Preposition definition: A preposition is a part of speech that shows the relation of a noun or pronoun to another word.
What are prepositions? Prepositions show the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. These relationships include where, when, who, or what.
Examples of Prepositions:
- above (where?)
- before (when?)
- for (whom?)
- with (what?)
Let’s look closer at a preposition example.
A preposition can be understood as anywhere a dog can be in relation to its doghouse.
A dog can be:
- in the doghouse
- around the doghouse
- near the doghouse
- on the doghouse
Each of these prepositions describe the relation between the dog and its doghouse. The dog can be inside the doghouse, it can be around the doghouse, it can be near the doghouse, it can be on the doghouse, etc.
All of these preposition examples show where the dog is in relation to its doghouse.
What is the Role of a Preposition?

Most often prepositions are used to introduce prepositional phrases.
Prepositions serve to modify and generally function in prepositional phrases as adjectives or adverbs.
Examples of prepositions indicating where:
- along (the path)
- amid (torment)
- throughout (the garden)
- within (men)
Examples of prepositions indicating when:
- since (the storm)
- after (the party)
- before (noon)
- until (tomorrow)
Examples of prepositions indicating who:
- besides (Petra)
- except (the children)
- with (everyone)
- for (the teacher)
Examples of prepositions indicating what:
- besides (the essay)
- of (the few)
- like (the dog)
- with (chocolate)
Preposition List

aboard
about
above
across
after
against
along
amid
among
anti
around
as
at
before
behind
below
beneath
beside
besides
between
beyond
but
by
concerning
considering
despite
down
during
except
excepting
excluding
following
for
from
in
inside
into
like
minus
near
of
off
on
onto
opposite
outside
over
past
per
plus
regarding
round
save
since
than
through
to
toward
towards
under
underneath
unlike
until
up
upon
versus
via
with
within
without
For a more full list of prepositions, see our full page on the subject. Prepositions list here.
Object of Prepositions

Examples:
- along (the path)
- The path is the object of the preposition.
- amid (torment)
- Torment is the object of the preposition.
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- The colorful garden is the object of the preposition.
Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions

The prepositions that can function in subordinate conjunctions include: after, as, before, since, until.
Prepositions together within subordinate conjunctions function as adverbs.
Preposition Examples:
- Since the movie premiered, the star has received much attention.
- We could not make an appointment until the office opened the following day.
- The student did not think before he asked a question.
What are Prepositional Phrases?
What does prepositional phrase mean? Almost always a preposition will function in a prepositional phrase.
A prepositional phrase is any preposition and its object (a noun). A prepositional phrase may also include any modifiers in the phrase.
Prepositional phrases clarify the relationship of the preposition to other words.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- along the path
- along (prep.) + the (article) + path (noun) = prepositional phrase
- amid torment
- amid (prep.) + torment (noun) = prepositional phrase
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- throughout (prep.) + the (article) + colorful (adj.) + garden (noun) = prepositional phrase
Multiple prepositional phrases may exist within one larger prepositional phrase.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- within all of the men
- within all + of the men = prepositional phrase
- by the lake in the forest
- by the lake + in the forest = prepositional phrase
- on the table at the restaurant
- on the table + at the restaurant = prepositional phrase
Summary: What are Prepositions?
Define preposition: To clarify, prepositions:
- show the relationship of a word to a noun or pronoun
- are almost always used in prepositional phrases
- sometimes begin subordinate conjunctions
Contents
- 1 What is a Preposition?
- 2 What is the Role of a Preposition?
- 3 Preposition List
- 4 Object of Prepositions
- 5 Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions
- 6 What are Prepositional Phrases?
- 7 Summary: What are Prepositions?
Prepositions are one of the eight parts of speech in the English language, and they’re pretty important. Prepositions allow us to create complex sentences and add in important details. They play a crucial role in helping sentences make sense, which is super important when you need to communicate clearly and effectively.
But if you have to sit down and give an accurate preposition definition, things can get a little tricky. You may know that prepositions are usually short words like at, for, in, on, or under, but what is a preposition as a part of speech? What do prepositions do, and how the heck do you identify a preposition in a sentence?
To help you become an expert on prepositions, we’re going to talk about the following in this article:
- Answer the questions “What is a preposition?” and “What does preposition mean?”
- Explain each type of preposition definition with examples of each type used in a sentence
- Provide a list of four top tips for identifying prepositions in sentences
If there’s a specific type of preposition you want to know more about—like prepositions of space—you can find the information quickly by holding Command + F on your keyboard, then typing in the term you’re looking for.
Now without further ado, let’s get started!
Feature Image: (Jmayereup / Wikimedia)
What’s a Preposition? Preposition Meaning and Usage in Sentences
Grammar rules for the English language state that prepositions are defined based on their function in a sentence. So, here’s how a preposition functions to create meaning in a sentence: A preposition combines with a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun to demonstrate a relationship between the noun and another component of the sentence, often another noun and verb.
In other words, prepositions help readers understand the relationship between different nouns and verbs in a single sentence.
Now that you’ve got an answer to the question, “What’s a preposition?” you’re probably wondering what kind of relationships prepositions show. Prepositions can show relationships of time, space, or possession between a subject and an object in a sentence.
For example, in the following sentences, each preposition (in bold) helps us better understand the relationship between the cat and the table:
- The cat sat on the table.
- The cat sat under the table.
- The cat sat beside the table.
- The cat sat at the table.
In the examples above, the prepositions on, under, beside, and at help clarify the nature of the relationship between the cat—the subject of the sentence—and the table—the object of the preposition. Notice that each sentence makes us visualize something different: a cat sitting on a table is not the same thing as a cat sitting under a table. And guess what? That’s what prepositions are designed to do!
Here’s a helpful list of prepositional phrases!
The Prepositional Phrase
The next thing you need to know about prepositions in sentences is that they almost always appear in a prepositional phrase. Prepositional phrases are important for communicating what types of actions and interactions occur between the subjects and objects of sentences.
A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition (or prepositions), the object of the preposition (a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun), and any other words that modify the object (an adjective or adverb). In the examples above involving the cat and the table, on the table, under the table, beside the table, and at the table are all prepositional phrases because they begin with a preposition that is followed by a noun (cat).
Quick note: if you’re not sure what things like nouns, adjectives, or adverbs are, don’t worry. We have a complete, expert guide to each part of speech that will teach you everything you need to know!
Keep in mind that prepositional phrases aren’t limited to a single preposition and a single object. Prepositional phrases can also contain modifiers of the object, which are usually adjectives and adverbs. Here’s an example of a prepositional phrase that also contains modifiers:
The cat sat under the dirty, decaying table.
In this example, under the dirty, decaying table is the entire prepositional phrase. It consists of the preposition (under), the object (the table), and the adjectives that modify the object (dirty, decaying). So while a prepositional phrase must contain at least one preposition and an object, it can also contain other types of words.
Now if someone asks you, “What is a preposition?” you have an answer! Next, we’ll break down the different types of prepositions for you so you’ll be a preposition expert.
2 Forms of Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases You Need to Know
Part of answering the question, “What is a preposition?” includes explaining the two different forms, or structures, that prepositions and prepositional phrases can take. Think of form like a formula: it’s a prescribed way that you can put different prepositional words together to make them work in a sentence!
Let’s look at the two forms of prepositions below.
#1: Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions are the first type of preposition, and it’s one of the two types that Defining simple prepositions is, well, simple: simple prepositions are one-word prepositions that appear at the beginning of a prepositional phrase in front of an object or in front of an article and an object. In other words, simple prepositions look something like this:
We’ve been playing since noon.
They walked through the field.
In both of the examples above, the prepositional phrases begin with a simple preposition: since is the simple preposition in the first example, and through is the simple preposition in the second example. In both examples, the simple prepositions are followed by an object (noon in the first example) or an article plus an object (the field in the second example).
These examples also explain how this is a form of preposition. While both of these are simple prepositions, the words we used totally changed the meaning of the sentence. In the first sentence, using since helps us understand the amount of time the person has been playing. That’s because since is a preposition of time! But the simple preposition structure also works in the second sentence, even though we’re using a preposition of movement (through) instead.
So just like math, prepositional forms let you swap words in and out to create meaning.
And that’s the definition of a simple preposition! Simple prepositions are used very frequently in the English language, so you’ll probably start to see them everywhere now that you know what you’re looking for.
#2: Complex (or Compound, or Double) Prepositions
There’s a little disagreement out there about what to call this form of preposition: sometimes they’re called complex prepositions, compound prepositions, or double prepositions. Just know that all of these terms refer to the same thing.
Complex prepositions are a group of prepositions that function like a simple preposition. That means complex prepositions always consist of more than one preposition (unlike simple prepositions, which only have one). Here are two examples of complex prepositions in a sentence:
Get these chips away from me.
She laughed at his joke in spite of herself.
As you can tell from these examples, complex prepositions can appear in two-word units or three-word units. When a complex preposition appears in a two-word unit, it involves two prepositions in a row which are followed by an object. In the first example, away from is our complex preposition, and the object that follows it is me.
When a complex preposition appears in a three-word unit, it follows a different formula. In three-word units, the first preposition and second preposition are separated by a noun, then the object comes afterward. In the second example, in and of are prepositions, spite is the noun, and herself is the object!
Remember how we talked about forms of prepositions working like a mathematical formula? That’s definitely the case for complex prepositions! Though there are many complex prepositions (which you’ll see in our list below), the most commonly used formulas for a complex preposition in English are the following:
- Preposition + of
- Preposition + from
- Preposition + to
To help you pick out complex prepositions when they’re used in sentences, here’s a list of commonly used complex prepositions:
|
According to |
For lack of |
Near to |
|
Ahead of |
In accordance with |
Next to |
|
Along with |
In addition to |
On account of |
|
Apart from |
In back of |
On behalf of |
|
As for |
In between |
On top of |
|
As well as |
In the case of |
Out of |
|
Aside from |
In charge of |
Outside of |
|
Away from |
In exchange for |
Owing to |
|
Because of |
In front of |
Prior to |
|
But for |
In light of |
Subsequent to |
|
By means of |
In line with |
Such as |
|
By virtue of |
In place of |
Thanks to |
|
By way of |
In the process of |
Together with |
|
Close to |
In regard to |
Up against |
|
Contrary to |
Inside of |
Up to |
|
Due to |
In spite of |
Up until |
|
Except for |
Instead of |
With respect to |
|
Far from |
In view of |
4 Types of Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases That Convey Meaning
These types of prepositions are used to convey meaning in a sentence. You can pop them into one of the forms we discussed above to help people better understand specific relationships between a subject and an object in a sentence. Specifically, these types of prepositions describe four different types of relationships: time, space, direction/movement, and agent/instrument.
These prepositions can be mixed and matched with the preposition forms we just talked about, so most prepositions fit into two categories: one for their form, and another for their meaning. Put another way, a preposition in a sentence can be both a simple/complex preposition and a preposition of time, space, direction/movement, or agent/instrument!
Now, let’s learn a little more about the four types of prepositions that help writers convey meaning.
#1: Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time demonstrate relationships between things in terms of when something occurred. Prepositions of time can show the specific, exact time when something happened or will happen. It can also express a more general, extended period of time.
Take a look at the table below for a list of prepositions that are frequently used to demonstrate relationships in terms of time:
|
After |
During |
On |
|
Around |
Following |
Over |
|
As |
For |
Since |
|
At |
From |
Until |
|
Before |
In |
Within |
|
By |
Next |
So how do prepositions express time, exactly? Let’s look at two examples:
Example #1: Sean will drop off the recycling after work.
In this first example, after is the preposition of time, and after work is the prepositional phrase. But how is after establishing a time-based relationship here? After establishes time by showing that Sean will perform a specific action—dropping off the recycling—only after he has finished with work. In this case, we can see how these two elements of the sentence relate to one another: one has to end before the other can happen.
It’s also worth noting that after is also part of a simple preposition…so it’s both a simple preposition and a preposition of time!
Now that you have a better understanding of how this works, here’s a second example of a preposition of time in a sentence:
Example #2: I’m going live at ten o’clock.
In this example, at is the preposition, and at ten o’clock is the prepositional phrase. More importantly, at is establishing a precise time. In this case, the person speaking is going to go live on television at an exact time. Thus, the preposition at establishes that the time-based relationship between the subject and the verb and the object is a precise one.
You use prepositions of time every day, even if you don’t realize it. Whether you’re giving directions, planning your day, or just telling a story, prepositions of time help us create chronological order.
#2: Prepositions of Space
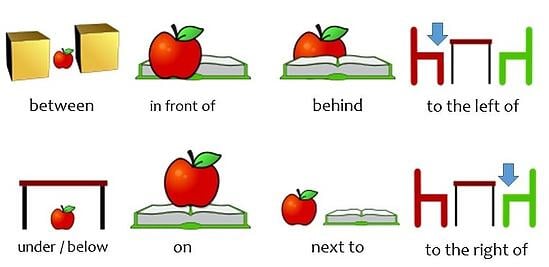
Prepositions of space are used to show where a person, living creature, or other object or entity is located in space (as in, like, physical space in the everyday world, not outer space).
The words in the following list are classified as this type of preposition, meaning they show where things are located in space, including location in relation to other things, direction, and movement.
|
About |
Beside |
Opposite |
|
Above |
Between |
Out |
|
Across |
Beyond |
Outside |
|
Across from |
By |
Over |
|
Against |
Down |
Through |
|
Along |
For |
To |
|
Amid |
From |
Toward |
|
Among |
In |
Under |
|
Around |
Inside |
Underneath |
|
At |
Into |
Up |
|
Away from |
Near |
Upon |
|
Before |
Of |
While |
|
Behind |
Off |
Within |
|
Below |
On |
Without |
|
Beneath |
Onto |
Now that we have a full list of prepositions of space, let’s look at an example of a preposition of space: one example that simply shows where something is located in space. Here we go:
There’s an owl in the chimney!
This example is pretty straightforward. Where is the owl? It’s located in the chimney. There’s a spatial relationship established between the owl and the chimney through the use of the preposition in.
Prepositions of direction and movement help readers understand movement. In this case, the dancer is lifting his partner off the ground!
#3: Prepositions of Direction/Movement
Prepositions of space are sometimes broken down into even smaller categories, and two of the categories you need to know about are prepositions of direction and movement. These types of prepositions show movement from one place to another. Because of this, prepositions of direction and movement are often used with verbs of motion.
Here’s a list of words that are classified as prepositions of direction and movement:
|
about |
between |
over |
|
across |
down |
through |
|
against |
from |
to |
|
along |
into |
toward(s) |
|
among |
off of |
under |
|
around |
onto |
up |
|
away from |
out of |
Prepositions of direction and movement connote that something is moving through space in relation to another object. Check out this example:
Sophia threw the dart at the bullseye.
In this example, the dart’s location in space is described in relation to the bullseye’s location in space through the use of the preposition at. We know that the dart is directed toward the bullseye, and since the dart has to move through space in order to actually hit the bullseye, we consider prepositions of direction/movement as falling into the bigger category of prepositions of space!
Here are a few more examples of prepositions that connote direction/movement:
They walked among the wildflowers.
The festival-goers twirled around the maypole.
Like the earlier example, both of these examples show that living beings are moving through space in relation to other objects. In the first example, they are moving through space in relation to some wildflowers. In the second example, the festival-goers are moving through space in relation to the maypole.
One way to recognize prepositions of space that connote direction/movement is to look for a verb right before the preposition, because prepositions of direction/movement often follow a verb in a sentence!
#4: Prepositions of Agent/Instrument
There are also prepositions that can be used to connote a different kind of relationship besides relationships of time or space. These prepositions are known as prepositions of agent/instrument, and they demonstrate a relationship in which one noun performs an action on or toward another noun in a sentence.
Here are the common prepositions of agent/instrument that you need to know:
Let’s have a look at an example of a preposition of agent/instrument in a sentence:
I think the movie was produced by Disney.
This example conveys a relationship of agency, or power, between a noun and a verb: the movie under discussion in this sentence was produced by Disney. This conveys a relationship in which a group of persons has caused something to occur. In this sentence, prepositions help us understand that Disney has control over the production of the movie. It’s also important to note that prepositions of agency are usually used in sentences that are constructed in the passive voice, like in the example above.
Now, here’s an example that shows a preposition of instrument. A preposition of instrument is used to describe machines, technologies, and devices. Basically, when you need to explain how a mechanical noun acts toward another noun, you use this type of preposition! Here’s an example:
She lit the candle with a match.
This sentence example uses the preposition meaning with to show a relationship between one noun—a match, which is an instrument—and another noun—the candle, which is also an instrument. In other words, the preposition with connotes a relationship in which the match acts upon the candle. Prepositions of instrument almost always describe use of devices, technologies, or other objects.
3 Top Tips for Identifying Prepositions in a Sentence
As you’ve probably guessed by now, prepositions can be a little bit sneaky in sentences. Sometimes words that are commonly used as prepositions are also used for other purposes, which can make identifying prepositions in a sentence a little bit confusing! We’ve come up with three top tips on preposition grammar to help you spot prepositions in a sentence correctly.
#1: Break Down the Word Itself
If you have trouble remembering where a preposition should appear in relation to the object that it modifies in a sentence, you can break down the actual word “preposition” as a memory hack. A preposition appears in front of its object, so you can think of it as being pre-positioned in front of the object.
Read the examples above one more time. In each one, the preposition comes before the object. And there’s an added bonus: when you can find the preposition in a sentence, you can also find its object, too!
#2: Remember That Prepositions Are “Anywhere a Cat Can Go”
We’ve already used cats in a couple of our example preposition sentences, but did you know that many people are taught in school that prepositions are anywhere a cat can go? Just think about it: how many videos have you watched of cats fitting themselves into bizarre places? They can go on, in, through, around, under, across, behind, between, through…pretty much any object (especially boxes). And as it turns out—all of those words are prepositions!
So If you’re looking for a way to remember prepositions of space, location, direction, and movement, just picture a cat playing with a box. If the word you’re using is somewhere the cat can go, then you’re probably dealing with a preposition.
#3: Watch Out for Verbs…and Look for the Prepositional Phrase
Something super important to know about words that are classified as prepositions is that they don’t necessarily function as prepositions every time they appear in a sentence.
This means that you can’t really just glance at a sentence and pick out a single word that is often used as a preposition and be sure that it’s working like a preposition in that particular sentence. You’ve got to look at the bigger picture of the sentence itself to determine whether the word is being used as a preposition!
So what do you look for to determine whether a word is being used as a preposition? Look at the words around the preposition to see if there’s a prepositional phrase. Remember: a word that is often used as a preposition must show a relationship between the noun and another part of the sentence in order to function as a preposition.
Additionally, preposition grammar rules indicate that when a word that looks like a preposition comes before a verb phrase instead of a noun phrase, that little word that looks like a preposition isn’t functioning as a preposition at all—it’s functioning as a particle instead. So, in addition to looking out for prepositional phrases, you can also look out for verbs. Here’s an example of what a particle looks like in a sentence:
We’re going to walk at the market.
In this example, the phrase to walk might look like a prepositional phrase at first glance, but walk is a verb, not a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun. So, in this case, to isn’t the beginning of a prepositional phrase and isn’t being used as a preposition. However, the phrase at the market at the end of the sentence is a prepositional phrase, since the market is a noun!
What’s Next?
Prepositions help make your writing clearer, which is incredibly important if you want to ace the writing portions of your standardized tests. Luckily for you, we have expert guides to help you ace your SAT and ACT essays! Click here to learn how to get a perfect 12 on your ACT essay. If you’re aiming to get a perfect 8 | 8 | 8 on the SAT essay, you’ll want to check out this article instead.
You’ll also have to write stellar admissions essays if you want to get into your dream school. Start by getting expert advice on how to tackle the Common App essay prompts, then check out our blog for school-specific tips. We have thorough guides about how to write essays for the top schools in the nation, including Harvard, Yale, Notre Dame, Michigan State, USC, and more!
If you’re interested in grammar because you love to write, you might consider majoring in creative writing. If this sounds like you, you should definitely check out this list of the best 12 creative writing programs in the United States.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
Have friends who also need help with test prep? Share this article!
About the Author
Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Last Update: Jan 03, 2023
This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. Now, we have got the complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested!
Asked by: Mario Padberg
Score: 4.4/5
(45 votes)
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions, are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations or mark various semantic roles.
A preposition or postposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object.
What is preposition and examples?
Preposition Basics
A preposition is a word or group of words used before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, time, place, location, spatial relationships, or to introduce an object. Some examples of prepositions are words like «in,» «at,» «on,» «of,» and «to.»
What is prepositions give 5 examples?
Some examples of common prepositions used in sentences are:
- He sat on the chair.
- There is some milk in the fridge.
- She was hiding under the table.
- The cat jumped off the counter.
- He drove over the bridge.
- She lost her ring at the beach.
- The book belongs to Anthony.
- They were sitting by the tree.
What are the 5 prepositions?
The five types of prepositions are simple, double, compound, participle, and phrase prepositions.
What are 10 common prepositions?
A preposition usually precedes a noun or a pronoun. Here is a list of commonly used prepositions: above, across, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, by, down, from, in, into, near, of, off, on, to, toward, under, upon, with and within.
37 related questions found
What are the 4 main types of prepositions?
There are following types of prepositions.
- Simple Preposition. When a preposition consists of one word is called single or simple preposition. …
- Double Preposition. …
- Compound Preposition. …
- Participle Preposition. …
- Disguised Prepositions. …
- Phrase Prepositions.
What are the 30 prepositions?
List of Prepositions
- A aboard, about, above, according to, across, after, against, ahead of, along, amid, amidst, among, around, as, as far as, as of, aside from, at, athwart, atop.
- B barring, because of, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, but (when it means except), by, by means of.
Where do we use the preposition at?
The preposition ‘at’ is used to speak about specific locations in cities or the countryside. We often have lunch at the docks. He told me he would be at the bus stop at three o’clock.
What is a simple preposition?
Simple prepositions are short words that we use before a noun/pronoun to indicate the relationship of the noun to the verb, adjective, or another noun. Simple prepositions are composed mainly of two types; time and place.
What are the 8 prepositions?
The 8 types of prepositions in English grammar with examples include prepositions of time, place, movement, manner, agent, measure, source and possession.
What are the 3 types of prepositions?
There are some prepositions which are common in every type of preposition as they function in a versatile way.
- Prepositions of Time.
- Prepositions of Place and Direction.
- Prepositions of Agents or Things.
- Phrasal Prepositions.
How can I use preposition in a sentence?
Prepositions are always used to indicate the relationship of a noun or phrase to something else. When using a preposition, you must always have the subject and verb before it, and follow it with a noun. You should never follow it with a verb! Let’s have a closer look at some examples.
How do you use preposition in a sentence?
Prepositions in the English language indicate the relationship of a noun or pronoun to something. When using a preposition, it is necessary to have the subject and verb before it and should be followed by a noun. Never follow a preposition with a verb.
How many prepositions are there?
There are about 150 prepositions in English. Yet this is a very small number when you think of the thousands of other words (nouns, verbs etc). Prepositions are important words.
What is a preposition for kids?
Prepositions are words which link nouns, pronouns and phrases to other words in a sentence. Prepositions usually describe the position of something, the time when something happens and the way in which something is done, although the prepositions «of,» «to,» and «for» have some separate functions.
How many simple prepositions are there?
In the English language we have approximately 70 simple prepositions. About half of them have two syllables (under, over, behind, without) or more (underneath, notwithstanding).
Can you end a sentence with a preposition?
The best-known rule about prepositions is that you shouldn’t end a sentence with one. And that rule is absolutely correct—if you’re speaking Latin. … The fact is that English presents many opportunities to compose sentences that would just sound awkward if we had to rewrite them to avoid leaving a preposition at the end.
What preposition is used with streets?
On is generally used for street locations (on Main Street), whereas in is used to talk about standing in the middle of the street.
What is preposition for time?
A preposition of time is a preposition that allows you to discuss a specific time period such as a date on the calendar, one of the days of the week, or the actual time something takes place. Prepositions of time are the same words as prepositions of place, however they are used in a different way.
What are common prepositions?
Common prepositions are at, by, for, on, of, off, to, and with. Remember, all prepositions are part of a prepositional phrase, they’re never followed by a verb, and prepositions are usually short words.
What is an example of ending a sentence with a preposition?
“Cheer up,” “run over,” “log on,” and “leave off” are all examples of phrasal verbs, and often sentences that use phrasal verbs end with a preposition: I wish he would cheer up. You should leave it off.
Types of Prepositions
There are several types of prepositions such as: Simple Prepositions, Double Prepositions, Compound Prepositions, Phrasal prepositions, Participle Prepositions, Disguised preposition, and Detached Prepositions.
1. Simple Prepositions:
Simple prepositions are used to denote a relation between nouns or pronouns. These can even be used to join different parts of sentences and clauses. Simple prepositions are one word prepositions. These are also called Single Prepositions. Common words used that come under the category of Simple Prepositions are as follows:
In, out, on, up, at, for, from, by, of, off, through, till, etc.
Examples of Simple Prepositions in sentences:
Keep your phones in your pockets.
Staring at people is not considered a good gesture.
In the above two examples, both prepositions consist of one simple word and hence are Single or Simple Prepositions.
2. Double Prepositions:
Double Prepositions are made by putting together two Single Prepositions. That is why they are called Double Prepositions. Common words used as Double Prepositions are as follows:
Onto, into, throughout, up till, up to, within, without, upon, etc.
Examples of Double Prepositions in sentences:
Complete this essay within two hours.
I am going to turn this scrap into a masterpiece.
In the first example, the Preposition within is made by combining two Single Prepositions with and in.
In the second example, the Preposition into is formed by putting together two Simple Prepositions in and two. These are hence Double Prepositions.
3. Compound Prepositions:
Compound Prepositions are those types of preposition that are usually formed by prefixing a preposition to nouns, adjectives or adverbs. They are different from double prepositions because they are not formed by two single prepositions. Common words, which come under the category of compound prepositions, are stated below:
Above, about, across, along, before, behind, beside, inside, outside, etc.
Examples of preposition in sentences:
He was going about his business.
The person beside Ali is my brother.
In the first example, the prefix ‘a’ is added to a root word ‘bout’ to make a preposition. In the second example, the prefix be is added to the root word side to make a preposition. Thus, these words are Compound Prepositions.
4. Phrasal Prepositions:
Phrasal Prepositions are groups of words or phrases that join the noun or pronoun in a sentence, to the remainder of the sentence. These groups of words express a single idea by coming together as a unit. Words that come under the category of Phrasal Prepositions are as follows:
In addition to, by means of, in spite of, according to, owing to, in favour of, etc.
Examples of Phrasal Prepositions in sentences:
He couldn’t pass the test, owing to his lack of knowledge of English Grammar.
She made it to the other side of the world, in spite of all the difficulties.
In the first example, the group of words ‘owing to’ is joining the two sentences with each other and is a phrase. Likewise, the group of words ‘in spite of’ is also a phrase and is working as a preposition. Hence, these are Phrasal Prepositions.
5. Participle Prepositions:
Participle Prepositions, indicating from their name, are the Present Participle forms of Verbs. These are used without any noun or pronoun attached with them. The words that are distinguished as Participle Prepositions are as follows:
Concerning, considering, barring, notwithstanding, touching, pending, during, etc.
Examples of Participle Prepositions in sentences:
Notwithstanding his efforts, he was still fired from the job.
Touching this matter, I do not have much information.
In above examples, both the verbs notwithstanding and touching are in Present Participle which is apparent from the ‘ing’ at the end of both words. These words are therefore Participle Prepositions.
6. Disguised Prepositions:
Disguised prepositions are those prepositions which are not used in the sentences directly, but we use them in a disguised way. Their shorter forms are used. The examples of Disguised Prepositions are ‘a’ and ‘o’.
Disguised preposition ‘a’ is shortened form of the preposition ‘on’ and similarly ‘o’ is the shortened form of the preposition ‘of’.
Examples of disguised prepositions in sentences:
The ceremony will be held at 5 o’ clock.
We all went to a party.
In the first example, instead of saying ‘5 of the clock’, we have used disguised form of the preposition of.
In the second example, instead of saying ‘went on partying’, we have used abbreviation of the preposition on and disguised the preposition as ‘a’. Hence these are Disguised Prepositions.
7. Detached Prepositions:
A preposition is called a detached preposition when it does not come before its object. It is detached from its object. When the object of a preposition is an interrogative pronoun or a relative pronoun, the preposition comes at the end of the sentence.
Look at the following examples of detached prepositions for further understanding.
She is the woman whom I was talking about.
Here are the books that you asked for.
Which of the houses were you working in?
In the first two of the above examples, we can see that because of relative pronouns whom and that, the prepositions about and for are being detached from their objects.
In the third example, the interrogative pronoun ‘which’ is detaching the preposition ‘in’ from its object.
Hence these are all detached prepositions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you end a sentence with a preposition?
There is nothing wrong with ending a sentence in a preposition like to, with, for, or at. English speakers have been doing so since the days of Old English. The people who claim that a terminal preposition is wrong are clinging to an idea born in the 17th century and largely abandoned by grammar and usage experts in the early 20th.
What exactly is a preposition?
A preposition is a word—and almost always a very small, very common word—that shows direction (to in «a letter to you»), location (at in «at the door»), or time (by in «by noon»), or that introduces an object (of in «a basket of apples»). Prepositions are typically followed by an object, which can be a noun (noon), a noun phrase (the door), or a pronoun (you).
What is an example of a preposition?
The most common prepositions are at, by, for, from, in, of, on, to, and with. Other common prepositions are about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, because of, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, close to, down, during, except, inside, instead of, into, like, near, off, on top of, onto, out of, outside, over, past, since, through, toward, under, until, up, upon, within, without.
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions
What is preposition
A preposition is a word that indicates the relationship between a noun and the other words of a sentence. They explain relationships of sequence, space, and logic between the object of the sentence and the rest of the sentence. They help us understand order, time connections, and positions.
Example:
- I am going to Canada.
- Alex threw a stone into the pond.
- The present is inside the box.
- They have gone out of the town.
There are a few interesting linguistic facts about prepositions.
First, they are a closed class of words which means no new preposition gets added to the language. We use a fixed set of prepositions.
Second, prepositions do not have any other form. They cannot be plural, possessive, inflection, or anything else.
Third, most of the prepositions have many different contextual and natural uses. So, it is easy to be confused about it.
Fourth, sometimes a preposition works as nouns, adjectives, and adverbs.
Prepositions can be of one, two, three, or even more words. Prepositions with two or more words are called phrasal prepositions.
There are some commonly used phrasal prepositions:
because of, in case of, instead of, by way of, on behalf of, on account of, in care of, in spite of, on the side of, etc.
Types of Preposition
Most of the prepositions have many uses. There are some prepositions which are common in every type of preposition as they function in a versatile way.
- Simple Preposition
- Double Preposition
- Compound Preposition
- Participle Preposition
- Disguised Preposition
- Detached Preposition
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place and Direction
- Prepositions of Agents or Things
- Phrasal Prepositions
Simple Preposition
These are among the most common type of prepositions. The prepositions used to express the relationship the Nouns and Pronouns of a sentence have with the rest of the words in it are called Simple Prepositions. They are often used to join two clauses in terms of Complex Sentence and Compound Sentence.
Examples:
| Most Popular Prepositions | |||||
| and | but | at | to | on | in |
| for | of | up | off | from | out |
| with | during | down | below | beside | over |
| by | near | behind | inside | among | along |
Double Preposition
Two Simple Prepositions joining together to form one which connects the Noun(s) or Pronoun(s) to the rest the words in a sentence.
Examples:
- Are you out of your mind?
- I was allowed the inside of the temple.
- She’s sandwiched in between two of her cousins.
Compound Preposition
Compound Prepositions are composed of prepositions as well as other words. Compound Prepositions are easily confused with Double Prepositions since they both require other prepositions or words to help with acting like a preposition.
Examples:
- According to my calculations, this color should work just fine.
- I started for home, with a view to celebrating Eid with my family.
- On behalf of our family, my father attended the family reunion.
Participle Preposition
Present Participles (-ing) and Past Participles (-ed and -en) that are used as Prepositions instead of Verbs, are called Participle Prepositions. These are participles as well as prepositions.
Examples:
| Present Participle Prepositions | Past Participles Prepositions |
| Assuming | Respected |
| Barring | Given |
| Considering | Gone |
| During | Barred |
| Notwithstanding | Provided |
| Regarding | Taken |
Participle Prepositions Used in Sentences:
- Barred from the entrance, he threw a fit.
- I was happy given the fact that I got great marks.
- Assuming the possibility of rain, she carried an umbrella.
Disguised Preposition
These prepositions are usually disguised as some other element in the English language. Often these prepositions are disguised as «a» and «o» in sentences.
Examples:
- I wake up at 5 o‘clock. (Of the clock)
- Keep striding ahead. (on the head)
- Pope went ashore. (onshore)
- Rimi visits the riverbank once a day. (in a day)
Detached Preposition
A preposition that has been detached and sent to the very end of the sentence is called Detached Preposition. These prepositions are detached from the interrogative or relative pronouns and adverbs but get detached for the sake of the integrity of sentences.
Examples:
- Where are you coming from?
- Is that the neighborhood you are headed to?
- I won’t tolerate being screamed at.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time show the relationship of time between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common preposition of time.
Example:
- He started working at 10 AM.
- The company called meeting on 25 October.
- There is a holiday in December.
- He has been ill since Monday.
Read More: Prepositions of Time Usage
Prepositions of Place and Direction
Prepositions of place show the relationship of place between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, by, from, to, towards, up, down, across, between, among, through, in front of, behind, above, over, under, below, etc. are the most common prepositions of place/direction.
Example:
- He is at home.
- He came from England.
- The police broke into the house.
- I live across the river.
Read More: Prepositions of Places & Direction Usage
Prepositions of Agents or Things
Prepositions of agents or things indicate a causal relationship between nouns and other parts of the sentence.
Of, for, by, with, about, etc. are the most used and common prepositions of agents or things.
Example:
- This article is about smartphones.
- Most of the guests have already left.
- I will always be here for you.
- He is playing with his brothers.
Phrasal Prepositions
A phrasal preposition is not a prepositional phrase, but they are a combination of two or more words that function as a preposition.
Along with, apart from, because of, by means of, according to, in front of, contrary to, in spite of, on account of, in reference to, in addition to, in regard to, instead of, on top of, out of, with regard to, etc. are the most common phrasal prepositions.
Example:
- They along with their children went to Atlanta.
- According to the new rules, you are not right.
- In spite of being a good player, he was not selected.
- I’m going out of the city.
In English, words are grouped into word classes based on the function they perform in a sentence. There are nine main word classes in English; nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, and interjections. This explanation is all about prepositions.
Preposition meaning
In short, a preposition is a small word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence.
A preposition shows how two parts of a sentence are connected in relation to time, place, movement/direction, or relationship. In other words, they tell us where or when something is in relation to something else in the sentence. Prepositions often come before a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun, but they may be used in various other ways.
Examples of prepositions
The most common examples of prepositions include;
-
At
-
On
-
In
These show time (‘I arrive on Monday’) and place (‘It’s in the fridge‘). However, these aren’t the only prepositions, and there are plenty of others that can also be used to show time and place, as well as movement/direction. E.g. ‘I travelled from New York to Washington’.
The same word can be used as a preposition in multiple ways. For example, the word ‘at’ can be used as a preposition of time (e.g. ‘I’m meeting Mickey Mouse at the weekend‘), or as a preposition of place (e.g. ‘I’m meeting him at Disneyland’).
Did you know? ‘As’ can function as a preposition in some contexts. As a preposition, it is used to indicate the role, function, or identity of someone or something. For example, in the sentence ‘He works as a teacher,’ ‘as’ is a preposition that shows the role of the subject ‘he’ as a teacher. In other contexts, ‘as’ can function as a conjunction or an adverb.
Preposition: List
Here is a list of some common prepositions in English:
- about
- above
- across
- after
- against
- along
- among
- around
- as
- at
- before
- behind
- below
- beneath
- beside
- between
- beyond
- by
- down
- during
- except
- for
- from
- in
- inside
- into
- like
- near
- of
- off
- on
- onto
- out
- outside
- over
- past
- since
- through
- throughout
- to
- toward
- under
- underneath
- until
- up
- upon
- with
- within
- without
Positioning of prepositions
The word ‘preposition’ has two parts: ‘pre’ and ‘position’. This is a useful reminder; the position of the preposition is usually before (‘pre’) a noun phrase or pronoun. For example:
‘The cat is stuck in the tree’
In this sentence, the preposition ‘in’ comes before the noun ‘tree’. Prepositions can sometimes work alongside adjectives, adverbs, and clauses too.
‘She is talented at playing the piano’
Here, the preposition ‘at’ connects the adjective ‘talented‘ to the verb ‘playing’. If we didn’t have the preposition then the sentence wouldn’t make sense. (Thank you, prepositions!).
Types of preposition
Prepositions can be split into three main groups; prepositions of time, prepositions of place, and prepositions of movement/direction. Each shows a relationship between one part of a sentence or phrase and the other.
Prepositions of time
Prepositions of time express a relationship of time. The table below shows the different ways in which prepositions of time can be used:

Prepositions of place
Prepositions of place express a relationship between location or space. They show how one person or thing is positioned in relation to another person or thing. Have a look at the table below, which will provide you with some examples of common prepositions of place:


Prepositions of movement/direction
Prepositions of movement/direction show movement from one place to another or the direction of movement. Whilst prepositions of place express the static position of something, prepositions of movement/direction show active movement. Here are some examples:

Other types of prepositions
Prepositions don’t just belong to one category. They can also be grouped based on how they look. This includes complex prepositions, such as single-word prepositions, two-word prepositions, and three-word prepositions.
Two-word and three-word prepositions are phrases that have a unique meaning separate from that of the individual words. The words usually stick together as a group to form a certain meaning and usually can’t change order.
For example, the three-word preposition ‘with regard to‘ cannot be changed to ‘to regard with’. It is a fixed expression with a fixed meaning, much like a one-word preposition.
Of course, there can be four-word or even five-word prepositions such as ‘from the point of view of’; however, single-word, two-word, and three-word prepositions are most common.
Single-word prepositions
Single-word prepositions are, as the name suggests, prepositions that consist of only one word. These prepositions are more flexible in meaning and can be used in different parts of the sentence.
Examples of single-word prepositions include:
-
during
-
from
-
on
-
towards
-
with
-
up
-
near
-
at
-
to
-
above
Two-word prepositions
Two-word prepositions contain two words that come together to form a preposition.
For example:
-
ahead of
-
because of
-
instead of
-
near to
-
due to
-
rather than
-
according to
-
prior to
Some of these two-word prepositions need both words to make sense. Take the preposition ‘instead of’. The sentence ‘I want pizza instead chicken nuggets’ does not make sense; the word ‘of’ is required.
Two-word prepositions are often longer words followed by a simple preposition such as ‘of’, ‘to’, ‘than’ etc.
Three-word prepositions
The three-word combination works together to form a preposition with a specific meaning, separate from that of each individual word. For example, the words ‘in’, ‘spite’, and ‘of’ each have a different meaning; however, when they are all put together they form the preposition ‘in spite of’, which has its own meaning.
Examples of three-word prepositions include:
-
in front of
-
by means of
-
in spite of
-
in addition to
-
in exchange for
-
in case of
-
on top of
-
as well as
Three-word prepositions often follow the structure Preposition + Noun/Adjective + Preposition. For example, the preposition ‘in addition to‘ contains the prepositions ‘in’ and ‘to’, and the noun ‘addition’.
Prepositional phrases
A prepositional phrase is a group of words that is built around a preposition. Prepositional phrases contain a preposition, along with the object (a noun or pronoun) and any modifiers.
Take a look at these examples:
The cat hid under a red car
In this example, the prepositional phrase ‘under the car‘ contains the preposition ‘under’ along with the noun phrase ‘a red car’. The car is the object of the sentence that receives the verb ‘hid’. The words ‘a’ and ‘red’ are modifiers that add extra information about the noun. This prepositional phrase gives information about the position of the cat.
I saw a man with a curly moustache
Here, the prepositional phrase is ‘with a curly moustache‘. The preposition ‘with’ is followed by a noun phrase that contains the noun ‘moustache’ and the modifiers ‘a‘ and ‘curly‘. This phrase functions in the same way as an adjective, it gives information about the noun (‘man’). These kinds of prepositional phrases can therefore also be called ‘adjective phrases’.
In the morning, we went home
Here the prepositional phrase ‘in the morning’ is used to set the scene. It modifies (gives more information about) the verb phrase ‘we went home‘ and can therefore also be called an ‘adverbial phrase’.
Preposition — key takeaways
- A preposition is often a small word showing how two parts of a sentence are connected in relation to time, place, movement/direction, or relationship.
- Prepositions often come before a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun; however, they may be used in a variety of ways.
- Prepositions can be split into three main groups: prepositions of time, prepositions of place, and prepositions of movement/direction.
- Prepositions can also be grouped based on how they look; this includes single-word prepositions, two-word prepositions, and three-word prepositions.
- A prepositional phrase is a group of words that is built around a preposition. They often contain a preposition, along with the object (a noun or pronoun) and any modifiers.
‘I have kept your book.’ Don’t you think you want to know where your book is kept? Doesn’t the sentence look incomplete? It is to denote the position of the objects in a sentence that the prepositions are used in the English language. This article discusses the meaning, definition and uses of prepositions. There are also examples of prepositions given to help you understand how they are used in sentences and also an extensive list of prepositions for your reference.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Preposition?
- Definition of a Preposition
- Uses of Prepositions
- Types of Prepositions
- Examples of Prepositions Used in Sentences
- List of Most Popular Prepositions for Everyday Communication
- Commonly Confused Prepositions
- Frequently Asked Questions on Prepositions in English
What Is a Preposition?
A preposition is a short word that is employed in sentences to show the relationship nouns, pronouns or phrases have with other parts within the respective sentences. Prepositions are normally found positioned in the latter part of the sentence, but before a noun or pronoun.
Definition of a Preposition
A preposition is defined as “a word that connects a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun to another word, esp. to a verb, another noun, or an adjective”, according to the Cambridge Dictionary. The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary says that a preposition is “a word or group of words, such as in, from, to, out of and on behalf of, used before a noun or pronoun to show place, position, time or method.”
The Collins Dictionary defines a preposition as “a word such as ‘by’, ‘for’, ‘into’, or ‘with’ which usually has a noun group as its object.” The Merriam Webster Dictionary provides a slightly different definition. According to it, a preposition is defined as “a function word that typically combines with a noun phrase to form a phrase which usually expresses a modification or predication.”
Prepositions are seen to show some key characteristics and perform some vital functions when used in sentences. Let us look at the various uses of prepositions in English.
- They are used to show the direction of something.
- They can refer to the time of something happening.
- They can be used to denote the position or location of an object in the sentence.
- They are also used to represent spatial relationships.
- Prepositional phrases, in particular, can be used to do all of these when used in sentences.
Types of Prepositions
Based on the different uses and functions of prepositions, they can be divided into four main types. They are as follows:
- Prepositions of Time – used to show when something is happening.
For example:
-
- We will be meeting on Friday.
- The supermarket will be closed from 9 p.m. to 9 a.m.
- Can you come after some time?
- We have been asked to work from home until the end of May.
- The whole country was asked to stay home during the pandemic to ensure safety and well-being.
- Prepositions of Place – indicate the place or position of something.
For example:
-
- I have kept the book I borrowed from you on the table.
- Henry hid behind the door.
- The dog jumped over the fence.
- Can you place the red roses in between the white daisies?
- He was waiting in front of the EB office.
- Prepositions of Direction – used to denote the direction in which something travels or moves.
For example:
-
- The girl ran toward her father the moment she saw him.
- Jerry jumped into the river to help his sister.
- Veena passed the book to Priya.
- When will Salvia be returning from London?
- Neena lives across the street.
- Prepositions of Location – employed to denote the location of a particular object.
For example:
-
- Kenny would be staying at his cousin’s place for the weekend.
- Make sure you keep all the toys back in its place after you play.
- I lay on the floor for a really long time.
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationship – used to denote an object’s movement away from the source and towards a source.
For example:
-
- Navya sat leaning against the wall.
- The circus was stationed opposite the children’s park.
- Lakshmi sat beneath the trees.
- Shankar sat beside the stairs.
- We spent the evening walking around the lake.
- Prepositional Phrase – a combination of a preposition and a noun(the object it is affecting).
For example:
-
- See to it that you reach the venue on time.
- The medicines you asked for are out of stock.
- Why don’t we try taking classes outside for a change.
- Make sure you fill in all the forms at once.
- Salmaan was able to finish it only with the help of his friends.
Examples of Prepositions Used in Sentences
To know how exactly prepositions can be used in sentences, check out the following sentences.
- I will be going to church in the morning.
- She placed the plates on the dining table.
- Baskar found the cat hiding under the bed.
- Will you be with Raimy or Mazeeka?
- I love sitting on the beach at night.
- Rachel met Phoebe by the lake.
- Finn stood opposite Lisa.
- The grocery store is right in front of the bus stop.
- My brother climbed onto the roof.
- It feels great to sit beneath the trees and read.
List of Most Popular Prepositions for Everyday Communication
Given below is an extensive list of prepositions that you can make use of in your daily communication.
| Examples of Prepositions | |||
| On | At | In | Over |
| Around | Through | Opposite to | In front of |
| Behind | Beneath | Beside | Above |
| Below | Under | Underneath | Down |
| Up | Out | With | Into |
| Onto | Across | After | Before |
| Near | Among | Along | Between |
| Toward | Away | From | To |
| Next to | By | Until | About |
Commonly Confused Prepositions
With the huge number of prepositions in the English language, it almost seems impossible to have no confusion at all. Here is a list of prepositions that cause confusion among the users of the language.
- In/On/At
These three prepositions can be used to depict both time and position. Take a look at the table below to have a better understanding of how it works.
| Prepositions of Place | ||
| In | On | At |
| Can be used to show general locations like neighbourhoods, cities, countries and places with a boundary | Can be used to refer to more specific locations like streets, avenues, islands, surfaces and large vehicles | Can be used to refer to very specific locations |
| For example: I live in India.
We will be staying in a hotel tonight. |
For example: Latha stays on the fourth floor.
The book you are looking for is on the rack. |
For example: You can find us at the park.
She is at home now. |
| Prepositions of Time | ||
|---|---|---|
| In | On | At |
| Can be used to depict general timings like months, years, centuries and parts of days | Can be used to refer to dates, days of the week, days of the month and holidays with ‘day’ (for example – Republic day) | Can be used to denote very specific time, times of the day and holidays without ‘day’ (for example – Easter) |
| For example: Dan was born in 2000.
Technological development in the field of science and medicine reached its zenith in the 21st century. |
For example: There is a national parade every year on Republic day.
All of us will be at home on Christmas day. |
For example: We decided to meet at 4 p.m.
I wished my brother at midnight. |
- To/From
To and from are two other prepositions that create confusion.
| To | From |
| Used to denote the end location | Used to denote the starting location |
| For example: We went to Sri Lanka with my family.
I gave my coat to Sandra. |
For example: Have you started from Bangalore?
I received a letter from my father. |
- By/With
The prepositions by and with have various meanings. They sometimes appear to be confusing for a second language learner of English
| By | With |
| Near or next to.
For example: Is the post office by the bus stop? |
In the company of
For example: Glint went to Chennai with his friends. |
| A given time or not later than
For example: See that you reach the exam hall by 8:30 a.m. |
In addition to
For example: would you like to have tea with breakfast? |
| Denotes the doer of the action mentioned in a sentence
For example: The poem was written by my brother. |
By means of
For example: I cut my birthday cake with a fruit knife. |
Frequently Asked Questions on Prepositions in English
Q1
What is a preposition?
A preposition is a short word that is employed in sentences to show the relationship of nouns, pronouns or phrases with other parts within the respective sentences. Prepositions are normally found positioned in the latter part of the sentence.
Q2
What is the definition of a preposition?
A preposition is defined as “a word that connects a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun to another word, esp. to a verb, another noun, or an adjective”, according to the Cambridge Dictionary. The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary says that a preposition is “a word or group of words, such as in, from, to, out of and on behalf of, used before a noun or pronoun to show place, position, time or method.” The Collins Dictionary defines a preposition as “a word such as ‘by’, ‘for’, ‘into’, or ‘with’ which usually has a noun group as its object.” The Merriam Webster Dictionary provides a slightly different definition. According to it, a preposition is defined as “a function word that typically combines with a noun phrase to form a phrase which usually expresses a modification or predication.”
Q3
What are the different types of prepositions?
Prepositions can be divided into different types by categorising them according to their functions. The different types of prepositions are:
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Direction
- Prepositions of Location
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationships
- Prepositional Phrase
Q4
Give some examples of prepositions.
In, on, at, through, across, above, over, up, down, to, with, by, beside, beneath, in front of, between, among, etc. are some examples of prepositions.
Q5
How can we use prepositions in sentences?
Given below are some examples of how prepositions can be used in sentences.
- The supermarket will be closed from 9 p.m. to 9 a.m.
- Can you come after some time?
- Will you be with Raimy or Mazeeka?
- I love sitting beside the beach at night.
- Rachel met Phoebe by the lake.