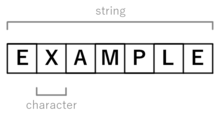
A character is any letter, number, space, punctuation mark, or symbol that can be typed on a computer. The word “computer,” for example, consists of eight characters. The phrase “Hi there.” takes up nine characters.The list of characters that can be typed is defined by the ASCII and extended ASCII set.
Contents
- 1 What are characters example?
- 2 What is a character in letters?
- 3 What are normal characters?
- 4 What does char mean in computer?
- 5 What is characters in a password?
- 6 Are characters letters or words?
- 7 What is character letter and number?
- 8 How do you write character letter?
- 9 What are the types of characters?
- 10 Is a character in C?
- 11 What are characters in a story?
- 12 Are characters stand for any character?
- 13 Is a character in Java?
- 14 What is a character number?
- 15 What is 6 characters in a password example?
- 16 What are 4 characters in a password?
- 17 How do I get special characters on my keyboard?
- 18 What are the 4 types of characters?
- 19 Are texts limited to 160 characters?
- 20 What are characters and words?
What are characters example?
Examples of characters include letters, numerical digits, common punctuation marks (such as “.” or “-“), and whitespace.Examples of control characters include carriage return or tab, as well as instructions to printers or other devices that display or otherwise process text.
What is a character in letters?
In general, a “character” is any mark or symbol that can appear in writing. A “letter” is a character that is part of an alphabet. Basically, a character that represents a sound in the language and that can be combined with other characters to form words.
What are normal characters?
In regular expressions, a normal character is an atom that denotes the singleton set of strings containing only itself.
What does char mean in computer?
In computer science, a character is a display unit of information equivalent to one alphabetic letter or symbol. This relies on the general definition of a character as a single unit of written speech. Character can also be abbreviated as “chr” or “char.”
What is characters in a password?
Passwords should contain three of the four character types: Uppercase letters: A-Z. Lowercase letters: a-z. Numbers: 0-9.
Are characters letters or words?
Senior Member. A character is a single letter, number, punctuation mark or space. Most word processing programs count the characters for you.
What is character letter and number?
‘Letter’ typically means alphabet, while ‘character’ could mean alphabet, numbers or special characters (@, #, £, etc).
How do you write character letter?
How to write a character reference letter
- Start by explaining your relationship to the candidate.
- Include long you’ve known the candidate.
- Add positive personal qualities with specific examples.
- Close with a statement of recommendation.
- Offer your contact information.
What are the types of characters?
The different types of characters include protagonists, antagonists, dynamic, static, round, flat, and stock. They can both fit into more than one category and change from one category to another throughout the course of a story.
Is a character in C?
C isalpha()
In C programming, isalpha() function checks whether a character is an alphabet (a to z and A-Z) or not. If a character passed to isalpha() is an alphabet, it returns a non-zero integer, if not it returns 0. The isalpha() function is defined in <ctype.
What are characters in a story?
A character is a person, animal, being, creature, or thing in a story. Writers use characters to perform the actions and speak dialogue, moving the story along a plot line.
Are characters stand for any character?
A character is any letter, number, space, punctuation mark, or symbol that can be typed on a computer. The word “computer,” for example, consists of eight characters.
Is a character in Java?
An object of type Character contains a single field, whose type is char .The Java compiler will also create a Character object for you under some circumstances. For example, if you pass a primitive char into a method that expects an object, the compiler automatically converts the char to a Character for you.
What is a character number?
A character is, well, a single character.If we have a variable which contains a character value, it might contain the letter `A’, or the digit `2′, or the symbol `&’. A string is a set of zero or more characters.
What is 6 characters in a password example?
Password is only 6 characters long. Password is 8 characters long. The password must contain at least three character categories among the following: Uppercase characters (A-Z)
Complexity requirements.
| Example | Valid | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Apple$$$ | No | Password contains a single English common word (“apple”). |
What are 4 characters in a password?
There are four types of characters you can use in passwords:
- lower-case letters (a, b, c)
- upper-case letters (A, B, C)
- digits (1, 2 3)
- “special characters,” which include punctuation (. ; !) and other characters (# * &)
How do I get special characters on my keyboard?
Entering special characters with the keyboard
On Windows, you can enter special characters directly from the keyboard using the numeric keypad. To do this, you must hold down the ALT key while typing a sequence of numbers. Each sequence corresponds to a different character.
What are the 4 types of characters?
One way to classify characters is by examining how they change (or don’t change) over the course of a story. Grouped in this way by character development, character types include the dynamic character, the round character, the static character, the stock character, and the symbolic character.
Are texts limited to 160 characters?
Yes. The maximum length of text message that you can send is 918 characters. However, if you send more than 160 characters then your message will be broken down in to chunks of 153 characters before being sent to the recipient’s handset.
What are characters and words?
A character in say English is the same as a letter of the alphabet. While a word can consist of only one letter (e.g., “I, a”) most words consist of multiple letters (or characters). A word, roughly defined, is a string of letters that carries a meaning and which can stand alone.
Can anyone tell me the difference between a letter and a character in the English language ?
What I found so far:
- letter is the basic unit of alphabet and
- character is a symbol.
Is there any elaborate explanation, please? I am having trouble understanding the nuances of what that means. When is something a character but not a letter, and vice versa? Is there any overlap between the two terms?
J.R.♦
109k9 gold badges160 silver badges288 bronze badges
asked Apr 23, 2015 at 6:43
1
You’ve asked for an «elaborate» explanation, so I’ll elaborate.
-
A character is a typographical symbol. For example, any of these could be classified as characters:
$ A m ; * 3 + -
A letter is a symbol corresponding to a letter in an alphabet, such as M or G. One dictionary defines it as:
letter (noun) a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech; any of the symbols of an alphabet (from NOAD)
Now, for some fun facts:
-
The English language has twenty-six letters, which are represented using fifty-two characters (each letter has an upper-case and lower-case character version).
-
The same letter can be represented by different-looking symbols (also known as fonts).
-
What might be a letter in some languages could be considered a symbol in others. For example, µ is a Greek letter, but an English symbol. Also, ñ is a letter in Spanish, but, in English, one might describe that as «the letter n with a tilde over it.»
-
The two are not mutually exclusive – a letter can function as a symbol. For example, the c in cat functions as a letter, but the c in E = mc2 functions as a symbol for a constant (the speed of light).
In summary, all letters can be symbols, but not all symbols can function as letters.
Fun exercise for the learner
From Wikipedia, under its entry for Angstrom:
The ångström or angstrom is a unit of length equal to 10−10 m (one ten-billionth of a metre) or 0.1 nm. Its symbol is Å, a letter in the Scandinavian alphabets. (emphasis added)
So, is Å a letter, or a symbol?
answered Apr 23, 2015 at 9:22
6
In general, a «character» is any mark or symbol that can appear in writing.
A «letter» is a character that is part of an alphabet. Basically, a character that represents a sound in the language and that can be combined with other characters to form words.
So in English, the letters are A-Z, in both capital and small versions. Characters include the letters, and also punctuation marks like a period or comma, and other symbols included in writing, like a dollar sign.
Note that in the computer world, «character» has a somewhat more specific technical meaning: it’s a value from the «character set» represented by a code and that can be stored in a character or string variable. The old ASCII character set includes a number of «non-printable characters», control codes that were sent between devices. The idea of «non-printable characters» doesn’t make much sense in conventional writing and printing.
answered Apr 23, 2015 at 7:07
JayJay
59.5k1 gold badge63 silver badges128 bronze badges
4
According to Oxford Learners Dictionary:
character:
- a letter, sign, mark or symbol used in writing, printing or computers
-e.g) Chinese characters / a line of 30 characters long
letter:
- a written or printed sign representing a sound in speech
-e.g,) ‘B’ is the second letter of the alphabet.
Write your name in capital letters.
So we can conclude that a letter is a kind of character that represents a sound in speech.
answered Apr 23, 2015 at 7:07
You’ve pretty much hit the nail on the head except that a character can be a letter from the alphabet as well as a symbol.
Look at it this way:
Imagine it like a role playing video game; Character is just the overall name of what the main player is, while Letter is their class/job role.
pyobum
2,5451 gold badge23 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Apr 23, 2015 at 8:52
1
What these terms mean depends on the context. Since we are using the internet, let’s choose digital representations of text and Unicode as our context.
In Unicode, a character is an idea or abstraction, and what we in the past referred to as a letter (or glyph) is the visual representation of that character, its image.
Character : «Infinity»
Glyph: ∞
The character is a unique identity and is assigned a unique identifier known as its codepoint. The codepoint for Infinity is 221E (hex).
Character: «Exclamation Mark»
Glyph: !
It can get a little circular when the name for the character uses a physical representation of the character it’s naming:
Character: «Latin Capital Letter A»
Glyph: A
answered Apr 23, 2015 at 11:31
TᴚoɯɐuoTᴚoɯɐuo
119k7 gold badges98 silver badges199 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Have you ever heard people referring to “Letters” and “Characters”, and found yourself confused? Most people seem unsure about what each one is, and what they represent.
Let’s find out what is a “Letter” and what is a “Character”, with some helpful examples to clarify the purpose of each.
Every “Letter” is a “Character”, but “Characters” comprise a larger group of things. Any “Letter”, number, sign, or symbol used to write or print content is a “Character”. So it’s not about the difference between “Letter” and “Character”, but the fact that “Letters” are a subset of “Characters”.
Take a look at the examples below:
- In Phillip’s line of work, every word, letter, and character should be accounted for.
- Blanca and Joanna communicated using characters that only they knew the meaning of.
- The teacher gave each student a big letter for the activity.
The examples show how “Letter” and “Character” are different concepts. They aren’t synonyms and can’t interchange.
Although “Letter” and “Character” are words connected to the idea of writing, creating content, and spreading information, they indicate different things. Always remember that “Character” is the larger group of symbols (which include “Letters”) used to communicate.
The first sentence in the example differentiates “Letter”, “Character” and word, as three separate things.
What Is a “Letter”?
A “Letter” is a set of symbols used to write language. They also represent a sound that is connected to the letter, used for oral communication. Equal letters may have completely different sounds, depending on the language they’re connected to, as well as some alphabets are different than others.
The Cambridge Dictionary agrees with our definition and adds that a “Letter” can also indicate a “message from one person to another”, and “a particular standardized size of paper”. For this article, the definition we’ll focus on is the one related to language.
Take a look at some examples below:
- Brianna wrote her name in large letters, on the board.
- Jimmy is learning his letters, and can now say all vowels.
- You should print your name on the form, making sure all letters are clear and readable.
- I was asked to transcribe a text, but some letters are impossible to read.
- I want to learn braille, but I think I should begin by learning the letters.
“Letters” can be different from one language to another. The alphabet for the English language contains 26 “Letters” which are 5 vowels and 21 consonants. Different languages have completely different alphabets, such as the Hebrew alphabet or the Greek alphabet, for example.
What Is a “Character”?
A “Character” is a letter, number, or any other mark or sign used in writing or printing. It also includes the space that those symbols would take. All “Letters” are “Characters”, but not all “Characters” are “Letters”.
The Cambridge Dictionary agrees with our definition of “Character”, adding that this word also refers to personality traits and, specifically, the quality of dealing well with challenges. To compare “Character” with “Letter” we’ll focus only on the definition related to language.
Take a look at some examples:
- I hate that now every password we create needs a special character.
- Joseph has a tattoo of a Japanese character.
- How many characters does a computer screen has?
- I couldn’t read the sign, because I wasn’t familiar with the character in it.
- Indian characters are very hard to read, but you’ll learn if you make an effort.
There are many characters all over the world, related to different cultures. Also, similar characters may have different meanings in different cultures.
Are “Characters” Words or Letters?
“Characters” aren’t words or letters. All “Letters” are “Characters”, but “Characters” are more than just letters. Also, “Characters” form words when put together.
So we can say that words are formed by “Characters”. However, “Characters” can have meaning by themselves, without the need to be combined form words.
Final Thoughts
“Letters” and “Characters” belong to the same realm but are different things. “Characters” are all “Letters”, symbols, numbers, or signs used to write or print content. “Letters” are a set of symbols used to write language, that also carries a sound (used for spoken communication).
Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer and machine-based telecommunications terminology, a character is a unit of information that roughly corresponds to a grapheme, grapheme-like unit, or symbol, such as in an alphabet or syllabary in the written form of a natural language.[1]
Examples of characters include letters, numerical digits, common punctuation marks (such as «.» or «-«), and whitespace. The concept also includes control characters, which do not correspond to visible symbols but rather to instructions to format or process the text. Examples of control characters include carriage return and tab as well as other instructions to printers or other devices that display or otherwise process text.
Characters are typically combined into strings.
Historically, the term character was used to denote a specific number of contiguous bits. While a character is most commonly assumed to refer to 8 bits (one byte) today, other options like the 6-bit character code were once popular,[2][3] and the 5-bit Baudot code has been used in the past as well. The term has even been applied to 4 bits[4] with only 16 possible values. All modern systems use a varying-size sequence of these fixed-sized pieces, for instance UTF-8 uses a varying number of 8-bit code units to define a «code point» and Unicode uses varying number of those to define a «character».
Encoding[edit]
Computers and communication equipment represent characters using a character encoding that assigns each character to something – an integer quantity represented by a sequence of digits, typically – that can be stored or transmitted through a network. Two examples of usual encodings are ASCII and the UTF-8 encoding for Unicode. While most character encodings map characters to numbers and/or bit sequences, Morse code instead represents characters using a series of electrical impulses of varying length.
Terminology[edit]
Historically, the term character has been widely used by industry professionals to refer to an encoded character, often as defined by the programming language or API. Likewise, character set has been widely used to refer to a specific repertoire of characters that have been mapped to specific bit sequences or numerical codes. The term glyph is used to describe a particular visual appearance of a character. Many computer fonts consist of glyphs that are indexed by the numerical code of the corresponding character.
With the advent and widespread acceptance of Unicode[5] and bit-agnostic coded character sets,[clarification needed] a character is increasingly being seen as a unit of information, independent of any particular visual manifestation. The ISO/IEC 10646 (Unicode) International Standard defines character, or abstract character as «a member of a set of elements used for the organization, control, or representation of data». Unicode’s definition supplements this with explanatory notes that encourage the reader to differentiate between characters, graphemes, and glyphs, among other things. Such differentiation is an instance of the wider theme of the separation of presentation and content.
For example, the Hebrew letter aleph («א») is often used by mathematicians to denote certain kinds of infinity (ℵ), but it is also used in ordinary Hebrew text. In Unicode, these two uses are considered different characters, and have two different Unicode numerical identifiers («code points»), though they may be rendered identically. Conversely, the Chinese logogram for water («水») may have a slightly different appearance in Japanese texts than it does in Chinese texts, and local typefaces may reflect this. But nonetheless in Unicode they are considered the same character, and share the same code point.
The Unicode standard also differentiates between these abstract characters and coded characters or encoded characters that have been paired with numeric codes that facilitate their representation in computers.
Combining character[edit]
The combining character is also addressed by Unicode. For instance, Unicode allocates a code point to each of
- ‘i ’ (U+0069),
- the combining diaeresis (U+0308), and
- ‘ï’ (U+00EF).
This makes it possible to code the middle character of the word ‘naïve’ either as a single character ‘ï’ or as a combination of the character ‘i ’ with the combining diaeresis: (U+0069 LATIN SMALL LETTER I + U+0308 COMBINING DIAERESIS); this is also rendered as ‘ï ’.
These are considered canonically equivalent by the Unicode standard.
char[edit]
A char in the C programming language is a data type with the size of exactly one byte,[6] which in turn is defined to be large enough to contain any member of the «basic execution character set». The exact number of bits can be checked via CHAR_BIT macro. By far the most common size is 8 bits, and the POSIX standard requires it to be 8 bits.[7] In newer C standards char is required to hold UTF-8 code units[6] which requires a minimum size of 8 bits.
A Unicode code point may require as many as 21 bits.[8] This will not fit in a char on most systems, so more than one is used for some of them, as in the variable-length encoding UTF-8 where each code point takes 1 to 4 bytes. Furthermore, a «character» may require more than one code point (for instance with combining characters), depending on what is meant by the word «character».
The fact that a character was historically stored in a single byte led to the two terms («char» and «character») being used interchangeably in most documentation. This often makes the documentation confusing or misleading when multibyte encodings such as UTF-8 are used, and has led to inefficient and incorrect implementations of string manipulation functions (such as computing the «length» of a string as a count of code units rather than bytes). Modern POSIX documentation attempts to fix this, defining «character» as a sequence of one or more bytes representing a single graphic symbol or control code, and attempts to use «byte» when referring to char data.[9][10] However it still contains errors such as defining an array of char as a character array (rather than a byte array).[11]
Unicode can also be stored in strings made up of code units that are larger than char. These are called «wide characters». The original C type was called wchar_t. Due to some platforms defining wchar_t as 16 bits and others defining it as 32 bits, recent versions have added char16_t, char32_t. Even then the objects being stored might not be characters, for instance the variable-length UTF-16 is often stored in arrays of char16_t.
Other languages also have a char type. Some such as C++ use 8 bits like C. Others such as Java use 16 bits for char in order to represent UTF-16 values.
See also[edit]
- Character literal
- Character (symbol)
- Fill character
- Combining character
- Universal Character Set characters
- Homoglyph
References[edit]
- ^ «Definition of CHARACTER». www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
- ^ Dreyfus, Phillippe (1958). «System design of the Gamma 60». Managing Requirements Knowledge, International Workshop on, Los Angeles. New York. pp. 130–133. doi:10.1109/AFIPS.1958.32.
[…] Internal data code is used: Quantitative (numerical) data are coded in a 4-bit decimal code; qualitative (alpha-numerical) data are coded in a 6-bit alphanumerical code. The internal instruction code means that the instructions are coded in straight binary code.
As to the internal information length, the information quantum is called a «catena,» and it is composed of 24 bits representing either 6 decimal digits, or 4 alphanumerical characters. This quantum must contain a multiple of 4 and 6 bits to represent a whole number of decimal or alphanumeric characters. Twenty-four bits was found to be a good compromise between the minimum 12 bits, which would lead to a too-low transfer flow from a parallel readout core memory, and 36 bits or more, which was judged as too large an information quantum. The catena is to be considered as the equivalent of a character in variable word length machines, but it cannot be called so, as it may contain several characters. It is transferred in series to and from the main memory.
Not wanting to call a «quantum» a word, or a set of characters a letter, (a word is a word, and a quantum is something else), a new word was made, and it was called a «catena.» It is an English word and exists in Webster’s although it does not in French. Webster’s definition of the word catena is, «a connected series;» therefore, a 24-bit information item. The word catena will be used hereafter.
The internal code, therefore, has been defined. Now what are the external data codes? These depend primarily upon the information handling device involved. The Gamma 60 [fr] is designed to handle information relevant to any binary coded structure. Thus an 80-column punched card is considered as a 960-bit information item; 12 rows multiplied by 80 columns equals 960 possible punches; is stored as an exact image in 960 magnetic cores of the main memory with 2 card columns occupying one catena. […] - ^ Blaauw, Gerrit Anne; Brooks Jr., Frederick Phillips; Buchholz, Werner (1962), «4: Natural Data Units» (PDF), in Buchholz, Werner (ed.), Planning a Computer System – Project Stretch, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc. / The Maple Press Company, York, PA., pp. 39–40, LCCN 61-10466, archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-04-03, retrieved 2017-04-03,
[…] Terms used here to describe the structure imposed by the machine design, in addition to bit, are listed below.
Byte denotes a group of bits used to encode a character, or the number of bits transmitted in parallel to and from input-output units. A term other than character is used here because a given character may be represented in different applications by more than one code, and different codes may use different numbers of bits (i.e., different byte sizes). In input-output transmission the grouping of bits may be completely arbitrary and have no relation to actual characters. (The term is coined from bite, but respelled to avoid accidental mutation to bit.)
A word consists of the number of data bits transmitted in parallel from or to memory in one memory cycle. Word size is thus defined as a structural property of the memory. (The term catena was coined for this purpose by the designers of the Bull GAMMA 60 [fr] computer.)
Block refers to the number of words transmitted to or from an input-output unit in response to a single input-output instruction. Block size is a structural property of an input-output unit; it may have been fixed by the design or left to be varied by the program. […] - ^ «Terms And Abbreviations». MCS-4 Assembly Language Programming Manual — The INTELLEC 4 Microcomputer System Programming Manual (PDF) (Preliminary ed.). Santa Clara, California, USA: Intel Corporation. December 1973. pp. v, 2-6. MCS-030-1273-1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-03-01. Retrieved 2020-03-02.
[…] Bit — The smallest unit of information which can be represented. (A bit may be in one of two states I 0 or 1). […] Byte — A group of 8 contiguous bits occupying a single memory location. […] Character — A group of 4 contiguous bits of data. […]
(NB. This Intel 4004 manual uses the term character referring to 4-bit rather than 8-bit data entities. Intel switched to use the more common term nibble for 4-bit entities in their documentation for the succeeding processor 4040 in 1974 already.) - ^ Davis, Mark (2008-05-05). «Moving to Unicode 5.1». Google Blog. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ^ a b «§1.7 The C++ memory model / §5.3.3 Sizeof». ISO/IEC 14882:2011.
- ^ «<limits.h>». pubs.opengroup.org. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
- ^ «Glossary of Unicode Terms – Code Point». Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ «POSIX definition of Character».
- ^ «POSIX strlen reference».
- ^ «POSIX definition of Character Array».
External links[edit]
- Characters: A Brief Introduction by The Linux Information Project (LINFO)
- ISO/IEC TR 15285:1998 summarizes the ISO/IEC’s character model, focusing on terminology definitions and differentiating between characters and glyphs
Before we move to the procedures involves, lets enlighten ourselves on the definition and necessary information surrounding character letter writing.
What Is a Character Letter?
A character letter, as the name implies, is a letter about a character. Character, in this context, refers to the distinctive characteristics or unique qualities of a person. Simply put, a character is a personality. Also, letter in this discourse signifies a written piece that communicates relevant information.
Before one can give accurate information about a person, he/she must have spent some time learning about that person, probably by engaging in activities with the person or spending time with him/her. Elsewise, the information may be vague of credibility as it will be concentrated with speculations and thoughts which may not be the truth about the person written about.
Therefore, a character letter is a written piece about ones personality by someone who has good knowledge about the person.
A character letter can also be described as a personal reference since it emphasizes on the personal qualities of an individual. It is not the same as the professional reference which dwells on the skills and professional qualities of a person. A person who writes a reference is known a reference.
What Is the Essence of a Character Letter?
A character letter is required when knowledge of the personality of an individual is wanted for one reason or the other. A judge may want a personal reference about a person who s/he is about to pass judgement on.
Also, a character reference can be included among the requirements for admission into an academic institution, grant of citizenship or employment at a cooperate body. It may also be required of someone who intends to join an organization or body. In short, a character letter is required for numerous reasons at countless fields of organization.
The demand for character references corresponds with their relevance. Though, generally, it exposes one’s personal qualities and skills to the requirer, the essence of this kind of reference is peculiar to the area where it is required.
Apart from it being demanded for, a personal reference may serve as an addition to a professional reference. One may include it among his or her credential when applying for a job. For instance, a person who has barely been employed can leverage on a character reference instead of a professional one.
Before Writing a Character Letter
It is important one examines shim/herself before agreeing to write a character letter for someone. One should be sure she/he can write positively, yet honestly about the person. One should also understand the reason for or purpose of the letter before signing up for the task of writing the character reference. One must not take these with levity as it may affect the effective role the letter is supposed to play.
How to Write a Character Letter
There are different ways of writing character letters just like there are different reasons why they are being written. The purpose of a character reference will determine the content of the letter. They are all to be written as letters addressing the appropriate officers all the same. A character letter written for the defendant in a court case will be addressed to the presiding magistrate while one written for a job-seeker will be written to the office of the ‘employer’; depending on the job.
How to Write a Character Letter to a Judge
Writing a character letter for a defendant can be instrumental as it will be considered by the judge before s/he passes judgement. Therefore, one has to be very careful when writing this kind of reference. It is best that the writer of the reference is an acquaintance to the defendant in order for the letter to be adequate and correctly contented.
A character letter is a letter and as such, should be written as a letter should be written. This insinuates that the reference should be dated and addressed to the appropriate office. This particular kind of character reference should be addressed to the resident judge.
A character reference is a formal piece. This implies that a respectful tone should be adopted for this kind of writing. It is therefore; appropriate to address the addressee as ‘Your Honour’ in the letter.
The first paragraph of the letter should be the introductory paragraph. This is where the writer is meant to introduce him/herself and state the purpose of the letter. Also, s/he is to describe his/her relationship to the referenced in this paragraph. In describing the relationship that exist between the writer and the referenced, the writer can describe the kind of relationship, how the relationship came to be, how long the relationship has been existing and the present state of the relationship. This will attest for the writer’s qualification to write a character reference for the defendant.
The next thing the writer should bring up after the introduction is his/her knowledge about the crime the defendant allegedly committed. At this point, s/he is to relay all s/he knows about the charges; if at all s/he knows about it, if s/he knows about it; if it was the person that informed her/him about it, how the defendant has reacted and is reacting to the case.
It being a character letter, one should also include information about the character of the defendant, that is; the writer’s knowledge of the person’s character. Knowledge about the defendant’s background should also be relayed here. S/he can now express what he thinks about the defendant and the crime, comparing or attempting to relate the personality of the defendant and the crime s/he allegedly committed.
Also, the writer can state the reasons, if at all any, why he thinks the defendant might have committed the crime s/he has been accused of. All these are important as they will aid the Judge in understanding the case better. For example, the defendant might have been suffering psychologically which might have resulted to the crime.
It may be the case that the defendant was not sane when s/he committed the crime, that is if s/he actually committed the crime. All these pieces of information are expedient and that is why it is best that the writer of a character letter is very knowledgeable about the defendant.
The last paragraph of the letter should conclude the letter and it should end with the usual compliment every formal letter ends with; ‘Yours sincerely’ and the signature and name of the writer.
How to Write a Character Letter to an Employer
Before writing this kind of letter, one should gather as much information as possible. S/he should also ask questions in order to clarify every misunderstanding concerning the letter. The writer should prepare his/her mind to write positively and be honest at the same time. As in any formal letter, this kind of character reference should be addressed to the appropriate office. Then, the introduction should come in.
The writer is to introduce the reason for the letter and also introduce himself. Next, the background of the writer and his relationship with the referenced should come in. The writer can give a brief history of his relationship with the person he is writing for. This can build the trust of the employer in the content of the letter.
While writing the body of the letter, which should consist of the personal characteristics and skills of the referenced, the writer should focus on the positive traits and strength of the person. Mentioning negative traits will alter the purpose of the letter as the letter is meant to qualify the person more for the job s/he has applied for or wishes to be employed for. The writer should try as much as possible to be honest but still, s/he should avoid discussing anything about the negative past or characteristics of the person being written for. Positive word should therefore, be employed.
Irrelevant discussions should also be avoided when writing this kind of letter. It is a formal letter and so only relevant information should be relayed in it. Still on formality, the writer should try as much as possible to maintain formality in this kind of letter. Informal terms should be avoided. Also, short forms of words and phrases should be avoided. The tone of the letter should depict formality and respect.
After giving positive information about the personal qualities of the person written for, the writer should close with a concluding paragraph and a compliment as in any other formal letter. The writer may also add his/her contact information so that the employer can be able to get back to the writer if s/he wishes to.
There are some services, where you can find expert help from a team of qualified college essay tutors.
Sample of a Character Letter
The Manager,
The Johnsons’ Company,
October 30Th 2018.
Sir/Ma,
I am Gundigan Josh, a former boss to Sophia Spike. Sophia worked under my watch for over ten years before resigning two years ago to start her own firm. She won the best employee award six consecutive times, beating over hundred fellow employee workers before her resignation. She was the Assistant Manager before she resigned and I can boldly say that her kind of service is very rare. With her as my assistant, I was able to study her very well and I ended up learning a lot from her style of service.
Sophia’s diligence in doing her job better than expected, spurred other members of staff of The Johnson’s, including me to sit up and aim for more. She is smart and swift. She dislikes delay in doing what is supposed to be one and her ideas are always thrilling.
I am recommending her for the job of the Personnel Manager at your company because I know that she will handle the job very well. I hope she is employed.
Yours faithfully,
(Writer’s Signature)
(Writer’s Name).
Conclusion
A character letter is a formal letter that gives personal details about a person and so should be written using the format of a formal letter. It must be written by one who is knowledgeable about the person to be written about. It is also known as character reference or personal reference.