На чтение 18 мин. Просмотров 75.2k.

сэр Артур Конан Дойл
Это большая ошибка — теоретизировать, прежде чем кто-то получит данные
Эта статья охватывает все, что вам нужно знать об использовании ячеек и диапазонов в VBA. Вы можете прочитать его от начала до конца, так как он сложен в логическом порядке. Или использовать оглавление ниже, чтобы перейти к разделу по вашему выбору.
Рассматриваемые темы включают свойство смещения, чтение
значений между ячейками, чтение значений в массивы и форматирование ячеек.
Содержание
- Краткое руководство по диапазонам и клеткам
- Введение
- Важное замечание
- Свойство Range
- Свойство Cells рабочего листа
- Использование Cells и Range вместе
- Свойство Offset диапазона
- Использование диапазона CurrentRegion
- Использование Rows и Columns в качестве Ranges
- Использование Range вместо Worksheet
- Чтение значений из одной ячейки в другую
- Использование метода Range.Resize
- Чтение Value в переменные
- Как копировать и вставлять ячейки
- Чтение диапазона ячеек в массив
- Пройти через все клетки в диапазоне
- Форматирование ячеек
- Основные моменты
Краткое руководство по диапазонам и клеткам
| Функция | Принимает | Возвращает | Пример | Вид |
| Range | адреса ячеек |
диапазон ячеек |
.Range(«A1:A4») | $A$1:$A$4 |
| Cells | строка, столбец |
одна ячейка |
.Cells(1,5) | $E$1 |
| Offset | строка, столбец |
диапазон | .Range(«A1:A2») .Offset(1,2) |
$C$2:$C$3 |
| Rows | строка (-и) | одна или несколько строк |
.Rows(4) .Rows(«2:4») |
$4:$4 $2:$4 |
| Columns | столбец (-цы) |
один или несколько столбцов |
.Columns(4) .Columns(«B:D») |
$D:$D $B:$D |
Введение
Это третья статья, посвященная трем основным элементам VBA. Этими тремя элементами являются Workbooks, Worksheets и Ranges/Cells. Cells, безусловно, самая важная часть Excel. Почти все, что вы делаете в Excel, начинается и заканчивается ячейками.
Вы делаете три основных вещи с помощью ячеек:
- Читаете из ячейки.
- Пишите в ячейку.
- Изменяете формат ячейки.
В Excel есть несколько методов для доступа к ячейкам, таких как Range, Cells и Offset. Можно запутаться, так как эти функции делают похожие операции.
В этой статье я расскажу о каждом из них, объясню, почему они вам нужны, и когда вам следует их использовать.
Давайте начнем с самого простого метода доступа к ячейкам — с помощью свойства Range рабочего листа.
Важное замечание
Я недавно обновил эту статью, сейчас использую Value2.
Вам может быть интересно, в чем разница между Value, Value2 и значением по умолчанию:
' Value2
Range("A1").Value2 = 56
' Value
Range("A1").Value = 56
' По умолчанию используется значение
Range("A1") = 56
Использование Value может усечь число, если ячейка отформатирована, как валюта. Если вы не используете какое-либо свойство, по умолчанию используется Value.
Лучше использовать Value2, поскольку он всегда будет возвращать фактическое значение ячейки.
Свойство Range
Рабочий лист имеет свойство Range, которое можно использовать для доступа к ячейкам в VBA. Свойство Range принимает тот же аргумент, что и большинство функций Excel Worksheet, например: «А1», «А3: С6» и т.д.
В следующем примере показано, как поместить значение в ячейку с помощью свойства Range.
Sub ZapisVYacheiku()
' Запишите число в ячейку A1 на листе 1 этой книги
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A1").Value2 = 67
' Напишите текст в ячейку A2 на листе 1 этой рабочей книги
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A2").Value2 = "Иван Петров"
' Запишите дату в ячейку A3 на листе 1 этой книги
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A3").Value2 = #11/21/2019#
End Sub
Как видно из кода, Range является членом Worksheets, которая, в свою очередь, является членом Workbook. Иерархия такая же, как и в Excel, поэтому должно быть легко понять. Чтобы сделать что-то с Range, вы должны сначала указать рабочую книгу и рабочий лист, которому она принадлежит.
В оставшейся части этой статьи я буду использовать кодовое имя для ссылки на лист.
Следующий код показывает приведенный выше пример с использованием кодового имени рабочего листа, т.е. Лист1 вместо ThisWorkbook.Worksheets («Лист1»).
Sub IspKodImya ()
' Запишите число в ячейку A1 на листе 1 этой книги
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = 67
' Напишите текст в ячейку A2 на листе 1 этой рабочей книги
Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = "Иван Петров"
' Запишите дату в ячейку A3 на листе 1 этой книги
Sheet1.Range("A3").Value2 = #11/21/2019#
End Sub
Вы также можете писать в несколько ячеек, используя свойство
Range
Sub ZapisNeskol()
' Запишите число в диапазон ячеек
Sheet1.Range("A1:A10").Value2 = 67
' Написать текст в несколько диапазонов ячеек
Sheet1.Range("B2:B5,B7:B9").Value2 = "Иван Петров"
End Sub
Свойство Cells рабочего листа
У Объекта листа есть другое свойство, называемое Cells, которое очень похоже на Range . Есть два отличия:
- Cells возвращают диапазон только одной ячейки.
- Cells принимает строку и столбец в качестве аргументов.
В приведенном ниже примере показано, как записывать значения
в ячейки, используя свойства Range и Cells.
Sub IspCells()
' Написать в А1
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = 10
Sheet1.Cells(1, 1).Value2 = 10
' Написать в А10
Sheet1.Range("A10").Value2 = 10
Sheet1.Cells(10, 1).Value2 = 10
' Написать в E1
Sheet1.Range("E1").Value2 = 10
Sheet1.Cells(1, 5).Value2 = 10
End Sub
Вам должно быть интересно, когда использовать Cells, а когда Range. Использование Range полезно для доступа к одним и тем же ячейкам при каждом запуске макроса.
Например, если вы использовали макрос для вычисления суммы и
каждый раз записывали ее в ячейку A10, тогда Range подойдет для этой задачи.
Использование свойства Cells полезно, если вы обращаетесь к
ячейке по номеру, который может отличаться. Проще объяснить это на примере.
В следующем коде мы просим пользователя указать номер столбца. Использование Cells дает нам возможность использовать переменное число для столбца.
Sub ZapisVPervuyuPustuyuYacheiku()
Dim UserCol As Integer
' Получить номер столбца от пользователя
UserCol = Application.InputBox("Пожалуйста, введите номер столбца...", Type:=1)
' Написать текст в выбранный пользователем столбец
Sheet1.Cells(1, UserCol).Value2 = "Иван Петров"
End Sub
В приведенном выше примере мы используем номер для столбца,
а не букву.
Чтобы использовать Range здесь, потребуется преобразовать эти значения в ссылку на
буквенно-цифровую ячейку, например, «С1». Использование свойства Cells позволяет нам
предоставить строку и номер столбца для доступа к ячейке.
Иногда вам может понадобиться вернуть более одной ячейки, используя номера строк и столбцов. В следующем разделе показано, как это сделать.
Использование Cells и Range вместе
Как вы уже видели, вы можете получить доступ только к одной ячейке, используя свойство Cells. Если вы хотите вернуть диапазон ячеек, вы можете использовать Cells с Range следующим образом:
Sub IspCellsSRange()
With Sheet1
' Запишите 5 в диапазон A1: A10, используя свойство Cells
.Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Value2 = 5
' Диапазон B1: Z1 будет выделен жирным шрифтом
.Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Font.Bold = True
End With
End Sub
Как видите, вы предоставляете начальную и конечную ячейку
диапазона. Иногда бывает сложно увидеть, с каким диапазоном вы имеете дело,
когда значением являются все числа. Range имеет свойство Address, которое
отображает буквенно-цифровую ячейку для любого диапазона. Это может
пригодиться, когда вы впервые отлаживаете или пишете код.
В следующем примере мы распечатываем адрес используемых нами
диапазонов.
Sub PokazatAdresDiapazona()
' Примечание. Использование подчеркивания позволяет разделить строки кода.
With Sheet1
' Запишите 5 в диапазон A1: A10, используя свойство Cells
.Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Value2 = 5
Debug.Print "Первый адрес: " _
+ .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Address
' Диапазон B1: Z1 будет выделен жирным шрифтом
.Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Font.Bold = True
Debug.Print "Второй адрес : " _
+ .Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Address
End With
End Sub
В примере я использовал Debug.Print для печати в Immediate Window. Для просмотра этого окна выберите «View» -> «в Immediate Window» (Ctrl + G).
Свойство Offset диапазона
У диапазона есть свойство, которое называется Offset. Термин «Offset» относится к отсчету от исходной позиции. Он часто используется в определенных областях программирования. С помощью свойства «Offset» вы можете получить диапазон ячеек того же размера и на определенном расстоянии от текущего диапазона. Это полезно, потому что иногда вы можете выбрать диапазон на основе определенного условия. Например, на скриншоте ниже есть столбец для каждого дня недели. Учитывая номер дня (т.е. понедельник = 1, вторник = 2 и т.д.). Нам нужно записать значение в правильный столбец.
Сначала мы попытаемся сделать это без использования Offset.
' Это Sub тесты с разными значениями
Sub TestSelect()
' Понедельник
SetValueSelect 1, 111.21
' Среда
SetValueSelect 3, 456.99
' Пятница
SetValueSelect 5, 432.25
' Воскресение
SetValueSelect 7, 710.17
End Sub
' Записывает значение в столбец на основе дня
Public Sub SetValueSelect(lDay As Long, lValue As Currency)
Select Case lDay
Case 1: Sheet1.Range("H3").Value2 = lValue
Case 2: Sheet1.Range("I3").Value2 = lValue
Case 3: Sheet1.Range("J3").Value2 = lValue
Case 4: Sheet1.Range("K3").Value2 = lValue
Case 5: Sheet1.Range("L3").Value2 = lValue
Case 6: Sheet1.Range("M3").Value2 = lValue
Case 7: Sheet1.Range("N3").Value2 = lValue
End Select
End Sub
Как видно из примера, нам нужно добавить строку для каждого возможного варианта. Это не идеальная ситуация. Использование свойства Offset обеспечивает более чистое решение.
' Это Sub тесты с разными значениями
Sub TestOffset()
DayOffSet 1, 111.01
DayOffSet 3, 456.99
DayOffSet 5, 432.25
DayOffSet 7, 710.17
End Sub
Public Sub DayOffSet(lDay As Long, lValue As Currency)
' Мы используем значение дня с Offset, чтобы указать правильный столбец
Sheet1.Range("G3").Offset(, lDay).Value2 = lValue
End Sub
Как видите, это решение намного лучше. Если количество дней увеличилось, нам больше не нужно добавлять код. Чтобы Offset был полезен, должна быть какая-то связь между позициями ячеек. Если столбцы Day в приведенном выше примере были случайными, мы не могли бы использовать Offset. Мы должны были бы использовать первое решение.
Следует иметь в виду, что Offset сохраняет размер диапазона. Итак .Range («A1:A3»).Offset (1,1) возвращает диапазон B2:B4. Ниже приведены еще несколько примеров использования Offset.
Sub IspOffset()
' Запись в В2 - без Offset
Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset().Value2 = "Ячейка B2"
' Написать в C2 - 1 столбец справа
Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(, 1).Value2 = "Ячейка C2"
' Написать в B3 - 1 строка вниз
Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(1).Value2 = "Ячейка B3"
' Запись в C3 - 1 столбец справа и 1 строка вниз
Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(1, 1).Value2 = "Ячейка C3"
' Написать в A1 - 1 столбец слева и 1 строка вверх
Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(-1, -1).Value2 = "Ячейка A1"
' Запись в диапазон E3: G13 - 1 столбец справа и 1 строка вниз
Sheet1.Range("D2:F12").Offset(1, 1).Value2 = "Ячейки E3:G13"
End Sub
Использование диапазона CurrentRegion
CurrentRegion возвращает диапазон всех соседних ячеек в данный диапазон. На скриншоте ниже вы можете увидеть два CurrentRegion. Я добавил границы, чтобы прояснить CurrentRegion.
Строка или столбец пустых ячеек означает конец CurrentRegion.
Вы можете вручную проверить
CurrentRegion в Excel, выбрав диапазон и нажав Ctrl + Shift + *.
Если мы возьмем любой диапазон
ячеек в пределах границы и применим CurrentRegion, мы вернем диапазон ячеек во
всей области.
Например:
Range («B3»). CurrentRegion вернет диапазон B3:D14
Range («D14»). CurrentRegion вернет диапазон B3:D14
Range («C8:C9»). CurrentRegion вернет диапазон B3:D14 и так далее
Как пользоваться
Мы получаем CurrentRegion следующим образом
' CurrentRegion вернет B3:D14 из приведенного выше примера
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion
Только чтение строк данных
Прочитать диапазон из второй строки, т.е. пропустить строку заголовка.
' CurrentRegion вернет B3:D14 из приведенного выше примера
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion
' Начало в строке 2 - строка после заголовка
Dim i As Long
For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count
' текущая строка, столбец 1 диапазона
Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value2
Next i
Удалить заголовок
Удалить строку заголовка (т.е. первую строку) из диапазона. Например, если диапазон — A1:D4, это возвратит A2:D4
' CurrentRegion вернет B3:D14 из приведенного выше примера
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion
' Удалить заголовок
Set rg = rg.Resize(rg.Rows.Count - 1).Offset(1)
' Начните со строки 1, так как нет строки заголовка
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To rg.Rows.Count
' текущая строка, столбец 1 диапазона
Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value2
Next i
Использование Rows и Columns в качестве Ranges
Если вы хотите что-то сделать со всей строкой или столбцом,
вы можете использовать свойство «Rows и
Columns» на рабочем листе. Они оба принимают один параметр — номер строки
или столбца, к которому вы хотите получить доступ.
Sub IspRowIColumns()
' Установите размер шрифта столбца B на 9
Sheet1.Columns(2).Font.Size = 9
' Установите ширину столбцов от D до F
Sheet1.Columns("D:F").ColumnWidth = 4
' Установите размер шрифта строки 5 до 18
Sheet1.Rows(5).Font.Size = 18
End Sub
Использование Range вместо Worksheet
Вы также можете использовать Cella, Rows и Columns, как часть Range, а не как часть Worksheet. У вас может быть особая необходимость в этом, но в противном случае я бы избегал практики. Это делает код более сложным. Простой код — твой друг. Это уменьшает вероятность ошибок.
Код ниже выделит второй столбец диапазона полужирным. Поскольку диапазон имеет только две строки, весь столбец считается B1:B2
Sub IspColumnsVRange()
' Это выделит B1 и B2 жирным шрифтом.
Sheet1.Range("A1:C2").Columns(2).Font.Bold = True
End Sub
Чтение значений из одной ячейки в другую
В большинстве примеров мы записали значения в ячейку. Мы
делаем это, помещая диапазон слева от знака равенства и значение для размещения
в ячейке справа. Для записи данных из одной ячейки в другую мы делаем то же
самое. Диапазон назначения идет слева, а диапазон источника — справа.
В следующем примере показано, как это сделать:
Sub ChitatZnacheniya()
' Поместите значение из B1 в A1
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1").Value2
' Поместите значение из B3 в лист2 в ячейку A1
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = Sheet2.Range("B3").Value2
' Поместите значение от B1 в ячейки A1 до A5
Sheet1.Range("A1:A5").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1").Value2
' Вам необходимо использовать свойство «Value», чтобы прочитать несколько ячеек
Sheet1.Range("A1:A5").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1:B5").Value2
End Sub
Как видно из этого примера, невозможно читать из нескольких ячеек. Если вы хотите сделать это, вы можете использовать функцию копирования Range с параметром Destination.
Sub KopirovatZnacheniya()
' Сохранить диапазон копирования в переменной
Dim rgCopy As Range
Set rgCopy = Sheet1.Range("B1:B5")
' Используйте это для копирования из более чем одной ячейки
rgCopy.Copy Destination:=Sheet1.Range("A1:A5")
' Вы можете вставить в несколько мест назначения
rgCopy.Copy Destination:=Sheet1.Range("A1:A5,C2:C6")
End Sub
Функция Copy копирует все, включая формат ячеек. Это тот же результат, что и ручное копирование и вставка выделения. Подробнее об этом вы можете узнать в разделе «Копирование и вставка ячеек»
Использование метода Range.Resize
При копировании из одного диапазона в другой с использованием присваивания (т.е. знака равенства) диапазон назначения должен быть того же размера, что и исходный диапазон.
Использование функции Resize позволяет изменить размер
диапазона до заданного количества строк и столбцов.
Например:
Sub ResizePrimeri()
' Печатает А1
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Address
' Печатает A1:A2
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(2, 1).Address
' Печатает A1:A5
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(5, 1).Address
' Печатает A1:D1
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(1, 4).Address
' Печатает A1:C3
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(3, 3).Address
End Sub
Когда мы хотим изменить наш целевой диапазон, мы можем
просто использовать исходный размер диапазона.
Другими словами, мы используем количество строк и столбцов
исходного диапазона в качестве параметров для изменения размера:
Sub Resize()
Dim rgSrc As Range, rgDest As Range
' Получить все данные в текущей области
Set rgSrc = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
' Получить диапазон назначения
Set rgDest = Sheet2.Range("A1")
Set rgDest = rgDest.Resize(rgSrc.Rows.Count, rgSrc.Columns.Count)
rgDest.Value2 = rgSrc.Value2
End Sub
Мы можем сделать изменение размера в одну строку, если нужно:
Sub Resize2()
Dim rgSrc As Range
' Получить все данные в ткущей области
Set rgSrc = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
With rgSrc
Sheet2.Range("A1").Resize(.Rows.Count, .Columns.Count) = .Value2
End With
End Sub
Чтение Value в переменные
Мы рассмотрели, как читать из одной клетки в другую. Вы также можете читать из ячейки в переменную. Переменная используется для хранения значений во время работы макроса. Обычно вы делаете это, когда хотите манипулировать данными перед тем, как их записать. Ниже приведен простой пример использования переменной. Как видите, значение элемента справа от равенства записывается в элементе слева от равенства.
Sub IspVar()
' Создайте
Dim val As Integer
' Читать число из ячейки
val = Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2
' Добавить 1 к значению
val = val + 1
' Запишите новое значение в ячейку
Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = val
End Sub
Для чтения текста в переменную вы используете переменную
типа String.
Sub IspVarText()
' Объявите переменную типа string
Dim sText As String
' Считать значение из ячейки
sText = Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2
' Записать значение в ячейку
Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = sText
End Sub
Вы можете записать переменную в диапазон ячеек. Вы просто
указываете диапазон слева, и значение будет записано во все ячейки диапазона.
Sub VarNeskol()
' Считать значение из ячейки
Sheet1.Range("A1:B10").Value2 = 66
End Sub
Вы не можете читать из нескольких ячеек в переменную. Однако
вы можете читать массив, который представляет собой набор переменных. Мы
рассмотрим это в следующем разделе.
Как копировать и вставлять ячейки
Если вы хотите скопировать и вставить диапазон ячеек, вам не
нужно выбирать их. Это распространенная ошибка, допущенная новыми пользователями
VBA.
Вы можете просто скопировать ряд ячеек, как здесь:
Range("A1:B4").Copy Destination:=Range("C5")
При использовании этого метода копируется все — значения,
форматы, формулы и так далее. Если вы хотите скопировать отдельные элементы, вы
можете использовать свойство PasteSpecial
диапазона.
Работает так:
Range("A1:B4").Copy
Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormats
Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormulas
В следующей таблице приведен полный список всех типов вставок.
| Виды вставок |
| xlPasteAll |
| xlPasteAllExceptBorders |
| xlPasteAllMergingConditionalFormats |
| xlPasteAllUsingSourceTheme |
| xlPasteColumnWidths |
| xlPasteComments |
| xlPasteFormats |
| xlPasteFormulas |
| xlPasteFormulasAndNumberFormats |
| xlPasteValidation |
| xlPasteValues |
| xlPasteValuesAndNumberFormats |
Чтение диапазона ячеек в массив
Вы также можете скопировать значения, присвоив значение
одного диапазона другому.
Range("A3:Z3").Value2 = Range("A1:Z1").Value2
Значение диапазона в этом примере считается вариантом массива. Это означает, что вы можете легко читать из диапазона ячеек в массив. Вы также можете писать из массива в диапазон ячеек. Если вы не знакомы с массивами, вы можете проверить их в этой статье.
В следующем коде показан пример использования массива с
диапазоном.
Sub ChitatMassiv()
' Создать динамический массив
Dim StudentMarks() As Variant
' Считать 26 значений в массив из первой строки
StudentMarks = Range("A1:Z1").Value2
' Сделайте что-нибудь с массивом здесь
' Запишите 26 значений в третью строку
Range("A3:Z3").Value2 = StudentMarks
End Sub
Имейте в виду, что массив, созданный для чтения, является
двумерным массивом. Это связано с тем, что электронная таблица хранит значения
в двух измерениях, то есть в строках и столбцах.
Пройти через все клетки в диапазоне
Иногда вам нужно просмотреть каждую ячейку, чтобы проверить значение.
Вы можете сделать это, используя цикл For Each, показанный в следующем коде.
Sub PeremeschatsyaPoYacheikam()
' Пройдите через каждую ячейку в диапазоне
Dim rg As Range
For Each rg In Sheet1.Range("A1:A10,A20")
' Распечатать адрес ячеек, которые являются отрицательными
If rg.Value < 0 Then
Debug.Print rg.Address + " Отрицательно."
End If
Next
End Sub
Вы также можете проходить последовательные ячейки, используя
свойство Cells и стандартный цикл For.
Стандартный цикл более гибок в отношении используемого вами
порядка, но он медленнее, чем цикл For Each.
Sub PerehodPoYacheikam()
' Пройдите клетки от А1 до А10
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To 10
' Распечатать адрес ячеек, которые являются отрицательными
If Range("A" & i).Value < 0 Then
Debug.Print Range("A" & i).Address + " Отрицательно."
End If
Next
' Пройдите в обратном порядке, то есть от A10 до A1
For i = 10 To 1 Step -1
' Распечатать адрес ячеек, которые являются отрицательными
If Range("A" & i) < 0 Then
Debug.Print Range("A" & i).Address + " Отрицательно."
End If
Next
End Sub
Форматирование ячеек
Иногда вам нужно будет отформатировать ячейки в электронной
таблице. Это на самом деле очень просто. В следующем примере показаны различные
форматы, которые можно добавить в любой диапазон ячеек.
Sub FormatirovanieYacheek()
With Sheet1
' Форматировать шрифт
.Range("A1").Font.Bold = True
.Range("A1").Font.Underline = True
.Range("A1").Font.Color = rgbNavy
' Установите числовой формат до 2 десятичных знаков
.Range("B2").NumberFormat = "0.00"
' Установите числовой формат даты
.Range("C2").NumberFormat = "dd/mm/yyyy"
' Установите формат чисел на общий
.Range("C3").NumberFormat = "Общий"
' Установить числовой формат текста
.Range("C4").NumberFormat = "Текст"
' Установите цвет заливки ячейки
.Range("B3").Interior.Color = rgbSandyBrown
' Форматировать границы
.Range("B4").Borders.LineStyle = xlDash
.Range("B4").Borders.Color = rgbBlueViolet
End With
End Sub
Основные моменты
Ниже приводится краткое изложение основных моментов
- Range возвращает диапазон ячеек
- Cells возвращают только одну клетку
- Вы можете читать из одной ячейки в другую
- Вы можете читать из диапазона ячеек в другой диапазон ячеек.
- Вы можете читать значения из ячеек в переменные и наоборот.
- Вы можете читать значения из диапазонов в массивы и наоборот
- Вы можете использовать цикл For Each или For, чтобы проходить через каждую ячейку в диапазоне.
- Свойства Rows и Columns позволяют вам получить доступ к диапазону ячеек этих типов
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for iPad Excel for iPhone Excel for Android tablets Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel for Android phones Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
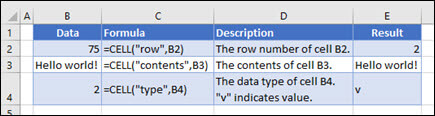
The CELL function returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell. For example, if you want to verify that a cell contains a numeric value instead of text before you perform a calculation on it, you can use the following formula:
=IF(CELL(«type»,A1)=»v»,A1*2,0)
This formula calculates A1*2 only if cell A1 contains a numeric value, and returns 0 if A1 contains text or is blank.
Note: Formulas that use CELL have language-specific argument values and will return errors if calculated using a different language version of Excel. For example, if you create a formula containing CELL while using the Czech version of Excel, that formula will return an error if the workbook is opened using the French version. If it is important for others to open your workbook using different language versions of Excel, consider either using alternative functions or allowing others to save local copies in which they revise the CELL arguments to match their language.
Syntax
CELL(info_type, [reference])
The CELL function syntax has the following arguments:
|
Argument |
Description |
|---|---|
|
info_type Required |
A text value that specifies what type of cell information you want to return. The following list shows the possible values of the Info_type argument and the corresponding results. |
|
reference Optional |
The cell that you want information about. If omitted, the information specified in the info_type argument is returned for cell selected at the time of calculation. If the reference argument is a range of cells, the CELL function returns the information for active cell in the selected range. Important: Although technically reference is optional, including it in your formula is encouraged, unless you understand the effect its absence has on your formula result and want that effect in place. Omitting the reference argument does not reliably produce information about a specific cell, for the following reasons:
|
info_type values
The following list describes the text values that can be used for the info_type argument. These values must be entered in the CELL function with quotes (» «).
|
info_type |
Returns |
|---|---|
|
«address» |
Reference of the first cell in reference, as text. |
|
«col» |
Column number of the cell in reference. |
|
«color» |
The value 1 if the cell is formatted in color for negative values; otherwise returns 0 (zero). Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«contents» |
Value of the upper-left cell in reference; not a formula. |
|
«filename» |
Filename (including full path) of the file that contains reference, as text. Returns empty text («») if the worksheet that contains reference has not yet been saved. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«format» |
Text value corresponding to the number format of the cell. The text values for the various formats are shown in the following table. Returns «-» at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted in color for negative values. Returns «()» at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«parentheses» |
The value 1 if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values; otherwise returns 0. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«prefix» |
Text value corresponding to the «label prefix» of the cell. Returns single quotation mark (‘) if the cell contains left-aligned text, double quotation mark («) if the cell contains right-aligned text, caret (^) if the cell contains centered text, backslash () if the cell contains fill-aligned text, and empty text («») if the cell contains anything else. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«protect» |
The value 0 if the cell is not locked; otherwise returns 1 if the cell is locked. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«row» |
Row number of the cell in reference. |
|
«type» |
Text value corresponding to the type of data in the cell. Returns «b» for blank if the cell is empty, «l» for label if the cell contains a text constant, and «v» for value if the cell contains anything else. |
|
«width» |
Returns an array with 2 items. The 1st item in the array is the column width of the cell, rounded off to an integer. Each unit of column width is equal to the width of one character in the default font size. The 2nd item in the array is a Boolean value, the value is TRUE if the column width is the default or FALSE if the width has been explicitly set by the user. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
CELL format codes
The following list describes the text values that the CELL function returns when the Info_type argument is «format» and the reference argument is a cell that is formatted with a built-in number format.
|
If the Excel format is |
The CELL function returns |
|---|---|
|
General |
«G» |
|
0 |
«F0» |
|
#,##0 |
«,0» |
|
0.00 |
«F2» |
|
#,##0.00 |
«,2» |
|
$#,##0_);($#,##0) |
«C0» |
|
$#,##0_);[Red]($#,##0) |
«C0-« |
|
$#,##0.00_);($#,##0.00) |
«C2» |
|
$#,##0.00_);[Red]($#,##0.00) |
«C2-« |
|
0% |
«P0» |
|
0.00% |
«P2» |
|
0.00E+00 |
«S2» |
|
# ?/? or # ??/?? |
«G» |
|
m/d/yy or m/d/yy h:mm or mm/dd/yy |
«D4» |
|
d-mmm-yy or dd-mmm-yy |
«D1» |
|
d-mmm or dd-mmm |
«D2» |
|
mmm-yy |
«D3» |
|
mm/dd |
«D5» |
|
h:mm AM/PM |
«D7» |
|
h:mm:ss AM/PM |
«D6» |
|
h:mm |
«D9» |
|
h:mm:ss |
«D8» |
Note: If the info_type argument in the CELL function is «format» and you later apply a different format to the referenced cell, you must recalculate the worksheet (press F9) to update the results of the CELL function.
Examples
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Change the format of a cell
Create or change a cell reference
ADDRESS function
Add, change, find or clear conditional formatting in a cell
Need more help?
In Microsoft Excel, a cell is a rectangular box that occurs at the intersection of a vertical column and a horizontal row in a worksheet. Vertical columns are numbered with alphabetic values such as A, B, C. Horizontal rows are numbered with numeric values such as 1, 2, 3.
Each cell has its own set of coordinates or position in the worksheet such as A1, A2, or M16. In the example above, we are positioned on cell A1 which is the intersection of column A and row 1.
A cell can only store 1 piece of data at a time. You can store data in a cell such as a formula, text value, numeric value, or date value.
There are many things that you can do with cells in Excel such as changing the font format, number format, background, alignment, and conditional formatting. Here is a list of topics that explain how to use cells in Excel.
Font Format
- Change the font in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Change the font color in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Change the font size in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Draw a line through a value in a cell (strikethrough) in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Create a subscript value in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Create a superscript value in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Use the Format Painter Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Number Format
- Format display of text in a cell (ie: numbers, dates, etc) in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Fill/Background Format
- Change the background color of a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Alignment Format
- Align text to the top of the cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Center text across multiple cells in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Wrap text in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Merge cells in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Wrap text in merged cells in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Rotate text in a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Stop «wrap text» when pasting in Excel 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Border/Line Format
- Draw a border around a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Protection
- Protect a cell in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Hide formulas from appearing in the edit bar in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Conditional Formatting
- Change the font color based on the value in the cell in Excel 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Automatically alternate row colors (one shaded, one white) in Excel 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Automatically alternate row colors (two shaded, two white) in Excel 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Automatically alternate row colors (three shaded, three white) in Excel 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Automatically highlight highest and lowest values in a range of cells in Excel 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Automatically highlight expired dates and dates that are 30 days from expiration in Excel 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Highlight 1st, 2nd, 3rd highest scores in Excel 2003
- Change the font color in one cell based on the value in another cell in Excel 2003
Data Validation
- Set up a cell to allow a maximum number of characters in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Set up a cell to allow a specific number of characters in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
- Set up a cell to allow positive numbers in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Comments
- Display comment indicator in Excel 2016 | 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
AutoCorrect
- Turn off AutoCorrect in Excel 2010 | 2007 | 2003
Miscellaneous
- Copy and paste only nonblank cells (condensing paste range) in Excel 2013 | 2011 | 2010 | 2007 | 2003
A cell is the storage unit in a spreadsheet program like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. Cells are the boxes in a spreadsheet that may contain data. The cells in a spreadsheet are organized within a column and row in the worksheet, and can be formatted for aesthetics or visibility.
Instructions in this article apply to Excel 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010; Excel for Microsoft 365; Excel Online; Excel for Mac; and Google Sheets.
Spreadsheet Cell Types
Cells hold four types of information (also called data types):
- Numbers that can include formulas, dates, and times.
- Text, often referred to as text strings or just strings.
- Boolean values of TRUE or FALSE.
- Errors including #NULL!, #REF!, and #DIV/0! that indicate a problem.
What Are Cell References?
Cell referencing is a system that identifies data and gives it an address so that data can be located in a spreadsheet. A cell reference is used in spreadsheets to identify individual cells and is a combination of the column letter and row number where it is located.
To write a cell reference, start with the column letter and end with the row number, such as A14 or BB329. In the image above, the word Household is located in cell F1 and the highlighted cell is G7.
Cell references are used in formulas to reference other cells. For example, instead of entering the number $360 into a formula found in cell D1, enter a reference to cell G5. When a cell reference is used, if the data in cell G5 changes, the formula in cell D1 also changes.
Cells Can Be Formatted
By default, all cells in a worksheet use the same formatting, but this makes large worksheets containing lots of data difficult to read. Formatting a worksheet draws attention to specific sections and makes data easier to read and understand.
Cell formatting involves making changes to the cell, such as changing the background color, adding borders, or aligning the data in the cell. In contrast, number formatting deals with the way numbers in the cells are displayed, for example, to reflect a currency or percent.
Displayed vs. Stored Numbers
In both Excel and Google Sheets, when number formats are applied, the number that displays in the cell may differ from the number that is stored in the cell and used in calculations.
When formatting changes are made to numbers in a cell, those changes affect the appearance of the number and not the number itself.
For example, if the number 5.6789 in a cell is formatted to display only two decimal places (two digits to the right of the decimal), the cell displays the number as 5.68 due to rounding of the third digit.
Calculations and Formatted Numbers
When using formatted cells of data in calculations, the entire number, in this case, 5.6789, is used in all calculations, not the rounded number appearing in the cell.
How to Add More Cells to a Worksheet
A worksheet has an unlimited number of cells, so you don’t need to add more to the sheet. But, you can add data inside the spreadsheet by adding a cell or group of cells between other cells.
To add a cell to a worksheet:
-
Right-click or tap-and-hold the cell location where you want to add a cell.
-
In Google Sheets, select Insert cells, then choose Shift right or Shift down. This moves every cell in that direction one space and inserts a blank cell in the selected area.
In Excel, choose Insert, then choose either Shift cells right, Shift cells down, Entire row, or Entire column. Select OK to insert the cell.
If you select more than one cell, the program inserts that many cells into the worksheet. For example, highlight one cell to insert just one cell or highlight five cells to add five cells to that location.
-
The cells move and blank cells are inserted.
Delete Cells and Cell Contents
Individual cells and their contents can be deleted from a worksheet. When this happens, cells and their data from either below or to the right of the deleted cell move to fill the gap.
-
Highlight one or more cells to be deleted.
-
Right-click the selected cells and choose Delete.
-
In Excel, choose either Shift cells left or Shift cells up, then select OK. The menu shown here is one way to remove rows and columns.
In Google Sheets, choose Shift left or Shift up.
-
The cells and the corresponding data are removed.
To delete the contents of one or more cells without deleting the cell, highlight the cells and press Delete.
FAQ
-
How do you reference a cell in another Google spreadsheet?
You can use Google Sheets to reference data from another sheet. First, place your cursor in the cell where you want the data and type an equal (=) sign. Next, go to the second sheet, select the cell you want to reference, and press Enter.
-
How do you change cell size in a Google spreadsheet?
To change cell sizes, you can resize rows or columns. One way to do so is with the mouse. Place the mouse pointer on the boundary line between columns or rows, then hold down the left mouse button and drag the double-headed arrow to the desired row or column size.
-
How do you change cell color in a Google spreadsheet?
Select the cell or range of cells to change. Next, select the Fill color icon in the menu bar, and choose the color you want to use.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
“It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data”- Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
This post covers everything you need to know about using Cells and Ranges in VBA. You can read it from start to finish as it is laid out in a logical order. If you prefer you can use the table of contents below to go to a section of your choice.
Topics covered include Offset property, reading values between cells, reading values to arrays and formatting cells.
A Quick Guide to Ranges and Cells
| Function | Takes | Returns | Example | Gives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Range |
cell address | multiple cells | .Range(«A1:A4») | $A$1:$A$4 |
| Cells | row, column | one cell | .Cells(1,5) | $E$1 |
| Offset | row, column | multiple cells | Range(«A1:A2») .Offset(1,2) |
$C$2:$C$3 |
| Rows | row(s) | one or more rows | .Rows(4) .Rows(«2:4») |
$4:$4 $2:$4 |
| Columns | column(s) | one or more columns | .Columns(4) .Columns(«B:D») |
$D:$D $B:$D |
Download the Code
The Webinar
If you are a member of the VBA Vault, then click on the image below to access the webinar and the associated source code.
(Note: Website members have access to the full webinar archive.)
Introduction
This is the third post dealing with the three main elements of VBA. These three elements are the Workbooks, Worksheets and Ranges/Cells. Cells are by far the most important part of Excel. Almost everything you do in Excel starts and ends with Cells.
Generally speaking, you do three main things with Cells
- Read from a cell.
- Write to a cell.
- Change the format of a cell.
Excel has a number of methods for accessing cells such as Range, Cells and Offset.These can cause confusion as they do similar things and can lead to confusion
In this post I will tackle each one, explain why you need it and when you should use it.
Let’s start with the simplest method of accessing cells – using the Range property of the worksheet.
Important Notes
I have recently updated this article so that is uses Value2.
You may be wondering what is the difference between Value, Value2 and the default:
' Value2 Range("A1").Value2 = 56 ' Value Range("A1").Value = 56 ' Default uses value Range("A1") = 56
Using Value may truncate number if the cell is formatted as currency. If you don’t use any property then the default is Value.
It is better to use Value2 as it will always return the actual cell value(see this article from Charle Williams.)
The Range Property
The worksheet has a Range property which you can use to access cells in VBA. The Range property takes the same argument that most Excel Worksheet functions take e.g. “A1”, “A3:C6” etc.
The following example shows you how to place a value in a cell using the Range property.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub WriteToCell() ' Write number to cell A1 in sheet1 of this workbook ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Value2 = 67 ' Write text to cell A2 in sheet1 of this workbook ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value2 = "John Smith" ' Write date to cell A3 in sheet1 of this workbook ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A3").Value2 = #11/21/2017# End Sub
As you can see Range is a member of the worksheet which in turn is a member of the Workbook. This follows the same hierarchy as in Excel so should be easy to understand. To do something with Range you must first specify the workbook and worksheet it belongs to.
For the rest of this post I will use the code name to reference the worksheet.
The following code shows the above example using the code name of the worksheet i.e. Sheet1 instead of ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(“Sheet1”).
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UsingCodeName() ' Write number to cell A1 in sheet1 of this workbook Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = 67 ' Write text to cell A2 in sheet1 of this workbook Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = "John Smith" ' Write date to cell A3 in sheet1 of this workbook Sheet1.Range("A3").Value2 = #11/21/2017# End Sub
You can also write to multiple cells using the Range property
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub WriteToMulti() ' Write number to a range of cells Sheet1.Range("A1:A10").Value2 = 67 ' Write text to multiple ranges of cells Sheet1.Range("B2:B5,B7:B9").Value2 = "John Smith" End Sub
You can download working examples of all the code from this post from the top of this article.
The Cells Property of the Worksheet
The worksheet object has another property called Cells which is very similar to range. There are two differences
- Cells returns a range of one cell only.
- Cells takes row and column as arguments.
The example below shows you how to write values to cells using both the Range and Cells property
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UsingCells() ' Write to A1 Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = 10 Sheet1.Cells(1, 1).Value2 = 10 ' Write to A10 Sheet1.Range("A10").Value2 = 10 Sheet1.Cells(10, 1).Value2 = 10 ' Write to E1 Sheet1.Range("E1").Value2 = 10 Sheet1.Cells(1, 5).Value2 = 10 End Sub
You may be wondering when you should use Cells and when you should use Range. Using Range is useful for accessing the same cells each time the Macro runs.
For example, if you were using a Macro to calculate a total and write it to cell A10 every time then Range would be suitable for this task.
Using the Cells property is useful if you are accessing a cell based on a number that may vary. It is easier to explain this with an example.
In the following code, we ask the user to specify the column number. Using Cells gives us the flexibility to use a variable number for the column.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub WriteToColumn() Dim UserCol As Integer ' Get the column number from the user UserCol = Application.InputBox(" Please enter the column...", Type:=1) ' Write text to user selected column Sheet1.Cells(1, UserCol).Value2 = "John Smith" End Sub
In the above example, we are using a number for the column rather than a letter.
To use Range here would require us to convert these values to the letter/number cell reference e.g. “C1”. Using the Cells property allows us to provide a row and a column number to access a cell.
Sometimes you may want to return more than one cell using row and column numbers. The next section shows you how to do this.
Using Cells and Range together
As you have seen you can only access one cell using the Cells property. If you want to return a range of cells then you can use Cells with Ranges as follows
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UsingCellsWithRange() With Sheet1 ' Write 5 to Range A1:A10 using Cells property .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Value2 = 5 ' Format Range B1:Z1 to be bold .Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Font.Bold = True End With End Sub
As you can see, you provide the start and end cell of the Range. Sometimes it can be tricky to see which range you are dealing with when the value are all numbers. Range has a property called Address which displays the letter/ number cell reference of any range. This can come in very handy when you are debugging or writing code for the first time.
In the following example we print out the address of the ranges we are using:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub ShowRangeAddress() ' Note: Using underscore allows you to split up lines of code With Sheet1 ' Write 5 to Range A1:A10 using Cells property .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Value2 = 5 Debug.Print "First address is : " _ + .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(10, 1)).Address ' Format Range B1:Z1 to be bold .Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Font.Bold = True Debug.Print "Second address is : " _ + .Range(.Cells(1, 2), .Cells(1, 26)).Address End With End Sub
In the example I used Debug.Print to print to the Immediate Window. To view this window select View->Immediate Window(or Ctrl G)
You can download all the code for this post from the top of this article.
The Offset Property of Range
Range has a property called Offset. The term Offset refers to a count from the original position. It is used a lot in certain areas of programming. With the Offset property you can get a Range of cells the same size and a certain distance from the current range. The reason this is useful is that sometimes you may want to select a Range based on a certain condition. For example in the screenshot below there is a column for each day of the week. Given the day number(i.e. Monday=1, Tuesday=2 etc.) we need to write the value to the correct column.
We will first attempt to do this without using Offset.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ ' This sub tests with different values Public Sub TestSelect() ' Monday SetValueSelect 1, 111.21 ' Wednesday SetValueSelect 3, 456.99 ' Friday SetValueSelect 5, 432.25 ' Sunday SetValueSelect 7, 710.17 End Sub ' Writes the value to a column based on the day Public Sub SetValueSelect(lDay As Long, lValue As Currency) Select Case lDay Case 1: Sheet1.Range("H3").Value2 = lValue Case 2: Sheet1.Range("I3").Value2 = lValue Case 3: Sheet1.Range("J3").Value2 = lValue Case 4: Sheet1.Range("K3").Value2 = lValue Case 5: Sheet1.Range("L3").Value2 = lValue Case 6: Sheet1.Range("M3").Value2 = lValue Case 7: Sheet1.Range("N3").Value2 = lValue End Select End Sub
As you can see in the example, we need to add a line for each possible option. This is not an ideal situation. Using the Offset Property provides a much cleaner solution
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ ' This sub tests with different values Public Sub TestOffset() DayOffSet 1, 111.01 DayOffSet 3, 456.99 DayOffSet 5, 432.25 DayOffSet 7, 710.17 End Sub Public Sub DayOffSet(lDay As Long, lValue As Currency) ' We use the day value with offset specify the correct column Sheet1.Range("G3").Offset(, lDay).Value2 = lValue End Sub
As you can see this solution is much better. If the number of days in increased then we do not need to add any more code. For Offset to be useful there needs to be some kind of relationship between the positions of the cells. If the Day columns in the above example were random then we could not use Offset. We would have to use the first solution.
One thing to keep in mind is that Offset retains the size of the range. So .Range(“A1:A3”).Offset(1,1) returns the range B2:B4. Below are some more examples of using Offset
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UsingOffset() ' Write to B2 - no offset Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset().Value2 = "Cell B2" ' Write to C2 - 1 column to the right Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(, 1).Value2 = "Cell C2" ' Write to B3 - 1 row down Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(1).Value2 = "Cell B3" ' Write to C3 - 1 column right and 1 row down Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(1, 1).Value2 = "Cell C3" ' Write to A1 - 1 column left and 1 row up Sheet1.Range("B2").Offset(-1, -1).Value2 = "Cell A1" ' Write to range E3:G13 - 1 column right and 1 row down Sheet1.Range("D2:F12").Offset(1, 1).Value2 = "Cells E3:G13" End Sub
Using the Range CurrentRegion
CurrentRegion returns a range of all the adjacent cells to the given range.
In the screenshot below you can see the two current regions. I have added borders to make the current regions clear.
A row or column of blank cells signifies the end of a current region.
You can manually check the CurrentRegion in Excel by selecting a range and pressing Ctrl + Shift + *.
If we take any range of cells within the border and apply CurrentRegion, we will get back the range of cells in the entire area.
For example
Range(“B3”).CurrentRegion will return the range B3:D14
Range(“D14”).CurrentRegion will return the range B3:D14
Range(“C8:C9”).CurrentRegion will return the range B3:D14
and so on
How to Use
We get the CurrentRegion as follows
' Current region will return B3:D14 from above example Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion
Read Data Rows Only
Read through the range from the second row i.e.skipping the header row
' Current region will return B3:D14 from above example Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion ' Start at row 2 - row after header Dim i As Long For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count ' current row, column 1 of range Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value2 Next i
Remove Header
Remove header row(i.e. first row) from the range. For example if range is A1:D4 this will return A2:D4
' Current region will return B3:D14 from above example Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("B3").CurrentRegion ' Remove Header Set rg = rg.Resize(rg.Rows.Count - 1).Offset(1) ' Start at row 1 as no header row Dim i As Long For i = 1 To rg.Rows.Count ' current row, column 1 of range Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value2 Next i
Using Rows and Columns as Ranges
If you want to do something with an entire Row or Column you can use the Rows or Columns property of the Worksheet. They both take one parameter which is the row or column number you wish to access
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UseRowAndColumns() ' Set the font size of column B to 9 Sheet1.Columns(2).Font.Size = 9 ' Set the width of columns D to F Sheet1.Columns("D:F").ColumnWidth = 4 ' Set the font size of row 5 to 18 Sheet1.Rows(5).Font.Size = 18 End Sub
Using Range in place of Worksheet
You can also use Cells, Rows and Columns as part of a Range rather than part of a Worksheet. You may have a specific need to do this but otherwise I would avoid the practice. It makes the code more complex. Simple code is your friend. It reduces the possibility of errors.
The code below will set the second column of the range to bold. As the range has only two rows the entire column is considered B1:B2
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UseColumnsInRange() ' This will set B1 and B2 to be bold Sheet1.Range("A1:C2").Columns(2).Font.Bold = True End Sub
You can download all the code for this post from the top of this article.
Reading Values from one Cell to another
In most of the examples so far we have written values to a cell. We do this by placing the range on the left of the equals sign and the value to place in the cell on the right. To write data from one cell to another we do the same. The destination range goes on the left and the source range goes on the right.
The following example shows you how to do this:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub ReadValues() ' Place value from B1 in A1 Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1").Value2 ' Place value from B3 in sheet2 to cell A1 Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 = Sheet2.Range("B3").Value2 ' Place value from B1 in cells A1 to A5 Sheet1.Range("A1:A5").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1").Value2 ' You need to use the "Value" property to read multiple cells Sheet1.Range("A1:A5").Value2 = Sheet1.Range("B1:B5").Value2 End Sub
As you can see from this example it is not possible to read from multiple cells. If you want to do this you can use the Copy function of Range with the Destination parameter
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub CopyValues() ' Store the copy range in a variable Dim rgCopy As Range Set rgCopy = Sheet1.Range("B1:B5") ' Use this to copy from more than one cell rgCopy.Copy Destination:=Sheet1.Range("A1:A5") ' You can paste to multiple destinations rgCopy.Copy Destination:=Sheet1.Range("A1:A5,C2:C6") End Sub
The Copy function copies everything including the format of the cells. It is the same result as manually copying and pasting a selection. You can see more about it in the Copying and Pasting Cells section.
Using the Range.Resize Method
When copying from one range to another using assignment(i.e. the equals sign), the destination range must be the same size as the source range.
Using the Resize function allows us to resize a range to a given number of rows and columns.
For example:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ResizeExamples() ' Prints A1 Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Address ' Prints A1:A2 Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(2, 1).Address ' Prints A1:A5 Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(5, 1).Address ' Prints A1:D1 Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(1, 4).Address ' Prints A1:C3 Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A1").Resize(3, 3).Address End Sub
When we want to resize our destination range we can simply use the source range size.
In other words, we use the row and column count of the source range as the parameters for resizing:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub Resize() Dim rgSrc As Range, rgDest As Range ' Get all the data in the current region Set rgSrc = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion ' Get the range destination Set rgDest = Sheet2.Range("A1") Set rgDest = rgDest.Resize(rgSrc.Rows.Count, rgSrc.Columns.Count) rgDest.Value2 = rgSrc.Value2 End Sub
We can do the resize in one line if we prefer:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ResizeOneLine() Dim rgSrc As Range ' Get all the data in the current region Set rgSrc = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion With rgSrc Sheet2.Range("A1").Resize(.Rows.Count, .Columns.Count).Value2 = .Value2 End With End Sub
Reading Values to variables
We looked at how to read from one cell to another. You can also read from a cell to a variable. A variable is used to store values while a Macro is running. You normally do this when you want to manipulate the data before writing it somewhere. The following is a simple example using a variable. As you can see the value of the item to the right of the equals is written to the item to the left of the equals.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UseVariables() ' Create Dim number As Long ' Read number from cell number = Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 ' Add 1 to value number = number + 1 ' Write new value to cell Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = number End Sub
To read text to a variable you use a variable of type String:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub UseVariableText() ' Declare a variable of type string Dim text As String ' Read value from cell text = Sheet1.Range("A1").Value2 ' Write value to cell Sheet1.Range("A2").Value2 = text End Sub
You can write a variable to a range of cells. You just specify the range on the left and the value will be written to all cells in the range.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub VarToMulti() ' Read value from cell Sheet1.Range("A1:B10").Value2 = 66 End Sub
You cannot read from multiple cells to a variable. However you can read to an array which is a collection of variables. We will look at doing this in the next section.
How to Copy and Paste Cells
If you want to copy and paste a range of cells then you do not need to select them. This is a common error made by new VBA users.
Note: We normally use Range.Copy when we want to copy formats, formulas, validation. If we want to copy values it is not the most efficient method.
I have written a complete guide to copying data in Excel VBA here.
You can simply copy a range of cells like this:
Range("A1:B4").Copy Destination:=Range("C5")
Using this method copies everything – values, formats, formulas and so on. If you want to copy individual items you can use the PasteSpecial property of range.
It works like this
Range("A1:B4").Copy Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormats Range("F3").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormulas
The following table shows a full list of all the paste types
| Paste Type |
|---|
| xlPasteAll |
| xlPasteAllExceptBorders |
| xlPasteAllMergingConditionalFormats |
| xlPasteAllUsingSourceTheme |
| xlPasteColumnWidths |
| xlPasteComments |
| xlPasteFormats |
| xlPasteFormulas |
| xlPasteFormulasAndNumberFormats |
| xlPasteValidation |
| xlPasteValues |
| xlPasteValuesAndNumberFormats |
Reading a Range of Cells to an Array
You can also copy values by assigning the value of one range to another.
Range("A3:Z3").Value2 = Range("A1:Z1").Value2
The value of range in this example is considered to be a variant array. What this means is that you can easily read from a range of cells to an array. You can also write from an array to a range of cells. If you are not familiar with arrays you can check them out in this post.
The following code shows an example of using an array with a range:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub ReadToArray() ' Create dynamic array Dim StudentMarks() As Variant ' Read 26 values into array from the first row StudentMarks = Range("A1:Z1").Value2 ' Do something with array here ' Write the 26 values to the third row Range("A3:Z3").Value2 = StudentMarks End Sub
Keep in mind that the array created by the read is a 2 dimensional array. This is because a spreadsheet stores values in two dimensions i.e. rows and columns
Going through all the cells in a Range
Sometimes you may want to go through each cell one at a time to check value.
You can do this using a For Each loop shown in the following code
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub TraversingCells() ' Go through each cells in the range Dim rg As Range For Each rg In Sheet1.Range("A1:A10,A20") ' Print address of cells that are negative If rg.Value < 0 Then Debug.Print rg.Address + " is negative." End If Next End Sub
You can also go through consecutive Cells using the Cells property and a standard For loop.
The standard loop is more flexible about the order you use but it is slower than a For Each loop.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub TraverseCells() ' Go through cells from A1 to A10 Dim i As Long For i = 1 To 10 ' Print address of cells that are negative If Range("A" & i).Value < 0 Then Debug.Print Range("A" & i).Address + " is negative." End If Next ' Go through cells in reverse i.e. from A10 to A1 For i = 10 To 1 Step -1 ' Print address of cells that are negative If Range("A" & i) < 0 Then Debug.Print Range("A" & i).Address + " is negative." End If Next End Sub
Formatting Cells
Sometimes you will need to format the cells the in spreadsheet. This is actually very straightforward. The following example shows you various formatting you can add to any range of cells
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub FormattingCells() With Sheet1 ' Format the font .Range("A1").Font.Bold = True .Range("A1").Font.Underline = True .Range("A1").Font.Color = rgbNavy ' Set the number format to 2 decimal places .Range("B2").NumberFormat = "0.00" ' Set the number format to a date .Range("C2").NumberFormat = "dd/mm/yyyy" ' Set the number format to general .Range("C3").NumberFormat = "General" ' Set the number format to text .Range("C4").NumberFormat = "Text" ' Set the fill color of the cell .Range("B3").Interior.Color = rgbSandyBrown ' Format the borders .Range("B4").Borders.LineStyle = xlDash .Range("B4").Borders.Color = rgbBlueViolet End With End Sub
Main Points
The following is a summary of the main points
- Range returns a range of cells
- Cells returns one cells only
- You can read from one cell to another
- You can read from a range of cells to another range of cells.
- You can read values from cells to variables and vice versa.
- You can read values from ranges to arrays and vice versa
- You can use a For Each or For loop to run through every cell in a range.
- The properties Rows and Columns allow you to access a range of cells of these types
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)