What is the difference between formal and informal English words/ phrases? Actually, there are no specific definitions about formal and informal words/phrases. But, formal and informal English words/phrases can be identified based on the tips below:
- More read. You will learn to associate certain words and phrases with different types of writing.
- Most uses of “get” are informal.
- In general – phrasal verbs are informal.
- Contractions are always informal.
- Many idioms are informal.
- Most shortened words are informal.
- If you have a dictionary that provides the etymology of a word, Latin and French root words usually are more formal than Germanic or old English root words.
There are a lot of differences between formal and informal English. These differences make us more understand that language is large, very unique and important to learn.
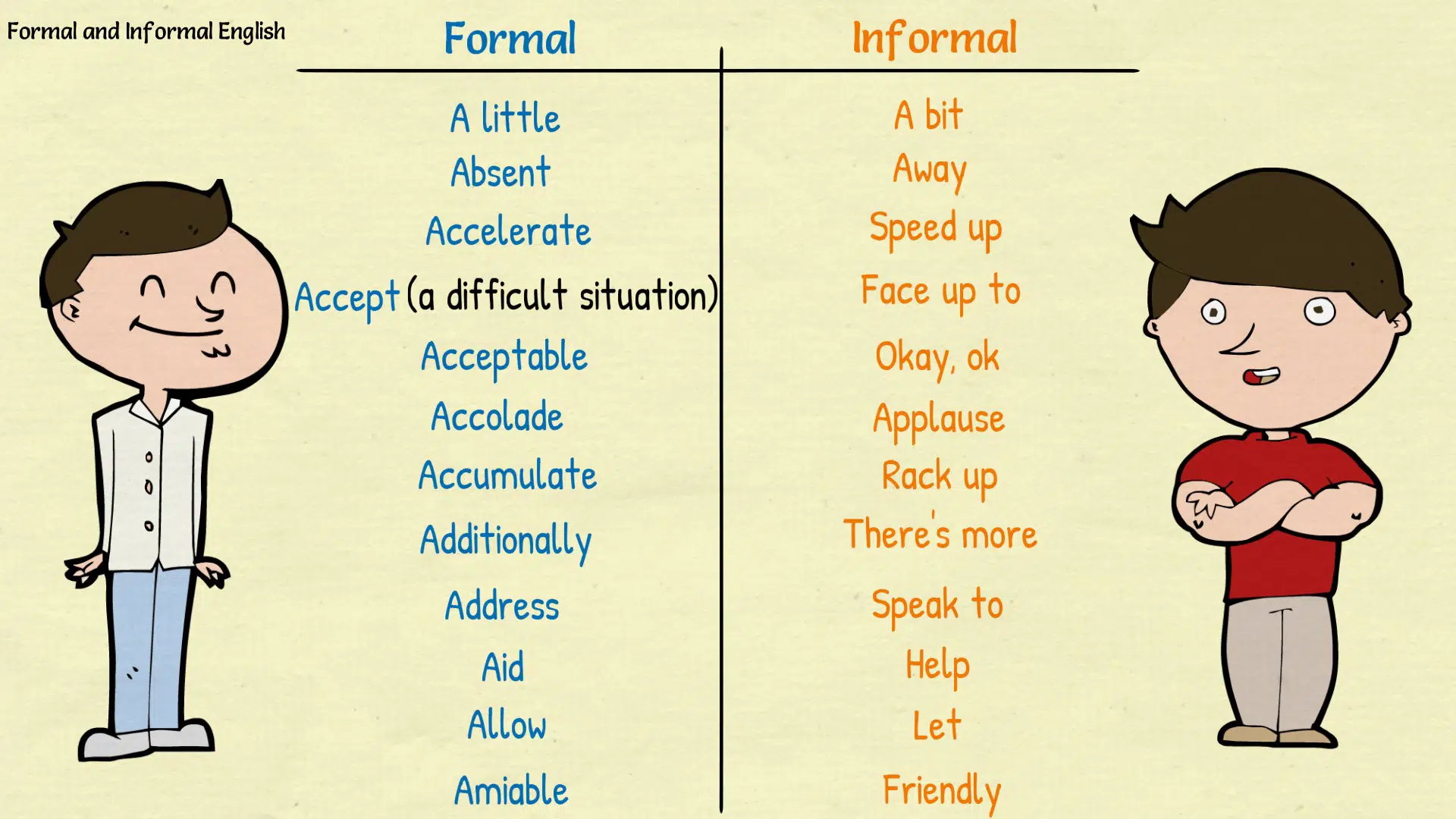
Formal and Informal English Words List
- Ask for – Request
- Come after – Follow
- Come up to – Reach/attain
- Deal with – Manage
- Go before – Precede
- Go out of – Exit
- Lead to – Cause
- Look at – Regard
- Look for – Seek
- Look into – Investigate
- Look like – Resemble
- Put up with – Tolerate
- Refer to – Consult
- Settle for – Choose
- Speak to – Address
- Talk about – Discuss/consider
- Think about – Consider/ponder
- Think of – Conceive
- Wait for – Await
- Really big – Considerable
- Lively – Energetic
- Whole – Entire/complete
- Exceptional – Marvelous
- Break down – fail/collapse
- Break off – Suspend/adjourn
- Break up – Disintegrate
- Bring in – Introduce
- Come back – Return
- Come/go in – Enter
- Get away – Escape
- Go ahead – Proceed
- Go away – Leave/depart
- Give/bring back – Return
- Give in – Yield
- Give out – Distribute
- Give up – Quit
- Link up – Connect
- Make out – Discern
- Make up – Invent
- Put/set down – Deposit
- Set out (1) – Display
- Set out (2) – Depart
- Take away – Remove
- Throw away – Discard
- Throw out – Eject
- Blow up – Explode
- Break down – Fail/collapse
- Hungry – Famished
- Tired – Fatigued
- Faithfulness – Fidelity
- Hopeless – Futile
- Go before – Precede
- Enjoyment – Gratification
- Thanks – Gratitude
- Funny – Humorous, amusing
- Childish – Immature
- Better – Improved
- Worse – Inferior
- Put in – Insert
- Make up – Invent
- Can – Is capable of
- Tons of, heaps of – Large quantities of, a number of
- Keep up – Maintain properly
- Could – Might be able to
- Plus/also – Moreover/futhermore
- Lots of/ a lot of – Much, many
- Anyways – Nevertheless
- A lot of – Numerous
- From (company) – On the behalf of
- Let – Permit
- Put off – Postpone
- Take out – Remove
- Mend – Repair
- Look like – Resemble
- House – Residence
- Keep – Retain
- Call on – Visit
- Try out – Test
- Drop out of – Withdraw (from)
- …
Example Sentences
Examples of Formal English Phrases
- Notice in cafe: Only food purchase (=bought) here may be eaten on the premises.
- Police statement: I apprehended (=caught) the accused outside the supermarket.
- Theatre announcement: They play will commence (=start) in the two minutes.
- Business meeting: The meeting will resume (=start again) this afternoon at 2 pm.
- Lawyers in court: My client had a broken ankle, thus (=so) he couldn’t drive the car.
- Business letter: I regret to inform you (I’m sorry to say) that we are unable to… (=can’t).
- Notice: If you require (=need) further assistance (more help) please contact…
- Airport announcement: Will passenger for Miami please proceed to (=go to) gate
Examples of Informal English Phrases
- I had to go and pick up (=collect) the kids (=children) from school.
- I reckon (=think) we’ll get (=receive/obtain) the money pretty (=quite) soon.
- I’m just going to the loo. (=toilet).
- Do you fancy going out? (= Would you like to go out?)
- I managed to fix up (=arrange/make) an appointment for 7.30.
- My flat is very handy for the shops. (near the shop and very convenient)
- I thought the book was terrific. (=marvelous)
- Most of the students are bright (=intelligent) but Paul is very thick. (=stupid)
- What’s up? (=what’s the matter?)
- We must get in touch with them (=contact them) very soon.
- When we get to (=reach/arrive) the hotel, I’ll have a word with (=speak to) them.
- I offered him ten quid (=pounds) but the gay (=man) wasn’t interested.
- A: Here’s the book I promised you. / B: Oh, cheers (=thank you. It can also mean good bye.)
Formal and Informal English – Images
Formal and Informal English Words | Infographic 1
Formal and Informal English Words | Infographic 2
It is extremely important to know when to use either formal or informal language. This will depend on the business you are working in, the industry you are in, the people you are speaking with, and the topic you are talking about. Learning the formal and informal way to speak is also a great way to master and learn the language.
Both formal and informal languages serve different individual purposes. The two styles vary depending on the tone you use, the words you choose to use, and the way you construct the words together. Using formal language is less personal than using informal language. Always remember that the type of language you decide to use in writing or speaking will solely depend on your purpose and the audience you are speaking to. Here are some tips you must remember to help you know when to use either formal or informal language.
Formal Language
As mentioned above, formal language is less personal than informal language. This is commonly used when writing or speaking for professional or academic purposes like emails for business, formal letters, academic write-ups, professional academic circumstances, presentations, reports, official and or legal documents, job interviews, and any scenario where formal language is appropriate. Since it is less personal, this can be used when you are communicating with a person you do not personally know well, like public speeches and tenders.
Note that very formal English in everyday situations may sound pompous at times, so always consider the context and the audience you are targeting. In situations that are more serious like job interviews or emailing your university professor, using formal language is highly encouraged. This can help you avoid sounding disrespectful and inappropriate and help you sound polite and professional instead. Remember that formal language has a more complex grammar where the sentences are generally phrased longer and use modal verbs. In pronunciation, speech is slower when using formal language and the tone should be serious.
Informal Language
Informal language is more casual and laid back. This is commonly used with people you know well as your family and friends. You usually use this when you are in a relaxed environment. When your agenda is to share your personal thoughts or you are telling a story, you should use language that is appropriate to the scenario. Informal language has a more conversational tone, frequently using personal pronouns, informal expressions, sentences are shorter, and the feelings are more personal.
This type of language is best suited to use when telling a story, personal narrations, and social forms like blogs and personal emails. This can also be used in advertising, spontaneous speeches, networking, or socializing with your clients, meetings with your teams, text messages, and everyday conversations with your family and friends you know well. Contractions are used in informal languages to ease the flow and make the speech faster. Abbreviations and acronyms are also used to shorten the words. Colloquial language is also used to allow the casual flow of conversation. You can even insert an emoji here and there when using informal language!
Examples of Differences between Formal and Informal Language
Here are some examples of formal and informal languages used below in terms of:
Contractions
Informal: It won’t turn on.
Formal: The device will not turn on.
Phrasal Verbs
Informal: I don’t want to drop out of school.
Formal: I have no intention of leaving the school.
Slang
Informal: Imma go hit him up.
Formal: I am going to contact him.
Collocations
Informal: My business is going bankrupt.
Formal: My business has now officially ceased to trade.
Acronyms
Informal: I will send the files asap.
Formal: I will send the files as soon as I can.
First-Person Pronouns
Informal: I think my study is very useful.
Formal: The researcher is certain that the research conducted serves a lot of purposes.
Formal language is commonly used when writing. Informal language is usually used when speaking. However, this is always not the case. Always refer to the situation you are in upon deciding when to use either formal or informal language. If you are ever uncertain about whether what type of language you should use in a conversation, especially when speaking to someone older than you are or in a work environment, pay close attention to how they talk to you and try to follow their lead. However, when you are emailing someone you do not know, it is best to use formal language to be respectful and polite to the person you are emailing to.
Formal vs. Informal Words/Phrases
Learn an extensive list of 400+ formal vs. informal words and phrases in English.
Ask >>——-<< Enquire
Ask for >>——-<< Request
Book >>——-<< Reserve
Check >>——-<< Verify
Get >>——-<< Receive
Help >>——-<< Assist
Need >>——-<< Request
Say sorry >>——-<< Apologise
Start/ Begin >>——-<< Commence
End >>——-<< Terminate/ Finish
Try >>——-<< Endeavour
Deal with >>——-<< Handle
Tell >>——-<< Inform
Wait for >>——-<< Await
Fight >>——-<< Combat
Use/Eat >>——-<< Consume
Go >>——-<< Depart
Tough >>——-<< Difficult
Small >>——-<< Diminutive
Explain >>——-<< Disclose
Set out >>——-<< Display
Throw out >>——-<< Eject
Old >>——-<< Elderly
Say >>——-<< Express
Afraid >>——-<< Fearful
In the end >>——-<< Finally
Lucky >>——-<< Fortunate
But >>——-<< However
Wrong >>——-<< Incorrect
Go up >>——-<< Increase
Cheap >>——-<< Inexpensive
At first >>——-<< Initially
Mad >>——-<< Insane
Formal Words vs. Informal Words in English | Image 1

Bright/smart >>——-<< Intelligent
Big/Large >>——-<< Enormous
Right >>——-<< Correct
A bit >>——-<< A little
Away >>——-<< Absent
Speed up >>——-<< Accelerate
Okay, ok >>——-<< Acceptable
Help >>——-<< Aid/ Assist
Let >>——-<< Allow
Call off >>——-<< Cancel
Friendly >>——-<< Amiable
Expect >>——-<< Anticipate
Seem >>——-<< Appear
Climb >>——-<< Ascend
Beat up >>——-<< Assault
Fall out >>——-<< Quarrel
Eager >>——-<< Avid
Stop >>——-<< Cease
Dare >>——-<< Challenge
Kids >>——-<< Children
Settle for >>——-<< Choose
Round >>——-<< Circular
Pick up >>——-<< Collect
Think of >>——-<< Conceive
Link up >>——-<< Connect
Think about >>——-<< Consider
Build >>——-<< Construct
Refer to >>——-<< Consult
Hurt >>——-<< Damage, harm
Go down >>——-<< Decrease
Want/ hope >>——-<< Desire
Lack >>——-<< Deficiency
Show >>——-<< Demonstrate
Brave >>——-<< Courageous
Pin down >>——-<< Determine
Put/ set down >>——-<< Deposit
Throw away >>——-<< Discard
Make out >>——-<< Discern
Talk about >>——-<< Discuss/consider
Give out >>——-<< Distribute
Give >>——-<< Donate
Remove >>——-<< Eliminate
Imagine >>——-<< Envisage
Break out >>——-<< Erupt
Get out >>——-<< Escape
Avoid >>——-<< Evade
Go through >>——-<< Examine
Make up >>——-<< Fabricate
Test >>——-<< Experiment
Ease >>——-<< Facilitate
Come after >>——-<< Follow
Sick >>——-<< Ill
Ask out >>——-<< Invite
Go away >>——-<< Leave/ depart
At once >>——-<< Immediately
Free >>——-<< Liberate
Deal with >>——-<< Manage
Bad >>——-<< Negative
Look into >>——-<< Investigate
Chance >>——-<< Opportunity
See >>——-<< Perceive
Happy >>——-<< Pleased
Give up >>——-<< Quit
Older >>——-<< Senior
Use >>——-<< Utilize
Enough >>——-<< Sufficient
End >>——-<< Terminate
Empty >>——-<< Vacant
Rich >>——-<< Wealthy
Mend >>——-<< Repair
Idea >>——-<< Notion
Mainly >>——-<< Principally
See >>——-<< Observe
Leave out >>——-<< Omit
Go against >>——-<< Oppose
Formal Words vs. Informal Words in English | Image 2

Hungry >>——-<< Famished
Childish >>——-<< Immature
Maybe >>——-<< Perhaps
Good >>——-<< Positive
Give >>——-<< Provide
Buy >>——-<< Purchase
Say no >>——-<< Reject
Free >>——-<< Release
Look for >>——-<< Seek
Choose >>——-<< Select
Get by >>——-<< Survive
So >>——-<< Therefore
Put up with >>——-<< Tolerate
Block >>——-<< Undermine
Catch up >>——-<< Understand
Sight >>——-<< Vision
Young >>——-<< Youthful
Get >>——-<< Obtain
Need >>——-<< Require
Pay back >>——-<< Repay
Live >>——-<< Reside
Point out >>——-<< Indicate
Find out >>——-<< Learn/Discover
Get away >>——-<< Elude
Come in >>——-<< Enter
Lively >>——-<< Energetic
Clear >>——-<< Transparent
Whole >>——-<< Entire/Complete
Blow up >>——-<< Explode
Break down >>——-<< Fail/Collapse
Hopeless >>——-<< Futile
Hit out at >>——-<< Criticise
Tired >>——-<< Exhausted/ Fatigued
Clothes >>——-<< Garment
Go before >>——-<< Precede
Thanks >>——-<< Gratitude
Hurry >>——-<< Haste, hasten
Funny >>——-<< Humorous, amusing
Better >>——-<< Improved
Dim >>——-<< Indistinct
Worse >>——-<< Inferior
Put in >>——-<< Insert
Bring in >>——-<< Introduce
Make up >>——-<< Invent
Kidding >>——-<< Jesting
Naked >>——-<< Nude
Childish >>——-<< Infantile
A lot of >>——-<< Numerous
Stubborn >>——-<< Obstinate
Danger >>——-<< Peril
Put off >>——-<< Postpone
Here >>——-<< Present
Keep >>——-<< Preserve
Go ahead >>——-<< Proceed
Go after >>——-<< Pursue
Anyways >>——-<< Nevertheless
Let >>——-<< Permit
Sweat >>——-<< Perspiration
Look at >>——-<< Regard
Laid back >>——-<< Relaxed
Take out >>——-<< Remove
Rack up >>——-<< Accumulate
Over >>——-<< At an end
Good looking >>——-<< Attractive
Good for >>——-<< Beneficial
By >>——-<< By means of
Lead to >>——-<< Cause
Complex >>——-<< Convoluted
Go out of >>——-<< Exit
Death >>——-<< Demise
Break off >>——-<< Suspend/adjourn
Also >>——-<< In addition, additionally
Wood >>——-<< Timber
Describe >>——-<< Depict
Go on >>——-<< Continue
In charge of >>——-<< Responsible
Enjoyment >>——-<< Gratification
Dirty/ polluted >>——-<< Contaminated
Again & again >>——-<< Repeatedly
Marvelous >>——-<< Exceptional
Really big >>——-<< Considerable
Can >>——-<< Is capable of
Fork out >>——-<< Pay (money)
Talk into >>——-<< Persuade
Come up to >>——-<< Reach/attain
Iron out >>——-<< Solve/overcome (a problem/difficulty)
Next/later >>——-<< Subsequently
Try out >>——-<< Test
Call on >>——-<< Visit
Drop out of >>——-<< Withdraw (from)
Look up to >>——-<< Respect
Look like >>——-<< Resemble
Job >>——-<< Occupation
Dad >>——-<< Father
Boss >>——-<< Employer
Formal and Informal Words | Images
Formal Words & Informal Words in English | Image 3

List of Formal Words & Informal Words in English | Image 4

Useful Formal Words & Informal Words in English | Image 5

Formal Words & Informal Words in English | Image 6

Formal vs. Informal Words Video
Last Updated on September 27, 2022
Learn the difference between formal and informal language and when to use them.

Studying from home?
Get everything you need to stay on top of uni this session — all in one spot!
Get uni sorted now
What is the difference between formal and informal language?
Formal and informal language serve different purposes. The tone, the choice of words and the way the words are put together vary between the two styles. Formal language is less personal than informal language. It is used when writing for professional or academic purposes like university assignments. Formal language does not use colloquialisms, contractions or first person pronouns such as ‘I’ or ‘We’.
Informal language is more casual and spontaneous. It is used when communicating with friends or family either in writing or in conversation. It is used when writing personal emails, text messages and in some business correspondence. The tone of informal language is more personal than formal language.
Examples of formal and informal language are shown below:
Contractions
Informal: The improvements canʼt be introduced due to funding restrictions.
Formal: Improvements cannot be introduced due to funding restrictions.
Informal: I donʼt believe that the results are accurate.
Formal: The results are not believed to be accurate.
Informal: The research project wonʼt continue next year.
Formal: The research project will not continue next year.
Phrasal verbs
Informal: The balloon was blown up for the experiment.
Formal: The balloon was inflated for the experiment.
Informal: The patient got over his illness.
Formal: The patient recovered from his illness.
Informal: The results of the study were mixed up.
Formal: The results of the study were confused.
Slang/Colloquialisms
Informal: The mob was very rowdy during the protest against cuts to university funding.
Formal: The crowd was very rowdy during the protest against the cuts to university funding.
Informal: Lecturers still count on students to use correct grammar and punctuation in essays.
Formal: Lecturers expect students to use correct grammar and punctuation in essays.
Informal: It was raining cats and dogs.
Formal: It was raining very heavily.
First person pronouns
Informal: I considered various research methods for the study.
Formal: Various research methods were considered for the study.
Informal: We believe the practice is unsustainable.
Formal: It is believed the practice is unsustainable.
Informal: During the interview, I asked students about their experiences.
Formal: During the interview, students were asked about their experiences.
Acronyms
TAFE Technical and Further Education
ANZAC Australian and New Zealand Army Corps
QANTAS Queensland and Northern Territory Aerial Services
Initialisms
UTS University of Technology Sydney
ISO International Standards Organisation
OECD Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development
The first time an acronym or initialism is used in an essay, it is acceptable to write the name in full with the acronym or initialism in brackets after it. Every subsequent time it is used the acronym or initialism can be used on its own. Commonly known acronyms such as ANZAC and QANTAS do not need to be written in full. If an acronym or initialism needs to be made into a plural, add a small ‘s’ to it without an apostrophe.
Do not use the acronyms ‘ATSI’ or ‘TSI’ to refer to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. This must be written in full. Always capitalise the word ‘Indigenous’ when referring to Australia’s Indigenous peoples.
Other academic style resouces
- UTS Publications Style Guide is available on Staff Connect (requires UTS staff login).
- RMIT’s Academic style
На чтение 8 мин Просмотров 3.4к. Опубликовано 2021-11-30
Чрезвычайно важно знать, когда следует использовать формальный или неформальный язык в общении с другими людьми. Возможно, вы общаетесь с кем-либо либо из клиентов, и вам нужно выбирать подходящие для этого выражения, уместные конструкции языка. Быть может, вы беседуете с близким другом и знакомым, и при этом используете множество разговорных выражений, слэнга, шуток и так далее. Изучение формального и неформального способа говорить является отличным способом овладеть иностранным языком. Определение того, когда использовать формальный язык (Formal English), а когда – неформальный (Informal English), является важной частью овладения языком.
Содержание
- Formal English
- Informal English
- Но в чем разница между Formal и Informal English?
- Особенности формального английского
- Особенности неформального стиля
- Таблица использования формального и неформального английского
- Таблица английских слов Formal и Informal с переводом
- Полезное видео по теме:
Formal English
В английском языке формальный язык используется в более серьезных ситуациях, например, когда вы проходите собеседование при приеме на работу или отправляете электронное письмо своему преподавателю. Его также можно использовать, когда вы разговариваете с кем-то, кого вы не очень хорошо знаете, и хотите убедиться, что вы говорите уважительно.
Такой язык обычно используется в профессиональных целях. К примеру, вы пишите электронные письма для бизнеса, делаете рецензии, презентации, отчеты, подготавливаете официальные и/или юридические документы. Или применяете формальный язык на собеседовании при приеме на работу. Formal English можно использовать, когда вы общаетесь с человеком, которого вы лично плохо знаете, например, в публичных выступлениях.
Обратите внимание, что очень формальный английский в повседневных ситуациях иногда может звучать напыщенно, поэтому всегда учитывайте контекст и аудиторию, на которую вы ориентируетесь. В более серьезных ситуациях, таких как собеседование при приеме на работу или переписка по электронной почте с профессором университета, настоятельно рекомендуется использовать формальный язык. Это может помочь вам избежать неуважительного и неуместного тона, и вместо этого звучать вежливо и профессионально. Помните, что формальный язык имеет более сложную грамматику, где предложения, как правило, длиннее. В таких предложениях часто используют модальные глаголы. При использовании формального языка речь становится более медленной. Тон выступающего должен быть серьезным.
Informal English
Неформальный язык используется в более непринужденных, повседневных ситуациях. Это беседы с друзьями, семьей и другими людьми, которых вы хорошо знаете. Однако, в отличие от многих других языков, большинство носителей английского языка предпочитают использовать неформальный язык с людьми, которых они только что встретили.
Этот тип языка лучше всего подходит при рассказе личной истории, ведения блога, отправления личных писем. Неформальный язык используется в рекламе, спонтанных выступлениях, общении в сети или разговоре с вашими клиентами, при встрече с вашими коллегами. Когда вы используете текстовые сообщения, смс, и ежедневно беседуете с вашей семьей и друзьями, которых вы хорошо знаете. Для ускорения речи и облегчения произнесения слов в неформальном языке могут использоваться сокращения. Разговорный язык используется для непринужденного разговора. Можно активно вставлять смайлики при использовании неформального языка! На самом деле, если вы начнете разговор с кем-то в поезде или поговорите с кем-то, работающим в магазине, им обычно покажется странным, если вы используете очень формальный язык! Очень часто при непродолжительном разговоре с незнакомым человеком мы можем быстро перейти от формального языка к неформальному.
Но в чем разница между Formal и Informal English?
В формальном английском языке используются более длинные предложения и сложная грамматика, более сложные языковые конструкции.
Например, если вы что-то описываете в формальном контексте, вы могли бы сказать что-то вроде:
«David, I am very grateful that you reviewed the terms of the contract and made the final decision. This will be a mutually beneficial cooperation for both parties».
[Перевод: Дэвид, я премного благодарен за то, что вы рассмотрели условия договора и приняли окончательное решение. Это станет взаимовыгодным сотрудничеством для обоих сторон].
С другой стороны, если бы вы рассказывали ту же историю другу, вы бы более спокойно относились к своей грамматике и упростили бы все высказывание. Вы можете использовать короткие предложения, повседневные фразы или сленг, а также множество других выражений. Например:
«Matt, thanks for inviting me to the party. I think we’ll have a blast».
[Перевод: Мэтт, спасибо за то, что пригласил меня на вечеринку. Думаю, мы отлично проведем время].
Мы гораздо чаще используем официальный английский, когда пишем, и гораздо чаще используем неофициальный английский, когда говорим, но это не всегда так.
Например, вы бы использовали более формальный язык, когда выступаете с академической презентацией или речью. И вы бы использовали неформальный язык, когда писали бы сообщение друзьям.
Если вы не уверены, следует ли вам использовать формальный или неформальный язык в разговоре, особенно когда вы разговариваете с кем-то старше вас или в рабочей ситуации, обратите внимание на то, как они говорят с вами, и попытайтесь сделать то же самое. Если вы отправляете кому-то электронное письмо или пишете кому-то и не уверены, рекомендуется использовать формальный язык. Это гарантирует, что вы всегда будете говорить вежливо и профессионально.
Можно привести простое сравнение с русским языком. Разговорную лексику используем при общении с друзьями – неформальный, книжная или публицистическая чаще всего применяется в деловых письмах, новостях, на собеседованиях – формальная.
Особенности формального английского
- Структурированность мыслей;
- Официальная речь всегда заготавливается заранее. Не содержит сложных длинных предложений, есть логичность и последовательность;
- Использование «высокой» лексики;
- В речи используется много синонимов, литературных тропов;
- Эрудированность
Общение на формальном английском требует большого словарного запаса. Для этого следует много читать как художественную, так и научную литературу. Избегайте фразовых глаголов, которые сложны для понимания большей части вашей аудитории. Лучше заменить на слова-синонимы. Так речь будет казаться простой, но в то же время серьёзной. Вместо длинных конструкций с вводными словами используйте сложные грамматические конструкции. Носители языка чаще всего используют страдательный залог, complex object или complex subject. Это даёт возможность понять собеседнику вашу грамотность и образованность.Старайтесь применять нейтральные формулировки без лишних прилагательных и литературных тропов. Используйте слова связки между предложениями (linking words). Так речь становится более логичной. Однако если сложно сразу употреблять, выучите несколько, как и в каких случаях используются. Потом постепенно добавляете. Через пару практик это уже никакого труда не будет составлять. Не начинайте предложения с союзов. But, as, well и другие. Это выдаёт просторечие и незнание разделения стилей. Лучше воспользоваться синонимами, словами связками. Пользуйтесь словарями. Если значение слова недостаточно ясное, следует зайти в словарь и посмотреть не только значение, но и стиль: формальный или неформальный.
Особенности неформального стиля
- Используется при общении с друзьями как в реальной жизни, так и в личных сообщениях;
- Присутствуют идиомы, сленги, смайлики;
- Эмоциональная речь;
- Часто использование междометий, жестов, ярко выражена мимика;
- В речи встречаются слова паразиты;
- Некоторые слова сокращаются или проглатываются окончания.
Прочитав эту статью, не нужно забывать, что это лишь маленькие советы. Применяя все и сразу, вы будете казаться нелепыми. Важно понимать что и как говорить. Если слишком усложнить предложение, то собеседник не поймёт и не уследит за вашими мыслями.
Каждый стиль преследует свои цели. Нет верного или неверного. В каждой ситуации перед тем как выбрать между двумя, следует оценить обстановку. Это дает возможность обойти стороной неприятные моменты.
Если, придя на собеседование в компанию, начнете использовать сленг, то скорее всего вам покажут дверь выхода. Для того чтобы не показаться грубым, понаблюдайте какую лексику используют окружающие вас люди
При получении приглашения на светское мероприятие следует заранее узнать тематику. Подготовить лексику, почитать журналы и научную литературу. Для ответа в электронном виде нельзя забывать о вежливом обращении. Использовать слова миссис и мистер, леди и т.д.
На вечеринке с друзьями или знакомыми, послушайте какие идиомы более часто используются, какие сленги, сокращения. Так быстрее можно влиться в компанию.
Однако не надо забывать, что при использовании формального или неформального стиля, надо оставаться настоящими. Фальшивость чувствуется в любом случае.
Таблица использования формального и неформального английского
| Формальный язык | Неформальный язык |
| Деловая переписка | Обычные письма |
| Когда вы общаетесь с человеком, с которым вы не знакомы | Когда вы общаетесь с друзьями или с близкими людьми |
| Конференция | Личная встреча |
| Научные журналы | Газеты, таблоиды |
| Научные работы/ статьи | Повседневный разговор |
| Обращение к старшим | Обращение к младшим |
| Официальные письма | Смс-сообщения |
| Презентации | Соцсети |
| Публичное общение (речь, лекции и т.д.) | Личное общение с клиентами |
Таблица английских слов Formal и Informal с переводом
| Informal | Formal | Перевод на русский |
| A bit | A little | Немного |
| Afraid | Fearful | Напуганный |
| Ask | Enquire | Спрашивать |
| Ask for | Request | Спрашивать |
| Ask out | Invite | Пригласить |
| At first | Initially | Сначала |
| At once | Immediately | Немедленно |
| Avoid | Evade | Избежать |
| Away | Absent | Далеко, вдали |
| Bad | Negative | Плохой, отрицательный |
| Beat up | Assault | Избивать, нападать |
| Big/Large | Enormous | Большой |
| Book | Reserve | Бронировать, резервировать |
| Brave | Courageous | Храбрый |
| Break out | Erupt | Прорываться |
| Bright/smart | Intelligent | Умный |
| Build | Construct | Строить |
| But | However | Но, тем не менее |
| Call off | Cancel | Отменить |
| Chance | Opportunity | Шанс, возможность |
| Cheap | Inexpensive | Дешевый |
| Check | Verify | Проверить, верифицировать |
| Climb | Ascend | Карабкаться |
| Come after | Follow | Следовать |
| Dare | Challenge | Отваживаться, осмеливаться |
| Deal with | Handle | Иметь дело (с кем-либо) |
| Deal with | Manage | Управиться |
| Eager | Avid | Желающий |
| Ease | Facilitate | Помогать, способствовать |
| Empty | Vacant | Пустой, свободный |
| End | Terminate | Закончить |
| End | Terminate | Заканчивать |
| Enough | Sufficient | Достаточно |
| Expect | Anticipate | Ожидать |
| Explain | Disclose | Объяснять |
| Fall out | Quarrel | Ссориться |
| Fight | Combat | Сражаться |
| Free | Liberate | Свободный |
| Friendly | Amiable | Дружелюбный |
| Get | Receive | Получать |
| Get out | Escape | Выбраться |
| Give | Donate | Дать, пожертвовать |
| Give out | Distribute | Распределить |
| Give up | Quit | Сдаваться |
| Go | Depart | Отправляться |
| Go away | Leave/ depart | Покинуть |
| Go down | Decrease | Уменьшать |
| Go through | Examine | Рассмотреть; проверить |
| Go up | Increase | Повышать |
| Happy | Pleased | Радостный |
| Help | Assist | Помогать, оказывать помощь |
| Help | Aid/ Assist | Помогать |
| Hurt | Damage, harm | Обидеть |
| Idea | Notion | Идея |
| Imagine | Envisage | Представить |
| In the end | Finally | В конце концов |
| Kids | Children | Дети |
| Lack | Deficiency | Отсутствие |
| Leave out | Omit | Опускать |
| Let | Allow | Позволять |
| Link up | Connect | Связывать |
| Look into | Investigate | Исследовать |
| Lucky | Fortunate | Счастливый |
| Mad | Insane | Бешеный |
| Mainly | Principally | Главным образом |
| Make out | Discern | Различить |
| Make up | Fabricate | Создавать, изобретать |
| Mend | Repair | Ремонтировать |
| Need | Request | Нуждаться |
| Okay, ok | Acceptable | В порядке |
| Old | Elderly | Старый |
| Older | Senior | Старший |
| Pick up | Collect | Собрать |
| Pin down | Determine | Определить |
| Put/ set down | Deposit | Хранить |
| Refer to | Consult | Обращаться к |
| Remove | Eliminate | Убрать, избавиться |
| Rich | Wealthy | Богатый |
| Right | Correct | Правильный |
| Round | Circular | Круглый |
| Say | Express | Говорить, выражать |
| Say sorry | Apologise | Извиниться |
| See | Perceive | Увидеть |
| See | Observe | Смотреть |
| Seem | Appear | Казаться |
| Set out | Display | Выделять, отмечать |
| Settle for | Choose | Выбрать |
| Show | Demonstrate | Показывать |
| Sick | Ill | Больной |
| Small | Diminutive | Маленький |
| Speed up | Accelerate | Ускорять |
| Start/ Begin | Commence | Начать, приступать |
| Stop | Cease | Останавливать |
| Talk about | Discuss/consider | Обсуждать |
| Tell | Inform | Сообщать |
| Test | Experiment | Протестировать |
| Think about | Consider | Думать о чем-либо |
| Think of | Conceive | Размышлять |
| Throw away | Discard | Выбрасывать |
| Throw out | Eject | Выбрасывать, извлекать |
| Tough | Difficult | Сложный, затруднительный |
| Try | Endeavour | Пытаться |
| Use | Utilize | Использовать |
| Use/Eat | Consume | Использовать |
| Wait for | Await | Ожидать |
| Want/ hope | Desire | Хотеть |
| Wrong | Incorrect | Неправильный |
Полезное видео по теме:

Formal English:
Formal Language is like a formal dress, in a formal language you have to be careful with words, you have to choose words with respect. We use it when writing essays for school, cover letters to apply for jobs, or emails and letters at work.
Informal English:
Informal Language is the language you speak in your friend’s circle. It is used in conversation with your family and friends, informal words are also respectful words, but they are less polite as compare to formal words.
Here are Formal and Informal words List in English
1. Verbs – Informal & Formal
| INFORMAL | FORMAL |
| a lot of | numerous |
| anyways | nevertheless |
| block | undermine |
| break down | fail/collapse |
| break up | disintegrate |
| bring in | introduce |
| can | is capable of |
| come back | return |
| come/go in | enter |
| deal with | handle |
| enjoyment | gratification |
| faithfulness | fidelity |
| find out | discover |
| from (company) | on the behalf of |
| get | obtain |
| get in touch with | contact |
| give in | yield |
| give the go-ahead | authorize |
| give/bring back | return |
| go against | oppose |
| go ahead | proceed |
| go away | leave/depart |
| go before | precede |
| go down | decrease |
| go out of | exit |
| go up | increase |
| hopeless | futile |
| house | residence |
| hungry | famished |
| it’s about | it concerns, it’s in regards to |
| keep | retain |
| keep up | maintain properly |
| lead to | cause |
| leave out | omit |
| let | permit |
| link up | connect |
| lively | energetic |
| look at | examine |
| look for | seek |
| look into | investigate |
| look like | resemble |
| lots of/ a lot of | much, many |
| make out | discern |
| makeup | fabricate |
| mend | repair |
| need to | required |
| plus/also | moreover/furthermore |
| point out | indicate |
| put in | insert |
| put off | postpone |
| put up | tolerate |
| put up with | tolerate |
| put/set down | deposit |
| rack up | accumulate |
| really big | considerable |
| refer to | consult |
| ring up | call |
| seem | appear |
| set out | display |
| set up | establish |
| settle for | choose |
| show | demonstrate, illustrate, portray |
| show up | arrive |
| speak to | address |
| stand for | represent |
| start | commence |
| take away | remove |
| take out | remove |
| talk about | discuss/consider |
| thanks | gratitude |
| think about | consider/ponder |
| think of | conceive |
| throw away | discard |
| throw out | eject |
| tired Formal and Informal words list in English Pdf | fatigued |
| tons of, heaps of | large quantities of, a number of |
| try out | test |
| wait for | await |
| whole | entire/complete |
| worse | inferior |
| say sorry | apologize, apologise |
2. Transitions – Informal & Formal
| Informal | Formal |
| Anyways | Nevertheless |
| Plus/Also | Moreover/ Furthermore |
| But | However |
| So | Therefore/Thus |
| Also | In addition, Additionally |
| ASAP | as soon as possible/at your earliest convenience |
| Okay, OK | acceptable |
| In the meantime | In the interim |
| I think | In my opinion, |
| In the end, | Finally |
| To sum up | In conclusion, |
| In a nutshell/Basically | To summarize, |
| Anyway, | Notwithstanding |
| All right | Acceptable |
| Well, | |
| To top it all off, | |
| On top of it all, | |
| In order to |
3. Emphasis Words – Informal & Formal
| Informal | Formal |
| lots of/ a lot of | much, many |
| tons of, heaps of | large quantities of, a number of |
| totally | completely, strongly |
| really, very | definitely |
4. Letter Expressions – Informal & Formal
| Informal | Formal |
| Hi Robert, | Dear Sir or Madam |
| Just wanted to let you know… | I am writing to inform you… |
| Love, | Yours sincerely, Yours faithfully, |
| Cheers, | |
| Yours Truly, Best regards, kind regards | |
| Hope to hear from you soon | I look forward to hearing from you |
| You can call me if you need anything | Please do not hesitate to contact me |
5. Abbreviations – Informal & Formal
| Informal | Formal |
| ASAP | as soon as possible |
| T.V. | television |
| photo | photograph |
| cell | cell phone |
| net | Internet |
6. Slang – Informal & Formal
| Informal | Formal |
| kids | children |
| bad | negative |
| good | positive |
| really big | considerable |
| right | correct |
| wrong | incorrect |
| smart | intelligent |
| cheap | inexpensive |
| loaded | rich |
Play Word coach Game: Click Here.
Download Word Coach Application
Read More:
Post Views: 71,880
This entry is about differences in vocabulary of formal and informal styles. For general differences, see this article.
Both formal and informal vocabulary can be found in all spheres of the language. As the language becomes more liberal, combining these two groups of words gets more common. Below is an example list of words and expressions in formal and informal registers.
What does ‘formal’ mean? Simply put, it means something or someone following established norms, traditions and habits. A formal letter should have certain structure and vocabulary, usually more official and strict. Think of formal as a rough synonym for ‘official’.
Vocabulary for letters
| Informal | Formal |
| To ask for help | To request assistance |
| To tell, to let know | To inform, to notify |
| Problem | Issue |
| Speak to | Address smb. |
| Talk about | Discuss, consider |
| Fix, take care of, put right | Rectify, amend |
| I think that … | I believe/hold it that … |
| I want to … | I wish to … |
| I’m ready to … | I am willing to … |
| I’m angry about … | I am dissatisfied with … |
| Deal with, take care of | Manage, resolve, settle |
| Put up with | Tolerate, bear, endure |
| Bring up | Mention |
| Take away | Remove |
| Thanks | I am grateful/thankful for … |
| I’m sorry about … | I regret about … |
| I’m writing about | I am writing regarding |
| I’ll get in touch … | I will contact … |
| If you have any questions | Should you have any questions |
General formal and informal vocabulary
| Informal | Formal |
| And | As well as … |
| But | Whereas/While |
| So, in this manner | Thus |
| If … | Should … /Whether … |
| If … or not | Whether … or not |
| For sure | Definitely/Assuredly/Certainly |
| Many | Numerous/Several |
| Get | Receive |
| Keep | Retain |
It is recommended to stick to either formal or informal words whenever possible. In other words, don’t mix two registers. It is as important as consistency in using English and American spelling. However, using two registers in your speech is not a serious error. At least as far as your speech is concerned. You should nevertheless pay attention to your writing — if you can use a less colloquial expression in your formal letter then you should do so. Sometimes mixing can’t be helped — for example, using phrasal verbs in a text. Phrasal verbs give life to your writing, so you shouldn’t abstain from using them. But such things as contracted forms or slang words — they do not belong in a formal text. Some dictionaries have detailed entries on formal and informal register.
Which register should I use?
The degree of formality is usually decided by the following factors:
- How well you know the person you’re writing to — the better you know the person, the less formal your writing will be (within reasonable limits)
- The purpose of your letter — business correspondence tends to be more formal
- The relative position of the person you’re writing to — a letter to your boss will be strictly formal. A letter to your subordinate is more likely to be semi-formal or fairly informal.
Use your judgement and common sense to decide on the register. For example, a letter to your boss who is much older than you, but whom you know very well is likely to be semi-formal, despite of his age and position. Conversely, if you are the head of department writing to a junior staff member whom you do not know, your letter should be on the formal side.
Conclusion
Bottom line is: if you are unsure whether to use formal or informal words, then stick to more respectable and tactful formal vocabulary. Nobody is going to hate you for being too formal. You will get a funny look or two if you overshoot with formality, but that is definitely not the end of the world!
On the other hand, opting for informal style and vocabulary in certain situations may be tactless and even rude. This in mind, use this simple rule:
When in doubt, keep it formal!
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies.
Difference between Formal VS Informal Language in Different Situations
Regardless of the language you speak, you have grown up knowing the importance of using formal language in the situations that best warrant it. Those situations being the ones that either circle around a serious subject or event, or involve people that we do not know well.
Informal language, on the other hand, is more commonly utilized in the situations or scenarios where we are more relaxed and will often involve people that we know on a more personal level.
The use of formal language is more prevalent when we write. Informal language is seen more when we speak. That being said, there are times when writing can be less formal. For example, if you were writing a postcard an email or a text message to a close friend, you aren’t likely to take care to use proper grammar and to write in complete sentences.
On the other hand, there are situations where the spoken word needs to be more formal, when delivering a speech or a lecture, for example. The majority of the time, the use of English is considered ‘neutral’ in the fact that is it neither formal nor informal.
Both formal and informal language is connected with specific grammatical and vocabulary choices.
Things like relative clauses void of a relative pronoun and ellipsis are much more prevalent in informal language.
Here is an example of formal language vs informal language.
Formal:
- They have been arguing all day
- She is very busy
- Many different outcomes were planned for the party
- It is felt that the objective is unreasonable
- The famous soccer team we saw at the bus station went to Toronto
- The receptionist who answered the phone was very rude
Informal
- They’ve been arguing all day
- She’s very busy
- I planned many different outcomes for the party
- We felt the objective was unreasonable
- The famous soccer team we saw at the bus station went to Toronto
- The receptionist who answered the phone was very rude
The appropriate use of Formal Vs. Informal Language
There is a time and a place for everything, and that same rule of thought can be applied to language. There are times when more formal language is required, but there are also times when it is appropriate to adopt a less formal approach.
What is the difference between formal and informal language?
Formal and informal language each serve a different purpose. The choice of words, the tone and the way that each word is strung together will vary depending on the situation and the level of formality. Formal language is, for all intents and purposes, far less personal than informal writing.
This is why it is the appropriate choice for use in professional or academic settings. Formal language does not make use of contractions, colloquialisms, or first person pronouns like “I” or “we.”
Informal language, on the other hand, is much more spontaneous and casual. This is the type of language used when communicating with friends or family members and can be used when either writing or speaking.
Informal language is used when writing a personal email, sending a text message and even in some business communications. (However, if you do not know your audience, always air on the side of caution and take a more formal approach.) The tone used in informal language is much more relaxed than it is in formal language.
Informal Writing
- Colloquial: Informal writing is similar to conversational English. It might include slang, figures of speech, etc. Informal writing has a more personal tone, similar to if you were to speak directly to your audience.
- Simple: Informal writing uses shorter sentence, and some of them might be incomplete.
- Contractions and Abbreviations: Informal writing consists of words that might be simplified or contracted.
- Empathy: Informal writing allows for the display of emotion or empathy
Formal Writing
- Complex: Formal writing uses longer sentences that are as through as possible. Each point is clearly introduced and concluded.
- Objective: Formal writing clearly states the primary point and offers supporting information. It avoids emotions or emotive punctuations like ellipses and exclamation points, unless being cited from another source.
- Full words: Formal writing requires full, complete sentences. No words should be simplified or contracted. Abbreviations are spelled out in full when first read.
- Third Person: Formal writing is not personal – meaning the writer is not connected to the topic and will not use a first or second person point of view.
When determining if it is best to deploy a formal or informal tone, try to mimic the language of those around you. If you are unsure, you should always teeter more on the formal side rather than risking coming across as unprofessional or uneducated. No one will fault you for speaking with confidence and professionalism, but, they will think twice if your conversations are filled with slang and regional dialect that no one but you understands.
What is Formal Language And Where You Need It?
In adulthood, we use formal language in settings where the subject matter is more serious or whenever the conversation includes people we do not know well.
Formal language is more commonly seen whenever we write.
By definition, formal language is defined as being ‘a language designed for use in situations where natural language (informal English language) is deemed to be unacceptable.
Learning when to best use formal language is all part of mastering the English language. In a business situation, it is always best to be more formal. Formal language uses longer and more complete sentences. Often, there are a few sub-clauses used to explain details and possibly even a few unnecessary words.
The school of thought typically suggests that we should be more formal when speaking to people we don’t know – but, this isn’t always the case.
Imagine how awkward or uncomfortable it might be if you were to meet a stranger on a bus or a train and the conversation started of extremely formal.
This is why it is important to clearly gauge your surroundings and use a level of formality that is equal to the situation.
A Few Formal Language Examples For Better Understanding
Outlined below are a few formal words and their informal equivalents. Notice how the formal words are often longer than the informal ones?
Formal:
- Cogitate
- Purchase
- Comestibles
- Penurious
- Abominate
- Emoluments
- Beverage
Informal:
- Think
- Buy
- Food
- Poor
- Hate
- Fee
- A Drink
You might be tempted to try to use more formal verbiage hoping that it might add more sophistication to what you are saying, or give you some sort of upper hand. You would be wise to try to avoid this urge, particularly if you don’t understand the meaning of a certain word.
Using overly formal language, in every day situations, has the potential to make your writing read like you are pompous or pretentious. Worse, if you use a word incorrectly, it might even make you sound like a fool who lacks credibility.
Consider the following examples:
The guests were stuck without comestibles and beverage for several hours.
OR
The guests were stuck without food and water for several hours.
The use of the more formal language in the first example is not only distracting, it also sounds odd and gets in the way of the intended meaning of the sentence. The use of less formal English, as seen in the second example, has a much better impact.
Remember, when in doubt, formal English is used in more serious situations or in professional text – like government documents, books, news reports, essays, articles, etc. Informal English is used in everyday conversations and in letters written to people you know on a personal level.
If you are writing something for school or work, like an academic report or a financial report, you should always use appropriately formal language.
If you are writing an email or text to a friend, or a Christmas letter to your grandmother, it is acceptable to use less formal language.