Preposition definition: A preposition is a part of speech that shows the relation of a noun or pronoun to another word.
What are prepositions? Prepositions show the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. These relationships include where, when, who, or what.
Examples of Prepositions:
- above (where?)
- before (when?)
- for (whom?)
- with (what?)
Let’s look closer at a preposition example.
A preposition can be understood as anywhere a dog can be in relation to its doghouse.
A dog can be:
- in the doghouse
- around the doghouse
- near the doghouse
- on the doghouse
Each of these prepositions describe the relation between the dog and its doghouse. The dog can be inside the doghouse, it can be around the doghouse, it can be near the doghouse, it can be on the doghouse, etc.
All of these preposition examples show where the dog is in relation to its doghouse.
What is the Role of a Preposition?

Most often prepositions are used to introduce prepositional phrases.
Prepositions serve to modify and generally function in prepositional phrases as adjectives or adverbs.
Examples of prepositions indicating where:
- along (the path)
- amid (torment)
- throughout (the garden)
- within (men)
Examples of prepositions indicating when:
- since (the storm)
- after (the party)
- before (noon)
- until (tomorrow)
Examples of prepositions indicating who:
- besides (Petra)
- except (the children)
- with (everyone)
- for (the teacher)
Examples of prepositions indicating what:
- besides (the essay)
- of (the few)
- like (the dog)
- with (chocolate)
Preposition List

aboard
about
above
across
after
against
along
amid
among
anti
around
as
at
before
behind
below
beneath
beside
besides
between
beyond
but
by
concerning
considering
despite
down
during
except
excepting
excluding
following
for
from
in
inside
into
like
minus
near
of
off
on
onto
opposite
outside
over
past
per
plus
regarding
round
save
since
than
through
to
toward
towards
under
underneath
unlike
until
up
upon
versus
via
with
within
without
For a more full list of prepositions, see our full page on the subject. Prepositions list here.
Object of Prepositions

Examples:
- along (the path)
- The path is the object of the preposition.
- amid (torment)
- Torment is the object of the preposition.
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- The colorful garden is the object of the preposition.
Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions

The prepositions that can function in subordinate conjunctions include: after, as, before, since, until.
Prepositions together within subordinate conjunctions function as adverbs.
Preposition Examples:
- Since the movie premiered, the star has received much attention.
- We could not make an appointment until the office opened the following day.
- The student did not think before he asked a question.
What are Prepositional Phrases?
What does prepositional phrase mean? Almost always a preposition will function in a prepositional phrase.
A prepositional phrase is any preposition and its object (a noun). A prepositional phrase may also include any modifiers in the phrase.
Prepositional phrases clarify the relationship of the preposition to other words.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- along the path
- along (prep.) + the (article) + path (noun) = prepositional phrase
- amid torment
- amid (prep.) + torment (noun) = prepositional phrase
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- throughout (prep.) + the (article) + colorful (adj.) + garden (noun) = prepositional phrase
Multiple prepositional phrases may exist within one larger prepositional phrase.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- within all of the men
- within all + of the men = prepositional phrase
- by the lake in the forest
- by the lake + in the forest = prepositional phrase
- on the table at the restaurant
- on the table + at the restaurant = prepositional phrase
Summary: What are Prepositions?
Define preposition: To clarify, prepositions:
- show the relationship of a word to a noun or pronoun
- are almost always used in prepositional phrases
- sometimes begin subordinate conjunctions
Contents
- 1 What is a Preposition?
- 2 What is the Role of a Preposition?
- 3 Preposition List
- 4 Object of Prepositions
- 5 Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions
- 6 What are Prepositional Phrases?
- 7 Summary: What are Prepositions?
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
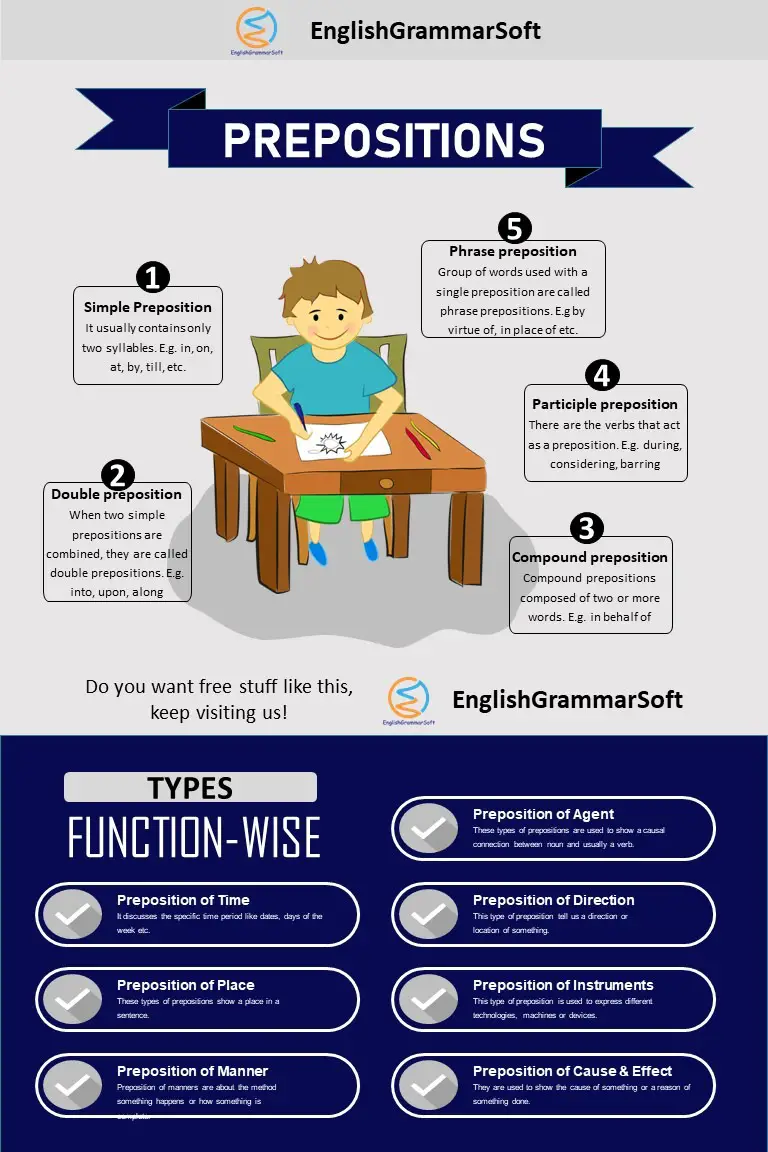
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions
“Watch out! There’s a snake!”
“Where?!”
“Behind you!”
Thank heavens for prepositions. Imagine not knowing where the threat was lurking. Prepositions describe the location or timing of something concerning something else.
Indeed, they play a vital role in our daily conversations with the people around us.
But what are prepositions exactly? Search no further, on this page we will discuss the 80+ prepositions and their uses. Please continue reading.
A preposition is a word that links nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words in a sentence.
Prepositions describe the position or chronology of something to something else.
They are short words that are frequently used in front of nouns and, in some cases, in front of gerund verbs.
In English, prepositions are quite idiomatic. Although there are some usage guidelines, fixed expressions govern many preposition usage. It is preferable to memorize the phrase rather than the individual preposition in these situations.
What are the Different Prepositions and their Functions?
In the English language, there are over 100 prepositions.
Furthermore, the possibilities for forming prepositional phrases (phrases that start with a preposition and end with a noun or pronoun) are limitless.
Remember that prepositions frequently express notions such as comparison, direction, place, purpose, source possession, and time as you read the examples and analyze the list below.
Note: Some prepositions have more than one function.
Here are the various functions of prepositions:
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationships
- Prepositions of Direction or Movement
- Prepositions that Show Connection Between Ideas
- Prepositions of Agency
- Prepositions of Instrument or Device
- Prepositions of Manner
- Prepositions of Reasons or Purpose
- Prepositions of Origin
- Prepositions of Possession
- Prepositions of Measure
1. Prepositions of Time
| Function | Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| For months, years, centuries, seasons, and times of day | in | “I first met my husband in 2002.”
“It’s always hot in June.” “I plan to visit my family in summer.” “The telephone was invented in the 19th century.” “I will go jogging in the afternoon.” |
| For days, dates, and specific holiday days | on | “I don’t go to school on Sundays.”
“Halloween is on October 31st.” “My parents never miss giving me presents on my birthday.” |
| For times, markers of exception, and festivals | at | “My dad leaves the house at 7 AM every morning.”
“She works better at night.” “They are always busy at Christmas time.” |
| To express when something occurred, is occurring, or will occur in relation to something else | before | “Before you go, make sure to lock the door.”
“We have to finish this before 3 PM.” |
| To express when something occurred, is occurring, or will occur in relation to something else | after | “They will go home after watching the concert.”
“Let’s have some drinks after work.” |
| To state a beginning time and an ending time | from and to | “The lecture is from 8 in the morning to 2 in the afternoon.”
“Winter lasts from December to March.” |
| To specify a time that separates any two given periods | between | “They have to be there between 6:00 and 7:00 in the morning.”
“The package is expected to arrive between the months of March and April.” “The best time to shop is between Thanksgiving and Christmas.” |
| To refer to a continuous event that started taking place in the past | since | “She has been living alone since she was a teenager.” |
| To refer to events that are simultaneous | during | “Flights are limited during the pandemic.” |
| To refer to a specific time action must be completed | by | “I should be at the airport by 5 in the morning.” |
| To state when an action will end at a specified time in the future | until | “I waited for your call until midnight.” |
| To state duration of time | for | “He lived in the US for ten years.” |
| To express a given time in relation to the succeeding hour of the day | to | “My phone says it’s ten minutes to five right now.” |
| To state how long an action is done | throughout | “The sale will last throughout the holiday season.” |
| To indicate a time that is not precise or exact | about | “It was about 7 in the evening when the accident happened.” |
| To indicate a time that is not precise or exact | around | “Expect me to be there at around 8 in the morning.” |
2. Prepositions of Place
| Function | Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| When talking about something with a flat surface | on | “The painting hangs on the wall.”
“The books are scattered on the floor.” |
| When anything is inside or within constrained borders. Anything, including a country, might be included |
in/inside | “Dan is in Germany visiting his relatives.”
“I put the excess food in the fridge.” “My things are inside my bag.” “I do not have any liquids inside my suitcase.” |
| When referring to anything at a certain/specific point | at | “I will meet him at the gate before he boards the plane.”
“The dairy products are at the fourth lane.” |
| When something is at the back of something | behind | “The boy is hiding behind the shelf.” |
| When something is situated before another | in front of you | “Pick up the trash in front of you.” |
| When something is lower than something/another | below | “She is waving at them from below the stairs.” |
| When something is lower than something/another | under | “The folder is under the pile of books.” |
| When something is higher than something | above | “One of my friends lives in a flat above mine.” |
| When something is higher than something | over | “There is a bee flying over your head.” |
| When something is not in a specific location but nearby | outside | “The kids are outside playing.” |
3. Prepositions of Spatial Relationships
| Function | Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| When something is in line with something long and wide or thin | along | “You can find the receipts along the counter.” |
| When something is located near another thing that is being mentioned | by | “The plates are by the cups and saucers at the counter.” |
| When something is located near another thing that is being mentioned | beside | “I want you to sit beside me at dinner.” |
| When something is located near another thing that is being mentioned | next to | “The lady sitting next to the city mayor is the widower.” |
| When something is farther from something | beyond | “That tollbooth is immediately beyond the bridge.” |
| When something is facing someone or on the other side | opposite | “The shop is opposite the drugstore.” |
| When something is on a lower level than another | beneath | “Just beneath the stairwell is a door.” |
| When something is beneath and covered by something else | underneath | “Underneath her coat, are three more layers of warmers.” |
4. Prepositions of Direction or Movement
| Function | Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| To emphasize that something is moving towards a specific goal | to | “She has gone to Paris for a vacation.”
“The whole family is going to the beach.” |
| To state that something is getting from one side to another | across | “She traveled across Asia for a month.”
“The interviewer extended his hand across the table to shake the hand of the applicant.” |
| To express that something is moving directly from something and out the other end | through | “I can see the streets through my window.”
“The bullet had gone through his right hand.” |
| To state that something is entering or peering into something | into | “She dove into the pool without hesitation.”
“He was staring into the darkness with no emotions.” |
| To state movement that ends up on top of something | onto | “The speaker stood and made his way onto the platform.”
“Be careful when you step onto that ledge.” |
| When a movement is closer or approaching something | towards
*’Toward’ and ‘towards’ are interchangeable. |
“She ran towards the door and hugged her parents.”
“He was driving towards the gate when he realized he left his glasses.” |
| To state a movement that is higher than something else | above | “She shot the arrow way above her target.” |
| To state a movement that is higher than something else | over | “On our route to Grandma’s house, we’ll travel over some tough terrain.” |
| To state a movement that is higher than something else | up | “They went up the mountains to hunt.” |
| To state a movement on a straight ledge or line | along | “He was walking along the shore and saw a dead starfish.” |
| To state a movement in a circular pattern | around | “He was roaming around the house wasting his time.” |
| To state a movement that is farther from something | away from | “I had to stay away from the fire because it was getting bigger.” |
| To state a movement that is farther from something | out of | “We need to get out of here before somebody comes and sees us.” |
| To state a movement that is lower than something | beneath | “The snake slithered beneath the earth.” |
| To state a movement that is lower than something | down | “He immediately got down the stage and left.” |
| To state a movement originating from a specific place | from | “He traveled from Spain to Prague to meet some old friends.” |
| To indicate a movement alongside and beyond something | past | “On the highway, a car sped past a truck. |
5. Prepositions that Show Connection Between Idea
| Function | Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| To signify ‘concerning’ or ‘on the subject of’ | about | “The meeting was about the new set of company policies.” |
| To mean something in oppose to something | against | “Our teams are going against each other in tonight’s match.” |
| To express the purpose of something or someone | as | “My mom works as a nurse in the city’s first-ever public hospital.” |
| To specify a direction or destination | to | “You can give that gift to her later this afternoon.” |
| To exclude something or someone | except | “I would love to catch up, except my break time is over.” |
| To express one’s someone’s thoughts and opinions | for | “This book is worth reading for me.” |
| To compare nouns | like | “The little boy looks like his grandfather when he was young.” |
| To show belonging or connection | of | “That scent reminds me of a very special moment in my life.” |
| To show belonging or connection | with | “She lives with her aunt, with their four cats.” |
6. Prepositions of Agency
A person or thing that has caused or is causing something to happen is described as a preposition of agency.
Sentences with prepositions of agency are often written in the passive voice and use the prepositions ‘by’ (for people) and ‘with’ (for things).
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| by | Passive: “This purse was given by my sister.”
Active: “My sister gave me this purse.” Passive: “Her gown was designed by a renowned fashion icon.” Active: “A renowned fashion icon designed her gown.” |
| with | Passive: “The room was filled with sadness.”
Active: Sadness filled the room.” Passive: “Her dress was adorned with a lot of crystals.” Active: A lot of crystals adorned her dress.” |
7. Prepositions of Instrument or Device
These discuss specific technologies, machines, or gadgets, the preposition instrument or device is utilized.
‘With’ and ‘on’ are usually used to explain the use of machines and other devices, whereas ‘by’ is used to describe modes of transportation.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| by | “They chose to travel to Georgia by plane.”
“You can reach the other island by ferry.” |
| on | “May I research my homework on your phone?”
“She edited her thesis on her mom’s laptop.” |
| with | “She filled up the questionnaire with a pencil.”
“He was able to open the door with an ATM card.” |
8. Prepositions of Manner
These explain the way things happen or by the means things happen, just like prepositions of device.
The only difference is it does not include any machine or device.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| like | “He sings like a professional and everyone is amazed.”
“Don’t act like a child.” |
| with | “He answered the question with eagerness in his voice.”
“They left the house with sadness in their eyes.” |
9. Prepositions of Reasons or Purpose
The reason or purpose prepositions explains why something happened or will happen.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| because | “Classes were canceled because of the storm.” |
| for | “I did it for my family.” |
| from | “She knows from past incidents how to handle the situation.” |
| on account of | “He pressed charges against his neighbor on account of trespassing.” |
| through | “They were able to get their freedom through their bravery.” |
10. Prepositions of Origin
These identify a person or thing’s origin such as nationality, hometown/state, ethnicity, and the location where something was made or designed.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| from | “I am from Chicago originally, but I have been living in Colorado for a decade now.”
“The new batch of computers are from the biggest software company in the country.” |
| of | “Our new classmate is of Turkish descent.”
“This toy is made of plastic.” |
11. Prepositions of Possession
These indicate that something or someone is owned by something or someone.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| of | “This house is the property of my brother.”
“The leg of the dog is wounded.” |
| to | “That red car over there belongs to my friend.”
“She gave the phone to her grandmother.” |
| with | “The lady in black with the sunglasses is my mom.”
“He met a girl with the most beautiful smile.” |
12. Prepositions of Measure
These state the quantity of something with someone or something.
| Prepositions | Examples |
|---|---|
| by | “The textile shop sells its products by yards.”
“They are entering the museum by batches.” |
| of | “My mom bought a kilogram of potatoes for the salad.”
“Half of the class was infected by the virus.” |
What are the Grammar Rules for Prepositions?
Prepositions play a crucial role in English grammar.
Although English appears to be simple, even grammar nazis have difficulty answering prepositions questions.
As such, it is a must that you familiarize yourself with the different rules governing prepositions.
Let us look at some instances to see how different rules for prepositions and usage work.
1. Prepositions must have an object.
The presence of an object is required for prepositions. The preposition is just an adverb without an object.
An object is always placed after a preposition, whereas an adverb is never followed by an object.
Example:
“My mom is in the kitchen.”
Preposition: in
Object: the kitchen
“Please get inside.”
‘Inside’ here is not a preposition but an adverb, because there is no object that comes after it.
2. Prepositions do not always come before its object.
This rule states that, in most cases, the preposition comes before the object, however, this is not always the case.
Before a noun or a pronoun, there should be a preposition.
Example:
“We will see you in December.”
Preposition: in
Object: December
It is a common English grammar fallacy that you cannot end a sentence with a preposition.
However, that is not true at times.
Example:
“Who were you with?”
Preposition: with
Object: Related to the pronoun ‘who’
3. When a preposition is followed by a pronoun, it should be in object form.
A ‘prepositional object’ is a noun or pronoun that comes after a preposition.
If it is a pronoun, use the objective form (me, her, them) rather than the subjective form (I, she, they).
Example:
“He bought a gift for her.”
Preposition: for
Object: her (object form)
4. Prepositions do not have a specific form.
Prepositions, in particular, do not have a formal structure.
The majority of prepositions are one word, however complex prepositions are two to three words long.
Example:
- one-word prepositions: in, on, from
- complex prepositions: away from, on account of, next to
5. ‘To’ as a preposition and ‘to’ as an infinitive are not the same.
If you are confused, always remember that ‘to’ as an infinitive comes before a verb (as in ‘to eat’, ‘to dance’ ‘to swim’).
To as a preposition always has an object (‘to me’, ‘to the park’, ‘to London’).
Do not interchange the function of the two.
‘To’ as a preposition:
- “She gave her old clothes to her younger sister.” (her younger sister – object)
- “He plans to go to the beach this weekend.” (the beach – object)
‘To’ as an infinitive:
- “I love to fish on weekends.” (fish – verb)
- “My friends forced me to go jogging with them.” (go – verb)
6. A preposition’s object cannot be a verb.
The Golden Rule of Preposition is this: the preposition ‘to’ can sometimes be followed by phrases that appear to be verbs, but a verb can never be the object of a preposition.
Example:
- “I love to bake.”
- “An oven is for baking.”
‘Bake’ and ‘baking’ are not verbs in the examples above. ‘To bake’ is part of the infinitive in the first example, and it happens if a verb is employed as an adverb, adjective, or noun.
Baking is not an action that is performed here, but rather something that a person enjoys doing.
‘Baking’, in the second example, is a gerund, which is essentially a noun but is created from a verb.
The oven is inextricably linked to her baking. In this sentence, no one is actually baking.
Are Prepositions Important?
Prepositions are a challenge for many English learners. The first thing we need to understand about prepositions is how they are used both in speaking and writing.
Using the wrong prepositions can entirely shift the context of a phrase, causing complications for the speaker. As a result, proper preposition usage in English is critical.
In the context of tossing a ball, for example, knowing the difference between ‘to’ and ‘at’ could save your life.
When someone asks, “Can I throw this ball to you?” they are expecting you to be prepared to catch the ball.
On the other hand, when someone asks, “Can I throw the ball at you?”, they are implying that they want to hit you with it. Prepare yourself as well.
Here is the difference:
“Can I throw this ball to you?”
“Sure, I’ll catch it.”
“Can I throw this ball at you?”
“Please don’t, it could hurt me.”
Another example is this one. Take note of the prepositions ‘about’ and ‘except’.
- “Everything about the hotel is fantastic.”
- “Okay, we’re going to book the same hotel when we go there.”
- “Everything except the hotel is fantastic.”
- “Oh, really? Well, I guess I should try to look for another hotel when we go there.”
Notice how a preposition can change the meaning of the sentence. So, as you can see, using the correct preposition is extremely crucial in expressing your thoughts and ideas.
With many prepositions out there, you have to exert any effort to learn them and how they should be used.
Otherwise, misunderstanding may occur and that is something you do not want.
What are the Most Common Mistakes in the Use of Prepositions?
Prepositions are tricky little beasts. There are a lot of them and their rules can be extremely perplexing!
Because there are so many possible prepositions, picking the right one might sometimes be influenced by the word that comes before it. It may also rely on what comes after the preposition in other circumstances.
For your reference, here are the most common mistakes when it comes to using prepositions:
1. Depending on the situation, use ‘with’ or ‘about’ after the word ‘upset’.
We use ‘about’ + something and ‘with’ + someone.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “I am upset with the flight being delayed.” | “I am upset about the flight being delayed.” |
| “She was upset about him for being rude.” | “She was upset with him for being rude.” |
2. The correct usage for ‘in’ and ‘at’ may differ depending on the time of day.
We use ‘in the’ with ‘morning’, ‘afternoon’, and ‘evening’.
When talking about the night, though, we commonly use ‘at’.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “I take my vitamins at the morning.” | “I take my vitamins in the morning.” |
| “I have a habit of writing in my journal before I go to sleep in night.” | “I have a habit of writing in my journal before I go to sleep at night.” |
3. When talking about journeys, you can use the preposition ‘to’.
However, use the words ‘in’ or ‘at’ to signify reaching a destination when we use the term ‘arrive’.
For cities, countries, and other major areas, use ‘in’.
For specific locations (e.g., a library, a bar, or someone’s home), use ‘at’.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “She arrived at Indonesia before midnight.” | “She arrived in Indonesia before midnight.” |
| “They arrived in the venue just minutes before the program started.” | “They arrived at the venue just minutes before the program started.” |
4. Depending on the situation, employ different prepositions when referring to a time or date.
When referring to a specific time of day, use ‘at’.
Meanwhile, use ‘on’ to refer to a certain day or date. The right preposition for a month or year is ‘in’.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “The concert starts in 8 PM.” | “The concert starts at 8 PM.” |
| “Let’s watch a movie at Saturday.” | “Let’s watch a movie on Saturday.” |
| “School ends on June.” | “School ends in June.” |
5. When using auxiliary verbs like ‘should’ or ‘must’, avoid using the preposition ‘of’.
Instead, use the verb ‘have’, which sounds similar to ‘of’ when uttered.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “You should of called me earlier.” | “You should have called me earlier.” |
| “I must of forgotten to turn off the tv.” | “I must have forgotten to turn off the tv.” |
6. Use the preposition ‘for’ to refer to a period of time when discussing how long something has been going on.
When referring to a certain time period, use ‘since’.
The difference is that the first relates to a unit of time, whereas the second refers to a specific point in time when the activity started.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “She has been crying since an hour.” | “She has been crying for an hour.” |
| “They have been waiting for the bus for 2 PM.” | “They have been waiting for the bus since 2 PM.” |
7. Because ‘talking’ and ‘discussing’ are comparable activities, many people use them interchangeably.
However, the word ‘about’ should only be used after ‘talking’.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “They were discussing about the project proposals.” | “They were discussing the project proposals.” |
| “I am talking about the plans for the party tonight.” | “I am talking about the plans for the party tonight.” |
8. It is correct to mention that one person is married ‘to’ (not ‘with’) another when describing someone’s marital status.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “Tom is married with Jane.” | “Tom is married to Jane.” |
9. Another difficulty for non-natives is whether or not to put a preposition between ‘ask’ and the name of the person to whom the verb refers.
| WRONG | CORRECT |
|---|---|
| “I asked to Sue what time we should get going.” | “I asked Sue what time we should get going.” |
Are Prepositions Challenging for Students?
It is extremely difficult to use prepositions effectively in English, and they cause a slew of issues for teachers and students alike.
To begin with, most prepositions, especially the most popular ones, have many purposes.
Depending on whose dictionary you consult, the preposition ‘at’ has as many as 18 different functions.
As vocabulary words, prepositions can be difficult to grasp on their own, and it is not uncommon for English learners to ask teachers to explain what a term like ‘at’ means.
Second, there is no rational way to determine which preposition is appropriate for a given noun, verb, or adjective.
Because it is not always possible to predict the correct preposition, the expression must be mastered in its whole.
The problem is compounded when a single vocabulary item, again, the most commonly used ones, flirts with a range of prepositions, prolonging the teaching-learning activities beyond what we might expect.
Finally, a learner’s native language can obstruct the learning process and prevent proper English usage.
Prepositional errors are possibly the most egregious example of this.
Some English formulations, for example, do not contain a preposition, although the same expression in another language does, and vice versa.
Additional FAQs – Prepositions in English Grammar
Can you End a Sentence with a Preposition?
Ending a statement with a preposition is not incorrect, but it is less professional.
It is absolutely okay in emails, text messages, and notes to friends.
If you are writing a research paper or presenting a business proposal, though, avoid using prepositions at the end of sentences.
Why Should I Care About Prepositions?
While prepositions are few in number, they are crucial because they serve as structural markers in sentences, indicating particular relationships between people, objects, and places.
Without prepositions, misunderstanding, confusion, and miscommunication may arise.
How Do I Use Prepositions Correctly?
Prepositions are always used to illustrate the relationship between a noun or phrase and anything else.
When using a preposition, it must always be followed by a noun and before by the subject and verb. A verb should never be used after it.
Additional Reading — ENGLISH GRAMMAR
What is a preposition? A preposition is a word or group of words that shows relationship of a noun or pronoun to some other word in the sentence. Prepositions add extra information to sentences such as direction, time and place.
Four Kinds of Prepositions
1. A Simple Preposition
A simply preposition is made up of one word, such as: by, for, in, at, with, on or of.
- David drove the car on the race track.
- Jonathan leaves for work at 8.00am everyday.
- Rachel brushes her hair with a special brush.
2. A Compound Preposition
A compound preposition consists of two words used as one, such as: into, without, before, inside, outside, upon, underneath or throughout.
- David drove the car into the shed.
- Jonathan leaves for work before dawn.
- Rachel brushes her hair throughout the day.
3. A Participial Preposition
A participial preposition is a present participle of certain verbs that function as a preposition, such as: during, regarding, barring, respecting or considering.
- David drove the car during the thunder storm.
- Jonathan works hard considering his age.
- Bec will travel overseas barring sickness.
4. A Phrasal Preposition
A phrasal preposition is a phrase that functions as a preposition, such as: according to, in spite of, with regard to, out of, round about or in reference to.
- David will drive his car in spite of his health.
- Jonathan arrives at work round about noon.
- Bradley won the game according to the rules.
Two Functions of the Prepositional Phrase
A preposition always has an object (noun or pronoun) and is called the object of the preposition.
- David drove the car into (preposition) the fence (object of preposition).
- Jonathan works late during the summer (object of preposition).
The preposition with its object becomes a prepositional phrase, which functions as either an adjective or an adverb.
1. Prepositional Phrases Functioning as An Adjective
If the prepositional phrase modifies a noun, then the phrase is functioning as an adjective.
- David will drive the car of the century. (of the century describes the car)
- The house with the new roof was repaired by Jonathan. (with the new roof describes the house)
2. Prepositional Phrases Functioning as An Adverb
If the prepositional phrase modifies a verb, then the phrase is functioning as an adverb.
- The boy ran through the field. (through the field modifies ran)
- David drove the car into the mud. (into the mud modifies drove)
Preposition Versus Adverb
Some words can be used as either prepositions for adverbs. If the word has an object, then the word is functioning as a preposition. If the word has no object, then it is functioning as an adverb.
- Please come inside. (adverb)
- The cat came inside the house. (preposition)
Resources For What is a Preposition
English Grammar in Use by Raymond Murphy
Plain English Handbook by J. Martyn Walsh and Anna Kathleen Walsh
The Only Grammar Book by Susan Thurman
Mastering English Grammar by S.H. Burton
Types of Prepositions
There are several types of prepositions such as: Simple Prepositions, Double Prepositions, Compound Prepositions, Phrasal prepositions, Participle Prepositions, Disguised preposition, and Detached Prepositions.
1. Simple Prepositions:
Simple prepositions are used to denote a relation between nouns or pronouns. These can even be used to join different parts of sentences and clauses. Simple prepositions are one word prepositions. These are also called Single Prepositions. Common words used that come under the category of Simple Prepositions are as follows:
In, out, on, up, at, for, from, by, of, off, through, till, etc.
Examples of Simple Prepositions in sentences:
Keep your phones in your pockets.
Staring at people is not considered a good gesture.
In the above two examples, both prepositions consist of one simple word and hence are Single or Simple Prepositions.
2. Double Prepositions:
Double Prepositions are made by putting together two Single Prepositions. That is why they are called Double Prepositions. Common words used as Double Prepositions are as follows:
Onto, into, throughout, up till, up to, within, without, upon, etc.
Examples of Double Prepositions in sentences:
Complete this essay within two hours.
I am going to turn this scrap into a masterpiece.
In the first example, the Preposition within is made by combining two Single Prepositions with and in.
In the second example, the Preposition into is formed by putting together two Simple Prepositions in and two. These are hence Double Prepositions.
3. Compound Prepositions:
Compound Prepositions are those types of preposition that are usually formed by prefixing a preposition to nouns, adjectives or adverbs. They are different from double prepositions because they are not formed by two single prepositions. Common words, which come under the category of compound prepositions, are stated below:
Above, about, across, along, before, behind, beside, inside, outside, etc.
Examples of preposition in sentences:
He was going about his business.
The person beside Ali is my brother.
In the first example, the prefix ‘a’ is added to a root word ‘bout’ to make a preposition. In the second example, the prefix be is added to the root word side to make a preposition. Thus, these words are Compound Prepositions.
4. Phrasal Prepositions:
Phrasal Prepositions are groups of words or phrases that join the noun or pronoun in a sentence, to the remainder of the sentence. These groups of words express a single idea by coming together as a unit. Words that come under the category of Phrasal Prepositions are as follows:
In addition to, by means of, in spite of, according to, owing to, in favour of, etc.
Examples of Phrasal Prepositions in sentences:
He couldn’t pass the test, owing to his lack of knowledge of English Grammar.
She made it to the other side of the world, in spite of all the difficulties.
In the first example, the group of words ‘owing to’ is joining the two sentences with each other and is a phrase. Likewise, the group of words ‘in spite of’ is also a phrase and is working as a preposition. Hence, these are Phrasal Prepositions.
5. Participle Prepositions:
Participle Prepositions, indicating from their name, are the Present Participle forms of Verbs. These are used without any noun or pronoun attached with them. The words that are distinguished as Participle Prepositions are as follows:
Concerning, considering, barring, notwithstanding, touching, pending, during, etc.
Examples of Participle Prepositions in sentences:
Notwithstanding his efforts, he was still fired from the job.
Touching this matter, I do not have much information.
In above examples, both the verbs notwithstanding and touching are in Present Participle which is apparent from the ‘ing’ at the end of both words. These words are therefore Participle Prepositions.
6. Disguised Prepositions:
Disguised prepositions are those prepositions which are not used in the sentences directly, but we use them in a disguised way. Their shorter forms are used. The examples of Disguised Prepositions are ‘a’ and ‘o’.
Disguised preposition ‘a’ is shortened form of the preposition ‘on’ and similarly ‘o’ is the shortened form of the preposition ‘of’.
Examples of disguised prepositions in sentences:
The ceremony will be held at 5 o’ clock.
We all went to a party.
In the first example, instead of saying ‘5 of the clock’, we have used disguised form of the preposition of.
In the second example, instead of saying ‘went on partying’, we have used abbreviation of the preposition on and disguised the preposition as ‘a’. Hence these are Disguised Prepositions.
7. Detached Prepositions:
A preposition is called a detached preposition when it does not come before its object. It is detached from its object. When the object of a preposition is an interrogative pronoun or a relative pronoun, the preposition comes at the end of the sentence.
Look at the following examples of detached prepositions for further understanding.
She is the woman whom I was talking about.
Here are the books that you asked for.
Which of the houses were you working in?
In the first two of the above examples, we can see that because of relative pronouns whom and that, the prepositions about and for are being detached from their objects.
In the third example, the interrogative pronoun ‘which’ is detaching the preposition ‘in’ from its object.
Hence these are all detached prepositions.

