- Текст
- Веб-страница
The word computer comes from a Latin word which means to count. A computer is a machine with a complex network of electronic circuits that operate switches or magnetize tiny metal cores. The switches, like the cores, are capable of being in one of two possible states, that is, on and off; magnetized or demagnetized. The machine is capable of storing and manipulating numbers, letters, and characters. The basic idea of the computer is that we can make the machine do what we want by inputting signals that turn certain switches on and turn others off, or that magnetize or do not magnetize the cores.
The basic job of computers is the processing of information. For this reason, computers can be defined as devices which accept information in the form of instructions called a program and characters called data, perform mathematical and/or logical operations on the information, and then supply results of these operations. The program, or part of it, which tells the computers what to do and data, which provide the information needed to solve the problem, are kept inside the computer in a place called memory.
Some of the most common methods of inputting information are to use punched cards, magnetic tape, disks, and terminals. The computer’s input device (which may be a card reader, a tape drive or disk drive, depending on the medium used in inputting information) reads the information into the computer.
For outputting information, two common devices used are a printer which prints the new information on paper, or a CRT display screen which shows the results on a TV-like screen.
There are different kinds of computers. Some do only one job over and over again. These are special-purpose computers. But there are some computers that can do many different jobs. They are called general-purpose computers. These are the “big brains” that solve the most difficult problems of science. They answer questions about rockets and planes, bridges and ships — long before these things are even built. Computers help our space program, our business and industry, medicine and education. They are powerful tools which help to change our life and the world around us.
0/5000
Результаты (русский) 1: [копия]
Скопировано!
Компьютер слово происходит от латинского слова, которое означает для подсчета. Компьютер является машина с сложной сети электронных схем, которые действуют коммутаторы или намагнитить маленькие металлические стержни. Переключатели, как ядра, могут быть в одном из двух возможных состояний, то есть, включения и выключения; намагничено или размагничена. Машина способна хранения и манипулирования чисел, букв и символов. Основная идея компьютера заключается в том, что мы можем сделать машины делать то, что мы хотим ввода сигналов, что определенные переключатели на и отключить другие, или что намагнитить или не намагнитить ядер.Основные задания компьютеров является обработка информации. По этой причине компьютеры могут быть определены как устройства, которые принимать информацию в виде инструкций, называемых программу и символы, называемые данные, выполнять математические и логические операции на информацию, а затем укажите результаты этих операций. Программы, или его часть, которая говорит компьютеры, что делать и данных, которые предоставляют информацию, необходимую для решения проблемы, хранятся внутри компьютера в месте под названием памяти.Некоторые из наиболее распространенных методов ввода информации должны использовать перфокарты, магнитные ленты, диски и терминалы. Устройства ввода на компьютере (который может быть кард-ридер, ленточный накопитель или диск, в зависимости от используемых в ввод информации) считывает информацию в компьютер.Для вывода информации, два общих устройств являются принтер, который печатает на бумаге, или CRT экран, который показывает результаты на экране ТВ как новой информации.Существуют различные виды компьютеров. Некоторые делают только одну работу снова и снова. Это специальные компьютеры. Но есть несколько компьютеров, которые могут сделать много различных рабочих мест. Они называются компьютеров общего назначения. Это «большой мозг», которые решают самые сложные проблемы науки. Они отвечают на вопросы о ракеты и самолеты, мосты и корабли — задолго до того, как эти вещи даже построены. Компьютеры помогают нашей космической программы, наш бизнес и промышленности, медицины и образования. Они являются мощными инструментами, которые помогают изменить нашу жизнь и мир вокруг нас.
переводится, пожалуйста, подождите..
Результаты (русский) 2:[копия]
Скопировано!
Слово компьютер происходит от латинского слова , которое означает считать. Компьютер представляет собой машину со сложной сетью электронных схем , которые работают переключатели или намагнитить крошечные металлические стержни. Переключатели, как и сердечников, способны быть в одном из двух возможных состояний, то есть, и выключается; намагниченный или размагничена. Машина способна хранить и манипулировать цифры, буквы и символы. Основная идея компьютера является то , что мы можем сделать машину делать то , что мы хотим, вводя сигналы , которые превращают некоторые переключатели на и включите другие выключен, или что намагнитить или не намагничивает ядра. Основная работа компьютеров является обработка информации , По этой причине, компьютеры могут быть определены как устройства , которые принимают информацию в форме инструкций называется программой и символов , называемых данных, выполнять математические и / или логические операции над информацией, а затем поставляют результаты этих операций. Программа, или часть его, которая говорит компьютерам , что делать и данных, которые предоставляют информацию , необходимую для решения проблемы, хранятся в компьютере в памяти место , которое называется. Некоторые из наиболее распространенных методов ввода информации являются использовать перфокарты, магнитные ленты, диски и терминалы. Устройство ввода компьютера (который может быть кардридер, накопитель на магнитной ленте диск или диск, в зависимости от используемой среды при вводе информации) читает информацию в компьютер. Для вывода информации, два распространенных устройства , используемые являются принтер , который печатает новую информация на бумаге или экране дисплея CRT , который показывает результаты на экране телевизора, как. Существуют различные виды компьютеров. Некоторые делают только одну работу снова и снова. Эти специализированные компьютеры. Но есть некоторые компьютеры , которые могут сделать много различных рабочих мест. Они называются компьютеры общего назначения. Эти «большие мозги» , которые решают самые сложные проблемы науки. Они отвечают на вопросы о ракет и самолетов, мостов и кораблей — задолго до того, эти вещи даже построили. Компьютеры помогают нашей космической программы, наш бизнес и промышленность, медицину и образование. Они являются мощными инструментами , которые помогают изменить нашу жизнь и мир вокруг нас.
переводится, пожалуйста, подождите..
Результаты (русский) 3:[копия]
Скопировано!
слово происходит от латинского слова компьютера, а значит, рассчитывать.компьютер, это машина со сложной сети электронных схем, которые действуют переключателей или намагничивай крошечные металлические стержни.выключатели, как ядер, способны быть одним из двух возможных государств, а именно on и off; намагничивание или demagnetized.машина способна хранения и манипулировании цифрами, букв и символов.основная идея компьютера состоит в том, что мы можем сделать компьютер делать то, что мы хотим путем введения сигналы, что очередь некоторые включается и очередь других, или что намагничивай или не намагничивай ядер.основная работа компьютеров обработки информации.по этой причине компьютеров можно определить как устройства, которые принимают информацию в виде инструкций, называется программа, и персонажи назвал данные, математических и / или логические операции на информацию, а затем поставки результатов этих операций.программу или ее часть, которая рассказывает компьютеры, что делать, и данных, которые предоставляют информацию, необходимую для того, чтобы решить проблему, хранятся в компьютере в месте под названием памяти.некоторые из наиболее распространенных методов получения информации для использования ударил карты, магнитные ленты, диски и терминалов.компьютер, это устройство ввода (который может быть кард — ридер, ленты или диск, в зависимости от среднего, используемых в ввода информации), считывает информацию в компьютер.на формирование информации, два обычных устройств используются принтер, который печатает новую информацию о документе, или элт — экраном, который показывает результаты по телевизору, как экран.существуют различные виды компьютеров.иногда только одно дело снова и снова.эти целевые компьютеры.но есть некоторые компьютеры, которые могут делать много разных мест.они называются компьютеров общего назначения.это «большой мозг», что решения самых сложных проблем науки.они отвечают на вопросы о ракеты и самолеты, мосты и судов — задолго до того, как эти вещи даже построил.компьютеры помогают нашей космической программы, наш бизнес и промышленность, медицина и образование.это мощный инструмент, который поможет изменить нашу жизнь и мир вокруг нас.
переводится, пожалуйста, подождите..
Другие языки
- English
- Français
- Deutsch
- 中文(简体)
- 中文(繁体)
- 日本語
- 한국어
- Español
- Português
- Русский
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- Ελληνικά
- العربية
- Polski
- Català
- ภาษาไทย
- Svenska
- Dansk
- Suomi
- Indonesia
- Tiếng Việt
- Melayu
- Norsk
- Čeština
- فارسی
Поддержка инструмент перевода: Клингонский (pIqaD), Определить язык, азербайджанский, албанский, амхарский, английский, арабский, армянский, африкаанс, баскский, белорусский, бенгальский, бирманский, болгарский, боснийский, валлийский, венгерский, вьетнамский, гавайский, галисийский, греческий, грузинский, гуджарати, датский, зулу, иврит, игбо, идиш, индонезийский, ирландский, исландский, испанский, итальянский, йоруба, казахский, каннада, каталанский, киргизский, китайский, китайский традиционный, корейский, корсиканский, креольский (Гаити), курманджи, кхмерский, кхоса, лаосский, латинский, латышский, литовский, люксембургский, македонский, малагасийский, малайский, малаялам, мальтийский, маори, маратхи, монгольский, немецкий, непальский, нидерландский, норвежский, ория, панджаби, персидский, польский, португальский, пушту, руанда, румынский, русский, самоанский, себуанский, сербский, сесото, сингальский, синдхи, словацкий, словенский, сомалийский, суахили, суданский, таджикский, тайский, тамильский, татарский, телугу, турецкий, туркменский, узбекский, уйгурский, украинский, урду, филиппинский, финский, французский, фризский, хауса, хинди, хмонг, хорватский, чева, чешский, шведский, шона, шотландский (гэльский), эсперанто, эстонский, яванский, японский, Язык перевода.
- Если у меня больше свободного времени я
- reboot system now
- Как ты проводишь летние каникулы ?
- reboot system now
- Как ты проводишь летние каникулы ?
- рождена быть счастливой
- у бабушки
- У нас в Казахстане нет развитой промышле
- Если у меня больше свободного времени я
- Michael with Lyre, BeckoningContrasted b
- Если у меня больше свободного времени я
- Michael with Lyre, BeckoningContrasted b
- Здравствуйте! Я не могу проследить свой
- 12 | School that Joseph Knecht studied a
- как он сказал
- Couldn’t ask for a better day to be prom
- 12 | School that Joseph Knecht studied a
- Если у меня больше свободного времени я
- (B) Based on an episode from The Pickwic
- останнім часом
- Dum spero amo
- Он решил бежать, он оставил деньги, дом
- (B) Based on an episode from The Pickwic
- Publishing services

Computer As It Is (Компьютер как он есть)
The word «computer» comes from a Latin word which means to count.
Слово «компьютер» происходит от латинского слова, означающего считать.
Initially, the computer was designed as a tool to manipulate numbers. Although designed originally for arithmetic purposes, at present it is applicable for a
great variety of tasks. Computers are now an integral part of our day-to-day lives. Today it would be difficult to find any task calling for the processing of large amounts of information that is not performed by a computer. The computer may be stated to have become an important and powerful tool for collecting, recording, analysing,
and distributing tremendous masses of information.
Первоначально компьютер был разработан как инструмент для манипулирования числами. Хотя предназначенный изначально для арифметических целей, в настоящее время он применяется для самых разнообразных задач. Компьютеры в настоящее время стали неотъемлемой частью нашей жизни изо дня в день. Сегодня было бы трудно найти любую задачу для обработки больших объемов информации, которую не берет на себя компьютер. Компьютер может быть важным и мощным инструментом для сбора, регистрации, анализа и распространения огромной массы информации.
In science, computers digest and analyse masses of measurements, such as the positions and velocities of a spacecraft and solve extraordinary long and complex mathematical problems, such as the trajectory of the spacecraft.
В науке, компьютеры считают и анализируют массу измерений, таких, как положения и скорости корабля и решают чрезвычайно длинные и сложные математические задачи, например, траекторию космических аппаратов.
In commerce, computers record and process inventories, purchases, bills, payrolls, bank deposits and the like and keep track of ongoing business transactions.
В торговле, компьютеры записывают и обработатывают запасы, закупки, вексели, платежные ведомости, банковские депозиты и т.п., и отслеживает текущие бизнес-операций.
In industry, they monitor and control manufacturing processes.
В промышленности они смотрят и контролируют производственные процессы.
In government, computers keep statistics, analyse and distribute information.
В правительстве, компьютеры ведут статистику, анализируют и распространяют информацию.
Computer technology has made dramatic strides in application of virtually every segment of a modern industrialized culture, from product design and manufacturing, through sales, warehousing and distribution. Nowadays computer-aided design can no longer be separated from computer-aided manufacturing, they are one and the same. Hence, the acronym, CAD/CAM. The list of applications is large and growing rapidly.
Компьютерная технология сделала серьезные успехи в применении, практически в каждом сегменте, современной индустриальной культуры, начиная с проектирования и производства, путем продажи, складирования и дистрибуции. В настоящее время система автоматизированного проектирования не может быть отделена от автоматизации производственных процессов, они являются одним и тем же. Отсюда, сокращение, CAD/CAM. Список приложений, большой и быстро растет.
To many people, the computer is a superhuman robot. Indeed, it can perform lightingfast calculations and can perform billions of operations in a second. But the computer is not superhuman for itcan accomplish none of these things by itself. Every computer
now in existence must be told what to do: it must have a set of instructions. The writing of these instructions is called programming. Programming is done by a man.
Для многих людей компьютер — сверхчеловеческий робот. В самом деле, он может выполнять сверхскоростные вычисления и может выполнять миллиарды операций в секунду. Но компьютер не сверхчеловек, так как он не может выполнить ни одну из этих вещей сам по себе. Каждому компьютеру, существующему в настоящее время нужно сказать, что делать: он должна иметь набор инструкций. Написания этих инструкций называется программированием. Программирование осуществляется с помощью человека.
Surely, there are similarities with human brain, but there exists one important difference. Despite all its accomplishments, the electronic brain must be programmed by a human brain.
Конечно, есть сходство с человеческим мозгом, но существует одно важное отличие. Несмотря на все свои достижения, электронный мозг должен быть запрограммирован человеческим мозгом.
Although accepted for different purposes, computers virtually do not differ in
structure. Regardless of their size or purpose most computer systems consist at least of three elements: the input-output ports, the memory hierarchy and the central processing unit.
Хотя принятые в различных целях, компьютеры практически не отличаются по своей структуре. Независимо от их размера или цели большинство компьютерных систем состоят как минимум из трех элементов: портов вводавывода, иерархии памяти и центрального процессора.
The input-output ports are known to be paths whereby information (instructions and data) is fed into the computer or taken out of it.
Порты ввода-вывода, как известно, это каналы, по которым информация (инструкции и данные) подается в компьютер или выводится из него.
There are several types of memory. Memory is essential to the computer’s operation. Items of information can be written to, stored in, retrieved from it on
demand by the central processing unit, or erased32 to make room for other information.
Есть несколько типов оперативной памяти. Память имеет важное значение для работы компьютера. Информация может записываться, храниться, извлекаться из компьютера по требованию центрального процессора, или удалятся, чтобы освободить место для другой информации.
The central processing unit, or CPU, controls the operation of the entire system
by issuing commands to other parts of the system and by acting on the responses. When required, itreads information from the memory, interprets instructions, performs operations on the data according to the instructions, writes the results back into the memory, and moves information between memory levels or through the input-output ports.
Центральный процессор, или просто процессор, управляет работой всей системы путем выдачи команд на другие части системы и, откликается на ответы. При необходимости, он считывает информацию из памяти, интерпретирует инструкции, выполняет операции над данными в соответствии с инструкциями, записывает результаты обратно в память, и передает информацию между уровнями памяти или с помощью портов ввода-вывода.
Advances in microelectronic components led to the development of smaller computers. In 1971 Intel. Corp. delivered the first microprocessor, the 4004. The central processing unit of a computer was put onto a single silicon chip less than 1/4 in square. When a central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is implemented in a single, or very small number of integrated circuits, we call it amicroprocessor. When a
computer incorporates a microprocessor as a major component, we call it a microcomputer. When the entire computer, including CPU, memory and input-output capability, is incorporated into a single 1C, we call the latter a one-chip microcompute.
Достижения в области микроэлектронных компонентов привели к развитию меньших компьютеров. В 1971 году Корпорация Intel поставила первый микропроцессор, 4004. Центральный процессор компьютера был поставлен на одном кристалле кремния менее 1/4 квадрата. Когда центральный процессор (CPU) компьютера реализован в виде одной микросхемы, или в виде очень небольшого количества интегральных схем, мы называем это микропроцессором. Когда компьютер включает в себя микропроцессор в качестве основного компонента, мы называем это микрокомпьютер. Когда весь компьютер, включая процессор, память и порты ввода-вывода, включен в одиночный 1С, мы называем это однокристальным микрокомпьютером.
The first design was followed by many others. The progress toward smaller computers is certain to continue: gradually there appear nano- computers and pico-computers. These computers are more flexible. Modern computers are virtually symbiotic.
Первый проект породил многие другие. Прогресс в сторону меньших компьютеров, несомненно, будет продолжаться: постепенно появляются нанокомпьютеров и пико-компьютеры. Эти компьютеры более гибкие. Современные компьютеры практически симбиотические.
Advances in microelectronics give rise to advances in computers. Computers today are providing an expanding range of services.
Достижения в области микроэлектроники привели к достижениям в области вычислительной техники. Компьютеры сегодня предоставляют расширение спектра услуг.
Computers are classified by size and capability as microcomputers, mainframes and supercomputers, depending on the size of their main memories and on their processing speed.
Компьютеры классифицируются по размеру и возможностям, на микрокомпьютеры, большие компьютеры (ЭВМ) и суперкомпьютеры, в зависимости от размера их основной памяти и от скорости обработки данных.
Most microcomputers are mostly used by individuals.
Большинство микрокомпьютеров в основном используются частными лицами.
Mainframes are used by large corporations, government agencies and other large institutions.
ЭВМ используются крупными корпорациями, правительственными агентствами и другими крупными учреждениями.
Supercomputers are the largest and fastest of all computers. They have memories and processing speeds that may be measured in several picoseconds (trillions of a second). The boundaries separating the categories change frequently as computer technology advances.
Суперкомпьютеры крупные и самые быстрые из всех компьютеров. У них есть память и скорость обработки, которые могут быть измерены в несколько пикосекунд (триллионы секунд). Границы, разделяющие категории часто меняются в зависимости от достижений техники.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Here’s what computer stands for:
Computer doesn’t stand for “Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research.”
Computer isn’t an acronym at all.
Computer is a combination of the Latin words Com and Putare, meaning respectively, “with” (com) and “reckon” (putare).
So if you want to learn all about the tech term computer, then you’re in the right place.
Let’s jump right into it!
Remember on Star Trek when the Captain used to start a conversation with the LCARS (Library Computer Access/Retrieval System) by saying, “Computer…?”
We’ve always enjoyed personifying computers, haven’t we?
Even in day-to-day life, we get a kick out of talking to Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant, imagining that we’re conversing with a humanlike persona, our loyal “Computer” that follows our commands.
In fact, forecasts suggest that by 2024, the number of digital voice assistants will reach 8.4 billion units.
Have you ever wondered where the title “Computer” came from or what the correct computer full form is?
What About that Computer Acronym?
The easiest answer suggests the full form of computer is “Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research.”

Unfortunately, this easy answer is also an urban legend. There is no evidence of that acronym appearing in the 20th century when modern computers debuted.
Besides, that acronym seems dishonest when you consider both the etymology and function of a computer.
A programmable machine “computes” or calculates equations.
Technically speaking, and in the words of programmers, a computer’s function is to respond to a set of instructions and then execute a list of further corresponding instructions.
For us, in simple words, these devices:
- Accept and interpret data
- Process the information
- Produce the desired results
- Store and retrieve data
Truly understanding the computer full form requires a bit of a history lesson.
What Are Human Computers?
According to BBC News, since the verb “compute” was used to refer to performing math equations, humans were the first computers.
We simply used pre-mechanical age devices, like the abacus, to compile our data.
The term “compute” comes from the Latin word “Putare.”
According to Professor William J. Rapaport, the word is a combination of Com and Putare, meaning respectively, “with” (com) and “reckon” (putare).
The compound word, Computare, refers to a reckoning of arithmetic, or to “settle an account.” Now that sounds like something a human might have to do. Robots, not so much!
Ancient Blurbs About Computers
References to the computer date well before the 20th century, but they are always about the act of computing, a distinctly human activity.
For example:
- The Roman poet Virgil wrote in Georgics of computing, or pruning vines
- Historian Tacitus used the word when counting soldiers
- Pliny wrote in Natural History how “the breadth of Asia should be “rightly calculated”, which was the same word—computetur)
- Author Richard Braithwait wrote in The Yong Mans Gleanings that he “had read the truest computer of times”
- Navy Administrator Samuel Pepys wrote of computing money for ships
The first known use of the word computer was in 1613 in a book called The Yong Mans Gleanings by English writer Richard Braithwait.
[Wikipedia]
Computers for Hire
Looking for employment today and searching for “computers” would return very different results than a job search in the 18th or 19th centuries. It was quite common for old job ads to say “hiring computers.”
Nineteenth-century steam-powered robots, you ask? Unlikely! No, the ad implied they wanted human calculators or “computers.”
Essayist and Reverend Jonathan Swift once wrote in the Edinburgh Weekly Journal, describing a young married woman’s job as a computer, one who knows of her husband’s income.
The perception changed, of course, when inventors introduced the first mechanical computer.
Computers By Any Other Name
We have to assume that before computer full form existed, people simply called their pre-mechanical devices “tools” or something similar.
For thousands of years, humans used tools to perform equations and keep account of numbers.
- The Ishango Bone dates back to prehistoric Africa and is thought to be a primitive calculator. Etchings are situated in three columns with marks that have been grouped into sets, implying decimals or prime numbers.
- The abacus dates back to at least 2400 B.C. in ancient Babylonia, or perhaps even longer. Since the word for abacus means literally “tablet,” it could etymologically be the closest relative to a mechanical “computer.”

- The Antikythera mechanism is more complex, so much so that this 100 B.C. era device is considered the first primitive analog computing device.
- Physicist Derek J. de Solla Price once wrote that the Antikythera mechanism could calculate astronomical positions.
What Did We Call Modern Computers?
We didn’t call modern computers “computers,” at least not when they first debuted.
Charles Babbage was the “father of the computer,” but to him and his 19th-century contemporaries, these steam-driven devices were called “machines.”
Babbage said, “A tool is usually more simple than a machine; it is generally used with the hand, while a machine is frequently moved by animal or steam power.”
When he created a highly advanced machine that helped perform navigational calculations, he called it an “Analytical Engine.”

Perhaps the reason these amazing analytical machines were never actually called computers back in the day was that they weren’t yet “programmable” in the literal sense.
They were limited to performing only specific functions.
They were also called all sorts of nicknames other than “computer,” such as:
- In 1927 H. L. Hazen and Vannevar Bush’s “mechanized calculus” machine
- In 1937, George Stibitz and his Model K “Adder”
- Alan Turing’s Universal Turing Machine, or the “computing machine”
The First Robotic “Computer”
By 1938, the name computer in full form applied to non-human computers, that is, the programmable electromechanical analog systems we all know and love.
Curiously, the first time we used the word “robot” was in 1920, after Czech author Karel Capek coined the phrase, robota, meaning “slave labor.” That’s right, so whenever Bender Rodriguez complains about the abuse of robots at the hands of humans, you know he’s got a good point.
The modern colloquial usage of the word “computer” also changed after 1938, with new achievements such as:
- The United States Navy naming their submarine-bound analog system a “Torpedo Data Computer”
- John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry naming the first electronic digital machine the Atanasoff-Berry Computer
- By 1946, the military-created Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) debuted, its complete system weighing 30 tons used for processing (its power literally dimmed the lights of the city of Philadelphia!)
- The ENIAC could perform numerous functions besides ballistics, including weather prediction, atomic energy calculations, and other “general purposes”

For more background on the ENIAC, read more about the first computers and their technologies in Scientific American.
The Marketed “Personal Computer”
The last evolution in computer etymology is the result of great achievements in manufacturing and marketing work alike.
Although modern computers developed rapidly from the 1950s to the 1970s, it took some time to transform the image of a giant machine used to perform highly specialized calculations, to a “microcomputer,” a tool for small businesses and individuals.
Much of the groundwork for the modern computer was laid in 1968 when Douglas Engelbart of SRI International gave the “mother of all demos,” showcasing many modern concepts like the mouse, email, word processing, and even video conferencing.
The identity of the “computer” was just now shaping into something that a modern, non-technical minded audience could embrace—something humanlike, a virtual assistant.
The First Microcomputers
Computers only became identifiable, and thus personalized as a persona, when microcomputers appeared. Competition during the 1970s and 1980s was intense, with many companies competing in this brand new market:
- Micral N debuted in 1972 as a mostly “hobbyist” product
- IBM Special Computer APL Machine Portable came in 1973, which gained a reputation as the first real PC
- IBM 5100 was a milestone, as it could be programmed in BASIC and APL
- Xerox Alto debuted a Graphical User Interface
- Altair 8800, which was the first true commercial success for a PC
- By 1980, the Epson HX-20 became the first portable “laptop” computer to run on rechargeable batteries
The next revolution happened in 1976 when Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak debuted the first Apple computer, which grew beyond the kit-style look of previous computers, marketing to the non-technical minded consumer.
Apple’s revenue from its Macintosh computers has seen an overall growth up to this day, with sales at around 7.1 billion U.S. dollars for the third quarter of 2020 alone.
Tandy made more strides with the TRS- 80, while Commodore released the Amiga, which introduced modern principles like multitasking and a windows operating system.
The Life and Death of a Computer
By 1982, “The Computer” was a household word, publicized by Time magazine, who awarded it “Machine of the Year”.
Marketing evolutions continued in the 1980s and 1990s with video game systems and the universal software-focused approach of Windows and DOS.
All was going well until…well, the computer died! Not so much in a Hal 9000 sort of way, but simply the end of a generation and the reinvention of an old market.
By the time desktops and laptops took a plunge in the 2000 era, in favor of smartphones and tablets, the colloquial use of “Computer” was all but finished.

These new internet-ready devices were computers, but no one called them by the computer full form anymore, nor was a computer acronym necessary.
Worldwide sales for these smartphones have been steadily increasing throughout the years. It is forecasted that by 2021, around 1.5 billion units would be sold to end users.
The “end” of the market even prompted many programmers to give a symbolic eulogy for the death of the computer, a persona we once voted “Machine of the Year.”
Ironically, humans were the first computers, not machines. We didn’t even think of these amazing machines as “computers” until we understood the groundbreaking idea that machines could operate as humans do.
To Be, or Not to Be: Other Vital Tech Words and Their Meanings
Here’s a list of particularly interesting tech acronyms—or maybe they’re not even acronyms?
Learn what these stands for:
- GOOGLE full form: what does it stand for?
- INTERNET full form: what does it stand for?
- WI-FI full form: what does it stand for?
I. The word «computer» comes from a Latin word which means to count.1 A computer is reallу a very special kind of counting machine.
Initially,2 the computer was designed as a tool to manipulate numbers and thus solve arithmetic problems. Although designed originally3 for arithmetic purposes at present it is applicable for a great variety of tasks.
Nowadays computers are considered to be complicated4 machines for doing arithmetic and logic. The computer may be stated to have become an important and powerful tool for collecting, recording,5 analysing, and distributing6 tremendous masses of information.
Viewed7 in the contemporary8 scene and historical perspective the computer simulates man. Indeed,9 two important and highly visible characteristics of man are his intelligence and his ability to perform in and control his environment.10
Significantly, man’s attempts to understand the phenomena of intelligence, control and power has led to simulations of his brain, of himself and of organizational and group structures in which he most often finds himself. In the last 30 years man has made extensive use of the computer for these simulations.
Surely, there are similarities with human brain, but there exists one very important difference. Despite11 all its accomplishments,12 the so-called electronic brain must be programmed by a human brain.
As already stated, originally computers were used only for doing calculations.
Today it would be difficult to find any task that calls for13 the processing of large amounts14 of information that is not performed by a computer. In science computers digest and analyse masses of measurements, such as the sequential15 positions and velocities of a spacecraft and solve extraordinary long and complex mathematical problems, such as the trajectory of the spacecraft. In commerce16 they record and process inventories, purchases (покупка), bills, payrolls (платежная ведомость), bank deposits and the like and keep track of ongoing business transactions.17 In industry they monitor18 and control manufacturing processes. In government they keep statistics and analyse economic information.
A computer system can perform millions of operations a second. In the mid-1950’s the average19 speed of main-memory20 was about 10 ms, in the mid-1960’s 1 ms, in the mid-1970’s a tenth to a hundredth of a microsecond and in the mid-1980’s it largely increased.
The computer’s role is influenced not only by its speed but also by its memory-size. A large memory makes it easier to work with large programs, including data (compare linear programming or regression analysis requiring large matrices).
The increase in main memory capacity has been spectacular21 too: mid-1950’s 100 thousand bits, mid-1960’s 1 to 10 million, mid-1970’s nearly 1 billion bits. Secondary storage22 has been greatly expanded by the use of discs. Primary and secondary storage have been integrated by the virtual memory technique.
Although accepted for different purposes computers virtually do not differ in structure.
Any computer is, architecturally, like any other computer. Regardless23 of their size or purpose most computer systems consist of three basic elements: the input-output ports,24 the memory hierarchy and the central processing unit. The input-output ports are paths whereby25 information (instructions and data) is fed26 into the computer or taken out of it by such means as punch cards,27 magnetic tages and terminals. The memory hierarchy stores the instructions (the program) and the data in the system so that they can be retrieved28 quickly on deinjpd by the central processing unit. The central processing unit controls the operation of the entire29 system by issuing30 commands to other parts of the system and by acting on the responses. When required it reads31 information from mememory, interprets32 instructions, performs operations on the data according to the instructions, writes the results back into the memory and moves information between memory levels or through the input-output ports. The operations it performs on the data can be either arithmetic or logical.
As stated above any computer is, architecturally, like any other computer in the early days of computers. However, there are differences. They are the following: An early processor used to be made of thousands of vacuum tubes. Reliability was measured in mere hours between failures, and the cooling plant was often larger than the computer itself. Then, the transistor was invented. The number of them was enormous in each mainframe. Besides, in computers of the 1950’s, the transistors, diodes, resistors, capacitors and other components were mounted33 on printed-circuit (PC) cards. A typical 5-in. card contained a dozen transistors and a hundred other parts. A card might have contained a single flip-flop34 and a thousand cards were required to build each computer.
In the early 1960’s semiconductors makers created a wholly new technology, a whole flip-flop could be integrated. Several of integrated circuits (ICs) could be mounted on a single printed card.35 Soon, improved fabrication processes enabled even more complex circuit to be created in a single IC. The new technology was called medium-scale integration (MSI), and the older technology was labelled36 small-scale integration (SSI). The progress towards smaller computers continued.
If used for computers discrete transistors were too costly and unreliable, they were too large and too slow.
In the 1960’s advances in microelectronic components led to the development of the minicomputer, followed more recently by an even smaller microcomputer. Both have filled a need for small but relatively flexible37 processing systems able to execute38 comparatively simple computing functions at lower cost.
In 1971, Intel Corp. delivered the first microprocessor, the 4004. All the logic to implement39 the CPU, the central processing unit, of a tiny computer was put onto a single silicon chip less than 1/4-in square. That design was soon followed by many others. The progress toward smaller computers is likely to continue: there is already talk of nano-computers and pico-computers.
When the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is implemented in a single or very small number of integrated circuits, we call it a microprocessor. When a computer incorporates40 a microprocessor as its major component, the resulting configuration is called a microcomputer. When the entire computer, including CPU, memory and input-output capability, is incorporated into a single IC, we also call that configuration a microcomputer. To distinguish41 between the two microprocessor types, we call the latter a one-chip microcomputer.
Modern computers and microelectronic devices have interacted so closely in their evolution that they can be regarded as virtually symbiotic. Microelectronics and data processing are linked.42
Today the hardware in data-processing machines is built out of microelectronic devices. Advances in microelectronic devices give rise to advances in data-processing machinery.
As previously pointed computers today are providing an expanding range of services to rapidly growing pool (количество) of users. Such facilities43 could make our lives easier, and indeed they already enhance the productivity. Yet a bottleneck (трудность) remains which hinders44 the wider availability of such systems; this bottleneck is the man-machine communication barrier.
Simply put, todays systems are not very good at communicating with their users. They often fail45, to understand what their users want them to do and then are unable to explain the nature of the misunderstanding to the user. Communication with the machines is sometimes time-consuming.46 What are the causes of this communication barrier?
One of the most important causes of the man-machine communication barrier is that an interactive computer system typically responds only to commands phrased with total accuracy in a highly restricted47 artificial48 language designed specifically for that system. If a user fails to use this language or makes a mistake, however small, an error49 message50 is the response he can expect.
II. Several developments have helped to reduce programming effort. High-level languages like FORTRAN, ALGOL, PL-1, and COBOL have replaced assembler languages to a great extent. There is a trend51 towards languages with a free format and more error checking.52 Thus programming itself takes less time since fewer errors are made and residual53 errors are detected and corrected more rapidly. ADA seems destined54 to become the dominant programming language of 1980’s. The term «ADA» comes from the name of Byron’s daughter Ada, Lady Lovelace. She was the first programmer in the world.
These high-level languages, however, require more compilation and running time, and more memory space.
Currently,55 almost all man-machine interaction takes place through typed input and output. Superficially,56 at least, it is this mode, that human communication needs.
However, this type of man-machine communication is rapidly becoming outmoded57 by a generation of powerful personal computers. These machines are intended58 for dedicated use by a single individual and feature an integral high-resolution, bit-map, graphics display with a pointing device, as well as a conventional keyboard. This allows the computers to provide multiple independent output channels. Besides extra communication channels, such machines provide for different communication modalities: a graphics screen59 can display line drawings or images60 and produce attention-commanding effects such as highlighting (высвечивать) or flashing the background61 of certain areas of the screen.
The multiple communication channels and modalities allow for more effective interaction.
Recent Computer technology advances are the following: Voice annotations Facsimile images, High-drawn sketches, Animated sequences. The potential advantages of multimedia communications technology are too great to ignore.
Many scientists are conducting a research on man-machine communication. The work is ongoing. Of particular interest are information systems that model complex real-world events.
Active information systems are database processing tools intended to represent and manipulate data descriptions of large real-world systems that have a complex dynamic behaviour.62
It is apparent63 that if the language of recipient and sender differs, the data of the message cannot be used. Problems in understanding the content must be resolved by cooperation between the sender and the recipient.
In automated information systems the computers must receive and at the same time interpret and act on the data. In information systems, to be more explicit, the fields of computers and communications are merging.64
In this case data reliability is a significant design factor. More and more data are stored in machines without paper or manual backup.65 That data must be accurate, protected, and available.
Besides computers and information systems are becoming more distributed. At the same time the integration and coordination of the individual information systems and computers in an organization are becoming more of necessity. This introduces new requirements, design parameters, and tradeoffs.66
These considerations affect system issues ranging from the architecture of specific computers to the architecture of overall information systems.
To sum up, computers have certain disadvantages. We have not given them those common-sense skills67 of interaction and communication that people find so natural and effortless. Nevertheless computers are fast enough to permit man to control mechanisms having rates of response exceeding his own reaction time.
The computer has made it possible to mechanize much of the information interchange and processing that constitute68 the nervous system of our society.
The versatility,69 and convenience70 of the microprocessor has altered the entire architecture of modern computer systems. No longer is the processing of information carried out only in the computer’s central processing unit. Today there is a trend toward distributing more processing capability throughout a computer system, with various areas having smafi local processors for handling operations in those areas.
There are a number of advantages to distributed processing. First, since many elements of the computer can be working on different portions of the same task, the work may be done faster. Second, if one element in the network malfunctions, its workload71 can be shifted to another element or shared among several elements, sothat the entire work is relatively immune to failure. Third, the network can be small enough to be contained within a single laboratory or building, or it can be spread out over a wide area.
A major obstacle72 to designing an effective distributed-processing system is the difficulty involved in writing the system’s software, which must enable the various elements of the network to operate and interact efficiently.
The method of processing data as well as available peripheral devices define computer generations.73 We are now operating third and fourth generation computers and looking ahead to the fifth. An advantage of the fifth generation will be the ability of people without knowledge of programming to use computer terminals. Remote74 processing will be common too.
|
Обзор компонентов Multisim Компоненты – это основа любой схемы, это все элементы, из которых она состоит. Multisim оперирует с двумя категориями… |
Композиция из абстрактных геометрических фигур Данная композиция состоит из линий, штриховки, абстрактных геометрических форм… |
Важнейшие способы обработки и анализа рядов динамики Не во всех случаях эмпирические данные рядов динамики позволяют определить тенденцию изменения явления во времени… |
ТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКАЯ МЕХАНИКА Статика является частью теоретической механики, изучающей условия, при которых тело находится под действием заданной системы сил… |
It is generally seen that most of the students think that computer means either desktop computer or laptop computer. Computers can be of many types. Sometimes the things that we do not consider to be a computer, are also a computer such as calculators, microwaves, digital cameras, etc.
Today, the world is becoming digital, in which the uses of computers is increasing day by day. In such a situation, it is necessary for everyone to know about computer.
Today, whether it is school or college, or any government office, computers are being used everywhere. Nowadays in many places, if you want a job, then you are also asked to have basic knowledge of computer.
So in today’s article, I am going to tell you some basic information about computers.
In this article, we will learn in detail about what is a computer. What is the definition of a computer? And What are the Advantages of a computer?
So without wasting time let’s first know What is a Computer?

Computer is an electronic data processing machine, that takes the data as input from the user then saves that data, And by processing the saved data whatever result comes, it gives the user as output and saves that result for further requirements.
Let’s understand this with an example:
Suppose you want to sum two numbers in the computer, then for this you will have to put two numbers in the computer, then the computer will take those two numbers and add them, and then whatever result will come it will show you on your computer screen.
In this whole process, the two numbers you put in the computer are called input, then the sum of those two numbers is done by the computer is called process. After that, the result you see on the computer screen is called output.
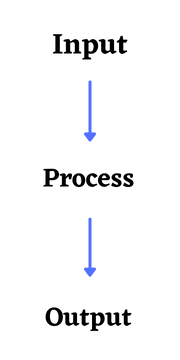
Computers can process both numerical and non-numerical calculations very easily.
Computers run according to the already written programs. Computers have their own memory in which data, programs, and process results are saved.
Physical parts of the computer such as Wires, Transistors, Circuits, Hard Disks are called Hardware, and the programs, applications inside the computer are called Software.
The computer was built to run applications and solve many difficulties through hardware and software.
The word computer originated from the Latin word “Computare” which means “Computation“. It’s believed that the first computer was Analytical Engine, invented by Charles Babbage in 1837. Therefore, Charles Babbage is also known as the father of computer or the inventor of computer.
But even before Charles Babbage built the Analytical Engine, the work of computer development was going on. As a result, many advanced computers came into existence.
Let’s understand how the development of computer has taken place.
How Did the Computer Develop?
In ancient times when people did not have much facilities and people hunt and lives. In those times If people had to do some calculations then for this, they used sticks, stones, and bones.
As time went gone, the brain of the people also started developing and they developed many machines for calculation.
It believed that the development of computers began with the invention of Abacus. It was invented by Tim Cranmer. After Abacus, Napier’s Bones computer was invented and then Slide Rule Computers came.
In this way, new computer technologies started coming into existence with the passage of time.
Let’s understand the development of computers through this table.
| Computer | Year | Developed By |
|---|---|---|
| Abacus | 2400 BC | Tim Cranmer |
| Napier’s Bones | 1614 | John Napier |
| Slide Rule | 1622 | William oughtred |
| Pascaline | 1642 | Blaise Pascal |
| Stepped Reckoner | 1672 | Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz |
| Jacquard loom | 1801 | Joseph Marie Jacquard |
| Arithmometer | 1820 | Thomas De Colmar |
| Difference Engine | 1822 | Charles Babbage |
| Analytical Engine | 1834 | Charles Babbage |
| Scheutizian Calculation Engine | 1843 | Pearl George Scheutiz |
| Tabulating machine | 1890 | Herman Hollerith |
| Harvard mark 1 | 1937-1944 | Dr.Howard Aiken |
| Z1 | 1936-1938 | Konrad Zuse |
| Atanasoff-Berry Computer | 1939 -1942 | John Vincent Atanasoff And Clifford Berry |
| ENIAC | 1946 | John Mauchly And J. Presper Eckert |
| EDVAC | 1949 | Von Neumann |
| UNIVAC 1 | 1951 | J. Presper Eckert And John Mauchly |
| Osborne 1 | 1981 | Osborne Computer Corporation |
Friends, if you want to know about these computers in detail, then read this article What is the history of computer? How did it develop?
Let’s now, we will learn what is the definition of a computer.
What is the Definition of a Computer?
“A computer is an electronic device that will take some data as input, process it, and gives output“. when any device fulfills these four conditions then that is a computer.
It is generally seen that most students think, computer means either a desktop computer or a laptop computer. Computers can be of many types. Many times the things that we do not consider to be a computer, are also a computer.
Like calculators, they also a computer because it is an electronic device, it also has some input, processing, and output.
The laptop computer and desktop computer are a General Purpose computer, we are able to do all kinds of work in these computers. In this, we can also play games, edit photos, listen to songs, even do programming, so these are all general-purpose computers.
But there are some computers that are made to do some specific tasks, such as washing machines, that is also a computer. If it has a microprocessor chip, it will also work according to the pre-set command, the microwave is also a computer. A digital camera is also a computer.
These are all electronic devices, they have a chip, it is an electronic circuit and it has input, processing, and output. So, all of them are also a computer.
Now you know what is a computer and what is the definition of a computer. Now Let’s learn about the basic parts of a computer.
What are the Basic Parts of a Computer?
- Processor -: It executes the instructions of hardware and software. It is also called CPU (Central Processing Unit). The processor is the brain of the computer because it works all tasks of the computer.
- Memory -: This is the primary memory that performs data transfer between CPU and Storage.
- Motherboard -: This is the main part of a computer that connects the remaining parts of the computer.
- Storage Device -: It stores data permanently in the computer such as a hard disk.
- Input Device -: It helps the user to input in the computer. Keyboard is a good example of an input device.
- Output Device -: It helps to show the output to the user. Monitor is a good example of an output device.
These were some basic parts of a computer without which computer cannot work.
Let’s now learn about some types of computer.
Types of Computer
A computer can be divided into several parts based on different criteria such as the ability to handle the data of the computer and the size of the computer.
Based on size, computer is divided into five parts -:
- Microcomputer
- Minicomputer
- mainframe computer
- Supercomputer
- Workstation
#1. Microcomputer
- A microcomputer is a single-user computer.
- Microcomputers are low speed and low storage capacity as compared to other types of computers. It uses a microprocessor as a CPU.
- The first microcomputer was built using an 8-bit microprocessor.
- Some examples of Microcomputers – Laptop computers, desktop computers, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), tablets, and smartphones.
- Microcomputers were generally made for general use such as Browsing, Searching for Information, Internet, MS Office, Social Media, etc.
#2. Minicomputer
- Minicomputers are also known as “Midrange Computers”.
- The mini-computer has been designed in such a way that it can support a lot of people at the same time.
- It is a computer with a mid-size multiprocessing system that is capable of supporting 250 users simultaneously, so it is commonly used by small businesses and firms.
- It is used for a specific purpose in different departments in a company. For example, Admission department of the university can use a mini-computer for its work.
#3. Mainframe computer
- Mainframes are very large in size and very expensive computer.
- It is a multiuser computer which is capable of supporting thousands of people very easily.
- Mainframe computers are mostly used by big companies and government organizations so that they can do their work easily. they can store and process large amounts of data.
- For example, universities, banks, and insurance companies uses mainframe computers to sequentially store the data of their students, customers, and policyholders.
#4. Supercomputer
- Supercomputers are very fast and very expensive computers compared to all other computers.
- Supercomputers have very high storage capacity.
- The speed of these computers is very high and they can work on Millions of Instruction every second.
- Supercomputers are used to solve large-scale numerical problems, in specific tasks and specific applications such as engineering and scientific disciplines, including weather forecasting, space research, electronics, petroleum engineering, medicine, and much more.
- For example, NASA uses supercomputers to launch satellites, monitor and control space satellites.
#5. Workstation
- It is a single-user computer. However, it is like a personal computer, which has a more powerful microprocessor and a higher-quality monitor than a microcomputer.
- Depending on storage capacity and speed, it falls between a Micro Computer and a Mini Computer.
- Workstations are commonly used for special applications such as desktop publishing, software development, and engineering applications (CAD / CAM).
- Workstations typically come with a large, high-resolution graphics screen, graphical user interface, inbuilt network support, and large amounts of RAM,
- Most workstations also have a disk storage device such as a disk drive, but a special type of workstation, called a diskless workstation, comes without a disk drive.
Advantages of Computer
- Increases your productivity
- Connects to the internet
- Storage
- Organized data and information
- Improves your abilities
- Help for the Physically Challenged
- Entertains you
1. Increases your Productivity
Computers increase your productive capacity. For example, if you have a basic understanding of word processors, then you can easily create a document, edit it, and you can save it if necessary. You can also print very easily and quickly.
2. Connects to the Internet
The computer helps you to connect to the internet, it helps you to send emails, browses about anything, gathers information, use platforms like social media (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp), etc. After connecting to the Internet, you can easily connect with your friend and your family, even if it is far away from you.
3. Storage
You can store a lot of data on the computer, such as you can keep an ebook, a project, a document, movies, pictures, songs, and much more.
4. Organized data and Information
Computers provide you the facility to store data, as well as you can share it with anyone. For example, you can create different folders in a computer to store different types of data and keep your data in it. And if you need that data, you can search it easily.
5. Improves your Abilities
It helps you to write English or Hindi well, whether or not you know more about its grammar and spelling. Similarly, if you do not know math and want to do some calculations, then first you have to save it on the computer, then you can calculate it with the help of computer and save its result on the computer.
6. Helping the Physically Disabled
It can be used to help physically handicapped people. Such as Stephen Hawking, who used a computer to speak, because they were incapable of speaking.
It is also used to help blind people. For this, special software is installed which reads what is on the screen and helps blind people to understand.
7. Entertains you
Computers are used for watching movies, playing games, listening to songs, etc.
The computer has become an important part of our life. There are many things in our daily life, for which we depend on the computer. Some common examples are:
ATM (Automated Teller Machine): When you are withdrawing money from ATM, then you are using a computer that enables you to give instructions to ATM and withdraw cash accordingly.
Digital Currency -: The computer keeps a record of the transactions in your account and your balance and stores the money deposited in your bank account as a digital record or digital currency in the bank.
Trading -: Use of computers for day-to-day trading in the stock market. There are many advanced algorithms based on computers that handle business without involving humans.
Smartphone -: The smartphone we use throughout the day for making calls, sending text messages, browsing is a computer itself.
VoIP -: All the voice-over IP communication is handled by the computer.
So friends, by this time you must have understood what is a computer?, What is the definition of a Computer, and what is the use of a computer?
Let’s now understand what is the full form of computer.
What is the Full form of Computer?
Oftentimes people ask their friends what is the full form of a computer? which most people do not know.
Here, let me tell you that there is no standard full form of computer, but a full form of computer is very famous and which is – “Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used Technical Educational Research“
| C | Commonly |
| O | Operated |
| M | Machine |
| P | Particularly |
| U | Used |
| T | Technical |
| E | Educational |
| R | Research |
Interesting Facts About Computers
Some interesting facts about the computer are as follows:
- The ENIAC considered the first electronic computer, weighed more than 27 tons and a size of 1800 sq ft.
- You can easily write “TYPEWRITER” (which is the longest word) using the text of only one row of the computer keyboard.
- Do you know the first computer mouse was made of wood? Which was built by Doug Engelbart around 1964.
- More than 5000 new computer viruses are released every month in the world.
- You must have heard the names of HP, Microsoft, and Apple, a very common interesting thing between these companies is that all were started in a garage.
- The original name of Windows was Interface Manager.
- The first microprocessor made by Intel was the “4004”. It was designed for a calculator.
- A man usually blinks 20 times a minute, but when using a computer, he only blinks 7 times a minute.
- The first word spoken on the Internet is “lo”. Actually, the word was “Login”, but the computer crashed after two characters. |
- Windows os does not allow us to create folders named CON, PRN, AUX, or NUL because these are reserved keywords by the DOS.
- IBM PC was designed by a group of 12 engineers.
Let’s understand some of the most Frequently asked questions.
FAQ -: Frequently Asked Questions
Who Invented Computer?
The British mathematician Charles Babbage invented the computer in 1837, so Charles Babbage is also called the Father of Computer, he created an Analytical Engine which is said to be the first computer in the world.
What is a Computer in Short Answer
A computer is an electronic machine that takes data as input, processes it, and gives the result to the user as output. Any machine that does all these things is a computer.
Which was the First Computer in the world
ENIAC was the first computer in the world that was built by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert
- What is PC
- What is MAC Computer
- Features of Computer
- Use of Computer
- History of Computer
- Generations of Computers
- Types of Computers
- What is Supercomputer
Computer Components
- Basic Components of Computer
- What is Input Device
- What is Output Device
- What is CPU
- What is Hardware
- What is Software
Computer Memory
- What is Memory
- What is Register Memory
- What is Cache Memory
- What is Primary Memory
- What is RAM
- What is ROM
- What is Secondary Memory
- What is Floppy Disk
- What is Magnetic Disk
- What is Magnetic Tape
- What is an optical disk
- What is Memory Units
- What is Computer Ports
- What is Data Information and Knowledge
Conclusion
Friends, after reading this post You must have known very well what is a computer What is the definition of it? And what are the features of a computer?
I hope you have found the answer to your question and you will not have to search about Computer.
However, if you want any information related to this post or related to computer science, then comment below I will clear your all doubts.
Friends, if you liked this post, then definitely share this post with your friends so that they can get information about the Computer.
To get the Computer Science, Programming Language, Coding, C, C ++, related information subscribe to our website newsletter. So that you will get information about our upcoming new posts soon.
Jeetu Sahu is A Web Developer | Computer Engineer | Passionate about Coding, Competitive Programming, and Blogging









