In Microsoft Excel, a column runs vertically in the grid layout of a worksheet. Vertical columns are numbered with alphabetic values such as A, B, C.Each column in the worksheet has its own column number which is used as part of a cell reference such as A1, A2, or M16.
Contents
- 1 What is column in Excel with example?
- 2 What does column () mean?
- 3 How do you use columns?
- 4 What is difference between column and columns in Excel?
- 5 Where are columns in Excel?
- 6 What is the column number in Excel?
- 7 What does column mean in writing?
- 8 What is column example?
- 9 How do I make columns in Excel?
- 10 What are columns in table?
- 11 What’s column and row?
- 12 How can you tell the difference between rows and Columns?
- 13 Whats a row and column?
- 14 How do you name a column in Excel?
- 15 How do I find a column number?
- 16 What does number of columns mean?
- 17 How do you add columns in sheets?
- 18 What is a column in a data table called?
What is column in Excel with example?
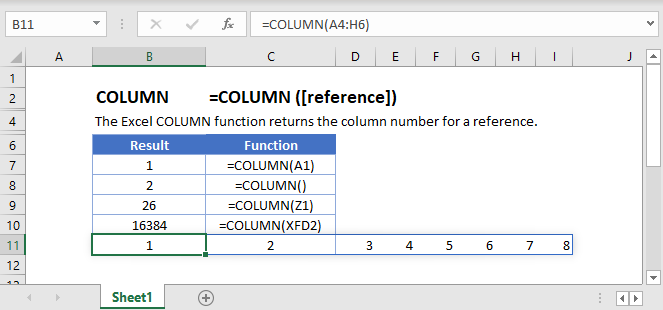
What is the COLUMN Function in Excel? The COLUMN function in Excel is a Lookup/Reference function. This function is useful for looking up and providing the column number of a given cell reference. For example, the formula =COLUMN(A10) returns 1, because column A is the first column.
The Microsoft Excel COLUMN function returns the column number of a cell reference. The COLUMN function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Lookup/Reference Function.
How do you use columns?
To add columns to a document:
- Select the text you want to format.
- Click the Page Layout tab.
- Click the Columns command. A drop-down menu will appear. Adding columns.
- Select the number of columns you want to insert. The text will then format into columns.
What is difference between column and columns in Excel?
Each row has a unique number that identifies it. A column is a vertical line of cells. Each column has a unique letter that identifies it.
Comparative Table.
| Basis | Excel Rows | Excel Columns |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Rows are ranging from 1 to 1,048,576 | Columns are ranging from A to XFD. |
Where are columns in Excel?
MS Excel is in tabular format consisting of rows and columns. Row runs horizontally while Column runs vertically. Each row is identified by row number, which runs vertically at the left side of the sheet. Each column is identified by column header, which runs horizontally at the top of the sheet.
What is the column number in Excel?
Excel Columns A-Z
| Column Letter | Column Number |
|---|---|
| A | 1 |
| B | 2 |
| C | 3 |
| D | 4 |
What does column mean in writing?
A column is a recurring piece or article in a newspaper, magazine or other publication, where a writer expresses their own opinion in few columns allotted to them by the newspaper organisation.
What is column example?
8. The definition of a column is a vertical arrangement of something, a regular article in a paper, magazine or website, or a structure that holds something up. An example of column is an Excel list of budget items. An example of column is a weekly recipe article.
How do I make columns in Excel?
To insert a single column: Right-click the whole column to the right of where you want to add the new column, and then select Insert Columns. To insert multiple columns: Select the same number of columns to the right of where you want to add new ones. Right-click the selection, and then select Insert Columns.
What are columns in table?
In a relational database, a column is a vertical group of cells within a table.In a table, each column is typically assigned a data type and other constraints which determine the type of value that can be stored in that column. For example, one column might email addresses, another might accept phone numbers.
What’s column and row?
A row is a series of data put out horizontally in a table or spreadsheet while a column is a vertical series of cells in a chart, table, or spreadsheet. Rows go across left to right. On the other hand, Columns are arranged from up to down.
How can you tell the difference between rows and Columns?
The row is an order in which people, objects or figures are placed alongside or in a straight line. A vertical division of facts, figures or any other details based on category, is called column. Rows go across, i.e. from left to right. On the contrary, Columns are arranged from up to down.
Whats a row and column?
Rows are a group of cells arranged horizontally to provide uniformity. Columns are a group of cells aligned vertically, and they run from top to bottom.
How do you name a column in Excel?
Single Sheet
- Click the letter of the column you want to rename to highlight the entire column.
- Click the “Name” box, located to the left of the formula bar, and press “Delete” to remove the current name.
- Enter a new name for the column and press “Enter.”
How do I find a column number?
Show column number
- Click File tab > Options.
- In the Excel Options dialog box, select Formulas and check R1C1 reference style.
- Click OK.
What does number of columns mean?
moreAn arrangement of figures, one above the other. This is a column of numbers: 12.
How do you add columns in sheets?
Step 1: Click anywhere in the column that’s next to where you want your new column. Step 2: Click Insert in the toolbar. Step 2: Select either Column left or Column right. Column left will insert a column to the left of the column you’re currently clicked into.
What is a column in a data table called?
A column can also be called an attribute. Each row would provide a data value for each column and would then be understood as a single structured data value.
Содержание
- What Are Columns In Excel?
- What are the rows and columns in Excel?
- What is column with example?
- What is row and column?
- What comes first row or column?
- What is row and?
- What are columns used for?
- What column means?
- How do I use columns in Excel?
- What is column in Table?
- Is a column across or down?
- What is Cell of MS Excel?
- What is the difference between row and column in a table?
- What is the matrix called?
- Why is Julia column-major?
- What is column article?
- How many column are there in Excel?
- How can you split a table?
- What are the 3 main parts of a column?
- Why are columns so strong?
- What is difference between column and columns in Excel?
- Row VS Column in Excel – What is the Difference?
- What is a row in Excel?
- What is a column in Excel?
- What is a cell in Excel?
- Conclusion
- How to find the column number in Excel?
- Method 1: Change column headers from general options
- Method 2: Use a formula to display the column number
- COLUMN Function Examples – Excel & Google Sheets
- COLUMN Function Overview
- COLUMN function Syntax and inputs:
- COLUMN Function – Single Cell
- COLUMN Function with no Reference
- COLUMN Function with a Range
- Excel 2019 or older
- Excel 365
- COLUMN Function in Google Sheets
- Additional Notes
What Are Columns In Excel?
In Microsoft Excel, a column runs vertically in the grid layout of a worksheet. Vertical columns are numbered with alphabetic values such as A, B, C. Horizontal rows are numbered with numeric values such 1, 2, 3.
What are the rows and columns in Excel?
Row and Column Basics
MS Excel is in tabular format consisting of rows and columns. Row runs horizontally while Column runs vertically. Each row is identified by row number, which runs vertically at the left side of the sheet. Each column is identified by column header, which runs horizontally at the top of the sheet.
What is column with example?
A column is a vertical series of cells in a chart, table, or spreadsheet. Below is an example of a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet with column headers (column letter) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. As you can see in the image, the last column H is the highlighted column in red and the selected cell D8 is in the D column.
What is row and column?
A row is a series of data put out horizontally in a table or spreadsheet while a column is a vertical series of cells in a chart, table, or spreadsheet. Rows go across left to right. On the other hand, Columns are arranged from up to down.
What comes first row or column?
By convention, rows are listed first; and columns, second. Thus, we would say that the dimension (or order) of the above matrix is 3 x 4, meaning that it has 3 rows and 4 columns. Numbers that appear in the rows and columns of a matrix are called elements of the matrix.
What is row and?
1 : a number of objects arranged in a usually straight line a row of bottles also : the line along which such objects are arranged planted the corn in parallel rows. 2a : way, street.
What are columns used for?
Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, “column” refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative features.
What column means?
Definition of column
1a : a vertical arrangement of items printed or written on a page columns of numbers. b : one of two or more vertical sections of a printed page separated by a rule or blank space The news article takes up three columns. c : an accumulation arranged vertically : stack columns of paint cans.
How do I use columns in Excel?
To insert columns:
- Select the column heading to the right of where you want the new column to appear. For example, if you want to insert a column between columns D and E, select column E.
- Click the Insert command on the Home tab. Clicking the Insert command.
- The new column will appear to the left of the selected column.
What is column in Table?
A column is collection of cells aligned vertically in a table. A field is an element in which one piece of information is stored, such as the eceived field. Usually, a column in a table contains the values of a single field.
Is a column across or down?
Columns run vertically, up and down.Rows, then, are the opposite of columns and run horizontally.
What is Cell of MS Excel?
Cells are the boxes you see in the grid of an Excel worksheet, like this one. Each cell is identified on a worksheet by its reference, the column letter and row number that intersect at the cell’s location. This cell is in column D and row 5, so it is cell D5. The column always comes first in a cell reference.
What is the difference between row and column in a table?
Rows are a group of cells arranged horizontally to provide uniformity. Columns are a group of cells aligned vertically, and they run from top to bottom.
What is the matrix called?
A matrix (whose plural is matrices) is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m×n m × n matrix or m -by-n matrix, where m and n are called the matrix dimensions.
Why is Julia column-major?
Probably because most numeric libraries were originally written in Fortran, which uses column-major storage, which then mimics the fact that vectors in math are by convention columns. Same applies to Matlab, which started as a convenient way to speak to some Fortran linear algebra packages.
What is column article?
A column is a recurring piece or article in a newspaper, magazine or other publication, where a writer expresses their own opinion in few columns allotted to them by the newspaper organisation. Columns are written by columnists.
How many column are there in Excel?
Worksheet and workbook specifications and limits
| Feature | Maximum limit |
|---|---|
| Open workbooks | Limited by available memory and system resources |
| Total number of rows and columns on a worksheet | 1,048,576 rows by 16,384 columns |
| Column width | 255 characters |
| Row height | 409 points |
How can you split a table?
Split a table
- Put your cursor on the row that you want as the first row of your second table. In the example table, it’s on the third row.
- On the LAYOUT tab, in the Merge group, click Split Table. The table splits into two tables.
What are the 3 main parts of a column?
Classical columns traditionally have three main parts:
- The base. Most columns (except the early Doric) rest on a round or square base, sometimes called a plinth.
- The shaft. The main part of the column, the shaft, may be smooth, fluted (grooved), or carved with designs.
- The capital.
Why are columns so strong?
Columns are vertical structural members designed to pass through a compressive load.Engineers have to design columns that are very strong under compression in order to keep buildings safe.
What is difference between column and columns in Excel?
Each row has a unique number that identifies it. A column is a vertical line of cells. Each column has a unique letter that identifies it.
Comparative Table.
Источник
Row VS Column in Excel – What is the Difference?
Microsoft Excel displays data in tabular format. This means that information is arranged in a table consisting of rows and columns.
Rows and columns are different properties that together make up a table.
These are the two most important features of Excel that allow users to store and manipulate their data.
Below we’ll discuss the definitions of a row and a column, along with the differences between these two features.
What is a row in Excel?
Each row is denoted and identified by a unique numeric value that you’ll see on the left hand side.
The row numbers are arranged vertically on the worksheet, ranging from 1-1,048,576 (you can have a total of 1,048,576 rows in Excel).
The rows themselves run horizontally on a worksheet.
Data is placed horizontally in the table, and goes across from left to right.
Row 1 is the first row in Excel.
As you can see in the example below, you can select the whole row with the number 3 by clicking on the number itself.
To navigate through the numbers and reach the last row, you can use:
- For Windows Users: Control down navigation arrow . You first press the Control key and then, while holding it down, press the down navigation arrow.
- For Mac Users: Command down navigation arrow . You first press the Command key and then, while holding it down, press the down navigation arrow.
To get back to the first row (the top) again, press Control up navigation arrow for Windows and Command up navigation arrow for Mac.
What is a column in Excel?
Columns are denoted and identified by a unique alphabetical header letter, which is located at the top of the worksheet.
Column headers range from A-XFD, as Excel spreadsheets can have 16,384 columns in total.
Columns run vertically in the worksheet, and the data goes from up to down.
Column A is the first column in Excel.
In the example below, you can see that the whole column with header B is selected by pressing/clicking on the letter at the top.
To move to the last column:
- For Windows Users: Control right navigation arrow . First press the Control key and then, while holding it down, press the right navigation arrow.
- For Mac Users: Command right navigation arrow . First press the Command key and then, while holding it down, press the right navigation arrow.
To get back to the first column again, press Control left navigation arrow for Windows and Command left navigation arrow for Mac.
What is a cell in Excel?
A cell is the intersection of a row and a column. A row and a column adjoined make up a cell.
You can define a cell by the combination of a row number and a column header.
For example, below the selected cell is C3. It has a column header C and a row number 3.
We can also select an entire row or column from a cell.
To select the whole row when in any cell, press Shift Space .
To select the whole column when in any cell, press Ctrl Space .
Conclusion
Now you know the definitions of rows and columns in Excel. You’ve learned their main differences and how they work.
In summary, information in a row is presented horizontally, whereas in a column information is vertical.
Источник
How to find the column number in Excel?
In Excel, column headers are represented by a letter A, B, C, . And when we reach column Z, the next column is AA.
And so on until you reach the final column; XFD. This means column number . 16384 😲😲😲
But how to find those numbers? There is two methods.
Method 1: Change column headers from general options
- Go to the File menu
- Then, you open the Options menu
- Then you go to the Formulas section.
- And there you check the option Reference Style R1C1
Reference R1C1 means that each cell is identified by numbers. And then, the columns headers are numbers

FYI, you should know that it was the only way to identify the cell references in the first Excel version. Fortunately, the letters for identifying columns were added later to make cell references easier to read 😉
This method isn’t the one I will recommend because not only the column headers have changed, but also the reference in your formulae.

As you can see, it’s not easy to understand such a formula and nearly impossible to visualize the absolute or relative reference
Method 2: Use a formula to display the column number
But the simplest technique is to use the COLUMN function 😀👍
And that’s it! This function returns the column number of the cell where is the formula. This function doesn’t need argument.
In this example, we know that our table contains 44 columns (46 — 2)

The ROW() function isn’t so helpful because it is enough to read the row number directly in the row headers.
Источник
COLUMN Function Examples – Excel & Google Sheets
Download the example workbook
This Tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel COLUMN Function in Excel to look up the column number.
COLUMN Function Overview
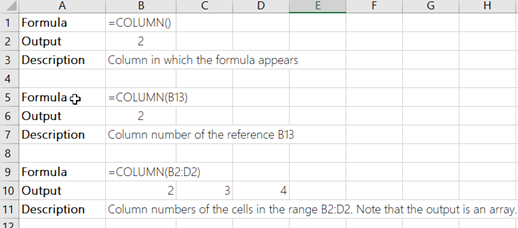
The COLUMN Function Returns the column number of a cell reference.
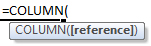
To use the COLUMN Excel Worksheet Function, select a cell and type:
(Notice how the formula inputs appear)
COLUMN function Syntax and inputs:
reference – Cell reference that you want to determine the column # of.
COLUMN Function – Single Cell
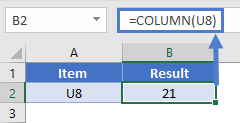
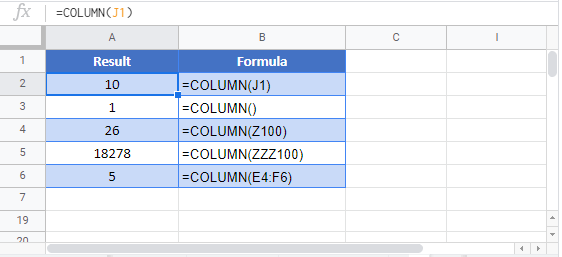
The COLUMN Function returns the column number of the given cell reference.
COLUMN Function with no Reference
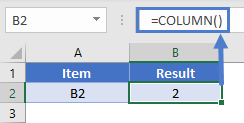
If no cell reference is provided, the COLUMN Function will return the column number where the formula is entered
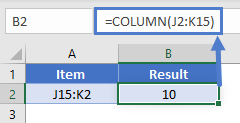
COLUMN Function with a Range
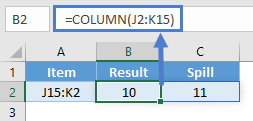
You can also input entire ranges of cells into the COLUMN Function. When doing so, the COLUMN Function behaves differently in Excel 2019 (or earlier) vs. Excel 365 or newer version of Excel.
Excel 2019 or older
In previous versions of Excel, the COLUMN Function returns an array containing the column values of all the cells in the range, but only displays the first result in the cell.
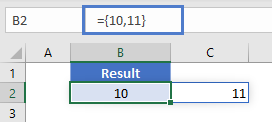
If you click the cell containing the formula and press F9, all the results are displayed in curly brackets as an array.
Excel 365
However, Excel 365 (and newer versions of Excel, presumably) comes with a spill range feature. Here, the COLUMN Function will return the columns of all cells in the range, “spilled” into the next cells.
COLUMN Function in Google Sheets
The COLUMN Function works exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel:
Additional Notes
Use the COLUMN Function to return the column number of a cell reference. What if you want the column letter of a cell reference? Use this complicated formula instead:
This formula calculates the column number with the COLUMN Function and calculates the address of a cell in row 1 of that column using the ADDRESS Function. Then it uses the SUBSTITUTE Function to remove the row number (1), so all that remains is the column letter.
Источник
How to Get a Column Number in Excel: Easy Tutorial (2023)
An Excel sheet is two-dimensional – it has rows and columns. By default, row headers in Excel are numbers, and column headers are alphabets.
As the data in your Excel sheet starts to grow in width, the number of columns grows. And this might make it difficult for you to track down a column by its number.
The article below explains different methods of how you can get column numbers in Excel. Also, it focuses on how column numbers might help you in your Excel jobs.
So stay tuned till the end! 😀
Practice the examples shown in the article below by downloading the sample workbook here.
How to get column number with the COLUMN function
If you have never before heard of the COLUMN function, it’s alright. Most Excel users have not.
The COLUMN function of Excel is designed to return the number of a column in Excel.
To find the column numbers for different columns in Excel, see the example below.

1. Write the COLUMN formula.
=COLUMN()
And this is it!
The COLUMN function has just one argument – the reference argument. Interestingly, this argument is also optional.
If omitted, Excel deems it equal to the Cell reference where the formula is written.

We had omitted the argument, so Excel set it equal to Cell B2. Column B comes second in the sequence, so Excel returned ‘2’ as the Column number.
Let’s see this the other way around.
2. Set the reference argument to AAX10.


This time Excel returns column number 726. This means Column AAX is the 726th Column of Excel.
How many columns are there in an Excel Sheet?
The last column of an Excel worksheet is Column XFD. So how many columns are there in a single worksheet?
Let’s do it quickly!
- Press Ctrl + the right arrow button ➡️ to fast forward to the last column of Excel.
- Write the Column formula.
=COLUMN()

16384 Excel Columns to each worksheet.
Let’s double-check the same from Google! 😆

Examples of uses for the COLUMN function
Why would anyone want to use the COLUMN function? The examples below tell why.
Example 1:
The image below shows the grades of a few students (to the left).

To the right side, we want to fetch out the grades for Henry. Easy solution = VLOOKUP.
1. Write the VLOOKUP function as follows.
= VLOOKUP (E1,

The lookup_value is referred to as Cell E1 because it contains the name of the student to look the result for.
2. Refer to the table array where the lookup and the return values are.
= VLOOKUP (E1, A1:B4,

3. For the col_index num argument, nest in the COLUMN function as follows:
= VLOOKUP (F1, A1:B4, COLUMN(B1))
The col_index num argument refers to the column from where the value is to be returned.
And this has to be the number of the column starting from the first column of the table_array.

We want the Grades of Henry to be returned. Grades are listed in column B, so we have referred to Cell B1 (any cell from Column B).

Instead of manually counting the columns, let the COLUMN function do the job.
The VLOOKUP function needs the column number starting from the table array. If the table array starts from any column other than the first column, the above function might not work.
For example, what if the table array above started from Column B and not A?

1. Write the VLOOKUP function as above, and it’d fail to function.
=VLOOKUP (G2, B1:C4, (COLUMN (C1))
It will take the col_index num argument as 3 (Column number of Column C).
Whereas, our table range has only two columns.

2. Deal with such a situation by changing the COLUMN function as follows.
= COLUMN(C1) – COLUMN(A1)
Subtract the number of the column before the table array (Column A) from the return value column (Column C).
3. Rewrite the VLOOKUP function as below.
= VLOOKUP (G1, B1:C4, COLUMN(C1) – COLUMN(A1))
Here are the results!

Example 2:
The COLUMN function is not only meant to find the number of a single column. You can also use it to find the number of multiple columns at once.
The data below shows the monthly utility bill of a household.

To find the accumulated utility bill for each month, let’s apply the COLUMN function.
1. Write the COLUMN function as follows.
=COLUMN(A2:F2)

The range A2:F2 tells the number of months for which we need the accumulated bill.

2. Multiply it with the particular cell of the monthly bill.
= H3 * COLUMN(A2:F2)
The cell reference is set to H3 as it contains the monthly bill.


It only takes a single click for Excel to compute the bills for all the months.
When the reference argument of the column function is defined as a range, the output is an array.
Caution! The SPILL Error:
If the cells of the array are not vacant before the array function operates, Excel gives the #SPILL! Error.

Show column number instead of letter
Only if Excel labeled both the rows and columns with numbers and not alphabets – things would have been much easier!
If you think like that, let’s do it for you.
To change the column letter to numbers in Excel, continue reading.
1. Go to File > Options
2. This opens up the Excel options dialog box.

3. Go to Formulas.
4. Under the tab, ‘Working with Formulas’, check the box R1C1 Reference Style.

And swish! Magic. The reference style of columns has changed. 😉

Your Excel worksheet looks all new with a new reference style! Both columns and rows are labeled by numbers.
The R1C1 style reference indicates the Row number and Column number. Accordingly, the cell references will automatically change.
For example, the traditional Cell reference C5 has now become R5C3 (Row number 5 and Column number 3).

This way, you can easily track down the number of columns.
That’s it – Now what?
By now, we have learned to find the column number in Excel through the COLUMN formula, to nest the COLUMN formula in VLOOKUP, and also to change the Column reference style in Excel.
But that’s all about basic Excel. To become an Excel pro you must master the VLOOKUP, SUMIF, and IF functions.
Where can you learn them? Click here to sign up for my free 30-minute email course that will help you master these functions (and more!).
Other relevant resources:
Finding the column number for a specific column or a group of columns can simplify your Excel jobs.
We suggest you also take a quick look into some shortcuts for adding, moving, splitting, clustering, and comparing columns. Once you have learned these shortcuts and tips, you’ll feel no less than an Excel whizz.
Kasper Langmann2023-01-19T12:23:31+00:00
Page load link
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
The COLUMN function returns the column number of the given cell reference. For example, the formula =COLUMN(D10) returns 4, because column D is the fourth column.
Syntax
COLUMN([reference])
The COLUMN function syntax has the following argument:
-
reference Optional. The cell or range of cells for which you want to return the column number.
-
If the reference argument is omitted or refers to a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the column numbers of reference as a horizontal array.
Notes:
-
If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
-
-
If the reference argument is a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is not entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the number of the leftmost column.
-
If the reference argument is omitted, it is assumed to be the reference of the cell in which the COLUMN function appears.
-
The reference argument cannot refer to multiple areas.
-
Example
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.