In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
Contents
- 1 What is word analysis in kindergarten?
- 2 What is a word level analysis?
- 3 What does analysis mean in an essay?
- 4 What is analysis in an essay?
- 5 What is text analysis used for?
- 6 What is word structure analysis?
- 7 What is content analysis?
- 8 What is word analysis on Istation?
- 9 How do you teach reading analysis?
- 10 What information about the word compliment can be found?
- 11 What is word analysis in NLP?
- 12 What are 3 types of word parts?
- 13 How do you analyze a text?
- 14 How do you write a good analysis paragraph?
- 15 What is analysis in English literature?
- 16 How do you Analyse information?
- 17 How do you write an analysis of a poem?
- 18 What is analysis of text called?
- 19 How do you respond to a text analysis?
- 20 What is the breakdown of words called?
What is word analysis in kindergarten?
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes.As such, students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and build their vocabulary.
What is a word level analysis?
Word analysis is a process of learning more about word meanings by studying their origins and parts. A “morpheme” is the smallest meaningful part of a word. Other terms for word analysis: Morphemic analysis. Word study.
What does analysis mean in an essay?
When asked to write an analysis, it is not enough to simply summarize. Analysis means breaking something down into its various elements and then asking critical thinking questions such as WHY and HOW in order to reach some conclusions of your own.
What is analysis in an essay?
Analytical essays usually concentrate on how the piece was written – for example how certain themes present themselves in a story. Thesis Statement To analyze something is to ask what that something means. An analytical essay answers how something does what it does or why it is as it is.
What is text analysis used for?
Text Analysis is about parsing texts in order to extract machine-readable facts from them. The purpose of Text Analysis is to create structured data out of free text content. The process can be thought of as slicing and dicing heaps of unstructured, heterogeneous documents into easy-to-manage and interpret data pieces.
What is word structure analysis?
Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. Structural analysis is a powerful vocabulary tool since knowledge of a few word parts can give you clues to the meanings of a large number of words.Roots – the basic meaningful part of a word.
What is content analysis?
Content analysis is a research tool used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within some given qualitative data (i.e. text). Using content analysis, researchers can quantify and analyze the presence, meanings and relationships of such certain words, themes, or concepts.
What is word analysis on Istation?
Spelling or Word Analysis
The Spelling assessment measures your child’s ability in applying Letter Knowledge and Alphabetic Decoding skills to correctly spell words.
How do you teach reading analysis?
Engaging and Effective Literary Analysis Activities
- First, acknowledge what is confusing or uncertain about the text.
- Second, make observations.
- Third, apply reading strategies (in this case, I used visualizing).
- Last, teach students to ask questions that probe at the deeper meaning and reason for the writing.
What information about the word compliment can be found?
an expression of praise, commendation, or admiration: A sincere compliment boosts one’s morale. a formal act or expression of civility, respect, or regard: The mayor paid him the compliment of escorting him. compliments, a courteous greeting; good wishes; regards: He sends you his compliments.
What is word analysis in NLP?
A regular expression (RE) is a language for specifying text search strings. RE helps us to match or find other strings or sets of strings, using a specialized syntax held in a pattern. Regular expressions are used to search texts in UNIX as well as in MS WORD in identical way.
What are 3 types of word parts?
Many words in the English language are made up of word parts called prefixes, roots, and suffixes. These word parts have specific meanings that, when added together, can help you determine the meaning of the word as a whole.
How do you analyze a text?
How to analyze a text?
- Read or reread the text with specific questions in mind.
- Marshal basic ideas, events and names.
- Think through your personal reaction to the book: identification, enjoyment, significance, application.
How do you write a good analysis paragraph?
Here is a step-by-step guide for writing an analytical essay.
- Choose a point of view.
- Write an introductory paragraph ending in a thesis statement.
- Carefully organize the body of your essay.
- Craft clear topic sentences.
- Populate your essay with evidence.
- Provide space for contrasting opinions.
What is analysis in English literature?
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
How do you Analyse information?
Process: How to Analyze Information
- Decide where you can find the information that you need.
- Gather the information from the sources that you identified.
- Quickly skim and scan the information.
- Determine accuracy, relevance and reliability of information.
- Differentiate – is there anything unique about the information?
How do you write an analysis of a poem?
Follow this step-by-step guide to analyze a poem:
- Read the poem. The first time you approach a poem, read it to yourself.
- Read the poem again, this time aloud.
- Map out the rhyme scheme.
- Scan the poem.
- Break down the structure.
- Determine the form of the poem.
- Study the language in the poem.
- Study the content of the poem.
What is analysis of text called?
Text analysis, also known as text mining, is the process of automatically classifying and extracting meaningful information from unstructured text.Another term you may have heard is text analytics.
How do you respond to a text analysis?
Use strong and thorough evidence from the text to support your analysis. Do not simply summarize the text. You may use the margins to take notes as you read and scrap paper to plan your response. Write your response in the spaces provided on pages 7 through 9 of your essay booklet.
What is the breakdown of words called?
The word etymology derives from the Greek word ἐτυμολογία (etumología), itself from ἔτυμον (étumon), meaning “true sense or sense of a truth”, and the suffix -logia, denoting “the study of”. The term etymon refers to a word or morpheme (e.g., stem or root) from which a later word or morpheme derives.
Asked by: Estibaliz Tieres
asked in category: technology and computing Last Updated: 19th October, 2020
Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. Structural analysis is a powerful vocabulary tool since knowledge of a few word parts can give you clues to the meanings of a large number of words.
Read full answer here. Keeping this in consideration, what are structure words?
Structure-class words, sometimes called function words, are words that signal how the form- class words (sometimes referred to as “content words”) relate to each other in a sentence.
Also, what are the different types of structure? Structures can be classified in a number of ways: Type: Solid.
- One-dimensional: Ropes, cables, struts, columns, beams, arches.
- Two-dimensional: Membranes, plates, slabs, shells, vaults, domes, synclastic, anticlastic.
- Three-dimensional: Solid masses.
- Composite. A combination of the above.
Subsequently, one may also ask, what is the suffix of analysis?
analyze — Suffix canvas; study; analyse; examine; canvass; analyze.
What is the structure of a writing?
Structure refers to the order of ideas; the progression of your writing should feel smooth with similar points linked together. Structuring your work is a key aspect of good academic writing ensuring that related sections are linked together and that the ideas and arguments progress in a logical and orderly manner.
- Размер: 241.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 21

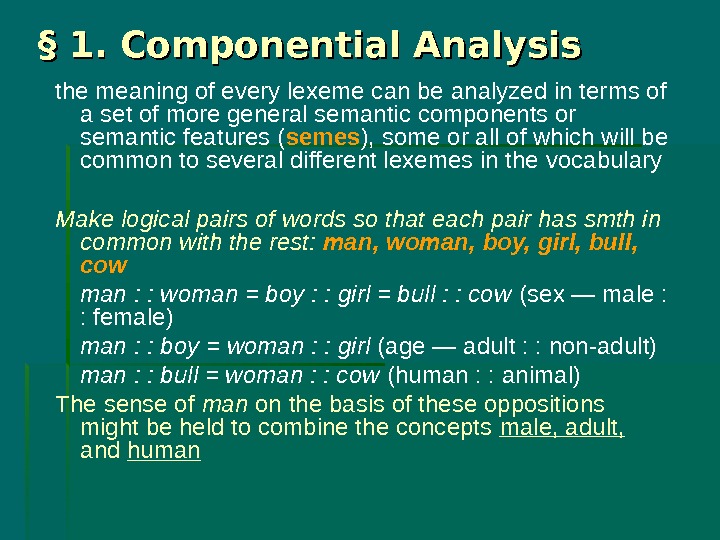


















Table of Contents
- What is word analysis?
- What is structural analysis of a word?
- How do you analyze structure in English?
- How do you write a structure analysis?
- What is the structure of an analysis?
- How do you write an analysis outline?
In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
What is structural analysis of a word?
Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. Structural analysis is a powerful vocabulary tool since knowledge of a few word parts can give you clues to the meanings of a large number of words.
How do you analyze structure in English?
When you analyse the structure of sentences, you can discuss the following elements:
- The sentence length (if it is particularly short or particularly long).
- The first or last word of the sentence (if they are noticeable for a particular reason).
- Repetition of words, word classes, or structures within the sentence.
How do you write a structure analysis?
Analytical Essay Structure
- Introduction: Introduce your topic. …
- Thesis statement: This is where you state your intentions for the essay. …
- Main body: This will always differ, depending on what you’re analysing. …
- Conclusion: this is where you’ll draw all your points together, and restate your thesis.
What is the structure of an analysis?
In most cases, an analytical essay will include an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your analytical essay should outline at least three main arguments that must be present in both thesis and body paragraphs. Remember to list all the main points in your analytical essay structure.
How do you write an analysis outline?
Add in the information from the topic and continue to add details as research progresses.
- Introduction. Hook. …
- Main Point 1. Topic Sentence: First Answer/ Example to Question. …
- Main Point 2. Topic Sentence: Second Answer/ Example to Question. …
- Main Point 3. Topic Sentence: Third Answer/ Example to Question. …
- Conclusion.
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
What does word analysis mean?, Word analysis is a process of learning more about word meanings by studying their origins and parts. A “morpheme” is the smallest meaningful part of a word. Other terms for word analysis: Morphemic analysis.
Furthermore, How do you analyze a word?, In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
Finally, What is analysis of word structure?, Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. … When using structural analysis, the reader breaks words down into their basic parts: Prefixes – word parts located at the beginning of a word to change meaning. Roots – the basic meaningful part of a word.
Frequently Asked Question:
How do you teach the word meaning?
How to teach:
- Introduce each new word one at a time. Say the word aloud and have students repeat the word. …
- Reflect. …
- Read the text you’ve chosen. …
- Ask students to repeat the word after you’ve read it in the text. …
- Use a quick, fun activity to reinforce each new word’s meaning. …
- Play word games. …
- Challenge students to use new words.
How do you understand words meaning?
To understand a word without a dictionary, try re-reading the entire sentence to see if the context helps you to find out what the word means. If it’s unclear, try to figure it out by thinking about the meaning of the words you’re familiar with, since the unknown word might have a similar meaning.
How do you teach word concepts?
The first step with Concept of Word Instruction is to teach the poem to the students. They need to have the poem memorized, so that they can accurately match the memorized words to the print they see. Teachers can use pictures that represent the text or hand motions with common nursery rhymes and finger plays.
How do you teach words with multiple meanings?
Play word games that ask students to recognize words‘ multiple meanings. For example, create—or have students illustrate—pairs of cards to tell or show two meanings of a specific word. Use the cards to play a matching game. Students should collect both pictures for a word and give a verbal definition of each picture.
How can we help students to understand meaning?
Follow these steps and try some different techniques in your classroom:
- Choose a lesson from your textbook. …
- Before the lesson, select some words that you think your students won’t know. …
- Decide how you could help your students understand these words. …
- Before your students read the lesson, write the words on the board.
What does structural analysis mean?
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS is a strategy that is used to facilitate decoding as students become more proficient readers. These advanced decoding strategies help students learn parts of words so they can more easily decode unknown multi-‐syllabic words. In structural analysis, students are taught to read prefixes and suffixes.
What is structure in structural analysis?
1.1 Structural Analysis Defined. A structure, as it relates to civil engineering, is a system of interconnected members used to support external loads. Structural analysis is the prediction of the response of structures to specified arbitrary external loads.
What is word analysis?
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
What are the types of structural analysis?
What are the types of Structural Analysis?
- Hand Calculations. Hand Calculations in Structural Analysis. …
- Finite Element Analysis. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) …
- Structural Analysis Software.
What is structural analysis of words?
Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. … When using structural analysis, the reader breaks words down into their basic parts: Prefixes – word parts located at the beginning of a word to change meaning. Roots – the basic meaningful part of a word.
How do I teach word study?
A cycle of instruction for word study might include the following:
- introduce the spelling pattern by choosing words for students to sort.
- encourage students to discover the pattern in their reading and writing.
- use reinforcement activities to help students relate this pattern to previously acquired word knowledge.
How do you teach the word meaning?
How to teach:
- Introduce each new word one at a time. Say the word aloud and have students repeat the word. …
- Reflect. …
- Read the text you’ve chosen. …
- Ask students to repeat the word after you’ve read it in the text. …
- Use a quick, fun activity to reinforce each new word’s meaning. …
- Play word games. …
- Challenge students to use new words.
What are some strategies for breaking words apart to get their meaning?
5 Ways To Have K-2 Students Practice Breaking Apart Words
- Segment the sounds in a CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) word.
- Read the onset and rime of a word (i.e. sh-ip)
- Recognize and read word families.
- Read “smaller” words inside compound words.
- Derive meaning from root words, prefixes, and suffixes.
What is word analysis?
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
How do you analyze a word?
In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
What is analysis example?
The definition of analysis is the process of breaking down a something into its parts to learn what they do and how they relate to one another. Examining blood in a lab to discover all of its components is an example of analysis. noun.
What is Analysis sentence?
The purpose of analysis is to make the complete grammatical structure of a sentence clear. Each part of the sentence is identified, its function des- cribed, and its relationship to the other parts of the sentence explained. There are different ways of presenting a sentence analysis.

