Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 More…Less
To make managing and analyzing a group of related data easier, you can turn a range of cells into an Excel table (previously known as an Excel list).
Note: Excel tables should not be confused with the data tables that are part of a suite of what-if analysis commands. For more information about data tables, see Calculate multiple results with a data table.
Learn about the elements of an Excel table
A table can include the following elements:
-
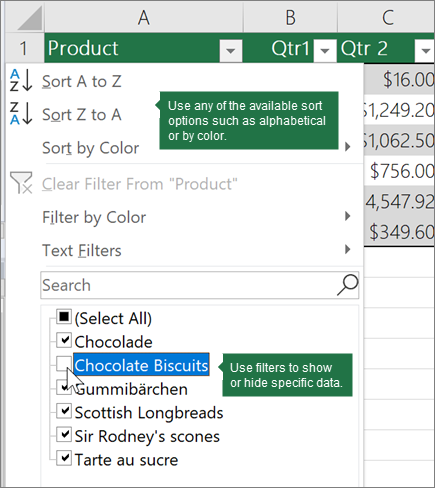
Header row By default, a table has a header row. Every table column has filtering enabled in the header row so that you can filter or sort your table data quickly. For more information, see Filter data or Sort data.
You can turn off the header row in a table. For more information, see Turn Excel table headers on or off.
-
Banded rows Alternate shading or banding in rows helps to better distinguish the data.
-
Calculated columns By entering a formula in one cell in a table column, you can create a calculated column in which that formula is instantly applied to all other cells in that table column. For more information, see Use calculated columns in an Excel table.
-
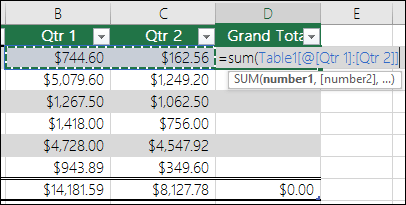
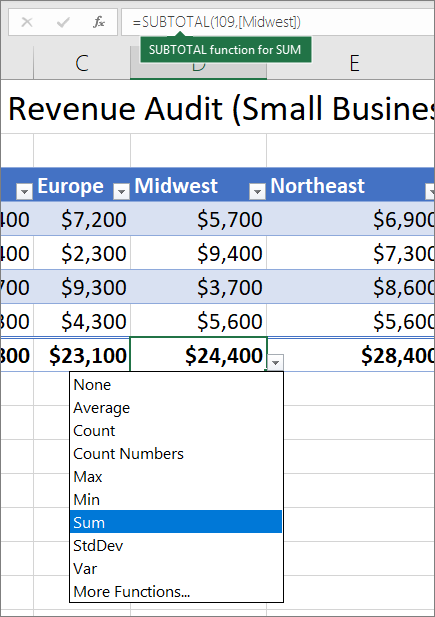
Total row Once you add a total row to a table, Excel gives you an AutoSum drop-down list to select from functions such as SUM, AVERAGE, and so on. When you select one of these options, the table will automatically convert them to a SUBTOTAL function, which will ignore rows that have been hidden with a filter by default. If you want to include hidden rows in your calculations, you can change the SUBTOTAL function arguments.
For more information, also see Total the data in an Excel table.
-
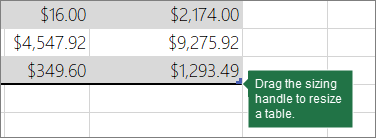
Sizing handle A sizing handle in the lower-right corner of the table allows you to drag the table to the size that you want.
For other ways to resize a table, see Resize a table by adding rows and columns.
Create a table
You can create as many tables as you want in a spreadsheet.
To quickly create a table in Excel, do the following:
-
Select the cell or the range in the data.
-
Select Home > Format as Table.
-
Pick a table style.
-
In the Format as Table dialog box, select the checkbox next to My table as headers if you want the first row of the range to be the header row, and then click OK.
Also watch a video on creating a table in Excel.
Working efficiently with your table data
Excel has some features that enable you to work efficiently with your table data:
-
Using structured references Instead of using cell references, such as A1 and R1C1, you can use structured references that reference table names in a formula. For more information, see Using structured references with Excel tables.
-
Ensuring data integrity You can use the built-in data validation feature in Excel. For example, you may choose to allow only numbers or dates in a column of a table. For more information on how to ensure data integrity, see Apply data validation to cells.
Export an Excel table to a SharePoint site
If you have authoring access to a SharePoint site, you can use it to export an Excel table to a SharePoint list. This way other people can view, edit, and update the table data in the SharePoint list. You can create a one-way connection to the SharePoint list so that you can refresh the table data on the worksheet to incorporate changes that are made to the data in the SharePoint list. For more information, see Export an Excel table to SharePoint.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Format an Excel table
Excel table compatibility issues
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
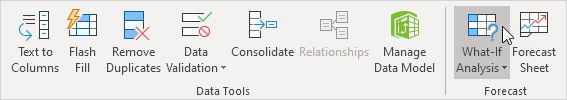
Go to the Data tab > Data Tools group, click the What-If Analysis button, and then click Data Table… In the Data Table dialog window, click in the Column Input cell box (because our Investment values are in a column), and select the variable cell referenced in your formula.
Contents
- 1 How does the data table function work in Excel?
- 2 How do you create a data table?
- 3 Why are data tables useful in Excel?
- 4 How do I add a data table to an Excel chart?
- 5 How do you run a data table?
- 6 Where do I find data tables in Excel?
- 7 How do I make a data Table in sheets?
- 8 What is Table in Excel?
- 9 What do you mean by data in Table?
- 10 Why do we put data in a table?
- 11 Why do we format data as a table?
- 12 What are the three components of a data table?
- 13 How do I align data in a chart in Excel?
- 14 How do I add a data table to a chart in Excel 2010?
- 15 Why Excel data table is not working?
- 16 How do I get data from another table in Excel?
- 17 How do I create a pivot table in a spreadsheet?
- 18 What are pivot tables used for?
- 19 How do I create a sortable table in Google Sheets?
- 20 Which is another word for a data table?
How does the data table function work in Excel?
A data table is a range of cells in which you can change values in some of the cells and come up with different answers to a problem. A good example of a data table employs the PMT function with different loan amounts and interest rates to calculate the affordable amount on a home mortgage loan.
How do you create a data table?
Here’s how to make a data table:
- Name your table. Write a title at the top of your paper.
- Figure out how many columns and rows you need.
- Draw the table. Using a ruler, draw a large box.
- Label all your columns.
- Record the data from your experiment or research in the appropriate columns.
- Check your table.
Why are data tables useful in Excel?
Microsoft Excel can be used to analyze vast amounts of data, and one of the best features in Excel for this purpose is changing your data range to a table. With tables, you can quickly sort and filter your data, add new records, and see your charts and PivotTables update automatically.
How do I add a data table to an Excel chart?
Add a Data Table
- Click anywhere on the chart you want to modify.
- Click Chart Tools Layout> Labels> Data Table.
- Make a Data Table selection.
- Select the Show Data Table option.
- Click OK.
How do you run a data table?
Go to the Data tab > Data Tools group, click the What-If Analysis button, and then click Data Table… In the Data Table dialog window, click in the Column Input cell box (because our Investment values are in a column), and select the variable cell referenced in your formula.
Where do I find data tables in Excel?
If you go to Formulas tab of the Ribbon > Name Manager you will see Table names listed amongst other defined names. They show a different icon next to them, but to make things even clearer you can use the Filter button at the top right to show tables only.
How do I make a data Table in sheets?
All you have to do is select the data that belong in your table, and then click “CTRL + T” (Windows) or “Apple + T” (Mac). Alternatively, there’s a Format as Table button in the standard toolbar. Unfortunately, Sheets doesn’t have a “one stop shop” for Tables.
What is Table in Excel?
What is a Table in Microsoft Excel? A table is a powerful feature to group your data together in Excel. Think of a table as a specific set of rows and columns in a spreadsheet.You might think that your data in an Excel spreadsheet is already in a table, simply because it’s in rows and columns and all together.
What do you mean by data in Table?
Data-table meaning. Filters. (computing) Any display of information in tabular form, with rows and/or columns named. noun.
Why do we put data in a table?
Tables are used to organize data that is too detailed or complicated to be described adequately in the text, allowing the reader to quickly see the results. They can be used to highlight trends or patterns in the data and to make a manuscript more readable by removing numeric data from the text.
Why do we format data as a table?
Formatting your range as a table tells Excel that those rows and columns are all related, and that there are headers in the first row. And by doing this, your range now has meaning. Excel understands it better. And with that, lots of additional benefits are born.
What are the three components of a data table?
A data table contains a header row at the top that lists column names, followed by rows for data.
- Table content.
- Column headers.
- Text alignment.
How do I align data in a chart in Excel?
Step-by-Step Guide
- Click anywhere inside the table, chart and cell that you want to align.
- Navigate to Menu “Report Elements”, then submenu “Position”
- Click on the button “Align” and pick an alignment, or select “Relative Alignment”.
How do I add a data table to a chart in Excel 2010?
In this article
- Introduction.
- 1Click anywhere on the chart you want to add a data table to.
- 2On the Chart Tools Layout tab, click the Data Table button in the Labels group.
- 3Make a selection from the Data Table menu.
- 4Click OK.
Why Excel data table is not working?
The cells must all either be “locked” or “unlocked”. Attempting to run the Data Table tool when all the cells in the table are not consistent will result in an error. To check or change the “locked” settings of a cell, select the cell, go to the Format Cells menu (CTRL + 1), and choose the Protection tab.
How do I get data from another table in Excel?
Click the tables tab. Click the table you want. on the data tab, click Existing Connections in the “get external connections” of the data tab. poof your table from another sheet is now reflected in the current worksheet.
How do I create a pivot table in a spreadsheet?
Open a Google Sheets spreadsheet, and select all of the cells containing data. Click Data > Pivot Table. Check if Google’s suggested pivot table analyses answer your questions. To create a customized pivot table, click Add next to Rows and Columns to select the data you’d like to analyze.
What are pivot tables used for?
A PivotTable is an interactive way to quickly summarize large amounts of data. You can use a PivotTable to analyze numerical data in detail, and answer unanticipated questions about your data.
How do I create a sortable table in Google Sheets?
Sort an entire sheet
- On your computer, open a spreadsheet in Google Sheets.
- At the top, right-click the letter of the column you want to sort by.
- Click Sort sheet A to Z or Sort sheet Z to A.
Which is another word for a data table?
“The table was laden with a plethora of scrumptious dishes.”
What is another word for table?
| desk | tabletop |
|---|---|
| escritoire | stand |
| worktop | board |
| platform | dresser |
| dining table | dinner table |
Data Tables
In Excel, a Data Table is a way to see different results by altering an input cell in your formula. Data tables are available in Data Tab » What-If analysis dropdown » Data table in MS Excel.
Data Table with Example
Now, let us see data table concept with an example. Suppose you have the Price and quantity of many values. Also, you have the discount for that as third variable for calculating the Net Price. You can keep the Net Price value in the organized table format with the help of the data table. Your Price runs horizontally to the right while quantity runs vertically down. We are using a formula to calculate the Net Price as Price multiplied by Quantity minus total discount (Quantity * Discount for each quantity).
Now, for creation of data table select the range of data table. Choose Data Tab » What-If analysis dropdown » Data table. It will give you dialogue asking for Input row and Input Column. Give the Input row as Price cell (In this case cell B3) and Input column as quantity cell (In this case cell B4). Please see the below screen-shot.
Clicking OK will generate data table as shown in the below screen-shot. It will generate the table formula. You can change the price horizontally or quantity vertically to see the change in the Net Price.
One Variable Data Table | Two Variable Data Table
Instead of creating different scenarios, you can create a data table to quickly try out different values for formulas. You can create a one variable data table or a two variable data table.
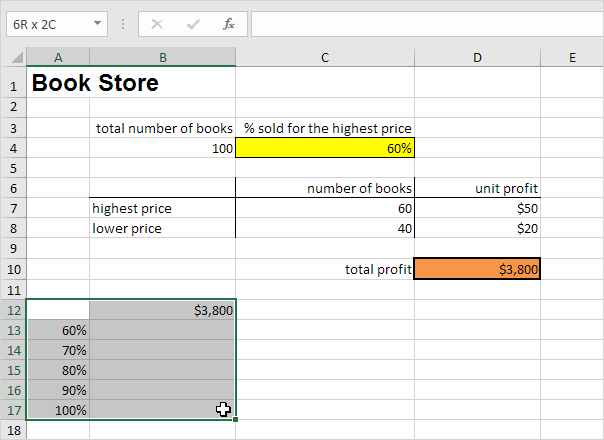
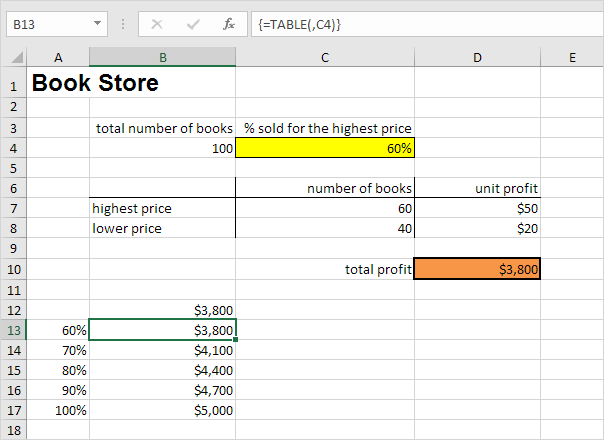
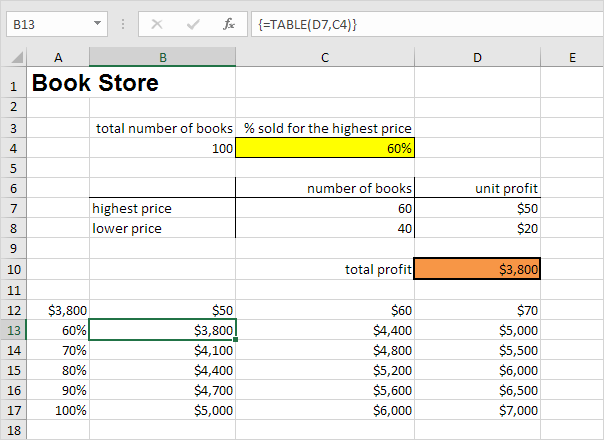
Assume you own a book store and have 100 books in storage. You sell a certain % for the highest price of $50 and a certain % for the lower price of $20. If you sell 60% for the highest price, cell D10 below calculates a total profit of 60 * $50 + 40 * $20 = $3800.
One Variable Data Table
To create a one variable data table, execute the following steps.
1. Select cell B12 and type =D10 (refer to the total profit cell).
2. Type the different percentages in column A.
3. Select the range A12:B17.
We are going to calculate the total profit if you sell 60% for the highest price, 70% for the highest price, etc.
4. On the Data tab, in the Forecast group, click What-If Analysis.
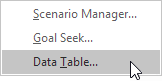
5. Click Data Table.
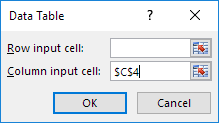
6. Click in the ‘Column input cell’ box (the percentages are in a column) and select cell C4.
We select cell C4 because the percentages refer to cell C4 (% sold for the highest price). Together with the formula in cell B12, Excel now knows that it should replace cell C4 with 60% to calculate the total profit, replace cell C4 with 70% to calculate the total profit, etc.
Note: this is a one variable data table so we leave the Row input cell blank.
7. Click OK.
Result.
Conclusion: if you sell 60% for the highest price, you obtain a total profit of $3800, if you sell 70% for the highest price, you obtain a total profit of $4100, etc.
Note: the formula bar indicates that the cells contain an array formula. Therefore, you cannot delete a single result. To delete the results, select the range B13:B17 and press Delete.
Two Variable Data Table
To create a two variable data table, execute the following steps.
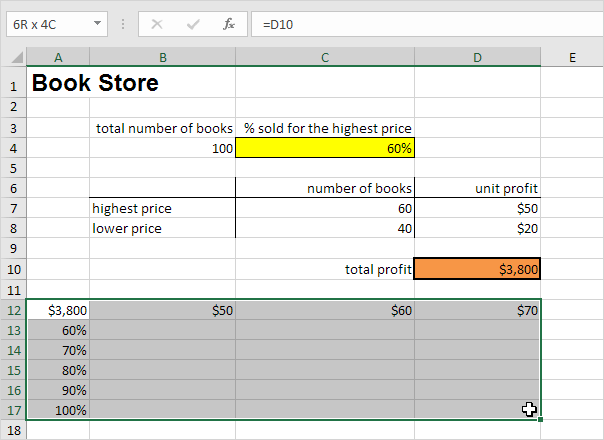
1. Select cell A12 and type =D10 (refer to the total profit cell).
2. Type the different unit profits (highest price) in row 12.
3. Type the different percentages in column A.
4. Select the range A12:D17.
We are going to calculate the total profit for the different combinations of ‘unit profit (highest price)’ and ‘% sold for the highest price’.
5. On the Data tab, in the Forecast group, click What-If Analysis.
6. Click Data Table.
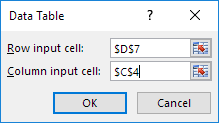
7. Click in the ‘Row input cell’ box (the unit profits are in a row) and select cell D7.
8. Click in the ‘Column input cell’ box (the percentages are in a column) and select cell C4.
We select cell D7 because the unit profits refer to cell D7. We select cell C4 because the percentages refer to cell C4. Together with the formula in cell A12, Excel now knows that it should replace cell D7 with $50 and cell C4 with 60% to calculate the total profit, replace cell D7 with $50 and cell C4 with 70% to calculate the total profit, etc.
9. Click OK.
Result.
Conclusion: if you sell 60% for the highest price, at a unit profit of $50, you obtain a total profit of $3800, if you sell 80% for the highest price, at a unit profit of $60, you obtain a total profit of $5200, etc.
Note: the formula bar indicates that the cells contain an array formula. Therefore, you cannot delete a single result. To delete the results, select the range B13:D17 and press Delete.
What is Data Table in Excel?
A Data Table in Excel helps study the different outputs obtained by changing one or two inputs of a formula. A data table does not allow changing more than two inputs of a formula. However, these two inputs can have as many possible values (to be experimented) as one wants. Excel Data tables, along with Scenarios and Goal Seek are parts of the What-If Analysis tools.
For example, an organization may want to study how changes in the cash possessed impact its working capital. A data table will help the organization know the optimum level of cash (from the specified possible values) to be held to meet its short-term obligations.
The purpose of creating data tables in Excel is to analyze the variation in outputs resulting from a change in the inputs. Moreover, one can have all the outputs in a single table which eases interpretation and allows quick sharing with other users.
Table of contents
- What is Data Table in Excel?
- Types of Data Tables in Excel
- One-Variable Data Table in Excel
- Example #1
- Two-Variable Data Table in Excel
- Example #2
- The Key Points Governing Data Tables in Excel
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
- One-Variable Data Table in Excel
Types of Data Tables in Excel
The kinds of data tables in Excel are specified as follows:
- One-variable data table
- Two-variable data table
Let us discuss each type of data table one by one with the help of examples.
Note: A data table is different from a regular Excel tableIn excel, tables are a range with data in rows and columns, and they expand when new data is inserted in the range in any new row or column in the table. To use a table, click on the table and select the data range.read more. The former shows the various combinations of inputs and outputs. These outputs are calculated by considering the source dataset as the base. In contrast, an Excel table shows related data that is grouped in one place.
One-Variable Data Table in Excel
A one-variable data tableOne variable data table in excel means changing one variable with multiple options and getting the results for multiple scenarios. The data inputs in one variable data table are either in a single column or across a row.read more is created to study how a change in one input of the formula causes a change in the output. A one-variable data table in excel can be either row-oriented or column-oriented. This implies that all the possible values that an input can assume are listed in either a single row (row-oriented) or a single column (column-oriented) of Excel.
You can download this DATA Table Excel Template here – DATA Table Excel Template
Example #1
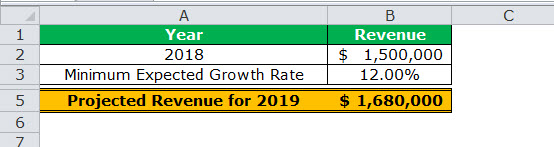
There are two images titled “image 1” and “image 2.” The following information is given:
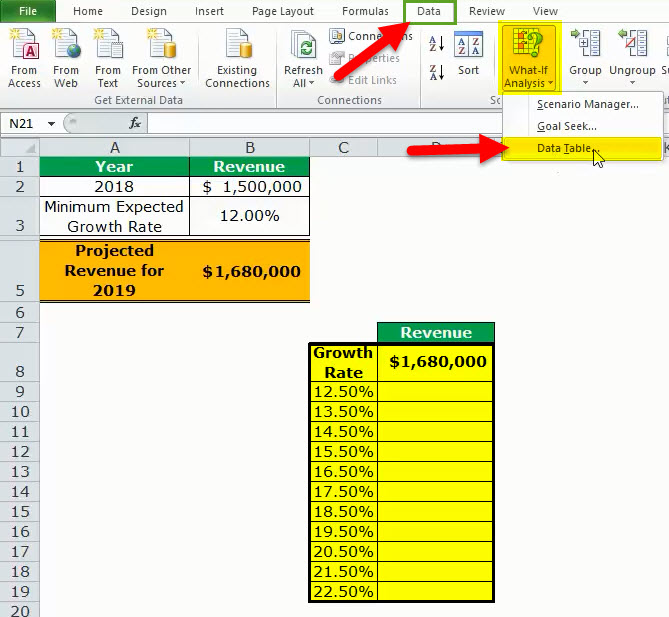
- Image 1 shows an organization’s revenue (in $) for 2018 in cell B2. The minimum growth rate expected is given as 12% in cell B3. The projected revenue (in $ in cell B5) for 2019 has been calculated by using the formula “=B2+(B2*B3).”
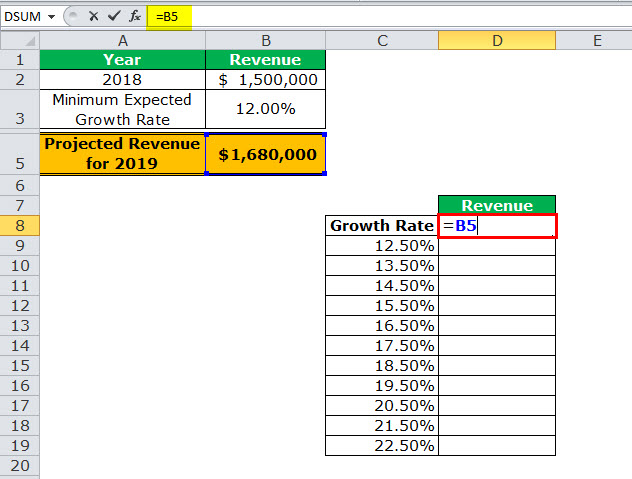
- Image 2 shows the possible values (in column C) that the growth rate can assume. The value of cell D8 has been explained in steps 1 and 2 (given further in this example).
We want to perform the following tasks:
- Calculate the projected revenues (in column D) according to the different growth rates (in column C) given in image 2.
- Create a “line with markers” chart showing the growth rates on the x-axis and the projected revenues on the y-axis. Replace the markers of the chart with arrows.
Use a one-variable data table of Excel. Interpret the data table thus created.
Image 1
Image 2
The steps for performing the given tasks by using a one-variable data table are listed as follows:
- Enter the data of the two images in Excel. In cell D8, type “equal to” (=) followed by the reference B5. This links cell D8 to cell B5.
The linking of the two cells is shown in the following image.
Since all the growth rates have been entered vertically (C9:C19), our data table is said to be column-oriented. The entire range C8:D19 is our one-variable data table. We are creating a one-variable data table as the change in outputs will be observed against a change in one input, i.e., the growth rate.
Note: Notice that either the formula “=B2+(B2*B3)” could be typed directly in cell D8 or cell D8 can be linked to cell B5. We have chosen to link the two cells.
The linking of cell D8 to cell B5 ensures that any updates in the formula of the latter are automatically reflected in the range D9:D19 of the data table. For instance, if the formula of cell B5 is multiplied by 2 [like =B2+(B2*B3)*2], all the outputs obtained in the range D9:D19 are automatically multiplied by 2.
Had we not linked cells D8 and B5, any changes to the formula of cell B5 would not have changed the value in cell D8. Consequently, the outputs in the range D9:D19 would not have been updated automatically.
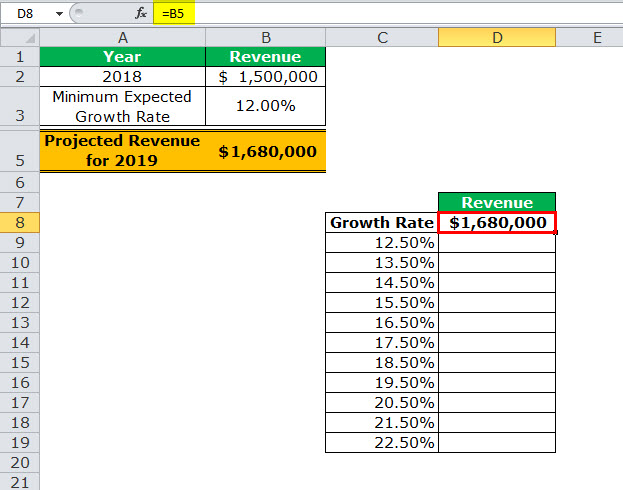
- Press the “Enter” key. Cell D8 shows the value of cell B5, as shown in the following image.
Notice that if one manually enters the value (1680000) in cell D8, the data table will not work. Moreover, one should always type the formula [=B2+(B2*B3)] or link the cell that is one row above and one column to the right of the possible input values (C9:C19). This is the reason we chose to link cell D8 to cell B5.
Note: If the data table is row-oriented, type the formula or link the cell that is one column to the left and one cell below the first possible input value. For instance, had the possible input values been in the range F2:P2, we would have entered the formula or linked cell E3 to cell B5.
- Select the range of the data table. This selection should include the linked cell (D8), the possible input values (C9:C19), and the empty cells for outputs (D9:D19). Hence, we have selected the range C8:D19, as shown in the following image.
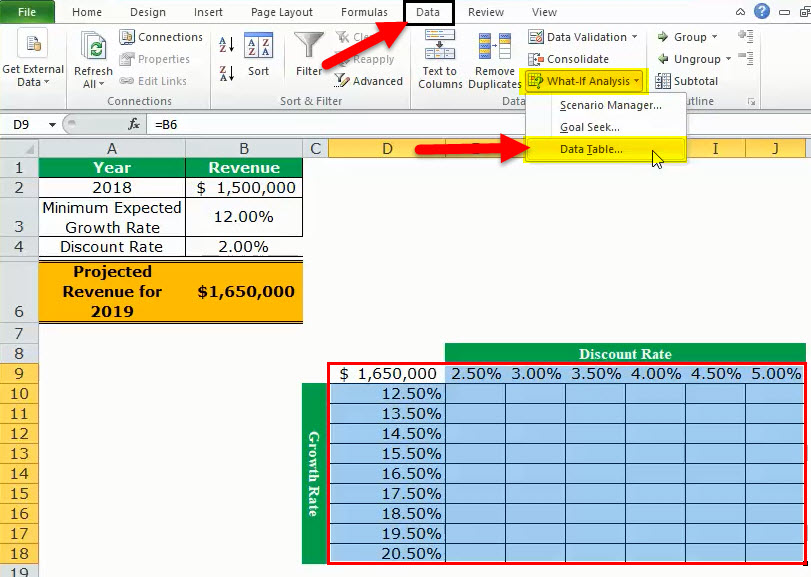
- From the Data tab, click the “what-if analysis” drop-down (in the “data tools” or “forecast” group). Select the option “data table.” This option is shown in the following image.
- The “data table” dialog box opens, as shown in the following image. In the box of “column input cell,” select cell B3, which contains the minimum expected growth rate. As a result, the reference $B$3 appears in this box. Leave the box of “row input cell” blank.
By giving the reference to cell B3 in the “column input cell,” we are telling Excel that at the growth rate of 12%, the projected revenue is $1,680,000. So, with this data table, Excel is being asked the projected revenue when the growth rates vary from 12.5% to 22.5%.
Note 1: A “row input cell” or “column input cell” is a reference to a cell that contains the input. This is the input that can assume the different possible values. Moreover, this input must necessarily be used in the formula whose outputs are to be studied.
In a one-variable data table, either the “row input cell” or the “column input cell” is specified depending on whether the data table is row-oriented or column-oriented.
Note 2: In a one-variable data table, Excel uses either the formula “=TABLE(row_input_cell,)” or “=TABLE(,column_input_cell)” to calculate the different outputs. The former formula is used when the possible input values are in a row, while the latter is used when the possible input values are in a column.
To view the TABLE formula, select any of the output cells and check the formula bar. In this example, the formula “=TABLE(,B3)” is used to calculate the outputs.
Further, Excel uses these TABLE formulas as array formulasArray formulas are extremely helpful and powerful formulas that are used in Excel to execute some of the most complex calculations. There are two types of array formulas: one that returns a single result and the other that returns multiple results.read more. However, these formulas cannot be edited manually, unlike the regular array formulas. But, one can delete all the output cells containing the TABLE formulas.
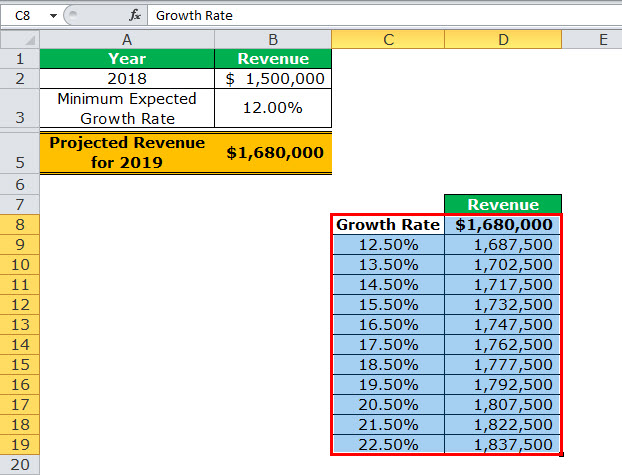
- Click “Ok” in the “data table” window. The range D9:D19 of the data table has been filled with values. The different outputs are shown in the following image.
Interpretation of the one-variable data table: By looking at the data table in the preceding image, one can say that when the growth rate is 12.5%, the projected revenue is $1,687,500. Likewise, when the growth rate is 13.5%, the projected revenue is $1,702,500. Hence, the larger the growth rate, the more the increase in the projected revenue.
The projected revenue is at its maximum ($1,837,500) when the growth rate is at its highest (22.5%). So, the organization can study the variation in outputs when a single input (growth rate) changes.
Note: For more examples related to the one-variable data table of Excel, refer to the hyperlink given before step 1.
- To create a “line with markers” chart that displays the growth rates on the x-axis and the projected revenues on the y-axis, follow the listed steps:
a. Select the range D9:D19 and click the Insert tab on the Excel ribbon.
b. Click the “insert line or area chart” icon from the “charts” group. Select the “line with markers” chart under the 2-D line charts. A “line with markers” chart appears, which displays the projected revenues on the y-axis.
c. Click anywhere on the chart. The “chart tools” menu becomes visible. This menu consists of the Design and Format tabs.
d. Click the Design tab of the “chart tools” menu. Choose “select data” from the “data” group. The “select data source” window opens.
e. Click “edit” under “horizontal (category) axis labels.” The “axis labels” window opens.
f. Select the range C9:C19 in the “axis label range” box. Click “Ok.” Click “Ok” again in the “select data source” window.The “line with markers” chart is created whose x-axis and y-axis look the way they are shown in the image of step 8.
- To replace the default markers of the chart with arrows, follow the listed steps:
a. Select the markers of the chart and right-click them. Choose the “format data series” option from the context menu. The “format data series” pane opens.
b. Click the “fill & line” tab. Expand the “line” tab. In “end arrow type,” select any of the arrows. We have chosen “open arrow.”
c. Select “marker” and expand the “marker options.” Choose the option “none.”
d. Close the “format data series” pane.The “line with markers” chart looks the way it is displayed in the following image. Notice that since the chart shows the projected revenues, we have titled it accordingly.
Two-Variable Data Table in Excel
A two-variable data table in excelA two-variable data table helps analyze how two different variables impact the overall data table. In simple terms, it helps determine what effect does changing the two variables have on the result.read more helps study how changes in two inputs of a formula cause a change in the output. In a two-variable data table, there are two ranges of possible values for the two inputs. From these two ranges, one range is in a row and the other is in a column of Excel.
Example #2
There are three images titled “image 1,” “image 2,” and “image 3.” The following information is given:
- Image 1 shows an organization’s revenue (in $ in 2018) and the minimum growth rate in cells B2 and B3 respectively. Both these figures are the same as that of the previous example. Additionally, the organization gives a 2% discount (in cell B4) to its customers. This is given to boost sales.
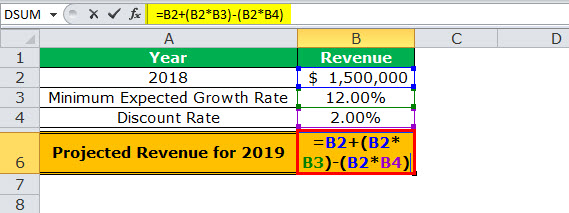
- Image 2 shows how the projected revenue (in $ in cell B6) for 2019 has been calculated. The formula “=B2+(B2*B3)-(B2*B4)” is used for this purpose. The amount obtained ($1,650,000) is the projected revenue after the discount.
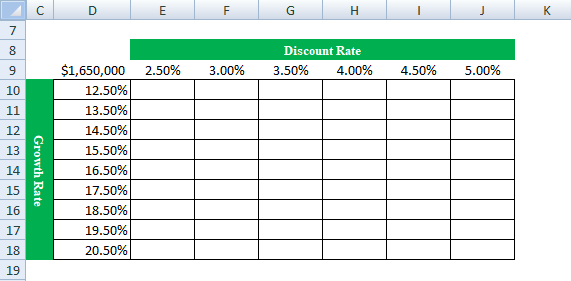
- Image 3 shows the different values in row 9 that the discount rate can assume. The possible values that the growth rate can assume are given in column D. The value of cell D9 has been explained in steps 1 and 2 (given further in this example).
Calculate the projected revenues (in E10:J18) according to the various discount rates (in row 9) and growth rates (in column D). Use a two-variable data table of Excel. Interpret the data table thus created.
Image 1
Image 2
Image 3
The steps for creating a two-variable data table are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the data of the preceding images in Excel. In cell D9, type the “equal to” operator followed by the reference B6.
This time we have chosen to link cell D9 to cell B6. Alternatively, we could have also entered the formula [=B2+(B2*B3)-(B2*B4)] in cell D9. This is because, in a two-variable data table, one should type the formula or link the cell that is one column to the left of the first horizontal input value (2.5%). At the same time, this cell should be one row above the first vertical input value (12.5%).
The linking of cells ensures that any changes to the formula of cell B6 are reflected in the value of cell D9. Further, any change in the value of cell D9 will update the outputs (in E10:J18) automatically.
Note: Please ignore the differences in font, colors, and alignment across the images of this example. These differences may be due to the different versions of Excel being used to create the images.
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. Cell D9 shows the value of cell B6, which is 1,650,000. This is shown in the following image.
The entire range D9:J18 is our two-variable data table. Notice that the excel data table shows the possible discount rates horizontally (in bold in row 9) and the possible growth rates vertically (in column D). This time the variation in outputs resulting from changes in both these inputs (discount rate and growth rate) need to be studied.
Note: If the value is entered manually in cell D9, the excel data table will not work.
Step 3: Select the range D9:J18. Note that the selection should include the linked cell (D9), possible discount rates (E9:J9), possible growth rates (D10:D18), and the empty cells for the outputs (E10:J18).
The selection is shown in the following image.
Step 4: Click the “what-if analysis” drop-down (in the “data tools” or “forecast” group) of the Data tab. Select the option “data table.”
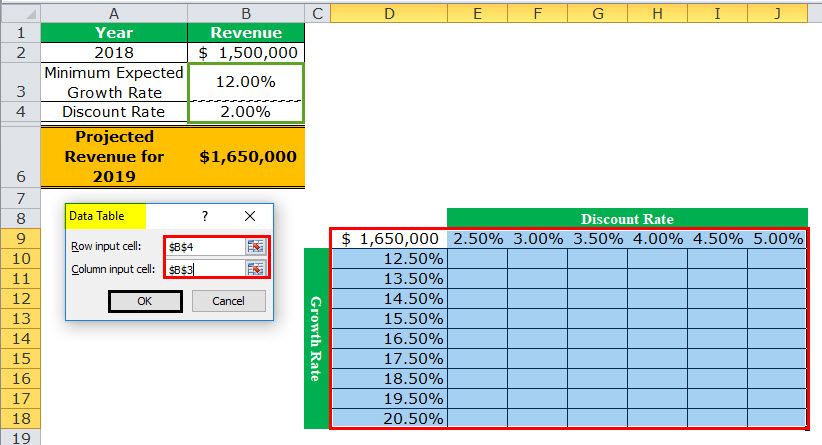
Step 5: The “data table” window opens, as shown in the following image. In the box of “row input cell,” select cell B4. In the box of “column input cell,” select cell B3. The absolute referencesAbsolute reference in excel is a type of cell reference in which the cells being referred to do not change, as they did in relative reference. By pressing f4, we can create a formula for absolute referencing.read more to cells B4 and B3 appear in the two boxes.
Cells B4 and B3 contain the minimum expected growth rate and the discount rate of the source dataset.
By making these selections, Excel is told that at a discount rate of 2% and a growth rate of 12%, the projected revenue is $1,650,000. Therefore, our two-variable data table instructs Excel to calculate the projected revenues when the discount rates and growth rates vary from 2.5% to 5% and 12.5% to 20.5% respectively.
Note: In a two-variable data table, both the “row input cell” and “column input cell” are specified, unlike a one-variable data table where one has to specify either of the two inputs.
Further a two-variable data table uses the formula “=TABLE(row_input_cell,column_input_cell)” to calculate the outputs. So, in this example, the formula “=TABLE(B4,B3)” has been used for the calculations. This formula is visible in the formula bar when an output cell is selected.
For the meaning of the “row input cell” and the “column input cell,” refer to “note 1” under step 5 of example #1.
Step 6: Click “Ok” in the “data table” window. The outputs appear in the range E10:J18, as shown in the following image.
Interpretation of the two-variable data table: When the discount rate is 2.5% and the growth rate is 12.5%, the organization’s projected revenue is $1,650,000 (in cell E10). Notice that this figure is the same as that of cell B6. However, the value in cell B6 takes into account 2% and 12% as the discount rate and growth rate respectively.
Notice that the numbers of cells E10 and B6 match those of cells G11 and I12. This implies that when the discount rate and growth rate are increased in the same proportion (like by 0.5%, 1.5% or 2.5%), the resulting value is the same as the output of the source dataset (in cell B6). Cells E10, G11, and I12 reflect 0.5%, 1.5%, and 2.5% increase in the two rates.
Likewise, had we increased both the discount and growth rates by 1%, the resulting value would have again been $1,650,000. In this case, the discount rate and growth rate would have been 3% and 13% respectively.
By obtaining the projected revenues in the range E10:J18, the organization can sell at an optimum discount rate and, at the same time, target an attainable growth rate. Hence, the organization can choose the most suitable combination of the two rates.
Note: For more examples related to the two-variable data table of Excel, click the hyperlink given before step 1 of this example.
The Key Points Governing Data Tables in Excel
The important points related to data tables of Excel are listed as follows:
- It helps select those input values that fit the business in the best possible manner.
- It facilitates the comparison of the different outputs as all the results are consolidated in one place.
- It presents the results in a tabular format that can neither be edited nor undone with the shortcut “Ctrl+Z.” The outputs can only be deleted by selecting them and pressing the “Delete” key.
- It uses the TABLE array formulas to calculate the outputs. The “row input cell” and the “column input cell” must be selected carefully to get accurate results. Moreover, the input cell or cells must be on the same worksheet as the data table.
- It need not be refreshed, unlike a pivot table. A change in the values or the formula of the source dataset causes the excel data table to update automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Define a data table and suggest when it should be used in Excel.
A data table helps analyze how a change in one or two inputs of a formula causes a change in the output. The resulting outputs are arranged in a tabular format, making them easy to compare and interpret.
A data table of Excel should be used in the following situations:
• When the outputs resulting from a change in one or two inputs need to be studied
• When the most optimum input value or values need to be chosen
• When all the combinations of inputs and outputs need to be explored in one glance
2. How to create a data table in Excel?
The steps to create a data table in Excel are listed as follows:
a. Enter the source dataset in an Excel worksheet. Use one or two inputs to calculate an output.
b. Arrange the possible values, which an input can assume, in a row and/or column.
c. Link one cell of the data table to the output cell of the source dataset. Alternatively, in a cell of the data table, enter the formula whose outputs need to be studied.
d. Select the data table. The selection should include the linked cell (or the formula cell of the data table), the possible input values, and the empty cells for outputs.
e. Select the “data table” option from the “what-if analysis” drop-down of the Data tab. The “data table” window opens.
f. Enter either the “row input cell” or “column input cell” if the impact of changing one input is to be studied. To study the impact of changing two inputs, enter both “row input cell” and “column input cell.”
g. Click “Ok” in the “data table” window.
A one-variable or two-variable data table is created depending on the execution of steps “a,” “b,” and “f.”
Note: For more details on creating a data table in Excel, refer to the examples of this article.
3. How does a data table work in Excel?
A data table works on the policy “what will be the result if one or two inputs of a formula are changed?” One cell of the data table is linked to the source dataset. In this way, Excel is told how the inputs are to be used in calculating the output.
Next, as the possible input values are supplied, Excel is asked to calculate the outputs using the same formula as that of the source dataset. The resulting table shows the different mixes of inputs and outputs, thereby assisting the user in decision-making.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Data Tables in Excel. Here we discuss how to create one-variable and two-variable data tables along with practical Excel examples. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles–
- Two-Variable Data Table in ExcelA two-variable data table helps analyze how two different variables impact the overall data table. In simple terms, it helps determine what effect does changing the two variables have on the result.read more
- VBA Refresh Pivot TableWhen we insert a pivot table in the sheet, once the data changes, pivot table data does not change itself; we need to do it manually. However, in VBA, there is a statement to refresh the pivot table, expression.refreshtable, by referencing the worksheet.read more
- Merge Tables ExcelWe can use a number of different methods to merge tables in Excel, including the VLOOKUP function, the INDEX function, and the MATCH function.read more
- Data Validation in ExcelThe data validation in excel helps control the kind of input entered by a user in the worksheet.read more