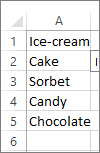Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
When you want to display a list of values that users can choose from, add a list box to your worksheet.
Add a list box to a worksheet
-
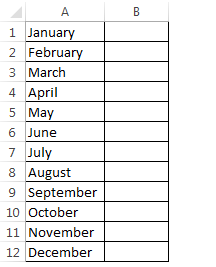
Create a list of items that you want to displayed in your list box like in this picture.
-
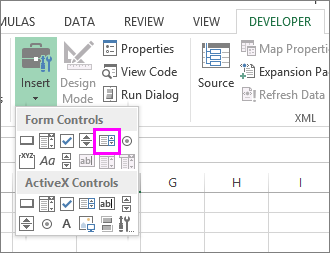
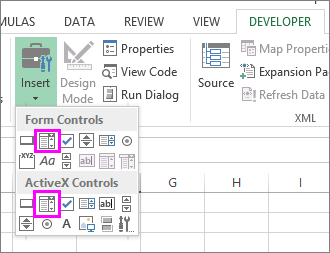
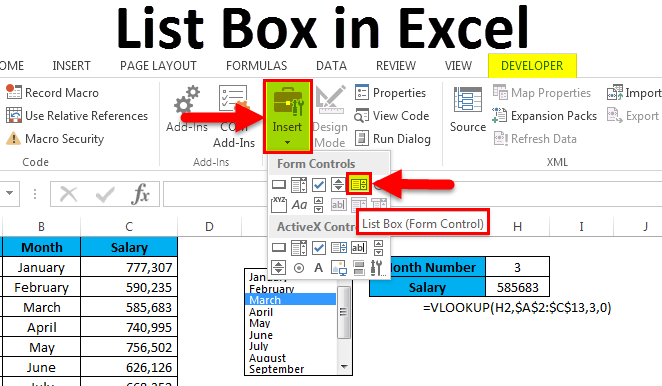
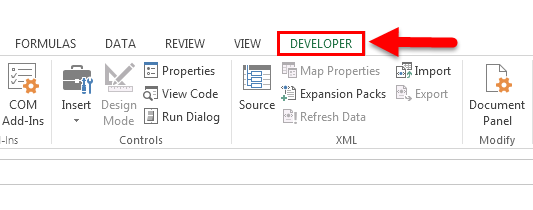
Click Developer > Insert.
Note: If the Developer tab isn’t visible, click File > Options > Customize Ribbon. In the Main Tabs list, check the Developer box, and then click OK.
-
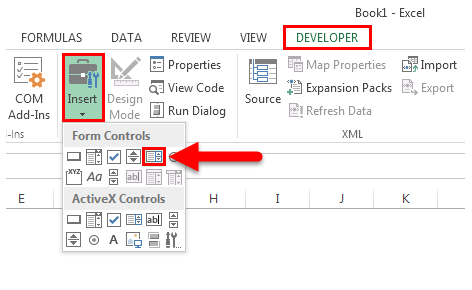
Under Form Controls, click List box (Form Control).
-
Click the cell where you want to create the list box.
-
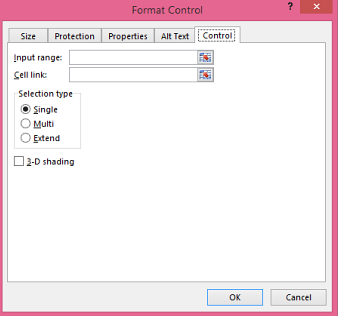
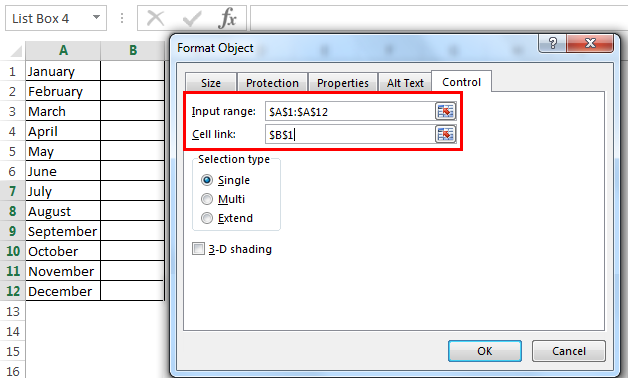
Click Properties > Control and set the required properties:
-
In the Input range box, type the range of cells containing the values list.
Note: If you want more items displayed in the list box, you can change the font size of text in the list.
-
In the Cell link box, type a cell reference.
Tip: The cell you choose will have a number associated with the item selected in your list box, and you can use that number in a formula to return the actual item from the input range.
-
Under Selection type, pick a Single and click OK.
Note: If you want to use Multi or Extend, consider using an ActiveX list box control.
-
Add a combo box to a worksheet
You can make data entry easier by letting users choose a value from a combo box. A combo box combines a text box with a list box to create a drop-down list.
You can add a Form Control or an ActiveX Control combo box. If you want to create a combo box that enables the user to edit the text in the text box, consider using the ActiveX Combo Box. The ActiveX Control combo box is more versatile because, you can change font properties to make the text easier to read on a zoomed worksheet and use programming to make it appear in cells that contain a data validation list.
-
Pick a column that you can hide on the worksheet and create a list by typing one value per cell.
Note: You can also create the list on another worksheet in the same workbook.
-
Click Developer > Insert.
Note: If the Developer tab isn’t visible, click File > Options > Customize Ribbon. In the Main Tabs list, check the Developer box, and then click OK.
-
Pick the type of combo box you want to add:
-
Under Form Controls, click Combo box (Form Control).
Or
-
Under ActiveX Controls, click Combo Box (ActiveX Control).
-
-
Click the cell where you want to add the combo box and drag to draw it.
Tips:
-
To resize the box, point to one of the resize handles, and drag the edge of the control until it reaches the height or width you want.
-
To move a combo box to another worksheet location, select the box and drag it to another location.
Format a Form Control combo box
-
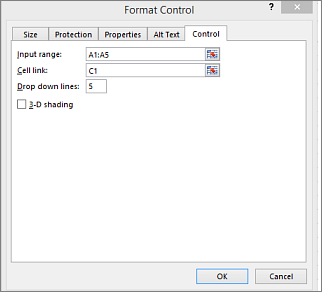
Right-click the combo box and pick Format Control.
-
Click Control and set the following options:
-
Input range: Type the range of cells containing the list of items.
-
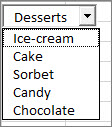
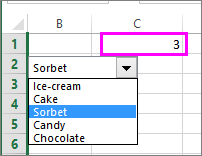
Cell link: The combo box can be linked to a cell where the item number is displayed when you select an item from the list. Type the cell number where you want the item number displayed.
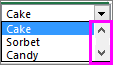
For example, cell C1 displays 3 when the item Sorbet is selected, because it’s the third item in our list.
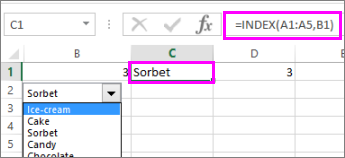
Tip: You can use the INDEX function to show an item name instead of a number. In our example, the combo box is linked to cell B1 and the cell range for the list is A1:A2. If the following formula, is typed into cell C1: =INDEX(A1:A5,B1), when we select the item «Sorbet» is displayed in C1.
-
Drop-down lines: The number of lines you want displayed when the down arrow is clicked. For example, if your list has 10 items and you don’t want to scroll you can change the default number to 10. If you type a number that’s less than the number of items in your list, a scroll bar is displayed.
-
-
Click OK.
Format an ActiveX combo box
-
Click Developer > Design Mode.
-
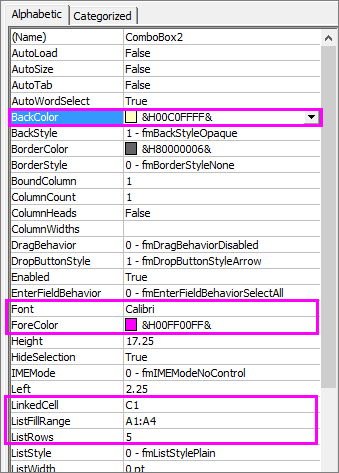
Right-click the combo box and pick Properties, click Alphabetic, and change any property setting that you want.
Here’s how to set properties for the combo box in this picture:
To set this property
Do this
Fill color
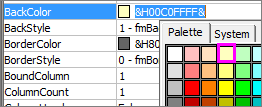
Click BackColor > the down arrow > Pallet, and then pick a color.
Font type, style or size
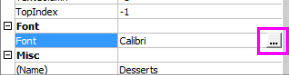
Click Font > the… button and pick font type, size, or style.
Font color
Click ForeColor > the down arrow > Pallet, and then pick a color.
Link a cell to display selected list value.
Click LinkedCell
Link Combo Box to a list
Click the box next to ListFillRange and type the cell range for the list.
Change the number of list items displayed
Click the ListRows box and type the number of items to be displayed.
-
Close the Property box and click Designer Mode.
-
After you complete the formatting, you can right-click the column that has the list and pick Hide.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Overview of forms, Form controls, and ActiveX controls on a worksheet
Add a check box or option button (Form controls)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Add a list box to a worksheet
- Create a list of items that you want to displayed in your list box like in this picture.
- Click Developer > Insert.
- Under Form Controls, click List box (Form Control).
- Click the cell where you want to create the list box.
- Click Properties > Control and set the required properties:
Contents
- 1 How do I create a fillable list in Excel?
- 2 How do I create a drop down list with multiple checkboxes in Excel?
- 3 How do I create a fill in the blank form in Excel?
- 4 Can you add checkboxes in Excel?
- 5 How do I create a list of names in Excel?
- 6 What is a list box in Excel?
- 7 How do I create a list in one cell in Excel?
- 8 How do I select multiple options in a drop-down list?
- 9 How do I create a drop-down list in Excel with multiple columns?
- 10 What is the difference between a combo box and a drop-down list?
- 11 What is VBA in Excel?
- 12 What is the blank boxes on a spreadsheet?
- 13 How do I create a fillable form?
- 14 How do I add a formula to a checkbox in Excel?
- 15 How do I link multiple checkboxes in Excel?
- 16 How do I create a custom list?
- 17 How do I create a list box?
- 18 How do I create a list box in Excel macro?
- 19 How do I create a list box in Excel VBA?
- 20 Where is the list function in Excel?
How do I create a fillable list in Excel?
1. Create Form in Excel
- STEP 1: Convert your Column names into a Table, go to Insert> Table.
- STEP 2:Let us add the Form Creation functionality to understand how to make a fillable form in Excel.
- STEP 3:Go to Customize Ribbon.
- STEP 4:Under the New Tab, select New Group, and click Add.
How do I create a drop down list with multiple checkboxes in Excel?
How to create drop down list with multiple checkboxes in Excel?
- Use List Box to create a drop down list with multiple checkboxes.
- Click Developer > Insert > List Box (Active X Control).
- Select the cell E4, enter ListBoxOutput into the Name Box and press the Enter key.
- Click Insert > Shapes > Rectangle.
How do I create a fill in the blank form in Excel?
Creating a New Entry
- Select any cell in the Excel Table.
- Click on the Form icon in the Quick Access Toolbar.
- Enter the data in the form fields.
- Hit the Enter key (or click the New button) to enter the record in the table and get a blank form for next record.
Can you add checkboxes in Excel?
To insert a checkbox in Excel, execute these steps: On the Developer tab, in the Controls group, click Insert, and select Check Box under Form Controls. To properly position the check box, hover your mouse over it and as soon as the cursor changes to a four-pointed arrow, drag the checkbox where you want it.
How do I create a list of names in Excel?
How to get a list of all names in the workbook
- Select the topmost cell of the range where you want the names to appear.
- Go to the Formulas tab > Define Names group, click Use in Formulas, and then click Paste Names… Or, simply press the F3 key.
- In the Paste Names dialog box, click Paste List.
What is a list box in Excel?
A list box is a list from where a user can select an item.For now, we will leave ListBox1 as the name of the list box. Create a Workbook Open Event. Code added to the Workbook Open Event will be executed by Excel VBA when you open the workbook.
How do I create a list in one cell in Excel?
Create a drop-down list
- In a new worksheet, type the entries you want to appear in your drop-down list.
- Select the cell in the worksheet where you want the drop-down list.
- Go to the Data tab on the Ribbon, then Data Validation.
- On the Settings tab, in the Allow box, click List.
How do I select multiple options in a drop-down list?
To select multiple options in a drop-down list, use the multiple properties. It allows you to select more than one option while pressing CTRL key.
How do I create a drop-down list in Excel with multiple columns?
In the same or in another spreadsheet, select a cell or several cells in which you want your primary drop-down list to appear. Go to the Data tab, click Data Validation and set up a drop-down list based on a named range in the usual way by selecting List under Allow and entering the range name in the Source box.
What is the difference between a combo box and a drop-down list?
A drop-down list is a list in which the selected item is always visible, and the others are visible on demand by clicking a drop-down button. A combo box is a combination of a standard list box or a drop-down list and an editable text box, thus allowing users to enter a value that isn’t in the list.
What is VBA in Excel?
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications. Excel VBA is Microsoft’s programming language for Excel.and all the other Microsoft Office programs, like Word and PowerPoint. The Office suite programs all share a common programming language.
What is the blank boxes on a spreadsheet?
The cell. An Excel worksheet is made up of columns and rows. Where these columns and rows intersect, they form little boxes called cells.
How do I create a fillable form?
How to create fillable PDF files:
- Open Acrobat: Click on the “Tools” tab and select “Prepare Form.”
- Select a file or scan a document: Acrobat will automatically analyze your document and add form fields.
- Add new form fields: Use the top toolbar and adjust the layout using tools in the right pane.
- Save your fillable PDF:
How do I add a formula to a checkbox in Excel?
Make checkbox checked based on cell value with formula
- After inserting the check box (Form Control), select it and link it to a specified cell C2 by entering =C2 into the Formula Bar.
- Select the lined cell (C2), then enter formula =IF(A2=”Test”,TRUE,FALSE) into the Formula Bar, and then press the Enter key.
How do I link multiple checkboxes in Excel?
After inserting the checkboxes in your worksheet, to select the checkbox, please press Ctrl key and then click the first checkbox that you want to link to other cell.
How do I create a custom list?
Create your own custom list. Select all of the cells in that list, and then click File > Options > Advanced. Scroll way down to the General section and click Edit Custom Lists… In the Custom Lists box, click Import.
Add a list box to a worksheet
- Create a list of items that you want to displayed in your list box like in this picture.
- Click Developer > Insert.
- Under Form Controls, click List box (Form Control).
- Click the cell where you want to create the list box.
- Click Properties > Control and set the required properties:
How do I create a list box in Excel macro?
Create a List Box on the Worksheet
- On the Excel Ribbon, click the Developer tab.
- Click Insert, then click the ListBox control tool.
- On the worksheet, draw a rectangle with the List Box tool, to create the List Box.
- With the List Box selected on teh worksheet, click the Properties command on the Ribbon’s Developer tab.
How do I create a list box in Excel VBA?
How to Create List Box in Excel?
- Step 1: Go to Developer Tab.
- Step 2: After selecting the list box, draw the list box in the excel sheet.
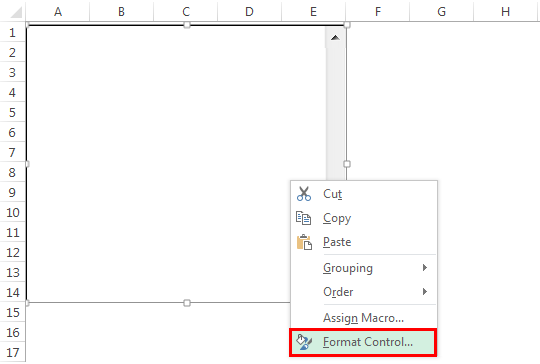
- Step 3: Right-click on the inserted list box and select Format Control.
- Step 4: Under Format Control, go to Control.
- Step 5: We will have a list of the month in the list box.
Where is the list function in Excel?
Click somewhere inside the data area and choose Data > List > Create List. Excel makes a guess as to the range containing the data and gives you the option of specifying whether or not your list has headers.
The list box in Excel (Table of Contents)
- List box in Excel
- How to Create List box in Excel?
- Examples of the List box in Excel
List Box in Excel
List Box in excel is used to create a list inside the box and choose them just we select the values from dropdown. List boxes are available in the Insert option in the Developer menu tab. We can use List boxes with VBA macro and also excel cells. Whatever values we select can be seen in the list box, and once we select any value that will be reflected, the cell linked to List Box.
List Box is located under Developer Tab in Excel. If you are not a VBA macro user, you may not see this DEVELOPER tab in your excel.
Follow the below steps to unleash the Developer Tab.
If the Developer tab is not showing, then follow the below steps to enable the Developer tab.
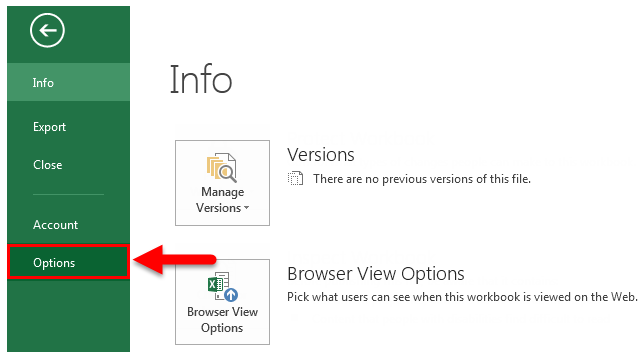
- Go to the FILE option (top of the left-hand side of the excel).
- Now go to Options.
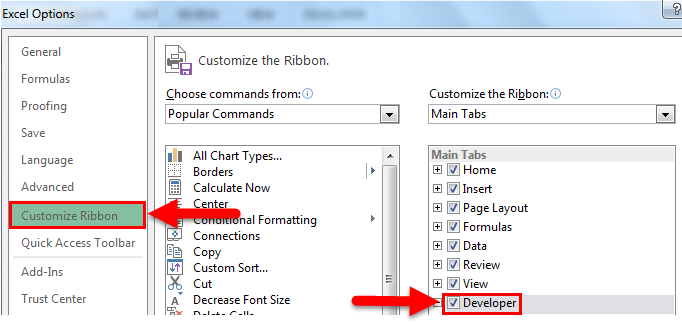
- Go to Custom Ribbon and click on the Developer tab check-box.
- Once the Developer Tab is enabled, you can see it on your excel ribbon.
How to Create List box in Excel?
Follow the below steps to insert the List box in excel.
You can download this List Box Excel Template here – List Box Excel Template
Step 1: Go to Developer Tab > Controls > Insert > Form Controls > List Box.
Step 2: Click on List Box and draw in the worksheet; then Right-click on the List Box and select the option Format Control.
Step 3: Create a month list in column A from A1 to A12.
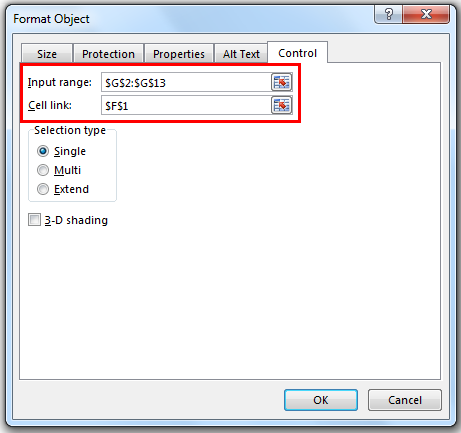
Step 4: Once you have selected Format Control, it will open the below dialog box; go to the Control tab in the input range select the month lists from A1 to A10. In the cell link, give a link to cell B1.
We have linked our cell to B1. Once the first value has selected the cell B1 will show 1. Similarly, if you select April, it will show 4 in cell B1.
Examples of List Box in Excel
Let’s look at a few examples of using Lise Box in Excel.
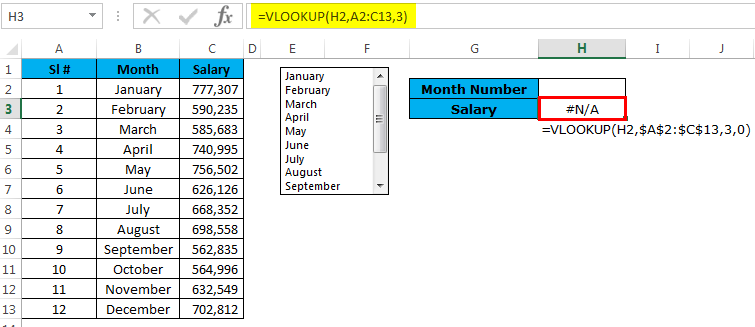
Example #1 – List Box with Vlookup Formula
Now we will look at the way of using List Box in excel.
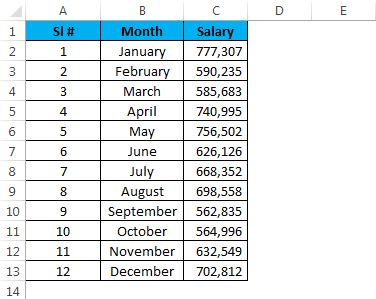
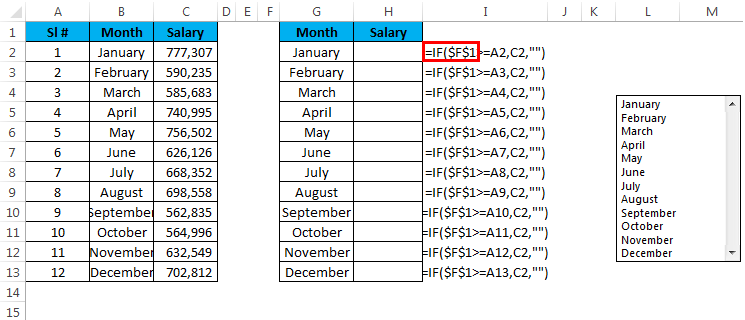
Assume you have salary data month-wise from A2 to A13. Based on the selection made from the list, it has to show the value for the selected month.
Step 1: Draw a List Box from the developer tab and create a list of months.
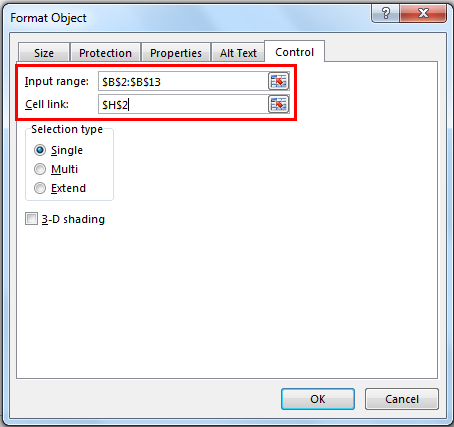
Step 2: I have given a cell link to H2. In G2 and G3, create a list like this.
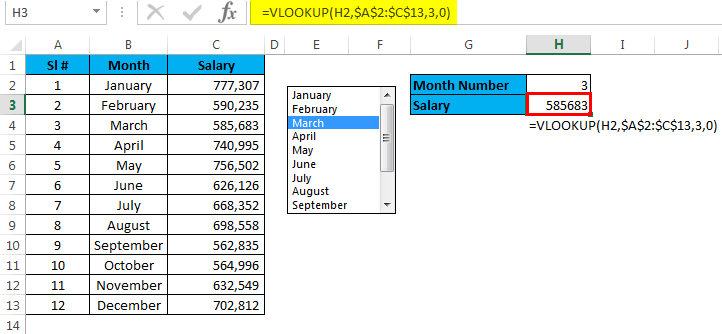
Step 3: Apply the VLOOKUP formula in cell H3 to get the salary data from the list.
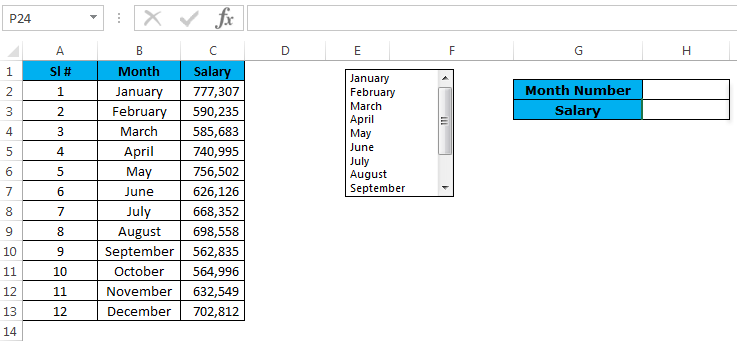
Step 4: Right now, it is showing an error as #N/A. Please select any of the months; it will show you the salary data for that month.
I have selected March month, and the number for March month is 3 and VLOOKUP showing the value for number 3 from the table.
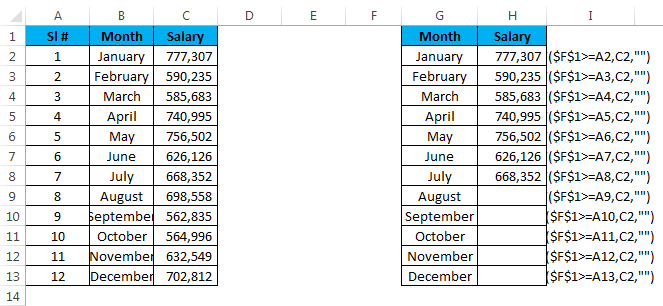
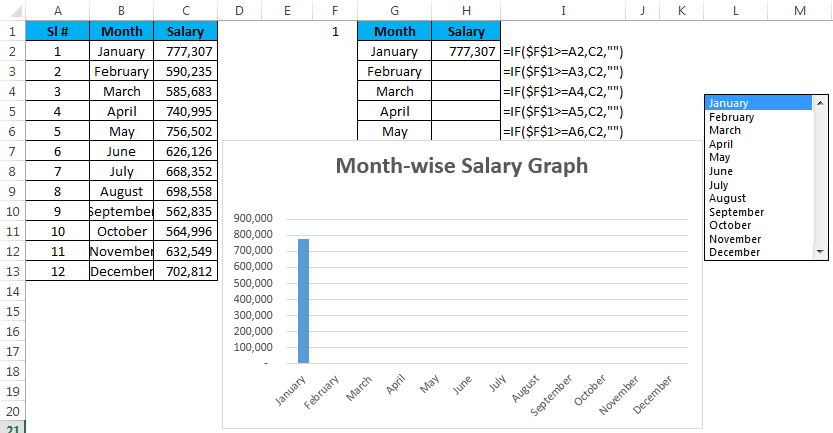
Example #2 – Custom Chart with List Box
In this example, I will explain how to create the custom chart using List Box. I will take the same example that I have used previously.
Step 1: Create a table like this.
Step 2: Insert List Box from the Developer tab. Go to Format Control give a link to the month list and a cell link to F1.
Step 3: Apply the IF formula in the newly created table.
I have applied the IF condition to the table. If I select the month March, the value in cell F1 will show the number 3 because March is the third value in the list. Similarly, it will show 4 for April, 10 for October and 12 for December.
IF condition checks if the value in the cell F1 is greater than equal to 4, it will show for the value for the first 4 months. If the value in cell F1 is greater than equal to 6, it will show the value for the first 6 months only.
Step 4: Now apply the chart for the modified table with the IF condition.
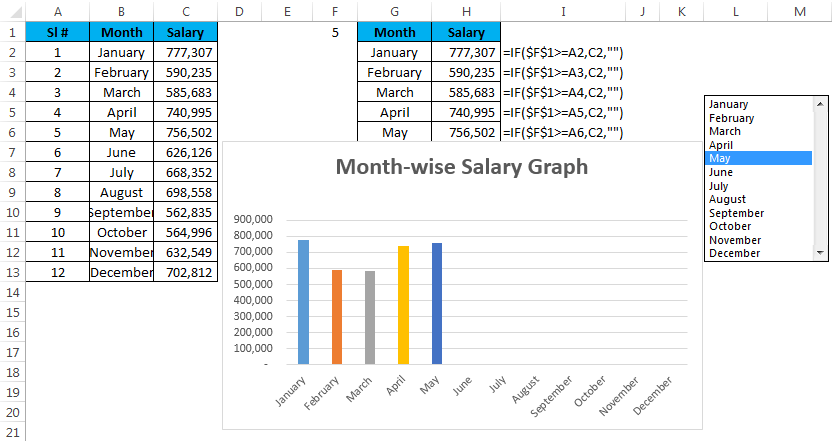
Step 5: Now it is showing the empty graph. Select the month to see the magic. I have selected the month of May, which is why it shows the graph for the first 5 months.
Things to Remember
- There is one more List Box under Active X Control in excel. This has mainly used in VBA macros.
- Cell link is to indicate which item from the list has selected.
- We can control the user to enter the data by using List Box.
- We can avoid wrong data entry by using List Box.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the List box in Excel. Here we discuss the List box in Excel and How to create the List box in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Name Box in Excel
- Excel Search Box
- CheckBox in Excel
- Compare Two Lists in Excel
Элемент управления пользовательской формы ListBox для выбора и ввода информации в VBA Excel. Свойства списка, его заполнение, извлечение данных, примеры кода.
UserForm.ListBox – это элемент управления пользовательской формы, предназначенный для передачи в код VBA информации, выбранной пользователем из одностолбцового или многостолбцового списка.
Список используется в тех случаях, когда необходимо добавить в форму информацию, которая заранее известна, а ее отдельные позиции можно сгруппировать в список. Элемент управления ListBox оправдывает себя при небольших списках, так как большой список будет занимать много места на форме.
Использование полос прокрутки уменьшает преимущество ListBox перед элементом управления ComboBox, которое заключается в том, что при открытии формы все позиции для выбора на виду без дополнительных действий со стороны пользователя. При выборе информации из большого списка удобнее использовать ComboBox.
Элемент управления ListBox позволяет выбрать несколько позиций из списка, но эта возможность не имеет практического смысла. Ввести информацию в ListBox с помощью клавиатуры или вставить из буфера обмена невозможно.
Свойства списка
| Свойство | Описание |
|---|---|
| ColumnCount | Указывает количество столбцов в списке. Значение по умолчанию = 1. |
| ColumnHeads | Добавляет строку заголовков в ListBox. True – заголовки столбцов включены, False – заголовки столбцов выключены. Значение по умолчанию = False. |
| ColumnWidths | Ширина столбцов. Значения для нескольких столбцов указываются в одну строку через точку с запятой (;). |
| ControlSource | Ссылка на ячейку для ее привязки к элементу управления ListBox. |
| ControlTipText | Текст всплывающей подсказки при наведении курсора на ListBox. |
| Enabled | Возможность выбора элементов списка. True – выбор включен, False – выключен*. Значение по умолчанию = True. |
| Font | Шрифт, начертание и размер текста в списке. |
| Height | Высота элемента управления ListBox. |
| Left | Расстояние от левого края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до левого края элемента управления ListBox. |
| List | Позволяет заполнить список данными из одномерного или двухмерного массива, а также обращаться к отдельным элементам списка по индексам для записи и чтения. |
| ListIndex | Номер выбранной пользователем строки. Нумерация начинается с нуля. Если ничего не выбрано, ListIndex = -1. |
| Locked | Запрет возможности выбора элементов списка. True – выбор запрещен**, False – выбор разрешен. Значение по умолчанию = False. |
| MultiSelect*** | Определяет возможность однострочного или многострочного выбора. 0 (fmMultiSelectSingle) – однострочный выбор, 1 (fmMultiSelectMulti) и 2 (fmMultiSelectExtended) – многострочный выбор. |
| RowSource | Источник строк для элемента управления ListBox (адрес диапазона на рабочем листе Excel). |
| TabIndex | Целое число, определяющее позицию элемента управления в очереди на получение фокуса при табуляции. Отсчет начинается с 0. |
| Text | Текстовое содержимое выбранной строки списка (из первого столбца при ColumnCount > 1). Тип данных String, значение по умолчанию = пустая строка. |
| TextAlign | Выравнивание текста: 1 (fmTextAlignLeft) – по левому краю, 2 (fmTextAlignCenter) – по центру, 3 (fmTextAlignRight) – по правому краю. |
| Top | Расстояние от верхнего края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до верхнего края элемента управления ListBox. |
| Value | Значение выбранной строки списка (из первого столбца при ColumnCount > 1). Value – свойство списка по умолчанию. Тип данных Variant, значение по умолчанию = Null. |
| Visible | Видимость списка. True – ListBox отображается на пользовательской форме, False – ListBox скрыт. |
| Width | Ширина элемента управления. |
* При Enabled в значении False возможен только вывод информации в список для просмотра.
** Для элемента управления ListBox действие свойства Locked в значении True аналогично действию свойства Enabled в значении False.
*** Если включен многострочный выбор, свойства Text и Value всегда возвращают значения по умолчанию (пустая строка и Null).
В таблице перечислены только основные, часто используемые свойства списка. Еще больше доступных свойств отображено в окне Properties элемента управления ListBox, а все методы, события и свойства – в окне Object Browser.
Вызывается Object Browser нажатием клавиши «F2». Слева выберите объект ListBox, а справа смотрите его методы, события и свойства.
Свойства BackColor, BorderColor, BorderStyle отвечают за внешнее оформление списка и его границ. Попробуйте выбирать доступные значения этих свойств в окне Properties, наблюдая за изменениями внешнего вида элемента управления ListBox на проекте пользовательской формы.
Способы заполнения ListBox
Используйте метод AddItem для загрузки элементов в список по одному:
|
With UserForm1.ListBox1 .AddItem «Значение 1» .AddItem «Значение 2» .AddItem «Значение 3» End With |
Используйте свойство List, чтобы скопировать одномерный массив значений в элемент управления ListBox.
|
UserForm1.ListBox1.List = Array(«Текст 1», _ «Текст 2», «Текст 3», «Текст 4», «Текст 5») |
Вместо функции Array можно использовать переменные одномерных и двухмерных массивов. При загрузке значений из двухмерного массива, требуется предварительно указать количество столбцов в списке.
Используйте свойство RowSource, чтобы загрузить в список значения из диапазона ячеек рабочего листа:
|
UserForm1.ListBox1.RowSource = «Лист1!A1:A6» |
При загрузке данных из диапазона, содержащего более одного столбца, требуется предварительно указать количество столбцов в списке:
|
With UserForm1.ListBox1 ‘Указываем количество столбцов .ColumnCount = 5 .RowSource = «‘Лист со списком’!A1:E10» End With |
В качестве имени листа используется имя ярлыка. Если имя листа содержит пробелы, оно заключается в одинарные кавычки.
Подробнее о заполнении элемента управления ListBox вы можете ознакомиться в отдельной статье с наглядными примерами.
Привязка списка к ячейке
Для привязки списка к ячейке на рабочем листе используется свойство ControlSource. Суть привязки заключается в том, что при выборе строки в элементе управления, значение свойства Value копируется в привязанную ячейку.
Если привязанная к списку ячейка содержит значение одной из строк элемента управления ListBox, то при запуске пользовательской формы список откроется с выделенной строкой, содержащей это значение. Если привязанная ячейка при загрузке формы пустая, то список откроется без выделения какой-либо строки.
В случае, когда при открытии формы в привязанной к списку ячейке содержится значение, которого нет ни в одной из строк элемента управления ListBox, будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Привязать ячейку к списку можно, указав адрес ячейки в поле свойства ControlSource в окне Properties элемента управления ListBox. Или присвоить адрес ячейки свойству ControlSource в коде VBA Excel:
|
UserForm1.ListBox1.ControlSource = «Лист1!A2» |
Теперь значение выбранной строки в списке автоматически копируется в ячейку «A2» на листе «Лист1»:
В окне Properties адрес указывается без двойных кавычек. Если имя листа содержит пробелы, оно заключается в одинарные кавычки.
Извлечение информации из списка
Первоначально элемент управления ListBox открывается со строками, ни одна из которых не выбрана. При выборе (выделении) строки, ее значение записывается в свойства Value и Text.
Из этих свойств мы с помощью кода VBA Excel извлекаем информацию, выбранную в списке пользователем:
|
Dim myVar as Variant, myTxt As String myVar = UserForm1.ListBox1.Value ‘или myTxt = UserForm1.ListBox1.Text |
Вторую строку кода можно записать myVar = UserForm1.ListBox1, так как Value является свойством списка по умолчанию.
Если ни одна позиция в списке не выбрана, свойство Value возвращает значение Null, а свойство Text – пустую строку. Если выбрана строка в многостолбцовом списке, в свойства Value и Text будет записана информация из первого столбца.
Что делать, если понадобятся данные из других столбцов многостолбцового списка, кроме первого?
Для получения данных из любого столбца элемента управления ListBox используется свойство List, а для определения выбранной пользователем строки – ListIndex.
Для тестирования приведенного ниже кода скопируйте таблицу и вставьте ее в диапазон «A1:D4» на листе с ярлыком «Лист1»:
| Звери | Лев | Тапир | Вивера |
| Птицы | Грач | Сорока | Филин |
| Рыбы | Карась | Налим | Парусник |
| Насекомые | Оса | Жук | Муравей |
Создайте в редакторе VBA Excel пользовательскую форму и добавьте на нее список с именем ListBox1. Откройте модуль формы и вставьте в него следующие процедуры:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() With Me.ListBox1 ‘Указываем, что у нас 4 столбца .ColumnCount = 4 ‘Задаем размеры столбцов .ColumnWidths = «50;50;50;50» ‘Импортируем данные .RowSource = «Лист1!A1:D4» ‘Привязываем список к ячейке «F1» .ControlSource = «F1» End With End Sub Private Sub UserForm_Click() MsgBox Me.ListBox1.List(Me.ListBox1.ListIndex, 2) End Sub |
В процедуре UserForm_Initialize() присваиваем значения некоторым свойствам элемента управления ListBox1 перед открытием пользовательской формы. Процедура UserForm_Click() при однократном клике по форме выводит в MsgBox значение из третьего столбца выделенной пользователем строки.
Теперь при выборе строки в списке, значение свойства Value будет записываться в ячейку «F1», а при клике по форме функция MsgBox выведет значение третьего столбца выделенной строки.
Обратите внимание, что при первом запуске формы, когда ячейка «F1» пуста и ни одна строка в ListBox не выбрана, клик по форме приведет к ошибке. Это произойдет из-за того, что свойство ListIndex возвратит значение -1, а это недопустимый номер строки для свойства List.
Если для списка разрешен многострочный выбор (MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti или MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectExtended), тогда, независимо от количества выбранных строк, свойство Value будет возвращать значение Null, а свойство Text – пустую строку. Свойство ListIndex будет возвращать номер строки, которую кликнули последней, независимо от того, что это было – выбор или отмена выбора.
Иногда перед загрузкой в ListBox требуется отобрать уникальные элементы из имеющегося списка. Смотрите, как это сделать с помощью объектов Collection и Dictionary.
The VBA ListBox is a very useful control. If you are creating any kind of UserForm application you will most likely use it.
In this post, I’m going to show you everything you need to know about the VBA ListBox so you can avoid the common pitfalls and get up and running quickly and easily.
What is the VBA ListBox used for?
The ListBox is used to display a list of items to the user so that the user can then select one or more. The ListBox can have multiple columns and so it is useful for tasks like displaying records.
VBA ListBox versus the VBA ComboBox
The ListBox is very similar to the ComboBox which also allows the user to select an item from a list of items. The main differences are:
- The Listbox allows multiple selections. The Combobox only allows one selection.
- Items in the ListBox are always visible. The Combobox items are only visible when you click on the “down” icon.
- The ComboBox has the ability to filter the contents when you type.
The VBA ListBox Properties Quick Guide
| Function | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| AddItem | Add an item | listbox.AddItem «Spain» |
| Clear | Remove all Items | listbox.Clear |
| ColumnCount | Set the number of visible columns | ComboBox1.ColumnCount = 2 |
| ColumnHeads | Make the column row visible | ComboBox1.ColumnHeads = True |
| List | Range to Listbox ListBox to Range |
Listbox.List = Range(«A1:A4»).Value Range(«A1:A4»).Value = Listbox.List |
| List | Update a column value | Listbox.List(1,2) = «New value» |
| ListCount | Get the number of items | cnt = listbox.ListCount |
| ListIndex | Get/set selected item | Idx = listbox.ListIndex combo.ListIndex = 0 |
| RemoveItem | Remove an item | listbox.Remove 1 |
| RowSource | Add a range of values from a worksheet | ComboBox1.RowSource = Sheet1.Range(«A2:B3»).Address |
| Value | Get the value of selected Item | Dim sCountry As String sCountry = listbox.Value |
How to Add Items to the ListBox
There are 3 ways to add items to the VBA Listbox:
- One at a time using the AddItem property.
- Adding an array/range using the List property.
- Adding a Range using the RowSource property.
The List and RowSource properties are the most commonly used. The table below provides a quick comparison of these properties:
| Task | RowSource | List |
|---|---|---|
| Column Headers | Yes | No |
| Update values in ListBox | No | Yes |
| Add new items | No | Yes |
| Data type | Range | Array(including Range.Value) |
| If source data changes | Listbox is automatically updated. | ListBox is not updated. |
VBA ListBox List Property
The List property allows you to add to contents of an array to a ListBox. As Range.Value is an array you can copy the contents of any range to the Listbox.
Here are some examples of using the List property:
' Add the contents of an array ListBox1.List = Array("Apple", "Orange", "Banana") ' Add the contents of a Range ListBox1.List = Range("A1:E5").Value
You can also use the List property to write from the ListBox to an array or range:
Range("A1:B3").Value = ListBox1.List
Important Note: If there is only one item in a range then VBA doesn’t covert it to an array. Instead, it converts the range to a string/double/date etc.
Sheet1.Range("A1:A2").Value ' Array Sheet1.Range("A1").Value ' Single value variable
In this case, you need to use AddItem to add the value to the ListBox:
If myRange.Count = 1 Then ListBox1.AddItem myRange Else ListBox1.List = myRange.Value End If
The List Property and Column Headers
The ListBox only displays column headers if you use RowSource. Otherwise, they are not available. The best way to add column headers(and it’s not a great way) is to add Labels above the ListBox columns. One advantage is that you can use the click event of the Label if you want to implement something like sorting.
Updating Items using the List Property
You can update individual items in the ListBox using the List Property.
Imagine we have a ListBox with data like this:
If we want to change Nelson in row 3, column 2 we do it like this:
ListBox1.List(2, 1) = "SMITH"
The result we get is:
The List property rows and columns are zero-based so this means row 1 is 0, row 2 is 1, row 3 is 2 and so on:
VBA ListBox RowSource
The RowSource property allows us to add a range to the ListBox. This is different from the List Property in that the Range is linked to the ListBox. If data in the Range changes then the data in the ListBox will update automatically.
When we use RowSource the data in the ListBox is read-only. We can change the RowSource range but we cannot change the values in the ListBox.
How to use RowSource
We add the RowSource range as a string like this:
ListBox1.RowSource = "Sheet1!A1:A5"
If you don’t specify the sheet the VBA will use the active sheet
ListBox1.RowSource = "A1:A5"
If you are using the Address of a range object with RowSource then it is important to use the External parameter. This will ensure that RowSource will read from the sheet of the range rather than the active sheet:
' Get the range Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A1:A5") ' Address will be $A$1:$A$5 which will use the active sheet ListBox1.RowSource = rg.Address Debug.Print ListBox1.RowSource ' Address will be [Book2]Sheet1!$A$1:$A$5 which will use Sheet1 ListBox1.RowSource = rg.Address(External:=True) Debug.Print ListBox1.RowSource
RowSource Column Headers
Column headers are automatically added to the ListBox when you use the RowSource property. The ColumnHeads property must be set to True or the headers will not appear. You can set this property in the code or in the properties window of the ListBox.
ListBox1.ColumnHeads = True
The column headers are taken from the row above the range used for the RowSource. For example, if your range is A2 to C5 then the column header will use the range A1 to C1:
Here is an example: We want to add the data below to our ListBox and we want A1 to C1 to be the header.
We set the RowSource property to A2:C5 and set the ColumnHeads property to true:
With ListBox1 .RowSource = "sheet1!A2:C5" .ColumnHeads = True .ColumnWidths = "80;80;80" End With
The result will look like this:
VBA ListBox AddItem
It is very rare that you would use the AddItem property to fill the ListBox. List and RowSource are much more efficient. AddItem is normally used when the Listbox already has items and you want to add a new item.
The AddItem property is simple to use. You provide the item you want to add as a parameter. The ListBox will automatically add it as the last item:
With ListBox .AddItem "Apple" .AddItem "Orange" End With
If you want to Insert the item at a certain position you can use the second parameter. Keep in mind that this is a zero-based position, so if you want the item in position one then the value is 0, position 2 the value is 1, and so on.
With ListBox1 .AddItem "Apple" .AddItem "Orange" ' Add "Banana" to position 1(Index 0) .AddItem "Banana", 0 End With
The order will be:
Banana
Apple
Orange
If you want to add multiple columns with AddItem then you need to use the List property after you use AddItem:
With listboxFruit .List = myRange.Value .AddItem "Banana" ' Add to the second column of 'Banana' row .List(2, 1) = "$2.99" End With
One reason for using AddItem is if you are adding from data that isn’t sequential so you cannot use the List or RowSource properties:
Dim cell As Range ' Fill items with first letter is A For Each cell In Sheet1.Range("A1:A50") If Left(cell.Value, 1) = "A" Then comboBoxFruit.AddItem cell.Value End If Next
Important Note: If you fill a ListBox with RowSource then you cannot use AddItem to add a new item. If you try you will get a “Runtime Error 70 – Permission Denied”.
VBA ListBox Selected Items
If only one item is selected then you can use ListIndex to get the selected row. Remember that it is zero-based so row 1 in the ListBox is at ListIndex 0, row 2 at ListIndex 1 and so on.
MsgBox "The selected item is " & ListBox1.ListIndex
If the ListBox has multiple columns then you can use the ListIndex and List properties together to return a value in the selected row:
' Display the value from the second column of the selected row
MsgBox ListBox1.List(ListBox1.ListIndex, 2)
If multiple items are selected then you can use the GetSelectedRows function which returns a collection of selected rows:
Sub Example() ' Store the row numbers of selected items to a collection Dim selectedRows As Collection Set selectedRows = GetSelectedRows() ' Print the selected rows numbers to the Immediate Window Dim row As Long For Each row In selectedRows ' Print to the Immediate Window Ctrl + G Debug.Print row Next row End Sub ' Returns a collection of all the selected items Function GetSelectedRows() As Collection ' Create the collection Dim coll As New Collection ' Read through each item in the listbox Dim i As Long For i = 0 To listboxFruit.ListCount - 1 ' Check if item at position i is selected If listboxFruit.Selected(i) Then coll.Add i End If Next i Set GetSelectedRows = coll End Function
Reading Data from the VBA Listbox
To read data from the ListBox we can use the ListBox.Value property. This only works when the ListBox is set to only select one item i.e. MultiSelect is set to frmMultiSelectSingle(see the section VBA ListBox MultiSelect below for more about this).
Single selection only with one column
When only one item is selected we can use the Value property to get the currently selected item:
Dim fruit As String fruit = ListBox1.Value
Keep in mind that if there are multiple columns, Value will only return the value in the first column.
Single selection only with multiple columns
If the ListBox has Multiple columns you can use the Value property to get the value in the first column. You need to read through the List property to get the values in the other column(s). The List property is essentially an array so you can treat it like one.
In the example below we read through the columns of row 1(the index of row 1 is 0):
With ListBox1 For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(.List, 2) ' Print the columns of the first row to the Immediate Window Debug.Print .List(0, j) Next j End With
Normally you want to print the values in the selected row. You can use the ListIndex property to get the selected item(Note that ListIndex returns the last selected items so it won’t work where there are multiple items selected):
' ExcelMacroMastery.com
Sub ReadValuesFromSelectedRow()
' Write contents of the row to the Immediate Window(Ctrl G)
With ListBox1
For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(.List, 2)
' Print the columns of the selected row to the Immediate Window
Debug.Print .List(.ListIndex, j) Next j
End With
End Sub
Multiple selections
If the ListBox has multiple selections and you want to get all the data from each then you can use the GetSelectedRows() sub from the section VBA ListBox Selected Items. This will get a collection of all selected rows. You can use this to print the data from the selected rows:
Sub PrintMultiSelectedRows() ' Get all the selected rows Dim selectedRows As Collection Set selectedRows = GetSelectedRows(Me.ListBox1) Dim i As Long, j As Long, currentRow As Long ' Read through the selected rows For i = 1 To selectedRows.Count With ListBox1 ' Get the current row currentRow = selectedRows(i) ' Print row header Debug.Print vbNewLine & "Row : " & currentRow ' Read items in the current row For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(ListBox1.List, 2) ' Print the columns of the first row to the Immediate Window Debug.Print .List(currentRow, j) Next j End With Next i End Sub Function GetSelectedRows(currentListbox As MSForms.ListBox) As Collection ' Create the collection Dim coll As New Collection ' Read through each item in the listbox Dim i As Long For i = 0 To currentListbox.ListCount - 1 ' Check if item at position i is selected If currentListbox.Selected(i) Then coll.Add i End If Next i Set GetSelectedRows = coll End Function
VBA ListBox MultiSelect
We can use the MultiSelect property of the ListBox to allow the user to select either a single item or multiple items:
There are 3 selections:
- 0 = frmMultiSelectSingle – [Default]Multiple selection isn’t allowed.
- 1 = frmMultiSelectMulti – Multiple items are selected or deselected by choosing them with the mouse or by pressing the Spacebar.
- 2 = frmMultiSelectExtended – Multiple items are selected by holding down Shift and choosing them with the mouse, or by holding down Shift and pressing an arrow key to extend the selection from the previously selected item to the current item. You can also select items by dragging with the mouse. Holding down Ctrl and choosing an item selects or deselects that item.
VBA ListBox Columns
You can have multiple columns in a ListBox. For example, you can load a Range or two-dimensional array to a ListBox using List or RowSource.
Often when you load data with multiple columns only one column appears. This can be very confusing when you are using the Listbox. To get the columns to appear you have to set the ColumnCount property to the number of Columns.
You should also make sure that the ColumnWidths property is correct or one of the columns may not appear.
You can do it like this:
With listboxFruit .RowSource = "Sheet1!A2:B4" .ColumnCount = 2 .ColumnWidths = "100,100" End With
In a real-world application, you could set the RowSource and ColumnCount properties like this:
With listboxFruit .RowSource = myRange.Address(External:=True) .ColumnCount = myRange.Columns.Count End With
See the AddItem section for how to add data to the other columns when you are using the AddItem property.
VBA ListBox Column Headers
Column Headers are another confusing element of the ListBox. If you use the RowSource property to add data to the ListBox then the line above the Range will be automatically used as the header.
For the Column headers to appear the ColumnHeads property must be set to true. You can do this in the properties window of the ListBox or in the code list this:
ListBox1.ColumnHeads = True
If you use the List or AddItem property to fill the ListBox then the column headers are not available. The best solution, albeit a frustrating one, is to use labels above the ListBox. I know it sounds crazy but that unfortunately is the reality. The one advantage is that you can use the Label click event which is useful if you plan to sort the data by a column.
Creating a ListBox Dynamically
Controls are normally created at design time but you can also create them dynamically at run time:
Dim myListbox As MSForms.ListBox
Set myListbox = Controls.Add("Forms.ListBox.1")
If you want to add an event to a dynamic control you can do it like this:
- First of all create a Class like this:
Public WithEvents myListBox As MSForms.ListBox Private Sub myListBox_Change() MsgBox "Selection changed" End Sub
- Name the class clsListBoxEvents. Create a variable of this class object in the UserForm like this:
Private listBoxEvents As New clsListBoxEvents
- Attach the events to the ListBox:
Sub CreateDynamicListBox() ' Create the ListBox Dim newListBox As MSForms.ListBox Set newListBox = Controls.Add("Forms.ListBox.1") ' Add some items newListBox.List = Array("Apple", "Orange", "Pear") ' Connect the ListBox to the ListBox events class Set listBoxEvents.myListBox = newListBox End Sub
Note that you can attach events to any ListBox. It doesn’t have to be created dynamically to do this.
Loop through ListBoxes
If you want to loop through all the ListBoxes on a UserForm you can do it like this:
Dim ctrl As Variant For Each ctrl In Me.Controls If TypeName(ctrl) = "ListBox" Then Debug.Print ctrl.Name End If Next ctrl
YouTube Video
Check out this video where I use the ListBox. The source code for the video is available from here
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out this Free VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)