VBA Boolean Operation
In Excel when we compare two cell contents or numbers by applying equal sign between them, we get output in TRUE or FALSE format. Which means values which we are comparing may be equal or may not be equal. In a similar manner, we have Boolean in VBA Excel. Boolean also gives the output in the form of TRUE or FALSE. Boolean is a form of data type which can only contain either TRUE or FALSE. When we give some input to Boolean and if the test becomes TRUE then we get an answer as TRUE or we get FALSE.
How to Use Boolean in VBA Excel?
Let’s see the examples of Boolean in Excel VBA.
You can download this VBA Boolean Excel Template here – VBA Boolean Excel Template
Example #1 – VBA Boolean
Let’s see a very simple example where we will see how to apply Boolean while comparing some.
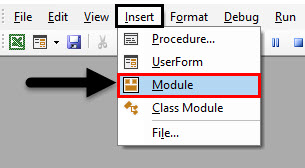
Step 1: For that go to the VBA window and click on the Insert menu tab. From the list select a Module as shown below.
Step 2: Now in the opened module, write the sub category of VBA Boolean. We can choose to write any name of subprocedure here.
Code:
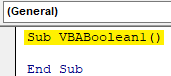
Sub VBABoolean1() End Sub
Step 3: Now define a Dim with any name, let’ say an A and assign the variable A as Boolean as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean1() Dim A As Boolean End Sub
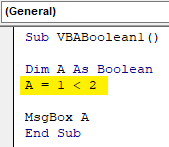
Step 4: Let’s consider two numbers, 1 and 2. And now we will test with the help of Boolean whether 2 is greater than 1 or not. So in the next line, write a mathematical expression of 1<2 under defined variable A.
Code:
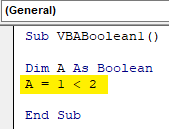
Sub VBABoolean1() Dim A As Boolean A = 1 < 2 End Sub
Step 5: Now assign a message box to variable A to see what outcome will appear when we run the code.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean1() Dim A As Boolean A = 1 < 2 MsgBox A End Sub
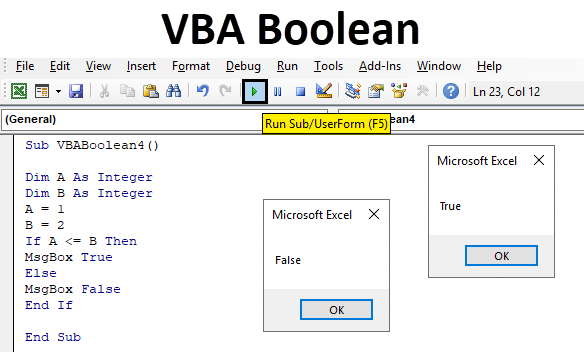
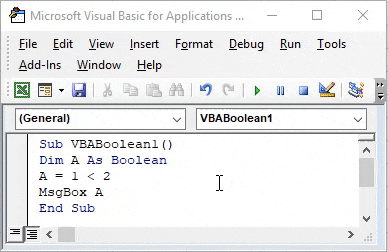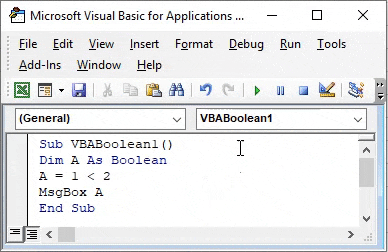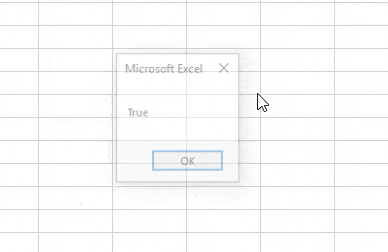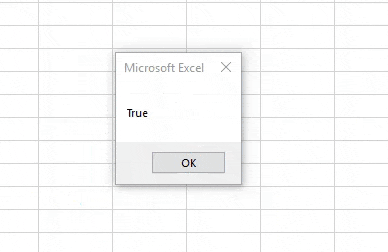
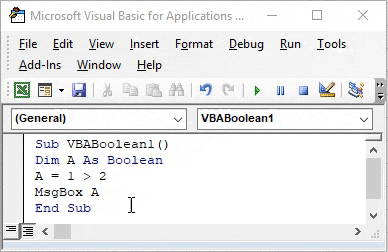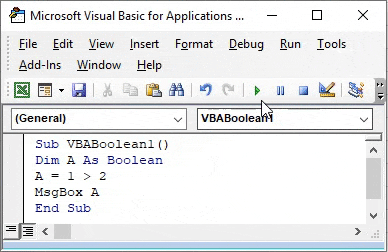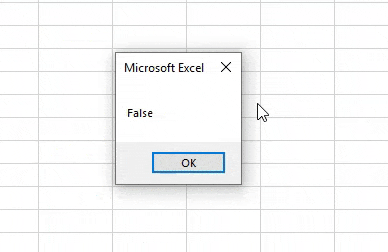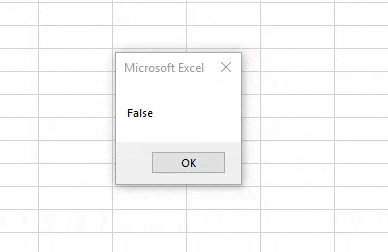
Step 6: For running the code, click on the Play button which is below the menu bar as shown below. As we can see, we got the output as TRUE which means 1 is less than 2.
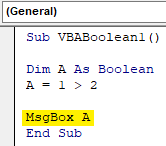
Step 7: If we change the sign as 1 is greater than 2 as shown below. What would we get?
Code:
Sub VBABoolean1() Dim A As Boolean A = 1 > 2 MsgBox A End Sub
Step 8: To test this, again run the code. We will see, Boolean has given FALSE as 1 cannot be greater than 2.
Example #2 – VBA Boolean
In this example, we will test if Boolean works for text or not. To apply this, we need a module.
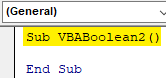
Step 1: Open a new Module and give it a subcategory in the name of VBA Boolean or any name as per your choice.
Sub VBABoolean2() End Sub
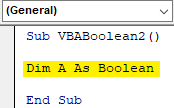
Step 2: Define a variable A and assign a Boolean function to it.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean2() Dim A As Boolean End Sub
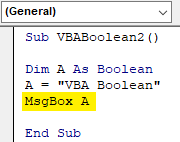
Step 3: Now assign a text to defined variable A. Let’s say that text is VBA Boolean. And it should be under inverted commas.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean2() Dim A As Boolean A = "VBA Boolean" End Sub
Step 4: At last, give that variable A in a message box to see the output as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean2() Dim A As Boolean A = "VBA Boolean" MsgBox A End Sub
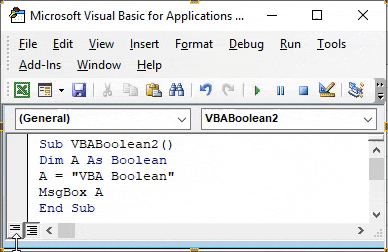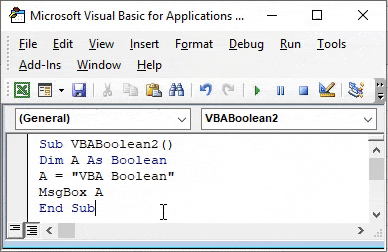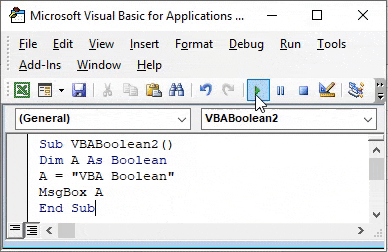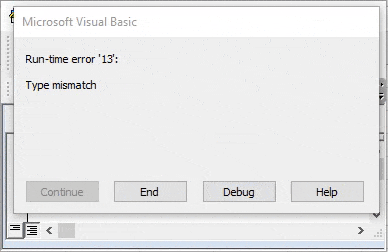
Step 5: Once done, run the code. We will get an error message as “Run-time error 12 – Type Mismatch” which means that Boolean doesn’t support input as Text.
Example #3 – VBA Boolean
In this example, we will see, if Boolean works for a number without any comparison.
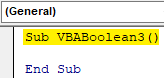
Step 1: Open a new module and give it a subcategory of VBA Boolean as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean3() End Sub
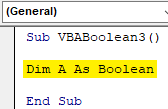
Step 2: Now define a Dim A variable as Boolean as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean3() Dim A As Boolean End Sub
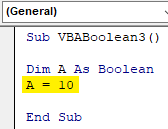
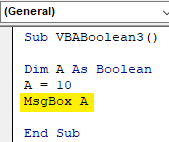
Step 3: As discussed above, we will give the variable A a number. Let’s consider that number is 10.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean3() Dim A As Boolean A = 10 End Sub
Step 4: After that, select the function msgbox and assign it to variable A. This will help us print the value with the help of Boolean.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean3() Dim A As Boolean A = 10 MsgBox A End Sub
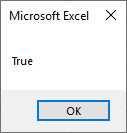
Step 5: Now run the code. We will get the message with the message as TRUE.
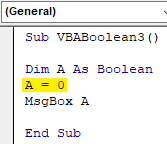
Step 6: Now let’s change that value to 0 from 10.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean3() Dim A As Boolean A = 0 MsgBox A End Sub
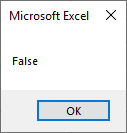
Step 7: Now run the code again. We will see the message box has returned the output as FALSE. In Boolean, any value greater than 0 will always give the returned answer as TRUE whereas the 0 will return the value as FALSE.
Example #4 – VBA Boolean
In this example, we will see how Greater Than-Equal to (>=) or Less Than-Equal to (<=) works in Boolean. This will be done with the help for If-End If loop.
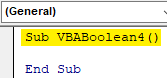
Step 1: Now, open a new module and write the subcategory of VBA Boolean as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean4() End Sub
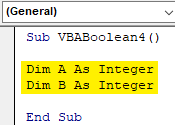
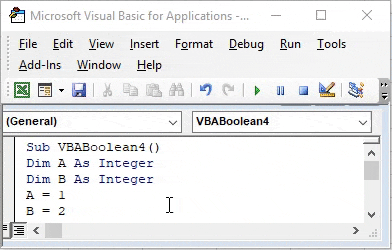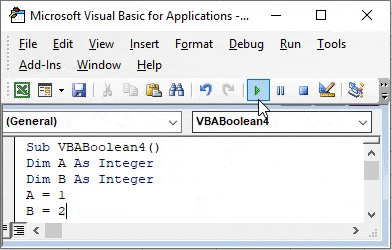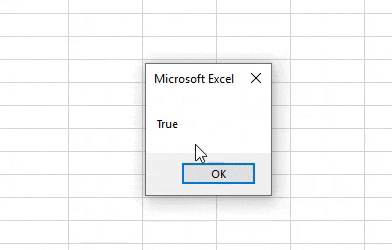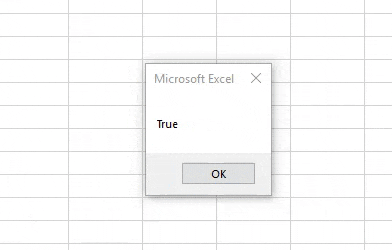
Step 2: Now define 2 variable with any name as per your choice. Here, we have selected A and B as Integer. Which means both will store numeric values.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean4() Dim A As Integer Dim B As Integer End Sub
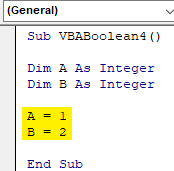
Step 3: Now assign any values to variable A and B. Here we have chosen number 1 and 2 for variable A and B as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean4() Dim A As Integer Dim B As Integer A = 1 B = 2 End Sub
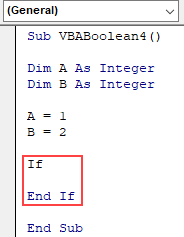
Step 4: As stated above, we will use the If-Else loop. Now open the If-End If loop where we will write the criteria.
Code:
Sub VBABoolean4() Dim A As Integer Dim B As Integer A = 1 B = 2 If End If End Sub
Step 5: Now write the code, If A is less than equal to B then show us the message as TRUE, else show us the message as FALSE.
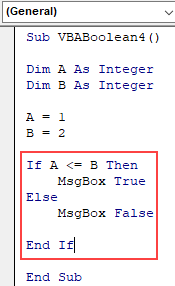
Code:
Sub VBABoolean4() Dim A As Integer Dim B As Integer A = 1 B = 2 If A <= B Then MsgBox True Else MsgBox False End If End Sub
Step 6: Now compile the above code step-by-step and then run if no error found. We will see, the message box has the message as TRUE which means value stored in variable A (which is 1) is less than the value stored in variable B (which is 2).
Pros of VBA Boolean
- It is quite useful when we are want to implement the process flow following TRUE and FALSE for each iteration.
- Conditional comparison with the help of any kind of loop can easily be implemented.
Cons of VBA Boolean
- Only numbers can be used in Boolean. It will show the error if used for text as seen in example-2.
Things to Remember
- Using Boolean with any loop will give users a better output. And comparison can be done in various ways.
- Boolean is a kind of cell comparison formula used in excel, but it only compares the numerical or mathematical values.
- Always save the file in macro enable format to retain the written code to be used in the future.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Boolean. Here we discuss how to use Boolean in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA IsNumeric
- VBA Get Cell Value
- VBA XML
- VBA UCASE
VBA Boolean data type can only be either TRUE or FALSE – expressed either as “1” (TRUE) or “0” (FALSE).
Boolean values are commonly used with IF statements to verify whether a given condition is met or not, allowing you to build complex logical comparisons.
A blank canvas in the VBA editor is waiting for us, so let’s get started.
Declaring Boolean Variables
First things first, let’s start with declaring Boolean variables so that you can use them in your VBA code.
There are two ways to declare a Boolean variable:
- on the module level, meaning the variable can only be used within a given module
- on the global level, meaning the variable can be used across the entire VBA project
Use the following Dim statement to create a Boolean value on the module level:
Dim BooleanValue As BooleanOn the other hand, copy this public statement to create a global Boolean variable:
Public BooleanValue As Boolean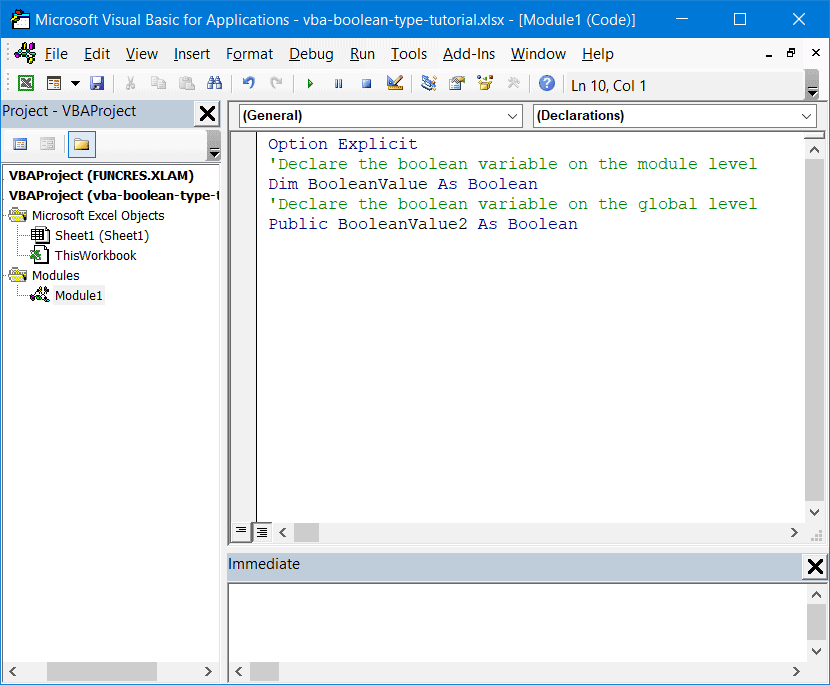
Example #1: Using Boolean Variables
Let’s move from theory to practice.
The examples below demonstrate how to use the Boolean data type in VBA.
Start with creating a new module (Insert > Module). Once there, copy the following code into the VBA editor and click “Run Sub/UserForm” or press F5 to execute it:
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim BooleanValue As Boolean
BooleanValue = 50 > 115
MsgBox BooleanValue
End Sub
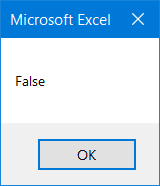
This simple Sub procedure compares whether 50 is greater than 115 and returns a message box with the corresponding Boolean value based on this simple logical comparison.
Let’s take a closer look at the VBA code to help you adjust accordingly:
- Dim BooleanValue As Boolean – This line of code creates a new variable named “BooleanValue” and converts it to the Boolean data type.
- BooleanValue = 50 > 115 – This determines the actual Boolean value of the variable based on the specified logical comparison. If 50 is greater than 115, the value is set to TRUE. If not, the value is set to FALSE.
- MsgBox BooleanValue – This VBA command creates a message box containing the output.
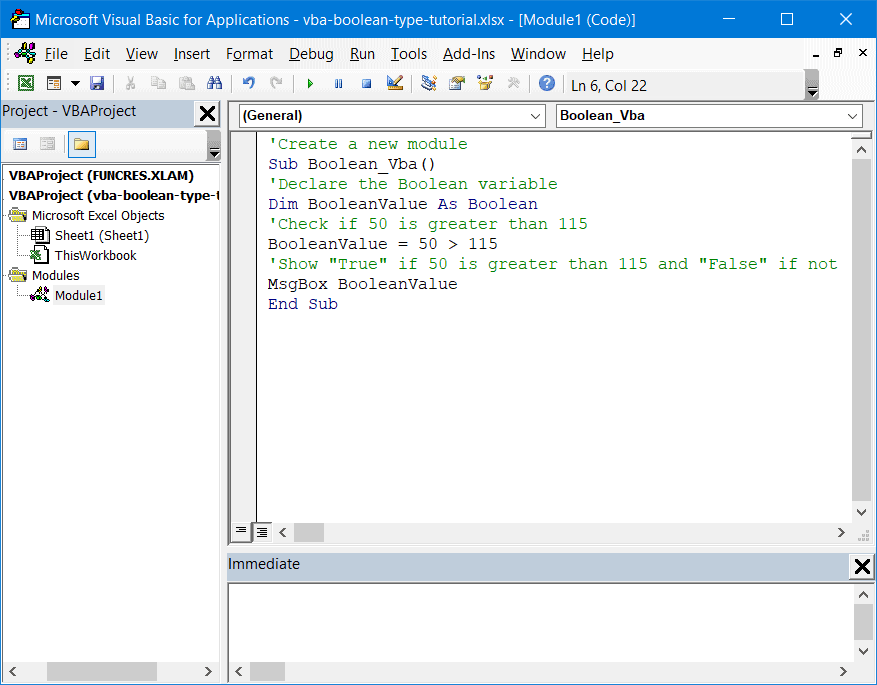
Predictably, VBA returns FALSE since 50 is not greater than 115.
Related Article: How to Change The Position And Size Of Excel Charts In VBA
Example #2: Boolean Variables & IF Statements
That was a simple example, so let’s ramp up the difficulty level and break down how you can use the VBA Boolean data type with IF statements.
Imagine you’re overseeing a web development project where the devs are getting paid based on their hourly rate. Your fictitious company allocated 54 hours to the project.
Armed with this data (and the knowledge of how to apply Boolean values), you can put together a simple IF statement to check if the project runs over budget at any stage of the development process:
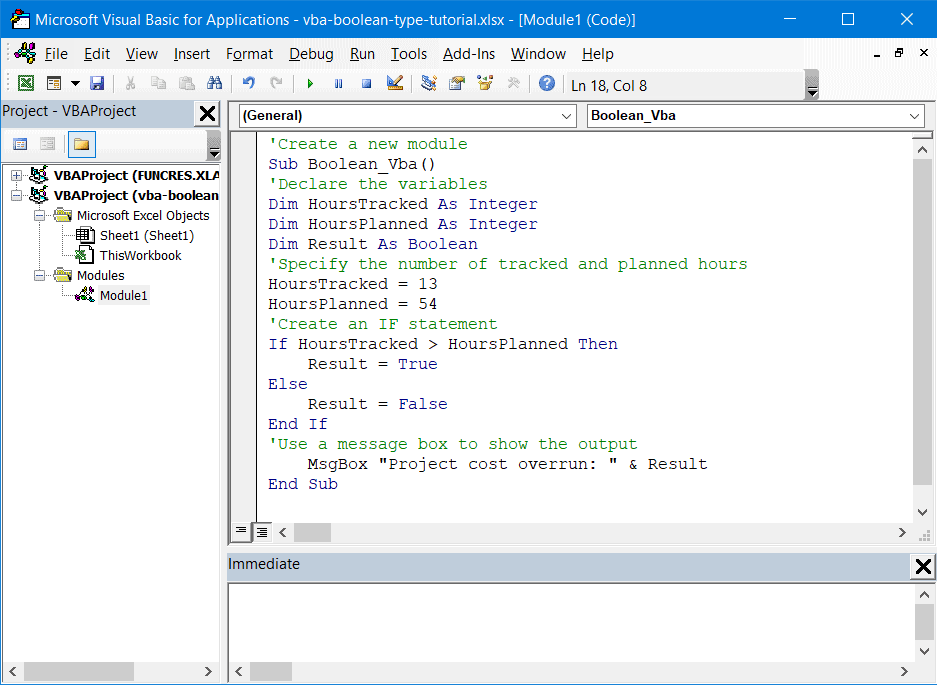
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim HoursTracked As Integer
Dim HoursPlanned As Integer
Dim Result As Boolean
HoursTracked = 13
HoursPlanned = 54
If HoursTracked > HoursPlanned Then
Result = True
Else
Result = False
End If
MsgBox "Project cost overrun: " & Result
End Sub
The screenshot below breaks down the building blocks of this Sub procedure in greater detail:
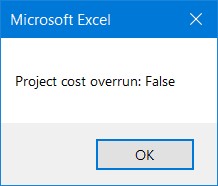
As a result, VBA will return this message box to help you spot any project cost overrun.
Boolean Operators
In VBA, Boolean operators make it possible for you to work with combinations of Boolean variables, providing you a lot more flexibility.
The four most common Boolean operators in VBA are AND, OR, NOT, and XOR. In this section, we will show you how to use each of them.
The AND Operator
The AND operator connects two or more Boolean expressions and returns TRUE only if all of the conditions are met.
In the example below, the variable “Result” equals TRUE only if both the first condition (50 > 155) and the second condition (50 < 55) are TRUE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = 50 > 155 And 50 < 55 // Use the AND operator to check if both of the conditions are met
MsgBox Result
End SubResult: FALSE
The OR Operator
The OR operator returns TRUE if at least one of the conditions is met.
In the same example, the variable “Result” equals TRUE if either the first or second condition is TRUE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = 50 > 155 Or 50 < 55 // Use the OR operator to check if any of the conditions are met
MsgBox Result
End SubResult: TRUE
The NOT Operator
The NOT operator turns TRUE into FALSE, and vice versa.
In this example, since 50 is not greater than 155, the VBA editor should return FALSE. However, since the NOT operator is applied, it takes truth to falsity. Another variation is the not-equal-to operator (<>) that works in a similar way.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = Not 50 > 155 // Use the NOT operator to reverse the TRUE and FALSE values
MsgBox Result
End Sub
Result: TRUE
The XOR Operator
The XOR operator returns TRUE only if two conditions are not TRUE or FALSE at the same time.
In the example below, the “Result” variable is TRUE because the first condition (50 > 155) is FALSE while the second condition (50 < 55) is TRUE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = 50 > 155 Xor 50 < 55 // Check if BOTH or NEITHER of the conditions are met
MsgBox Result
End Sub
Result: TRUE
Usage Notes
1. The default Boolean value is FALSE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
MsgBox Result
End Sub
Result: FALSE
2. By default, every nonzero number is TRUE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = 15
MsgBox Result
End SubResult: TRUE
3. Zero is equal to FALSE.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Result = 0
MsgBox Result
End SubResult: TRUE
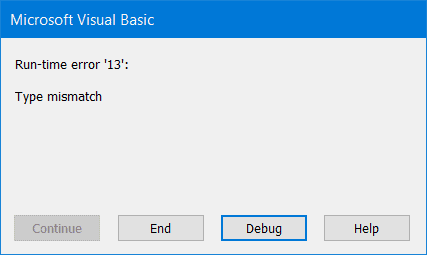
4. Boolean values can’t be anything but TRUE or FALSE. If you try to turn a Boolean variable into any other data type, this breaks the code and triggers an error.
Sub Boolean_Vba()
Dim Result As Boolean
Result = “Bird is the word”
MsgBox Result
End Sub
Result: a type-mismatch error – as shown on the screenshot below.
In this Article
- Boolean Variable Type
- Declare Boolean Variable at Module or Global Level
- Module Level
- Global Level
- Using a Boolean Variable
- Using Boolean Operators
- Using the AND operator
- Using the OR operator
- Using the NOT operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
Boolean Variable Type
The VBA Boolean data type is used to store True or False values. True can also be represented by 1 and False by 0.
To declare an Boolean variable, you use the Dim Statement (short for Dimension):
Dim blnA as Boolean
Then, to assign a value to a variable, you simply use the equal sign:
blnA = TrueWhen you put this in a procedure, it could look like this:
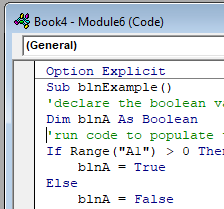
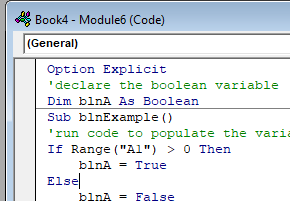
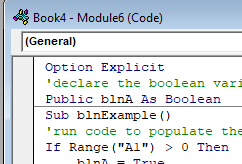
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA as Boolean
'run code to populate the variable - usually the code is an if or a case statement
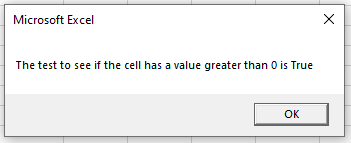
If Range("A1") > 0 then
blnA = true
Else
blnA = False
End If
'show the message box
MsgBox "The test to see if the cell has a value greater than 0 is " & blnA
End SubIf you run the code above, the following message box will be shown.
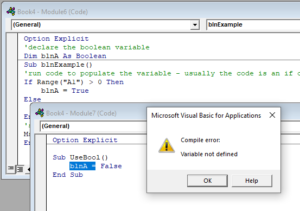
Declare Boolean Variable at Module or Global Level
In the previous example, we’ve declared the Boolean variable within a procedure. Variables declared with a procedure can only be used within that procedure.
Instead, you can declare Boolean variables at the module or global level.
Module Level
You declare Module level variables at the top of code modules with the Dim statement.
These variables can be used with any procedure in that code module.
Global Level
You also declare Global level variables at the top of code modules. However, instead of using the Dim statement, you would use the Public statement to indicate that the Boolean variable is available to be used throughout your VBA Project.
Public blnA as BooleanIf you were to declare the Boolean variable at a module level and then try to use it in a different module, you would get an error.
However, if you had used the Public keyword to declare the Boolean variable, the error would not occur and the procedure would run perfectly.
Using a Boolean Variable
You use the Boolean variable in logical comparison. These are often used with If statements to test if a condition is True or False as per the example above, or in a line of code to apply a logical test – perhaps to see if one value is greater than another.
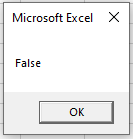
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA As Boolean
'test to see if one number is greater than the next number
blnA = 45 > 68
'show the message box
MsgBox blnA
End SubIf you run the code above, you will get the following message box.
because of course 45 is not greater than 68!
Using Boolean Operators
As Boolean variables are used in logical comparison, we can use the logical operators AND and OR to test to see if more than one condition is true or false.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Using the AND operator
We can use the AND function to see if BOTH conditions are met.
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA As Boolean
'use the AND operator to test to see if both conditions are true
blnA = 10 > 13 And 15 > 12
'show the message box
MsgBox blnA
End Subor we could run the same test using an If Statement:
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA As Boolean
'use the AND operator to test to see if both conditions are true
If 10 > 13 And 15 > 12 Then
blnA = True
Else
blnA = False
End If
'show the message box
MsgBox blnA
End SubBoth examples above would return FALSE due to the fact that 10 is NOT greater than 13 – and BOTH conditions have to be True for the Boolean to be True.
Using the OR operator
We can use the OR function to see if ONE OF the conditions is met.
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA As Boolean
'use the OR operator to test to see if one of conditions is true
blnA = 10 > 13 Or 15 > 12
'show the message box
MsgBox blnA
End Subor we could run the same test using an If Statement:
Sub blnExample()
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnA As Boolean
'use the OR operator to test to see if one of conditions is true
If 10 > 13 OR 15 > 12 Then
blnA = True
Else
blnA = False
End If
'show the message box
MsgBox blnA
End SubThese examples would return TRUE due to the fact that 10 is NOT greater than 13 BUT 15 IS greater than 12 – and ONLY ONE condition has to be True for the Boolean to be True.
Using If statements allows us to use more logical operators
Using the NOT operator
We can also use the NOT operator with the Boolean variable. The NOT operator negates the value of the condition – so if a condition is true, the NOT operator will return false.
Sub FindDifferences()
'declare range variables
Dim rng1 As Range
Dim rng2 As Range
'activate sheet one
Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate
'populate the ranges
Set rng1 = Range("A3")
Set rng2 = Range("B3")
'use the NOT operator to see if the values are equal or not
If Not rng1.Value = rng2.Value Then
MsgBox "The values in the cells are not equal"
Else
MsgBox "The values in the cells are equal"
End If
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator is used to compare two or more conditions. If one of the conditions is true, it will return TRUE. If there are 2 conditions, and NEITHER are true or BOTH are true, it will return FALSE.
Sub blnExample()
'declare the integers
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnResult As Boolean
'populate the variables
intA = 5
intB = 10
'check to see if one is true
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
MsgBox blnResult
End SubIn the above example, as ONE of the conditions is TRUE, the message box will return TRUE.
Sub blnExample()
'declare the integers
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnResult As Boolean
'populate the variables
intA = 5
intB = 5
'check to see if one is true
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
MsgBox blnResult
End SubHowever, in the example above, as BOTH conditions are true, the message box will return FALSE.
Sub blnExample()
'declare the integers
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
'declare the boolean variable
Dim blnResult As Boolean
'populate the variables
intA = 6
intB = 8
'check to see if one is true
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
MsgBox blnResult
End Suband finally, as both conditions are FALSE, the message box will also return FALSE.
Excel VBA Boolean Operator
Boolean is a data type. It is also a built-in data type in VBA. This data type is used for logical references or logical variables because the value this data type holds is either TRUE or FALSE, used for logical comparison. The declaration of this data type is similar to all the other data types.
As we said, the Boolean data type can hold either TRUE or FALSE as the data, but it can also hold number 1 as TRUE and 0 as FALSE. So, TRUE is represented by 1, and FALSE is represented by 0. So, when we declare the variable as BOOLEAN, it occupies 2 bytes of computer memory.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Boolean Operator
- Working with Boolean Data Type in VBA Programming Language
- Boolean Data Type Cannot Hold Other than TRUE or FALSE.
- All the Numbers are TRUE, and Zero is FALSE
- VBA Boolean Operator with IF Condition
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Boolean (wallstreetmojo.com)
Working with Boolean Data Type in VBA Programming Language
Let us see the example of setting Boolean operator values to variables using the VBA CodeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
You can download this VBA Boolean Data Type Excel Template here – VBA Boolean Data Type Excel Template
Follow the steps below to gain adequate knowledge of Boolean data types in VBA.
Step 1: First, start the subprocedure by naming the macro name.
Code:
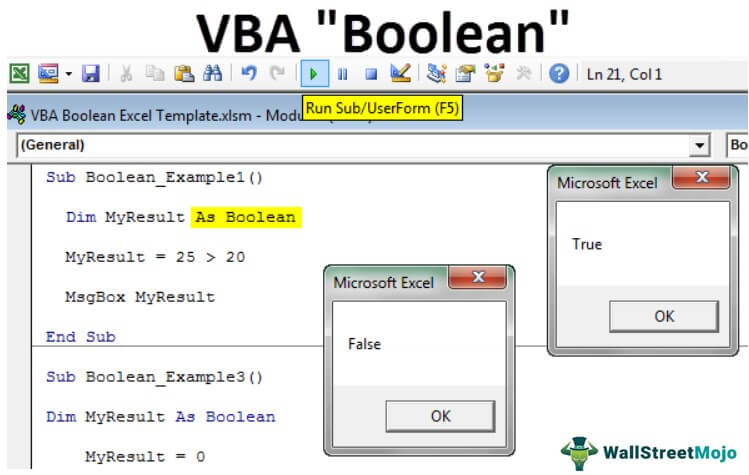
Sub Boolean_Example1() End Sub
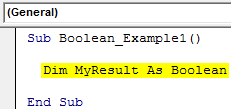
Step 2: Declare the variable as “BOOLEAN.”
Code:
Sub Boolean_Example1() Dim MyResult As Boolean End Sub
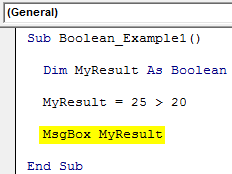
Step 3: Now, for the variable “MyResult,” apply the simple logical testA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more as 25 > 20.
Code:
Sub Boolean_Example1() Dim MyResult As Boolean MyResult = 25 > 20 End Sub
Step 4: Now, show the result in a message box in VBAVBA MsgBox function is an output function which displays the generalized message provided by the developer. This statement has no arguments and the personalized messages in this function are written under the double quotes while for the values the variable reference is provided.read more.
Code:
Sub Boolean_Example1() Dim MyResult As Boolean MyResult = 25 > 20 MsgBox MyResult End Sub
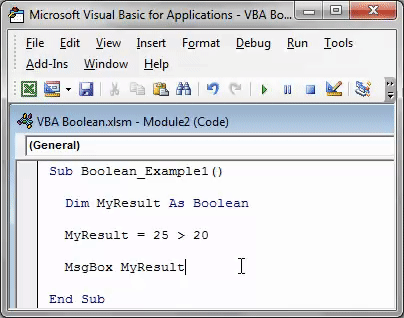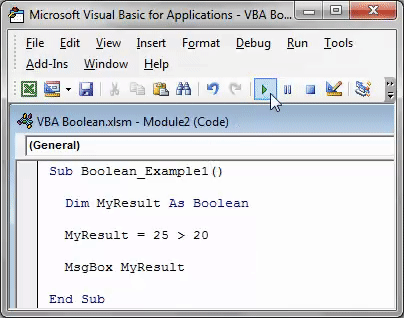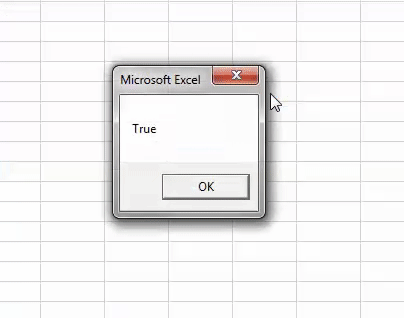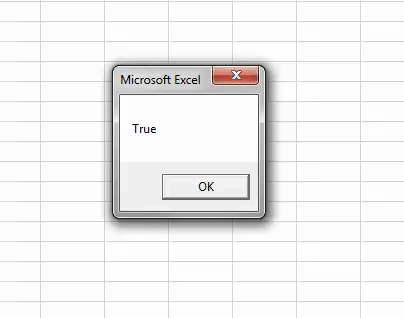
Now, run the excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more through the F5 key or manually and see the result.
We got the result as TRUE because the number 25 is greater than the number 20, so the logical test is correct, and the result is TRUE.
It is the basic structure of VBA Boolean data types.
Boolean Data Type Cannot Hold Other than TRUE or FALSE.
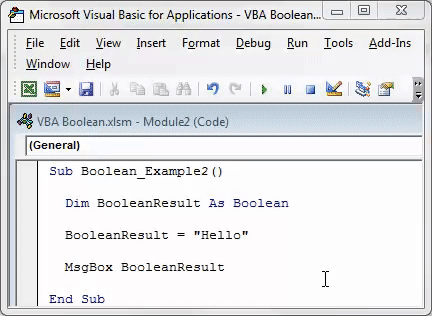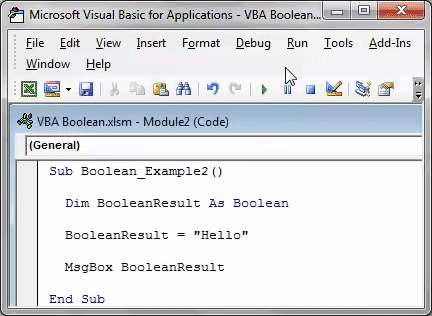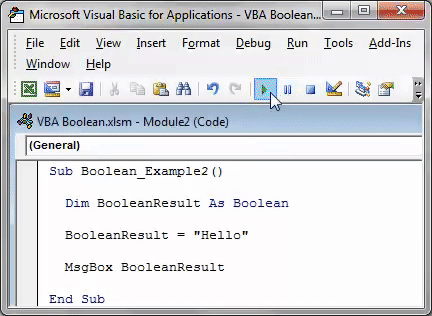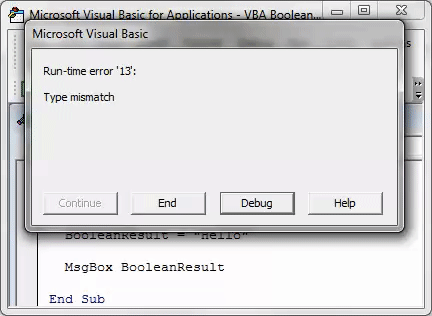
VBA Boolean is a logical data type. It holds either TRUE or FALSE. Anything other than TRUE or FALSE will show an error message as “Type Mismatch” in VBA.
For example, look at the below code.
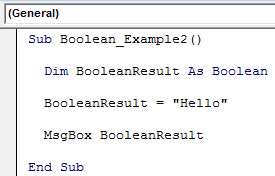
Code:
Sub Boolean_Example2() Dim BooleanResult As Boolean BooleanResult = "Hello" MsgBox BooleanResult End Sub
In the above code, we have declared the variable “BooleanResult” as Boolean.
Dim BooleanResult As Boolean
In the next line, we have assigned the value to the declared variable as “Hello.”
BooleanResult = "Hello"
We have declared the variable as Boolean, but we have assigned the value as “Hello,” which is other than logical values: TRUE or FALSE.
When we run this code using the F5 key or manually, we will get the type mismatch error because of the data type mismatch value.
All the Numbers are TRUE, and Zero is FALSE
As we said, TRUE is represented by the number 1, and FALSE is represented by 0. For example, look at the below code in VBA.
Code:
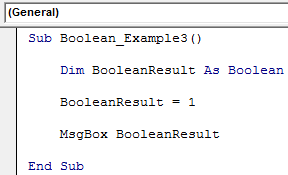
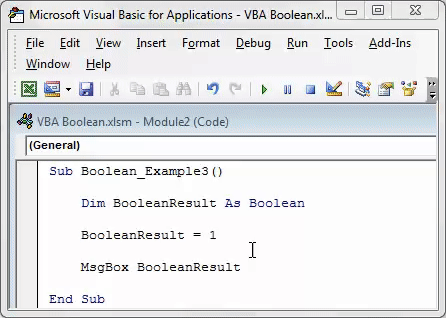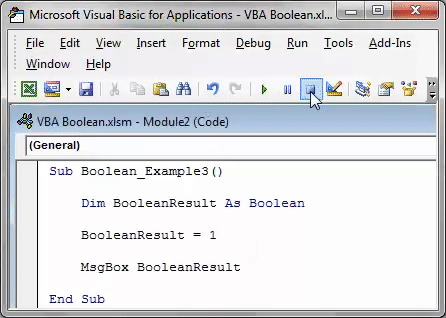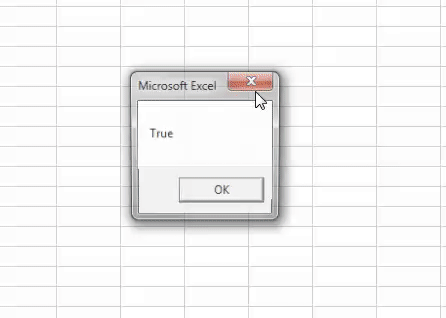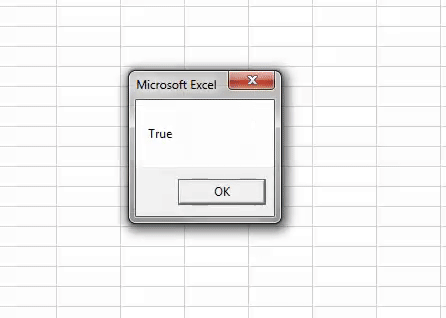
Sub Boolean_Example3() Dim BooleanResult As Boolean BooleanResult = 1 MsgBox BooleanResult End Sub
We assigned the value to the variable as 1, showing the result as TRUE.
Now, look at the code below.
Code:
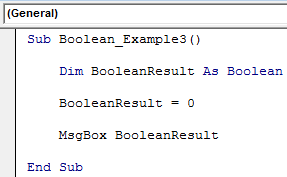
Sub Boolean_Example3() Dim BooleanResult As Boolean BooleanResult = 0 MsgBox BooleanResult End Sub
In this code, we have assigned the value to the variable as 0, showing the result as FALSE.
Not only 1 or 0, but it can also treat any number assigned to the variable except zero as TRUE. It will only treat zero as 1.
VBA Boolean Operator with IF Condition
Since the Boolean data type can hold only logical values, it is best suited to use with the IF condition in VBA.
Code:
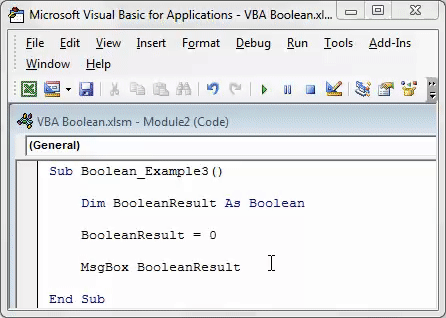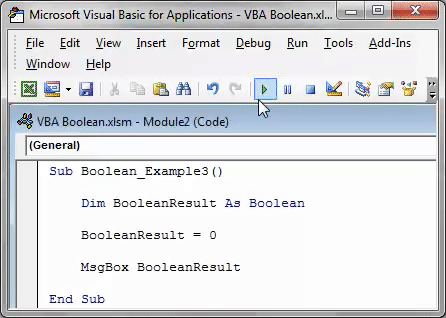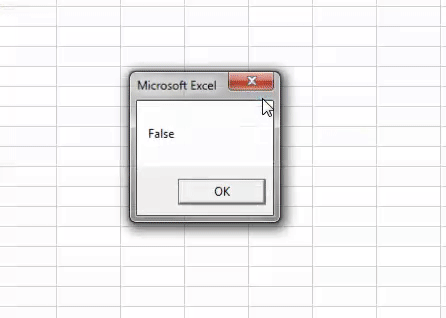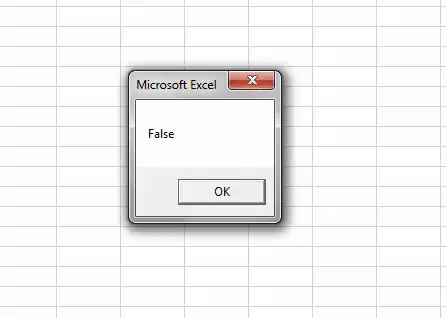
Sub Boolean_Example2() Dim Number1 As Integer Dim Number2 As Integer Number1 = 80 Number2 = 75 If Number1 >= Number2 Then MsgBox True Else MsgBox False End If End Sub
Like this, we can use Excel VBA Boolean data types to store the results as either TRUE or FALSE.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA Boolean Operator. Here, we learn how to use Boolean data type in Excel VBA, which gives the logical output, i.e., TRUE or FALSE, along with examples and downloadable templates. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA End Function
- Use IF OR Function in VBA
- IFERROR Function in VBA
- Do Until Loop in VBA
Содержание
- Тип данных Boolean (Visual Basic)
- Remarks
- Преобразования типов
- Советы по программированию
- Пример
- Boolean Data Type in Excel VBA
- Boolean VBA Data Type Syntax in Excel
- Example on the Boolean VBA Data Type when value is TRUE
- Example on the Boolean VBA Data Type when value is TRUE
- Convert an Expression to Boolean VBA Data Type in Excel
- VBA Data Types
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
- Other Useful Resources:
- VBA Boolean Data Type (Dim Variable)
- Boolean Variable Type
- Declare Boolean Variable at Module or Global Level
- Module Level
- Global Level
- Using a Boolean Variable
- Using Boolean Operators
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- Using the AND operator
- Using the OR operator
- Using the NOT operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- VBA Boolean
- Excel VBA Boolean Operator
- Working with Boolean Data Type in VBA Programming Language
- Boolean Data Type Cannot Hold Other than TRUE or FALSE.
- All the Numbers are TRUE, and Zero is FALSE
- VBA Boolean Operator with IF Condition
- How to☝️ Use the Boolean Data Type in Excel VBA
- Declaring Boolean Variables
- Example #1: Using Boolean Variables
- Example #2: Boolean Variables & IF Statements
- Boolean Operators
- The AND Operator
- The NOT Operator
- The XOR Operator
Тип данных Boolean (Visual Basic)
Содержит значения, которые могут быть только True или False . Ключевые True слова и False соответствуют двум состояниям переменных Boolean .
Используйте логический тип данных (Visual Basic), чтобы содержать значения двух состояний, такие как true/false, да/нет или вкл./выкл.
Значением свойства Boolean по умолчанию является False .
Boolean значения не хранятся в виде чисел, а сохраненные значения не должны быть эквивалентными числам. Никогда не следует писать код, основанный на эквивалентных числовых значениях и True False . По возможности следует ограничить использование Boolean переменных логическими значениями, для которых они разработаны.
Преобразования типов
При Visual Basic преобразует числовые значения Boolean типов данных в значение 0 False и все остальные значения становятся True . Когда Visual Basic преобразует Boolean значения в числовые типы, False он становится 0 и True становится -1.
При преобразовании между Boolean значениями и числовыми типами данных следует помнить, что методы преобразования платформа .NET Framework не всегда создают те же результаты, что и ключевые слова преобразования Visual Basic. Это связано с тем, что преобразование Visual Basic сохраняет поведение, совместимое с предыдущими версиями. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе «Логический тип не преобразуется в числовой тип точно» в разделе «Устранение неполадок типов данных».
Советы по программированию
Отрицательные числа. Boolean не является числовым типом и не может представлять отрицательное значение. В любом случае не следует использовать Boolean для хранения числовых значений.
Символы типов. Boolean не имеет символа литерального типа или символа типа идентификатора.
Тип Framework. В .NET Framework данный тип соответствует структуре System.Boolean.
Пример
В следующем примере runningVB это переменная Boolean , в которой хранится простой параметр yes/no.
Источник
Boolean Data Type in Excel VBA
Boolean Data Type in Excel VBA explained with syntax and examples. We use the Boolean VBA data type to store logical data. The Boolean VBA data type contains only two states of values either TRUE or FALSE. In other words we can also refer as 1 for True and 0 for False. The default value is False. It is most common frequently used VBA data type to represent True or False. It occupies 2 bytes(16 bits) in memory. We can convert number or numeric data type to boolean data type by using CBool VBA conversion function. Here True and False are keywords in VBA. It doesn’t have literal.
Boolean VBA Data Type Syntax in Excel
Let us see Data Type Boolean Syntax in Excel VBA.
Where VariableName represents the name of the variable.
and Boolean represents the type of data.
Example on the Boolean VBA Data Type when value is TRUE
Here is an example on the Boolean VBA Data Type in Excel.
Example on the Boolean VBA Data Type when value is TRUE
Here is an example on the Boolean VBA Data Type in Excel.
Convert an Expression to Boolean VBA Data Type in Excel
You can convert an expression to Boolean VBA data type using VBA CBool function. Click on the following link to learn about CBool function and complete tutorial and examples.
VBA Data Types
Also read about all other data types. VBA Data Types
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
Источник
VBA Boolean Data Type (Dim Variable)
In this Article
Boolean Variable Type
The VBA Boolean data type is used to store True or False values. True can also be represented by 1 and False by 0.
To declare an Boolean variable, you use the Dim Statement (short for Dimension):
Then, to assign a value to a variable, you simply use the equal sign:
When you put this in a procedure, it could look like this:
If you run the code above, the following message box will be shown.
Declare Boolean Variable at Module or Global Level
In the previous example, we’ve declared the Boolean variable within a procedure. Variables declared with a procedure can only be used within that procedure.
Module Level
You declare Module level variables at the top of code modules with the Dim statement.
These variables can be used with any procedure in that code module.
Global Level
You also declare Global level variables at the top of code modules. However, instead of using the Dim statement, you would use the Public statement to indicate that the Boolean variable is available to be used throughout your VBA Project.
If you were to declare the Boolean variable at a module level and then try to use it in a different module, you would get an error.
However, if you had used the Public keyword to declare the Boolean variable, the error would not occur and the procedure would run perfectly.
Using a Boolean Variable
You use the Boolean variable in logical comparison. These are often used with If statements to test if a condition is True or False as per the example above, or in a line of code to apply a logical test – perhaps to see if one value is greater than another.
If you run the code above, you will get the following message box.
because of course 45 is not greater than 68!
Using Boolean Operators
As Boolean variables are used in logical comparison, we can use the logical operators AND and OR to test to see if more than one condition is true or false.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Using the AND operator
We can use the AND function to see if BOTH conditions are met.
or we could run the same test using an If Statement:
Both examples above would return FALSE due to the fact that 10 is NOT greater than 13 – and BOTH conditions have to be True for the Boolean to be True.
Using the OR operator
We can use the OR function to see if ONE OF the conditions is met.
or we could run the same test using an If Statement:
These examples would return TRUE due to the fact that 10 is NOT greater than 13 BUT 15 IS greater than 12 – and ONLY ONE condition has to be True for the Boolean to be True.
Using If statements allows us to use more logical operators
Using the NOT operator
We can also use the NOT operator with the Boolean variable. The NOT operator negates the value of the condition – so if a condition is true, the NOT operator will return false.
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator is used to compare two or more conditions. If one of the conditions is true, it will return TRUE. If there are 2 conditions, and NEITHER are true or BOTH are true, it will return FALSE.
In the above example, as ONE of the conditions is TRUE, the message box will return TRUE.
However, in the example above, as BOTH conditions are true, the message box will return FALSE.
and finally, as both conditions are FALSE, the message box will also return FALSE.
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
VBA Boolean
Excel VBA Boolean Operator
Boolean is a data type. It is also a built-in data type in VBA. This data type is used for logical references or logical variables because the value this data type holds is either TRUE or FALSE, used for logical comparison. The declaration of this data type is similar to all the other data types.
As we said, the Boolean data type can hold either TRUE or FALSE as the data, but it can also hold number 1 as TRUE and 0 as FALSE. So, TRUE is represented by 1, and FALSE is represented by 0. So, when we declare the variable as BOOLEAN, it occupies 2 bytes of computer memory.
Table of contents
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Boolean (wallstreetmojo.com)
Working with Boolean Data Type in VBA Programming Language
Step 1: First, start the subprocedure by naming the macro name.
Code:
Step 2: Declare the variable as “BOOLEAN.”
Code:
Code:
Code:
We got the result as TRUE because the number 25 is greater than the number 20, so the logical test is correct, and the result is TRUE.
It is the basic structure of VBA Boolean data types.
Boolean Data Type Cannot Hold Other than TRUE or FALSE.
VBA Boolean is a logical data type. It holds either TRUE or FALSE. Anything other than TRUE or FALSE will show an error message as “Type Mismatch” in VBA.
For example, look at the below code.
Code:
In the above code, we have declared the variable “BooleanResult” as Boolean.
In the next line, we have assigned the value to the declared variable as “Hello.”
We have declared the variable as Boolean, but we have assigned the value as “Hello,” which is other than logical values: TRUE or FALSE.
When we run this code using the F5 key or manually, we will get the type mismatch error because of the data type mismatch value.
All the Numbers are TRUE, and Zero is FALSE
As we said, TRUE is represented by the number 1, and FALSE is represented by 0. For example, look at the below code in VBA.
Code:
We assigned the value to the variable as 1, showing the result as TRUE.
Now, look at the code below.
Code:
In this code, we have assigned the value to the variable as 0, showing the result as FALSE.
Not only 1 or 0, but it can also treat any number assigned to the variable except zero as TRUE. It will only treat zero as 1.
VBA Boolean Operator with IF Condition
Since the Boolean data type can hold only logical values, it is best suited to use with the IF condition in VBA.
Code:
Like this, we can use Excel VBA Boolean data types to store the results as either TRUE or FALSE.
Источник
How to☝️ Use the Boolean Data Type in Excel VBA
This Article Contains:
VBA Boolean data type can only be either TRUE or FALSE – expressed either as “1” (TRUE) or “0” (FALSE).
Boolean values are commonly used with IF statements to verify whether a given condition is met or not, allowing you to build complex logical comparisons.
A blank canvas in the VBA editor is waiting for us, so let’s get started.
Declaring Boolean Variables
First things first, let’s start with declaring Boolean variables so that you can use them in your VBA code.
There are two ways to declare a Boolean variable:
- on the module level, meaning the variable can only be used within a given module
- on the global level, meaning the variable can be used across the entire VBA project
Use the following Dim statement to create a Boolean value on the module level:
On the other hand, copy this public statement to create a global Boolean variable:
Example #1: Using Boolean Variables
Let’s move from theory to practice.
The examples below demonstrate how to use the Boolean data type in VBA.
Start with creating a new module (Insert > Module). Once there, copy the following code into the VBA editor and click “Run Sub/UserForm” or press F5 to execute it:
This simple Sub procedure compares whether 50 is greater than 115 and returns a message box with the corresponding Boolean value based on this simple logical comparison.
Let’s take a closer look at the VBA code to help you adjust accordingly:
- Dim BooleanValue As Boolean – This line of code creates a new variable named “BooleanValue” and converts it to the Boolean data type.
- BooleanValue = 50 > 115 – This determines the actual Boolean value of the variable based on the specified logical comparison. If 50 is greater than 115, the value is set to TRUE. If not, the value is set to FALSE.
- MsgBox BooleanValue – This VBA command creates a message box containing the output.
Predictably, VBA returns FALSE since 50 is not greater than 115.
Example #2: Boolean Variables & IF Statements
That was a simple example, so let’s ramp up the difficulty level and break down how you can use the VBA Boolean data type with IF statements.
Imagine you’re overseeing a web development project where the devs are getting paid based on their hourly rate. Your fictitious company allocated 54 hours to the project.
Armed with this data (and the knowledge of how to apply Boolean values), you can put together a simple IF statement to check if the project runs over budget at any stage of the development process:
The screenshot below breaks down the building blocks of this Sub procedure in greater detail:
As a result, VBA will return this message box to help you spot any project cost overrun.
Boolean Operators
In VBA, Boolean operators make it possible for you to work with combinations of Boolean variables, providing you a lot more flexibility.
The four most common Boolean operators in VBA are AND, OR, NOT, and XOR. In this section, we will show you how to use each of them.
The AND Operator
The AND operator connects two or more Boolean expressions and returns TRUE only if all of the conditions are met.
In the example below, the variable “Result” equals TRUE only if both the first condition (50 > 155) and the second condition (50 The OR Operator
The OR operator returns TRUE if at least one of the conditions is met.
In the same example, the variable “Result” equals TRUE if either the first or second condition is TRUE.
Result: TRUE
The NOT Operator
The NOT operator turns TRUE into FALSE, and vice versa.
In this example, since 50 is not greater than 155, the VBA editor should return FALSE. However, since the NOT operator is applied, it takes truth to falsity. Another variation is the not-equal-to operator (<>) that works in a similar way.
Result: TRUE
The XOR Operator
The XOR operator returns TRUE only if two conditions are not TRUE or FALSE at the same time.
In the example below, the “Result” variable is TRUE because the first condition (50 > 155) is FALSE while the second condition (50 Usage Notes
1. The default Boolean value is FALSE.
Result: FALSE
2. By default, every nonzero number is TRUE.
Result: TRUE
3. Zero is equal to FALSE.
Result: TRUE
4. Boolean values can’t be anything but TRUE or FALSE. If you try to turn a Boolean variable into any other data type, this breaks the code and triggers an error.
Result: a type-mismatch error – as shown on the screenshot below.
Источник