Continue Learning about Other Math
What is the number and word notation for 10 to the 5th power?
Number notation: 100,000
Word notation: One hundred-thousand
What is number and word notation for 9500000?
number notation is 9.5 * 106
word notation is nine million five hundred thousand
Word and number notation for 3000000000?
3000000000:Word form: Three billionStandard (number) notation: 3,000,000,000
What is the number and word notation for 4050000000?
Word notation: four billion fifty million.Number notation: 4,050,000,000
What is 43000000 in numeral in number and word notation?
Number notation: 43,000,000Word notation: Forty-three million.
This article is about number words. For the mathematical notation of numbers, see numeral system.
In linguistics, a numeral in the broadest sense is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity. Some theories of grammar use the word «numeral» to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner that specify the quantity of a noun, for example the «two» in «two hats». Some theories of grammar do not include determiners as a part of speech and consider «two» in this example to be an adjective. Some theories consider «numeral» to be a synonym for «number» and assign all numbers (including ordinal numbers like the compound word «seventy-fifth») to a part of speech called «numerals».[1][2] Numerals in the broad sense can also be analyzed as a noun («three is a small number»), as a pronoun («the two went to town»), or for a small number of words as an adverb («I rode the slide twice»).
Numerals can express relationships like quantity (cardinal numbers), sequence (ordinal numbers), frequency (once, twice), and part (fraction).[3]
Identifying numeralsEdit
Numerals may be attributive, as in two dogs, or pronominal, as in I saw two (of them).
Many words of different parts of speech indicate number or quantity. Such words are called quantifiers. Examples are words such as every, most, least, some, etc. Numerals are distinguished from other quantifiers by the fact that they designate a specific number.[3] Examples are words such as five, ten, fifty, one hundred, etc. They may or may not be treated as a distinct part of speech; this may vary, not only with the language, but with the choice of word. For example, «dozen» serves the function of a noun, «first» serves the function of an adjective, and «twice» serves the function of an adverb. In Old Church Slavonic, the cardinal numbers 5 to 10 were feminine nouns; when quantifying a noun, that noun was declined in the genitive plural like other nouns that followed a noun of quantity (one would say the equivalent of «five of people»). In English grammar, the classification «numeral» (viewed as a part of speech) is reserved for those words which have distinct grammatical behavior: when a numeral modifies a noun, it may replace the article: the/some dogs played in the park → twelve dogs played in the park. (Note that *dozen dogs played in the park is not grammatical, so «dozen» is not a numeral in this sense.) English numerals indicate cardinal numbers. However, not all words for cardinal numbers are necessarily numerals. For example, million is grammatically a noun, and must be preceded by an article or numeral itself.
Numerals may be simple, such as ‘eleven’, or compound, such as ‘twenty-three’.
In linguistics, however, numerals are classified according to purpose: examples are ordinal numbers (first, second, third, etc.; from ‘third’ up, these are also used for fractions), multiplicative (adverbial) numbers (once, twice, and thrice), multipliers (single, double, and triple), and distributive numbers (singly, doubly, and triply). Georgian,[4] Latin, and Romanian (see Romanian distributive numbers) have regular distributive numbers, such as Latin singuli «one-by-one», bini «in pairs, two-by-two», terni «three each», etc. In languages other than English, there may be other kinds of number words. For example, in Slavic languages there are collective numbers (monad, pair/dyad, triad) which describe sets, such as pair or dozen in English (see Russian numerals, Polish numerals).
Some languages have a very limited set of numerals, and in some cases they arguably do not have any numerals at all, but instead use more generic quantifiers, such as ‘pair’ or ‘many’. However, by now most such languages have borrowed the numeral system or part of the numeral system of a national or colonial language, though in a few cases (such as Guarani[5]), a numeral system has been invented internally rather than borrowed. Other languages had an indigenous system but borrowed a second set of numerals anyway. An example is Japanese, which uses either native or Chinese-derived numerals depending on what is being counted.
In many languages, such as Chinese, numerals require the use of numeral classifiers. Many sign languages, such as ASL, incorporate numerals.
Larger numeralsEdit
English has derived numerals for multiples of its base (fifty, sixty, etc.), and some languages have simplex numerals for these, or even for numbers between the multiples of its base. Balinese, for example, currently has a decimal system, with words for 10, 100, and 1000, but has additional simplex numerals for 25 (with a second word for 25 only found in a compound for 75), 35, 45, 50, 150, 175, 200 (with a second found in a compound for 1200), 400, 900, and 1600. In Hindustani, the numerals between 10 and 100 have developed to the extent that they need to be learned independently.
In many languages, numerals up to the base are a distinct part of speech, while the words for powers of the base belong to one of the other word classes. In English, these higher words are hundred 102, thousand 103, million 106, and higher powers of a thousand (short scale) or of a million (long scale—see names of large numbers). These words cannot modify a noun without being preceded by an article or numeral (*hundred dogs played in the park), and so are nouns.
In East Asia, the higher units are hundred, thousand, myriad 104, and powers of myriad. In the Indian subcontinent, they are hundred, thousand, lakh 105, crore 107, and so on. The Mesoamerican system, still used to some extent in Mayan languages, was based on powers of 20: bak’ 400 (202), pik 8000 (203), kalab 160,000 (204), etc.
Numerals of cardinal numbersEdit
The cardinal numbers have numerals. In the following tables, [and] indicates that the word and is used in some dialects (such as British English), and omitted in other dialects (such as American English).
This table demonstrates the standard English construction of some cardinal numbers. (See next table for names of larger cardinals.)
| Value | Name | Alternate names, and names for sets of the given size |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Zero | aught, cipher, cypher, donut, dot, duck, goose egg, love, nada, naught, nil, none, nought, nowt, null, ought, oh, squat, zed, zilch, zip, zippo, Sunya (Sanskrit) |
| 1 | One | ace, individual, single, singleton, unary, unit, unity, Pratham (Sanskrit) |
| 2 | Two | binary, brace, couple, couplet, distich, deuce, double, doubleton, duad, duality, duet, duo, dyad, pair, span, twain, twin, twosome, yoke |
| 3 | Three | deuce-ace, leash, set, tercet, ternary, ternion, terzetto, threesome, tierce, trey, triad, trine, trinity, trio, triplet, troika, hat-trick |
| 4 | Four | foursome, quadruplet, quatern, quaternary, quaternity, quartet, tetrad |
| 5 | Five | cinque, fin, fivesome, pentad, quint, quintet, quintuplet |
| 6 | Six | half dozen, hexad, sestet, sextet, sextuplet, sise |
| 7 | Seven | heptad, septet, septuple, walking stick |
| 8 | Eight | octad, octave, octet, octonary, octuplet, ogdoad |
| 9 | Nine | ennead |
| 10 | Ten | deca, decade, das (India) |
| 11 | Eleven | onze, ounze, ounce, banker’s dozen |
| 12 | Twelve | dozen |
| 13 | Thirteen | baker’s dozen, long dozen[6] |
| 20 | Twenty | score, |
| 21 | Twenty-one | long score,[6] blackjack |
| 22 | Twenty-two | Deuce-deuce |
| 24 | Twenty-four | two dozen |
| 40 | Forty | two-score |
| 50 | Fifty | half-century |
| 55 | Fifty-five | double nickel |
| 60 | Sixty | three-score |
| 70 | Seventy | three-score and ten |
| 80 | Eighty | four-score |
| 87 | Eighty-seven | four-score and seven |
| 90 | Ninety | four-score and ten |
| 100 | One hundred | centred, century, ton, short hundred |
| 111 | One hundred [and] eleven | eleventy-one[7] |
| 120 | One hundred [and] twenty | long hundred,[6] great hundred, (obsolete) hundred |
| 144 | One hundred [and] forty-four | gross, dozen dozen, small gross |
| 1000 | One thousand | chiliad, grand, G, thou, yard, kilo, k, millennium, Hajaar (India) |
| 1024 | One thousand [and] twenty-four | kibi or kilo in computing, see binary prefix (kilo is shortened to K, Kibi to Ki) |
| 1100 | One thousand one hundred | Eleven hundred |
| 1728 | One thousand seven hundred [and] twenty-eight | great gross, long gross, dozen gross |
| 10000 | Ten thousand | myriad, wan (China) |
| 100000 | One hundred thousand | lakh |
| 500000 | Five hundred thousand | crore (Iranian) |
| 1000000 | One million | Mega, meg, mil, (often shortened to M) |
| 1048576 | One million forty-eight thousand five hundred [and] seventy-six | Mibi or Mega in computing, see binary prefix (Mega is shortened to M, Mibi to Mi) |
| 10000000 | Ten million | crore (Indian)(Pakistan) |
| 100000000 | One hundred million | yi (China) |
English names for powers of 10Edit
This table compares the English names of cardinal numbers according to various American, British, and Continental European conventions. See English numerals or names of large numbers for more information on naming numbers.
| Short scale | Long scale | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | American | British (Nicolas Chuquet) |
Continental European (Jacques Peletier du Mans) |
| 100 | One | ||
| 101 | Ten | ||
| 102 | Hundred | ||
| 103 | Thousand | ||
| 106 | Million | ||
| 109 | Billion | Thousand million | Milliard |
| 1012 | Trillion | Billion | |
| 1015 | Quadrillion | Thousand billion | Billiard |
| 1018 | Quintillion | Trillion | |
| 1021 | Sextillion | Thousand trillion | Trilliard |
| 1024 | Septillion | Quadrillion | |
| 1027 | Octillion | Thousand quadrillion | Quadrilliard |
| 1030 | Nonillion | Quintillion | |
| 1033 | Decillion | Thousand quintillion | Quintilliard |
| 1036 | Undecillion | Sextillion | |
| 1039 | Duodecillion | Thousand sextillion | Sextilliard |
| 1042 | Tredecillion | Septillion | |
| 1045 | Quattuordecillion | Thousand septillion | Septilliard |
| 1048 | Quindecillion | Octillion | |
| 1051 | Sexdecillion | Thousand octillion | Octilliard |
| 1054 | Septendecillion | Nonillion | |
| 1057 | Octodecillion | Thousand nonillion | Nonilliard |
| 1060 | Novemdecillion | Decillion | |
| 1063 | Vigintillion | Thousand decillion | Decilliard |
| 1066 | Unvigintillion | Undecillion | |
| 1069 | Duovigintillion | Thousand undecillion | Undecilliard |
| 1072 | Trevigintillion | Duodecillion | |
| 1075 | Quattuorvigintillion | Thousand duodecillion | Duodecilliard |
| 1078 | Quinvigintillion | Tredecillion | |
| 1081 | Sexvigintillion | Thousand tredecillion | Tredecilliard |
| 1084 | Septenvigintillion | Quattuordecillion | |
| 1087 | Octovigintillion | Thousand quattuordecillion | Quattuordecilliard |
| 1090 | Novemvigintillion | Quindecillion | |
| 1093 | Trigintillion | Thousand quindecillion | Quindecilliard |
| 1096 | Untrigintillion | Sexdecillion | |
| 1099 | Duotrigintillion | Thousand sexdecillion | Sexdecilliard |
| 10120 | Novemtrigintillion | Vigintillion | |
| 10123 | Quadragintillion | Thousand vigintillion | Vigintilliard |
| 10153 | Quinquagintillion | Thousand quinvigintillion | Quinvigintilliard |
| 10180 | Novemquinquagintillion | Trigintillion | |
| 10183 | Sexagintillion | Thousand trigintillion | Trigintilliard |
| 10213 | Septuagintillion | Thousand quintrigintillion | Quintrigintilliard |
| 10240 | Novemseptuagintillion | Quadragintillion | |
| 10243 | Octogintillion | Thousand quadragintillion | Quadragintilliard |
| 10273 | Nonagintillion | Thousand quinquadragintillion | Quinquadragintilliard |
| 10300 | Novemnonagintillion | Quinquagintillion | |
| 10303 | Centillion | Thousand quinquagintillion | Quinquagintilliard |
| 10360 | Cennovemdecillion | Sexagintillion | |
| 10420 | Cennovemtrigintillion | Septuagintillion | |
| 10480 | Cennovemquinquagintillion | Octogintillion | |
| 10540 | Cennovemseptuagintillion | Nonagintillion | |
| 10600 | Cennovemnonagintillion | Centillion | |
| 10603 | Ducentillion | Thousand centillion | Centilliard |
There is no consistent and widely accepted way to extend cardinals beyond centillion (centilliard).
Myriad, Octad, and -yllion systemsEdit
The following table details the myriad, octad, Chinese myriad, Chinese long and -yllion names for powers of 10.
There is also a Knuth-proposed system notation of numbers, named the -yllion system.[8] In this system, a new word is invented for every 2n-th power of ten.
| Value | Myriad System Name | Octad System Name | Chinese Myriad Scale | Chinese Long Scale | Knuth-proposed System Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | One | One | 一 | 一 | One |
| 101 | Ten | Ten | 十 | 十 | Ten |
| 102 | Hundred | Hundred | 百 | 百 | Hundred |
| 103 | Thousand | Thousand | 千 | 千 | Ten hundred |
| 104 | Myriad | Myriad | 萬 (万) | 萬 (万) | Myriad |
| 105 | Ten myriad | Ten myriad | 十萬 (十万) | 十萬 (十万) | Ten myriad |
| 106 | Hundred myriad | Hundred myriad | 百萬 (百万) | 百萬 (百万) | Hundred myriad |
| 107 | Thousand myriad | Thousand myriad | 千萬 (千万) | 千萬 (千万) | Ten hundred myriad |
| 108 | Second Myriad | Octad | 億 (亿) | 億 (亿) | Myllion |
| 1012 | Third myriad | Myriad Octad | 兆 | 萬億 | Myriad myllion |
| 1016 | Fourth myriad | Second octad | 京 | 兆 | Byllion |
| 1020 | Fifth myriad | Myriad second octad | 垓 | 萬兆 | |
| 1024 | Sixth myriad | Third octad | 秭 | 億兆 | Myllion byllion |
| 1028 | Seventh myriad | Myriad third octad | 穰 | 萬億兆 | |
| 1032 | Eighth myriad | Fourth octad | 溝 (沟) | 京 | Tryllion |
| 1036 | Ninth myriad | Myriad fourth octad | 澗 (涧) | 萬京 | |
| 1040 | Tenth myriad | Fifth octad | 正 | 億京 | |
| 1044 | Eleventh myriad | Myriad fifth octad | 載 (载) | 萬億京 | |
| 1048 | Twelfth myriad | Sixth octad | 極 (极) (in China and in Japan) | 兆京 | |
| 1052 | Thirteenth myriad | Myriad sixth octad | 恆河沙 (恒河沙) (in China) | 萬兆京 | |
| 1056 | Fourteenth myriad | Seventh octad | 阿僧祇 (in China); 恆河沙 (恒河沙) (in Japan) | 億兆京 | |
| 1060 | Fifteenth myriad | Myriad seventh octad | 那由他, 那由多 (in China) | 萬億兆京 | |
| 1064 | Sixteenth myriad | Eighth octad | 不可思議 (不可思议) (in China), 阿僧祇 (in Japan) | 垓 | Quadyllion |
| 1068 | Seventeenth myriad | Myriad eighth octad | 無量大数 (in China) | 萬垓 | |
| 1072 | Eighteenth myriad | Ninth octad | 那由他, 那由多 (in Japan) | 億垓 | |
| 1080 | Twentieth myriad | Tenth octad | 不可思議 (in Japan) | 兆垓 | |
| 1088 | Twenty-second myriad | Eleventh Octad | 無量大数 (in Japan) | 億兆垓 | |
| 10128 | 秭 | Quinyllion | |||
| 10256 | 穰 | Sexyllion | |||
| 10512 | 溝 (沟) | Septyllion | |||
| 101,024 | 澗 (涧) | Octyllion | |||
| 102,048 | 正 | Nonyllion | |||
| 104,096 | 載 (载) | Decyllion | |||
| 108,192 | 極 (极) | Undecyllion | |||
| 1016,384 | Duodecyllion | ||||
| 1032,768 | Tredecyllion | ||||
| 1065,536 | Quattuordecyllion | ||||
| 10131,072 | Quindecyllion | ||||
| 10262,144 | Sexdecyllion | ||||
| 10524,288 | Septendecyllion | ||||
| 101,048,576 | Octodecyllion | ||||
| 102,097,152 | Novemdecyllion | ||||
| 104,194,304 | Vigintyllion | ||||
| 10232 | Trigintyllion | ||||
| 10242 | Quadragintyllion | ||||
| 10252 | Quinquagintyllion | ||||
| 10262 | Sexagintyllion | ||||
| 10272 | Septuagintyllion | ||||
| 10282 | Octogintyllion | ||||
| 10292 | Nonagintyllion | ||||
| 102102 | Centyllion | ||||
| 1021,002 | Millyllion | ||||
| 10210,002 | Myryllion |
Fractional numeralsEdit
This is a table of English names for non-negative rational numbers less than or equal to 1. It also lists alternative names, but there is no widespread convention for the names of extremely small positive numbers.
Keep in mind that rational numbers like 0.12 can be represented in infinitely many ways, e.g. zero-point-one-two (0.12), twelve percent (12%), three twenty-fifths (3/25), nine seventy-fifths (9/75), six fiftieths (6/50), twelve hundredths (12/100), twenty-four two-hundredths (24/200), etc.
| Value | Fraction | Common names |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/1 | One, Unity, Whole |
| 0.9 | 9/10 | Nine tenths, [zero] point nine |
| 0.833333… | 5/6 | Five sixths |
| 0.8 | 4/5 | Four fifths, eight tenths, [zero] point eight |
| 0.75 | 3/4 | three quarters, three fourths, seventy-five hundredths, [zero] point seven five |
| 0.7 | 7/10 | Seven tenths, [zero] point seven |
| 0.666666… | 2/3 | Two thirds |
| 0.6 | 3/5 | Three fifths, six tenths, [zero] point six |
| 0.5 | 1/2 | One half, five tenths, [zero] point five |
| 0.4 | 2/5 | Two fifths, four tenths, [zero] point four |
| 0.333333… | 1/3 | One third |
| 0.3 | 3/10 | Three tenths, [zero] point three |
| 0.25 | 1/4 | One quarter, one fourth, twenty-five hundredths, [zero] point two five |
| 0.2 | 1/5 | One fifth, two tenths, [zero] point two |
| 0.166666… | 1/6 | One sixth |
| 0.142857142857… | 1/7 | One seventh |
| 0.125 | 1/8 | One eighth, one-hundred-[and-]twenty-five thousandths, [zero] point one two five |
| 0.111111… | 1/9 | One ninth |
| 0.1 | 1/10 | One tenth, [zero] point one, One perdecime, one perdime |
| 0.090909… | 1/11 | One eleventh |
| 0.09 | 9/100 | Nine hundredths, [zero] point zero nine |
| 0.083333… | 1/12 | One twelfth |
| 0.08 | 2/25 | Two twenty-fifths, eight hundredths, [zero] point zero eight |
| 0.076923076923… | 1/13 | One thirteenth |
| 0.071428571428… | 1/14 | One fourteenth |
| 0.066666… | 1/15 | One fifteenth |
| 0.0625 | 1/16 | One sixteenth, six-hundred-[and-]twenty-five ten-thousandths, [zero] point zero six two five |
| 0.055555… | 1/18 | One eighteenth |
| 0.05 | 1/20 | One twentieth, five hundredths, [zero] point zero five |
| 0.047619047619… | 1/21 | One twenty-first |
| 0.045454545… | 1/22 | One twenty-second |
| 0.043478260869565217391304347… | 1/23 | One twenty-third |
| 0.041666… | 1/24 | One twenty-fourth |
| 0.04 | 1/25 | One twenty-fifth, four hundredths, [zero] point zero four |
| 0.033333… | 1/30 | One thirtieth |
| 0.03125 | 1/32 | One thirty-second, thirty one-hundred [and] twenty five hundred-thousandths, [zero] point zero three one two five |
| 0.03 | 3/100 | Three hundredths, [zero] point zero three |
| 0.025 | 1/40 | One fortieth, twenty-five thousandths, [zero] point zero two five |
| 0.02 | 1/50 | One fiftieth, two hundredths, [zero] point zero two |
| 0.016666… | 1/60 | One sixtieth |
| 0.015625 | 1/64 | One sixty-fourth, ten thousand fifty six-hundred [and] twenty-five millionths, [zero] point zero one five six two five |
| 0.012345679012345679… | 1/81 | One eighty-first |
| 0.010101… | 1/99 | One ninety-ninth |
| 0.01 | 1/100 | One hundredth, [zero] point zero one, One percent |
| 0.009900990099… | 1/101 | One hundred-first |
| 0.008264462809917355371900… | 1/121 | One over one hundred twenty-one |
| 0.001 | 1/1000 | One thousandth, [zero] point zero zero one, One permille |
| 0.000277777… | 1/3600 | One thirty-six hundredth |
| 0.0001 | 1/10000 | One ten-thousandth, [zero] point zero zero zero one, One myriadth, one permyria, one permyriad, one basis point |
| 0.00001 | 1/100000 | One hundred-thousandth, [zero] point zero zero zero zero one, One lakhth, one perlakh |
| 0.000001 | 1/1000000 | One millionth, [zero] point zero zero zero zero zero one, One ppm |
| 0.0000001 | 1/10000000 | One ten-millionth, One crorth, one percrore |
| 0.00000001 | 1/100000000 | One hundred-millionth |
| 0.000000001 | 1/1000000000 | One billionth (in some dialects), One ppb |
| 0.000000000001 | 1/1000000000000 | One trillionth, One ppt |
| 0 | 0/1 | Zero, Nil |
Other specific quantity termsEdit
Various terms have arisen to describe commonly used measured quantities.
- Unit: 1
- Pair: 2 (the base of the binary numeral system)
- Leash: 3 (the base of the trinary numeral system)
- Dozen: 12 (the base of the duodecimal numeral system)
- Baker’s dozen: 13
- Score: 20 (the base of the vigesimal numeral system)
- Shock: 60 (the base of the sexagesimal numeral system)[9]
- Gross: 144 (= 122)
- Great gross: 1728 (= 123)
Basis of counting systemEdit
Not all peoples count, at least not verbally. Specifically, there is not much need for counting among hunter-gatherers who do not engage in commerce. Many languages around the world have no numerals above two to four (if they’re actually numerals at all, and not some other part of speech)—or at least did not before contact with the colonial societies—and speakers of these languages may have no tradition of using the numerals they did have for counting. Indeed, several languages from the Amazon have been independently reported to have no specific number words other than ‘one’. These include Nadëb, pre-contact Mocoví and Pilagá, Culina and pre-contact Jarawara, Jabutí, Canela-Krahô, Botocudo (Krenák), Chiquitano, the Campa languages, Arabela, and Achuar.[10] Some languages of Australia, such as Warlpiri, do not have words for quantities above two,[11][12][13] and neither did many Khoisan languages at the time of European contact. Such languages do not have a word class of ‘numeral’.
Most languages with both numerals and counting use base 8, 10, 12, or 20. Base 10 appears to come from counting one’s fingers, base 20 from the fingers and toes, base 8 from counting the spaces between the fingers (attested in California), and base 12 from counting the knuckles (3 each for the four fingers).[14]
No baseEdit
Many languages of Melanesia have (or once had) counting systems based on parts of the body which do not have a numeric base; there are (or were) no numerals, but rather nouns for relevant parts of the body—or simply pointing to the relevant spots—were used for quantities. For example, 1–4 may be the fingers, 5 ‘thumb’, 6 ‘wrist’, 7 ‘elbow’, 8 ‘shoulder’, etc., across the body and down the other arm, so that the opposite little finger represents a number between 17 (Torres Islands) to 23 (Eleman). For numbers beyond this, the torso, legs and toes may be used, or one might count back up the other arm and back down the first, depending on the people.
2: binaryEdit
Binary systems are base 2, using zeros and ones. With only two symbols binary is used for things with coding like computers.
3: ternaryEdit
Base 3 counting has practical usage in some analog logic, in baseball scoring and in self–similar mathematical structures.
4: quaternaryEdit
Some Austronesian and Melanesian ethnic groups, some Sulawesi and some Papua New Guineans, count with the base number four, using the term asu or aso, the word for dog, as the ubiquitous village dog has four legs.[15] This is argued by anthropologists to be also based on early humans noting the human and animal shared body feature of two arms and two legs as well as its ease in simple arithmetic and counting. As an example of the system’s ease a realistic scenario could include a farmer returning from the market with fifty asu heads of pig (200), less 30 asu (120) of pig bartered for 10 asu (40) of goats noting his new pig count total as twenty asu: 80 pigs remaining. The system has a correlation to the dozen counting system and is still in common use in these areas as a natural and easy method of simple arithmetic.[15][16]
5: quinaryEdit
Quinary systems are based on the number 5. It is almost certain the quinary system developed from counting by fingers (five fingers per hand).[17] An example are the Epi languages of Vanuatu, where 5 is luna ‘hand’, 10 lua-luna ‘two hand’, 15 tolu-luna ‘three hand’, etc. 11 is then lua-luna tai ‘two-hand one’, and 17 tolu-luna lua ‘three-hand two’.
5 is a common auxiliary base, or sub-base, where 6 is ‘five and one’, 7 ‘five and two’, etc. Aztec was a vigesimal (base-20) system with sub-base 5.
6: senaryEdit
The Morehead-Maro languages of Southern New Guinea are examples of the rare base 6 system with monomorphemic words running up to 66. Examples are Kanum and Kómnzo. The Sko languages on the North Coast of New Guinea follow a base-24 system with a sub-base of 6.
7: septenaryEdit
Septenary systems are very rare, as few natural objects consistently have seven distinctive features. Traditionally, it occurs in week-related timing. It has been suggested that the Palikúr language has a base-seven system, but this is dubious.[18]
8: octalEdit
Octal counting systems are based on the number 8. Examples can be found in the Yuki language of California and in the Pamean languages of Mexico, because the Yuki and Pame keep count by using the four spaces between their fingers rather than the fingers themselves.[19]
9: nonaryEdit
It has been suggested that Nenets has a base-nine system.[18]
10: decimalEdit
A majority of traditional number systems are decimal. This dates back at least to the ancient Egyptians, who used a wholly decimal system. Anthropologists hypothesize this may be due to humans having five digits per hand, ten in total.[17][20] There are many regional variations including:
- Western system: based on thousands, with variants (see English numerals)
- Indian system: crore, lakh (see Indian numbering system. Indian numerals)
- East Asian system: based on ten-thousands (see below)
12: duodecimalEdit
Duodecimal systems are based on 12.
These include:
- Chepang language of Nepal,
- Mahl language of Minicoy Island in India
- Nigerian Middle Belt areas such as Janji, Kahugu and the Nimbia dialect of Gwandara.
- Melanesia[citation needed]
- reconstructed proto-Benue–Congo
Duodecimal numeric systems have some practical advantages over decimal. It is much easier to divide the base digit twelve (which is a highly composite number) by many important divisors in market and trade settings, such as the numbers 2, 3, 4 and 6.
Because of several measurements based on twelve,[21] many Western languages have words for base-twelve units such as dozen, gross and great gross, which allow for rudimentary duodecimal nomenclature, such as «two gross six dozen» for 360. Ancient Romans used a decimal system for integers, but switched to duodecimal for fractions, and correspondingly Latin developed a rich vocabulary for duodecimal-based fractions (see Roman numerals). A notable fictional duodecimal system was that of J. R. R. Tolkien’s Elvish languages, which used duodecimal as well as decimal.
16: hexadecimalEdit
Hexadecimal systems are based on 16.
The traditional Chinese units of measurement were base-16. For example, one jīn (斤) in the old system equals sixteen taels. The suanpan (Chinese abacus) can be used to perform hexadecimal calculations such as additions and subtractions.[22]
South Asian monetary systems were base-16. One rupee in Pakistan and India was divided into 16 annay. A single anna was subdivided into four paisa or twelve pies (thus there were 64 paise or 192 pies in a rupee). The anna was demonetised as a currency unit when India decimalised its currency in 1957, followed by Pakistan in 1961.
20: vigesimalEdit
Vigesimal numbers use the number 20 as the base number for counting. Anthropologists are convinced the system originated from digit counting, as did bases five and ten, twenty being the number of human fingers and toes combined.[17][23]
The system is in widespread use across the world. Some include the classical Mesoamerican cultures, still in use today in the modern indigenous languages of their descendants, namely the Nahuatl and Mayan languages (see Maya numerals). A modern national language which uses a full vigesimal system is Dzongkha in Bhutan.
Partial vigesimal systems are found in some European languages: Basque, Celtic languages, French (from Celtic), Danish, and Georgian. In these languages the systems are vigesimal up to 99, then decimal from 100 up. That is, 140 is ‘one hundred two score’, not *seven score, and there is no numeral for 400 (great score).
The term score originates from tally sticks, and is perhaps a remnant of Celtic vigesimal counting. It was widely used to learn the pre-decimal British currency in this idiom: «a dozen pence and a score of bob», referring to the 20 shillings in a pound. For Americans the term is most known from the opening of the Gettysburg Address: «Four score and seven years ago our fathers…».
24: quadrovigesimalEdit
The Sko languages have a base-24 system with a sub-base of 6.
32: duotrigesimalEdit
Ngiti has base 32.
60: sexagesimalEdit
Ekari has a base-60 system. Sumeria had a base-60 system with a decimal sub-base (with alternating cycles of 10 and 6), which was the origin of the numbering of modern degrees, minutes, and seconds.
80: octogesimalEdit
Supyire is said to have a base-80 system; it counts in twenties (with 5 and 10 as sub-bases) up to 80, then by eighties up to 400, and then by 400s (great scores).
799 [i.e. 400 + (4 x 80) + (3 x 20) + {10 + (5 + 4)}]’
See alsoEdit
Numerals in various languagesEdit
A database Numeral Systems of the World’s Languages compiled by Eugene S.L. Chan of Hong Kong is hosted by the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany. The database currently contains data for about 4000 languages.
- Proto-Indo-European numerals
- English numerals
- Indian numbering system
- Polish numerals
- Hindustani numerals
- Proto-Semitic numerals
- Hebrew numerals
- Chinese numerals
- Japanese numerals
- Korean numerals
- Vietnamese numerals
- Australian Aboriginal enumeration
- Balinese numerals
- Dzongkha numerals
- Finnish numerals
- Javanese numerals
- Yoruba numerals
Edit
- Long and short scales
- Names of large numbers
- Numeral system
- Numeral prefix
- Names of small numbers
NotesEdit
- ^ Charles Follen: A Practical Grammar of the German Language. Boston, 1828, p. 9, p. 44 and 48. Quote: «PARTS OF SPEECH. There are ten parts of speech, viz. Article, Substantive or Noun, Adjective, Numeral, Pronoun, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, and Interjection.», «NUMERALS. The numbers are divided into cardinal, ordinal, proportional, distributive, and collective. […] Numerals of proportion and distribution are […] &c. Observation. The above numerals, in fach or fäl´tig, are regularly declined, like other adjectives.»
- ^ Horace Dalmolin: The New English Grammar: With Phonetics, Morphology and Syntax, Tate Publishing & Enterprises, 2009, p. 175 & p. 177. Quote: «76. The different types of words used to compose a sentence, in order to relate an idea or to convey a thought, are known as parts of speech. […] The parts of speech, with a brief definition, will follow. […] 87. Numeral: Numerals are words that express the idea of number. There are two types of numerals: cardinal and ordinal. The cardinal numbers (one, two, three…) are used for counting people, objects, etc. Ordinal numbers (first, second, third…) can indicate order, placement in rank, etc.»
- ^ a b «What is a numeral?».
- ^ «Walsinfo.com».
- ^ «Numbers in Guaraní (Papapy Avañe’ême)». omniglot.com. Retrieved 2021-06-11.
- ^ a b c Blunt, Joseph (1 January 1837). «The Shipmaster’s Assistant, and Commercial Digest: Containing Information Useful to Merchants, Owners, and Masters of Ships». E. & G.W. Blunt – via Google Books.
- ^ Ezard, John (2 Jan 2003). «Tolkien catches up with his hobbit». The Guardian. Retrieved 6 Apr 2018.
- ^ «Large Numbers (page 2) at MROB». mrob.com. Retrieved 2020-12-23.
- ^ Cardarelli, François (2012). Encyclopaedia of Scientific Units, Weights and Measures: Their SI Equivalences and Origins (Second ed.). Springer. p. 585. ISBN 978-1447100034.
- ^ «Hammarström (2009, page 197) «Rarities in numeral systems»» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-08. Retrieved 2010-06-16.
- ^ UCL Media Relations, «Aboriginal kids can count without numbers» Archived 2018-06-20 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Butterworth, Brian; Reeve, Robert; Reynolds, Fiona; Lloyd, Delyth (2 September 2008). «Numerical thought with and without words: Evidence from indigenous Australian children». PNAS. 105 (35): 13179–13184. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10513179B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806045105. PMC 2527348. PMID 18757729.
[Warlpiri] has three generic types of number words: singular, dual plural, and greater than dual plural.
- ^ The Science Show, Genetic anomaly could explain severe difficulty with arithmetic, Australian Broadcasting Corporation
- ^ Bernard Comrie, «The Typology of Numeral Systems Archived 2011-05-14 at the Wayback Machine», p. 3
- ^ a b Ryan, Peter. Encyclopaedia of Papua and New Guinea. Melbourne University Press & University of Papua and New Guinea,:1972 ISBN 0-522-84025-6.: 3 pages p 219.
- ^ Aleksandr Romanovich Luriicac, Lev Semenovich Vygotskiĭ, Evelyn Rossiter. Ape, primitive man, and child: essays in the history of behavior. CRC Press: 1992: ISBN 1-878205-43-9.
- ^ a b c Heath, Thomas, A Manual of Greek Mathematics, Courier Dover: 2003. ISBN 978-0-486-43231-1 page, p:11
- ^ a b Parkvall, M. Limits of Language, 1st edn. 2008. p.291. ISBN 978-1-59028-210-6
- ^ Ascher, Marcia (1994), Ethnomathematics: A Multicultural View of Mathematical Ideas, Chapman & Hall, ISBN 0-412-98941-7
- ^ Scientific American Munn& Co: 1968, vol 219: 219
- ^ such as twelve months in a year, the twelve-hour clock, twelve inches to the foot, twelve pence to the shilling
- ^ «算盤 Hexadecimal Addition & Subtraction on a Chinese Abacus». totton.idirect.com. Retrieved 2019-06-26.
- ^ Georges Ifrah, The Universal History of Numbers: The Modern Number System, Random House, 2000: ISBN 1-86046-791-1. 1262 pages
Further readingEdit
- James R. Hurford (2010) [1975]. The Linguistic Theory of Numerals. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-13368-5.
Number words are the alphabetical form of numbers. As the name suggests, these are numbers written in words. Word form is writing the numerical/number as you would say it in words.
‘Number words’ or ‘number names’ are simply the names assigned to numbers so that we can identify each number uniquely. When we talk about “math,” what is the first thing that comes to your mind? Numbers! Are you aware that numbers also have names called number names? Yes, like everything else in the world, numbers have names. Let us know the number name definition and the rules to write them.
Related Games
Number Words: Definition
A number word or number name is a way to express numbers in their word form. We can express numbers using their number name form. The spelling of numbers in English is something we should focus on while writing the numbers in word form.
For example, we can write 1 as “one.” So, the number name for 1 is “one.”
Similarly, we can express the number 2 as “two” in its word form.
The number 3 as “three” in its word form, and so on.
For example:
With the help of the number words from one to ten, we can make number words of higher value.
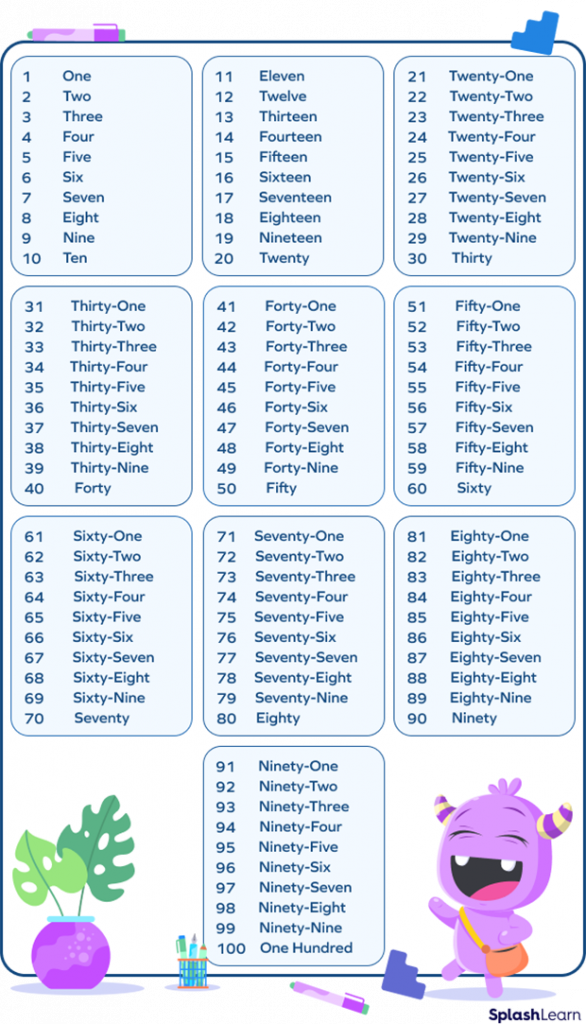
It is important to learn every number word from One to Twenty to learn other number words. Also, the number words from eleven to twenty are very different from other number words.
After learning the number words up to twenty, it is important to learn the number words such as thirty, forty, fifty, sixty until hundred.
Once you know these number words, it is easy to make number words for higher value numbers.
For example:
The above two number words are made from learning the basic number words from one to ten, and the number words for tens value, like sixty, seventy and eighty.
As the numbers increase in value and become larger with three, four, five, six, seven and more digits, the names start to change.
Related Worksheets
Rules to Write Numbers in Word Form
While writing numbers in their number words form, we have to follow certain rules. These rules are as follows:
Rule 1
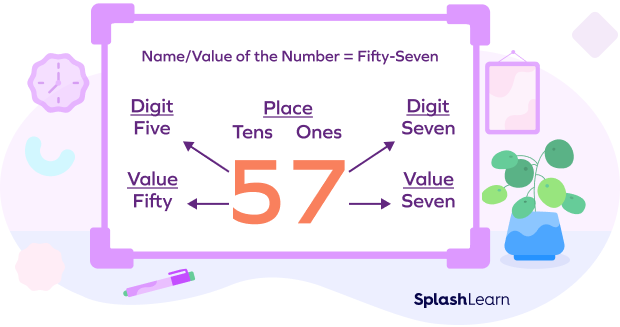
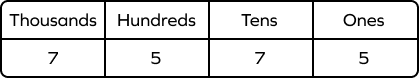
Always consider place values while writing numbers in the word form.
For example, the digit 2 at the ones place is read as 2. The same digit at the tens place has the value “twenty.” So, 22 can be written as “twenty-two.”
Rule 2
To write numbers between 1–20, refer to the number names chart.
To express numbers beyond 20 in words, you must follow a certain pattern. As per this pattern, the multiples of 10 up to 90 are written as thirty, forty, fifty, sixty, seventy, eighty, and ninety.
Rule 3
For writing multiples of 100 in word form, you can write the digit in the word form and add the word hundred after it.
For example, you can express 200 as two hundred in the word form, 600 as six hundred, and so on.
You can follow the same rule while writing multiples of 1000 in word form. The only difference is that you have to add the word thousand instead of hundred. For example, you can write 3000 as three thousand in the word form.
Rule 4
For writing two-digit or three-digit numbers in word form, you have to write them in their expanded form. Ensure that you take the position of 0 in account.
For example, you can write 107 (expanded into $100 + 0 + 7$) as one hundred seven.
The word form of 125 (expanded into $100 + 20 + 5$) is one hundred twenty-five.
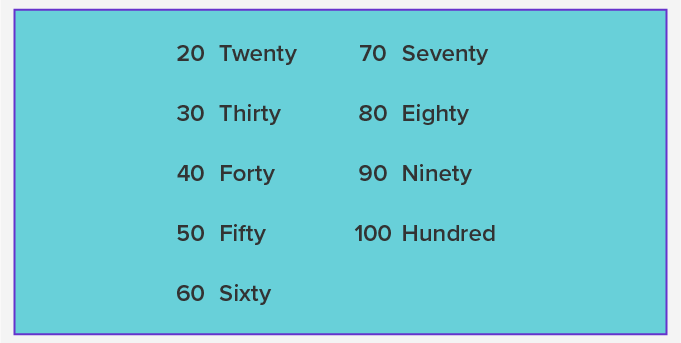
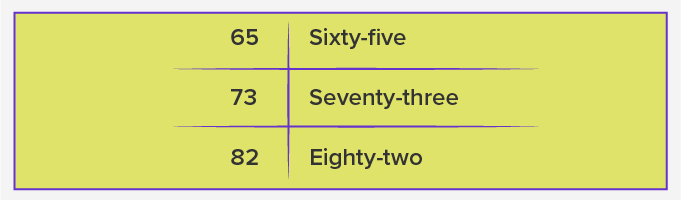
Number Words or Number Names from 1 to 100
Here’s a table containing numbers 1 to 100 and their corresponding word forms:
The Number Words for Higher Values
It becomes easy to convert numbers to number words and number words to number if we know the number words.
For example:
Write the given numbers in words.
Write the given numbers in numerals.
Number Names as per the International Number System
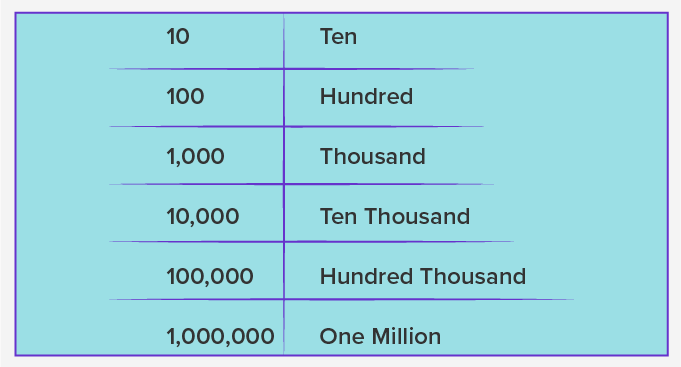
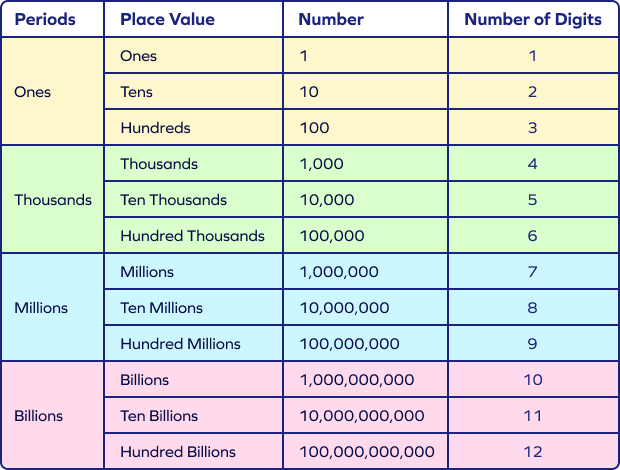
In the international system, the numbers are organized into periods and groups. The periods are categorized as ones, thousands, millions, etc. Each period is grouped into three place values. While writing numbers in this system, we insert a comma or separator after every three digits from the right.
The place value names in the international system are as follows:
- Ones
- Tens
- Hundreds
- Thousands
- Ten Thousands
- Hundred Thousands
- Millions
- Ten Millions
- Hundred Millions
- Billions
- Ten Billions
- Hundred Billions
- Trillions, and so on
Example: Suppose you have to write the word form of the number 6,342,715 in the international system.
6,342,715 is Six Million Three Hundred Forty-two Thousand Seven Hundred Fifteen.
Place Value Chart for International System
Here is the place value chart for the international system:
From this place value chart, we understand:
- 1 million $= 1000$ thousand
- 1 billion $= 1000$ million
Tips and Tricks to Learn Numbers Names
Here are a few tips to help you learn and write numbers in their word forms:
- Write down 1 to 20 as numbers and their spellings.
- Write down the multiples of 10 up to 90 and their spellings.
For example, 10: Ten, 20: Twenty, 30: Thirty, and so on.
- Write down the multiples of 100 and their spellings.
For example, 100: Three hundred, 200: Two hundred, and so on.
- For two-digit numbers beyond 20, expand them and write them in words in their expanded form. For example, you can expand 32 as $30 + 2$ and write “thirty-two.”
- Follow the same technique for large numbers.
For example, you can expand 471 as “$400 + 70 + 1$” and write “four hundred seventy-one” or “four hundred and seventy-one.”
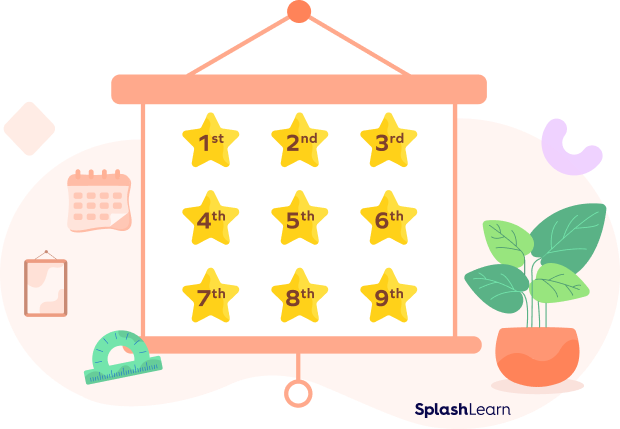
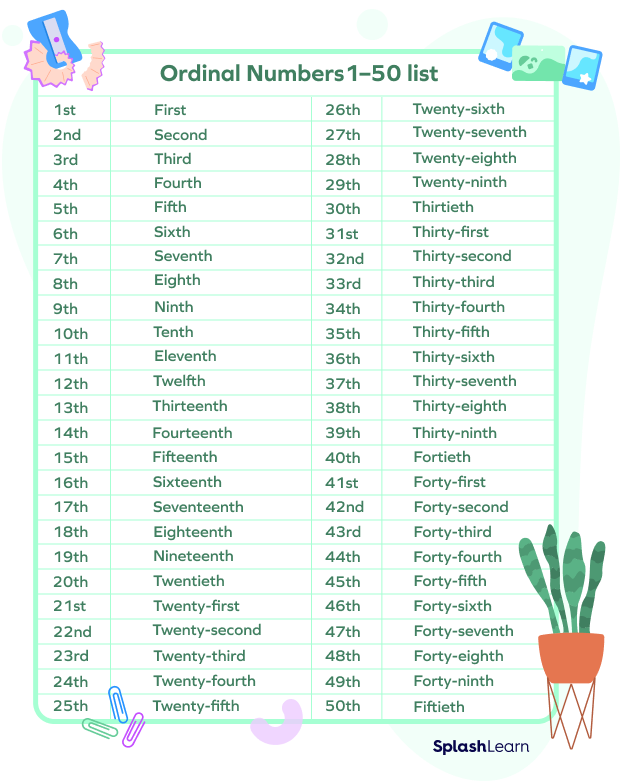
Number Names as per the Ordinal System
An ordinal number expresses the rank or position of something. That is why they are also known as ranking or positioning numbers.
Ordinal numbers are written as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and so on.
Here is a chart of the first 50 ordinal numbers and their number names:
Fun Facts
- When writing ordinal numbers in their word form, we use the suffix -th for the numbers 11, 12, and 13; but for all other numbers ending with 1, 2, or 3, we use the suffixes -st, -nd, and -rd, respectively. For example, we express 51 as fifty-first, 52 as fifty-second, and 53 as fifty-third.
- The word form of the number 40 is forty and not fourty.
- When writing numbers between 21 and 99, we use a hyphen $(-)$ in between.
- To write number words, we can write the word form of the numbers as we say them.
Conclusion
Number names offer an easy way to identify and learn numbers. They can help us to understand how the number system functions. Knowing to read and write numbers in words can enable us to identify how numbers relate to one another.
Solved Examples
- Write the number 7575 in words.
Solution:
We can expand 7575 as $7000 + 500 + 70 + 5$.
7575 in word form is “seven thousand five hundred seventy-five.”
- What comes after the given number name: twenty-nine?
Solution:
Twenty-nine $= 29$
The number after 29 is $29 + 1 = 30$
30 in the word form is Thirty.
So, thirty comes after twenty-nine.
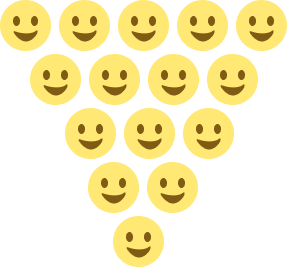
- Count the emojis in the given image and write the number in words.
Solution:
$5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 15$
The given image has fifteen or 15 smileys.
- Express 2022 in words and also in the ordinal system.
Solution:
$2022 = 2000 + 0 + 20 + 2$
In words, we write it as “two thousand twenty-two.”
Also, 2022 is written as “two thousand twenty-second” in the ordinal system.
- Write the word form of 404.
Solution:
$404 = 400 + 0 + 4$
404 is four hundred four.
Practice Problmes
Fifty-seven
Five & seven
Seventy five
None of the above
Correct answer is: Fifty-seven
We expand 57 as $50 + 7$. So, it would be written as “fifty-seven.”
Sixty-tenth
Seventieth
Seventy
None of the above
Correct answer is: Seventieth
As per the ordinal system, “seventieth” comes after “sixty-ninth.”
4040 is four thousand forty
4004 is four thousand four
4400 is four thousand four hundred
4440 is four thousand forty-four
Correct answer is: 4440 is four thousand forty-four
4440 is four thousand four hundred forty.
$gt$
$=$
$lt$
None of the above
Correct answer is: $lt$
Four hundred sixty-three is 463. Thus, $436 lt 463$.
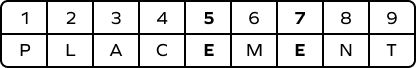
Fifth and eighth
Fifth and seventh
Fourth and seventh
Sixth and eighth
Correct answer is: Fifth and seventh
By counting the letters in the word “PLACEMENT,” we can see that the letter E appears in the fifth and seventh positions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do we have to use commas when writing a number in its word form?
No, we don’t use commas when writing a number in its word form.
Does the word zero appear in any number name?
No, we don’t use the word “zero” when writing a number in words.
Can we write decimal numbers in words?
Yes, we can write decimal numbers in words. For example, we can write 42.35 as forty-two point three five.
Are there any real-life applications of writing numbers in words?
Yes, there are real-life applications of writing numbers in words. For example, it is mandatory to write the amount in both figures and words in a bank cheque.
Why is place value important for writing numbers in words?
The place value helps to determine the place of a digit in a number. This is important for reading a number and writing it in words.
Related Articles
- Word Form
- Natural Number
- Number Words
what is number and word notation
What is it? A notation consisting of the significant digits of a large number and words for the place value. For example: 27 trillion; 2.4 million; 1.09 billion.
How do I write notation in Word?
Go to Insert > Symbol. Pick a symbol, or choose More Symbols. Scroll up or down to find the symbol you want to insert. Different font sets often have different symbols in them and the most commonly used symbols are in the Segoe UI Symbol font set.
What is an example of a notation?
The definition of a notation is a system of using symbols or signs as a form of communication, or a short written note. An example of a notation is a chemist using AuBr for gold bromide. An example of a notation is a short list of things to do. … She made a notation in the margin of the book.
How do you write in standard notation?
A number is written in standard form when it is represented as a decimal number times a power of 10. As an example, consider the speed of light which travels at about 671,000,000 miles per hour. Written in standard form this number is equivalent to 6.71 x 108.
How do you write numbers in words and symbols?
explain what symbol notation says should be done to the numbers … Asks students to write the phrases using symbols instead of words.
How do you write word notation?
Standard notation calculator converts number word combinations into numbers … way to write numbers since words are not used in standard number notation.
What is a notation in math example?
A system of symbols used to represent special things. Example: In mathematical notation «∞» means «infinity».
What are the examples of set notation?
Common Set Notation For example, if A={(1,2),(3,4)}, then |A|=2. A=B if and only if they have precisely the same elements. For example, if A={4,9} and B={n2:n=2 or n=3}, then A=B.
What are the type of notation?
There are two types of notation: Pure Notation. Mixed Notation.
What does notation mean in maths?
Mathematical notation is a writing system used for recording concepts in mathematics. The notation uses symbols or symbolic expressions that are intended to have a precise semantic meaning. In the history of mathematics, these symbols have denoted numbers, shapes, patterns, and change.
What is an example of a notation?
The definition of a notation is a system of using symbols or signs as a form of communication, or a short written note. An example of a notation is a chemist using AuBr for gold bromide. An example of a notation is a short list of things to do. … She made a notation in the margin of the book.
How do you write math notation?
viết bởi KP Lee · Trích dẫn 28 bài viết — Use mathematical notation correctly. As you learn to write more complicated formulas, it is all too easy to leave out symbols from formulas. Learn how to use.17 trang
What is standard notation example?
Illustrated definition of Standard Notation: Just the number as we normally write it. Example: 382 is in Standard Notation.
What is common notation in math?
Just the number as we normally write it. Example: 382 is in Standard Notation. See: Expanded Notation. Composing and Decomposing Numbers.
What is a notation in math example?
A system of symbols used to represent special things. Example: In mathematical notation «∞» means «infinity».
What is an example of standard notation?
Illustrated definition of Standard Notation: Just the number as we normally write it. Example: 382 is in Standard Notation.
How do you write numbers in standard form?
A number written in standard form is presented as A x 10 n, where A is a number bigger than or equal to 1 and less than 10. 34 × 10 7 is not in standard form as the first number is not between 1 and 10. To correct this, divide 34 by 10.
How do you convert to standard notation?
Convert a number to and from scientific notation, e notation, engineering notation, standard form, and real numbers. Enter a number or a decimal number or …
How do you write a number in notation?
To write a number in scientific notation, move the decimal point to the right of the first digit in the number. Write the digits as a decimal number between 1 and 10. Count the number of places n that you moved the decimal point. Multiply the decimal number by 10 raised to a power of n.
How do you write a number in standard notation?
Standard form of a number is a x 10b where a is a number, 1 ≤ |a| < 10. b is the power of 10 required so that the standard form is mathematically equivalent to the original number. Move the decimal point in your number until there is only one non-zero digit to the left of the decimal point.
If you still have questions like the ones below, please contact us for answers:
word notation calculator
word notation in math
what is number notation in mathematics
Translate word to number
number notation grade 3
fractional notation
Name to number Converter
Number to word
See more articles in the category: Wiki
Post Views:
68
Updated: 11/18/2022 by
A number may refer to any of the following:
1. Sometimes abbreviated as num, a number is any character that’s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 0. Any negative number is any earlier characters beginning with a hyphen; for example, «-12» is a negative number. Numbers have many relationships with computers. Examples include measuring the clock speed of a CPU or the binary numbers that send the CPU instructions.
Note
A number with a minus (hyphen) in front of it is known as a negative number and not a minus number.
How to type numbers
On the computer keyboard, you can use the numbers on the number keys row at the top of the keyboard if you’re typing letters and numbers. If you need help determining what finger to use for each letter, see the link below. If you’re only typing numbers or doing a calculation and it’s available, use the numeric keypad.
- Where should fingers be placed on the keyboard?
How to perform arithmetic with numbers?
With a computer, the user can perform arithmetic using a calculator, programming language, or spreadsheet.
Number pages
The following links are the number pages on Computer Hope that contain further information about each number.
- Zero (0)
- One (1)
- Two (2)
- Three (3)
- Four (4)
- Five (5)
- Six (6)
- Seven (7)
- Eight (8)
- Nine (9)
- Ten (10)
2. The term number also refers to an ordered list or number list. See our numbering definition for information about creating this type of list.
3. Number is cell format available in Microsoft Excel.
4. A number is an abbreviation often used for «phone number.»
Average, Cardinal number, Computer abbreviations, Count, Floating-point, Googolplex, Integer, Job number, Letter, Measurements, Negative Integer, No, Number format, Numbering, Number list, Number lock, Numeric, Prime number, Real number, Scientific notation, Serial number, Whole numbers