From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In linguistics, clipping, also called truncation or shortening,[1] is word formation by removing some segments of an existing word to create a synonym.[2] Clipping differs from abbreviation, which is based on a shortening of the written, rather than the spoken, form of an existing word or phrase. Clipping is also different from back-formation, which proceeds by (pseudo-)morpheme rather than segment, and where the new word may differ in sense and word class from its source.[3]
Creation[edit]
According to Hans Marchand, clippings are not coined as words belonging to the core lexicon of a language.[2] They originate as jargon or slang of an in-group, such as schools, army, police, and the medical profession. For example, exam(ination), math(ematics), and lab(oratory) originated in school slang; spec(ulation) and tick(et = credit) in stock-exchange slang; and vet(eran) and cap(tain) in army slang. Clipped forms can pass into common usage when they are widely useful, becoming part of standard English, which most speakers would agree has happened with math/maths, lab, exam, phone (from telephone), fridge (from refrigerator), and various others. When their usefulness is limited to narrower contexts, they remain outside the standard register. Many, such as mani and pedi for manicure and pedicure or mic/mike for microphone, occupy a middle ground in which their appropriate register is a subjective judgment, but succeeding decades tend to see them become more widely used.
Types[edit]
According to Irina Arnold [ru], clipping mainly consists of the following types:[4]
- Final clipping or apocope
- Initial clipping, apheresis, or procope
- Medial clipping or syncope
- Complex clipping, creating clipped compounds
Final and initial clipping may be combined and result in curtailed words with the middle part of the prototype retained, which usually includes the syllable with primary stress. Examples: fridge (refrigerator), Polly (Apollinaris), rona (coronavirus), shrink (head-shrinker), tec (detective); also flu (which omits the stressed syllable of influenza), jams (retaining the binary noun -s of pajamas/pyjamas) or jammies (adding diminutive -ie).
Final[edit]
In a final clipping, the most common type in English, the beginning of the prototype is retained. The unclipped original may be either a simple or a composite. Examples include ad and advert (advertisement), cable (cablegram), doc (doctor), exam (examination), fax (facsimile), gas (gasoline), gym (gymnastics, gymnasium), memo (memorandum), mutt (muttonhead), pub (public house), pop (popular music), and clit (clitoris).[5]: 109 An example of apocope in Israeli Hebrew is the word lehit, which derives from להתראות lehitraot, meaning «see you, goodbye».[5]: 155
Initial[edit]
Initial (or fore) clipping retains the final part of the word. Examples: bot (robot), chute (parachute), roach (cockroach), gator (alligator), phone (telephone), pike (turnpike), varsity (university), net (Internet).
Medial[edit]
Words with the middle part of the word left out are few. They may be further subdivided into two groups: (a) words with a final-clipped stem retaining the functional morpheme: maths (mathematics), specs (spectacles); (b) contractions due to a gradual process of elision under the influence of rhythm and context. Thus, fancy (fantasy), ma’am (madam), and fo’c’sle may be regarded as accelerated forms.
Complex[edit]
Clipped forms are also used in compounds. One part of the original compound most often remains intact. Examples are: cablegram (cable telegram), op art (optical art), org-man (organization man), linocut (linoleum cut). Sometimes both halves of a compound are clipped as in navicert (navigation certificate). In these cases it is difficult to know whether the resultant formation should be treated as a clipping or as a blend, for the border between the two types is not always clear. According to Bauer (1983),[6] the easiest way to draw the distinction is to say that those forms which retain compound stress are clipped compounds, whereas those that take simple word stress are not. By this criterion bodbiz, Chicom, Comsymp, Intelsat, midcult, pro—am, photo op, sci-fi, and sitcom are all compounds made of clippings.
See also[edit]
- Clipping (phonetics)
- Compound (linguistics)
- Contraction (grammar)
- Diminutive
- Portmanteau
- Word formation
References[edit]
- ^ «Shortenings». Oxford Dictionaries Online. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on May 10, 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ a b Marchand, Hans (1969). The Categories and Types of Present-Day English Word-formation. München: C.H.Beck’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung.
- ^ NAGANO, AKIKO (2007). «Marchand’s Analysis of Back-Formation Revisited» (PDF). Acta Linguistica Hungarica. 54 (1): 33–72. doi:10.1556/ALing.54.2007.1.2. ISSN 1216-8076. JSTOR 26190112.
- ^ Arnold, Irina (1986). The English word. Moscow: Высшая школа.
- ^ a b Zuckermann, Ghil’ad (2003), Language Contact and Lexical Enrichment in Israeli Hebrew. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9781403917232 / ISBN 9781403938695 [1]
- ^ Bauer, Laurie (1983). English Word-Formation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
In contradiction to the
eighteenth century British English purism, the American English of
the nineteenth century reveled in the process of clipping. Clipping
is a process of word formation which shortens a polysyllabic word by
deleting one or more syllables, thus retaining only a part of the
stem, e.g., lab
(laboratory), bra
(brassiиre), bus
(omnibus), car
(motorcar), and mob
(mobile vulgus). Clipping is synonymous to shortening, so these terms
will be used interchangeably.
Various classifications of
shortened words have been offered. The generally accepted one is that
based on the position of the clipped part. According to whether it
is the final, the initial, or the middle part of the word that is cut
off we distinguish initial clipping (aphaeresis),
and medial clipping (syncope),
final clipping (apocope).
-
Aphaeresis:
the loss of one or more
letters at the beginning of a word:
story
(history), cello
(violoncello), phone
(telephone). -
Syncope:
the loss of one or more
letters in the interior of a word:
specs
(spectacles), aphesis
(aphaeresis). -
Apocope:
the loss of one or more
letters at the end of a word:
ad (advertisement), ed
(editor), fab
(fabulous), prof
(professor), and gym
(gymnastics or gymnasium).
In some cases, speakers do not
even realize that a particular word is the product of clipping; for
example, the word zoo
was formed from
zoological garden.
4.9 Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronyms are formed by taking the
initial letters of some or all the words in a phrase or title and
pronouncing them as a word. This type of word formation is prevalent
in names of organizations, military, and scientific terminology.
Common examples are American
Psychological Association (APA),
Modern Language
Association (MLA),
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), United Nations
International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Antisocial
Behavior Order (ASBO), frequently asked questions (FAQ), Scholastic
Achievement (or Aptitude) Test(s) (SAT), Joint Photographic Experts
Group (JPEG), Designer Shoe Warehouse (DSW), Personal Identification
Number (PIN), Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), random access memory
(RAM), very important person (VIP), read only memory (ROM), and
others.
In numerous cases, speakers do
not realize that they are using an acronym. One example is radar
(radio detecting and
ranging), an acronym common throughout many languages. Other examples
of acronyms are scuba
(self-contained underwater breathing apparatus), and laser
(light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation). It is
widely assumed that the use of text shorthand known as acronyms was
started as a result of the use of Morse Code to send and receive
messages in the 19th century. Because telegraph companies charged
the sender by the word, acronyms were invented to save the sender
costs and to quicken the time and effort of the sending agent.
Telegraph companies would not only charge by the word but would
charge additional fees for numerals and words that could not be
easily pronounced. So, acronyms which had no vowels were given
vowels so as to make them pronounceable. A good example of this is
the apparatus used for Radio Ranging and Detection. To send this
collection of words, a sender would be charged for four separate
words. Sending RRD would be only one word but charged an extra fee
because it was not pronounceable. Sending radar gets the sender
charged for only one pronounceable word. Modern society uses
acronyms for many of the same reasons as the telegraph companies,
e.g. ease of typing and speed of communication, be it on the modern
day computer keyboard or the ubiquitous cell phone. Technically there
is a difference between acronyms and abbreviations. This difference
becomes vague in many instances and makes it sometimes difficult to
assign either word to the usage. While N.A.T.O. would be an
abbreviation, it is also an acronym as in NATO. Some scholars
distinguish between acronyms and initialisms; however, we do not
recognize a sharp distinction between acronyms and initialisms,
preferring the former as an inclusive label.
Abbreviation is defined as “a
reduced version of a word, phrase, or sentence”. Abbreviations are
societal slangs. Abbreviations come and go in waves. The reason for
abbreviations is linguistic economy; communicators value succinct
language, and abbreviations contribute to concise style.
Technological constraints contribute to the use of abbreviations.
Abbreviations also help to convey “a sense of social identity; to
use an abbreviated form is to be ‘in the know’—a part of the
social group to which the abbreviation belongs” (Crystal, 2005,
p.120). Those who are computer savvy will be recognized by their
extensive use of abbreviations such as WYSIWYG (What you see is what
you get), and others.
Now abbreviations
are part netspeak and textspeak, which is a rapidly emerging jargon,
used among Internet users. David Crystal compiled a glossary of
netspeak and textspeak, and some examples illustrated here are
borrowed from the Glossary:
bps (bits per second), four-oh-four [404] (a term identifying an
error message shown on screen when a browser makes a faulty request
to a server), and others (Crystal, 2004). There are a lot of
abbreviations used by “species of spoken shorthand” (as cited in
Crystal, 2004, p.120): OK (all correct), PDQ (pretty damn quick), GTT
(gone to Texas), BTW (by the way), ETA (estimated time of arrival),
FYI (for your information), POS (parent over shoulder), ROFL (rolling
on the floor laughing), RSVP (Rйpondez s’il vous plait), BRB (Be
right back), TTYL (Talk to you later), and others.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Three types of clipped words with 60+ examples
What are Clipped Words?
In English language, clipping is the process of forming new
words by dropping one or more syllables from a larger word, thereby
resulting in a shorter word. Clipped Words are the words that are
formed by clipping one or more syllables from a larger word or phrase, while
retaining the meaning of the original word or phrase.
Being shorter, clipped words are easy to spell and pronounce. Clipped words
are more commonly used in everyday language. It is interesting to note, in
some cases, the clipped form of a word is more popular (and more frequently
used) than the original word itself.
Clipping is also known as shortening or truncation. Clipping
refers to part of a word that provides for the whole, such as the word
«bike» from «motorbike», and «cooker» from «pressure cooker».
There are three types of clipped words:
-
Front clipped words: Such words are formed by clipping front part
of a larger word or phrase. In front clipping, the end of the word is
retained. -
Back clipped words: Such words are formed by clipping back part
of a larger word or phrase. In back clipping, the beginning of the word
is retained. -
Middle clipped words: Such words are formed by clipping both
front and back parts of a larger word or phrase. In middle clipping, the
middle of the word is retained.
The image below shows the three types of clipped words with one example of
each type:

Before we take look at some of the examples of Clipped Words, I should note
that sometimes two words are joined together or blended to form a new word.
This process of
blending words
together results in the formation of completely new words called «blend words«. We encourage you to read more about blend words in our article decicated
to the topic.
Front clipping
| Clipped Word | Original word |
|---|---|
| phone | telephone |
| bike | motorbike |
| burger | hamburger |
| cooker | pressure cooker |
| pen | fountain pen |
| plane | aeroplane |
| bus | omnibus |
| tie | neck-tie |
| van | caravan |
| pike | turnpike |
| mum | chrysanthemum |
Back clipping
The image below shows a few common examples of back-clipped words:

| Clipped Word | Original word |
|---|---|
| gym | gymnasium |
| cable | cablegram |
| pub | public house |
| exam | examination |
| specs | spectacles |
| veg | vegetarian |
| memo | memorandum |
| gas | gasoline |
| photo | photograph |
| cafe | cafeteria |
| lab | laboratory |
| ad | advertisement |
| lunch | luncheon |
| fan | fanatic |
| cab | cabriolet |
| zoo | zoological garden |
| sitcom | situation comedy |
| piano | pianoforte |
| pants | pantaloons |
| movie | moving picture |
| ag | agriculture |
| alum | alumna |
| bio | biology |
| auto | auto-mobile |
| disco | discotheque |
| chimp | chimpanzee |
| dad | daddy |
| fab | fabulous |
| mom | mommy |
| prep | preparatory |
| quad | quadrangle |
| frank | frankfurter |
| pug | pugnacious |
| math | mathematics |
| grad | graduate |
| limo | limousine |
| dorm | dormitory |
| sub | submarine |
| taxi | taxicab |
| teen | teenager |
| tux | tuxedo |
| typo | typographical error |
| co-op | cooperative |
| rhino | rhinoceros |
| stereo | stereophonics |
| stats | statistics |
| rev | revolution |
| cuke | cucumber |
| con | convict |
| store | storehouse |
| ref | referee |
| non-veg | non-vegetarian |
| vet | veterinary surgeon |
| sis | sister |
| vibes | vibrations |
| ID | identification |
Middle clipping
| Clipped Word | Original word |
|---|---|
| fridge | refrigerator |
| flu | influenza |
| script (for medicine) | Prescription |
Note: Clipped words are different from abbreviations and
contractions. Although, an abbreviation is also a shortened
form of a word or phrase, they often end with a period (.), such as Lib. for Library.
Abbreviations are clearly understood to be substitutes for the full term. On
the other hand, a contraction is a word or phrase that has been
shortened by dropping one or more letters. When writing a contraction, an
apostrophe (‘) replaces the missing
letters, such as let‘s go for
let us go.
Please also take a look at some of our trending online practice tests:
- Practice subject-verb agreement
- Transitive and Intransitive verbs
- Identifying Gerunds and participles
- practice test on blend words
- A Level Organic Chemistry introduction
- A Level Organic Chemistry Halogenoalkanes
Thanks for reading this article. We sincerely hope you enjoyed it.
If you noticed any mistake, or have suggestions for us, please let us know
in the comments below. Thanks again.
Copyright © 2016-2021, www.notesflux.com
See Also:
English Grammar:
- 10 useful IELTS preparation tips
- 6 useful online resources for IELTS preparation:
- Gerunds, participles and infinitives
- What are simile and metaphor?
- Clauses and their types
- Finite and non-finite verbs
- what are imperative sentences?
- Transitive and intransitive verbs
- Direct and indirect objects
Physics:
- Changes in Energy Stores
- Work, Power and Efficiency
- Electric Current and Circuits
- Static Electricity
Biology:
- Cell Structure
- Cell Division
- Transport in Cells
- Bacteria, Viruses, Pathogens and Communicable Diseases
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Plant-disease
Language changes and evolves both subtly and quite obviously; one of the more obvious ways is through clipping, where shorter words are cut out of longer words.
Believe me, you don’t become a language translation professional by chance. While some students and young adults might drift into a field through inertia or because of a family legacy – or simply having no idea what to do with their lives and needing a job – those of us in translation services are here because of one primary reason: We have a love for language. From a young age we were fascinated by the way people could communicate just by making different noises with their mouths and throats, and how the same noises, arranged in different ways, formed wholly different languages.
That also means we’re all familiar with the basic ideas of language studies, whether we’re experts in the field or just interested amateurs who use our off-hours to read about language and how it’s formed. This means we’re all either the best person to wind up sitting next to at a dinner party, or the worst, depending on your own interests. Recently, for example, I’ve been reading about the fascinating process of Clipping in language evolution.
The Clipped Word
What is “clipping”? It’s actually something you’re likely very familiar with. It’s the simple process of forming a new word by clipping off part of an existing word. An easy example is the word exam, which of course comes from the longer word examination. The letters “ination” have simply been clipped off, forming a new word that shares the definition and context of the older word.
Clipping is, of course, a reductive process that shortens words and thus shortens the effort involved in speech and writing, albeit by a tiny increment. However, you can imagine how this process can slowly reduce the time spent expressing thoughts, paring language down to shorter and shorter words. Anyone who has read Shakespeare might see how language has sped up and become much faster and more clipped over the centuries.
Clipping also reduces formality. Examination is a word that would be used by a teacher or in official language on a school’s policy page, while exam is the word all the students would use.
Types of Clipping
- Clipping comes in four basic varieties:
- Back Clipping: As we’ve seen in exam and examination, back clipping is when the back half of a word is deleted. Another example is memo, the back-clipped form of memorandum.
- Fore Clipping: The process can be reversed, deleting the beginning of a word, as in varsity, which is a fore-clipped (and slightly mutated) version of university.
- Mid Clipping: More rare is when the beginning and end of a word is clipped to form a new word. A good example is flu, clipped out of influenza.
- Compound Clipping: Much rarer, this involves clipping more than one word to form a new word. The best example I can think of is cablegram, taken from the phrase cable telegram.
If you found this fascinating, you might have a future as a translator!
Learn more about our professional document translation services.

Liraz Postan
Liraz is an International SEO and Content Expert with over 13 years of experience.
What our customers are saying
Table of Contents
- What are the word formation processes and examples?
- Is an example of clipping word formation?
- What are the examples of clipping words?
- What is clipping and example?
- How many types of clipping are there?
- How many methods of clipping are there?
- Which is the clipping algorithm?
- What are the steps of line clipping?
- What is a clipping area?
- What is the aim of line clipping algorithms?
- Can we use line clipping algorithm for polygon clipping?
- What is difference between line clipping and polygon clipping?
- Why clipping is used in graphics?
- What clipping means?
- Why does clipping occur in games?
- Is clipping a glitch?
- What does clipping look like?
- Can clipping damage amp?
- Why is my amplifier clipping?
In morphology, clipping is the process of forming a new word by dropping one or more syllables from a polysyllabic word, such as cellphone from cellular phone. In other words, clipping refers to part of a word that serves for the whole, such as ad and phone from advertisement and telephone, respectively.
What are the word formation processes and examples?
Types of Word Formation Processes
- Compounding.
- Rhyming compounds (subtype of compounds)
- Derivation Derivation is the creation of words by modification of a root without the addition of other roots.
- Affixation (Subtype of Derivation)
- Blending.
- Clipping.
- Acronyms.
- Reanalysis.
Is an example of clipping word formation?
Initial (or fore) clipping retains the final part of the word. Examples: bot (robot), chute (parachute), roach (cockroach), gator (alligator), phone (telephone), pike (turnpike), varsity (university), net (Internet).
What are the examples of clipping words?
Clipped Words
| ad – advertisement | memo – memorandum |
|---|---|
| flu – influenza | stats – statistics |
| fridge – refrigerator | stereo – stereophonics |
| gas – gasoline | sub – submarine |
| grad – graduate | taxi – taxicab |
What is clipping and example?
Clipping is one of the ways new words are created in English. It involves the shortening of a longer word, often reducing it to one syllable. Maths, which is a clipped form of mathematics, is an example of this. Informal examples include ‘bro’ from brother and ‘dis’ from disrespect.
How many types of clipping are there?
four types
How many methods of clipping are there?
1) All or none string clipping 2) All or none character clipping 3) Text clipping.
Which is the clipping algorithm?
There are two common algorithms for line clipping: Cohen–Sutherland and Liang–Barsky. A line-clipping method consists of various parts. Tests are conducted on a given line segment to find out whether it lies outside the view volume.
What are the steps of line clipping?
Algorithm
- Step 1 − Assign a region code for each endpoints.
- Step 2 − If both endpoints have a region code 0000 then accept this line.
- Step 3 − Else, perform the logical ANDoperation for both region codes.
- Step 3.1 − If the result is not 0000, then reject the line.
- Step 3.2 − Else you need clipping.
- Step 3.2.
- Step 3.2.
What is a clipping area?
A clipping region is one of the graphic objects that an application can select into a device context (DC). It is typically rectangular. Some device contexts provide a predefined or default clipping region while others do not.
What is the aim of line clipping algorithms?
It enables the detection of all the cases where the line segment is completely inside the given rectangle and cases where the line segment has both end points outside a particular clipping boundary very quickly.
Can we use line clipping algorithm for polygon clipping?
Line clipping against a polygon is widely used in computer graphics such as the hidden line problem. A new line-clipping algorithm against a general polygon is presented in this paper. Each edge of the polygon is processed against a horizontal line, which makes the clipping process simpler.
What is difference between line clipping and polygon clipping?
the polygon clipper clips against 4 edges in succession, whereas the line clipper tests the outcode to see which edge is Crossed, and clips only when necessary.
Why clipping is used in graphics?
Clipping, in the context of computer graphics, is a method to selectively enable or disable rendering operations within a defined region of interest. A well-chosen clip allows the renderer to save time and energy by skipping calculations related to pixels that the user cannot see.
What clipping means?
: something that is clipped off or out of something else grass clippings especially : an item clipped from a publication.
Why does clipping occur in games?
Clipping , in computer graphics, correctly refers to a graphic element, such as a polygon, being chopped against the view frustum or some other graphic element, to reduce the visible area of the element. Clipping is an old and well known technique for speeding up graphics rendering.
Is clipping a glitch?
Clipping. A clipping glitch occurs when a player or an object within a game environment passed through a texture or level geometry. Clipping is often used to gain access to previously inaccessible parts of a level.
What does clipping look like?
It’s called clipping because that’s what the clipping waveform ends up looking like. A smooth, rounded sine wave has its peaks and troughs ‘clipped off,’ resulting in the flat plateau of a square wave.
Can clipping damage amp?
Facts about clipping: Any clipped signal can potentially damage a speaker. It does not matter whether the mixer, amplifier, or any other piece of audio equipment clips the signal in the system. Damage can occur even when the amplifier is not at full output.
Why is my amplifier clipping?
Generally speaking, the amplifier gain is not properly set or the volume is too high. The most common, and avoidable, form of amplifier clipping occurs when an audio amplifier is driven beyond its ability to generate sufficient voltage or current to reproduce the original signal to your speakers.
In morphology, clipping is the process of forming a new word by dropping one or more syllables from a polysyllabic word, such as cellphone from cellular phone. In other words, clipping refers to part of a word that serves for the whole, such as ad and phone from advertisement and telephone, respectively. The term is also known as a clipped form, clipped word, shortening, and truncation.
A clipped form generally has the same denotative meaning as the word it comes from, but it’s regarded as more colloquial and informal. Clipping also makes it easier to spell and write many words. For example, a clipped form may replace the original word in everyday usage—such as the use of piano in place of pianoforte.
Examples and Observations
According to the book, «Contemporary Linguistics: An Introduction,» Some of the most common products of clipping are names—Liz, Ron, Rob, and Sue, which are shortened forms of Elizabeth, Ronald, Robert, and Susan. The authors note that clipping is especially popular in the speech of students, where it has yielded forms like prof for professor, phys-ed for physical education, and poli-sci for political science.
However, many clipped forms have also been accepted in general usage: doc, ad, auto, lab, sub, porn, demo, and condo. The authors add:
«A more recent example of this sort that has become part of general English vocabulary is fax, from facsimile (meaning ‘exact copy or reproduction’).»
Other examples of clipped forms in English include biz, caps, celebs, deli, exam, flu, gator, hippo, hood, info, intro, lab, limo, mayo, max, perm, photo, ref, reps, rhino, sax, stats, temp, thru, tux, ump, veep, and vet.
Clipping Basics
«As noted, clipped words form through a social process, such as students preferring to use shortened forms of common terms, as noted in ‘Contemporary Linguistics.’ The same kind of social forces lead to the creation of clipped words in other English-speaking countries such as Britain,» says David Crystal, a leading authority on language.
«There are also several clippings which retain material from more than one part of the word, such as maths (UK), gents, and specs….Several clipped forms also show adaptation, such as fries (from french fried potatoes), Betty (from Elizabeth), and Bill (from William).»
Clipped words are not abbreviations, contractions, or diminutives. True, an abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. But abbreviations often end with a period, such as Jan. for January, and are clearly understood to be stand-ins for the full term. A contraction is a word or phrase—such as that’s, a form of that has—that has been shortened by dropping one or more letters. In writing, an apostrophe takes the place of the missing letters. A diminutive is a word form or suffix that indicates smallness, such as doggie for dog and Tommie for Thomas.
Types of Clipping
There are several types of clipping, including final, initial, and complex.
Final clipping, also called apocope, is just what the term implies: clipping or cutting off the last syllable or syllables of a word to form the clipped term, such as info for information and gas for gasoline. Initial clipping, also called apheresis, is the clipping of the initial part of the beginning of the word, also called fore-clipping, according to the Journal of English Lexicology. Examples of fore-clipping include bot for robot and chute for parachute.
«Complex clipping, as the name implies, is more involved. It is the shortening of a compound word by preserving and combining its initial parts (or first syllables),» says ESL.ph, an online site for learning English as a second language. Examples include:
- Sci-fi for science fiction
- Sitcom for situation comedy
- Grandma for grandmother
- Perm for permanent wave
- Shrink for head shrinker
As you see, clipped words are not always respectful terms. Indeed, some great literary figures vigorously opposed them, such as Jonathan Swift, who made his feelings clear in the tellingly named «A Proposal for Correcting, Improving and Ascertaining the English Tongue,» first published in 1712. He saw clipping as a symptom of «barbaric» social forces that had to be tamped down:
«This perpetual Disposition to shorten our Words, by retrenching the Vowels, is nothing else but a tendency to lapse into the Barbarity of those Northern Nations from whom we are descended, and whose Languages labour all under the same Defect.»
So, the next time you hear or use a clipped word, do so knowing that it is considered acceptable in English, but remember that these shortened terms have a long and somewhat controversial history.
Sources
O’Grady, William, John Archibald, Mark Aronoff, et al. Contemporary Linguistics: An Introduction. 4th ed, Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2000.
Crystal, David. The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language. 3rd ed, Cambridge University Press, 2019.
Jamet, Denis. «A morphophonological approach to clipping in English.» Lexis Journal of English Lexicology, HS 1, 2009.
Swift, Jonathan. A Proposal for Correcting, Improving, and Ascertaining the English Tongue: In a Letter to the Most Honorable Robert Earl of Oxford and Mortimer, Lord High Treasurer of Great Britain (1712). H. Kessinger Publishing, 2010.
Clipping/clipped words (or morphology if you prefer the linguistic term) is a way of creating new words in English by shortening the original word. It’s very trendy to clip words these days, with our fast-paced lives, we need to be able to speak faster, right? I’ll tell you how clipping works if you don’t already know…
A long word is reduced by removing some of the word. This creates a new word (usually one syllable long). This word is then used instead of the original word as an informal/slang term.
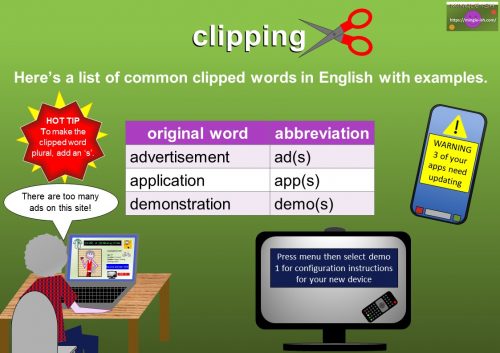
I’m pretty certain you’ve come across clipped words before, but maybe you just don’t know it! Look at the slide for some examples of clipped words and their meaning.
clipped words with examples and pictures
Let’s take a look at some common clipped words in action.
List of clipped words
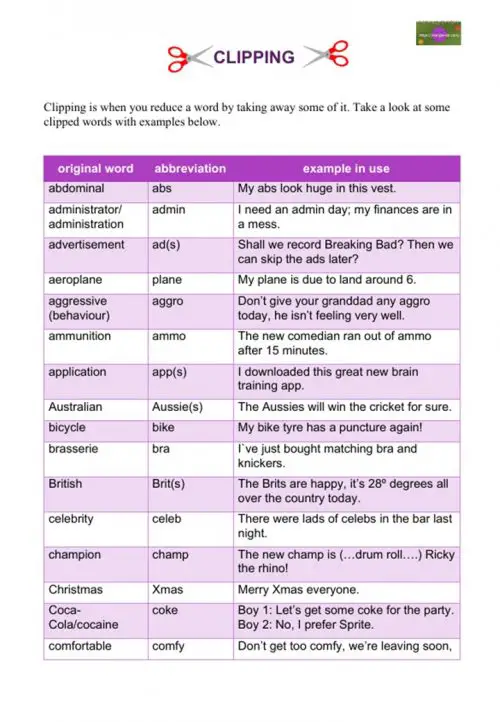
Here is a list of some of the most common clipped words we use in English with examples. A nice little practice exercise for you is to make up some sentences of your own.
- abdominal
abbreviation – abs
example – My abs look huge in this vest. - administrator/administration
abbreviation – admin
example – I need an admin day; my finances are in a mess. - advertisement
abbreviation – ad(s)
example – Shall we record Breaking Bad? Then we can skip the ads later? - aeroplane
abbreviation – plane
example – My plane is due to land around 6. - aggressive (behaviour)
abbreviation – aggro
example – Don’t give your granddad any aggro today, he isn’t feeling very well. - ammunition
abbreviation – ammo
example – The new comedian ran out of ammo after 15 minutes. - application
abbreviation – app(s)
example – I downloaded this great new brain training app. - Australian
abbreviation – Aussie(s)
example – The Aussies will win the cricket for sure. - bicycle
abbreviation – bike
example – My bike tyre has a puncture again! - brasserie
abbreviation – bra
example – I`ve just bought matching bra and knickers. - British
abbreviation – Brit(s)
example – The Brits are happy, it’s 28º degrees all over the country today. - celebrity
abbreviation – celeb
example – There were lads of celebs in the bar last night. - champion
abbreviation – champ
example – The new champ is (…drum roll….) Ricky the rhino! - Christmas
abbreviation – Xmas
example – Merry Xmas everyone. - Coca-Cola/cocaine
abbreviation – coke
example – Boy 1: Let’s get some coke for the party.
Boy 2: No, I prefer Sprite. - comfortable
abbreviation – comfy
example – Don’t get too comfy, we’re leaving soon, - congratulations
abbreviation – congrats
example – Congrats in the new job
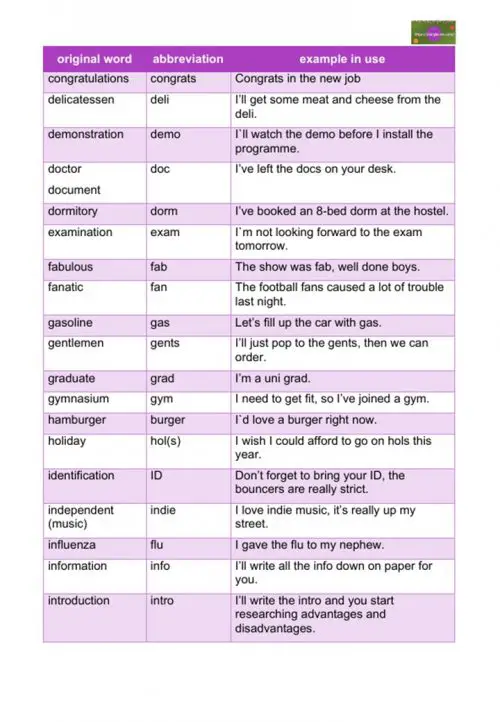
- delicatessen
abbreviation – deli
example – I’ll get some meat and cheese from the deli. - demonstration
abbreviation – demo
example – I`ll watch the demo before I install the programme. - doctor/document
abbreviation – doc
example – I’ve left the docs on your desk. - dormitory
abbreviation – dorm
example – I’ve booked an 8-bed dorm at the hostel. - examination
abbreviation – exam
example – I`m not looking forward to the exam tomorrow. - fabulous
abbreviation – fab
example – The show was fab, well done boys. - fanatic
abbreviation – fan
example – The football fans caused a lot of trouble last night. - gasoline
abbreviation – gas
example – Let’s fill up the car with gas. - gentlemen
abbreviation – gents
example – I’ll just pop to the gents, then we can order. - graduate
abbreviation – grad
example – I’m a uni grad. - gymnasium
abbreviation – gym
example – I need to get fit, so I’ve joined a gym. - hamburger
abbreviation – burger
example – I`d love a burger right now. - holiday
abbreviation – hol(s)
example – I wish I could afford to go on hols this year. - identification
abbreviation – ID
example – Don’t forget to bring your ID, the bouncers are really strict. - independent (music)
abbreviation – indie
example – I love indie music, it’s really up my street. - influenza
abbreviation – flu
example – I gave the flu to my nephew. - information
abbreviation – info
example – I’ll write all the info down on paper for you. - introduction
abbreviation – intro
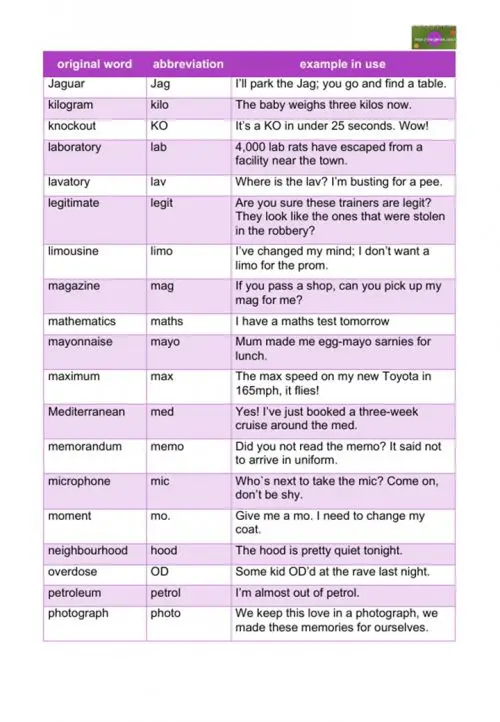
example – I’ll write the intro and you start researching advantages and disadvantages. - Jaguar
abbreviation – Jag
example – I’ll park the Jag; you go and find a table. - kilogram
abbreviation – kilo
example – The baby weighs three kilos now. - knockout
abbreviation – KO
example – It’s a KO in under 25 seconds. Wow! - laboratory
abbreviation – lab
example – 4,000 lab rats have escaped from a facility near the town. - lavatory
abbreviation – lav
example – Where is the lav? I’m busting for a pee. - legitimate
abbreviation – legit
example – Are you sure these trainers are legit? They look like the ones that were stolen in the robbery? - limousine
abbreviation – limo
example – I’ve changed my mind; I don’t want a limo for the prom.
- magazine
abbreviation – mag
example – If you pass a shop, can you pick up my mag for me? - mathematics
abbreviation – maths
example – I have a maths test tomorrow - mayonnaise
abbreviation – mayo
example – Mum made me egg-mayo sarnies for lunch. - maximum
abbreviation – max
example – The max speed on my new Toyota in 165mph, it flies! - Mediterranean
abbreviation – med
example – Yes! I’ve just booked a three-week cruise around the med. - memorandum
abbreviation – memo
example – Did you not read the memo? It said not to arrive in uniform. - microphone
abbreviation – mic
example – Who`s next to take the mic? Come on, don’t be shy. - moment
abbreviation – mo.
example – Give me a mo. I need to change my coat. - neighbourhood
abbreviation – hood
example – The hood is pretty quiet tonight. - overdose
abbreviation – OD
example – Some kid OD’d at the rave last night. - petroleum
abbreviation – petrol
example – I’m almost out of petrol. - photograph
abbreviation – photo
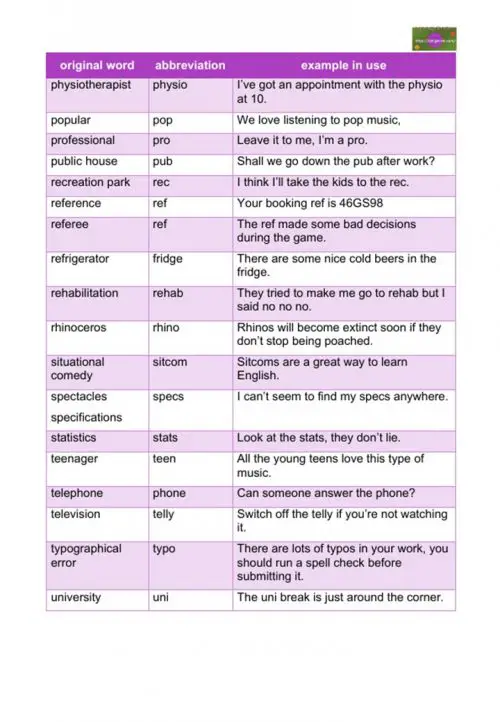
example – We keep this love in a photograph, we made these memories for ourselves. - physiotherapist
abbreviation – physio
example – I’ve got an appointment with the physio at 10. - popular
abbreviation – pop
example – We love listening to pop music, - professional
abbreviation – pro
example – Leave it to me, I’m a pro. - public house
abbreviation – pub
example – Shall we go down the pub after work?
- recreation park
abbreviation – rec
example – I think I’ll take the kids to the rec. - reference
abbreviation – ref
example – Your booking ref is 46GS98 - referee
abbreviation – ref
example – The ref made some bad decisions during the game. - refrigerator
abbreviation – fridge
example – There are some nice cold beers in the fridge. - rehabilitation
abbreviation – rehab
example – They tried to make me go to rehab but I said no no no. - rhinoceros rhino
abbreviation – Rhinos
example – will become extinct soon if they don’t stop being poached. - situational comedy
abbreviation – sitcom
example – Sitcoms are a great way to learn English. - spectacles/specifications
abbreviation – specs
example – I can’t seem to find my specs anywhere. - statistics
abbreviation – stats
example – Look at the stats, they don’t lie. - teenager
abbreviation – teen
example – All the young teens love this type of music. - telephone
abbreviation – phone
example – Can someone answer the phone? - television
abbreviation – telly
example – Switch off the telly if you’re not watching it. - typographical error
abbreviation – typo
example – There are lots of typos in your work, you should run a spell check before submitting it. - university
abbreviation – uni
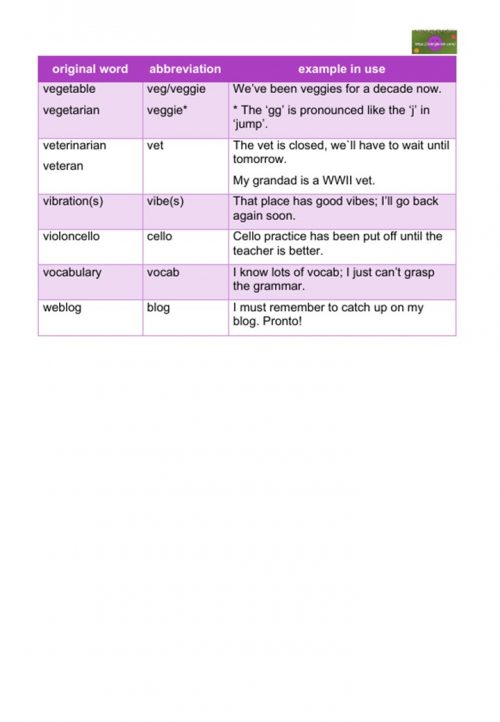
example – The uni break is just around the corner. - vegetable/vegetarian
abbreviation – veg/veggie
example – veggie* We’ve been veggies for a decade now.
* The ‘gg’ is pronounced like the ‘j’ in ‘jump’. - veterinarian/veteran
abbreviation – vet
example – The vet is closed, we`ll have to wait until tomorrow.
example – My grandad is a WWII vet. - vibration(s)
abbreviation – vibe(s)
example – That place has good vibes; I’ll go back again soon. - violoncello
abbreviation – cello
example – Cello practice has been put off until the teacher is better. - vocabulary
abbreviation – vocab
example – I know lots of vocab; I just can’t grasp the grammar. - weblog
abbreviation – blog
example – I must remember to catch up on my blog. Pronto!
Here’s the table for you to download and study at your leisure.
Can you think of any other clipped words? If you have, let me know in the comments below.
clipping exercises
Test yourself and see what you’ve learnt with these clipped word exercises.
The ‘Word Formation Process’ is regarded as the branch of Morphology, and it has a significant role in expanding the vocabulary that helps us communicate very smoothly. The main objectives of the word-formation process are to form new words with the same root by deploying different rules or processes.
In other words, we can say that the word-formation process is a process in which new words are formed by modifying the existing terms or completely changing those words.
Let us see the fundamental word-formation processes in linguistics:
Derivation
‘Derivation’ is a significant word-formation process that attaches derivation affixes to the main form to create a new word. Affixes (prefixes or suffixes) are regarded as bound morphemes.
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful syntactical or grammar unit of a language that cannot be divided without changing its meaning. In contrast to the free morpheme, a bound morpheme doesn’t have any independent meaning, and it needs the help of a free morpheme to form a new word.
Let us see some examples of derivation in the below table:
| Base Forms | New Words |
| Appear | Disappear |
| Justice | Injustice |
| Lighten | Enlighten |
| Friend | Friendship |
| Happy | Happiness |
Back Formation
‘Back-Formation’ is a word-formation process that eliminates the actual derivational affix from the main form to create a new word. However, Back-Formation is contrary to derivation in terms of forming new words. Let us see some examples of Back-Formation in the below table:
| Base Forms | Back Formation |
| Insertion | Insert |
| Donation | Donate |
| Precession | Process |
| Obsessive | Obsess |
| Resurrection | Resurrect |
Conversion
In conversion, a word of one grammatical form converts into another without changing spelling or pronunciation. For example, the term ‘Google’ originated as a noun before the verb.
A few years ago, we only used the term as a noun (search it on Google), but now we say ‘Google it. Let us see some examples of conversion in the below table:
| Noun | To Verb |
| Access | – to access |
| – to google | |
| – to email | |
| Name | – to name |
| Host | – to host |
| Verb | To Noun |
| To hope | Hope |
| To cover | Cover |
| To increase | Increase |
| To attack | Attack |
Compounding
‘Compounding’ is a word-formation process that allows words to combine to make a new word. Compounding words can be formed as two words joined with a hyphen. Let us see some examples in the below table:
| Words | Compounding Words |
| Class+room | Classroom |
| Note+book | Notebook |
| Break+up | Breakup |
| Brother+in+law | Brother in law |
| High+light | Highlight |
Clipping
‘Clipping’ is another essential word-formation process that reduces or shortens a word without changing the exact meaning. In contrast to the back-formation process, it reserves the original meaning.
Clipping is divided into four types. They are:
- Back Clipping
- Fore Clipping
- Middle Clipping
- Complex Clipping
Every Clipping has different roles in words when they are assigned. Back Clipping removes the end part of a word; Fore Clipping removes the beginning part of a word; Middle Clipping reserves the middle position. Finally, Complex Clipping removes multiple pieces from multiple words.
Let us see some examples in the below table:
| Words | Clippings |
| Advertisement | Ad |
| Photograph | Photo |
| Telephone | Phone |
| Influenza | Flue |
| Cabletelegram | Cablegram |
Blending
In the ‘Blending’ word-formation method, the parts of two or more words combine to form a new word. Let us see some examples in the below table:
| Words | Blendings |
| Breakfast+lunch | Brunch |
| Biographical+picture | Biopic |
| Motor+hotel | Motel |
| Spanish+English | Spanglish |
| Telephone+marathon | Telethon |
Abbreviation
‘Abbreviation’ is another famous and widely used word-formation method used to shorten a word or phrase. In the modern era, ‘Abbreviation is becoming more popular. Nowadays, people used to use it everywhere. Let us see some examples in the below table:
| Words/Phrases | Abbreviation |
| Junior | Jr. |
| Mister | Mr. |
| Mistress | Miss. |
| Doctor | Dr. |
| Department | Dept. |
| Bachelor of Arts | B.A. |
| Master of Arts | M.A. |
| Master of Business Administration | MBA |
Acronyms
An Acronym is a popular word-formation process in which an initialism is pronounced as a word. It forms from the first letter of each word in a phrase, and the newly formed letters create a new word that helps us speedy communication. For example, ‘PIN’ is an initialism for Personal Identification Number used as the word ‘pin.’
However, let us see some other famous examples of acronyms in the below table for a better understanding:
| Acronyms | Words/Phrases |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| AIDS | Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| ASAP | As Soon As Possible |
| AWOL | Absent Without Leave |
Borrowing
‘Borrowing’ is another word-formation process in which a word from one language is borrowed directly into another language. Let us see some English words which are borrowed from another language:
| Algebra | Arabic |
| Cherub | Hebrew |
| Murder | French |
| Pizza | Italian |
| Tamale | Spanish |
Conclusion
Now we know that Word-Formation Processes are the methods by which words are formed by deploying different types of rules. We can create new words by following the above word-formation methods.
We need to do one thing: we have to follow the fundamental rules or processes of word formation.
Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com. He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.