1. What is a possible pitfall of utilizing Excel as a way to manipulate small databases?
- Excel does not enforce many principles of relational data models.
- Excel is a user program and thus cannot run on a server.
- Excel does not allow algorithms for data manipulation.
2. What does the term “atomic” mean in the context of relational databases?
- Fixed schema of a particular database.
- A tuple that cannot be reduced.
- A column or row of data. Depends on the context.
- One unit of information that cannot be decomposed.
3. What is the Pareto-Optimality problem?
- Find the shortest path from source node to target node.
- Find the best possible path given two or more optimization criteria where neither constraint can be fully optimized simultaneously.
- Find the optimal path that requires going through specific nodes given by the user.
4. What constitutes a community within a graph?
- High density of nodes at a certain location.
- A neighborhood defined by an integer constant K around a specific node. All K+1 nodes belong in another community.
- A dense amount of edge connections between nodes in a community and a few connections across communities.
- Many anomalous neighborhoods within the same vicinity.
5. Why are trees useful for semi-structured data such as XML and JSON?
- Computers can easily visualize the data with a tree structure.
- It is not always the case that XML and JSON can be represented as trees.
- Trees take advantage of the parent-child relationship of the data for easy navigation.
- They are only useful for XML data as tree-like structure is apparent with tags. While JSON does not contain a tree-like structure as it contains arrays.
6. What is the general purpose of modeling data as vectors?
- Enables weighting of the query.
- The ability to normalize vectors allowing probability distributions.
- Enables image searching.
- Results can be ordered by similarity using vector projection.
7. For the following questions 7, 8, and 9, suppose a registration website creates data with the following fields for each person registered (note: if the user does not input a value, NULL is stored instead): Name, Date, Address, and Account Number.
Suppose we collect data month by month. Each month, we would have a batch of data containing the fields listed above. At the end of the year, we want to summarize our registrant activities for the entire year, so we would remove redundancies in our data by removing any records with duplicate account numbers from month to month. What type of operation do we use in this scenario?
- Join
- Not an Operation
- Subsetting
- Union
8. From the information given in question 7, what are the constraints, if any, which we have placed on the Account Number field for the end of year collection?
- Account should have at most n digits.
- If we had n duplicate Account Numbers then we will remove n-1 duplicate fields.
- There are no constraints.
- Account Number should be unique.
9. Suppose 100 people signup for our system and of the 100 people, 60 of them did not input an address. The system lists the values as NULL for these empty entries in the address field. Would this situation still have structure for our data?
- No because the majority of data do not have a specific field filled, thus our originally defined structure is lost.
- Yes the data has structure because we have placed a structural constraint on the data, thus the data will always have the originally defined structure.
Big Data Integration and Processing complete course is currently being offered by UC San Diego through Coursera platform and is Course 2 of 6 in the Big Data Specialization.
About this Course: This course is for those new to data science. Completion of Intro. to Big Data is recommended. No prior programming experience is needed, although the ability to install applications and utilize a virtual machine is necessary to complete the hands-on assignments. Refer to the specialization technical requirements for complete hardware and software specifications.
Also Check: How to Apply for Coursera Financial Aid
Big Data Modeling and Management Systems Week 1 Quiz Answers!
Q1. (Questions 1-3 pertain to the video lecture “Exploring
the Relational Data Model of CSV”) What is the approximate population of La Paz
County in the state of Arizona for the CENSUS2010POP (column H)? (Choose the
best answer.)
- 15000
- 25000
- 10000
- 20000
Q2. What county in the state of Wyoming has the smallest
estimated population?
- Platte
- Uinta
- Niobrara
- Sweetwater
Q3. At 2:45 of the video, the Instructor creates a filter
for all of the counties in California with a population greater than 1,000,000.
However, included in the results is the entire state of California. This
anomalous value might skew our analysis if, for example, we wanted to compute
the average population of these results. What additional filter might work to
resolve this problem?
- Add
a filter to detect and remove results which do not include the word
“County” in column G. - Add
a filter which finds all counties with population greater than 100,000 AND
less than 10,000,000 for column H (CENSUS2010POP). - Add
a filter where the value in column E is greater than 1,000,000. - None
of the above
Q4. (Questions 4 and 5 pertain to the video “Exploring
Sensor Data”) How often (in seconds) do the R5 measurements occur?
- 60
- 40
- 50
- 30
Q5. What is the field for rain accumulation?
- Sm
- Dn
- Rc
- Dx
Q6. (Questions 6 and 7 pertain to the video lecture
“Exploring the Array Data Model of an Image”) What is the (Red, Green, Blue)
pixel value for location 500, 2000?
- (163,
118, 79) - (134,
145, 46) - (50,
156, 182) - (100,
123, 149)
Q7. Is this value likely to be land or ocean?
- Land
- Ocean
Q8. (Questions 8 and 9 pertain to the video lecture
“Exploring the Semistructured Data Model of JSON”) Given a tweet, what path
would you most likely enter to obtain a count of the number of followers for a
user?
- user/followers_count
- user/statuses_count
- user/listed_count
- None
of the above
Q9. Which of the following fields are nested within the
‘entities’ field (select all that apply)?
- tweets
- user_mentions
- events
- views
- symbols
- urls
Big Data Modeling and Management Systems Week 2 Quiz Answers — Data Models Quiz Answers!
Q1. What is a possible pitfall of utilizing Excel as a way
to manipulate small databases?
- Excel
does not enforce many principles of relational data models. - Excel
is a user program and thus cannot run on a server. - Excel
does not allow algorithms for data manipulation.
Q2. What does the term “atomic” mean in the context of
relational databases?
- Fixed
schema of a particular database. - A
tuple that cannot be reduced. - A
column or row of data. Depends on the context. - One
unit of information that cannot be decomposed.
Q3. What is the Pareto-Optimality problem?
- Find
the shortest path from source node to target node. - Find
the best possible path given two or more optimization criteria where
neither constraint can be fully optimized simultaneously. - Find
the optimal path that requires going through specific nodes given by the
user.
Q4. What constitutes a community within a graph?
- High
density of nodes at a certain location. - A
neighborhood defined by an integer constant K around a specific node. All
K+1 nodes belong in another community. - A
dense amount of edge connections between nodes in a community and a few
connections across communities. - Many
anomalous neighborhoods within the same vicinity.
Q5. Why are trees useful for semi-structured data such as
XML and JSON?
- Computers
can easily visualize the data with a tree structure. - It
is not always the case that XML and JSON can be represented as trees. - Trees
take advantage of the parent-child relationship of the data for easy
navigation. - They
are only useful for XML data as tree-like structure is apparent with tags.
While JSON does not contain a tree-like structure as it contains arrays.
Q6. What is the general purpose of modeling data as vectors?
- Enables
weighting of the query. - The
ability to normalize vectors allowing probability distributions. - Enables
image searching. - Results
can be ordered by similarity using vector projection.
Q7. For the following questions 7, 8, and 9, suppose a
registration website creates data with the following fields for each person
registered (note: if the user does not input a value, NULL is stored instead):
Name, Date, Address, and Account Number.
Suppose we collect data month by month. Each month, we would
have a batch of data containing the fields listed above. At the end of the
year, we want to summarize our registrant activities for the entire year, so we
would remove redundancies in our data by removing any records with duplicate account
numbers from month to month. What type of operation do we use in this scenario?
- Join
- Not
an Operation - Subsetting
- Union
Q8. From the information given in question 7, what are the
constraints, if any, which we have placed on the Account Number field for the
end of year collection?
- Account
should have at most n digits. - If
we had n duplicate Account Numbers then we will remove n-1 duplicate
fields. - There
are no constraints. - Account
Number should be unique.
Q9. Suppose 100 people signup for our system and of the 100
people, 60 of them did not input an address. The system lists the values as
NULL for these empty entries in the address field. Would this situation still
have structure for our data?
- No
because the majority of data do not have a specific field filled, thus our
originally defined structure is lost. - Yes
the data has structure because we have placed a structural constraint on
the data, thus the data will always have the originally defined structure.
Big Data Modeling and Management Systems Week 3 Quiz Answers: Data Formats and Streaming Data Quiz Answers!
Q1. What is true between data modeling and the formatting of
the data?
- There
is a one to one correspondence between formatting data and data modeling.
For every model of data, there is only one way to store the data. - There
is always one specific schema for storing model data that is the best and
preferred method for the specific data representation. - The
data does not necessarily need to be formatted in a way that represents
the data model. Just so long as it can be extrapolated.
Q2. What is streaming?
- Calculating
results using real time data otherwise known as streaming data. - Using
static data stored from a real time source in order to process and guide
the application. - Utilizing
real time data to compute and change the state of an application
continuously. - Using
sensors to manipulate the system, such as a smart car being able to drive
by itself using sensors to detect road hazards.
Q3. Of the following, what best describes the properties of
working with streaming data?
- Small
time windows for working with data. - Data
is always utilized for streaming the application. - Data
manipulation is near real time. - Independent
computations that do not rely on previous or future data. - Always
unbounded in sequence, in other words, data is not guaranteed to be in
order. - Does
not ping the source interactively for a response upon receiving the data.
Q4. What is a characteristic of streaming data?
- Data
is unbounded in size but requires only finite time and space to process
it. - The
data is unbounded in size and the size determines the time and space of
processing the data. - The
data is finite and requires only finite time and space to process the
data. - Data
is finite in size and size determines the time and space of processing the
data.
Q5. What type of algorithm is required for analyzing
streaming data?
- Accurate
and Consistent - Accurate
and Memory Efficient - Fast
and Complex - Fast
and Simple
Q6. What is lambda architecture?
- A
specific method for processing streaming data using special real time
processes. - A
specific hardware architecture for a server made specifically for
processing real time data. - A
method to process streaming data by utilizing batch processing and real
time processing.
Q7. Of the following, which best represents the challenge
regarding the size and frequency of data?
- The
size and frequency of the streaming data may be too small. - The
size and frequency of the streaming data may be sporadic. - There
may not be data to produce the notion of size and frequency.
Q8. What is the difference between data lakes and data
warehouses?
- Data
lakes house raw data while data warehouses contain pre-formatted data. - Data
lakes contain only files while data warehouses contain only databases. - Data
lakes utilize hierarchical systems while data warehouses use object
storage.
Q9. What is schema-on-read?
- The
process where formatted data is given structure when read. - Another
name for data lakes. - Data
is stored as raw data until it is read by an application where the
application assigns structure. - The
process where data is pre-formatted prior to being read but the schema is
loaded on read.
Big Data Modeling and Management Systems Week 4 Quiz Answers:
BDMS Quiz Answers!
Q1. The desired characteristics of a BDMS include (select
all that apply):
- Narrow
range of query sizes - Continuous
data ingestion - Support
for common “Big Data” data types - Support
for ACID - A
full query language - A
flexible semi-structured data model
Q2. Fill in the blank with the best answer: CAP theorem
states that _________ all at once within a distributed computer system?
- it
is impossible to have consistency, accuracy, and partial tolerance - it
is necessary to have consistency, accuracy, and partial tolerance - it
is necessary to have consistency, availability, and partition tolerance - it
is impossible to have consistency, availability, and partition tolerance
Q3. What is the purpose of the acronym BASE?
- The
same as ACID. - To
overcome CAP theorem. - To
impose properties on a BDMS in order to guarantee certain results. - Enables
stricter enforcement of ACID type design.
Q4. What are ziplists in Redis?
- A
special type of data type that can store up to 512 mb of image data. - A
look up table that is stored as a value in the database. Look up table
points to actual values in memory. - A
compressed list that is stored within the value of the database. - A
special type of data type that can store hashes that point to multiple
attributes.
Q5. What is one of the main features of Aerospike?
- Images
as values within the database. - Enables
real time data streaming from external sources. - Support
for geospatial data storage and geospatial queries. - Better
equipped for string based search applications.
Q6. What database would be best suited for the following
scenario: An app development company is trying to implement a cloud based
storage system for their new map-based app. The cloud will manage the longitude
and latitude of the data in order to track user location.
- Solr
- Vertica
- Aerospike
- Redis
Q7. What database would be best suited for the following
scenario: A big wholesale company is trying to implement a search engine for
their products.
- Redis
- Aerospike
- Solr
- Vertica
Q8. Which of the following data types are supported by
Redis? (select all that apply)
- Sorted
Sets - Images
- Hashes
- Lists
- Streaming
Video - Strings
Example: What is CanCollide in roblox?
-- CanCollide is command a that will be able to make a Part collide or not
-- To make an object not fall off a part
script.Parent.CanCollide = true
-- To make an object fall off a part
script.Parent.CanCollide = falseTags:
Lua Example
Related
Introduction to big data
Test 1 “why big data and where did it come from?”
1. Which of the following is an example of big data utilized in action today?
a. The internet
b. Individual,unconnected hospital databases
c. Social media
d. Wi—fi networks
2. What reasoning was given for the following: why is the “data storage to price ratio” relevant to big data?
a. Companies can’t afford to own, maintain and spend the energy to support large data storage unless the cost is sufficiently low.
b. It isn’t, it was just an arbitrary example of big data usage.
c. Larger storage means easier accessibility to big data for every user because it allows users to download in bulk.
d. Lower prices mean larger storage becomes easier to access for everyone, creating bigger amounts of data for client—
facing services to work with.
3. What is the best description of personalized marketing enabled by big data?
a. Being able to use personalized data from every single customer for personalized marketing needs.
b. Marketing to each customer on an individual level and suiting to their needs.
c. Being able to obtain and use customer information for groups of consumers and utilize them for marketing needs.
4. Of the following, which are some examples of personalized marketing related to big data?
a. Facebook revealing posts that cater towards similar interests.
b. A survey that asks your age and markets to you a specific brand.
c. News outlets gathering information from the internet in order to report them to the public.
5. What is the workflow for working with big data?
a. Big data—>Better models—> Higher precision
b. Theory—>Models—> Precise advice
c. Extrapolation—> Understanding—> Reproducing
6. Which is the most compelling reason why mobile advertising is related to big data?
a. Since most everyone owns a cell/mobile phone, the mobile advertising market is large and thus requires bug data to contain
all the information.
b. Mobile advertising benefits from data integration with location which requires big data.
c. Mobile advertising in and of itself is always associated with big data.
d. Mobile advertising allows massive cellular/mobile texting to a wide audience, thus providing large amounts of data.
7. What are the three types of diverse data sources?
a. Machine data, Map data, and Social Media
b. Information Networks, Map Data, and People
c. Machine Data, Organizational Data, and People
d. Sensor Data, Organizational Data, and Social Media
8. What is an example of machine data?
a. Sorted data from Amazon regarding customer info.
b. Social media
c. Weather station sensor output.
9. What is an example of an organizational data?
a. Social media
b. Disease data from Center for Disease Control
c. Satellite data
10.Of the three data sources, which is the hardest to implement and streamline into a model?
Content Infrastructure for the Connected World
CONTENT IS DATA
TerminusCMS is an open-source headless content and knowledge management system. A dev-first enterprise knowledge graph to break down departmental knowledge silos. Incorporate content with operational and transactional data to discover and use organization-wide knowledge for your front-of-house and back-office front ends.
An organization-wide knowledge graph with the analytical power to unlock enterprise potential
Build a semantically connected content and knowledge model to curate cross-divisional data, content, and documentation. Data is stored as machine-readable JSON documents which are exposed as GraphQL and Datalog APIs for schema, query, and updates.
Demo
Admin UI
Model Schema
GraphQL API
Change Requests
Demo
Admin UI
Model Schema
GraphQL API
Change Requests
KNOWLEDGE & CONTENT MANAGEMENT
Back Office, Apps, Portals, Websites, & Analytics
TerminusCMS is an enterprise knowledge graph to make content, knowledge, and data discoverable and usable.
Greater Query Power
Graph queries leveraging semantic relationships and analytics engine powered by GraphQL & Datalog.
Schema as Code
Flexible and extendable JSON schema syntax to model semantically enriched content models with code.
Provenance & Version Control
Immutable data provides Git-like features such as branch, rebase, clone, rollback, and time-travel.
Change Request Workflows
Change request workflows built into the data layer to provide approval processes and security.
Interoperable Standards
Using JSON & RDF standards ensures interoperability across applications and devices.
100% Open Source
Choose a package that works for you. Self-host with our open-source install, or choose a hosted version, including dedicated compute resources.
USE CASES
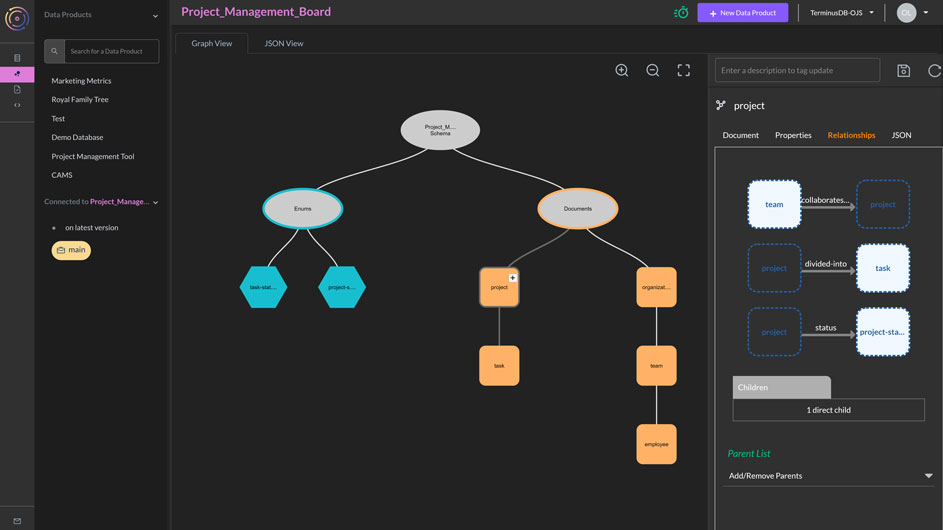
Document properties,
ID, relationships,
key strategy, and
JSON view
Create teams &
data products to
work collaboratively.
Visual schema
builder & validator
Database admin &
query playground
tools
TERMINUSDB — THE DATABASE
An in-memory, distributed, and open-source document graph database for people who want the convenience of documents with the query power of graph relationships. For people who want data to be the star of their builds.


So much more than CMS
Get started in minutes and for free with our TerminusCMS Community Package. Clone an example from the dashboard to experiment and play today.

