The term Worksheet used in Excel documents is a collection of cells organized in rows and columns.Each worksheet contains 1048576 rows and 16384 columns and serves as a giant table that allows you to organize information.
Contents
- 1 Where is sheet in Excel?
- 2 What is a sheet or workbook?
- 3 What is sheet 1 Excel?
- 4 How do you use sheets in Excel?
- 5 What is Excel sheet and its uses?
- 6 What is the difference between spreadsheet and sheet?
- 7 What is the difference between worksheet and Excel sheet?
- 8 What is sheet in computer?
- 9 What is function sheet?
- 10 What is Excel ribbon?
- 11 How do you use sheet functions?
- 12 How do you use sheet names in Excel?
- 13 What are the 5 functions in Excel?
- 14 Why is Excel called Excel?
- 15 What are the types of worksheet data?
- 16 What is the difference between word processing and spreadsheet?
- 17 What is meant by row and column?
- 18 How do you remove everything from a cell?
- 19 What are some important parts of an Excel spreadsheet worksheet?
- 20 What is an answer sheet?
For all other Excel versions, click File > Options > Advanced—in under Display options for this workbook—and then ensure that there is a check in the Show sheet tabs box.
What is a sheet or workbook?
A worksheet or sheet is a single page in a file created with an electronic spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. A workbook is the name given to an Excel file and contains one or more worksheets.
What is sheet 1 Excel?
In Microsoft Excel, a sheet, sheet tab, or worksheet tab is used to display the worksheet that a user is currently editing.These tabs are labeled “Sheet 1,” “Sheet 2,” and “Sheet 3.” Users may add, move, and rename worksheets.
How do you use sheets in Excel?
Create a simple formula in Excel
- On the worksheet, click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
- Type the = (equal sign) followed by the constants and operators (up to 8192 characters) that you want to use in the calculation. For our example, type =1+1. Notes:
- Press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac).
What is Excel sheet and its uses?
Microsoft Excel is a helpful and powerful program for data analysis and documentation. It is a spreadsheet program, which contains a number of columns and rows, where each intersection of a column and a row is a “cell.” Each cell contains one point of data or one piece of information.
What is the difference between spreadsheet and sheet?
A spreadsheet is primarily designed to provide a digital form of the paper-based worksheet. Spreadsheets work through spreadsheet application software. The rows and columns within the spreadsheet contain cells that are filled with data to create unique operations.
What is the difference between worksheet and Excel sheet?
The worksheet is single page spreadsheet or page in Excel, where you can write, edit and manipulate data, whereas the collection of such worksheets is referred as a workbook. It is very similar to a single page (worksheet) and a complete book (workbook).
What is sheet in computer?
A sheet is another name for a single piece of paper or a hard copy. 2. In software, a sheet is a single page in a word processor or single worksheet in a spreadsheet.Sheets is also another name for Google Sheets.
What is function sheet?
Function Sheet means the document that details all the particulars of an event and will be the basis of agreement between The Council and The Hirer.
What is Excel ribbon?
First introduced in Excel 2007, the ribbon is the strip of buttons and icons located above the work area. The ribbon replaces the menus and toolbars found in earlier versions of Excel.
How do you use sheet functions?
How to Use Google Sheets Functions
- Select the cell where you want to display the result of the calculation.
- On the toolbar, select Functions, then choose a function.
- Choose the cells to include in the range.
- Press Enter.
- The result appears in the selected cell.
How do you use sheet names in Excel?
Reference the current sheet tab name in cell with formula
1. Select a blank cell, copy and paste the formula =MID(CELL(“filename”,A1),FIND(“]”,CELL(“filename”,A1))+1,255) into the Formula Bar, and the press the Enter key. See screenshot: Now the sheet tab name is referenced in the cell.
What are the 5 functions in Excel?
5 Functions of Excel/Sheets That Every Professional Should Know
- VLookup Formula.
- Concatenate Formula.
- Text to Columns.
- Remove Duplicates.
- Pivot Tables.
Why is Excel called Excel?
The name of Excel was picked to give impression of ‘It can do everything Lotus 123 does, but exceptionally better’. Microsoft was initially developed Multiplan, a spreadsheet program for CP/M system but unfortunately in MS-DOS, Multiplan was losing to Lotus 123.
What are the types of worksheet data?
Identifying Types of Data
Excel worksheets contain four types of data: text, values, dates, and formulas.
What is the difference between word processing and spreadsheet?
Spreadsheet and word processing programs are similar, but a spreadsheet application is geared toward numerical data and a word processing application is geared toward composing documents.
What is meant by row and column?
Rows are a group of cells arranged horizontally to provide uniformity. Columns are a group of cells aligned vertically, and they run from top to bottom.
How do you remove everything from a cell?
Clearing cell contents
- Select the cells containing the content you want to clear.
- Click the Clear button (the one with the eraser) in the Editing group on the Home tab.
- Click one of the following options on the Clear drop-down menu: Clear All gets rid of all formatting, comments, and entries in the cell selection.
What are some important parts of an Excel spreadsheet worksheet?
Also called a spreadsheet, the workbook is a unique file created by Excel XP.
- Title bar. The title bar displays both the name of the application and the name of the spreadsheet.
- Menu bar.
- Column headings.
- Row headings.
- Name box.
- Formula bar.
- Cell.
- Navigation buttons and sheet tabs.
What is an answer sheet?
noun. 1A sheet of paper used to write the answers to a test, examination, quiz, etc. 2A sheet of paper containing the correct answers to a test, examination, quiz, etc., used as a guide for marking students’ answers.
Содержание
- Spreadsheet
- Spreadsheet overview
- Difference between a workbook, worksheet, and spreadsheet
- Examples of spreadsheet programs
- Examples and uses of a spreadsheet
- Finance
- Forms
- School and grades
- Lists
- Sports
- How do I enter data in a spreadsheet?
- Why not use a word processor instead of a spreadsheet?
- How to tell if a worksheet is active?
- How many worksheets open by default?
- How many worksheets can you have in a workbook?
- What is the length limit of a worksheet name?
- How are rows and columns labeled?
- Download an example of a spreadsheet file
- What did people use before spreadsheets?
- What is Microsoft Excel and What Does It Do?
- What Excel Is Used For
- Spreadsheet Cells and Cell References
- Data Types, Formulas, and Functions
- Excel and Financial Data
- Excel’s Other Uses
- Excel Alternatives
- What is Excel?
- What is Excel in Computer?
- What is Excel Used for?
- Where Excel is Used?
- Features of MS Excel:
- Graphical Features of Excel
- Data Base Features of Excel
- Functional Features of Excel
- Key Components:
- Usage
- Industries
- Interface
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Templates
- Enhancing Excel Features
- Programming Language
- Macros
- Add-ins
- Integration with Other Office Applications:
- Security Features
- Resource and Support Communities:
- Limitations
- Data security and privacy
- Data accuracy and integrity
- Alternative Applications
- Conclusion
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet or worksheet is a file made of rows and columns that help sort, organize, and arrange data efficiently, and calculate numerical data. What makes a spreadsheet software program unique is its ability to calculate values using mathematical formulas and the data in cells. An example of how a spreadsheet may be utilized is creating an overview of your bank’s balance.
Spreadsheet overview
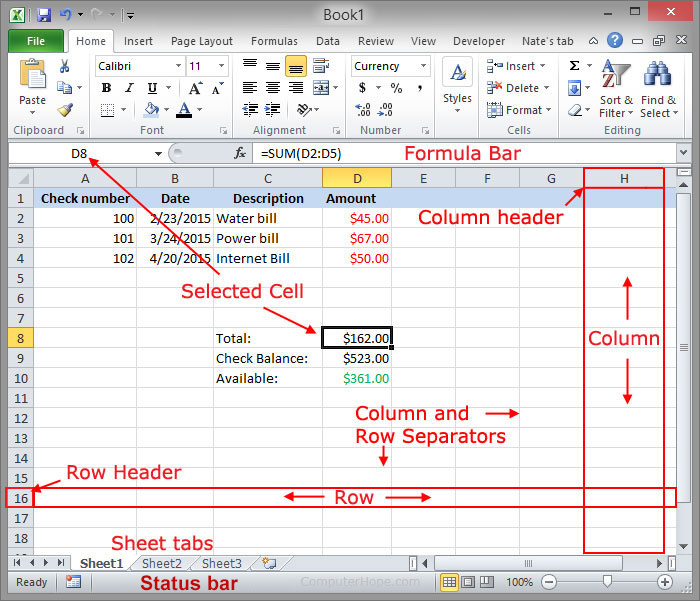
Below is a basic example of what a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet looks like, with all the important features of a spreadsheet highlighted.
In the above example, this spreadsheet is listing three different checks, the date, their description, and the value of each check. These values are then added together to get the total of $162.00 in cell D6. That value is subtracted from the check balance to give an available $361.00 in cell D8.
Difference between a workbook, worksheet, and spreadsheet
Because the terms spreadsheet, workbook, and worksheet are so similar, there often is confusion when trying to understand their differences. When you open Microsoft Excel (a spreadsheet program), you’re opening a workbook. A workbook can contain one or more different worksheets that are accessed through the tabs at the bottom of the worksheet your currently viewing. What’s often most confusing is that a worksheet is synonymous with a spreadsheet. In other words, a spreadsheet and worksheet mean the same thing. However, most people only refer to the program as a spreadsheet program and the files it creates as spreadsheet files or worksheets.
Examples of spreadsheet programs
Today, Microsoft Excel is a popular and widely used spreadsheet program, but there are also many alternatives. Below is a list of spreadsheet programs used to create a spreadsheet.
Examples and uses of a spreadsheet
Although spreadsheets are often used with anything containing numbers, the uses of a spreadsheet are almost endless. Below are some other popular uses of spreadsheets.
Finance
Spreadsheets are ideal for financial data, such as your checking account information, budgets, taxes, transactions, billing, invoices, receipts, forecasts, and any payment system.
Forms
Form templates can be created to handle inventory, evaluations, performance reviews, quizzes, time sheets, patient information, and surveys.
School and grades
Teachers can use spreadsheets to track students, calculate grades, and identify relevant data, such as high and low scores, missing tests, and students who are struggling.
Lists
Managing a list in a spreadsheet is a great example of data that does not contain numbers, but still can be used in a spreadsheet. Great examples of spreadsheet lists include telephone, to-do, and grocery lists.
Sports
Spreadsheets can keep track of your favorite player stats or stats on the whole team. With the collected data, you can also find averages, high scores, and statistical data. Spreadsheets can even be used to create tournament brackets.
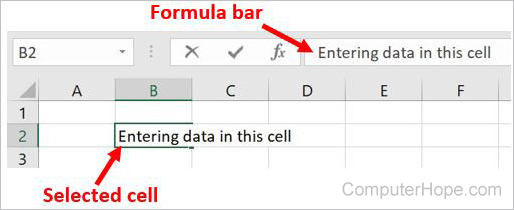
How do I enter data in a spreadsheet?
In a spreadsheet, data is entered in one or more cells. To enter data in a cell, follow the steps below.
- Click the cell where you want to enter data.
- Start typing the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
- Click the cell where you want to enter additional data.
- Click in the formula bar, located between the Ribbon and all cells, where you want to start entering the additional data.
- Type the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
If you want to add additional data to a cell that already has data entered in it, follow the steps below.
- Click the cell where you want to enter additional data.
- Click in the formula bar, located between the Ribbon and all cells, where you want to start entering the additional data.
- Type the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell where the mouse cursor is placed in the formula bar.
Why not use a word processor instead of a spreadsheet?
Although some uses above could be done in a word processor, spreadsheets have a considerable advantage over word processors when using numbers. It would be impossible to calculate multiple numbers in a word processor and have the value of the calculation immediately appear. Spreadsheets are also more dynamic with the data and can hide, show, and sort information to make processing lots of information easier.
How to tell if a worksheet is active?
An active worksheet is the worksheet that is currently open. For example, in the earlier Excel picture, the sheet tabs at the bottom show «Sheet1,» «Sheet2,» and «Sheet3,» with Sheet1 being the active worksheet. The active tab usually has a white background behind the tab name.
How many worksheets open by default?
In Microsoft Excel 2016 and earlier, and OpenOffice Calc, there are three sheet tabs that open (Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3) by default. In Google Sheets, your spreadsheets starts with one sheet (Sheet1).
In Microsoft Excel 365, by default, there is only one sheet tab that opens (Sheet1) when you create a workbook.
How many worksheets can you have in a workbook?
The default number of worksheets in a new workbook is 255. However, once the file is saved, you can add as many as your hard drive capacity allows.
What is the length limit of a worksheet name?
Not to be confused with the file name, in Microsoft Excel, there is a 31 character limit for each worksheet name.
How are rows and columns labeled?
In all spreadsheet programs, including Microsoft Excel, rows are labeled using numbers (e.g., 1 to 1,048,576). All columns are labeled with letters from A to Z, then with two letters. For example, after the letter Z, the next column is AA, AB, AC, . AZ and then incrementing to BA, BB, BC, etc., to the last column XFD.
When working with a cell, you combine the column with the row. For example, the very first cell is in column A and on row 1, so the cell is labeled as A1.
Download an example of a spreadsheet file
We’ve created a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that can be downloaded and opened in any spreadsheet program including Microsoft Excel. This spreadsheet helps illustrate some a spreadsheet capability, formulas, and functions used in a spreadsheet, and lets you experiment with a spreadsheet.
The same spreadsheet is also available on Google Sheets. Visit the link below to open the spreadsheet in view mode in Google Sheets. If you want to edit any of the values, click File and then Make a copy option to save it to your Google Drive.
What did people use before spreadsheets?
Before computerized spreadsheets ledger paper was used to keep track of numbers and make calculations. In fact, many accountants and other individuals continued to use ledger paper even after the release of spreadsheet programs because they didn’t trust computers to make proper calculations.
Источник
What is Microsoft Excel and What Does It Do?
This versatile program helps you make sense of your data
Excel is an electronic spreadsheet program that is used for storing, organizing, and manipulating data.
The information we’ve prepared refers to Microsoft Excel in general and is not limited to any specific version of the program.
What Excel Is Used For
Electronic spreadsheet programs were originally based on paper spreadsheets used for accounting. As such, the basic layout of computerized spreadsheets is the same as the paper ones. Related data is stored in tables — which are a collection of small rectangular boxes or cells organized into rows and columns.
All versions of Excel and other spreadsheet programs can store several spreadsheet pages in a single computer file. The saved computer file is often referred to as a workbook and each page in the workbook is a separate worksheet.
Spreadsheet Cells and Cell References
When you look at the Excel screen — or any other spreadsheet screen — you see a rectangular table or grid of rows and columns.
In newer versions of Excel, each worksheet contains roughly a million rows and more than 16,000 columns, which necessitates an addressing scheme in order to keep track of where data is located.
The horizontal rows are identified by numbers (1, 2, 3) and the vertical columns by letters of the alphabet (A, B, C). For columns beyond 26, columns are identified by two or more letters such as AA, AB, AC or AAA, AAB, etc.
The intersection point between a column and a row is the small rectangular box known as a cell. The cell is the basic unit for storing data in the worksheet, and because each worksheet contains millions of these cells, each one is identified by its cell reference.
A cell reference is a combination of the column letter and the row number such as A3, B6, and AA345. In these cell references, the column letter is always listed first.
Data Types, Formulas, and Functions
The types of data that a cell can hold include:
- Numbers
- Text
- Dates and times
- Boolean values
- Formulas
Formulas are used for calculations — usually incorporating data contained in other cells. These cells, however, may be located on different worksheets or in different workbooks.
Creating a formula starts by entering the equal sign in the cell where you want the answer displayed. Formulas can also include cell references to the location of data and one or more spreadsheet functions.
Functions in Excel and other electronic spreadsheets are built-in formulas that are designed to simplify carrying out a wide range of calculations – from common operations such as entering the date or time to more complex ones such as finding specific information located in large tables of data.
Excel and Financial Data
Spreadsheets are often used to store financial data. Formulas and functions that are used on this type of data include:
- Performing basic mathematical operations such as summing columns or rows of numbers
- Finding values such as profit or loss
- Calculating repayment plans for loans or mortgages
- Finding the average, maximum, minimum and other statistical values in a specified range of data
- Carrying out What-If analysis on data, where variables are modified one at a time to see how the change affects other data, such as expenses and profits
Excel’s Other Uses
Other common operations that Excel can be used for include:
- Graphing or charting data to assist users in identifying data trends
- Formatting data to make important data easy to find and understand
- Printing data and charts for use in reports
- Sorting and filtering data to find specific information
- Linking worksheet data and charts for use in other programs such as Microsoft PowerPoint and Word
- Importing data from database programs for analysis
Spreadsheets were the original «killer apps» for personal computers because of their ability to compile and make sense of information. Early spreadsheet programs such as VisiCalc and Lotus 1-2-3 were largely responsible for the growth in popularity of computers like the Apple II and the IBM PC as a business tool.
Excel Alternatives
Other current spreadsheet programs that are available for use include:
- Google Sheets: A free, web-based spreadsheet program
- Excel Online: A free, scaled-down, web-based version of Excel
- Open Office Calc: A free, downloadable spreadsheet program.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Источник
What is Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program available in the Microsoft Office Package. MS Excel is used to create Worksheets (spreadsheets) to store and organize data in a table format.
Microsoft Excel is one of the most used software application in the world. Excel have the Powerful Tools and Functions, using it for wide verity of applications across the global IT Companies. It is easy to enter the data, read and manipulate the data. Excel stores the data in a table format in Rows and Columns.
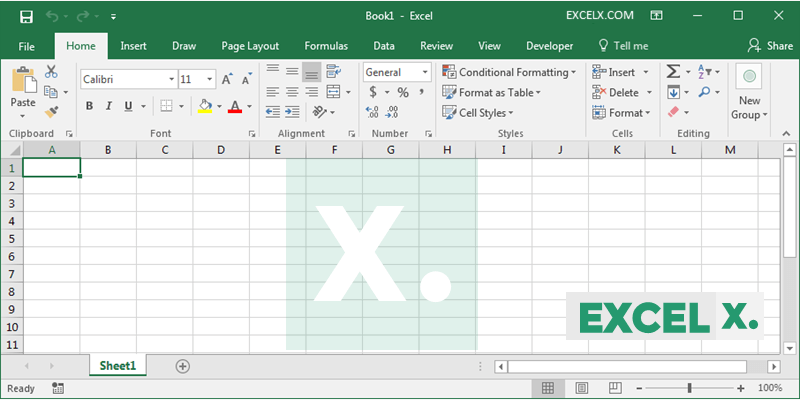
Here is a screen-shot of a Microsoft Excel File:
What is Excel in Computer?
In computer terms, Excel is a spreadsheet application in Microsoft Office Pack. It is one of the most using Applications in business industries. We can store any kind of the data in the spreadsheets in the Excel Range or Excel Cells. We can also insert Images, Shapes, Charts, Pivot Tables in the Excel Sheets to understand the data.
What is Excel Used for?
Microsoft Excel used for storing the data, processing the data, analyzing and presenting the data.
- We can enter data in Strings, Dates or Numerical type of Data in the Excel Cells and Save the Files for future reference
- We can use verity of formulas available in Excel to perform calculations
- We can Develop Tools and Dashboards
- We can Interact with Other Applications
- We can connect to verity of Data Bases
- We can represent data in Charts
- We can drill down and analyze the data using Pivot Tables
Where Excel is Used?
Microsoft Excel used in almost all industries. Here are the some of the real-time Excel Using industries and domains:
- Financial sector is excessively using to perform different kind of calculations.
- Analytical professional use Excel almost everyday for applying the basic analytical techniques and tools.
- Banking Sector use to understand the Customer
- Retail Associates uses for analyzing the POS data to check the change and trend in sales
- Reporting Analysts uses for generating Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly and Yearly Reports.
- Healthcare Teams uses for performing the longitudinal data analysis.
- Market Research Analysts uses for finding the frequencies and cumulative aggregates.
- VBA Developers uses for developing the Office Applications, Tools, Office Add-ins and Dashboards.
Features of MS Excel:
The following features of Excel made the Excel as most widely using application:
Graphical Features of Excel
Excel have verity of the graphical features to represent the data in Charts and pictorial format. For Example, Charts, Shapes, Smart Arts, Clip Arts, Pictures.
Data Base Features of Excel
Excel can be used as data base and perform of verity of data operations. For example, Pivot Tables, Slicers, Tables, Spark lines, Database, Sorting, Filtering, Data Validation, Grouping, etc.
Functional Features of Excel
Excel Tools and Functions will help to perform powerful calculations and enhance the Excel Application Features. For example, Formulas, VBA Macros, Add-ins, Hyperlinks, Conditional Formatting, Spell Check, Protection, etc.
Key Components:
Excel is a spreadsheet software developed by Microsoft that is used to perform calculations, data analysis, and data visualization. Some of the key components of Excel include:
- Workbook: A workbook is the main file that contains one or more worksheets where you can enter data, perform calculations, and create charts and graphs.
- Worksheet: A worksheet is a single spreadsheet within a workbook that consists of rows, columns, and cells.
- Cell: A cell is a rectangular box in a worksheet where you can enter data, formulas, and functions.
- Range: A group of adjacent cells, which can be selected and formatted together.
- Chart: A chart is a visual representation of data in a worksheet that can help you to identify patterns and trends.
- PivotTable: A PivotTable is a powerful tool that allows you to summarize and analyze large amounts of data quickly and easily.
- Sparklines: Sparklines are small, simple charts that are used to show trends in data over time.
- Ribbon: The Ribbon is a graphical user interface that contains all the tools and commands you need to work with Excel. It is organized into tabs, which are further divided into groups of related commands.
- Quick Access Toolbar: The Quick Access Toolbar is a customizable toolbar that provides quick access to frequently used commands.
- Name box: The box located to the left of the formula bar, which displays the reference of the selected cell or range.
- Solver: Solver is an add-in tool that allows you to find the optimal solution to a problem by changing the values of certain variables.
- Goal Seek: Goal Seek is a tool that allows you to determine the value of a variable that will achieve a certain goal in a formula.
- Scenario Manager: Scenario Manager is a tool that allows you to create and compare different scenarios for a worksheet by changing the input values of certain variables.
- Power Query: Power Query is a tool that allows you to transform and analyze large amounts of data from various sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, and web pages.
- Power Pivot: Power Pivot is an add-in tool that allows you to create advanced data models and perform complex data analysis using large amounts of data.
- Data Tables: Data Tables are tools that allow you to calculate multiple results based on different sets of input values for one or more formulas.
- Web Queries: Web Queries are tools that allow you to import data from a website directly into Excel, making it easier to collect and analyze data from the internet.
- Get & Transform: Get & Transform is a feature that allows you to connect to various data sources, transform and reshape data, and load it into Excel for analysis and reporting.
- Freeze Panes: Freeze Panes is a feature that allows you to keep certain rows or columns visible as you scroll through a worksheet, making it easier to view and analyze large amounts of data.
- Collaboration Tools: Excel also provides various collaboration tools that allow multiple users to work on the same worksheet simultaneously, such as shared workbooks and co-authoring.
- Protect Workbook/Worksheet: Protect Workbook/Worksheet is a feature that allows you to restrict access to certain parts of a workbook or worksheet by setting password protection, so that only authorized users can view or edit the data.
- Error Checking: Error Checking is a feature that allows you to identify and correct errors in your formulas and functions, which can help to ensure data accuracy.
- Templates: Excel Templates are pre-designed spreadsheets that you can use to quickly create different types of documents, such as budgets, calendars, and invoices.
- Macro: A macro is a set of instructions that automate repetitive tasks in Excel.
- Office Add-ins: Office Add-ins are third-party tools that you can install in Excel to extend its functionality, such as data connectors, visualization tools, and productivity apps.
- Merge cells: A tool that allows you to combine multiple cells into a single, larger cell.
- Autofill: A tool that allows you to quickly fill a series of cells with a pattern or sequence of data.
- Data Validation: Data Validation is a feature that allows you to restrict the type of data that can be entered into a cell. This can help to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Custom Number Formats: Custom Number Formats are tools that allow you to create your own number formats, making it easier to display numbers in a way that is more meaningful for your data.
- Text to Columns: Text to Columns is a feature that allows you to split data in a column into multiple columns based on a delimiter, such as a comma or space.
- Flash Fill: Flash Fill is a tool that allows you to automatically fill in data based on a pattern that you specify, making it easier to clean and transform data.
- Print Options: Excel also provides various print options that allow you to customize the layout and formatting of your worksheet before printing, such as page orientation, margins, and scaling.
- Page Layout View: Page Layout View is a feature that allows you to view your worksheet as it will appear when printed, making it easier to adjust the layout and formatting.
- Filter: A tool that allows you to display only specific data in a worksheet, based on certain criteria.
- Sort: A tool that allows you to arrange data in a worksheet in ascending or descending order, based on certain criteria.
- Function: A function is a built-in formula that performs a specific calculation or task, such as SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, and MIN.
- Formula: A formula is an equation that performs a calculation in a cell based on the values in other cells.
- Formula bar: The area at the top of the Excel window where you can view and edit the contents of a selected cell.
- Cell reference: A way to identify a cell in a worksheet, which is a combination of the column letter and row number, such as A1, B2, etc.
- Relative reference: A cell reference that changes when you copy or move a formula to a different location in a worksheet.
- Absolute reference: A cell reference that remains constant when you copy or move a formula to a different location in a worksheet, which is denoted by a dollar sign ($).
- Mixed reference: A cell reference that has both absolute and relative components, which is denoted by a dollar sign ($) before the column or row reference.
- Dynamic Arrays: Dynamic Arrays are a new feature in Excel that allow you to create formulas that automatically expand or shrink to fit the size of the data, making it easier to perform calculations on large datasets.
- Formula auditing: A tool that allows you to trace the relationships between cells and formulas in a worksheet, which can help you identify errors and troubleshoot problems.
Usage
Excel is a widely used spreadsheet program developed by Microsoft. It is part of the Microsoft Office suite of applications and is used to organize, analyse, and manipulate data. Excel allows users to create, format, and manipulate tables of numerical and textual data in rows and columns.
Users can perform various mathematical and statistical calculations on the data, create charts and graphs to visualize the data, and use formulas and functions to automate calculations and analysis. Excel also provides various tools and features for data analysis, such as sorting, filtering, and pivot tables, that allow users to extract insights quickly and easily from large data sets.
Industries
Excel can be used in a variety of industries and professions, including finance, accounting, marketing, and research. It is often used for budgeting, financial forecasting, tracking expenses, inventory management, and analyzing sales data.
Interface
Excel has a user-friendly interface and is widely available on Windows and Mac OS systems. Additionally, Excel supports collaboration features, such as sharing workbooks and co-authoring, which allow multiple users to work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously.
Data Analysis
Another important feature of Excel is its ability to handle large amounts of data. Excel can handle millions of rows of data and thousands of columns, making it ideal for working with large datasets. Additionally, Excel provides several features for managing large datasets, such as sorting, filtering, and searching.
Excel also allows users to collaborate on workbooks in real-time using cloud-based solutions like OneDrive or SharePoint. This feature makes it easy for teams to work on the same document simultaneously and ensures that everyone is working with the most up-to-date version of the data.
Data Visualization
Excel also provides various tools for data visualization, which make it easy to create charts, graphs, and other visualizations that help to communicate data insights. With features like sparklines and conditional formatting, users can quickly identify trends and patterns in data without the need for complex analysis.
Overall, Excel is an essential tool for anyone who works with data. Its extensive feature set, customizability, and ease of use make it an ideal choice for businesses, researchers, educators, and individuals. Whether you are working with small datasets or large, Excel can help you manage and analyze your data efficiently, saving you time and improving your productivity.
Templates
Excel also provides various templates that help users get started with common tasks, such as budgeting, invoicing, and project management. These templates can be customized to meet specific needs, making it easy for users to create professional-looking spreadsheets without starting from scratch.
Enhancing Excel Features
Another way to overcome some of the limitations of Excel is to use Excel add-ins or plugins that provide additional features and capabilities. There are many add-ins available that can help users automate tasks, perform advanced analysis, and enhance visualization.
- For example, the Analysis ToolPak add-in provides a wide range of statistical and engineering functions, while the Power Query add-in allows users to extract and transform data from a variety of sources. The Solver add-in can help users find optimal solutions for complex problems, while the Power Pivot add-in provides advanced data modeling and analysis capabilities.
- In addition to add-ins, users can also consider using Excel templates or pre-built solutions that provide pre-configured spreadsheets and models for specific use cases. There are many templates available for financial modeling, budgeting, project management, and other applications. These templates can help users save time and avoid errors by providing pre-built formulas and templates for common tasks.
Finally, to improve collaboration and data sharing, users can consider using cloud-based collaboration platforms such as Microsoft Teams or SharePoint. These platforms allow users to share and collaborate on Excel spreadsheets in real-time, providing a more efficient and collaborative workflow.
Programming Language
Excel also has a programming language called VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) that allows users to automate repetitive tasks and create custom solutions. With VBA, users can create macros, which are small programs that automate common tasks, such as formatting data or generating reports.
VBA also provides access to many of Excel’s built-in features, as well as the ability to create custom functions and procedures. This allows users to create highly customized solutions that can save time and increase efficiency.
Macros
In addition to add-ins, templates, and complementary tools, users can also consider using Excel macros to automate repetitive tasks and improve productivity. Macros are small programs written in Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) that can be used to automate tasks and add custom functionality to Excel.
- With macros, users can automate tasks such as formatting, data entry, and data cleaning, as well as perform more advanced tasks such as data analysis and modeling. Macros can also be used to create custom functions and formulas that can be reused in other Excel spreadsheets.
- To create macros, users need to have a basic understanding of VBA programming. Excel provides a built-in macro recorder that allows users to record their actions and convert them into VBA code. Users can also write their own code from scratch or modify existing code to create more complex macros.
- Macros can be saved as part of the Excel spreadsheet or as a separate file, and can be easily shared with other users. However, it is important to be cautious when using macros as they can potentially contain malicious code that can harm your computer or compromise your data.
- Excel VBA Macros can be a powerful tool for automating tasks and improving productivity in Excel. By learning how to write and use macros, users can save time and improve their workflow, and add custom functionality to Excel spreadsheets. However, it is important to be careful when using macros, and to ensure that they come from a trusted source and do not contain any malicious code.
Add-ins
In addition to its core features, Excel also supports a wide range of add-ins and third-party applications that can further extend its functionality. For example, users can install add-ins to enhance data visualization, automate data entry, or integrate Excel with other software tools.
Integration with Other Office Applications:
One of the advantages of Excel is its compatibility with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and PowerPoint. Excel data can easily be copied and pasted into these applications, allowing users to create professional-looking documents and presentations that include charts, tables, and graphs.
Excel also supports a wide range of file formats, including CSV, TXT, XML, and HTML, making it easy to share data with other applications or import data from external sources. Additionally, Excel can connect to external data sources such as SQL databases, SharePoint lists, and OData feeds, allowing users to work with data from a wide range of sources.
Security Features
Excel also provides various security features, such as password protection and file encryption, that help to keep data safe and secure. This is especially important when working with sensitive or confidential information.
Finally, Excel is widely supported by third-party tools and services, which can further enhance its capabilities. For example, there are many add-ins and plug-ins available that provide additional functionality, such as data analysis tools, charting software, and collaboration platforms.
In conclusion, Excel is a powerful and versatile tool that provides many features and capabilities for managing and analyzing data. Whether you are a business owner, financial analyst, researcher, or student, Excel can help you work with data more efficiently and effectively. Its ease of use, customizability, and compatibility with other applications make it an ideal choice for anyone who works with data on a regular basis.
Resource and Support Communities:
Excel’s popularity has led to the development of many resources and support communities, which can help users learn how to use the software effectively. These resources include online tutorials, user forums, and training courses, which can help users become proficient in Excel quickly.
- Furthermore, Excel’s features are constantly evolving, with new updates being released on a regular basis. These updates often include new tools and functionality that help users work with data more effectively.
- In addition to its features, Excel’s versatility and wide range of applications make it an essential tool for many industries and professions. For example, Excel is commonly used in finance and accounting for budgeting, forecasting, and financial modeling. It is also used in marketing and sales for data analysis, customer segmentation, and campaign tracking.
- In research, Excel is used for data cleaning, manipulation, and analysis. Excel is also frequently used in education, where it is used to teach data analysis, statistics, and financial modeling.
In summary, Excel is a powerful and versatile tool that provides many features and capabilities for managing and analyzing data. Its ease of use, customizability, compatibility with other applications, and wide range of applications make it an essential tool for many industries and professions. With its continued development and support, Excel is likely to remain a key tool for data management and analysis for years to come.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, Excel is not without its limitations. One limitation is its ability to handle extremely large datasets. While Excel can handle millions of rows of data, it may become slow and unwieldy with datasets that exceed this limit.
- Additionally, Excel is not well-suited for complex data modeling and analysis. While it provides many tools and features for data analysis, it may not be the best choice for advanced statistical analysis or machine learning.
- Another limitation of Excel is its potential for errors. Because it relies on manual data entry and manipulation, it is vulnerable to human errors such as typos and miscalculations. Additionally, its use of cell-based formulas and references can lead to errors when cells are moved or deleted.
- Finally, Excel’s use of proprietary file formats can make it difficult to share data with users who do not have access to the software. While Excel can save files in a variety of formats, users may need to use specialized software to open or work with these files.
- While Excel is a powerful and versatile tool for managing and analyzing data, it does have some limitations. Users should be aware of these limitations and choose the appropriate tools and software for their specific needs. Despite its limitations, Excel remains a popular and widely used tool for data management and analysis, and its continued development and support make it a valuable tool for many industries and professions.
Data security and privacy
Another important consideration when working with Excel is data security and privacy. Excel files can contain sensitive and confidential data, such as financial records, personal information, or trade secrets. As such, it is important to take appropriate measures to protect this data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- One way to improve data security in Excel is to use password protection. Excel allows users to password-protect their spreadsheets and workbooks, which can prevent unauthorized access or editing. Passwords should be strong and complex, and users should avoid sharing passwords with others or storing them in an insecure location.
- Another way to improve data security is to restrict access to Excel files. Users can use file permissions to control who has access to their Excel files and what they can do with them. For example, users can set read-only permissions for certain users, or prevent users from copying or printing the file.
- Users should also be aware of the risks associated with sharing Excel files over email or cloud storage services. Excel files can be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties if they are not encrypted or secured properly. To avoid these risks, users can use secure file-sharing services or encrypt their Excel files before sharing them.
- Finally, users should be aware of privacy laws and regulations that may apply to their use of Excel. For example, certain types of data, such as personal information or medical records, may be subject to specific data protection laws. Users should ensure that they are complying with applicable privacy laws and regulations when working with Excel.
In conclusion, data security and privacy are important considerations when working with Excel. By using password protection, access restrictions, secure file-sharing, and complying with privacy laws, users can protect their sensitive data and ensure that it is not disclosed or accessed by unauthorized parties.
Data accuracy and integrity
Another important consideration when working with Excel is data accuracy and integrity. Excel spreadsheets can be prone to errors, such as data entry mistakes, formula errors, or incorrect formatting. These errors can lead to incorrect analysis, decision-making, or reporting, and can have serious consequences for businesses or organizations.
- To ensure data accuracy and integrity, users should follow best practices for data entry and management in Excel. This includes using consistent and clear naming conventions for data and columns, validating data as it is entered, using data validation rules to restrict data entry to specific formats or ranges, and using formulas and functions to perform calculations and analysis.
- Users should also be careful when using copy-and-paste or importing data from external sources, as these actions can introduce errors or inconsistencies in the data. Users should validate and clean data as it is imported, and ensure that data is formatted consistently with the rest of the spreadsheet.
- Another way to improve data accuracy and integrity is to perform regular checks and audits of Excel spreadsheets. Users can use tools such as Excel’s auditing and error-checking features to identify potential errors or inconsistencies in their data, and correct them before they become serious issues. Users can also use third-party tools or add-ins that provide more advanced auditing and error-checking capabilities.
In conclusion, data accuracy and integrity are critical considerations when working with Excel. By following best practices for data entry and management, validating and cleaning data, performing regular checks and audits, and using tools and add-ins that improve data accuracy and integrity, users can ensure that their Excel spreadsheets are reliable, accurate, and trustworthy.
Alternative Applications
To mitigate some of the limitations of Excel, there are several alternatives and complementary tools that users can consider. For example, users can consider using more advanced data analysis software such as Python, R, or MATLAB, which offer more powerful statistical analysis and machine learning capabilities.
- Users can also consider using cloud-based data management and analysis tools such as Google Sheets or Microsoft Power BI, which offer collaborative features, more powerful data visualization options, and support for larger datasets.
- Finally, to ensure compatibility and interoperability with other software and systems, users can consider using open-source or non-proprietary file formats such as CSV or JSON, which can be read and manipulated by a wide range of software tools and platforms.
- In summary, while Excel remains a valuable tool for data management and analysis, it is important for users to be aware of its limitations and consider using complementary tools and software to meet their specific needs. By combining Excel with other tools and techniques, users can work more efficiently, reduce errors, and extract more value from their data.
Conclusion
Excel is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added with each new version. For example, recent updates have introduced new functions, new chart types, improved data analysis tools, and enhanced collaboration features.
- Excel is also widely used in data analysis and business intelligence. With features like Power Query and Power Pivot, users can easily connect to external data sources, clean and transform data, and create interactive dashboards and reports.
- In addition to its business applications, Excel is also used extensively in education, where it is used to teach data analysis, mathematical modeling, and financial analysis.
- Overall, Excel is a powerful and versatile tool that can be used to perform a wide range of tasks. Whether you are a small business owner, financial analyst, researcher, or student, Excel can help you manage and analyse data more efficiently, saving you time and improving your productivity. With its user-friendly interface, extensive feature set, and customizability, Excel is a valuable tool for businesses, professionals, and individuals alike.
In conclusion, while Excel has some limitations, there are many ways to overcome these limitations and enhance its capabilities. By using add-ins, templates, and complementary tools and software, users can work more efficiently, perform advanced analysis, and share data more effectively. With its continued development and support, Excel is likely to remain a key tool for data management and analysis for years to come.
Источник
Updated: 03/12/2022 by
A spreadsheet or worksheet is a file made of rows and columns that help sort, organize, and arrange data efficiently, and calculate numerical data. What makes a spreadsheet software program unique is its ability to calculate values using mathematical formulas and the data in cells. An example of how a spreadsheet may be utilized is creating an overview of your bank’s balance.
Spreadsheet overview
Below is a basic example of what a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet looks like, with all the important features of a spreadsheet highlighted.
In the above example, this spreadsheet is listing three different checks, the date, their description, and the value of each check. These values are then added together to get the total of $162.00 in cell D6. That value is subtracted from the check balance to give an available $361.00 in cell D8.
Difference between a workbook, worksheet, and spreadsheet
Because the terms spreadsheet, workbook, and worksheet are so similar, there often is confusion when trying to understand their differences. When you open Microsoft Excel (a spreadsheet program), you’re opening a workbook. A workbook can contain one or more different worksheets that are accessed through the tabs at the bottom of the worksheet your currently viewing. What’s often most confusing is that a worksheet is synonymous with a spreadsheet. In other words, a spreadsheet and worksheet mean the same thing. However, most people only refer to the program as a spreadsheet program and the files it creates as spreadsheet files or worksheets.
Examples of spreadsheet programs
Today, Microsoft Excel is a popular and widely used spreadsheet program, but there are also many alternatives. Below is a list of spreadsheet programs used to create a spreadsheet.
- Google Sheets — (online and free).
- iWork Numbers — Apple Office Suite.
- LibreOffice -> Calc (free).
- Lotus 1-2-3 (discontinued).
- Lotus Symphony — Spreadsheets.
- Microsoft Excel.
- OpenOffice -> Calc (free).
- VisiCalc (discontinued).
Examples and uses of a spreadsheet
Although spreadsheets are often used with anything containing numbers, the uses of a spreadsheet are almost endless. Below are some other popular uses of spreadsheets.
Finance
Spreadsheets are ideal for financial data, such as your checking account information, budgets, taxes, transactions, billing, invoices, receipts, forecasts, and any payment system.
Forms
Form templates can be created to handle inventory, evaluations, performance reviews, quizzes, time sheets, patient information, and surveys.
School and grades
Teachers can use spreadsheets to track students, calculate grades, and identify relevant data, such as high and low scores, missing tests, and students who are struggling.
Lists
Managing a list in a spreadsheet is a great example of data that does not contain numbers, but still can be used in a spreadsheet. Great examples of spreadsheet lists include telephone, to-do, and grocery lists.
Sports
Spreadsheets can keep track of your favorite player stats or stats on the whole team. With the collected data, you can also find averages, high scores, and statistical data. Spreadsheets can even be used to create tournament brackets.
How do I enter data in a spreadsheet?
In a spreadsheet, data is entered in one or more cells. To enter data in a cell, follow the steps below.
- Click the cell where you want to enter data.
- Start typing the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
or
- Click the cell where you want to enter additional data.
- Click in the formula bar, located between the Ribbon and all cells, where you want to start entering the additional data.
- Type the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
If you want to add additional data to a cell that already has data entered in it, follow the steps below.
- Click the cell where you want to enter additional data.
- Click in the formula bar, located between the Ribbon and all cells, where you want to start entering the additional data.
- Type the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell where the mouse cursor is placed in the formula bar.
Why not use a word processor instead of a spreadsheet?
Although some uses above could be done in a word processor, spreadsheets have a considerable advantage over word processors when using numbers. It would be impossible to calculate multiple numbers in a word processor and have the value of the calculation immediately appear. Spreadsheets are also more dynamic with the data and can hide, show, and sort information to make processing lots of information easier.
How to tell if a worksheet is active?
An active worksheet is the worksheet that is currently open. For example, in the earlier Excel picture, the sheet tabs at the bottom show «Sheet1,» «Sheet2,» and «Sheet3,» with Sheet1 being the active worksheet. The active tab usually has a white background behind the tab name.
How many worksheets open by default?
In Microsoft Excel 2016 and earlier, and OpenOffice Calc, there are three sheet tabs that open (Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3) by default. In Google Sheets, your spreadsheets starts with one sheet (Sheet1).
In Microsoft Excel 365, by default, there is only one sheet tab that opens (Sheet1) when you create a workbook.
How many worksheets can you have in a workbook?
The default number of worksheets in a new workbook is 255. However, once the file is saved, you can add as many as your hard drive capacity allows.
What is the length limit of a worksheet name?
Not to be confused with the file name, in Microsoft Excel, there is a 31 character limit for each worksheet name.
How are rows and columns labeled?
In all spreadsheet programs, including Microsoft Excel, rows are labeled using numbers (e.g., 1 to 1,048,576). All columns are labeled with letters from A to Z, then with two letters. For example, after the letter Z, the next column is AA, AB, AC, …, AZ and then incrementing to BA, BB, BC, etc., to the last column XFD.
When working with a cell, you combine the column with the row. For example, the very first cell is in column A and on row 1, so the cell is labeled as A1.
- How many sheets, rows, and columns can a spreadsheet have?
Download an example of a spreadsheet file
We’ve created a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that can be downloaded and opened in any spreadsheet program including Microsoft Excel. This spreadsheet helps illustrate some a spreadsheet capability, formulas, and functions used in a spreadsheet, and lets you experiment with a spreadsheet.
- Download example.xls.
The same spreadsheet is also available on Google Sheets. Visit the link below to open the spreadsheet in view mode in Google Sheets. If you want to edit any of the values, click File and then Make a copy option to save it to your Google Drive.
- View Google Sheets example spreadsheet.
What did people use before spreadsheets?
Before computerized spreadsheets ledger paper was used to keep track of numbers and make calculations. In fact, many accountants and other individuals continued to use ledger paper even after the release of spreadsheet programs because they didn’t trust computers to make proper calculations.
Absolute cell reference, Active cell, Business terms, Cell, Column, Formula, Gnumeric, Google Sheets, Gridlines, Multiplan, Office, Office 365, Office Online, Pivot table, Relative cell reference, Row, Sheet tab, Software terms, Spreadsheet terms, Workbook
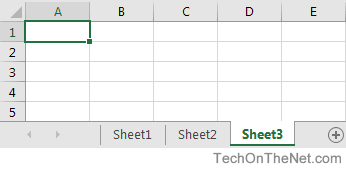
In Microsoft Excel, a sheet is often called a worksheet. A sheet is a single page that contains its own collection of cells to help you organize your data. There can be many sheets in your Excel document and you can see the sheets listed as tabs along the bottom of your document. In this example, we have three sheets in our spreadsheet — Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3.
Each sheet has its own name and you can switch between the sheets by clicking on the name of the sheet you want to view. In the example above, we have selected Sheet3.
Traditionally when you create a new Excel document, three sheets (Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3) are created in the spreadsheet and Excel automatically selects Sheet1 for you. In Excel 2016, your spreadsheet will be created with only one sheet called Sheet1. You can then add more sheets as you need them.
There are many things that you can do with sheets in Excel such as inserting, deleting, hiding, unhiding, and renaming sheets. Here is a list of topics that explain how to use sheets in Excel.
193
193 people found this article helpful
Learn about worksheets and spreadsheets in Excel and Google Sheets
Updated on April 26, 2020
A worksheet or sheet is a single page in a file created with an electronic spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. A workbook is the name given to an Excel file and contains one or more worksheets. When you open an electronic spreadsheet program, it loads an empty workbook file consisting of one or more blank worksheets for you to use.
Instructions in this article apply to Excel for Microsoft 365, Excel 2019, 2016, 2013, and 2010; Excel for Mac, Excel Online, and Google Sheets.
Worksheet Details
You use worksheets to store, manipulate, and display data.
The primary storage unit for data in a worksheet is a rectangular-shaped cell arranged in a grid pattern in every sheet. Individual cells of data are identified and organized using the vertical column letters and horizontal row numbers of a worksheet, which create a cell reference, such as A1, D15, or Z467.
Worksheet specifications for current versions of Excel include:
- 1,048,576 rows per worksheet
- 16,384 columns per worksheet
- 17,179,869,184 cells per worksheet
- A limited number of sheets per file based on the amount of memory available on the computer
For Google Sheets:
- 256 columns per sheet
- 400,000 cells for all worksheets in a file
- 200 worksheets per spreadsheet file
Worksheet Names
In both Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets, each worksheet has a name. By default, the worksheets are named Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3, and so on, but you can change these names.
Workbook Details
- Add worksheets to a workbook using the context menu or the New Sheet/Add Sheet icon (+) next to the current sheet tabs.
- Delete or hide individual worksheets in a workbook.
- Rename individual worksheets and change worksheet tab colors to make it easier to identify single sheets in a workbook using the context menu.
- Select the sheet tab at the bottom of the screen to change to another worksheet.
In Excel, use the following shortcut key combinations to switch between worksheets:
- Ctrl+PgUp (page up): Move to the right
- Ctrl+PgDn (page down): Move to the left
In Google Sheets, the shortcut key combinations to switch between worksheets are:
- Ctrl+Shift+PgUp: Move to the right
- Ctrl+Shift+PgDn: Move to the left
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/RowsandColumns-5a690dd96edd650037ee83cd.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Formula-5a690e6d1f4e130039a7d806.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FinancialData-5a690eff3de423001a6bea13.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Charttools-5a690f77c673350019bb304b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TCSQ1-5a690c6b3418c6001912517e.jpg)