third and fourth
lines, below.
When more than the expected number of digits
are entered in Phone Number format, extra numbers are displayed within the area
code parentheses.
Note that Phone Number format in Excel does not handle the number 1 before an area code. This entry would be treated like any other extra number.
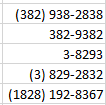
- Social Security Number
Social Security Number format automatically
creates a dash – before the last four numbers in the social security number
and a dash before the last six numbers in the social security number.
When less than nine numbers are entered in
Social Security Number format, leading zeros will be added to bring the total
to nine numbers.
When more than nine numbers are entered in Social Security Number format, extra numbers are displayed prior to the first dash –.

12- Custom format
Custom formats can be used or added through the
“Format Cells” dialog box, accessible from the “Number” group of commands in
the “Home” tab of the ribbon by clicking the “Number Format” launcher arrow.
This can be useful if the above formatting options do not work for your needs. Custom number formats can be created or updated by typing into the “Type” field of the “Format Cells” dialog box.
When creating a new custom format, be sure to use an existing custom format that you are okay with changing.
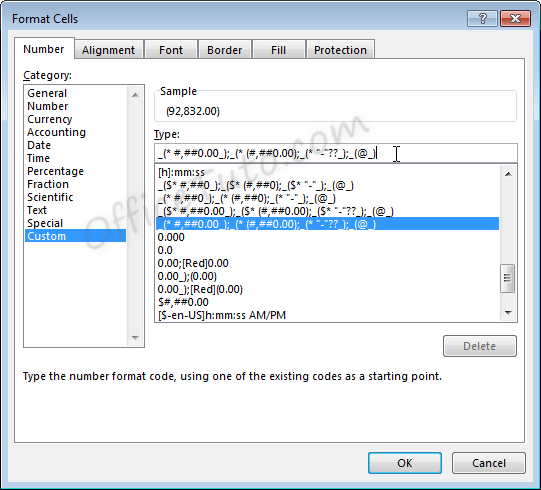
Custom number formats are separated, at
maximum, into four parts separated by semicolons ; .
- Part 1: How
to handle positive number values - Part 2: How
to handle negative number values - Part 3: How
to handle zero number values - Part 4: How
to handle text values
Note that if fewer parts are included in the custom format coding, Excel will determine how best to merge the above options: As an example, if two parts are listed, positive and zero values will be grouped.
Note that Excel may update the formatting of some fields to Custom automatically depending on what actions are taken on the field.
C- Common issues caused by wrong cell format types in Excel
1- Common issues due to wrong cell format types in Excel
The most common problems you may encounter with a wrong cell format type in Excel are of 3 types:
– Getting a wrong value.
– Getting an error.
– Formula displayed as-is and not calculated.
Let’s illustrate these 3 cases with some examples:
- Getting a wrong value
This may occur when you enter a value in an already formatted cell with an inappropriate format type, or when you apply a different format to a cell already containing a value.
The following table details some examples:
- Getting an error
This occurs when you enter a text preceded with a symbol of a dash, or plus, or equal, as an element of a list.
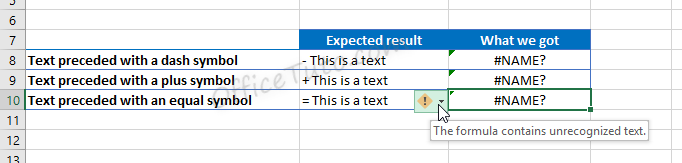
Excel wrongly interprets the text as a formula and show the error “The formula contains unrecognized text”.
- Formula displayed as-is and not calculated
In the following example, we tried to calculate the total of prices from cell B2 to B6 using the Excel SUM function, but Excel doesn’t calculate our formula and just displayed it as-is.
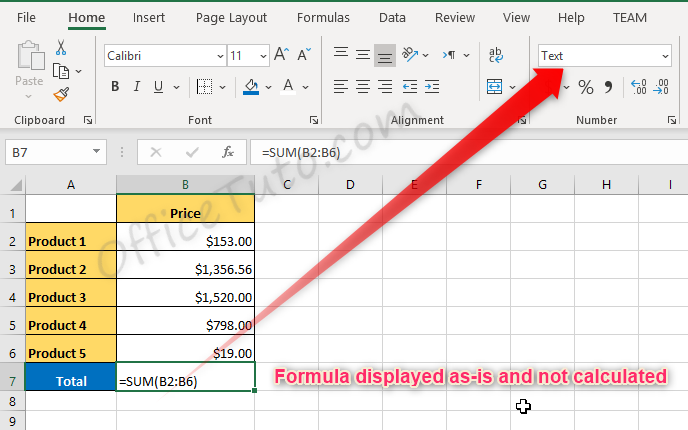
The source of the problem is that the result cell, B7, was previously formatted as text before entering the formula.
2- How to correct wrong cell format type issues in Excel
To correct cell format type issues in Excel, apply the right format in the “Number Format” drop-down list, and sometimes, you’ll also need to re-enter the content of the cell. For cells with formulas displayed as text, choose the “General” format, then double click in the cell and press Enter.
Jeff Golden is an experienced IT specialist and web publisher that has worked in the IT industry since 2010, with a focus on Office applications.
On this website, Jeff shares his insights and expertise on the different Office applications, especially Word and Excel.
In Excel, you aren’t limited to using built-in number formats. You can define your own custom number formats to display values as thousands or millions (23K or 95.3M), add leading zeros, display » — » for zero values, make negative values red, add bullets, and much more.
This Article (bookmarks):
- Watch the Video Overview
- How to Create a Custom Number Format
- Number Format Codes
- Examples
- Format for Thousands and Millions
- Display Leading Zeros and Include Commas
- Display Units Without Converting to Text
- Special Time Formats
- Including Special Symbols
- Displaying Fractions
- Trailing and Leading Characters to Fill a Cell
- Chart Axes and Labels
- Using Color Codes
- Conditional Operators
- Custom Location Codes for Dates
Watch the video we created to go along with this article!
How to Create a Custom Number Format
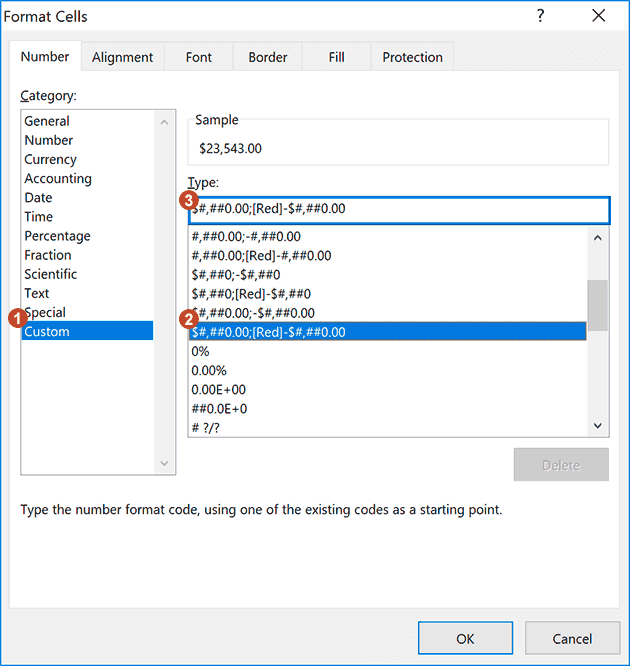
To create a custom number format, it is easiest to begin with a built-in format. Open the Format Cells dialog box by pressing Ctrl+1 (or right-click on a cell and select Format Cells) and select the Number tab (see the image below). Then (1) Choose Custom from the Category list, (2) Select a built-in format similar to what you want, and (3) Edit the format string in the Type field.
Number Format Codes
A number format string uses up to 4 different codes, separated by semicolons, as shown in the image below.
Instead of explaining the syntax in detail at this point, let’s take a look at some examples and learn as we go.
Some of the characters like #, 0, @, etc. have special meanings. Some codes like [Red] can change the font color, and quotes can be used to display text or special characters. The table below summarizes some of these special characters.
Special Characters in Number Formats
| Character | Description |
|---|---|
| # | A digit placeholder |
| 0 | A digit that is to be displayed even if it is zero |
| , | (Comma) Interpreted as a 1000’s marker |
| @ | Represents the value displayed as text |
| * | (Asterisk) Repeats the next character to fill the cell |
| [ColorCode] | See the section below about using color codes |
| [<=100] | Conditional operators (valid only in the Positive and Negative sections) |
| / | Used for fractions such as # #/12 or as the / character for dates |
| » « | (Quotes) Used to display whatever is contained within the quotes as text, such as 0.00 «feet» |
| d or dd ddd dddd |
Day number (0-31 or 00-31) Abbreviated day of week (Mon, Tue, etc.) Full day of week (Monday, Tuesday, etc.) |
| m or mm mmm mmmm mmmmm |
Month number (0-12 or 00-12) Abbreviated month name (Jan, Feb, etc.) Full month name (January, February, etc.) First letter of the month (J, F, M, etc.) |
| y or yy yyyy |
Year (0-99 or 00-99) Full year (1900-9999) |
| h or hh m or mm s or ss |
Hour (0-23 or 00-23) Minutes (0-59 or 00-59) Seconds (0-59 or 00-59) |
NOTE Some characters are specific to locale/language settings. For example J is used for Year in some countries.
Custom Number Format Examples
The examples below show some of the custom number formats that I’ve found the most useful. This isn’t a comprehensive list of all possible number formats. See support.microsoft.com to search for other articles on this subject.
TIP Using a custom number format only affects the displayed value. A formula that references the cell will use the stored value no matter how it is displayed. This means you can still use a formula to refer to the value even though the number might be displayed as «12 ft.»
To see these examples in action, download the Excel file below.
Download the Example File (CustomNumberFormats.xlsx)
Custom Number Format for Thousands and Millions
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0,K 0.0,K 0.0, «Thousand» |
23543 | 24K 23.5K 23.5 Thousand |
Display values in thousands, using the letter K to indicate thousands. The «K» is just a displayed character — it has no special meaning in the number format string. If you want to display more than one letter, you need to enclose the characters in quotes, like the «Thousand» example. |
| 0,,»M» 0.0,,»M» 0.0,, «Million» |
23543000 | 24M 23.5M 23.5 Million |
Display values in millons, using the letter M to indicate millions. Note that in this case, you need two commas. |
NOTE These are very useful for chart axes and labels.
Display Leading Zeros and Include Commas
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 000 00000 |
50.8 | 051 00051 |
Display values with leading zeros. This does not convert the value to text — it is only a display format. |
| #,##0.0 | 3543.46 | 3,543.5 | Display values using commas to separate thousands, millions, etc. The # sign is used as a placeholder, meaning that if there are no 10’s, 100’s, or 1000’s, don’t display them. |
Display Units Without Converting to Text
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As |
|---|---|---|
| • Display a number and text in the same cell using the conditions [=1] and [>1]. The value is stored as a number, so you can still do calculations on the number of people. | ||
| [=1]# «person»;[>1]# «people»;0 | 1 5 0 |
1 person 5 people 0 |
| • Display a number and text in the same cell. The value is stored as a number, so you can still do calculations. | ||
| 0.0 «ft» 0.0 «kg» # #/## «in» |
2.2 4.5 6.25 |
2.2 ft 4.5 kg 6 1/4 in |
| • Display a numeric YYMMDD value in years, months, days. | ||
| ##»y» ##»m» ##»d» | 360712 | 36y 07m 12d |
Special Time Formats
There are quite a few built-in time formats to choose from. The following may be less known.
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| [h]:mm:ss [h]:mm [mm]:ss [ss] |
49:03:47 | 49:03:47 49:03 2943:47 176627 |
Shows elapsed time in hours, minutes or seconds. Note that time does not round up. |
| h:mm A/P h:mm a/p |
2:25 PM | 2:25 P 2:25 p |
Displays time using «a» for AM and «p» for PM. Useful when trying to minimize column widths without making fonts smaller. |
Including Special Symbols
Some ascii and unicode characters can be copied and pasted directly into the format code. This can be handy for displaying the degrees symbol for temperatures as well as other tricks like showing up and down arrows or bulleted lists.
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
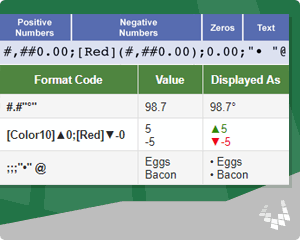
| #.#»°» | 98.7 | 98.7° | Display temperature in degrees with the ° symbol. |
| [Color10]▲0;[Red]▼-0 | 5 -5 |
▲5 ▼-5 |
Display special symbols for positive and negative, combined with colors. |
| ;;;»•» @ | Eggs Bacon |
• Eggs • Bacon |
Create a bulleted list using a special symbol for the bullet. When you enter text, the bullet will be displayed. Numbers and zero values will not be displayed. |
Displaying Fractions
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| # ??/12 | 5.75 12.5 |
5 9/12 12 6/12 |
Display a decimal number of feet as feet and inches (rounded to the nearest inch). Or display a decimal year in terms of years and months. |
| # ??/100 | 5.2 5.05 12.81 |
5 20/100 5 5/100 12 81/100 |
Using ??/100 will help line up values in a column (as opposed to just using ?/100). Note that fractions are automatically rounded. |
| ?/2 | 5.2 | 10/2 | Displays a simple fraction as numerator/denominator. |
Trailing and Leading Characters to Fill a Cell
The asterisk (*) in a format code repeats the following character to fill the width of the cell.
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| — @ *- | ✁ | — ✁ —————- | Trailing characters. |
| *.@ | pg 2 | ………………pg 2 | Leading characters |
Custom Number Formats for Chart Axes and Labels
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 «AD»;0 «BC» | 247 -600 |
247 AD 600 BC |
AD and BC Years. Use negative numbers for BC years and positive numbers for AD years. |
| mmm{Ctrl+j}yyyy | 8/20/18 | Aug 2018 |
Add a Carriage Return within the custom number format (e.g. between dddd and mmm) by pressing Ctrl+j. |
| [Color10]▲0.0%;[Red]▼-0.0% | 15.23% -23.57% |
▲15.2% ▼-23.6% |
Display arrows for positive and negative, combined with colors and percentages. |
A couple of these examples can be seen in the image below. However, notice that the data labels don’t use color codes, so the percentages are shown only as black text rather than red and green. Too bad. Maybe Microsoft will fix that some day.
NOTE Editing a custom number format that contains a carriage return is tricky because you can’t see the second row. This is why I write out the code first using «{Ctrl+j}» or just «{j}» and then delete the «{j}» and press Ctrl+j in its place.
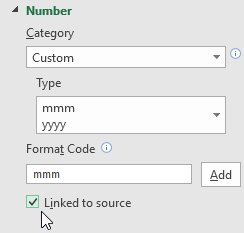
When adding a custom number format using the Format Axis window pane, you may not be able to press Ctrl+j to add a carriage return. In that case, first edit the format of the data source, then click on the Link to Source box as shown in the image to the right. After doing that, you can uncheck the Link to Source box and modify the original data source formatting.
Other Tricks
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ;;; | anything | Display nothing, regardless of the value. | |
| 0.# | 2 | 2. | Display a decimal point without a 0 after the decimal (2. instead of 2.0) |
| ???.??? | 1.2 12.3 123.456 |
1.2 12.3 123.456 |
Vertically align the decimal point when displaying a column of numbers. |
NOTE If you are looking for format codes for phone numbers, social security numbers, or zip codes, look in the Special category within the list of built-in number formats.
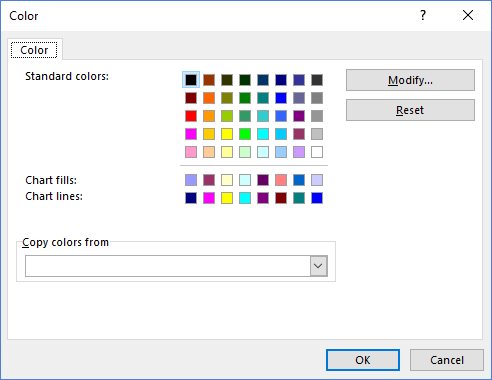
Custom Number Format Color Codes
By using color format codes such as [Red] or [Blue] or [Color10], you have a limited ability to alter the color of the font via custom number formats. The most common use I’ve seen is to color negative values red. However, one of the examples above also shows how you might want to use a green arrow.
Even though a new color palette was introduced in Excel 2007, the color codes for custom number formats are still based on the old color palette for the Excel 97-2003 format. I created the graphic below to provide a quick reference.
I made the above color code reference match the layout of the old color palette because there is not a consistent pattern to the numbering.
Define Your Own Color: You can modify the color palette in newer versions of Excel by going to File > Options > Save > Colors. This allows you to change the color associated with the Color1 through Color56 codes. This means that Color10 might not always be a dark green. If you purposely change the color palette (or somebody else does), Color10 might be some other color.
Excel 2016: File > Options > Save > Colors
NOTE The Color1-56 codes in Google Sheets are fixed colors and aren’t changed when you upload an Excel file with a customized color palette.
Conditional Operators
Conditional operators such as [<100] can be used to change the formatting in cases where positive;negative;0 is not how you want the divisions defined.
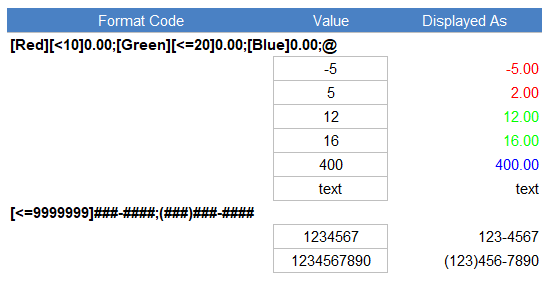
For example, the following format will display numbers less than 10 red, numbers between 10 and 20 green, other numbers blue, and text will be displayed based on the cell’s font color: [Red][<10]0.00;[Green][<=20]0.00;[Blue]0.00;@
You are limited to 2 numeric conditions, which you place in the negative and positive sections of the format code.
Another use of conditional operators is to display phone numbers with and without an area code, depending on how many digits are in the phone number like this: [<=9999999]###-####;(###)###-####. This assumes that the phone numbers are entered as numbers and not text values. Meaning, that if you actually enter 123-1234 into a cell in Excel, it will be interpreted as a text value, not a number. The phone number format will display 1234567 to 123-4567 and it will display 1234567890 to (123)456-7890.
Custom Location Codes for Dates
When displaying month names and weekday names for dates, you can use location codes such as [$-fr-CA] at the beginning of the format code to tell Excel to display the names in other languages. To learn what the code is for a specific language and location, use the Format Cells dialog in Excel, choose one of the built-in Date formats, then choose the Locale (location) from the drop-down list. Then you can return to the Format Cells dialog box and click on the Custom tab to see what location code was added.
| Format Code | Value | Displayed As | Language/Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| [$-en-US](ddd) mmm d, yyyy | 10/1/2018 | (Mon) Oct 1, 2018 | English (United States) |
| [$-fr-CA](ddd) mmm d, yyyy | 8/1/2018 | (mer.) août 1, 2018 | French (Canada) |
| [$-de-DE](ddd) mmm d, yyyy | 10/1/2018 | (Mo) Okt 1, 2018 | German (Germany) |
Other Notes About Custom Number Formats
To delete a custom number format, open the Format Cells dialog box, select the custom format from the list, then click Delete. When you delete a custom number format, all values in your workbook that use that format will revert to the General format.
Custom number formats that you create are saved with the file. If you want to use the custom format in a different file, you can copy/paste the formatting from your other file by copying and pasting the formatted cell or using the Format Painter tool.
References
- Number Formats for Charts by Jon Peltier, Excel MVP
- Excel Custom Number Format Guide by Mynda Treacy, Excel MVP
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel FORMAT function (as it applies to string values) with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel FORMAT function takes a string expression and returns it as a formatted string.
The FORMAT function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a String/Text Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Syntax
The syntax for the FORMAT function in Microsoft Excel is:
Format ( expression, [ format ] )
Parameters or Arguments
- expression
- The string value to format.
- format
-
Optional. It is the format to apply to the expression. You can either define your own format or use one of the named formats that Excel has predefined such as:
Format Explanation General Number Displays a number without thousand separators. Currency Displays thousand separators as well as two decimal places. Fixed Displays at least one digit to the left of the decimal place and two digits to the right of the decimal place. Standard Displays the thousand separators, at least one digit to the left of the decimal place, and two digits to the right of the decimal place. Percent Displays a percent value — that is, a number multiplied by 100 with a percent sign. Displays two digits to the right of the decimal place. Scientific Scientific notation. Yes/No Displays No if the number is 0. Displays Yes if the number is not 0. True/False Displays False if the number is 0. Displays True if the number is not 0. On/Off Displays Off if the number is 0. Displays On is the number is not 0. General Date Displays date based on your system settings Long Date Displays date based on your system’s long date setting Medium Date Displays date based on your system’s medium date setting Short Date Displays date based on your system’s short date setting Long Time Displays time based on your system’s long time setting Medium Time Displays time based on your system’s medium time setting Short Time Displays time based on your system’s short time setting
Returns
The FORMAT function returns a string value.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- VBA function (VBA)
Example (as VBA Function)
The FORMAT function can only be used in VBA code in Microsoft Excel.
Let’s look at some Excel FORMAT function examples and explore how to use the FORMAT function in Excel VBA code:
Format("210.6", "#,##0.00")
Result: '210.60'
Format("210.6", "Standard")
Result: '210.60'
Format("0.981", "Percent")
Result: '98.10%'
Format("1267.5", "Currency")
Result: '$1,267.50'
Format("Sep 3, 2003", "Short Date")
Result: '9/3/2003'
For example:
Dim LValue As String
LValue = Format("0.981", "Percent")
In this example, the variable called LValue would now contain the value of ‘98.10%’.

 , and then click More Number Formats.
, and then click More Number Formats.