Within
the domain of syntax two levels should be distinguished: that of
phrases and that of sentences.
The
phrase can generally be defined as a combination of two or more words
which is a grammatical unit but is not an analytical form of some
word. The constituent elements of a phrase may belong to any part of
speech. A word-combination can also be defined as a compound
nominative unit of speech which is semantically global and
articulated.
The
difference between a phrase and a sentence is a fundamental one. A
phrase is a means of naming some phenomena or processes, just as a
word is. Each component of a phrase can undergo grammatical changes
while a sentence is a unit with every word having its definite form.
A change in the form of one or more words would produce a new
sentence.
Grammar
has to study the
aspects of phrases which spring from the grammatical peculiarities of
the words making up the phrase, and of the syntactical functions
of the phrase as a whole, while lexicology has to deal with the
lexical meaning of the words and their semantic groupings. For
example from
the grammatical point of view the two phrases
read
letters and
invite
friends are
identical (the
same pattern verb +
noun
indicating the object of the
action).
Phrases
can be divided according
to their function in the sentence into:
(1)
those
which
perform the function of one or more parts of the sentence (predicate,
or predicate and object, or predicate and adverbial
modifier, etc.)
(2)
those
which do not perform any such function
but whose function is equivalent to that of a preposition, or
conjunction, and which are equivalents
of those parts of speech.
1.3. Syntagmatic Connections of Words.
Words
in an utterance form various syntagmatic connections with one
another:
-
syntagmatic
groupings of notional words alone,
Such
groups (notional phrases) have self-dependent nominative destination,
they denote complex phenomena and their properties (semi-predicative
combinations): a
sudden trembling; a soul in pain; hurrying along the stream;
strangely familiar; so sure of their aims.
-
syntagmatic
groupings of notional words with functional words,
Such
combinations (formative phrases) are equivalent to separate words by
their nominative function: with
difficulty; must finish; but a moment; and Jimmy; too cold; so
unexpectedly.
They are contextually dependent (synsemantism).
-
syntagmatic
groupings of functional words alone.
They
are analogous to separate functional words and are used as connectors
and specifiers of notional elements:
from out of; up to; so that; such as; must be able; don’t let’s.
Combinations
of notional
words
fall into two mutually opposite types:
1)
combinations of words related to one another on an equal rank
(equipotent
combinations)
2)
combinations of words which are syntactically unequal (dominational
combinations)
Equipotent
connection
is realised with the help of conjunctions (syndetically), or without
the help of conjunctions (asyndetically):
prose and poetry; came and went; on the beach or in the water; quick
but not careless; —
no
sun, no moon; playing, chatting, laughing; silent, immovable, gloomy;
Mary’s, not John’s.
The
constituents of such combinations form coordinative consecutive
connections.
Alongside
of these, there exist equipotent connections of a non-consecutive
type. In such combinations a sequential element is unequal to the
foregoing element in its character of nomination connections is
classed as (cumulative connections): agreed,
but reluctantly; satisfied, or nearly so.
Dominational
connection
is effected in such a way that one of the constituents of the
combination is principal (dominating/headword) and the other is
subordinate (dominated/adjunct, adjunct-word, expansion).
Dominational
connection can be both consecutive
and cumulative:
a
careful observer; an observer, seemingly careful; definitely out of
the point;
out
of the point, definitely; will be helpful in any case will be
helpful;
at
least, in some cases.
The
two basic types of dominational connection are:
-
bilateral
(reciprocal, two-way) domination (in predicative connection of
words); -
monolateral
(one-way) domination (in completive connection of words).
The
predicative connection
of words, uniting the subject and the predicate, builds up the basis
of the sentence. The nature of this connections is reciprocal (the
subject dominates the predicate and vice versa).
Such
word combinations are divided into:
-
complete
predicative combinations (the subject + the finite verb-predicate); -
incomplete
predicative/semi-predicative/potentially-predicative combinations (a
non-finite verbal form + a substantive element): for
the pupil to understand his mistake; the pupil’s understanding his
mistake;
the
pupil understanding his mistake.
Monolateral
domination is considered as subordinative since the syntactic status
of the whole combination is determined by the head-word:
a nervous wreck. astonishingly beautiful.
The
completive connections fall into two main divisions:
-
objective
connections -
qualifying
connections.
Objective
connections
reflect the relation of the object to the process. By their form
these connections are subdivided into:
-
non-prepositional;
-
prepositional.
From
the semantico-syntactic point of view they are classed as:
-
direct
(the immediate transition of the action to the object); -
indirect
or oblique (the indirect relation of the object to the process).
Direct
objective connections are non-prepositional, the preposition serving
as an intermediary of combining words by its functional nature.
Indirect objective connections may be both prepositional and
non-prepositional.
Further
subdivision of objective connections is realised on the basis of
subcategorising the elements of objective combinations, and first of
all the verbs; thus, we recognise objects of immediate action, of
perception, of speaking, etc.
Qualifying
completive connections
are divided into
-
attributive
(an
enormous appetite; an emerald ring; a woman of strong character, the
case for the prosecution);
They
unite a substance with its attribute expressed by an adjective or a
noun.
-
adverbial:
-
primary
(the verb + its adverbial modifiers):
to talk glibly, to come nowhere; to receive (a letter) with
surprise; to throw (one’s arms) round a person’s neck; etc -
secondary
(the non-verbal headword expressing a quality + its adverbial
modifiers):
marvellously becoming; very much at ease; strikingly alike; no
longer oppressive; unpleasantly querulous; etc.
-
Completive
noun combinations are directly related to whole sentences
(predicative combinations of words): The
arrival of the train → The train arrived. The baked potatoes →
The potatoes are baked. The gifted pupil → The pupil has a gift.
Completive
combinations of adjectives and adverbs (adjective-phrases and
adverb-phrases) are indirectly related to predicative constructions:
utterly
neglected — utter neglect — The neglect is utter; very carefully
— great carefulness — The carefulness is great; speechlessly
reproachful — speechless reproach
— The reproach is speechless.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Подборка по базе: Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Microsoft Word Document.docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx
Семинар 6 Combinability. Word Groups
KEY TERMS
Syntagmatics — linear (simultaneous) relationship of words in speech as distinct from associative (non-simultaneous) relationship of words in language (paradigmatics). Syntagmatic relations specify the combination of elements into complex forms and sentences.
Distribution — The set of elements with which an item can cooccur
Combinability — the ability of linguistic elements to combine in speech.
Valency — the potential ability of words to occur with other words
Context — the semantically complete passage of written speech sufficient to establish the meaning of a given word (phrase).
Clichе´ — an overused expression that is considered trite, boring
Word combination — a combination of two or more notional words serving to express one concept. It is produced, not reproduced in speech.
Collocation — such a combination of words which conditions the realization of a certain meaning
TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION AND EXERCISES
1. Syntagmatic relations and the concept of combinability of words. Define combinability.
Syntagmatic relation defines the relationship between words that co-occur in the same sentence. It focuses on two main parts: how the position and the word order affect the meaning of a sentence.
The syntagmatic relation explains:
• The word position and order.
• The relationship between words gives a particular meaning to the sentence.
The syntagmatic relation can also explain why specific words are often paired together (collocations)
Syntagmatic relations are linear relations between words
The adjective yellow:
1. color: a yellow dress;
2. envious, suspicious: a yellow look;
3. corrupt: the yellow press
TYPES OF SEMANTIC RELATIONS
Because syntagmatic relations have to do with the relationship between words, the syntagms can result in collocations and idioms.
Collocations
Collocations are word combinations that frequently occur together.
Some examples of collocations:
- Verb + noun: do homework, take a risk, catch a cold.
- Noun + noun: office hours, interest group, kitchen cabinet.
- Adjective + adverb: good enough, close together, crystal clear.
- Verb + preposition: protect from, angry at, advantage of.
- Adverb + verb: strongly suggest, deeply sorry, highly successful.
- Adjective + noun: handsome man, quick shower, fast food.
Idioms
Idioms are expressions that have a meaning other than their literal one.
Idioms are distinct from collocations:
- The word combination is not interchangeable (fixed expressions).
- The meaning of each component is not equal to the meaning of the idiom
It is difficult to find the meaning of an idiom based on the definition of the words alone. For example, red herring. If you define the idiom word by word, it means ‘red fish’, not ‘something that misleads’, which is the real meaning.
Because of this, idioms can’t be translated to or from another language because the word definition isn’t equivalent to the idiom interpretation.
Some examples of popular idioms:
- Break a leg.
- Miss the boat.
- Call it a day.
- It’s raining cats and dogs.
- Kill two birds with one stone.
Combinability (occurrence-range) — the ability of linguistic elements to combine in speech.
The combinability of words is as a rule determined by their meanings, not their forms. Therefore not every sequence of words may be regarded as a combination of words.
In the sentence Frankly, father, I have been a fool neither frankly, father nor father, I … are combinations of words since their meanings are detached and do not unite them, which is marked orally by intonation and often graphically by punctuation marks.
On the other hand, some words may be inserted between the components of a word-combination without breaking it.
Compare,
a) read books
b) read many books
c) read very many books.
In case (a) the combination read books is uninterrupted.In cases (b) and (c) it is interrupted, or discontinuous(read… books).
The combinability of words depends on their lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical meanings. It is owing to the lexical meanings of the corresponding lexemes that the word wise can be combined with the words man, act, saying and is hardly combinable with the words milk, area, outline.
The lexico-grammatical meanings of -er in singer (a noun) and -ly in beautifully (an adverb) do not go together and prevent these words from forming a combination, whereas beautiful singer and sing beautifully are regular word-combinations.
The combination * students sings is impossible owing to the grammatical meanings of the corresponding grammemes.
Thus one may speak of lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical combinability, or the combinability of lexemes, grammemes and parts of speech.
The mechanism of combinability is very complicated. One has to take into consideration not only the combinability of homogeneous units, e. g. the words of one lexeme with those of another lexeme. A lexeme is often not combinable with a whole class of lexemes or with certain grammemes.
For instance, the lexeme few, fewer, fewest is not combinable with a class of nouns called uncountables, such as milk, information, hatred, etc., or with members of ‘singular’ grammemes (i. e. grammemes containing the meaning of ‘singularity’, such as book, table, man, boy, etc.).
The ‘possessive case’ grammemes are rarely combined with verbs, barring the gerund. Some words are regularly combined with sentences, others are not.
It is convenient to distinguish right-hand and left-hand connections. In the combination my hand (when written down) the word my has a right-hand connection with the word hand and the latter has a left-hand connection with the word my.
With analytical forms inside and outside connections are also possible. In the combination has often written the verb has an inside connection with the adverb and the latter has an outside connection with the verb.
It will also be expedient to distinguish unilateral, bilateral and multilateral connections. By way of illustration we may say that the articles in English have unilateral right-hand connections with nouns: a book, the child. Such linking words as prepositions, conjunctions, link-verbs, and modal verbs are characterized by bilateral connections: love of life, John and Mary, this is John, he must come. Most verbs may have zero
(Come!), unilateral (birds fly), bilateral (I saw him) and multilateral (Yesterday I saw him there) connections. In other words, the combinability of verbs is variable.
One should also distinguish direct and indirect connections. In the combination Look at John the connection between look and at, between at and John are direct, whereas the connection between look and John is indirect, through the preposition at.
2. Lexical and grammatical valency. Valency and collocability. Relationships between valency and collocability. Distribution.
The appearance of words in a certain syntagmatic succession with particular logical, semantic, morphological and syntactic relations is called collocability or valency.
Valency is viewed as an aptness or potential of a word to have relations with other words in language. Valency can be grammatical and lexical.
Collocability is an actual use of words in particular word-groups in communication.
The range of the Lexical valency of words is linguistically restricted by the inner structure of the English word-stock. Though the verbs ‘lift’ and ‘raise’ are synonyms, only ‘to raise’ is collocated with the noun ‘question’.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is different, cf. English ‘pot plants’ vs. Russian ‘комнатные цветы’.
The interrelation of lexical valency and polysemy:
• the restrictions of lexical valency of words may manifest themselves in the lexical meanings of the polysemantic members of word-groups, e.g. heavy, adj. in the meaning ‘rich and difficult to digest’ is combined with the words food, meals, supper, etc., but one cannot say *heavy cheese or *heavy sausage;
• different meanings of a word may be described through its lexical valency, e.g. the different meanings of heavy, adj. may be described through the word-groups heavy weight / book / table; heavy snow / storm / rain; heavy drinker / eater; heavy sleep / disappointment / sorrow; heavy industry / tanks, and so on.
From this point of view word-groups may be regarded as the characteristic minimal lexical sets that operate as distinguishing clues for each of the multiple meanings of the word.
Grammatical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in specific grammatical (or rather syntactic) structures. Its range is delimited by the part of speech the word belongs to. This is not to imply that grammatical valency of words belonging to the same part of speech is necessarily identical, e.g.:
• the verbs suggest and propose can be followed by a noun (to propose or suggest a plan / a resolution); however, it is only propose that can be followed by the infinitive of a verb (to propose to do smth.);
• the adjectives clever and intelligent are seen to possess different grammatical valency as clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern: Adj. + Prep. at +Noun(clever at mathematics), whereas intelligent can never be found in exactly the same word-group pattern.
• The individual meanings of a polysemantic word may be described through its grammatical valency, e.g. keen + Nas in keen sight ‘sharp’; keen + on + Nas in keen on sports ‘fond of’; keen + V(inf)as in keen to know ‘eager’.
Lexical context determines lexically bound meaning; collocations with the polysemantic words are of primary importance, e.g. a dramatic change / increase / fall / improvement; dramatic events / scenery; dramatic society; a dramatic gesture.
In grammatical context the grammatical (syntactic) structure of the context serves to determine the meanings of a polysemantic word, e.g. 1) She will make a good teacher. 2) She will make some tea. 3) She will make him obey.
Distribution is understood as the whole complex of contexts in which the given lexical unit(word) can be used. Есть даже словари, по которым можно найти валентные слова для нужного нам слова — так и называются дистрибьюшн дикшенери
3. What is a word combination? Types of word combinations. Classifications of word-groups.
Word combination — a combination of two or more notional words serving to express one concept. It is produced, not reproduced in speech.
Types of word combinations:
- Semantically:
- free word groups (collocations) — a year ago, a girl of beauty, take lessons;
- set expressions (at last, point of view, take part).
- Morphologically (L.S. Barkhudarov):
- noun word combinations, e.g.: nice apples (BBC London Course);
- verb word combinations, e.g.: saw him (E. Blyton);
- adjective word combinations, e.g.: perfectly delightful (O. Wilde);
- adverb word combinations, e.g.: perfectly well (O, Wilde);
- pronoun word combinations, e.g.: something nice (BBC London Course).
- According to the number of the components:
- simple — the head and an adjunct, e.g.: told me (A. Ayckbourn)
- Complex, e.g.: terribly cold weather (O. Jespersen), where the adjunct cold is expanded by means of terribly.
Classifications of word-groups:
- through the order and arrangement of the components:
• a verbal — nominal group (to sew a dress);
• a verbal — prepositional — nominal group (look at something);
- by the criterion of distribution, which is the sum of contexts of the language unit usage:
• endocentric, i.e. having one central member functionally equivalent to the whole word-group (blue sky);
• exocentric, i.e. having no central member (become older, side by side);
- according to the headword:
• nominal (beautiful garden);
• verbal (to fly high);
• adjectival (lucky from birth);
- according to the syntactic pattern:
• predicative (Russian linguists do not consider them to be word-groups);
• non-predicative — according to the type of syntactic relations between the components:
(a) subordinative (modern technology);
(b) coordinative (husband and wife).
4. What is “a free word combination”? To what extent is what we call a free word combination actually free? What are the restrictions imposed on it?
A free word combination is a combination in which any element can be substituted by another.
The general meaning of an ordinary free word combination is derived from the conjoined meanings of its elements
Ex. To come to one’s sense –to change one’s mind;
To fall into a rage – to get angry.
Free word-combinations are word-groups that have a greater semantic and structural independence and freely composed by the speaker in his speech according to his purpose.
A free word combination or a free phrase permits substitution of any of its elements without any semantic change in the other components.
5. Clichе´s (traditional word combinations).
A cliché is an expression that is trite, worn-out, and overused. As a result, clichés have lost their original vitality, freshness, and significance in expressing meaning. A cliché is a phrase or idea that has become a “universal” device to describe abstract concepts such as time (Better Late Than Never), anger (madder than a wet hen), love (love is blind), and even hope (Tomorrow is Another Day). However, such expressions are too commonplace and unoriginal to leave any significant impression.
Of course, any expression that has become a cliché was original and innovative at one time. However, overuse of such an expression results in a loss of novelty, significance, and even original meaning. For example, the proverbial phrase “when it rains it pours” indicates the idea that difficult or inconvenient circumstances closely follow each other or take place all at the same time. This phrase originally referred to a weather pattern in which a dry spell would be followed by heavy, prolonged rain. However, the original meaning is distanced from the overuse of the phrase, making it a cliché.
Some common examples of cliché in everyday speech:
- My dog is dumb as a doorknob. (тупой как пробка)
- The laundry came out as fresh as a daisy.
- If you hide the toy it will be out of sight, out of mind. (с глаз долой, из сердца вон)
Examples of Movie Lines that Have Become Cliché:
- Luke, I am your father. (Star Wars: The Empire Strikes Back)
- i am Groot. (Guardians of the Galaxy)
- I’ll be back. (The Terminator)
- Houston, we have a problem. (Apollo 13)
Some famous examples of cliché in creative writing:
- It was a dark and stormy night
- Once upon a time
- There I was
- All’s well that ends well
- They lived happily ever after
6. The sociolinguistic aspect of word combinations.
Lexical valency is the possibility of lexicosemantic connections of a word with other word
Some researchers suggested that the functioning of a word in speech is determined by the environment in which it occurs, by its grammatical peculiarities (part of speech it belongs to, categories, functions in the sentence, etc.), and by the type and character of meaning included into the semantic structure of a word.
Words are used in certain lexical contexts, i.e. in combinations with other words. The words that surround a particular word in a sentence or paragraph are called the verbal context of that word.
7. Norms of lexical valency and collocability in different languages.
The aptness of a word to appear in various combinations is described as its lexical valency or collocability. The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical. This is only natural since every language has its syntagmatic norms and patterns of lexical valency. Words, habitually collocated, tend to constitute a cliché, e.g. bad mistake, high hopes, heavy sea (rain, snow), etc. The translator is obliged to seek similar cliches, traditional collocations in the target-language: грубая ошибка, большие надежды, бурное море, сильный дождь /снег/.
The key word in such collocations is usually preserved but the collocated one is rendered by a word of a somewhat different referential meaning in accordance with the valency norms of the target-language:
- trains run — поезда ходят;
- a fly stands on the ceiling — на потолке сидит муха;
- It was the worst earthquake on the African continent (D.W.) — Это было самое сильное землетрясение в Африке.
- Labour Party pretest followed sharply on the Tory deal with Spain (M.S.1973) — За сообщением о сделке консервативного правительства с Испанией немедленно последовал протест лейбористской партии.
Different collocability often calls for lexical and grammatical transformations in translation though each component of the collocation may have its equivalent in Russian, e.g. the collocation «the most controversial Prime Minister» cannot be translated as «самый противоречивый премьер-министр».
«Britain will tomorrow be welcoming on an official visit one of the most controversial and youngest Prime Ministers in Europe» (The Times, 1970). «Завтра в Англию прибывает с официальным визитом один из самых молодых премьер-министров Европы, который вызывает самые противоречивые мнения».
«Sweden’s neutral faith ought not to be in doubt» (Ib.) «Верность Швеции нейтралитету не подлежит сомнению».
The collocation «documentary bombshell» is rather uncommon and individual, but evidently it does not violate English collocational patterns, while the corresponding Russian collocation — документальная бомба — impossible. Therefore its translation requires a number of transformations:
«A teacher who leaves a documentary bombshell lying around by negligence is as culpable as the top civil servant who leaves his classified secrets in a taxi» (The Daily Mirror, 1950) «Преподаватель, по небрежности оставивший на столе бумаги, которые могут вызвать большой скандал, не менее виновен, чем ответственный государственный служащий, забывший секретные документы в такси».
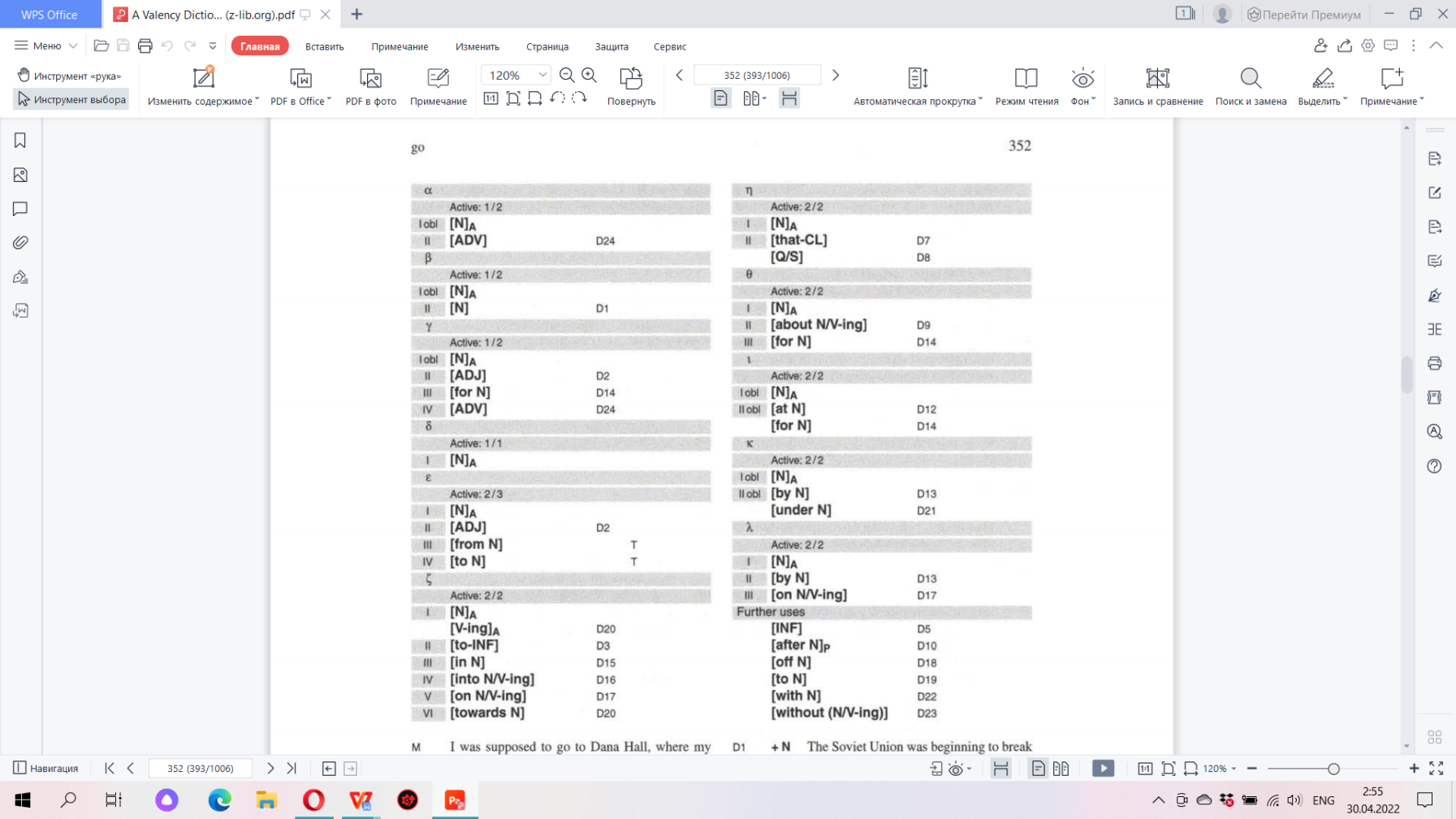
8. Using the data of various dictionaries compare the grammatical valency of the words worth and worthy; ensure, insure, assure; observance and observation; go and walk; influence and влияние; hold and держать.
| Worth & Worthy | |
| Worth is used to say that something has a value:
• Something that is worth a certain amount of money has that value; • Something that is worth doing or worth an effort, a visit, etc. is so attractive or rewarding that the effort etc. should be made. Valency:
|
Worthy:
• If someone or something is worthv of something, they deserve it because they have the qualities required; • If you say that a person is worthy of another person you are saying that you approve of them as a partner for that person. Valency:
|
| Ensure, insure, assure | ||
| Ensure means ‘make certain that something happens’.
Valency:
|
Insure — make sure
Valency:
|
Assure:
• to tell someone confidently that something is true, especially so that they do not worry; • to cause something to be certain. Valency:
|
| Observance & Observation | |
| Observance:
• the act of obeying a law or following a religious custom: religious observances such as fasting • a ceremony or action to celebrate a holiday or a religious or other important event: [ C ] Memorial Day observances [ U ] Financial markets will be closed Monday in observance of Labor Day. |
Observation:
• the act of observing something or someone; • the fact that you notice or see something; • a remark about something that you have noticed. Valency:
|
| Go & Walk | |
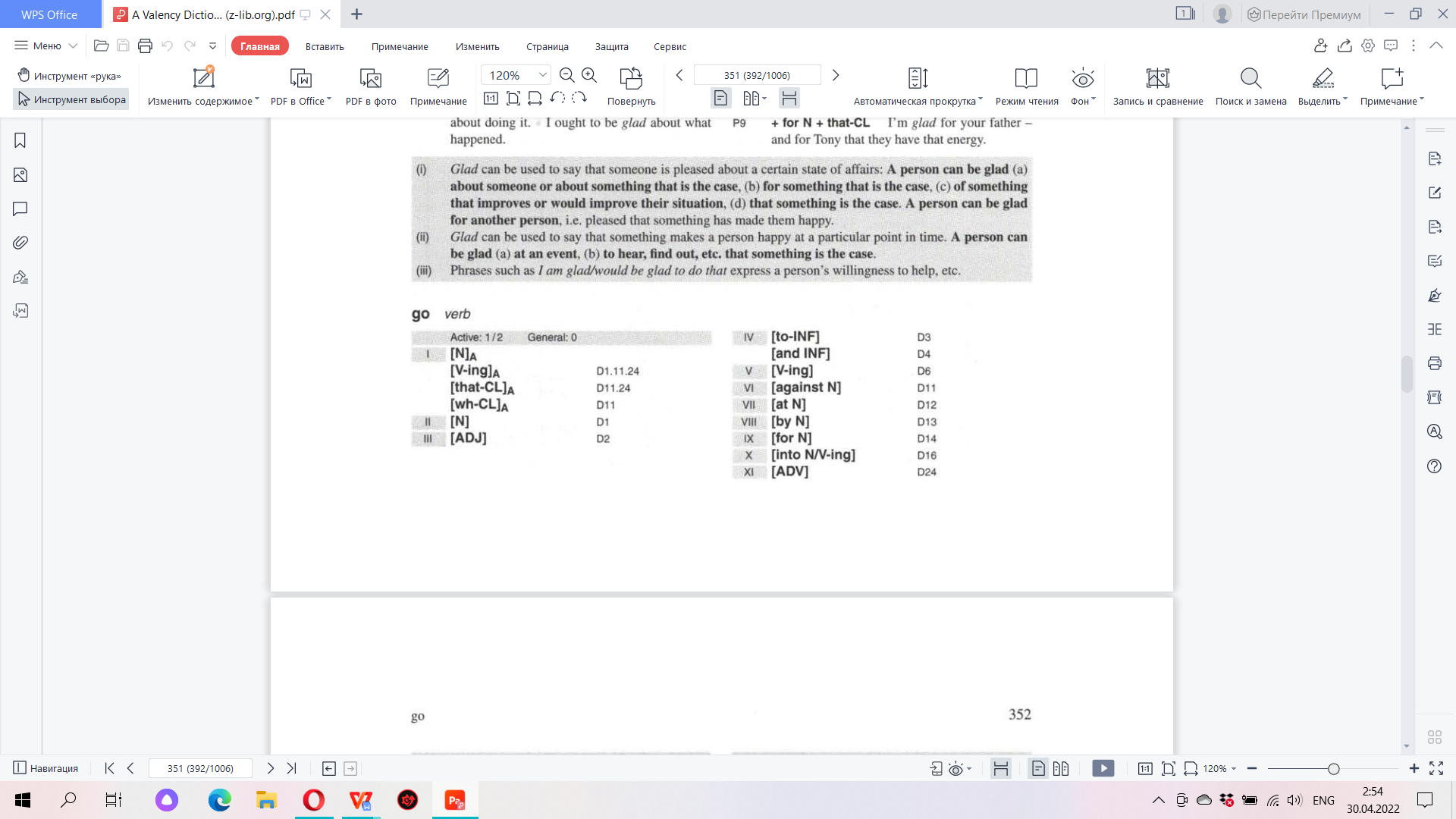
|
Walk can mean ‘move along on foot’:
• A person can walk an animal, i.e. exercise them by walking. • A person can walk another person somewhere , i.e. take them there, • A person can walk a particular distance or walk the streets. Valency:
|
| Influence & Влияние | |
| Influence:
• A person can have influence (a) over another person or a group, i.e. be able to directly guide the way they behave, (b) with a person, i.e. be able to influence them because they know them well. • Someone or something can have or be an influence on or upon something or someone, i.e. be able to affect their character or behaviour in some way Valency:
|
Влияние — Действие, оказываемое кем-, чем-либо на кого-, что-либо.
Сочетаемость:
|
| Hold & Держать | |
| Hold:
• to take and keep something in your hand or arms; • to support something; • to contain or be able to contain something; • to keep someone in a place so that they cannot leave. Valency:
|
Держать — взять в руки/рот/зубы и т.д. и не давать выпасть
Сочетаемость:
|
- Contrastive Analysis. Give words of the same root in Russian; compare their valency:
| Chance | Шанс |
|
|
| Situation | Ситуация |
|
|
| Partner | Партнёр |
|
|
| Surprise | Сюрприз |
|
|
| Risk | Риск |
|
|
| Instruction | Инструкция |
|
|
| Satisfaction | Сатисфакция |
|
|
| Business | Бизнес |
|
|
| Manager | Менеджер |
|
|
| Challenge | Челлендж |
|
|
10. From the lexemes in brackets choose the correct one to go with each of the synonyms given below:
- acute, keen, sharp (knife, mind, sight):
• acute mind;
• keen sight;
• sharp knife;
- abysmal, deep, profound (ignorance, river, sleep);
• abysmal ignorance;
• deep river;
• profound sleep;
- unconditional, unqualified (success, surrender):
• unconditional surrender;
• unqualified success;
- diminutive, miniature, petite, petty, small, tiny (camera, house, speck, spite, suffix, woman):
• diminutive suffix;
• miniature camera/house;
• petite woman;
• petty spite;
• small speck/camera/house;
• tiny house/camera/speck;
- brisk, nimble, quick, swift (mind, revenge, train, walk):
• brisk walk;
• nimble mind;
• quick train;
• swift revenge.
11. Collocate deletion: One word in each group does not make a strong word partnership with the word on Capitals. Which one is Odd One Out?
1) BRIGHT idea green
smell
child day room
2) CLEAR
attitude
need instruction alternative day conscience
3) LIGHT traffic
work
day entertainment suitcase rain green lunch
4) NEW experience job
food
potatoes baby situation year
5) HIGH season price opinion spirits
house
time priority
6) MAIN point reason effect entrance
speed
road meal course
7) STRONG possibility doubt smell influence
views
coffee language

advantage
situation relationship illness crime matter
- Write a short definition based on the clues you find in context for the italicized words in the sentence. Check your definitions with the dictionary.
| Sentence | Meaning |
| The method of reasoning from the particular to the general — the inductive method — has played an important role in science since the time of Francis Bacon. | The way of learning or investigating from the particular to the general that played an important role in the time of Francis Bacon |
| Most snakes are meat eaters, or carnivores. | Animals whose main diet is meat |
| A person on a reducing diet is expected to eschew most fatty or greasy foods. | deliberately avoid |
| After a hectic year in the city, he was glad to return to the peace and quiet of the country. | full of incessant or frantic activity. |
| Darius was speaking so quickly and waving his arms around so wildly, it was impossible to comprehend what he was trying to say. | grasp mentally; understand.to perceive |
| The babysitter tried rocking, feeding, chanting, and burping the crying baby, but nothing would appease him. | to calm down someone |
| It behooves young ladies and gentlemen not to use bad language unless they are very, very angry. | necessary |
| The Academy Award is an honor coveted by most Hollywood actors. | The dream about some achievements |
| In the George Orwell book 1984, the people’s lives are ruled by an omnipotent dictator named “Big Brother.” | The person who have a lot of power |
| After a good deal of coaxing, the father finally acceded to his children’s request. | to Agree with some request |
| He is devoid of human feelings. | Someone have the lack of something |
| This year, my garden yielded several baskets full of tomatoes. | produce or provide |
| It is important for a teacher to develop a rapport with his or her students. | good relationship |
Word combinations in Modern English Lexicology of the English language
�A Word combination (phrase ) is a non-predicative unit of speech which is, semantically, both global and articulated. 1. Word combination
�In grammar, it is seen as a group of words that functions as a single unit in the syntax of a sentence. It is an intermediate unit between a word and a sentence. �The main function of a word combination is polinomination (it describes an object, phenomenon or action and its attributes and properties at the same time). 2.
� There are two types of word combinations (also known as set-expressions, set-phrases, fixed word-groups, etc): � Free word combinations in which each component may enter different combinations � Set (phraseological) combinations consist of elements which are used only in combination with one another 3.
�Differences between free and set word combinations: SEMANTIC CRITERION �The meaning in phraseological units has partially or fully shifted. The words have a transferred (metaphorical or metonymical) meaning. �cf: a wolf in sheep’s clothing – a man in cheap clothing 4.
STRUCTURAL CRITERION. � Phraseological units are characterized by stability of components: � It is impossible to change the components of a phraseological unit; e. g. to have a bee in the bonnet (hat) � It is impossible to add new components; � It is impossible to change grammatical form of components, even if their form violates grammar rules: e. g. at (the) first sight, from head to foot (feet), to find faults with � However the degree of stability varies: a skeleton/skeletons in the cupboard, a (big) white elephant. � Other features ensuring stability are rhythm, alliteration, contrast, repetition, simile etc. � e. g. on and on, safe and sound, as busy as a bee � Free 5. word combinations allow any changes.
Classifications of phraseological units � According to thematic (etymological) classification, idioms are classified according to their sources of origin. ◦ E. g. Word-groups associated with the sea and the life of seamen are especially numerous in English vocabulary. Thus there may be singled out a group of “marine” phraseological units. � To be all at sea — to be unable to understand; to be in a state of ignorance or bewilderment about something (e. g. How can I be a judge in a situation in which I am all at sea? I’m afraid I’m all at sea in this problem � To sink or swim — to fail or succeed (e. g. It is a case of sink or swim. All depends on his own effort. ) � In deep water — in trouble or danger. � In low water, on the rocks — in strained financial circumstances. 6.
Semantic classification � describes word combinations from the viewpoint of the shift in meaning of words: � Phraseological fusions (idioms) are most idiomatic, the meaning of both words is fully transferred. � e. g. tit for tat, to skate on thin ice � Phraseological unities are motivated semantically, based on imagination. Usually one of the components has retained its meaning. � e. g. to fall ill, to fall in love, small talk � Phraseological combinations are less idiomatic, most motivated � e. g. as dead as mutton 7.
Structural classification takes into consideration the fact that phraseologisms are, in fact, equivalents of words. Phraseological units can perform the same functions as words. So, set expressions are classified according to their function. � Verbal : to run for one’s life, to get the upper hand � Substantive: dog’s life, red tape � Adjectival: high and mighty, safe and sound � Adverbial: high and low � Equivalents of auxiliary parts of speech: by way of, as long as, Good God! � Stereotyped sentences: take your time! 8.
Stylistic classification �Set expressions, as well as words, may be stylistically neutral and stylistically marked. �e. g. it’s raining cats and dogs (bookish) �to do smb. brown (colloquial) 9.
Notions related to set expressions �A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two different things, usually by employing the words «like» , «as» , or «than» . �Even though both similes and metaphors are forms of comparison, similes indirectly compare the two ideas and allow them to remain distinct in spite of their similarities, whereas metaphors compare two things directly. �e. g. as alike as two peas in a pod (identical or nearly so) �as blind as a bat (completely blind) 10.
�A cliché is a stereotyped expression mechanically reproduced in speech, very often overused to the point of losing its intended force or novelty. �e. g. Love is blind. ◦ Put two and two together. 11.
�A proverb is a simple and concrete saying popularly known and repeated, which expresses a truth, based on common sense or the practical experience of mankind. They are often metaphorical. A proverb that describes a basic rule of conduct may also be known as a maxim. �If a proverb is distinguished by particularly good phrasing, it may be known as an aphorism. 12.
�A collocation is sequence of words or terms which co-occur more often than would be expected by chance. e. g. �time flies �Times passes �the appointed time �Present time �Right time �Wrong time �Opening time �Closing time 13.
�A phrasal verb is a phrase (as take off or look down on) that combines a verb with a preposition or adverb or both and that functions as a verb whose meaning is different from the combined meanings of the individual words. 14.
Translation Tips � Free word combinations and collocations are usually translated by calque (word-for-word). However, translating attributive word groups is challenging, because one and the same attributive word may be translated differently depending on the meaning of the defined head word. � E. g. public opinion – общественное мнение, jamoatchilik fikri � Public debt – государственный долг, davlat qarzlari � Public scandal – публичный скандал, ommaviy janajal � Sometimes more complicated transformations are needed: � E. g. working expectancy – ожидаемая продолжительность трудовой деятельности, ishchini kutilayotgan ishlash muddati 15.
� Phraseological unities are usually translated by one word or equivalent combinations: � e. g. to take a chance – рисковать, imkoniyat berish � To take offence – обидеться, arazlamoq � To put an end to – положить конец, преодолеть, tugatish � To take into account – принимать во внимание, e’tiborga olish � Phraseological fusions (idioms) are translated by their equivalents or analogues or description. e. g. � whip-and-carrot policy – политика кнута и пряника, qamchi va sabzi siyosati (equivalent) � To beat about the bush – ходить вокруг да около, butani o’rab olish (analogue) � Carbon footprint — негативные экологические последствия какой-либо деятельности, faoliyatni salbiy ekologik natijalari (decription) 16.
Origin of set expressions � One of the words becomes archaic: kith and kin of the meanings of a word becomes archaic: to be in two minds � An expression may pass from professional use into common use: to hit below the belt (from boxing) � Part of a proverb may become isolated: the last straw (that was the last straw which broke the camel’s neck) � Literary sources: a Troyan horse; to be or not to be � Translation borrowings: to kill two birds with one stone (calque translation from French) � 17.
� � � � � What do we call word combinations in which the components retain their main meaning, and can freely enter different combinations? What do we call word combinations in which the components typically have shifted meaning and are not freely chosen? What do we call a figure of speech that directly compares two different things, usually by employing the words «like» , «as» , or «than» ? What do we call a trite or overused phrase or expression? What is a simple and concrete saying popularly known and repeated, which expresses a truth, based on common sense or the practical experience of mankind? What do we call a familiar grouping of words that habitually appear together and thereby convey meaning by association? Which of the following underlined word combinations with the word “stand” is free and which one is fixed? a) The British government would not stand in the way of such a proposal. b) She was standing beside my bed staring down at me. 18. CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
� Which of the following word combinations in bold are set phrases? 1) Where do you think you lost your purse? 2) Don’t lose your temper when you talk to her. 3) Have a look at the reverse side of the coat. 4) The reverse side of the medal is that we’ll have to do it ourselves. 5) Keep the butter in the refrigerator. 6) Keep an eye on the child. 19. Case study
� � � 1) lost your purse — it is a free word combination, as it allows any combinations without change of the basic (denotative) meaning of words, e. g. lost you bag, found your purse etc. 2) lose your temper – it is a set (phraseological) word combination, as the meaning of the word ‘lose’ in this combination is not direct but figurative (= to become angry). 3) reverse side of the coat — it is a free word combination, as it allows any combinations without change of the basic (denotative) meaning of words, e. g. reverse side of the dress 4) reverse side of the medal — it is a set (phraseological) word combination, as the meaning of the words in this combination is not direct but figurative (= other side of the matter) 5) Keep the butter — it is a free word combination, as it allows any combinations without change of the basic (denotative) meaning of words, e. g. keep the cheese in the refrigerator etc. 6) Keep an eye — it is a set (phraseological) word combination, as the meaning of the words in this combination is not direct but figurative (= to watch closely or carefully) 20. Key
ONE NINE TWO THREE FOUR(S) FIVE SIX(ES)S EVEN(S) TEN 1) 2) She crawled on all _____ to the window = on her knees, feet and hands. He is at _____ and _____ = He is confused and doesn’t know what to do. 3) He puts _____ and _____ together. = He begins to draw conclusions about something 4) He looks out for number _____ = He only thinks about his interests. 5) «the _____ R’s. » = The basics of education 6) He has a _____ o’clock shadow. = A man hasn’t shaved for a day or two 7) Things that are very cheap and common are _____ a penny. 
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 
As already mentioned, only those combinations of words (or single words) which convey communication are sentences – the object of syntax. All other combinations of words regularly formed in the process of speech are the object of morphology as well as single words. Like separate words they name things, phenomena, actions, qualities, etc., but in a complex way, for example: manners and table manners, blue and dark blue, speak and speak loudly. Like separate words they serve as a building material for sentences.
The combinability of words is as a rule determined by their meanings, not their forms. Therefore not every sequence of words may be regarded as a combination of words. In the sentence Frankly, my friend, I have told you the truth neither Frankly, my friend nor friend, I … are combinations of words since their meanings are detached and do not unite them.
On the other hand, some words may be inserted between the components of a word combination without breaking it. Compare:
a) read books; b) read many books; c) read very many books.
In case (a) the combination read books is uninterrupted. In cases (b) and (c) it is interrupted, or discontinuous (read … books).
The combinability of words depends on their lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical meanings. It is owing to lexical meanings of the corresponding lexemes that the word hot can be combined with the words water, temper, news, dog and is hardly combinable with the words ice, square, information, cat.
The lexico-grammatical meanings of -er in runner (a noun) and -ly in quickly (an adverb) do not go together and prevent these words from forming a combination, whereas quick runner and run quickly are regular word combinations.
The combination * students writes is impossible owing to the grammatical meanings of the corresponding grammemes (Remark: with “*” we mark grammatically incorrect word-combinations or sentences).
Thus one may speak of lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical combinability, or the combinability of lexemes, grammemes and parts of speech.
Each word belonging to a certain part of speech is characterized by valency (валентність) or, in other words, the combinability of lexical units. For example, in the sentence I tell you a joke the verb tell is two valent, and in the sentence I will tell you a joke about a Scotchman – three valent. We can also say that modal verbs are valent for infinitives and not valent for gerunds, e.g. I can’t sing; nouns are valent for an article, e.g. a (the) table, that is modal verbs are combined with infinitives not gerunds, and nouns are practically the only part of speech that can be combined with articles.
It is convenient to distinguish right-hand and left-hand connections or combinability. In the combination my friend the word my has a right-hand connection with the word friend and the latter has a left-hand connection with the word my.
With analytical forms inside and outside connections are also possible. In the combination has already done the verb has an inside connection with the adverb and the latter has an outside connection with the verb.
It will also be expedient to distinguish unilateral, bilateral and multilateral combinability (одностороння, двостороння та багатостороння сполучуваність). For instance, we may say that the articles in English have unilateral right-hand connections with nouns: a book, the boy. Such linking words as prepositions, conjunctions, link verbs and modal verbs are characterized by bilateral combinability: book of John, John and Marry, this is John, the boy must leave. Most verbs may have:
– zero (Go!),




– and multilateral (Yesterday I saw him there) connections. In other words, the combinability of verbs is variable.
One should also distinguish direct and indirect connections. In the combination Look at him the connection between look and at, between at and him are direct, whereas the connection between look and him is indirect, though the preposition at [24; 28–31].
5. The notions of grammatical opposition
and grammatical category
There is essential difference in the way lexical and grammatical meanings exist in the language and occur in speech. Lexical meanings can be found in a bunch only in a dictionary or in a memory of a man, or, scientifically, in the lexical system of a language. In actual speech a lexical morpheme displays only one meaning of the bunch in each case, and that meaning is singled out by the context or the situation of speech (in grammar terms, syntagmatically). As mentioned already, words of the same lexeme convey different meanings in different surroundings.
The meanings of a grammatical morpheme always come together in the word. In accordance with their relative nature they can be singled out only relatively in contrast to the meanings of other grammatical morphemes (in grammar terms, paradigmatically).
Supposing we want to single out the meaning of “non-continuous aspect” in the word runs. We have then to find another word which has all the meanings of the word runs except that of “non-continuous aspect”. The only word that meets these requirements is the analytical word is running. Run and is running belong to the same lexeme and their lexical meanings are identical. As to the grammatical meanings the two words do not differ in tense (“present”), number (“singular”), person (“third”), mood (“indicative”), etc. They differ only in aspect. The word runs has the meaning of “non-continuous aspect” and is running – that of “continuous aspect”.
When opposed, the two words, runs and is running, form a particular language unit. All their meanings but those of aspects counterbalance one another and do not count. Only the two particular meanings of “non-continuous” and “continuous” aspect united by the general meaning of “aspect” are revealed in this opposition or opposeme. The general meaning of this opposeme (“aspect”) manifests itself in the two particular meanings (“non-continuous aspect” and “continuous aspect”) of the opposite members (or opposites) [24; 22–24].
Thus, the elements which the opposition/opposeme is composed of are called opposites or members of the opposition. Opposites can be different: 1) non-marked, 2) marked. Compare the pair of noun forms table – tables. Together they create the “number” opposeme, where table represents the singular number expressed by a zero morpheme that is why it is called the non-marked member of the opposition, and tables – the plural number expressed by the positive morpheme -s is called the marked member of the opposition. Non-marked opposite is used more often than the marked opposite is. The marked opposite is peculiar by its limited use.
Ferdinand de Saussure claimed that everything in language is based on opposition. On phonetic level we have opposition of sounds. On all levels of the language we have opposition. Any grammatical form has got its contrast or counterpart. Together they make up a grammatical category.
A part of speech is characterized by its grammatical categories manifested in the opposemes (the elements of the opposition – оппозема, член опозиції) and paradigms of its lexemes. Nouns have the categories of number and case. Verbs possess the categories of tense, voice, mood etc. That is why paradigms belonging to different parts of speech are different. The paradigm of a verb lexeme is long: write, writes, wrote, will write, is writing etc. The paradigm of a noun lexeme is much shorter: sister, sister’s, sisters, sisters’. The paradigm of an adjective lexeme is still shorter: cold, colder, coldest. The paradigm of an adverb always consists only of one word.
Thus, the paradigm of a lexeme shows what part of speech the lexeme belongs to.
It must be borne in mind, however, that not all the lexemes of a part of speech have the same paradigms. Compare:
sister book information
sister’s books –
sisters – –
sisters’ – –
The first lexeme has opposemes of two grammatical categories: number and case. The second lexeme has only one opposeme – that of number. It has no case opposemes. The third lexeme is outside both categories: it has no opposemes at all. We may say that the number opposeme with its opposite grammatical meanings of “singularity” and “plurality” is neutralized in nouns like information, bread, milk etc. owing to their lexical meaning which can hardly be associated with “oneness” or “more-than-oneness”.
We may define neutralization as the reduction of an opposeme to one of its members under certain circumstances. This member may be called the member of neutralization. Usually it is the unmarked member of an opposeme.
The term grammatical category implies that:
1) there exist different morphological forms in the words of a part of speech possessing different referential meanings;
2) the oppositions of different forms possessing referential meanings are systematic that is they cover the whole class of words of that part of speech.
In other words a grammatical category is a systematic opposition of different morphological forms possessing different referential meanings. Each grammatical category is composed of at least two contrasting forms. Otherwise category would stop existing.
In general, an opposeme of any grammatical category consists of as many members (or opposites) as there are particular manifestations of the general meaning. Thus, a morphological opposeme is a minimum set of words revealing (by the difference in their forms) only (and all) the particular manifestations of some general grammatical meaning. Any morphological category is the system of such opposemes whose members differ in form to express only (and all) the particular manifestations of the general meaning of the category [24; 23–24].
Grammatical category unites in itself particular grammatical meanings. For example, the grammatical category of gender unites the meanings of the masculine, feminine, neuter and common genders in the Ukrainian language. Each grammatical category is connected, as a minimum, with two forms. For example, the grammatical category of number comprises the forms of singularity and plurality.
Grammatical meaning isan abstract meaning added to the lexical meaning of a word, expressing its relations other words or classes of words. As a rule, a word has several grammatical meanings. Grammatical meanings are realized in a grammatical word form.
Grammatical form of a word is the variety of the same word differing from other forms of this word by its grammatical meaning. For example, in the Ukrainian word-form батьку the ending -у expresses the grammatical meaning of the masculine gender, singular number, dative case.
Grammatical form of a word can be simple (synthetic), in which the grammatical meanings are formed by the ending, suffix, prefix or stress, etc. (дощ – дощ – дощем); or composite (analytical), created by adding several words (буду говорити, більш привабливий). The analytical-synthetic grammatical word form is a combination of two previous types of word forms. For example, в університеті (the local case is expressed by the flexion and the preposition); малював би, малювала б (the grammatical meaning of number and gender is expressed by the form of the main verb, and the meaning of the conditional mood – by the particle би) [2; 40–41].
|
Важнейшие способы обработки и анализа рядов динамики Не во всех случаях эмпирические данные рядов динамики позволяют определить тенденцию изменения явления во времени… |
ТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКАЯ МЕХАНИКА Статика является частью теоретической механики, изучающей условия, при которых тело находится под действием заданной системы сил… |
Теория усилителей. Схема Основная масса современных аналоговых и аналого-цифровых электронных устройств выполняется на специализированных микросхемах… |
Логические цифровые микросхемы Более сложные элементы цифровой схемотехники (триггеры, мультиплексоры, декодеры и т.д.) не имеют… |