Функции для работы с датой и временем в VBA Excel. Синтаксис, параметры, спецсимволы, примеры. Функции, возвращающие текущие дату и время по системному таймеру.
Функция Date
Date – это функция, которая возвращает значение текущей системной даты. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDate() MsgBox «Сегодня: « & Date End Sub |
Функция DateAdd
DateAdd – это функция, которая возвращает результат прибавления к дате указанного интервала времени. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
DateAdd(interval, number, date) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее интервал времени, который требуется добавить. |
| number | Обязательный параметр. Числовое выражение, задающее количество интервалов, которые необходимо добавить. Может быть как положительным (возвращается будущая дата), так и отрицательным (возвращается предыдущая дата). |
| date | Обязательный параметр. Значение типа Variant/Date или литерал, представляющий дату, к которой должен быть добавлен интервал. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1».
Примечание к таблице аргументов: три символа – y, d, w – указывают функции DateAdd на один день, который необходимо прибавить к исходной дате number раз.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateAdd() MsgBox «31.01.2021 + 1 месяц = « & DateAdd(«m», 1, «31.01.2021») ‘Результат: 28.02.2021 MsgBox «Сегодня + 3 года = « & DateAdd(«yyyy», 3, Date) MsgBox «Сегодня — 2 недели = « & DateAdd(«ww», —2, Date) MsgBox «10:22:14 + 10 минут = « & DateAdd(«n», 10, «10:22:14») ‘Результат: 10:32:14 End Sub |
Функция DateDiff
DateDiff – это функция, которая возвращает количество указанных интервалов времени между двумя датами. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Long.
Синтаксис
|
DateDiff(interval, date1, date2, [firstdayofweek], [firstweekofyear]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее интервал времени, количество которых (интервалов) требуется вычислить между двумя датами. |
| date1, date2 | Обязательные параметры. Значения типа Variant/Date, представляющие две даты, между которыми вычисляется количество указанных интервалов. |
| firstdayofweek | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
| firstweekofyear | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первую неделю года. По умолчанию – неделя, в которую входит 1 января. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1».
Примечание к таблице аргументов: в отличие от функции DateAdd, в функции DateDiff спецсимвол "w", как и "ww", обозначает неделю. Но расчет осуществляется по разному. Подробнее об этом на сайте разработчиков.
Параметры firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear определяют правила расчета количества недель между датами.
Таблицы констант из коллекций firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear смотрите в параграфах «Приложение 2» и «Приложение 3».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateDiff() ‘Даже если между датами соседних лет разница 1 день, ‘DateDiff с интервалом «y» покажет разницу — 1 год MsgBox DateDiff(«y», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1 год MsgBox DateDiff(«d», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1 день MsgBox DateDiff(«n», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1440 минут MsgBox «Полных лет с начала века = « & DateDiff(«y», «2000», Year(Now) — 1) End Sub |
Функция DatePart
DatePart – это функция, которая возвращает указанную часть заданной даты. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Есть предупреждение по использованию этой функции.
Синтаксис
|
DatePart(interval, date, [firstdayofweek], [firstweekofyear]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее часть даты, которую требуется извлечь. |
| date | Обязательные параметры. Значение типа Variant/Date, представляющее дату, часть которой следует извлечь. |
| firstdayofweek | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
| firstweekofyear | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первую неделю года. По умолчанию – неделя, в которую входит 1 января. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1». В третьей графе этой таблицы указаны интервалы значений, возвращаемых функцией DatePart.
Таблицы констант из коллекций firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear смотрите в параграфах «Приложение 2» и «Приложение 3».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDatePart() MsgBox DatePart(«y», «31.12.2020») ‘Результат: 366 MsgBox DatePart(«yyyy», CDate(43685)) ‘Результат: 2019 MsgBox DatePart(«n», CDate(43685.45345)) ‘Результат: 52 MsgBox «День недели по счету сегодня = « & DatePart(«w», Now, vbMonday) End Sub |
Функция DateSerial
DateSerial – это функция, которая возвращает значение даты для указанного года, месяца и дня. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
DateSerial(year, month, day) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| year | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее значение от 100 до 9999 включительно. |
| month | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 1 до 12.* |
| day | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 1 до 31.* |
* Функция DateSerial автоматически пересчитывает общее количество дней в полные месяцы и остаток, общее количество месяцев в полные годы и остаток (подробнее в примере).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateSerial() MsgBox DateSerial(2021, 2, 10) ‘Результат: 10.02.2020 MsgBox DateSerial(2020, 1, 400) ‘Результат: 03.02.2021 End Sub |
Разберем подробнее строку DateSerial(2020, 1, 400):
- 400 дней = 366 дней + 31 день + 3 дня;
- 366 дней = 1 год, так как по условию month:=1, значит февраль 2020 входит в расчет, а в нем – 29 дней;
- 31 день = 1 месяц, так как сначала заполняется январь (по условию month:=1);
- 3 дня – остаток.
В итоге получается:
DateSerial(2020+1, 1+1, 3) = DateSerial(2021, 2, 3)
Функция DateValue
DateValue – это функция, которая преобразует дату, указанную в виде строки, в значение типа Variant/Date (время игнорируется).
Синтаксис
Параметр date – строковое выражение, представляющее дату с 1 января 100 года по 31 декабря 9999 года.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateValue() MsgBox DateValue(«8 марта 2021») ‘Результат: 08.03.2021 MsgBox DateValue(«17 мая 2021 0:59:15») ‘Результат: 17.05.2021 End Sub |
Функция DateValue игнорирует время, указанное в преобразуемой строке, но если время указано в некорректном виде (например, «10:60:60»), будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Функция Day
Day – это функция, которая возвращает день месяца в виде числа от 1 до 31 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDay() MsgBox Day(Now) End Sub |
Функция IsDate
IsDate – это функция, которая возвращает True, если выражение является датой или распознается как допустимое значение даты или времени. В остальных случаях возвращается значение False.
Синтаксис
Параметр expression – это переменная, возвращающая дату или строковое выражение, распознаваемое как дата или время.
Значение, возвращаемое переменной expression, не должно выходить из диапазона допустимых дат: от 1 января 100 года до 31 декабря 9999 года (для Windows).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerIsDate() MsgBox IsDate(«18 апреля 2021») ‘Результат: True MsgBox IsDate(«31 февраля 2021») ‘Результат: False MsgBox IsDate(«4.10.20 11:12:54») ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция Hour
Hour – это функция, которая возвращает количество часов в виде числа от 0 до 23 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerHour() MsgBox Hour(Now) MsgBox Hour(«22:36:54») End Sub |
Функция Minute
Minute – это функция, которая возвращает количество минут в виде числа от 0 до 59 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMinute() MsgBox Minute(Now) MsgBox Minute(«22:36:54») End Sub |
Функция Month
Month – это функция, которая возвращает день месяца в виде числа от 1 до 12 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMonth() MsgBox Month(Now) End Sub |
Функция MonthName
MonthName – это функция, которая возвращает название месяца в виде строки.
Синтаксис
|
MonthName(month, [abbreviate]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| month | Обязательный параметр. Числовое обозначение месяца от 1 до 12 включительно. |
| abbreviate | Необязательный параметр. Логическое значение: True – возвращается сокращенное название месяца, False (по умолчанию) – название месяца не сокращается. |
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMonthName() MsgBox MonthName(10) ‘Результат: Октябрь MsgBox MonthName(10, True) ‘Результат: окт End Sub |
Функция Now
Now – это функция, которая возвращает текущую системную дату и время. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerNow() MsgBox Now MsgBox Day(Now) MsgBox Hour(Now) End Sub |
Функция Second
Second – это функция, которая возвращает количество секунд в виде числа от 0 до 59 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerSecond() MsgBox Second(Now) MsgBox Second(«22:30:14») End Sub |
Функция Time
Time – это функция, которая возвращает значение текущего системного времени. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTime() MsgBox «Текущее время: « & Time End Sub |
Функция TimeSerial
TimeSerial – это функция, которая возвращает значение времени для указанного часа, минуты и секунды. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
TimeSerial(hour, minute, second) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| hour | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее значение от 0 до 23 включительно. |
| minute | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 0 до 59.* |
| second | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 0 до 59.* |
* Функция TimeSerial автоматически пересчитывает общее количество секунд в полные минуты и остаток, общее количество минут в полные часы и остаток (подробнее в примере).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTime() MsgBox TimeSerial(5, 16, 4) ‘Результат: 5:16:04 MsgBox TimeSerial(5, 75, 158) ‘Результат: 6:17:38 End Sub |
Разберем подробнее строку TimeSerial(5, 75, 158):
- 158 секунд = 120 секунд (2 минуты) + 38 секунд;
- 75 минут = 60 минут (1 час) + 15 минут.
В итоге получается:
TimeSerial(5+1, 15+2, 38) = TimeSerial(6, 17, 38)
Функция TimeValue
TimeValue – это функция, которая преобразует время, указанное в виде строки, в значение типа Variant/Date (дата игнорируется).
Синтаксис
Параметр time – строковое выражение, представляющее время с 0:00:00 по 23:59:59 включительно.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTimeValue() MsgBox TimeValue(«6:45:37 PM») ‘Результат: 18:45:37 MsgBox TimeValue(«17 мая 2021 3:59:15 AM») ‘Результат: 3:59:15 End Sub |
Функция TimeValue игнорирует дату, указанную в преобразуемой строке, но если дата указана в некорректном виде (например, «30.02.2021»), будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Функция Weekday
Weekday – это функция, которая возвращает день недели в виде числа от 1 до 7 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
|
Weekday(date, [firstdayofweek]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| date | Обязательный параметр. Любое выражение (числовое, строковое), отображающее дату. |
| firstdayofweek | Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
Таблицу констант из коллекции firstdayofweek смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 2».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerWeekday() MsgBox Weekday(«23 апреля 2021», vbMonday) ‘Результат: 5 MsgBox Weekday(202125, vbMonday) ‘Результат: 6 End Sub |
Функция WeekdayName
WeekdayName – это функция, которая возвращает название дня недели в виде строки.
Синтаксис
|
WeekdayName(weekday, [abbreviate], [firstdayofweek]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| weekday | Обязательный параметр. Числовое обозначение дня недели от 1 до 7 включительно. |
| abbreviate | Необязательный параметр. Логическое значение: True – возвращается сокращенное название дня недели, False (по умолчанию) – название дня недели не сокращается. |
| firstdayofweek | Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
Таблицу констант из коллекции firstdayofweek смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 2».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerWeekdayName() MsgBox WeekdayName(3, True, vbMonday) ‘Результат: Ср MsgBox WeekdayName(3, , vbMonday) ‘Результат: среда MsgBox WeekdayName(Weekday(Now, vbMonday), , vbMonday) End Sub |
Функция Year
Year – это функция, которая возвращает номер года в виде числа. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerYear() MsgBox Year(Now) End Sub |
Приложение 1
Таблица аргументов (значений) параметраinterval для функций DateAdd, DateDiff и DatePart:
| Аргумент | Описание | Интервал значений |
|---|---|---|
| yyyy | Год | 100 – 9999 |
| q | Квартал | 1 – 4 |
| m | Месяц | 1 – 12 |
| y | День года | 1 – 366 |
| d | День месяца | 1 – 31 |
| w | День недели | 1 – 7 |
| ww | Неделя | 1 – 53 |
| h | Часы | 0 – 23 |
| n | Минуты | 0 – 59 |
| s | Секунды | 0 – 59 |
В третьей графе этой таблицы указаны интервалы значений, возвращаемых функцией DatePart.
Приложение 2
Константы из коллекции firstdayofweek:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Используются системные настройки |
| vbSunday | 1 | Воскресенье (по умолчанию) |
| vbMonday | 2 | Понедельник |
| vbTuesday | 3 | Вторник |
| vbWednesday | 4 | Среда |
| vbThursday | 5 | Четверг |
| vbFriday | 6 | Пятница |
| vbSaturday | 7 | Суббота |
Приложение 3
Константы из коллекции firstweekofyear:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Используются системные настройки. |
| vbFirstJan1 | 1 | Неделя, в которую входит 1 января (по умолчанию). |
| vbFirstFourDays | 2 | Неделя, в которую входит не менее четырех дней нового года. |
| vbFirstFullWeek | 3 | Первая полная неделя года. |
Главная » Функции VBA »
28 Апрель 2011 326683 просмотров
- Date() — возвращает текущую системную дату. Установить ее можно при помощи одноименного оператора, например, так:
- Time() — возвращает текущее системное время
- Now() — возвращает дату и время вместе.
- DateAdd() — возможность добавить к дате указанное количество лет, кварталов, месяцев и так далее — вплоть до секунд. Интервалы(год, месяц и т.д.) указываются в текстовом формате. Список допустимых значений:
«yyyy» Год
«q» Квартал
«m» Месяц
«y» День года
«d» День
«w» День недели
«ww» Неделя
«h» Час
«n» Минута
«s» Секунда
Сам синтаксис обращения незамысловат. Сначала указываем интервал, затем сколько единиц добавить и самый последний аргумент — к какой дате(включая время, кстати). Например, чтобы добавить 3 года к текущей дате-времени, надо записать функцию так:
MsgBox DateAdd(«yyyy», 3, Now)
Но что интереснее — можно не только добавлять, но и отнимать. Функция не изменится, мы просто должны записать кол-во добавляемых периодов со знаком минус. Отнимем три года от текущей даты-времени:
MsgBox DateAdd(«yyyy», -3, Now) - DateDiff() — возможность получить разницу между датами (опять таки в единицах от лет до секунд).
Dim lDaysCnt As Long lDaysCnt = DateDiff("d", "20.11.2012", Now) MsgBox "С 20.11.2012 прошло дней: " & lDaysCnt
Первый аргумент определяет период времени, в котором необходимо вернуть разницу между датами. Допустимые значения:
«yyyy» Год
«q» Квартал
«m» Месяц
«y» День года
«d» День
«w» День недели
«ww» Неделя
«h» Час
«n» Минута
«s» Секунда
Наиболее полезна DateDiff при вычислении полных лет. Например, чтобы вычислить сколько лет на текущий момент человеку, в зависимости от даты рождения, можно использовать функцию так:MsgBox DateDiff("yyyy", "20.12.1978", Now)
Без этой функции вычислить кол-во полных лет гораздо сложнее.
- DatePart() — функция возвращает указанную часть даты (например, только год, только месяц или только день недели), на основании заданной даты. Часто применяется для получения номера недели для даты.
Первый аргумент — период времени. Принимаемые значения те же, что и для функции DateDiff(годы, месяцы, недели и т.д.)
Второй аргумент — непосредственно дата, часть которой необходимо получить:MsgBox "Номер недели года: " & DatePart("ww", Now)
- DateSerial() — возможность создать значение даты, задавая месяц, год и день числовыми значениями:
- DateValue()— делает то же, что и DateSerial(). Отличия — в формате принимаемых значений. Эта функция в качестве аргумента принимает дату в текстовом формате и преобразует её в формат даты:
MsgBox DateValue("07.06.12")Аналогичным образом (для времени) работают TimeSerial() и TimeValue()
- Day(), Year(), Month(), Weekday(), Hour(), Minute(), Second() — специализированные заменители функции DatePart(), которые возвращают нужную часть даты/времени (которую именно — видно из названия).
- MonthName() — возвращает имя месяца словами по его номеру. Возвращаемое значение зависит от региональных настроек. Если они русские, то вернется русское название месяца.
- Timer() — возвращает количество секунд, прошедших с полуночи.
MsgBox DateSerial(2012, 6, 7)
Статья помогла? Сделай твит, поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Date and Time Functions are the inbuilt functions that give us the opportunity to see the date or time according to the user’s need. Suppose a user needs to see the month or the day or the year then it can be easily seen by different date functions. Similarly, for the time function, also we can manipulate it according to the need of the user. Date and Time functions are used to interconvert date and time in different formats. In this article, we will learn about the most commonly used date and time functions.
VBA Date Functions
There are fifteen-plus different date functions in VBA, but here we will talk about some of the most commonly used date functions.
VBA Date Function
The Date() function returns the current date. The Date() function does not require any arguments. For example, declare a variable name date_1 of Date data type, call the Date() function, and store the return value in date_1, then print the date_1 in the console.
Syntax of the function: Date()
VBA DateAdd Function
The DateAdd() function is used to add an interval of date/time to the respective date or time. The function will return the resulting date or time. The function takes three arguments, Interval, Number, and Date/Time.
Syntax of the function: DateAdd(Interval, Number, Date/Time)
Interval: The first argument, represents, which part of the Date/Time, you want the interval to be added.
Types of intervals are discussed in the following table:
| Intervals | Specification |
| “d” | Day |
| “ww” | Week |
| “m” | Month |
| “q” | Quarter |
| “yyyy” | Year |
| “y” | Day of the year |
| “h” | Hour |
| “n” | Minute |
| “s” | Second |
Number: The second argument represents, the number of Intervals we want to add to the Date/Time.
Date/Time: The third argument represents, the Date/Time on which the changes have to occur.
For example, the current date is “20/11/2020”, and we want to increase the month count by 8. Then use, DateAdd(“m”, 8, “20/11/2020”), and the final output date will be “20/07/2021”.
VBA DateDiff Function
The DateDiff() function is used to get the difference between two dates, in terms of the year, month, day, hours, seconds, etc. The function will return the resulting Date/Time. The functions take three mandatory arguments, Interval, Date1, and Date2.
Syntax of the function: DateDiff(Interval, Date1, Date2)
Interval: The first argument, represents, the part of the Date/Time, you want to see the difference. For example, in terms of the year, day, month, etc. Refer to the table in VBADateAdd() function, for the values of Interval.
Date1: Date1 is the second argument. It tells the start date in an interval.
Date 2: Date2 is the third argument. It tells the end date in an interval.
For example, consider Date1 as “20/10/2020”, and Date2 as “20/12/2021”, and the difference in terms of “d”(days). The final output of the function will be 426.
VBA DatePart Function
The DatePart() function is used to get a particular part(day, week, year) from the date. The function returns the part of date in asked format by the user. The function takes two mandatory arguments, Interval, Date.
Syntax of the function: DatePart(Interval, Date)
Interval: The first argument, represents, the part of the Date/Time, one wants to see. For example, “yyyy” represents the year, and tells the DatePart function to return the year of an input Date.
Date: The second argument, which represents the date user will enter, to check a particular part of a date.
For example, consider the Date as “10/10/2020”, and it has been asked to print the year of this particular date. So, we will use “yyyy” as the first argument. The final output is 2020.
VBA MonthName Function
The MonthName() function returns the name of the month according to the integer value. The function takes one mandatory argument, a number.
Syntax of the function: MonthName(number)
number: The first argument, which tells about the number of the month.
For example, 11 is the argument of the MonthName() function, the function returns “November”.
VBA Time Functions
There are ten-plus different time functions in VBA, but here we will talk about some of the most commonly used time functions.
VBA Now Function
The Now() function is used to get the current date and time of the system. The function does not take any arguments. For example, declare a variable name date_2 of Date data type, call the Now() function, and store the return value in date_2, then print the date_2 in the console.
Syntax of the function: Now()
VBA Time Function
The Time() function is used to get the current time of your system. The function does not take any arguments. For example, call the Time() function, and the system will return the current time i.e. 5:20:20 PM.
Syntax of the function: Time()
VBA Hour Function
The hour() function is used to get the hour from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: hour(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the hour of this particular time. The final output will be 1.
VBA Minute Function
The minute() function is used to get the minute from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: minute(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the minute of this particular time. The final output will be 08.
VBA Second Function
The second() function is used to get the seconds from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: second(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the seconds of this particular time. The final output will be 42.
Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use VBA Time Functions.
Dates and Time in Excel are stored as numbers, and then formatted to show as a date. Day 1 in the world of Excel was the 1st January 1900 (Windows default) or 1st January 1904 (Macintosh default) – which means that the 5th August 2021 is day 44413 since the 1st January 1900. To use the Time functions in Excel, we need to include decimal points in the number, so for example, 44413.456 is 10.56am on the 5th August 2021 where 44413.5 will be exactly 12 noon.
Time Function
The VBA Time Function does not require any arguments. The syntax is simply Time()
Sub GetCurrentTime()
MsgBox "The time right now is " & Time()
End SubRunning the above procedure will return the following message to the user:
Hour Function
The Hour Function in VBA will return the hour part of the time inputted.
Sub GetHour()
MsgBox "The current hour is " & Hour(Time())
End SubThe procedure above combines the Time() and Hour() functions to give us the current hour of the day.
We can also input the time, and the hour for that time will be returned.
Sub GetHour()
MsgBox "The current hour is " & Hour("5:25:16 AM")
End SubMinute Function
As with the Hour Function, the Minute function will return the minute part of the time inputted.
Sub GetMinute()
MsgBox "The current minute is " & Minute(Time())
End SubSimilarly, we can input the time, and the minute will be returned.
Sub GetMinute()
MsgBox "The current minute is " & Minute("5:25:16 AM")
End SubWe can also input the time as a serial number and get the minute or hour from the decimal amount.
Sub GetMinute()
MsgBox "The current minute is " & Minute(44651.597)
End Sub
Second Function
The second function returns the second part of the time inputted in the same way as the hour and minute functions.
Sub GetSecond()
MsgBox "The current second is " & Minute(Time())
End SubNow Function
The Now() function returns the current date and time
Sub GetNow()
MsgBox "The current date and time is " & Now()
End SubTo just get the time from the Now() function, we can use the Format() Function to format the returned value just to show the time.
Sub GetNow()
MsgBox "The current time is " & Format(Now(), "hh:mm:ss AMPM")
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Excel VBA Time
VBA TIME function returns the current time as output and can also be used as an input to different macro lines of code. This function does not have any parameter set for it and thus, by far has the simplest syntax as TIME word with empty parentheses which can be seen as below:
The syntax for VBA TIME function:
Time()
In fact, there is no need for parentheses as well, you can simply use the word TIME itself in your block of code which allows your system to return the current time. We also have a similar function called NOW() under Excel VBA which returns the current time along with the date. However, in this article, our entire focus would be on using TIME function and looking at different working examples of the same.
How to Use Excel VBA Time Function?
We will learn how to use a VBA Time function with few examples in excel.
You can download this VBA Time Excel Template here – VBA Time Excel Template
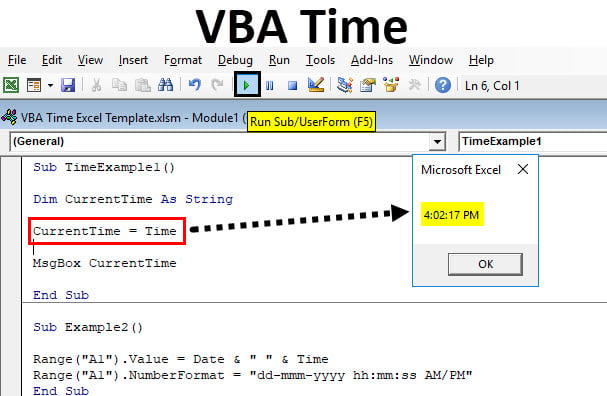
VBA Time Function – Example #1
Current System Time Using TIME function:
Follow the below steps to display the current time of your system.
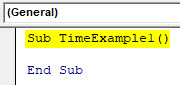
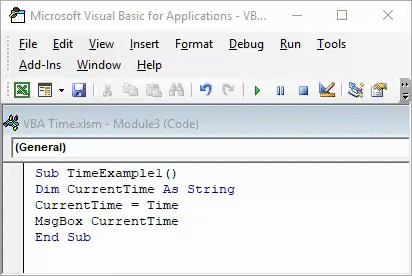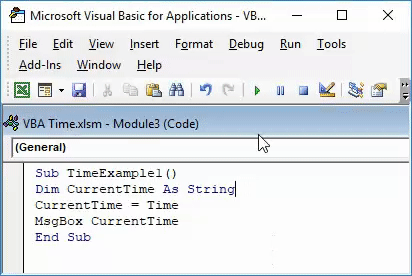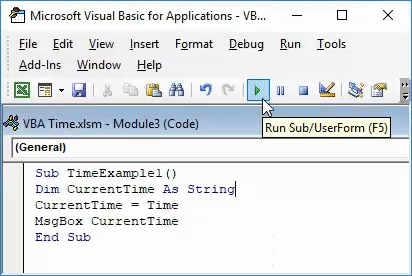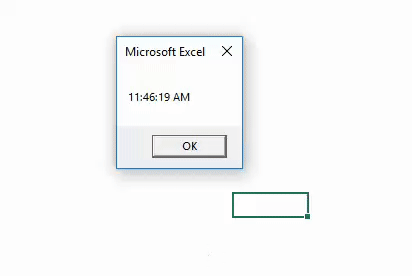
Step 1: Define a sub-procedure.
Code:
Sub TimeExample1() End Sub
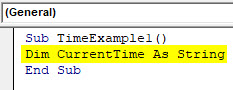
Step 2: Define a variable which will be useful to hold the value of time for you. Define it as String.
Code:
Sub TimeExample1() Dim CurrentTime As String End Sub
Note: The reason behind defining this variable as String is, the output of the TIME function is in a string.
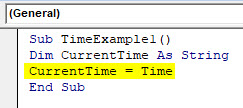
Step 3: Use VBA TIME function to assign current time to the variable defined in the step above using an assignment operator.
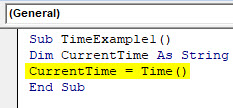
Code:
Sub TimeExample1() Dim CurrentTime As String CurrentTime = Time End Sub
Step 4: As I mentioned earlier, there is no need to add parentheses after TIME function as this is a volatile function. Having said that, the following code will give the equivalent output in comparison with the above code.
Code:
Sub TimeExample1() Dim CurrentTime As String CurrentTime = Time() End Sub
Step 5: Now, use a MsgBox function to display the current time using the display message box.
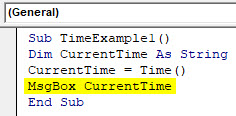
Code:
Sub TimeExample1() Dim CurrentTime As String CurrentTime = Time() MsgBox CurrentTime End Sub
Step 6: Run this code by hitting F5 or Run button and see the output. You should get the output as shown in the image below.
Please note that the time reflecting in the image above is the time by which this code is run on the system. While trying it by yourself, your output may vary depending on the time you are working on this code.
VBA Time Function – Example #2
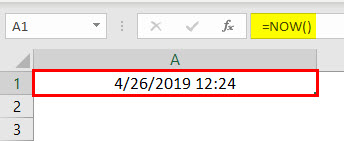
VBA TIME in combination with a Date function to return the current time with Today’s Date:
As it has been informed earlier in the introduction of this article, there is a function called NOW() which gives you current date as well as time in Microsoft Excel. See the screenshot given below.
However, in VBA we don’t have this function working. Therefore, in VBA we have to use a combination of VBA Date and VBA TIME functions to get the current date and current time. VBA Date will give a current date and VBA Time will give current time (which we already have seen in the 1st example).
Let’s see step by step how we can achieve this.
Step 1: Insert a new module in your Excel VBA script.
Step 2: Define a new sub-procedure by giving a name to the macro.
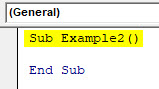
Code:
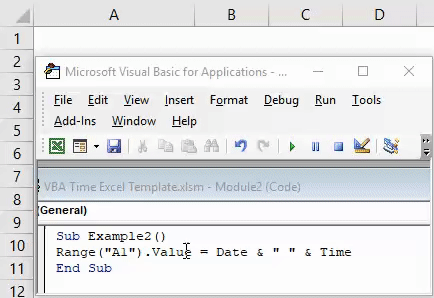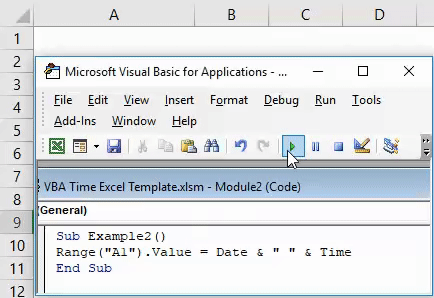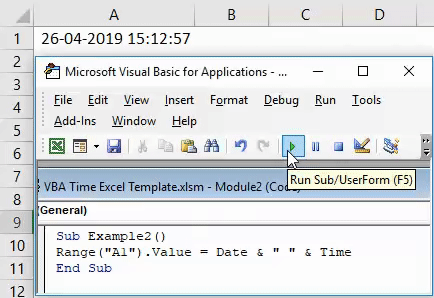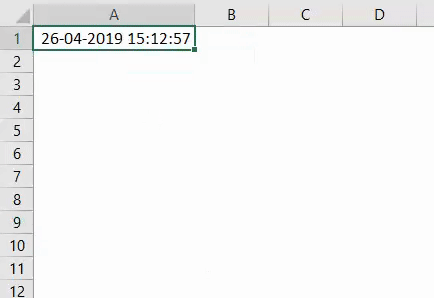
Sub Example2() End Sub
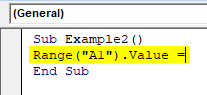
Step 3: We wanted our output to be stored in cell A1 of our excel sheet. For that, start writing the code as below.
Code:
Sub Example2() Range("A1").Value = End Sub
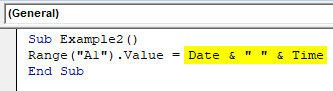
Step 4: Now, use a combination of VBA DATE and VBA TIME functions as shown below and assign it’s value to cell A1.
Code:
Sub Example2() Range("A1").Value = Date & " " & Time End Sub
The DATE function will return the current date of system and TIME function will return the current time. The white space enclosed in double quotes (“ “) allows having a space between date and time in the final output. Two & (and) operators work as concatenating operators which concatenate DATE and TIME with space in it.
Step 5: Run the code by hitting F5 or Run button manually. You will see the output in cell A1 of your worksheet as blow:
Here, again please note that the time reflecting in cell A1 is date and time by which this code is being run by myself. Therefore, when you’ll run this code the outputs will be different.
We also can format the date and time values using NumberFormat function under VBA.
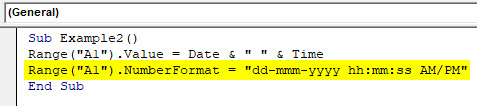
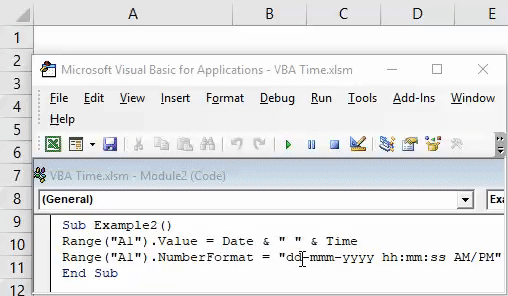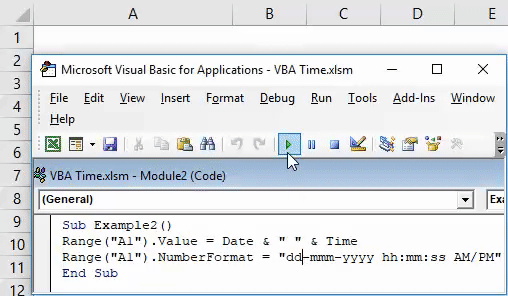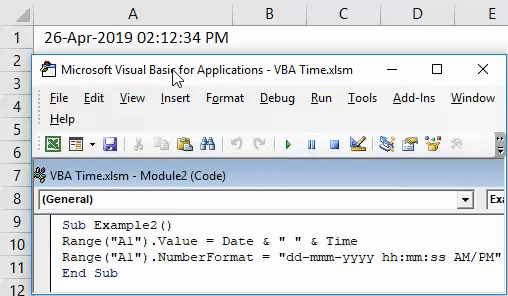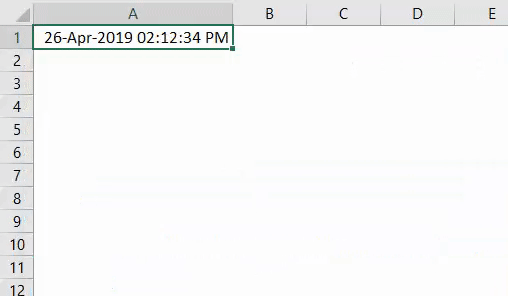
Step 6: Write the code mentioned below in your VBA script.
Code:
Sub Example2() Range("A1").Value = Date & " " & Time Range("A1").NumberFormat = "dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss AM/PM" End Sub
Step 7: Hit F5 or Run button manually and you’ll see the output as below in cell A1 of your worksheet.
VBA Time Function – Example #3
VBA TIME function to track the opening time and date of a workbook:
Sometimes, there is one spreadsheet which we open frequently (Like Employee list of an organization) and make changes into it. We might be interested in knowing the date and time on which the changes have been made in the worksheet. VBA Time function can be used to track the date and time every time a workbook is opened. See the steps below to work on the same.
Step 1: Create a new worksheet in your Excel workbook and rename it as per your convenience. I will rename it as (Time_Track).
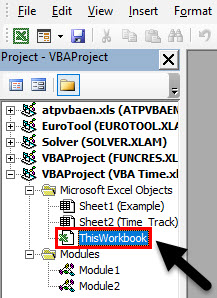
Step 2: Double click on ThisWorkbook under VBE (Visual Basics Editor).
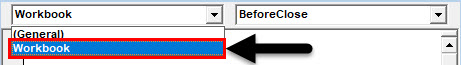
Step 3: From object drop-down list select Workbook instead of General.
Step 4: You’ll see a new private sub-procedure will get defined under the name Workbook_Open() in VBE.
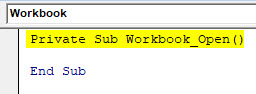
Code:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() End Sub
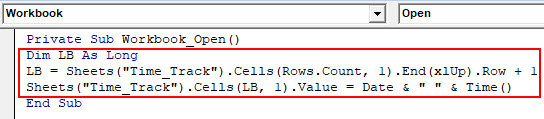
Step 5: Write down the below-mentioned code in this macro sub-procedure as shown in the image below:
Code:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim LB As Long LB = Sheets("Time_Track").Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row + 1 Sheets("Time_Track").Cells(LB, 1).Value = Date & " " & Time() End Sub
Here a variable LB of type Long is defined to find out the cell next to last used cell where the output can be stored. Then, using a combination of VBA DATE and TIME functions, we have assigned a value under that cell.
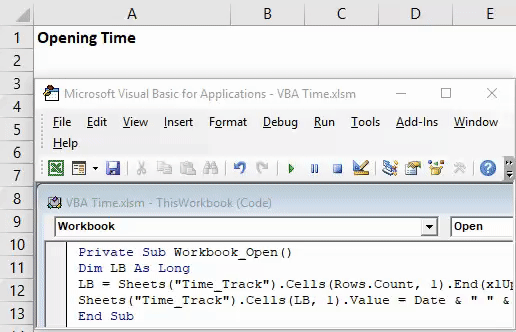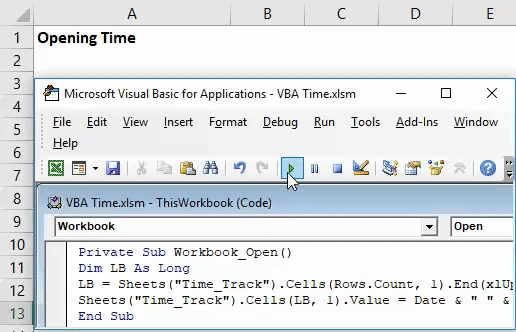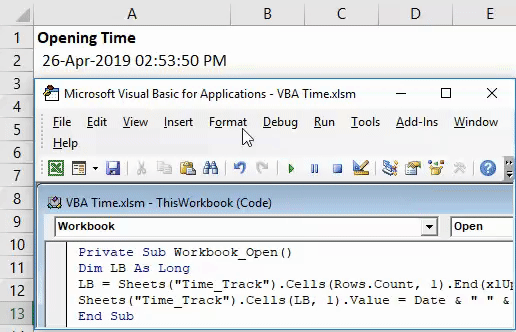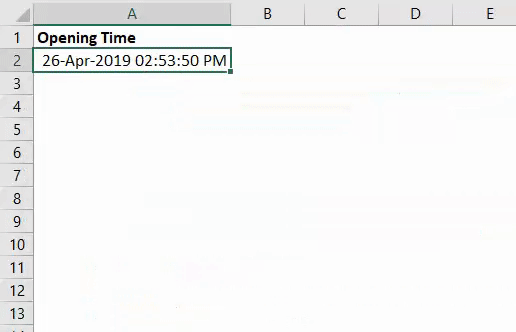
Step 6: Run the code by hitting F5 or Run button manually and see the output under column A of a worksheet.
This code will store the value of Date and Time every time you open the worksheet Time_Track.
This is it from this article. Let’s wrap the things up by writing some things to remember.
Things to Remember
- VBA TIME function stores output as a string in excel. However, we also can store it as Date format while defining a variable as Date instead of a string.
- TIME function does not require any argument in it. It’s a volatile function.
- Even it does not need parentheses to call the function. Only TIME is enough to get the current time.
- TIME function by default stores time value in hh:mm:ss format (24 hours clock format). However, sometimes the output format depends on your system time format as well.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA Time Function. Here we have discussed how to use Excel VBA Time Functions and also we learned the Combination of date and time as an alternative to Now() Function and tracks the workbook open records along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA MsgBox
- VBA Do While Loop
- VBA IsError
- VBA XML