Asked by: Gussie Luettgen III
Score: 4.8/5
(48 votes)
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix un- is added to the word happy, it creates the word unhappy.
What is an example of a prefix word?
A prefix is a group of letters placed before the root of a word. For example, the word “unhappy” consists of the prefix “un-” [which means “not”] combined with the root (or stem) word “happy”; the word “unhappy” means “not happy.”
What is a suffix word example?
countable noun. A suffix is a letter or group of letters, for example ‘-ly’ or ‘-ness,’ which is added to the end of a word in order to form a different word, often of a different word class. For example, the suffix ‘-ly’ is added to ‘quick’ to form ‘quickly.
What is an example of a base word?
A base word can stand alone and has meaning (for example, help). A suffix is a word part added to the end of a word (for example, -ful). If you add the suffix -ful to the base word, help, the word is helpful. A prefix is a word part added to the beginning of a word or base word (for example, un-).
What is a affix word?
An affix is officially defined as “a bound inflectional or derivational element, as a prefix, infix, or suffix, added to a base or stem to form a fresh stem or a word, as –ed added to want to form wanted, or im– added to possible to form impossible.”
43 related questions found
What is the base word for beginning?
beginning (n.)
1200, «initial stage or first part,» verbal noun from begin. Meaning «act of starting something» is from early 13c. The Old English word was fruma (see foremost).
What is the base word of unhappy?
The root word in unhappy is happy; ‘un’ is a prefix. … The root word in exciting is excite; ‘ing’ is a suffix.
What is the base word?
A base word is a complete word that can stand alone. It can also be combined with a word part, such as a prefix, to form a new word. A prefix attaches to the beginning of a base word, altering or adding meaning to it. For example, consider the word impolite.
What is the most common suffix?
The most common suffixes are: -tion, -ity, -er, -ness, -ism, -ment, -ant, -ship, -age, -ery.
How do you use name suffix?
The suffix is an explanation of the first name, not the last. «John Doe Jr.» means he is John, the son of John. In a full name listing, the suffix follows the last name because the person is primarily known by is given name and surname, the suffix being a secondary piece of information.
What is a word with a prefix and suffix?
A basic word to which affixes (prefixes and suffixes) are added is called a root word because it forms the basis of a new word. The root word is also a word in its own right. For example, the word lovely consists of the word love and the suffix -ly.
What is a prefix and examples?
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix un- is added to the word happy, it creates the word unhappy. … In English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose.
What is the root or base word for illegal?
The root word of illegality is legal, which is from the Latin word legalis, which means related to or pertaining to the law.
How do you find the base of a word?
A base word is the core unit of the word that has no extra parts. While the base word gives the basic meaning of the word, the addition of prefixes, letters added to the beginning of words, and suffixes, letters added to the end of words, will change the base word’s meaning.
How do you describe an unhappy person?
1 unhappy, despondent, disconsolate, discouraged, gloomy, downcast, downhearted, depressed, dejected, melancholy.
What is a beginning word?
Words related to beginning
outset, opening, introduction, inauguration, creation, onset, birth, inception, dawn, top, heart, origin, dawning, rudiment, infancy, spring, preface, kickoff, takeoff, threshold.
How do you use the word beginning?
Beginning sentence example
- She gazed up at him, her heart beginning to flutter. …
- She was beginning to relax when he launched the question. …
- I was beginning to be vexed with you. …
- She was beginning to get a bad feeling. …
- He was beginning to hate the cold. …
- Why, we were beginning to despair!
What is a correct pronunciation?
Pronunciation is the way in which a word or a language is spoken. This may refer to generally agreed-upon sequences of sounds used in speaking a given word or language in a specific dialect («correct pronunciation») or simply the way a particular individual speaks a word or language.
What is a affix in grammar?
Affix, a grammatical element that is combined with a word, stem, or phrase to produce derived or inflected forms. There are three main types of affixes: prefixes, infixes, and suffixes.
What is an infix in grammar?
An infix is an affix inserted inside a word stem (an existing word or the core of a family of words). It contrasts with adfix, a rare term for an affix attached to the outside of a stem such as a prefix or suffix.
Prefixes in English Grammar
In the English language, there are times when we come across a one-two syllable, or a group of letters being added to a base word to alter its meaning. For example, let us the consider the word “possible”. Adding the letters “im-” before it creates a new word called impossible which means the opposite of possible.
Such type of syllables or group of letters (im-) are called prefixes and they play a key role in English grammar. Knowledge of prefixes are helpful in enhancing vocabulary and comprehension.
What Is a Prefix in English?
Prefix is a group of letters (sometimes a single letter) which is added at the start of a base word to alter its meaning. These letters are affixes. Affixes do not have any significance or meaning when used independently. They are either added before or after words to create new words with new meanings. When affixes are added before a word, they are called prefixes and when they are added after a word, they are known as suffixes.
Example of a prefix: Use of the letters “hemi-” before the word ”sphere” to create a new word hemisphere which means half of a sphere.
When to Use Prefixes
Prefixes can be used for multiple purposes. One of the common uses of prefixes is to mean the opposite or negative of the base word. For example, using the prefix “un-” before necessary to create the word unnecessary or using “dis-” before approve to form disapprove. Both the new words unnecessary and disapprove are the opposites of their base words respectively.
Prefixes are also used to reduce a sentence or a phrase to a single word without changing. For example, instead of saying “He is showing way too much confidence than required”, we can simply say “He is overconfident”.
How to use prefixes
It is important to understand the way prefixes are used. It should be noted that while adding a prefix to a base word, there should not be a change in the spelling of either the base word or the prefix. For example: unkind (combination of “un-” and “kind”). Even if it leads to double consonants, the same rule should be followed. Example: coordinate, irresponsible.
There are also certain rules that need to be followed while using hyphen to join prefixes with words. This will be discussed in the next section.
Writing Prefixes With Hyphens
Use of hyphens in prefixes can be confusing as some prefixes use hyphens while some don’t. Also, there are certain prefixes which may or may not use prefixes based on their meanings. Let is take the case of the prefix “ex-“. There are two meanings of this prefix- “belonging to the past” and “out of/from”. When it means belonging to the past, hyphens are used (ex-husband, ex-president). When it means “out of/ from”, then hyphens are not required (exterritorial, exstipulate)
Hyphens are used when prefixes are added to proper nouns. Example: pro-Nazi, un-Indian, trans-Pacific.
Hyphens are required when the prefix ends with a vowel and the base word starts with the same vowel. Common examples include re-enter, semi-industrious, semi-independent. However, English is a language of exceptions and for some cases, if the vowel is “o” for both the prefix and the word, then the hyphen is not required. For example: coordinate, cooperate.
When the prefix ends with a vowel and the base word starts with a different vowel, hyphens are not required. For example: hydroelectricity, proactive, reactivate.
35 Most Common Prefixes in English
Here are some of the most common prefixes in English with their meanings and examples.
Ambi-
Meaning: both and around
Examples: ambidextrous, ambivalence, ambiguous, ambidexterity
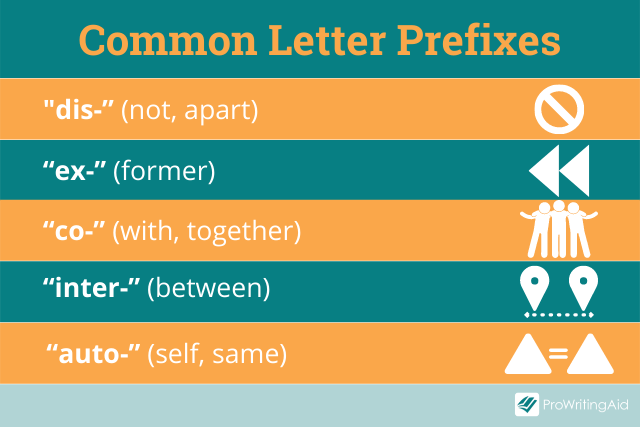
Co-
Meaning: together
Examples: coexist, correlation, colleague, co-worker
Anti-
Meaning: against
Examples: anti-national, antibiotic, antibody, antisocial
Mono-
Meaning: one
Examples: Monogamy, monotonous, monolingual, monologue
Semi-
Meaning: half
Examples: Semifinal, semicircle, semiautomatic, semiconscious
Sub-
Meaning: below
Examples: subconscious, subtropical, submerge, subordinate
Un-
Meaning: opposite or not
Examples: unacceptable, unabashed, unlike, unfair
Uni-
Meaning: one
Examples: universe, unilateral, unicycle, uniform
Under-
Meaning: not enough
Examples: underage, underperform, undervalue, underrate
In-
Meaning: opposite or not
Examples: insufficient, insane, independent, invalid
Bi-
Meaning: two
Examples: bilingual, bicycle, biweekly, bilateral
Homo-
Meaning: same
Examples: homogenous, homogeny, homosexual, homonym
Contra-
Meaning: against or opposite
Examples: contradict, contraceptive, contrary, contradictory
Dis-
Meaning: opposite or not
Examples: dislike, disintegrate, dishonour, disappear
Em-
Meaning: to make or put into
Examples: empathy, empirical, emphasis, embankment
Hetero-
Meaning: different
Examples: heterosexual, heterogeneous, heterogamous, heteronomous
Hind-
Meaning: after or back
Examples: hindsight, hindlimb, hindwing, hindquarters
Im-
Meaning: opposite or not
Examples: Immoral, impatient, impartial, imperfect
Inter-
Meaning: between
Examples: interstate, international, intermediate, interaction
Mis-
Meaning: wrong
Examples: miscommunication, miscalculate, misconception, misfortune
Trans-
Meaning: across or changed
Examples: transform, translate, translucent, transgender
Tri-
Meaning: three
Examples: triangle, tripod, trilingual, triathlon
Non-
Meaning: without
Examples: nonsense, non-alcoholic, nonstop, non-fiction
On-
Meaning: near or connected
Examples: onset, online, ongoing, onlooker
Pan-
Meaning: all
Examples: pandemic, pan-Indian, pansexual, pancreatic
Ped-
Meaning: foot
Examples: pedicure, pedestrian, pedal, pedometer
Post-
Meaning: after
Examples: postpone, postseason, postgraduate, postnatal
Pre-
Meaning: before
Examples: prepone, precaution, prejudice, premeditated
Pro-
Meaning: forward or for
Examples: progress, product, promise, procrastinate
Re-
Meaning: again
Examples: research, repeat, rework, recycle
Sur-
Meaning: over
Examples: surface, surcharge, surplus, surpass
Twi-
Meaning: two
Examples: twin, twice, twi-headed
Ultra-
Meaning: beyond
Examples: ultra-conservative, ultraviolet, ultrasound, ultrasonic
Extra-
Meaning: more than
Examples: extraterrestrial, extra-curricular, extramarital, extraordinary
Up-
Meaning: higher or better
Examples: uphill, upgrade, update, upturned
How to Learn Prefixes in English
Prefixes are hidden in thousands of words and it is important to learn them to improve vocabulary skills. One of the best ways to learn prefixes is by creating a list of the most popular prefixes and studying them. Try to understand how they are used in a sentence to know them better.
Taking online tests, quizzes can also go a long way to help you get accustomed to prefixes. Sources of visual entertainments like movies, videos, tv series can also aid you to learn prefixes. Keep the subtitles on if it is difficult to understand and interpret the audio.
Examples on Prefixes in English Grammar
Some of the most common examples of Prefixes are:
1. Unpopular
2. Bicycle
3. Misunderstanding
4. Prepone
5. Online
6. Underage
7. Coexist
8. Pandemic
9. Independent
10. Extraordinary
Practice questions on Prefixes in English Grammar
1. Put words in the blanks as per required.
Que. She was ________. She started crying. (happy)
A. Unhappy
Que. I think you should ________ the decision. The move will have big consequences. (consider)
A. Reconsider
Que. Even though she is young, she is quite ________ (dependent)
A. Independent
Que. All these quarrels have made him ________ among his peers. (popular)
A. Unpopular
2. Write prefixes that mean the Opposite of the following words-
a) Agree- disagree
b) Correct- incorrect
c) Fold- unfold
d) Spell- misspell
e) Behave- misbehave
f) Connect- disconnect
g) Understand- misunderstand
Frequently Asked Questions on Prefixes
Que 1. What is Prefix?
Prefix is a group of letters (sometimes a single letter) which is added at the start of a base word to alter its meaning.
Example of a prefix: Use of the letters “hemi-” before the word ”sphere” to create a new word hemisphere which means half of a sphere.
Que 2. How do Prefixes work?
Prefixes work by getting added to a base word and changing the meaning of it. They are an integral part of the English language. They are always added before a word. Examples:
1. Please “postpone” the meeting.
2. The animals and birds “coexist” in an ecosystem.
3. She is “riding” a bicycle.
Que 3. How to use a Prefix?
It is important to understand the way prefixes are used. It should be noted that while adding a prefix to a base word, there should not be a change in the spelling of either the base word or the prefix. For example: unkind (combination of “un-” and “kind”). Even if it leads to double consonants, the same rule should be followed. Example: coordinate, irresponsible.
There are also certain rules that need to be followed while using hyphen to join prefixes with words. Hyphens are used when prefixes are added to proper nouns. Example: pro-Nazi, un-Indian, trans-Pacific.
Hyphens are required when the prefix ends with a vowel and the base word starts with the same vowel. Common examples include re-enter, semi-industrious, semi-independent. However, English is a language of exceptions and for some cases, if the vowel is “o” for both the prefix and the word, then the hyphen is not required. For example: coordinate, cooperate.
When the prefix ends with a vowel and the base word starts with a different vowel, hyphens are not required. For example: hydroelectricity, proactive, reactivate.
Que 4. How can we learn Prefixes?
One of the best ways to learn prefixes is by creating a list of the most popular prefixes and studying them.
Taking online tests, quizzes can also go a long way to help you get accustomed to prefixes. Sources of visual entertainments like movies, videos, tv series can also aid you to learn prefixes. Keep the subtitles on if it is difficult to understand and interpret the audio.
Que 5. What are the advantages of using Prefix?
Prefixes have the following advantages:
1. It can shorten a phrase into a single word. For example, instead of saying “He is showing way too much confidence than required”, we can simply say “He is overconfident”.
2. They can be used to mean the opposite of any word. Example: use- misuse, correct- incorrect.
What are the 10 examples of prefix?
10 Examples of Prefixes
- Sub- Definition: under. Example Sentence: He has never seen a blue submarine in the my life.
- Post- Definition: postgraduate.
- Auto- Definition: self.
- Un- Definition: not.
- Semi- Definition: half.
- Mis- Definition: Wrong, wrongly.
- Dis- Definition: Not, opposite of.
- Re- Definition: Again.
What is an example of prefix in a sentence?
10 Examples of Prefixes Used in a Sentence
| Prefix | Examples | Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Super– | superstar, supernatural | He became a superstar overnight. |
| Mis- | misjudge, misguided | If I’ve misjudged you, I’m terribly sorry. |
| Re- | rewrite, return | My boss told me to rewrite the report. |
| Mid– | midnight, midday | We reached Paris at midnight. |
What are the 5 examples of prefixes?
The prefixes are: anti-, auto-, counter-, de-, dis-, ex-, il-, in-, mis-, non-, over-, pre-, pro-, re-, un-.
What are the 20 prefixes?
20 Examples of Prefixes
| de-, dis- | opposite of, not | depose, detour, dehydrated, decaffeinated, discord, discomfort, disengage |
|---|---|---|
| en-, em- | cause to | enjoy, endure, enlighten, entail, empathy, |
| un- | opposite | uncover, unlock, unsafe, unemployment |
| semi- | half | semicircle, semiprecious, semicolon, semifinal |
| re- | again; back | rewrite, reread, return |
What are the 30 prefixes?
Prefix List
- a, ab, abs. Meaning: Away from. Example: Absent , Abscond.
- ad, a, ac, af, ag, an, ar, at, as. Meaning: To, toward. Example: Adapt , Adhere , Annex, Attract.
- ante. Meaning: Before.
- anti. Meaning: Against.
- auto. Meaning: Self.
- bi, bis. Meaning: Two.
- circum, cir. Meaning: Around.
- com, con, co,col. Meaning: With, together.
What are some common prefixes?
Common Prefixes
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| ante- | before, earlier, in front of | antecedent, antedate, antemeridian, anterior |
| anti- | against, opposite of | anticlimax. antiaircraft, antiseptic, antibody |
| auto- | self, same | autopilot, autobiography, automobile, autofocus |
| circum- | around, about | circumvent, circumnavigate, circumscribe |
What are the types of prefixes?
List of Common Prefixes:
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| ante | before | antedate (before date) |
| anti | against opposite of | antiseptic (against septic) anticlimax (opposite of climax) |
| auto | self | autobiography (self-biography) |
| bi | two | bilateral (two sides) |
What is prefix list?
A prefix list consists of an IP address and a bit mask. The bit mask is entered as a number from 1 to 32. An implicit deny is applied to traffic that does not match any prefix-list entry. You can configure prefix lists to match an exact prefix length or a prefix range.
What is prefix and examples?
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix un- is added to the word happy, it creates the word unhappy. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually bound morphemes.
What are prefixes words?
A prefix is a group of letters placed before the root of a word. For example, the word “unhappy” consists of the prefix “un-” [which means “not”] combined with the root (or stem) word “happy”; the word “unhappy” means “not happy.”
What is a prefix and suffix examples?
A suffix is a word part added to the end of a word (for example, -ful). If you add the suffix -ful to the base word, help, the word is helpful. A prefix is a word part added to the beginning of a word or base word (for example, un-).
What are prefix and suffix words?
A prefix is a word part added to the beginning of a word that changes the word’s meaning. A suffix is a word part added to the end of a word that changes the word’s meaning. Learning the meanings of prefixes and suffixes will help expand your vocabulary, which will help improve your writing.
Do all words have a prefix and suffix?
Words do not always have a prefix and a suffix. Some words have neither a prefix nor a suffix (read).
What is difference between prefix and suffix?
The suffix “s” can also be added to form the word “arms” which is the plural form of the word “arm.” Summary: 1. A prefix is an affix that is added before a root word or a stem to modify its meaning while a suffix is an affix that is added after a stem or root word.
How do you use prefix and suffix?
With prefixes, the start of the word will change. So if the prefix ends in a vowel, such as “a-“, a root word starting with a consonant will use it as it is, for example “atypical”. But if the root words starts with vowel as well, then a consonant is added in. With suffixes, the end of the word may change.
How do we use prefixes?
Prefixes are a syllable, or group of syllables, added to the beginning of a word to alter its meaning. Prefixes help to add complexity to the English language and make it possible to create new words that are easily understood by speakers everywhere.
What is suffix happy?
Suffix of happy is happiness.
How do I use suffix in Word?
Use keyboard shortcuts to apply superscript or subscript
- Select the text or number that you want.
- For superscript, press Ctrl, Shift, and the Plus sign (+) at the same time. For subscript, press Ctrl and the Equal sign (=) at the same time. (Do not press Shift.)
What is the suffix for a Word document?
File formats that are supported in Word
| Extension | Name of file format |
|---|---|
| .doc | Word 97-2003 Document |
| .docm | Word Macro-Enabled Document |
| .docx | Word Document |
| .docx | Strict Open XML Document |
How do you make a suffix?
A suffix is a letter or group of letters added to the end of a word. Suffixes are commonly used to show the part of speech of a word. For example, adding “ion” to the verb “act” gives us “action,” the noun form of the word. Suffixes also tell us the verb tense of words or whether the words are plural or singular.
How do you write 22 in words?
Ordinal number 22nd written in words: twenty-second, it indicates posion or order.
What is the suffix for easy?
easy – Suffix easy; leisurely. cushy; soft. what a cushy job!
What is suffix give example?
A suffix is a letter or group of letters, for example ‘-ly’ or ‘-ness’, which is added to the end of a word in order to form a different word, often of a different word class. For example, the suffix ‘-ly’ is added to ‘quick’ to form ‘quickly’. Compare affix and , prefix.
What are some common suffixes?
The most common suffixes are: -tion, -ity, -er, -ness, -ism, -ment, -ant, -ship, -age, -ery.
What is the suffix of your name?
A name suffix, in the Western English-language naming tradition, follows a person’s full name and provides additional information about the person. Post-nominal letters indicate that the individual holds a position, educational degree, accreditation, office, or honor (e.g. “PhD”, “CCNA”, “OBE”).
What is suffix in English?
A suffix is a letter or group of letters added at the end of a word which makes a new word.
How do you use the word suffix in a sentence?
Suffix in a Sentence ?
- Adding the suffix “tion” to the word “operate,” changes the word from a verb to a noun.
- When I was trying to figure out the meaning of the word, I realized that I knew the suffix of the word which helped me determine the full meaning.
- After studying affixes, Ms.
What is suffix in job application?
What does “suffix” mean on a job application? In a job application, a suffix is a word that follows your name, like Jr. (junior), Sr. (senior) and III (the third), or a relevant professional degree like JD (Juris Doctor), PhD (Philosophical Doctor) or MBA (Master in Business Administration).
Is Dr A suffix?
‘Dr’ or ‘DR’ are abbreviations, not suffixes. The most common use of ‘Dr’ is as an abbreviation of ‘doctor’ and is use as a title, e.g., ‘Dr Jones’. Similarly, ‘Mr’ is an abbreviation of ‘mister’. Angela, the placement of academic degree information after a person’s name is known as postnominals, and not suffix.
What is E word?
The e-word is “emotional.” If a man cries or shows his emotions, we say that he is “sensitive” or “sentimental.” Those words don’t carry the same negative connotation as “emotional,” which implies that your feelings are running rampant and you’ve lost control. Men can get away with it.
What does E in front of a word mean?
e stands for electronic We usually hyphenate these words when they are new.
What does the prefix E mean in eject?
out
Is exit a prefix?
Answer. Answer: An easy way to remember that the prefix ex- means “out” is through the word exit, for when you exit a room, you go “out” of it.
What is the root word of E?
Quick Summary. The prefixes e- and ex-, besides meaning “out,” can also act as intensive prefixes. For instance, the prefix e-, such as in elude, means to “thoroughly” avoid someone, whereas the intensive prefix ex- in exclaim means to “thoroughly” shout out.
What is a word with the prefix ex?
Quick Summary. The prefix ex-, with its variants e- and ec-, mean “out.” Examples using this prefix include exceed, eject, and eccentric. An easy way to remember that the prefix ex- means “out” is through the word exit, for when you exit a room, you go “out” of it.
Where does the prefix ex come from?
ex- 1 ,prefix. ex- comes from Latin, where it has the meaning “out, out of, away, forth. ” It is found in such words as: exclude, exhale, exit, export, extract.
What words have the prefix in?
Review (Answers)
| Word | = Prefix | + Stem |
|---|---|---|
| 1. involve | = in | + volve |
| 2. incomplete | = in | + complete |
| 3. insignificant | = in | + significant |
| 4. invent | = in | + vent |
Does inside have a prefix?
Inside is an adjective, adverb, or prepositions, and is its own word without a grammatical prefix.
What is an example of a prefix?
What are common prefixes?
What is called prefix?
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.
What are the four prefixes?
The four most common prefixes are dis-, in-, re-, and un-. (These account for over 95% of prefixed words.)
What is a prefix Year 1?
Prefixes are a group of letters that change the meaning of a word when they are added to the start. The prefix un- usually means not, so the new word means the opposite of the original.
Is Mr A prefix?
3. If no prefix is provided, the default is Mr or Ms. 4. In situations where both a prefix and a suffix could be used ie….PREFIX.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| Mr | Mister |
| Mrs | Married Woman |
| Ms | Single or Married Woman |
| Prince | Prince |
Is Mr Short for Master?
The title ‘Mr’ derived from earlier forms of master, as the equivalent female titles Mrs, Miss, and Ms all derived from earlier forms of mistress. Master is sometimes still used as an honorific for boys and young men.
Is Dr a prefix?
2. A physician or surgeon may use the prefix “Dr.” or “Doctor”, and shall add after the person’s name the letters, “M. D.” 3. An osteopathic physician and surgeon may use the prefix “Dr.” or “Doctor”, and shall add after the person’s name the letters, “D. O.”, or the words “osteopathic physician and surgeon”.
Who can be called Mr?
Mr.: Used for Married and Unmarried Men It is an abbreviation of the word “Mister,” and is used to address a man whether or not he is married. The usage of this term dates back to the 15th century.
What is prefix for unmarried woman?
Miss
Is a 16 year old Mr or master?
What does master mean? Master is a title for an underage male. If a person is under 18, master would be used. Once a person turns 18 and enters adulthood, mister would be used.
What is the prefix for unmarried man?
Mister or Mr.: This is the term that is used to address men, whether they are married or unmarried. Abbreviate the term “mister” to “Mr.” if you are using it as part of a man’s title. Master: This title can sometimes be used to address young boys.
Can you say mr first name?
Technically, it’s not appropriate to use a person’s first name, without permission. The right thing to do is use an honorific (Mr., Ms., Mrs., Dr. …) until the person says, “Please call me (first name).”
What is Mrs short for?
Mrs originated as a contraction of the honorific Mistress (the feminine of Mister or Master) which was originally applied to both married and unmarried women.
What does MS stand for woman?
Ms or Ms. (normally /ˈmɪz/, but also /məz/, or /məs/ when unstressed) is an English-language honorific used with the last name or full name of a woman, intended as a default form of address for women regardless of marital status.
What does MS stand for in front of a woman’s name?
Miss or what each indicates. Let’s take a closer look: Ms. is a title of respect before a woman’s name or position that does not indicate her marital status.
What is Mr Ms Mrs called?
Mr. is a title used before a surname or full name of a male, whether he is married or not. Mr. is an abbreviation for Mister, it is pronounced like the word Mister. Mrs. is a title used before a surname or full name of a married female. Mrs. is an abbreviation for the word Missus, it is pronounced like the word Missus.
How do you address a woman informally?
In the U.S., I would address a woman in an informal and friendly manner by using her name. Instead of saying, “hey, baby”, I’d say “hey, Valerie” or whatever her name was. In the US, “doll” was fashionable prior to the 1970’s, but not anymore. Some women consider “baby” a sexist term.
There are many different ways to form new words in the English language. One of the ways is with the use of prefixes.
This article will define what a prefix is, provide plenty of examples of the different prefixes used in the English language, and explain how and when you should use them.
What is a prefix?
A prefix is a type of affix attached to the beginning of a base word (or root) to change its meaning.
Affix — Letters that are added to the base form of a word to give it a new meaning.
The word prefix itself actually contains a prefix! The letters ‘pre’ is a prefix that means before or in front of. It is attached to the root word fix, which means attach.
Prefixes are always derivational, meaning once a prefix is used, it creates a new word with a different meaning from the base word.
When the prefix ‘un ‘ is added to the base word ‘happy ‘, it creates the new word ‘unhappy’.
This new word (unhappy) has the opposite meaning of the base word (happy).
What is Prefix as a Verb?
As a verb, the term prefix means placing in front of
Redo: Here, the letters ‘re’ are prefixed to the base word ‘do’. This creates a new word with a new meaning.
What is prefix as a noun?
As a noun, a prefix is a type of affix that is attached to the beginning of a base word to alter its meaning.
Polyglot: the prefix ‘poly’ (meaning: many ) is attached to the base word ‘glot’ (meaning: speaking or writing in a language ), to form a new word — polyglot — which is used to refer to a person who knows and can speak in more than one language.
What are some examples of prefixes?
The following table shows a comprehensive but not complete list of prefixes used in the English language.
Examples of prefixes that negate a word:
Certain prefixes create a new word with the opposite or nearly opposite meaning of the base word. In many cases, the word changes from something positive to something more negative. Here is a list of prefixes that negate (make negative) a word:
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
| a / an | lack of, without, not | asymmetric, atheist, anaemic |
| ab | away, not | abnormal, absent |
| anti | contrary to, against | anti-inflammatory, antisocial |
| counter | contrary to, against | counter-argument, counterproposal |
| de | undo, remove | deter, deactivate |
| ex | previous, former | ex-husband |
| il | not, without | illegal, illogical |
| im | not, without | improper, impossible |
| in | no, lacking | injustice, incomplete |
| ir | not | irreplaceable, irregular |
| non | not, lacking | non-fiction, nonnegotiable |
| un | not, lacking | unkind, unresponsive |

Examples of common prefixes in English:
Some prefixes don’t necessarily negate the meaning of a base word but alter it to express the word’s relationship with time, place, or manner.
| Prefix | Meaning | Example |
| ante | before, prior to | anterior, antebellum |
| auto | self | autobiography, autograph |
| bi | two | bicycle, binomial |
| circum | around, to go around | circumnavigate, circumvent |
| co | jointly, together | copilot, coworker |
| di | two | diatomic, dipole |
| extra | beyond, more | extracurricular |
| hetero | different | heterogeneous, heterosexual |
| homo | same | homogeneous, homosexual |
| inter | in between | intersect, intermittent |
| mid | middle | midpoint, midnight |
| pre | before | preschool |
| post | after | post-workout |
| semi | partial | semicircle |
Using hyphens with prefixes
There are no fixed and complete rules regarding when you should and should not use a hyphen to separate a base word from its prefix. However, there are a few things you should be aware of to help you use prefixes and hyphens correctly.
Use a hyphen with a proper noun
You must use a hyphen if a prefix is attached to a proper noun.
- Pre-World War I
- Anti-American
Use a hyphen to avoid ambiguity
A hyphen should be used with a prefix in cases where it may lead to confusion over meaning or spelling. Confusion most commonly arises when the base word plus a prefix creates a word that already exists.
Re-cover vs Recover
Adding the prefix ‘re’ to the word ‘cover’ creates a new word ‘recover’, which means to cover again.
However, this may cause confusion as the word recover already exists (a verb meaning to return to health).
Adding a hyphen makes it more apparent that ‘re’ is a prefix.
Use a hyphen to avoid double vowels
If a prefix ends with the same vowel that the base word starts with, use a hyphen to separate the two.
- Re-enter
- Ultra-argumentative
There may be exceptions to this rule with the vowel «o». For example, ‘coordinate’ is correct, but ‘coowner’ is incorrect. In such cases, using a spellchecker may prove to be helpful.
Use a hyphen with ‘ex’ and ‘self’
Certain prefixes such as ‘ex’ and ‘self’ are always followed by a hyphen.
- Ex-wife
- self-control
What is the Importance of prefixes in English?
Knowing how to use prefixes will make you more proficient in the language and improve your vocabulary. It will also allow you to convey information in a more concise and precise manner.
Using the word ‘reestablish’ instead of ‘establish it again’ will allow for more concise communication.
Prefix — Key takeaways
- A prefix is a type of affix attached to the beginning of a base word (or root) to change its meaning.
- The word prefix itself is the combination of the prefix — pre and the base word — fix.
- Some examples of prefixes are — ab, non, and ex.
- A hyphen must be used alongside a prefix for several reasons, such as to prevent ambiguity, when the root word is a proper noun, when the last letter of the prefix is the same as the first letter of the root word, and when the prefix is either ex or self.
Prefix is an English word with many meanings.
This article will explain what the word prefix means, where it originates from, and how to use it in a sentence.
Prefix Definition
According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, prefix can be a noun or a verb.
As a noun, it can mean “a group of words placed at the beginning of a word to create a new word” or “a title used before a person’s name.”
As a verb, it can mean “to fix or appoint beforehand” or “to place in front.”
Prefix Meaning
Let’s take a closer look at what each of these definitions means.
Prefix as a Noun
As a noun, prefix most commonly refers to a letter or group of letters that you attach before a root word in order to form a new word.
Common prefixes in English include:
- micro- (which adds the meaning “small” to an adjective)
- co- (which adds the meaning “together” to a verb)
- anti- (which adds the meaning “opposite” or “against” to a noun)
Many prefixes in English come from Greek and Latin, so studying these languages can help you understand how English words are put together.
The opposite of a prefix is a suffix, which is a group of letters that you attach to the end of a word
- -er (which adds the meaning “more” to an adjective)
- -est (which adds the meaning “most” to an adjective)
- -ness (which turns an adjective into a noun)
We also use prefix to describe the title you put before someone’s name. For example, Mr., Mrs., and Dr. are all common prefixes.
Finally, we sometimes use prefix to refer to telephone numbers. In this context, prefix refers to the first set of digits after the country and area codes.
Here are some examples of the noun prefix used in a sentence:
- Adding the prefix “un” to a word can transform the word into the opposite of what it would normally mean, such as when you say someone is “unkind” instead of “kind.”
- “Pro” is a prefix that shows your support for a certain cause, such as when you say you’re “pro-suffrage.”
- “Do you prefer the prefix Miss, Ms. or Mrs.?”
Prefix as a Verb
As a verb, the basic meaning of prefix is “to place at the beginning.” For example, you might prefix a fancy title to your name if you want to impress everyone, which means you add a title like “Dr.” or “His Royal Highness” to the beginning of your name.
The verb prefix can also mean “to determine beforehand.” A restaurant might prefix the price of their menu for a special holiday, which means they charge a predetermined price regardless of which dishes you order.
Similarly, a taxi company might prefix the rate for a ride to and from the airport, which means they charge a predetermined fee regardless of how far you go.
Here are some other examples of the verb prefix used in a sentence:
- She likes to prefix the word “literally” to almost everything she says.
- This company prefixes the prices for the different services they offer.
- I suspect that the corrupt mayor might have prefixed the winner of the last election.
Examples of Prefix in a Sentence
Let’s look at some examples of the word prefix in successful books.
“Our citizens must act as Americans; not as Americans with a prefix and qualifications; not as Irish-Americans, German-Americans, native Americans—but as Americans pure and simple.”—The Joy of Life by Mary Beth Smith
“He had just reached the time of life at which ‘young’ is ceasing to be the prefix of ‘man’ in speaking of one. He was at the brightest period of masculine life, for his intellect and emotions were clearly separate; he had passed the time during which the influence of youth indiscriminately mingles them in the character of impulse, and he had not yet arrived at the state wherein they become united again, in the character of prejudice, by the influence of a wife and family. In short, he was twenty-eight and a bachelor.”—Far From the Madding Crowd by Thomas Hardy
“All languages that derive from Latin form the word ‘compassion’ by combining the prefix meaning ‘with’ (com-) and the root meaning ‘suffering’ (Late Latin, passio). In other languages, Czech, Polish, German, and Swedish, for instance—this word is translated by a noun formed of an equivalent prefix combined with the word that means ‘feeling.’”—The Unbearable Lightness of Being by Milan Kundera
“One could prefix the words ‘deranged lunatic insists’ to any headline, and only increase its accuracy. It’s practically implied, and the reading public would hardly read the little phrase as a disclaimer these days.”—The Damned Highway by Brian Keene and Nick Mamatas
“If you choose to say, ‘God can give a creature free will and at the same time withhold free will from it,’ you have not succeeded in saying anything about God: meaningless combinations of words do not suddenly acquire meaning simply because we prefix to them the two other words, ‘God can.’ It remains true that all things are possible with God: the intrinsic impossibilities are not things but nonentities.”—The Problem of Pain by C.S. Lewis
“Love affair. Doesn’t that sound so middle-aged? And also ill-fated. Like ill-fated is an understood prefix to love affair.”—Night of Cake and Puppets by Laini Taylor
“An alliterative prefix served as an ornament of oratory.”—The Picture of Dorian Gray by Oscar Wilde
Origin of the Word Prefix
The word prefix was first used in the 16th century. It stems from the Latin word praefixum, meaning “fix in front, fasten on before.” This word is the combination of the Latin roots fix (meaning “attach”) and pre- (meaning “before”).
Now you know what “prefix” means and how to use this word in your own writing.
Take your writing to the next level:
20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas.
This guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers.