I. Word accent. Word accent in English.
1.
In
the English language the word accent is the constitutive function of
a word as of lexical and morphological element of a language in its
absolute form. The word accent can be observed both in monosyllabic
and polysyllabic words. For the latter it is typical to single out
one or more syllables by increasing the degree of their prominence.
Thus, the word accent organizes a word as complex auditory unit and
at the same time gives prominence to separate syllables. Such
syllables are considered to be singled out accentually (accented) or
stressed.
It is a
common knowledge that stress
or accent
means greater degree of prominence to certain syllable or syllables.
Such prominence is achieved through the greater force of exhalation
and higher level of voice pitch and slight change in the direction of
voice.
The
nature of an accent
— still represents a ground for disputes.
Gimson
believes
that the effect of prominence
is
achieved through the combination of 4 major factors: degree of
tenseness, tone, intensity and length of a vowel. The prominence of a
syllable in the languages with the rhythmic tendency is achieved by
higher muscular tension while pronouncing the given syllable.
In the European languages,
such as English, German, French, Russian the dynamic tendency in a
word accent prevails. In the Scandinavian languages the accent is
considered to be dynamic and musical. Musical character of a word
accent may be observed in Chinese, Japanese and Vietnamese languages.
So, passing
directly to the English language, it is necessary to mention, that
word accent in the English language is
dynamic.
It is accepted practically by all the linguists. However,
experimental researches testify, and such linguists as Gimson
and
Crystal point out as well, that the word accents in English is a
complex and complicated phenomenon marked by changes in the energy,
in the voice height, characterized by qualitative and quantitative
changes. Dynamic and tonal features of the English word accent
prevail over the other characteristics.
Qualitative
and
quantitative
aspects of a stress or accent
are
important components of a word accent. In this case we deal with the
qualitative or quantitative changes of a vowel in the unstressed
syllables in comparison with the stressed ones. It is natural, that
in a stressed syllable a vowel is longer and of full quality
(possesses all the qualitative characteristics). The qualitative
aspect of an accent is revealed through the change of a colour or
quality of a vowel in the stressed position while quantitative aspect
— with the change in the length of a vowel sound.
The nature
of Russian
stress differs from
English.
The qualitative component of an accent plays bigger role in the
system of Russian word accent as Russian vowels in the unstressed
position always undergo a qualitative reduction. While in the English
language we may find vowels of full quality in the unstressed
position (we spoke about it at our last lecture).
One more
fact that deserves our attention here is the
position
of a stress in different languages. So, according to this aspect we
may single out languages that have
fixed
stress and those whose word accent has free
character.
In the
languages with
the fixed accent,
the position of a word accent is fixed on a concrete syllable. Thus,
for example, in the French language it is the last syllable in a word
(Paris, a cachenez, an orchestra),
in the Finnish and Czech languages — on the first syllable
(Helsinki, the Sauna, Карловы
Вары,
Gold Prague),
and in Polish — on the last but one.
In
languages with a free
stress,
the word accent is not fixed on any concrete syllable. For example,
appetite, beginning, balloon
and
lake, weather, milk.
It is
necessary to note, that in the English language the accent is not
only free, but even has a shifting character, i.e. carries out
semantic function, distinguishing lexical units, parts of speech,
grammar forms.
The phonologic status of a
word accent also doesn’t possess any stability in the world of
linguistics. Anyway, all the linguists are of the same opinion — the
analysis of a word accent should be carried out from the point of
view of its degree.
Thus, it is
accepted, that the English word stress has three degrees:
primary, secondary
and
weak stress.
These ideas are reflected in the works of Jones, Gimson, Kingdon,
Torsuev, Vasiliev. Some phoneticians distinguish four degrees of a
word accent:
primary, secondary, tertiary
and
weak stress.
Primary
accent
falls either on the third or on the second syllable from the end.
In the
majority of words
the secondary
stress falls on the syllable separated from a stressed (nuclear)
syllable by one unstressed syllable. Something like in the following
words,
pro’nunciֽaton,
ֽ
occupation,
governmental, patriotic.
In many
derivative nouns the secondary accent falls on the same syllable
which has a primary accent in the initial word, i.e. in the word from
which the noun is derived:
organize
—
organization,
peculiar
—
peculiarity.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Content
- Rules of accentuation according to the prosodic accent
- Sharp words
- Examples
- Plain words
- Examples
- Words esdrújulas
- Examples
- Overdrug words
- Examples
- Accentuation of hiatuses, diphthongs and triphthongs
- Hiatuses
- Examples
- Diphthongs
- Examples
- Triphthongs
- Examples
- Diacritical tilde
- Monosyllables
- Examples
- Interrogatives and exclamatory
- Examples
- Compound words
- Examples
- Accentuation of adverbs ending in -mente
- Examples
- Verb forms with enclitics
- Examples
- Capital accentuation
- Examples
- Suppression of diacritical marks by the RAE
- Examples
- Examples
- References
The accentuation rules are the rules for placing the graphic mark called tilde (´). Its purpose is to indicate the greatest voice force in a syllable. The Royal Spanish Academy defines the accent or graphic or orthographic accent, as an auxiliary orthographic sign that represents the prosodic accent in writing.
In the case of the Spanish language, it is a small oblique line on a vowel. This indicates that the syllable on which it falls is pronounced with greater force and intensity. This must always be drawn from right to left (´). Now, the accent mark must be distinguished.
All words carry a certain load of intensity in their pronunciation (accent), even if they have only one syllable. In case of having two or more syllables, the intensity falls on one of them. However, not all words in the Spanish language have an accent; in general, its use is restricted.
Words have a standard in terms of accent. Those words that deviate from that standard are those with an accent. For example, most words in Spanish are flat (with greater voice force in the penultimate syllable) and end in the sounds «n» and «s». So, words that do not meet that standard carry an accent.
In general terms, the stress rules take into account the position of the syllable where the greatest voice force lies, the need to distinguish words that sound the same, and whether a group of two or three vowels are pronounced together or not.
In addition, when it comes to compound words (two or more words together that produce a word with a new meaning), their particularities must be considered to establish whether or not they carry an accent.
Rules of accentuation according to the prosodic accent
The prosodic accent is the greater relief or prominence given to a particular syllable over the others within a word. For example, the syllable that has the prosodic accent in the word “curtain” is “ti”.
On the other hand, the syllable with a prosodic accent is called a stressed syllable, and the others are called unstressed. This prosodic accent is only indicated orthographically — with the accent — only in certain cases. This can be seen in the following word pairs:
— Situation and truth
– Tree and grass
The stressed syllable in the first pair of words is the last. However, only one word has a graphic mark. The same happens with the second pair: the greatest voice force falls on the penultimate syllable, but only one word has an accent.
These differences obey accentuation rules that take into account both the distribution of the prosodic accent in the word and its final sound. These rules will be explained in detail below.
Sharp words
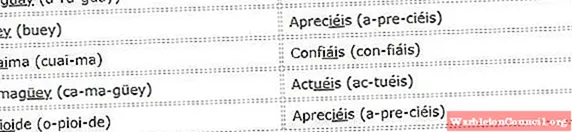
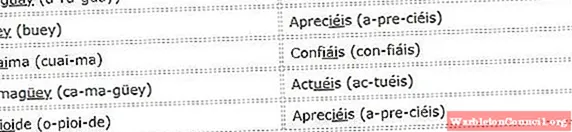
When the stressed syllable of a polysyllable word (more than one syllable) is in final position, it is known as an acute word.
According to the rules of accentuation, all acute words carry an accent if they end in a vowel or the consonants «n» and «s». The exception to this rule is when there is a consonant before the «s» (chalets).
Plain words
The stressed syllable of flat or grave words falls on the penultimate syllable. All plain words have a spelling accent when they do not end in a vowel or the consonants «n» and «s». Those ending in consonant + s (closets) are excepted
Examples
Words esdrújulas
Esdrújulas words are those whose stressed syllable falls on the penultimate syllable. Without exception, the rules of accentuation dictate that all esdrújulas words carry accent marks.
Examples
– Numbers.
– Hypothesis.
– Formula.
– Jurassic.
– Practice.
– Method.
– Cumulus.
– Particle.
– Mathematics.
– Macroscopic.
Overdrug words
In the case of overdrugal words, they have the prosodic accent (or stressed syllable) before the third to last syllable, and they always have an accent.
Examples
– Take it away.
– Tell him.
– Stirring us.
– Allowing them.
– Work them out.
Accentuation of hiatuses, diphthongs and triphthongs
The presence of a sequence of two or three vowels within the same word can form hiatuses, diphthongs or triphthongs. There are also specific accentuation rules for each of these cases.
Hiatuses
The hiatus occurs when a sequence of two vowels belongs to two different syllables; that is, they are articulated separately. It occurs in the following combinations:
– Two equal vowels: zo-ó-lo-go, al-ba-ha-ca *, cre-é-mos.
– Two different open vowels (a, e, o): ca-ma-le-ón, ca-os, a-e-ro-pla-no.
– A closed vowel (i, u) stressed and an open vowel (a, e, o) unstressed: con-fí-e, ow-ho *, spark plug.
– An unstressed open vowel and a stressed closed vowel: e-go-ís-ta, baúl, corn.
* Note: the letter “h” inserted between the vowels does not influence the formation of the hiatus.
As can be seen in the examples, in the first and second case the general accentuation rules explained in the previous section are taken into account. In the last two cases, the stressed closed vowel always carries an accent.
Examples
Diphthongs
A diphthong is a sequence of two vowels that are pronounced on the same syllable. The possible combinations are:
— An open vowel (a, e, o) and a closed vowel (i, u) unstressed: frai-le, ahu-ma-do * *, di-réis, Eu-ro-pa.
— An unstressed closed vowel and an open vowel: en-vi-dia, a-quantico, con-ci-lio.
— Two closed vowels: ciu-dad, a-cuí-fe-ro
* * Note: the letter “h” inserted between the vowels does not prevent the formation of the diphthong.
With regard to the tilde, for diphthongs the general rules of accentuation must be taken into account. In the case of the closed vowel + closed vowel sequence, the graphic mark is placed on the second vowel.
Examples
Triphthongs
A tripthong is the conjunction of three vowels that are in the same syllable. The combination is closed vowel (unstressed) + open vowel + closed vowel (unstressed).
As in the case of diphthongs, the use of the tilde is governed by the general rules of accentuation. When it has a spelling accent, it is placed on the strong vowel.
Examples
Diacritical tilde
Monosyllables
In general, monosyllable words do not have a graphic mark. However, in some cases a diacritical mark is used.
This is used to determine the grammatical category of homonymous monosyllable (one-syllable) words (words that have the same form).
For example, the pair “de” and “dé” are distinguished, since “de” is a preposition and “dé” is a verb form of “give”.
Another case of the use of the diacritical tilde is the pair even / still. «Still» is used when it means «even», «even» or «also» (For example: «even the poorest …»), while «still» is equivalent to «still» (For example: «still is early»).
Examples
— Tú (personal pronoun) / Tu (possessive adjective)
You are my friend / Your bag is lost.
— He (personal pronoun) / the (determiner)
He always listens / The story was very long.
— Mí (personal pronoun) / Mi (possessive adjective)
This tires me / My house is not far away.
— Tea (noun / Te (personal pronoun)
I love to drink tea / I warned you.
— Sí (adverb of affirmation) / Si (conjunction)
Yes, I agree / If you don’t tell the truth, you will regret it.
— Sé (verb form of saber) / se (personal pronoun)
I know I’m going to succeed / He didn’t tell her.
Interrogatives and exclamatory
Relative adverbs (where, how, how, when and how much) and relative pronouns (what, who, who, which and which) are written without an accent when they have no interrogative or exclamatory value. Otherwise, they must bear this graphic mark.
Examples
— Where where
He always goes where the wind takes him / We don’t know where this adventure will end
— How / How
I feel like it’s just up to her / How is she going to do it?
— How / How
How long was it fell / How difficult is the road to happiness!
— When when
You are going to travel when you finish your studies / When did all that happen?
— How much How much
Everything he has he earned with sacrifice / You don’t know how sorry I am!
— What what
He said he didn’t care / What did he say?
— Who who
Her mother, who always took care of her, was already tired / She didn’t know who was home.
— Who is who is
He rewarded those who helped him / Who will come this afternoon?
— Which which
Take whatever / They didn’t know which one to choose!
— Which / Which
Bring your materials, without which you will not be able to work / Which institutions are better?
Compound words
Some compound words are presented together graphically (moody, rainbow); on the other hand, others are separated with a script (theoretical-practical, social-democratic).
For the purposes of the stress rules, the former behave as a single word. The latter are treated as separate words, keeping their original form.
Examples
— Rectilinear (straight + line).
— Fifteenth (tenth + fifth).
— Scarecrow (scare + birds).
— Kick (toe + foot).
— Camcorder (video + camera).
— Physico-chemical (physical + chemical).
— Technical-administrative (technical + administrative).
— Spanish-German (Hispanic + German).
— Lyrical-epic (lyrical + epic).
— Arab-Israeli (Arab + Israeli).
Accentuation of adverbs ending in -mente
Adverbs ending in -mente are an exception to the general rules of stress, since they are plain words ending in vowels. However, these words retain the same spelling of the adjective that gives them origin.
Examples
Verb forms with enclitics
The forms «me», «te», «se», «le», «les», «lo», «los», «la», «las», «se» and «us» can be linked to the verb (for example: promise me). In these cases they are called enclitic pronouns. These verb forms must follow the general stress rules.
Examples
— Send me (the combination is a hiatus. The word is esdrújula).
— Get dressed (word esdrújula).
— Tell him (plain word, ending in a vowel).
— Let’s try it (word esdrújula).
— Recommending them (word sobreesdrújula).
Capital accentuation
The spelling sign should not be omitted for capital letters if required by the rules. In the past, accent placement was a bit difficult when using typewriters; today, this omission is no longer justified.
Examples
— “CAPITAL LETTERS ARE ALSO CALLED VERSAL BECAUSE THEY HAVE BEEN USED IN THE INITIAL OF ALL AND EACH OF THE VERSES OF THE POEMS. CAPITAL LETTERS — OFTEN DIFFERENT NOT ONLY IN SIZE BUT IN FIGURE AND TRAILING — REPRESENT EXACTLY THE SAME SOUNDS OR PHONEMES AS THE CORRESPONDING SMALL LETTERS «.
— “Green trees bloomed in the field. Unique in their style, the trees of this tropical forest provided freshness and beauty. We were just two people enjoying this beautiful and imposing landscape ”.
Suppression of diacritical marks by the RAE
Previously, the adverb “solo” (only) had a diacritical mark to distinguish it from the homonymous adjective “solo”. The Royal Spanish Academy (RAE) removed this accent in 2010.
In addition, the accent in «this», «this», «these», «these», «that», «that», «those», «those», «that», «that» and «those» was removed. . Thus, they are written without the spelling sign when they function as pronouns or as determiners.
Examples
– That man studied mathematics / That is a good doctor
– These changes are very good news / These tires need replacement.
– That book is not mine / He who is there is calling you.
The tilde in the disjunctive conjunction «or» was also deleted, regardless of whether it appears between words, figures or signs.
Examples
— I prefer fruit juice or wine.
— He was born in 1988 or 1989.
— You can use the + or — signs if you want.
References
- Ávila, F. (2002). Where does the tilde go? Bogotá: Editorial Norma.
- Royal Spanish Academy. (2005). Pan-Hispanic Dictionary of Doubts. Taken from lema.rae.es
- Rodríguez Guzmán, J. P. (2005). Graphic grammar to the juampedrino mode. Barcelona: Carena Editions.
- Hualde, J. I .; Olarrea, A and Escobar, A. M. (2001). Introduction to Hispanic Linguistics.
New York: Cambridge University Press. - Pastor, A. Escobar, D .; Mayoral, E. and Ruiz, F. (2014). Communication and Society I. Madrid: Ediciones Paraninfo.
- De Vecchi Language School. (2012). Correct Spanish Spelling. Barcelona: De Vecchi Ediciones.
- García, S .; Meilán, A. J. and Martínez, H. (2004). Build well in Spanish: the form of words. Oviedo: Ediuno.
- García-Macho, M.L .; García-Page Sánchez, M .; Gómez Manzano, P and Cuesta Martínez; P. (2017). Basic knowledge of the Spanish language. Madrid: Editorial Universitaria Ramon Areces.
- Veciana, R. (2004). The Spanish accentuation: new manual of the accentual norms. Santander: University of Cantabria.
- Royal Spanish Academy. (2010). Main novelties of the last edition of the Spelling of the Spanish language (2010). Taken from rae.es.
Today we bring you a article that will surely interest you.
You’re going to learn what are the Spanish accent rules.
We will also see the use of accents in the words.
Surely this topic usually gives you problems, right? Well after reading our article that won’t happen again.
You will be able to write respecting the rules of accentuation in Spanish and finally you will know What are the words that have tilde.
No more putting the tildes by intuition!
It’s time for you to learn to write perfectly🙌🏻
Tildes: What are they?
We start by explaining what are accents.
The accents are graphic signs that are placed on a letter to indicate that it has the stronger pronunciation.
Almost all languages have accents and there are many types.
In Spanish, the tilde is a line that faces to the right (´) and can only be placed over the 5 vowels.
You will see the tildes in Spanish in this way: a e i o u.
⚠️We never put it over the consonants.
⚠️We can’t put words with accents in several vowels at once. A word can only have one tilde in Spanish.
And in capital letters? Do capital letters have tilde?
For a long time they were eliminated because in the old typewriters you could not put the tilde in the capital letters.
But today, on the keyboards of modern devices, it is possible.
Therefore, the answer is yes, capital letters can carry tilde.
Difference between accent and tilde
Not all words have accents. But they all have a stronger syllable.
You do not know what is a syllable?
A syllable is a group of letters that make up a word. They are usually made up of consonants and vowels.
For example, the word «maleta» consists of three syllables: MA / LE / TA
And the word «computer»? It is divided into four syllables: OR / DE / NA / DOR
Sometimes there is more than one vowel in the same syllable. We call this phenomenon diphthong.
For example, in the word «handsome»: GUA /PO
Or in «television»: TE / LE / VI / SION
Great, you know what a syllable is. Well, absolutely all words have a syllable that is pronounced stronger than the others.
That more intense pronunciation in one syllable is the accent.
For example, in the word «casa», the accent is on «ca».
The word «ham» has an accent, therefore, it is clear that the accent is on «món».
In short, accent and tilde express the strongest pronunciation of a vowel or a syllable. But not all words have an accent. Instead, all the words yes they have an accent.
Do you already know how to appreciate the differences between accents or tildes? Surely yes.
We move forward! 😉
stressed and unstressed syllable of words
As we have said before, all words are made up of syllables.
There are two types of syllables, the stressed and unstressed syllable.
Next, we explain how they differian.
What is a tonic syllable
¿What is the tonic syllable?
Both stressed syllable is the syllable whose pronunciation is stronger. In each word there is only one tonic syllable.
For example, in the word «camiseta», the tonic syllable is in «se».
CA/MI/ SE / TA
Do you know what the tonic syllable is in the word «arbol»? Come tell me!
It is «ár»: AR / BOWL
Here it is easy because it has tilde 😊
What is an unstressed syllable
On the contrary, the unstressed syllable is the syllable that does not carry the accent and therefore is pronounced with less intensity.
Depending on the syllables in a word, there may be one or more unstressed syllables.
For example, in the word «carretera», the accent is on «te». The rest of the syllables are unstressed: CA / RR / TEA / RA
In this word we have 3 unstressed syllables.
In the word «chair» there is only one: YEAH / ALL
Now you can distinguish between the unstressed and stressed syllables and you know the differences between tilde and accent.
This is the introduction to the word stress rules.
Do you want to continue ampliangive your knowledge about Spanish accentuation rules? Of course you do!
Read 👉
Types of words according to their stressed syllable
On the accentuation rule Spanish, we distinguish 4 types of words according tonic syllable position.
These four classifications are:
- Sharp words
- Plain words
- Words esdrújulas
- Words about esdrújulas
You want to know the general rules of accentuation of these types of words? Let’s see them!
Sharp words
¿What are sharp words?
They are all the words that have the stressed syllable in the last.
Meaning, when sharp words are accentuated, it will always be in the last syllable.
For example, the word «natural» is acute because the tonic syllable is at the end: NA / TU / RAL
The same happens in the word «hotel»: HO / TEL
More sharp words?
These are some examples:
reshop, pREDAsfaith, orderpain, officecial, Colaugh, Rubless…
Plain words
The time has come to see the rules of accentuation of plain words.
¿When do flat words accentuate?
They always have the accent in the penultimate syllable.
There are many flat words in Spanish. Is he most common type of words.
We give you some examples:
Movile, cohsummer, perro, raTaconeyo, servedlleyou, youclaof, maNo, Lófish, seayounez, camiseta, pantalones, florero, vivíah, habíto…
There are so many that we could spend the whole article writing only plain words, but it would not be much fun. 😁
We have to continue, now they play the esdrújulas!
Words esdrújulas
Both esdrújula word always has the accent on the penultimate syllable.
Therefore, they are words that have three syllables or more.
There are not so many words of this type as with the flat or the sharp ones.
Some examples we have:
Wallciélake, AIdelicious, bruJula, thislula, pagina, pajaro, Rotulle, booligraph, plaso…
Words about esdrújulas
After seeing the Sharp, flat and proparoxytones, we only have the words on esdrújulas.
These have the stress on a syllable before the penultimate. By needing a minimum of four syllables, it is not so common to find a sobresdrújula word.
We see them especially in the adverbs of manner.
Thebilly, Ifishonly, willaskly, faeasily, youmoderately…
Don’t you understand well the adverbs of manner? Too easy.
They are always formed with the following structure: ADJECTIVE + MIND
They are used to express the way in which something is done:
- For example: «Ricardo works very quickly. He is very productive ».
It is also common to find sobreesdrújula words in imperatives with pronouns of verbs that have three or more syllables:
Repifear it, regalick it, redutell us…
Perfect, now you know what are the general rules of accentuation. But we haven’t talked about the tilde rules yet.
Because there words with tilde and others that do not have it?
You will discover it in the following sections 👌
When do acute words have an accent?
Sharp words have a tilde when:
end in VOWEL or in the consonants -N o -S.
There are many sharp words with tilde who follow this rule. These are some examples:
- They end in a vowel:
Maybe, committee, coffee, taboo, dad, mom, there, there, hopefully, purée, hummingbird, baby…
- End in -S:
Never, compass, Japanese, polite, others, stress, after, bus, English…
- End in -N:
Plane, truck, bra, fraction, action, dolphin, sleepyhead, balcony, function…
All nouns that ending in -ion are sharp words and have a tilde.
Many conjugated verb forms in Different times They are acute words with tilde.
For example, the first y third person singular of the regular verbs pretérito indefinido they always have an accent.
Let’s see it with the verb to speak:
I havewheat
You spoke
He/she/you havebló
We talk
You spoke
They talked
The forms of infinitives with -er or -ir also have tilde:
Move: moved, moved.
Write: wrote, wrote.
En Simple future, all persons have tilde, except the first person plural (us or us).
Example with the verb respond:
I answerre
You answeryou will
He answerswill
we will answer
you answerreis
they answerfry
In the time present , the form of vosotros or vosotras also has an accent:
You look, you have, you drive, you read, you open…
As a recap, we have seen these 3 tenses that have acute words with tilde:
- Present
- Indefinite past tense
- Simple future
Acute words without tilde
There are also sharp words without tilde.
Each infinitives in spanish they are sharp words. The stressed syllable is produced on the endings -ar, -er, -ir:
sing, speak, play, move, flee, live, be able, remember…
Why don’t they have an accent? Because they end in -r.
remember the acute accentuation rules: they only have tilde when end in VOWEL or in the consonants -N o -S.
There are many sharp words that end in -or.
These also do not have an accent. For example:
Love, explorer, teacher, radiator, entrepreneur, fork, marker…
The nouns ending in -dad They are also acute words without tilde:
Truth, university, brevity, reality…
And what about words that only have one syllable? Are they considered acute? Can they have accent?
The stress rules for monosyllables they are very simple: They do NOT have tilde.
Some examples of monosyllabic words are the following:
Flower, sea, salt, sun, bread, peace, law…
Yet there are words monosyllables that do have an accent. They are the words that have different meanings such as yes (affirmation) or if (conditional) and carry the tilde to differentiate them.
This tilde is called diacritical tilde. The most used monosyllables that have this tilde are the following:
Me (personal pronoun) My (possessive)
Tea (drink) Te (personal pronoun)
You (subject pronoun) You (possessive)
I know (first person verb to know) I know (personal pronoun)
Yes (affirmation) Yes (conditional)
Botton line, the following sharp words they never have an accent:
- infinitives
- Words that end in -or
- Nouns ending in -dad
- Monosyllables (except diacritical accents)
When do flat words have an accent?
the plain words have a tilde in the following situation:
When DO NOT finish in VOCAL, -N o -S
In other words, it is just the opposite of sharp words.
Brilliant! So you don’t have to learn a new rule. 😎
- Some examples of plain words with tilde
Agile, easy, femur, album, tree, poster, grass, cocktail, simile, ether, character…
In this type we find many words with gap. In a hiatus there are two vowels together but pronouncedian in different syllables.
Sometimes in the gaps it is necessary to put the tilde to know that there is a separation between the vowels,
Even if the word ends in a vowel, you also have to put it.
- Examples of hiatus with tilde in plain words:
Shipping, distracted, Lucía, María, ate, crane, photography, country, philosophy…
The hiatus «ÍA» is very common. This always has a tilde in the «i».
do you know the time pretérito imperfecto? Now you know why verbs that end in -er or -ir always have words with i with tilde 😉
- Examples of imperfect tense with «ÍA»:
MOVER
I moveded
you moveeds
he/she/you moved
We / we movedWe
You / you movedis
They / they / you movedn
LOGOUT
I go outed
Your salteds
he/she/you go outed
we saltedWe
you / you saltedis
they / they / you saltedn
Plain words without tilde
In nouns, we find more words without tildes in the plains because most of them end in a vowel.
These are some examples:
Sishe, meyou know, moultwheat, Plato, vaso, whatchafrog, cothat, calle, raexceedingper, disco, butson / A, stinkta, manzan / A, pewow, youchugo, carne, carpisper, texdude, smartgeneyou, interestSt.you, pauto…
There are so many.
When do esdrújula words have an accent?
With esdrújula words we have it easy. The accent rule here is that ALL have tilde.
So now you know, whenever you write an esdrújula word, put the accent on it.
Examples of esdrújulas words:
TUEmosubway, Áafrica, piwillmeasure, youyouphone, isdruJula, brocoli hoophastic, fishMary, sathelite, terMy no, haswho, you will drástico, echohellogica, orxígene, echonómonkey…
many verbs in imperative with pronouns They are also squishy words:
From theApple tree, bringI know, comPrala, ofjanos…
Esdrújula words without tilde
No esdrújula words without tilde. As we have said before, they all have an accent.
This point has been short 😁
When do the words sobreesdrújulas have an accent?
Like the esdrújulas, there are always tilde in words sobresdrújulas
Most are:
- Adverbs of manner: fiphysically, I laughedstiffly, withmodally…
- Imperatives with pronouns: whatgive it to you, withmassage them, comPramela…
- Gerunds with pronoun: sadogcanopy, ranheytame it…
Exhausted and in need of examples with gerunds to understand it better?
No problem, remember that many times we use them after the verb «to be» to express actions in progress:
Amanda will have her driver’s license very soon. is taking it off».
«My teacher is looking at my test. It’s correcting me».
Sobreesdrújula words without tilde
As with esdrújulas, we also do not have sobreesdrújula words without accents. Fantastic! 🙌🏻
Accent rules exercises
How are you? I’m sure you’ve learned a lot about the general rules of accentuation with this article.
Now that you know everything about how to use tildes, we suggest you practice the stress rules with activities. You will see how it becomes clearer.
Activity 1
In this activity you have a short text. There are 10 words that should have a tilde and don’t. Write the 10 words with the tilde in the boxes below.