From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the grammatical use. For the typographical sense, see Homoglyph. For the geometrical sense, see Homography.
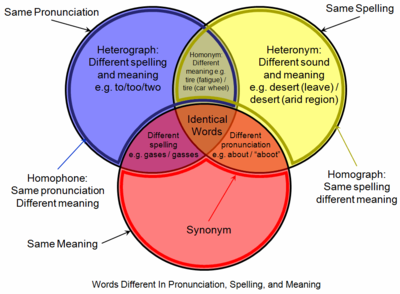
Venn diagram showing the relationships between homographs (yellow) and related linguistic concepts
A homograph (from the Greek: ὁμός, homós, «same» and γράφω, gráphō, «write») is a word that shares the same written form as another word but has a different meaning.[1] However, some dictionaries insist that the words must also be pronounced differently,[2] while the Oxford English Dictionary says that the words should also be of «different origin».[3] In this vein, The Oxford Guide to Practical Lexicography lists various types of homographs, including those in which the words are discriminated by being in a different word class, such as hit, the verb to strike, and hit, the noun a blow.[4]
If, when spoken, the meanings may be distinguished by different pronunciations, the words are also heteronyms. Words with the same writing and pronunciation (i.e. are both homographs and homophones) are considered homonyms. However, in a broader sense the term «homonym» may be applied to words with the same writing or pronunciation. Homograph disambiguation is critically important in speech synthesis, natural language processing and other fields. Identically written different senses of what is judged to be fundamentally the same word are called polysemes; for example, wood (substance) and wood (area covered with trees).
In English[edit]
Examples:
- sow (verb) – to plant seed
- sow (noun) – female pig
where the two words are spelt identically but pronounced differently. Here confusion is not possible in spoken language but could occur in written language.
- bear (verb) – to support or carry
- bear (noun) – the animal
where the words are identical in spelling and pronunciation (), but differ in meaning and grammatical function. These are called homonyms.
More examples[edit]
| Word | Example of first meaning | Example of second meaning |
|---|---|---|
| lead | Gold is heavier than lead . | The mother duck will lead her ducklings around. |
| close | «Will you please close that door!» | The tiger was now so close that I could smell it… |
| wind | The wind howled through the woodlands. | Wind your watch. |
| minute | I will be there in a minute . | That is a very minute amount. |
In Chinese[edit]
Many Chinese varieties have homographs, called 多音字 (pinyin: duōyīnzì) or 重形字 (pinyin: chóngxíngzì), 破音字 (pinyin: pòyīnzì).
Old Chinese[edit]
Modern study of Old Chinese has found patterns that suggest a system of affixes.[5] One pattern is the addition of the prefix /*ɦ/, which turns transitive verbs into intransitive or passives in some cases:[6]
| Word | Pronunciationa | Meaninga | Pronunciationb | Meaningb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 見[7] | *kens | see | *ɦkens | appear |
| 敗[8] | *prats | defeat | *ɦprats | be defeated |
| All data from Baxter, 1992.[6] |
Another pattern is the use of a /*s/ suffix, which seems to create nouns from verbs or verbs from nouns:[6]
| Word | Pronunciationa | Meaninga | Pronunciationb | Meaningb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 傳 | *dron | transmit | *drons | (n.) record |
| 磨 | *maj | grind | *majs | grindstone |
| 塞 | *sɨk | (v.) block | *sɨks | border, frontier |
| 衣 | *ʔjɨj | clothing | *ʔjɨjs | wear, clothe |
| 王 | *wjaŋ | king | *wjaŋs | be king |
| All data from Baxter, 1992.[6] |
Middle Chinese[edit]
Many homographs in Old Chinese also exist in Middle Chinese. Examples of homographs in Middle Chinese are:
| Word | Pronunciationa | Meaninga | Pronunciationb | Meaningb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易 | /jĭe꜄/ | easy | /jĭɛk꜆/ | (v.) change |
| 別 | /bĭɛt꜆/ | (v.) part | /pĭɛt꜆/ | differentiate, other |
| 上 | /꜂ʑĭaŋ/ | rise, give | /ʑĭaŋ꜄/ | above, top, emperor |
| 長 | /꜀dʲʱĭaŋ/ | long | /꜂tʲĭaŋ/ | lengthen, elder |
| Reconstructed phonology from Wang Li on the tables in the article Middle Chinese. Tone names in terms of level (꜀平), rising (꜂上), departing (去꜄), and entering (入꜆) are given. All meanings and their respective pronunciations from Wang et al., 2000.[9] |
Modern Chinese[edit]
Many homographs in Old Chinese and Middle Chinese also exist in modern Chinese varieties. Homographs which did not exist in Old Chinese or Middle Chinese often come into existence due to differences between literary and colloquial readings of Chinese characters. Other homographs may have been created due to merging two different characters into the same glyph during script reform (See Simplified Chinese characters and Shinjitai).
Some examples of homographs in Cantonese from Middle Chinese are:
| Word | Pronunciationa | Meaninga | Pronunciationb | Meaningb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易 | [jiː˨] | easy | [jɪk˨] | (v.) change |
| 上 | [ɕœːŋ˩˧] | rise, give | [ɕœːŋ˨] | above, top, emperor |
| 長 | [tɕʰœːŋ˨˩] | long | [tɕœːŋ˧˥] | lengthen, elder |
See also[edit]
- Synonym
- Interlingual homograph
- IDN homograph attack
- Syncretism (linguistics)
- False friend
References[edit]
- ^
«One of two or more words that have the same spelling but differ in origin, meaning, and sometimes pronunciation, such as fair (pleasing in appearance) and fair (market) or wind (wĭnd) and wind (wīnd)».
- ^ Homophones and Homographs: An American Dictionary, 4th ed., McFarland, 2006, p. 3.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary: homograph.
- ^ Atkins, BTS.; Rundell, M., The Oxford Guide to Practical Lexicography, OUP Oxford, 2008,
pp. 192 — 193. - ^ Norman, Jerry (1988). Chinese. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-521-22809-1.
- ^ a b c d Baxter, William H. (1992). A Handbook of Old Chinese Phonology (Trends in Linguistics. Studies and Monographs). Berlin and New York: de Gruyter Mouton. pp. 218–220. ISBN 978-3-11-012324-1.
- ^ The two meanings were later distinguished through the means of radicals, so that 見 (‘to see’, Std. Mand. jiàn) was unchanged, while 見 (‘to appear’, Std. Mand. xiàn) came to be written as 現.
- ^ This distinction was preserved in Middle Chinese using voiced and unvoiced initials. Thus, 敗 (transitive, ‘to defeat’) was read as 北邁切 (Baxter, paejH), while 敗 (intransitive, ‘to collapse; be defeated’) was read as 薄邁切 (Baxter, baejH). 《增韻》:凡物不自敗而敗之,則北邁切。物自毀壞,則薄邁切。Modern Wu dialects (e.g., Shanghainese, Suzhounese), which preserve the three-way Middle Chinese contrast between voiced/aspirated/unaspirated initials, do not appear to preserve this distinction.
- ^ Wang Li et al. (2000). 王力古漢語字典. Beijing: 中華書局. ISBN 7-101-01219-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
External links[edit]
Look up homograph in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
Asked by: Drew Willms V
Score: 5/5
(10 votes)
A homograph is a word that shares the same written form as another word but has a different meaning. However, some dictionaries insist that the words must also sound different, while the Oxford English Dictionary says that the words should also be of «different origin».
What is homographs and examples?
The -graph in homograph means “written.” Homographs are words that are written the same—meaning they always have the same spelling—but have different meanings. … For example, tear (rhymes with ear) and tear (rhymes with air) are homographs. So are bear (the animal) and bear (the verb meaning “to carry”).
What are the 20 examples of homographs?
20 example of homograph
- Bear — To endure ; Bear — Animal.
- Close — Connected ; Close — Lock.
- Lean — Thin ; Lean — Rest against.
- Bow — Bend forward ; Bow — Front of a ship.
- Lead — Metal ; Lead — Start off in front.
- Skip — Jump ; Skip — Miss out.
- Fair — Appearance ; Fair — Reasonable.
What are the 10 examples of homographs?
Homograph Examples
- agape – with mouth open OR love.
- bass – type of fish OR low, deep voice.
- bat — piece of sports equipment OR an animal.
- bow – type of knot OR to incline.
- down – a lower place OR soft fluff on a bird.
- entrance – the way in OR to delight.
- evening – smoothing out OR after sunset.
- fine – of good quality OR a levy.
What does D homograph mean?
: one of two or more words spelled alike but different in meaning or derivation or pronunciation (such as the bow of a ship, a bow and arrow)
21 related questions found
Is hit a homograph?
In this vein, The Oxford Guide to Practical Lexicography lists various types of homographs, including those in which the words are discriminated by being in a different word class, such as hit, the verb to strike, and hit, the noun a blow.
What are Homographs kids?
A homograph is one of a group of words that have the same spelling but have different meanings. They can also have different pronunciations.
What is polysemy English?
When a symbol, word, or phrase means many different things, that’s called polysemy. The verb «get» is a good example of polysemy — it can mean «procure,» «become,» or «understand.» … Generally, polysemy is distinguished from simple homonyms (where words sound alike but have different meanings) by etymology.
Is fish a homograph?
The word homograph merges homos, the Greek word for «same,» with graph, «to write.» If two words are written identically but don’t share a meaning, they are homographs. Some examples are close («to shut») and close («nearby»); and bass («deep») and bass («the fish»).
How do you use Homographs?
How to use these 12 Homographs in a sentence
- Bow. a) Type of knot: She always wraps her presents with colourful bows /bəʊz/
- Bat. a) in baseball or cricket: Tom has a strange way of holding his cricket bat.
- Minute. a) tiny: The chances of success were minute /maɪnju:t/
- Ball. …
- Fly. …
- Left. …
- Pupil. …
- Sewer.
What does Heterograph mean?
The word heterographs literally means ‘different writing‘. It refers to two words in the English language which have different spellings but sound the same.
What is homograph of content?
Heteronyms are a type of homograph, which is a word that is spelled the same as another word but has a different meaning. … Related words are contents, contented, contenting. contentment. The word content is derived from the Latin word contentus, which means satisfied.
What collocation means?
: the act or result of placing or arranging together the collocation of atoms specifically : a noticeable arrangement or conjoining of linguistic elements (such as words) «To save time» and «make the bed» are common collocations.
Why do English words have so many meanings?
That’s because the other important element of language is context. … The more of these words included in a language, the faster, and more efficiently, people could understand one another — as long as they were also good at parsing out which of the words’ different meanings were appropriate.
What is it called when something has two meanings?
A double entendre (plural double entendres) is a figure of speech or a particular way of wording that is devised to have a double meaning, of which one is typically obvious, whereas the other often conveys a message that would be too socially awkward, sexually suggestive, or offensive to state directly.
What is a Homograph 4th grade?
Homographs are words that sound the same and are spelled the same but have a different meaning. In this language arts worksheet, your child will fill in the missing homophones to complete pre-written sentences and then write sentences to convey each homograph’s alternate meaning. WRITING | GRADE: 4th, 5th.
What is an example of a Heteronym?
Heteronyms are words that are spelled identically but have different meanings when pronounced differently. For example: Lead, pronounced LEED, means to guide. However, lead, pronounced LED, means a metallic element.
How do you memorize Homographs?
Homophones always sound alike, so remember the ending «-phone,» which is a Greek root meaning «sound.» Homographs are always spelled the same, so remember the ending «-graph,» which is a Greek root meaning «writing.»
What is the homograph of ring?
Homophones are words that sound the same. A homophone for ‘ring’ is ‘wring.
Is Row A homograph?
one of two or more words that are written in exactly the same way but have unrelated meanings. For example, row meaning linear arrangement and row meaning argument are homographs.
What are the 10 homonyms?
10 Homonyms with Meanings and Sentences
- Cache – Cash:
- Scents – Sense:
- Chile – Chili:
- Choir – Quire:
- Site – Sight:
- Facts- Fax:
- Finnish – Finish:
What are homonyms and give example?
Homonyms are words that are pronounced the same as each other (e.g., «maid» and «made») or have the same spelling (e.g., «lead weight» and «to lead»).
What are 2 words that sound the same?
Homophones are words that sound the same but are different in meaning or spelling. Homographs are spelled the same, but differ in meaning or pronunciation. Homonyms can be either or even both.
Last Update: Jan 03, 2023
This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. Now, we have got the complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested!
Asked by: Darwin Lehner DVM
Score: 4.8/5
(69 votes)
Homographs can be pronounced the same or not. For example, tear (rhymes with ear) and tear (rhymes with air) are homographs. … When words are both homographs and homophones—meaning they have both the same spelling and the same pronunciation, but different meanings—they can be called homonyms.
What are the 20 examples of homographs?
20 example of homograph
- Bear — To endure ; Bear — Animal.
- Close — Connected ; Close — Lock.
- Lean — Thin ; Lean — Rest against.
- Bow — Bend forward ; Bow — Front of a ship.
- Lead — Metal ; Lead — Start off in front.
- Skip — Jump ; Skip — Miss out.
- Fair — Appearance ; Fair — Reasonable.
What are some examples of homographs?
Homophone — Homophones are words that share the same pronunciation but have different spellings. The ‘phone’ part in homophone means sound. Examples of homophones include the words “write” and “right”, “knight” and “night”, and the words “see” and “sea.” They sound the same but have very different meanings.
What is homograph and give example?
Homographs are words that have same spelling but can be used in different meanings and/or pronunciations. For examples – wind, bear, founded, wound, row, evening, bat etc… Some common homographs. Wind. The usual pronunciation is similar to ‘I’ in the words ‘is’ or ‘in’.
What are homographs 10 examples?
Homograph Examples
- agape – with mouth open OR love.
- bass – type of fish OR low, deep voice.
- bat — piece of sports equipment OR an animal.
- bow – type of knot OR to incline.
- down – a lower place OR soft fluff on a bird.
- entrance – the way in OR to delight.
- evening – smoothing out OR after sunset.
- fine – of good quality OR a levy.
19 related questions found
What is a homograph word?
: one of two or more words spelled alike but different in meaning or derivation or pronunciation (such as the bow of a ship, a bow and arrow)
What does Heterograph mean?
Heterographs are words that sound the same as other words, but they have different spellings and different meanings. For the English language learner or for young students, these words can be very confusing. There are 335 heterographs in the English language.
How do you use homograph in a sentence?
Homograph sentences to read and enjoy
- The bandage was wound around the wound.
- The farm was used to produce produce.
- The dump was so full that it had to refuse more refuse.
- We must polish the Polish furniture.
- He could lead if he would get the lead out.
- The soldier decided to desert his dessert in the desert.
How do you teach Homographs?
Brainstorming homographs:
Write the words fast and fair on the board and ask students to try to come up with other common homographs. As students provide examples, list them on the board—pointing out that some homograph word pairs have the same pronunciation (e.g., fast, fair, wave, well, etc.)
Is present a homograph?
‘Present’ is an example of a homograph — a group of words that have two different pronunciations and two different meanings.
Is head a homograph?
noun. Each of two or more words spelled the same but not necessarily pronounced the same and having different meanings and origins. … ‘Identification and explanation: The homograph ‘head’ can be interpreted as a noun meaning either chief or the anatomical head of a body.
Is fish a homograph?
Homographs are words that have the same spelling but different meanings, whether they’re pronounced the same or not. Bass (the fish, rhymes with class) and bass (the instrument, rhymes with ace) are homographs.
Is nail a homograph?
Answer: Homographs are words with multiple meanings, or two definitions for one word. — Nails and a hammer are used to build things. — Each finger and toe has a nail on it.
Is subject a homograph?
‘Subject’ is an example of a homograph — words that have two different pronunciations and two different meanings even though they are spelt the same. Read on to learn more about how to use it as a verb and noun. … The verb is pronounced “sub-JECT.”
What is an example of a Heteronym?
Heteronyms are words that are spelled identically but have different meanings when pronounced differently. For example: Lead, pronounced LEED, means to guide. However, lead, pronounced LED, means a metallic element.
What is a homonym example?
Homonyms are two or more words with the same spelling or pronunciation, but with different meanings. … One of the most common examples of a homonym in English is the word ‘bat’. ‘Bat’ can mean a piece of equipment you use in some sports, and it’s also the name of an animal.
Is Rose a homonym?
Rows and rose are two words that are pronounced in the same manner but are spelled differently and have different meanings, which makes them homophones. Homophones exist because of our ever-changing English language.
What are Heterotrophs examples?
Heterotrophs are known as consumers because they consume producers or other consumers. Dogs, birds, fish, and humans are all examples of heterotrophs. Heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels in a food chain, a sequence of organisms that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms.
What are some examples of Heterophones?
All of the examples above (record, insult, direct, produce) are examples of heterophones that can be nouns or verbs. In the example, “I can keep a record of my quiz scores,” record is a noun. In the example, “I can record the scores in a notebook,” record is a verb.
Is duck a homograph?
The word homonym means, roughly, “same name.” According to the Oxford English Grammar, homonyms are “distinct words that happen to have the same form.” And they’re pronounced the same, too. So when you see a duck and when you duck your head, those are homonyms.
What are the 2 types of homonyms?
There are two types of homonyms: homophones and homographs.
- Homophones sound the same but are often spelled differently.
- Homographs have the same spelling but do not necessarily sound the same.
What Are Homographs?
Homographs are words that have the same spelling but differ in origin, meaning, and sometimes pronunciation, such as the verb bear (to carry or endure) and the noun bear (the animal with a shaggy coat).
Some homographs are also heteronyms, or words with the same spelling but different pronunciations and meanings, such as the verb moped (past tense of mope) and the noun moped (a motorbike). A homograph is generally considered a type of homonym.
Etymology
From the Latin, «to write the same»
Examples and Observations
- David Rothwell
A homograph is a word that is spelt identically to another word but none the less has a different meaning and probably a different origin. You will doubtless be annoyed if you tear your trousers while climbing over a fence. Indeed, you may be so upset that you shed a tear. As you can see, ‘tear’ and ‘tear’ are spelt identically, but they are pronounced differently and have entirely different meanings. They are good examples of a homograph. Many homographs are not even pronounced differently. Thus the word ‘hide’ sounds exactly the same whether you are talking about the skin of an animal, a measure of land or the verb meaning to conceal or keep out of sight. . . .
«[H]omonym is just the collective noun for homograph and homophone.» - Richard Watson Todd
Another illustration of the extreme inconsistencies of English spelling and pronunciation comes in homographs. These are words that can be pronounced in two separate ways without changing the spelling. So, for example, wind can mean either moving air or to twist or wrap, and the pronunciation is different depending on the meaning. Similarly, the past tense of wind is wound, but with a different pronunciation the latter can mean an injury. A tear as a rip or eye water has two pronunciations, as does resume depending on whether it means continue or curriculum vitae (in the latter case it should strictly be written résumé, but the accents are generally dropped). - Howard Jackson and Etienne Ze Amvela
Etymology is not an intuitive basis for homograph distinction for the contemporary user; but it is a more certain basis for the lexicographer than its more slippery alternative, perceived difference in meaning. - Homographic Riddles:
- Why is a polka like beer?
Because there are so many hops in it. - What’s a frank frank?
A hot dog who gives his honest opinion. - How do pigs write?
With a pigpen. - Why was the picture sent to jail?
Because it was framed. - Why would a pelican make a good lawyer?
Because he knows how to stretch his bill.
- Why is a polka like beer?
Pronunciation: HOM-uh-graf
What word is a Homograph?
Put quite simply, a homograph is a group (usually a pair) of words that are spelled the same way, and may or may not be pronounced the same way, although the difference in pronunciation is often just a shift in the accented syllable.
Is Homograph a literary device?
Definition of Homograph For instance, the word “bear” (verb) means “to endure,” and “bear” (noun) is the name of an animal. This can be considered one example of homograph. This literary device is one of the types of pun (paronomasia).
What are Homographs examples?
Homographs are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings. For example, “lead” would be a homograph because its two meanings—a noun referring to a metal that was once added to paint, and a verb meaning to guide the way for others—come from different root words.
What is the purpose of Homographs?
The Importance of Homographs. It is important to be capable of identifying homographs. The most vital purpose in this is the avoidance of confusion, particularly if the words are written, not spoken, and one must rely solely on context to infer meaning from otherwise identical spelling.
What are Homographs give 2 examples?
Homograph Examples
- agape – with mouth open OR love.
- bass – type of fish OR low, deep voice.
- bat – piece of sports equipment OR an animal.
- bow – type of knot OR to incline.
- down – a lower place OR soft fluff on a bird.
- entrance – the way in OR to delight.
- evening – smoothing out OR after sunset.
- fine – of good quality OR a levy.
What are two Homographs?
Homographs are words that have same spelling but can be used in different meanings and/or pronunciations. For examples – wind, bear, founded, wound, row, evening, bat etc… Some common homographs. Wind. The usual pronunciation is similar to ‘I’ in the words ‘is’ or ‘in’.
What are homophones and give examples?
A homophone can be defined as a word that, when pronounced, seems similar to another word, but has a different spelling and meaning. For example, the words “bear” and “bare” are similar in pronunciation, but are different in spelling as well as in meaning.
What are your you’re called?
Your is the second person possessive adjective, used to describe something as belonging to you. Your is always followed by a noun or gerund. You’re is the contraction of “you are” and is often followed by the present participle (verb form ending in -ing).
What is the answer of my pleasure?
Answer. “My pleasure” is an idiomatic response to “Thank you.” It is similar to “You’re welcome,” but more polite and more emphatic. Use it in formal conversation when someone thanks you for doing a favor, and you want to respond in a way that tells them that you were very happy to help and that you enjoyed it.
How do you reply to take care?
What is an appropriate answer to: “Take care”? “Thanks! I will.” “You too!”…Seeing that “take care” is pretty much a standard phrase people use when ending a conversation, there are a host of ways you could reply:
- Bye!
- See ya!
- Hasta manana!
- Ciao.
- Toodles.
How do you write a Take Care message?
Take care of yourself today so that I can have you for all of your tomorrows. Please feel better soon. I’m far too greedy to live in this world without you for even a minute. Praying for a fast recovery.
What is the reply to have a good one?
“Thanks, you too!” They are wishing you a good night, morning, day, or a good day tomorrow, depending on the situation, it’s just a polite farewell. So, wishing them one back is the polite response.
How do you respond to stay in touch?
If you want to stay in touch and you’re prepared to make that effort, then say “Thanks, I will!” If you want to stay in touch but you’re ambivalent about being responsible for making contact, say “You too!” If you have no intention of staying in touch, but you want to be polite, say “Thanks! Bye!”