1. The Word-Group Theory
The WordGroup Theory
Lecture 4. Part 2
2. Lecture outline
Lecture outline
Syntactic relations.
The definition and general characteristics.
Classification of word-groups.
3. The syntactic notions
The syntactic notions
Syntactic relations: the syntagmatic (linear)
relations between the syntactic units.
1)
Coordination
and
subordination
(traditionally);
2) + predication;
3) + accumulation (Burlakova et al.).
Barkhudarov: on the basis of equality/inequality
of the syntactic function of the whole group
and its IC (immediate constituents)
4. The syntactic relations
The syntactic relations
Coordination (independence):
word group, sentence, text;
the syntactic function of the whole group
coincides with the syntactic function of every
IC: pens and pencils were purchased (pens
were purchased, pencils were purchased);
symmetric and asymmetric (pens and pencils,
ladies and gentlemen);
copulative (you and me), disjunctive (you or
me), adversative (strict but just), causativeconsecutive (He didn’t come, because…).
5. The syntactic relations
The syntactic relations
Subordination (dependence, difference
linguistic rank):
word-group and sentence;
the syntactic function of the whole coincides
with the function of one of ICs: A tall boy came
in (A boy came in, * Tall came in);
adverbial (to run slowly), objective (to help a
friend); attributive (a new house) (Burlakova,
the functions in a sentences);
the head and the adjunct.
6. Syntactic relations
Syntactic relations
Predication (interdependence):
the syntactic function of the whole group is
different from the syntactic function of every
IC: The boy reads well (* the boy well, * reads
well);
primary (the subject and the predicate): men
worked;
secondary (non-finite forms of the verb and
nominal elements): his reading, for me to
know, the boy running, I saw him run;
Burlakova: the term is not very good (in not
consistent
with
coordination
and
subordination; interdependence – the relation
7. Syntactic relations
Syntactic relations
Accumulative
The relations b/w the constituents can be
identified only with regard to the word which
is not the part of the word combination:
(write) his friend a letter; these important
(decisions);
the positions of the components are fixed
(*important these);
and cannot be used (*these and important;
not coordinate).
8. The word-group. The definition.
The wordgroup. The definition.
the basic unit of syntax (as well as the
sentence);
2 components minimum;
grammatical structure.
No generally accepted definition; negative
approach (sth the word-group is not or does
not have);
Non-communicative (vs. the sentence).
9. The views on word-groups
The views on wordgroups
Broad (every syntactically organized group,
the relations do not matter);
Narrow (two notional words).
General characteristics:
As a naming unit it differs from a compound
word: two constituents = two denotates (a
blackbird, a black bird);
A
dependent
syntactic
unit;
noncommunicative, no intonation.
10. The broad view: syntagmatic groupings (by Blokh)
The broad view: syntagmatic groupings
(by Blokh)
Notional words (notional phrases): denote
complex phenomena and their properties in
their interconnection (a caring mother);
Notional word + functional word (formative
combinations): equivalent to separate words
in terms of their nominative function, can be
expanded (in a box = in an old box);
Functional words: used as connectors or
specifiers of notional elements of various
status: up to, must be able.
Burlakova supports the broad view.
11. The notional phrases (classification)
The notional phrases (classification)
Equipotent (words are related on equal rank);
Dominational (words are syntactically
unequal).
Equipotent syndetic and asyndetic (prose and
poetry vs. dark, gloomy);
Equipotent coordinative (quick and careless)
and cumulative (agreed, but reluctantly; quick
– and careless): equal formally, not in terms of
domination.
12. Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational connection (Blokh)
The principal (dominating) – kernel, kernel
element, head word – and the subordinate
constituents (adjunct, adjunct-word,
expansion).
Dominational consecutive (a careful
observer);
Domination cumulative (an observer,
seemingly careful).
13. Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational bilateral (reciprocal, two-way):
predicative (complete and incomplete) – the
train arrived, the arrival of the train, the pupil
understanding his mistakes.
Dominational mono-lateral (completive): the
syntactic status of the whole element is
determined by the nature of the head-word.
14. Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational completive connection:
objective and qualifying.
Objective: direct non-prepositional (saw me),
indirect non-prepositional (show me), indirect
prepositional (sympathised with the child).
Qualifying: attributive (the woman of strong
character; a beautiful ring); adverbial primary
(verb+ adverbial modifier = receive with
surprise); adverbial secondary (non-verbal
kernel + adverbial modifier+ strikingly alike).
15. The narrow view (Barkhudarov)
The narrow view (Barkhudarov)
Word-group (phrase) is a group of syntactically
related notional words, which is the component
of a sentence, but does not constitute a
sentence on its own.
According to syntactic relations: subordinate
(ready to go, politically active, cold water), coordinate (pens and pencils, strict but just),
predicative (for you to go).
According to the number of types of relations
expresses: elementary (three black dogs –
subordination); compound (red and blue
pencils – coordination and subordination).
16. The subordinate phrase
The subordinate phrase
Syntactically unequal;
The head and the adjunct.
Types:
The word class to which the head belongs:
noun phrases (wonderful weather), verb
phrases (run fast), adverb phrases (extremely
quickly),
pronoun
phrases
(nothing
interesting).
17. The subordinate phrase: types
The subordinate phrase: types
ICs represented with a word or a word phrase:
simple (cold water);
with the expanded head (saw him there, three
black dogs);
with the expanded adjunct (politically active
youth);
with the expanded head and adjunct (the
reception of the delegation by the President of
the republic).
18. The subordinate phrase: types
The subordinate phrase: types
ICs separated / non-separated from each other:
Continuous: nicely dressed;
Discontinuous: Slowly, Mr Johnson got out of
the chair; Of the threat she said nothing.
19. Noun Phrases
Noun Phrases
The place of the adjunct:
Noun phrases with pre-posed adjuncts: cold
water, her shoulders, thirty-five minutes,
slanting stroke, quoted material, Paul’s room,
consonant change.
Noun phrases with post-posed adjuncts: the
roof of the house, the people present, every
creature alive, a man hard to please, desire to
come, my life as an artist.
20. Verb Phrases
Verb Phrases
Verb
Verb
Verb
verb
According to the class of the verb:
phrases with transitive head;
phrases with the intransitive head;
phrases with the transitive or intransitive
head.
The adjuncts are divided accordingly:
Extensions (can be used with any head –
transitive or intransitive);
Complements (the distribution is limited, with
the verb of a particular class only).
21. Verb phrases
Verb phrases
Adjuncts (complements):
object complements (transitive head):
prepositional and non-prepositional (wait for John, insist
on doing vs. says not to worry, read a book, turn the
page).
!!! Prepositional complements vs. extensions !!!
the preposition is determined by the verb vs. the
preposition does not depend on the verb
He believes in God vs. He lives in Chicago.
!!! Non-preposition complements vs. extensions !!!
I came to speak with you vs. I wanted to speak with you
Extension can be substituted for ‘in order to’
22. Verb phrases
Verb phrases
Adjuncts (complements):
qualifying complements (intransitive head):
rise slowly: seemed quite the best plan, died
an old man, look severe, become proficient in.
23. Verb phrases
Verb phrases
According to the number and type of adjuncts:
simple (see a boy, walk slowly);
verb phrases with two extensions: He ran hastily
downstairs;
verb phrases with an extension and a compliments: I
watched her closely;
verb phrases with two non-prepositional object
complements: gave Tom a book;
verb
phrases with a propositional and nonprepositional object complements: explained the
whole affair to Mr Jones;
verb phrases with an object complement and a
qualifying complement: consider it a privilege.
24. Other types of phrases
Other types of phrases
Adjective phrases:
Politically active; rich in possible
modulations; larger units than the sentence;
loudest of all.
Adverb phrases:
Awfully quickly, rather sharply, high in the air.
Pronoun phrases:
Some of the workers, nothing to do,
something personal.
25. Coordinate phrases
Coordinate phrases
According to the means used to connect the
constituents:
Syndetic (with the conjunction): simple syndetic
phrases (with the continuous conjunction) – and,
but, yet, or, rather, than, as well as – and
correlative
syndetic
phrases
(with
the
discountinuous conjunction): both … and, either
… or, neither … not, from … to.
Harsh and loud, precious nut remote, structural
rather than historical.
Either a gerund or a participle, neither reading
nor writing.
26. Coordinate phrases
Coordinate phrases
According to the means used to connect the
constituents:
Asyndetic:
copulative
(the
co-ordinate
conjunction can be used) and appositive
(conjunction cannot be used).
Hot, dusty, tired…
Bill, the dean’s boy; you young people; the
young man Edgar.
27. Predicative phrases
Predicative phrases
The combinations of the subject and the predicate
are not included; The head is only NON-FINITE!
Infinitive predicative phrases (for John to go, for
her daughter to look at her);
Gerund predicative phrases (John’s going, John
being late);
Absolute
predicative
phrases:
all
things
considered; (with) his voice trembling.
Other opinions: predicative phrases of two times:
primary (the boy runs) and secondary (the boy’s
running).
28. Conclusion
The word-group is a combination of at least
two notional words (?) which do not constitute
the sentence but are syntactically connected.
The type of syntagmatic relations: coordinate,
subordinate, predicative.
The internal structure (simple, expanded – to
read and translate the text, extended – a very
beautiful flower).
Subordinate word-groups: the head and the
adjunct; noun, verb, adjective, adverb,
pronoun phrases.
Слайд 1
The Word-Group Theory
Lecture 4. Part 2

Слайд 2
Lecture outline
Syntactic relations.
The definition and general characteristics.
Classification of

word-groups.
Слайд 3
The syntactic notions
Syntactic relations: the syntagmatic (linear) relations
between the syntactic units.
1) Coordination and subordination (traditionally);
2) +
predication;
3) + accumulation (Burlakova et al.).
Barkhudarov: on the basis of
equality/inequality of the syntactic function of the whole group and its IC (immediate constituents)
Слайд 4
The syntactic relations
Coordination (independence):
word group, sentence, text;
the syntactic function of the whole group coincides with
the syntactic function of every IC: pens and pencils were
purchased (pens were purchased, pencils were purchased);
symmetric and asymmetric (pens and pencils, ladies and gentlemen);
copulative (you and me), disjunctive (you or me), adversative (strict but just), causative-consecutive (He didn’t come, because…).
Слайд 5
The syntactic relations
Subordination (dependence, difference linguistic rank):
word-group and
sentence;
the syntactic function of the whole coincides with the
function of one of ICs: A tall boy came in
(A boy came in, * Tall came in);
adverbial (to run slowly), objective (to help a friend); attributive (a new house) (Burlakova, the functions in a sentences);
the head and the adjunct.
Слайд 6
Syntactic relations
Predication (interdependence):
the syntactic function of the whole

group is different from the syntactic function of every
IC: The boy reads well (* the boy well, *
reads well);
primary (the subject and the predicate): men worked;
secondary (non-finite forms of the verb and nominal elements): his reading, for me to know, the boy running, I saw him run;
Burlakova: the term is not very good (in not consistent with coordination and subordination; interdependence – the relation b/w the IC).
Слайд 7
Syntactic relations
Accumulative
The relations b/w the constituents can be

identified only with regard to the word which is
not the part of the word combination: (write) his friend
a letter; these important (decisions);
the positions of the components are fixed (*important these);
and cannot be used (*these and important; not coordinate).
Слайд 8
The word-group. The definition.
the basic unit of syntax

(as well as the sentence);
2 components minimum;
grammatical structure.
No generally
accepted definition; negative approach (sth the word-group is not or
does not have);
Non-communicative (vs. the sentence).
Слайд 9
The views on word-groups
Broad (every syntactically organized group,

the relations do not matter);
Narrow (two notional words).
General characteristics:
As
a naming unit it differs from a compound word: two
constituents = two denotates (a blackbird, a black bird);
A dependent syntactic unit; non-communicative, no intonation.
Слайд 10
The broad view: syntagmatic groupings
(by Blokh)
Notional words

(notional phrases): denote complex phenomena and their properties in
their interconnection (a caring mother);
Notional word + functional word (formative
combinations): equivalent to separate words in terms of their nominative function, can be expanded (in a box = in an old box);
Functional words: used as connectors or specifiers of notional elements of various status: up to, must be able.
Burlakova supports the broad view.
Слайд 11
The notional phrases (classification)
Equipotent (words are related on

equal rank);
Dominational (words are syntactically unequal).
Equipotent syndetic and asyndetic
(prose and poetry vs. dark, gloomy);
Equipotent coordinative (quick and careless)
and cumulative (agreed, but reluctantly; quick – and careless): equal formally, not in terms of domination.
Слайд 12
Dominational connection (Blokh)
The principal (dominating) – kernel, kernel

element, head word – and the subordinate constituents (adjunct,
adjunct-word, expansion).
Dominational consecutive (a careful observer);
Domination cumulative (an observer, seemingly
careful).
Слайд 13
Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational bilateral (reciprocal, two-way): predicative (complete
and incomplete) – the train arrived, the arrival of
the train, the pupil understanding his mistakes.
Dominational mono-lateral (completive): the
syntactic status of the whole element is determined by the nature of the head-word.
Слайд 14
Dominational connection (Blokh)
Dominational completive connection: objective and qualifying.
Objective:
direct non-prepositional (saw me), indirect non-prepositional (show me), indirect
prepositional (sympathised with the child).
Qualifying: attributive (the woman of strong
character; a beautiful ring); adverbial primary (verb+ adverbial modifier = receive with surprise); adverbial secondary (non-verbal kernel + adverbial modifier+ strikingly alike).
Слайд 15
The narrow view (Barkhudarov)
Word-group (phrase) is a group

of syntactically related notional words, which is the component
of a sentence, but does not constitute a sentence on
its own.
According to syntactic relations: subordinate (ready to go, politically active, cold water), co-ordinate (pens and pencils, strict but just), predicative (for you to go).
According to the number of types of relations expresses: elementary (three black dogs – subordination); compound (red and blue pencils – coordination and subordination).
Слайд 16
The subordinate phrase
Syntactically unequal;
The head and the adjunct.
Types:
The

word class to which the head belongs: noun phrases
(wonderful weather), verb phrases (run fast), adverb phrases (extremely quickly),
pronoun phrases (nothing interesting).
Слайд 17
The subordinate phrase: types
ICs represented with a word

or a word phrase:
simple (cold water);
with the
expanded head (saw him there, three black dogs);
with the
expanded adjunct (politically active youth);
with the expanded head and adjunct (the reception of the delegation by the President of the republic).
Слайд 18
The subordinate phrase: types
ICs separated / non-separated from

each other:
Continuous: nicely dressed;
Discontinuous: Slowly, Mr Johnson got
out of the chair; Of the threat she said nothing.
Слайд 19
Noun Phrases
The place of the adjunct:
Noun phrases with

pre-posed adjuncts: cold water, her shoulders, thirty-five minutes, slanting
stroke, quoted material, Paul’s room, consonant change.
Noun phrases with post-posed
adjuncts: the roof of the house, the people present, every creature alive, a man hard to please, desire to come, my life as an artist.
Слайд 20
Verb Phrases
According to the class of the verb:

Verb phrases with transitive head;
Verb phrases with the intransitive
head;
Verb phrases with the transitive or intransitive verb head.
The adjuncts
are divided accordingly:
Extensions (can be used with any head – transitive or intransitive);
Complements (the distribution is limited, with the verb of a particular class only).
Слайд 21
Verb phrases
Adjuncts (complements):
object complements (transitive head):
prepositional and non-prepositional

(wait for John, insist on doing vs. says not
to worry, read a book, turn the page).
!!! Prepositional complements
vs. extensions !!!
the preposition is determined by the verb vs. the preposition does not depend on the verb
He believes in God vs. He lives in Chicago.
!!! Non-preposition complements vs. extensions !!!
I came to speak with you vs. I wanted to speak with you
Extension can be substituted for ‘in order to’
Слайд 22
Verb phrases
Adjuncts (complements):
qualifying complements (intransitive head): rise slowly:

seemed quite the best plan, died an old man,
look severe, become proficient in.
Слайд 23
Verb phrases
According to the number and type of

adjuncts:
simple (see a boy, walk slowly);
verb phrases with two
extensions: He ran hastily downstairs;
verb phrases with an extension and
a compliments: I watched her closely;
verb phrases with two non-prepositional object complements: gave Tom a book;
verb phrases with a propositional and non-prepositional object complements: explained the whole affair to Mr Jones;
verb phrases with an object complement and a qualifying complement: consider it a privilege.
Слайд 24
Other types of phrases
Adjective phrases:
Politically active;

rich in possible modulations; larger units than the sentence;
loudest of all.
Adverb phrases:
Awfully quickly, rather sharply, high
in the air.
Pronoun phrases:
Some of the workers, nothing to do, something personal.
Слайд 25
Coordinate phrases
According to the means used to connect

the constituents:
Syndetic (with the conjunction): simple syndetic phrases (with
the continuous conjunction) – and, but, yet, or, rather, than,
as well as – and correlative syndetic phrases (with the discountinuous conjunction): both … and, either … or, neither … not, from … to.
Harsh and loud, precious nut remote, structural rather than historical.
Either a gerund or a participle, neither reading nor writing.
Слайд 26
Coordinate phrases
According to the means used to connect

the constituents:
Asyndetic: copulative (the co-ordinate conjunction can be used)
and appositive (conjunction cannot be used).
Hot, dusty, tired…
Bill, the dean’s
boy; you young people; the young man Edgar.
Слайд 27
Predicative phrases
The combinations of the subject and the

predicate are not included; The head is only NON-FINITE!
Infinitive
predicative phrases (for John to go, for her daughter to
look at her);
Gerund predicative phrases (John’s going, John being late);
Absolute predicative phrases: all things considered; (with) his voice trembling.
Other opinions: predicative phrases of two times: primary (the boy runs) and secondary (the boy’s running).
Слайд 28
Conclusion
The word-group is a combination of at least

two notional words (?) which do not constitute the
sentence but are syntactically connected.
The type of syntagmatic relations: coordinate,
subordinate, predicative.
The internal structure (simple, expanded – to read and translate the text, extended – a very beautiful flower).
Subordinate word-groups: the head and the adjunct; noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun phrases.
The word-group theory in Modern English
word-group
theory in Modern English
Content
Introduction
.
Definition and general characteristics of the
word-group
.
Classification of word-groups
.
Semantic features of word-groups
.
Motivated and non-motivated word-groups
.
Phraseological word-groups
Introduction
is a branch of linguistics — the
science of language. Lexicology as a branch of linguistics has its own aims and
methods of scientific research. Its basic task — being a study and systematic
description of vocabulary in respect to its origin, development and its current
use. Lexicology is concerned with words, variable word-groups, phraseological
units and morphemes which make up words.the object of the linguistic research
within the frameworks of the lexicological analysis, word-groups draw much
attention of different scientists at different stages of the research
history.linguists as Shveitser, Arnold, Nikitin, Akhmanova, Marchenko, and many
others devoted their research papers to the matter of the word-groups, their
classification, semantic features, and other specific characteristics. They
have contributed linguistic research with a number of works, connected with
this lexical units. The matter of the word-group thorough study is topical with
a glance at their specific features, some phraseological peculiarities and
semantic-grammatical structure.above-mentioned aspects have predetermined our
choice of the topic of the present report «The word-group theory in Modern
English».object of the investigation are word-groups of Modern
English.subject of the present report includes specific features and
characteristics of word-groups.purpose of the report writing is to investigate
word-groups functioning in the Modern English language.purporse of the report
has predetermined the following tasks of the investigation:
to define the notion of the
word-group and outline its general characteristics;
to suggest the classification of the
word-group;
to consider semantic features of
word-groups;
to characterize motivated and
non-motivated word-groups;
to specify peculiar features of
phraseological word-groups.practical value of the present report is performed
by the possibility of using its materials for the further thorough study of
this matter.
1. Definition and general
characteristics of the word-group
word group is the simplest
nonpredicative (as contrasted to the sentence) unit of speech. The word group
is formed on a syntactic pattern and based on a subordinating grammatical
relationship between two or more content words. This relationship may be one of
agreement, government, or subordination. The grammatically predominant word is
the main element of the word group, and the grammatically subordinated word the
dependent element.word group denotes a fragment of extralinguistic reality. The
word group combines formally syntactic and semantically syntactic features.
Such features reveal the compatibility of grammatical and lexical meanings with
the structure of the object-logical relations that these meanings
reflect.groups may be free or phraseological. Free word groups are formed in
accordance with regular and productive combinative principles; their meanings
may be deduced from those of the component words.are a lot of definitions
concerning the word-group. The most adequate one seems to be the following: the
word-group is a combination of at least two notional words which do not
constitute the sentence but are syntactically connected. According to some
other scholars (the majority of Western scholars and professors B.Ilyish and
V.Burlakova — in Russia), a combination of a notional word with a function word
(on the table) may be treated as a word-group as well. The problem is
disputable as the role of function words is to show some abstract relations and
they are devoid of nominative power. On the other hand, such combinations are
syntactically bound and they should belong somewhere.characteristics of the
word-group are:
) As a naming unit it differs from a
compound word because the number of constituents in a word-group corresponds to
the number of different denotates: a black bird — чорний птах (2), a blackbird
— дрізд (1);loud speaker (2), a loudspeaker (1).
) Each component of the word-group
can undergo grammatical changes without destroying the identity of the whole
unit: to see a house — to see houses.
) A word-group is a dependent
syntactic unit, it is not a communicative unit and has no intonation of its own
[4; p. 28].
groups can be classified on the
basis of several principles:
a)
According to the type of syntagmatic
relations: coordinate (you and me), subordinate (to see a house, a nice dress),
predicative (him coming, for him to come),
b)
According to the structure: simple
(all elements are obligatory), expanded (to read and translate the text —
expanded elements are equal in rank), extended (a word takes a dependent
element and this dependent element becomes the head for another word: a beautiful
flower — a very beautiful flower).
1) Subordinate
word-groups.word-groups are based on the relations of dependence between the
constituents. This presupposes the existence of a governingwhich is called the
head and the dependent element which is called the adjunct (in noun-phrases) or
the complement (in verb-phrases).to the nature of their heads, subordinate
word-groups fall into noun-phrases (NP) — a cup of tea, verb-phrases (VP) — to
run fast, to see a house, adjective phrases (AP) — good for you, adverbial
phrases (DP) — so quickly, pronoun phrases (IP) — something strange, nothing to
do.formation of the subordinate word-group depends on the valency of its
constituents. Valency is a potential ability of words to combine. Actual
realization of valency in speech is called combinability [6; p. 162-163].
) The noun-phrase (NP).word-groups
are widely spread in English. This may be explained by a potential ability of
the noun to go into combinations with practically all parts of speech. The NP
consists of a noun-head and an adjunct or adjuncts with relations of
modification between them. Three types of modification are distinguished here:
a)
Premodification that comprises all
the units placed before the head: two smart hard-working students. Adjuncts used
in pre-head position are called pre-posed adjuncts.
b)
Postmodification that comprises all
the units all the units placed after the head: students from Boston. Adjuncts
used in post-head position are called post-posed adjuncts.
c)
Mixed modification that comprises
all the units in both pre-head and post-head position: two smart hard-working
students from Boston.
) Noun-phrases with pre-posed
adjuncts.noun-phrases with pre-posed modifiers we generally find adjectives, pronouns,
numerals, participles, gerunds, nouns, nouns in the genitive case (see the
table) [8; p. 43]. According to their position all pre-posed adjuncts may be
divided into pre-adjectivals and adjectiavals. The position of adjectivals is
usually right before the noun-head. Pre-adjectivals occupy the position before
adjectivals. They fall into two groups: a) limiters (to this group belong
mostly particles): just, only, even, etc. and b) determiners (articles,
possessive pronouns, quantifiers — the first, the last).of nouns by nouns (N+N)
is one of the most striking features about the grammatical organization of
English. It is one of devices to make our speech both laconic and expressive at
the same time. Noun-adjunct groups result from different kinds of transformational
shifts. NPs with pre-posed adjuncts can signal a striking variety of
meanings:peace — peace all over the worldbox — a box made of silverlamp — lamp
for tableslegs — the legs of the tablesand — sand from the riverchild — a child
who goes to schoolgrammatical relations observed in NPs with pre-posed adjuncts
may convey the following meanings:
1)
subject-predicate relations: weather
change;
2)
object relations: health service,
women hater;
3)
adverbial relations: a) of time:
morning star,
b) place: world peace, country
house,) comparison: button eyes,) purpose: tooth brush.is important to remember
that the noun-adjunct is usually marked by a stronger stress than the
head.special interest is a kind of ‘grammatical idiom’ where the modifier is
reinterpreted into the head: a devil of a man, an angel of a girl.
) Noun-phrases with post-posed
adjuncts.with post-posed may be classified according to the way of connection
into prepositionless and prepositional. The basic prepositionless NPs with post-posed
adjuncts are: Nadj. — tea strong, NVen — the shape unknown, NVing — the girl
smiling, ND — the man downstairs, NVinf — a book to read, NNum — room
ten.pattern of basic prepositional NPs is N1 prep. N2. The most common
preposition here is ‘of’ — a cup of tea, a man of courage. It may have quite
different meanings: qualitative — a woman of sense, predicative — the pleasure
of the company, objective — the reading of the newspaper, partitive — the roof
of the house.
) The verb-phrase.VP is a definite
kind of the subordinate phrase with the verb as the head. The verb is
considered to be the semantic and structural centre not only of the VP but of
the whole sentence as the verb plays an important role in making up primary
predication that serves the basis for the sentence. VPs are more complex than
NPs as there are a lot of ways in which verbs may be combined in actual usage.
Valent properties of different verbs and their semantics make it possible to
divide all the verbs into several groups depending on the nature of their
complements [7; p. 91].of verb-phrases.can be classified according to the
nature of their complements — verb complements may be nominal (to see a house)
and adverbial (to behave well). Consequently, we distinguish nominal, adverbial
and mixed complementation.complementation takes place when one or more nominal
complements (nouns or pronouns) are obligatory for the realization of potential
valency of the verb: to give smth. to smb., to phone smb., to hear smth.(smb.),
etc.complementation occurs when the verb takes one or more adverbial elements
obligatory for the realization of its potential valency: He behaved well, I
live …in Kyiv (here).complementation — both nominal and adverbial elements are
obligatory: He put his hat on he table (nominal-adverbial).to the structure VPs
may be basic or simple (to take a book) — all elements are obligatory; expanded
(to read and translate the text, to read books and newspapers) and extended (to
read an English book).
) Predicative word-groups.word
combinations are distinguished on the basis of secondary predication. Like
sentences, predicative word-groups are binary in their structure but actually
differ essentially in their organization. The sentence is an independent
communicative unit based on primary predication while the predicative
word-group is a dependent syntactic unit that makes up a part of the sentence.
The predicative word-group consists of a nominal element (noun, pronoun) and a
non-finite form of the verb: N + Vnon-fin. There are Gerundial, Infinitive and
Participial word-groups (complexes) in the English language: his reading, for
me to know, the boy running, etc.)
. Semantic features of word-groups
word-group is the largest two-facet
lexical unit comprising more than one word but expressing one global
concept.lexical meaning of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of
the component words. The meaning of the word groups is motivated by the
meanings of the component members and is supported by the structural pattern.
But it’s not a mere sum total of all these meanings! Polysemantic words are
used in word groups only in 1 of their meanings. These meanings of the
component words in such word groups are mutually interdependent and inseparable
(blind man — «a human being unable to see», blind type — «the
copy isn’t readable).groups possess not only the lexical meaning, but also the
meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of their constituents.
The structural pattern of word groups is the carrier of a certain semantic component
not necessarily dependent on the actual lexical meaning of its members (school
grammar — «grammar which is taught in school», grammar school —
«a type of school»). We have to distinguish between the structural
meaning of a given type of word groups as such and the lexical meaning of its
constituents [11; p. 62-64].is often argued that the meaning of word groups is
also dependent on some extra-linguistic factors — on the situation in which
word groups are habitually used by native speakers.put together to form lexical
units make phrases or word-groups. One must recall that lexicology deals with
words, word-forming morphemes and word-groups.degree of structural and semantic
cohesion of word-groups may vary. Some word-groups, e.g. at least, point of
view, by means, to take place, etc. seem to be functionally and semantically
inseparable. They are usually described as set phrases, word-equivalents or
phraseological units and are studied by the branch of lexicology which is known
as phraseology. In other word-groups such as to take lessons, kind to people, a
week ago, the component-members seem to possess greater semantic and structural
independence. Word-groups of this type are defined as free word-groups or
phrases and are studied in syntax.discussing phraseology it is necessary to
outline the features common to various word-groups irrespective of the degree
of structural and semantic cohesion of the component-words [18; p. 231].are two
factors which are important in uniting words into word-groups:
the lexical valency of words;
. Motivated and non-motivated
word-groups
word group semantic
motivated
The term motivation is used to
denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition
and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the
other.are three main types of motivation:
) phonetical
) morphological
) semantic
. Phonetical motivation is used when
there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word. For
example: buzz, cuckoo, gigle. The sounds of a word are imitative of sounds in
nature, or smth that produces a characteristic sound. This type of motivation
is determined by the phonological system of each language.
. Morphological motivation — the
relationship between morphemic structure and meaning. The main criterion in
morphological motivation is the relationship between morphemes. One-morphemed
words are non-motivated. Ex — means «former» when we talk about humans
ex-wife, ex-president. Re — means «again»: rebuild, rewrite. In
borrowed words motivation is faded: «expect, export, recover (get
better)». Morphological motivation is especially obvious in newly coined
words, or in the words created in this century. In older words motivation is
established etymologically.structure-pattern of the word is very important too:
«finger-ring» and «ring-finger». Though combined lexical
meaning is the same. The difference of meaning can be explained by the arrangement
of the components.motivation has some irregularities: «smoker» — si
not «the one who smokes», it is «a railway car in which
passenger may smoke».degree of motivation can be different:
«endless» is completely
motivated
«cranberry» is partially
motivated: morpheme «cran-» has no lexical meaning.
. Semantic motivation is based on
the co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word within the
same synchronous system. «Mouth» denotes a part of the human face and
at the same time it can be applied to any opening: «the mouth of a
river». «Ermine» is not only the anme of a small animal, but
also a fur. In their direct meaning «mouth» and «ermine»
are not motivated [13; p. 86].compound words it is morphological motivation
when the meaning of the whole word is based on direct meanings of its
components and semantic motivation is when combination of components is used
figuratively. For example «headache» is «pain in the head»
(morphological) and «smth. annoying» (sematic).the connection between
the meaning of the word and its form is conventional (there is no perceptible
reason for the word having this phonemic and morphemic composition) the word is
non-motivated (for the present state of language development). Words that seem
non-motivated now may have lost their motivation: «earn» is derived
from «earnian — to harvest», but now this word is non-motivated.to
compounds, their motivation is morphological if the meaning of the whole is
based on the direct meaning of the components, and semantic if the combination
is used figuratively: watchdog — a dog kept for watching property
(morphologically motivated); — a watchful human guardian (semantically
motivated) [5; p. 94-95].vocabulary is in a state of constant development.
Words that seem non-motivated at present may have lost their motivation [16; p.
34]. When some people recognize the motivation, whereas others do not,
motivation is said to be faded.all word-groups may be classified into motivated
and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological
units or idioms.groups may be described as lexically motivated if the combined
lexical meaning of the groups is based on the meaning of their components. Thus
take lessons is motivated; take place — ‘occur’ is lexically
non-motivated.groups are said to be structurally motivated if the meaning of
the pattern is deduced from the order and arrangement of the member-words of
the group. Red flower is motivated as the meaning of the pattern quality —
substance can be deduced from the order and arrangement of the words red and
flower, whereas the seemingly identical pattern red tape (‘official
bureaucratic methods’) cannot be interpreted as quality — substance.identical
word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on
their semantic interpretation. Thus apple sauce, e.g., is lexically and
structurally motivated when it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to
denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated [15; p. 90].groups like words may
be also analyzed from the point of view of their motivation. Word-groups may be
called as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is
deducible from the meaning of the components. All free phrases are completely
motivated.follows from the above discussion that word-groups may be also
classified into motivated and non-motivated units. Non-motivated word-groups
are habitually described as phraseological units or idioms.
. Phraseological word-groups
of English phraseology began not
long ago. English and American linguists as a rule are busy collecting
different words, word-groups and sentences which are interesting from the point
of view of their origin, style, usage or some other features. All these units
are habitually described as «idioms», but no attempt has been made to
describe these idioms as a separate class of linguistic units or a specific
class of word-groups.in terminology («set-phrases»,
«idioms» and «word-equivalents») reflects certain
differences in the main criteria used to distinguish types of phraseological
units and free word-groups. The term «set phrase» implies that the
basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and
grammatical structure of word-groups.is a certain divergence of opinion as to
the essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from other
word-groups and the nature of phrases that can be properly termed
«phraseological units». The habitual terms «set-phrases»,
«idioms», «word-equivalents» are sometimes treated
differently by different linguists. However these terms reflect to certain
extend the main debatable points of phraseology which centre in the divergent
views concerning the nature and essential features of phraseological units as
distinguished from the so-called free word-groups.term «set
expression» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is
stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of
word-groups.term «word-equivalent» stresses not only semantic but
also functional inseparability of certain word-groups, their aptness to
function in speech as single words [10; p. 31].term «idioms»
generally implies that the essential feature of the linguistic units under
consideration is idiomaticity or lack of motivation. Uriel Weinreich expresses
his view that an idiom is a complex phrase, the meaning of which cannot be
derived from the meanings of its elements. He developed a more truthful
supposition, claiming that an idiom is a subset of a phraseological unit. Ray
Jackendoff and Charles Fillmore offered a fairly broad definition of the idiom,
which, in Fillmore’s words, reads as follows: «…an idiomatic expression or
construction is something a language user could fail to know while knowing
everything else in the language». Chafe also lists four features of idioms
that make them anomalies in the traditional language unit paradigm:
non-compositionality, transformational defectiveness, ungrammaticality and
frequency asymmetry.work in this field has been done by the outstanding Russian
linguist A. Shakhmatov in his work «Syntax». This work was continued
by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. Great investigations of English phraseology were done
by Prof. A. Cunin, I. Arnold and others [1; p. 121].units are habitually
defined as non-motivated word-groups that cannot be freely made up in speech
but are reproduced as ready-made units; the other essential feature of
phraseological units is stability of the lexical components and grammatical
structure.components of free word-groups which may vary according to the needs
of communication, member-words of phraseological units are always reproduced as
single unchangeable collocations. E.g., in a red flower (a free phrase) the
adjective red may be substituted by another adjective denoting colour, and the
word-group will retain the meaning: «the flower of a certain colour»
[2; p. 54].the phraseological unit red tape (bürokratik
metodlar) no such substitution is possible, as a change of the adjective would
cause a complete change in the meaning of the group: it would then mean «tape
of a certain colour». It follows that the phraseological unit red tape is
semantically non-motivated, i.e. its meaning cannot be deduced from the meaning
of its components, and that it exists as a ready-made linguistic unit which
does not allow any change of its lexical components and its grammatical
structure [9; p. 45-46].structure of phraseological units is to a certain
degree also stable:tape — a phraseological unit;tapes — a free word-group;go to
bed — a phraseological unit;go to the bed — a free word-group.ways of forming
phraseological units are those when a unit is formed on the basis of a free
word-group 
phraseological units by means of transferring the meaning of terminological
word-groups, e.g. in cosmic technique we can point out the following phrases:
«launching pad» in its terminological meaning is «стартова
площадка», in its transferred meaning — «відправний пункт»,
«to link up» — «cтикуватися, стикувати космічні човни» in
its tranformed meaning it means -«знайомитися»;) a large group of
phraseological units was formed from free word groups by transforming their
meaning, e.g. «granny farm» — «пансионат для старих людей»,
«Troyan horse» — «компьютерна програма, яка навмиснестворена для
пвиведення з ладу компьютера»;) phraseological units can be formed by
means of alliteration, e.g. «a sad sack» — «нещасний
випадок», «culture vulture» — «людина, яка цікавиться
мистецтвом», «fudge and nudge» — «ухильність».) they
can be formed by means of expressiveness, especially it is characteristic for
forming interjections, e.g. «My aunt!», «Hear, hear !» etc)
they can be formed by means of distorting a word group, e.g. «odds and
ends» was formed from «odd ends»,) they can be formed by using
archaisms, e.g. «in brown study» means «in gloomy
meditation» where both components preserve their archaic meanings,) they
can be formed by using a sentence in a different sphere of life, e.g.
«that cock won’t fight» can be used as a free word-group when it is
used in sports (cock fighting ), it becomes a phraseological unit when it is
used in everyday life, because it is used metaphorically,) they can be formed
when we use some unreal image, e.g. «to have butterflies in the
stomach» — «відчувати хвилювання», «to have green
fingers» — «досягати успіхів як садовод-любитель» etc.) they can
be formed by using expressions of writers or polititions in everyday life, e.g.
«corridors of power» (Snow), «American dream» (Alby)
«locust years» (Churchil) , «the winds of change» (Mc
Millan).into consideration mainly the degree of idiomaticity phraseological
units may be classified into three big groups. This classification was first
suggested by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. These groups are:
phraseological fusions,
phraseological unities,
phraseological collocations, or
habitual collocations.fusions are completely non-motivated word-groups.
Themeaning of the components has no connection at least synchronically with the
meaning of the whole group. Idiomaticity is combined with complete stability of
the lexical components and the grammatical structure of the fusion [19; p.
37].unities are partially non-motivated word-groups as their meaning can
usually be understood through (deduced from) the metaphoric meaning of the
whole phraseological unit [3; p. 84].unities are usually marked by a
comparatively high degree of stability of the lexical components and
grammatical structure. Phraseological unities can have homonymous free phrases,
used in direct meanings.
§ to skate on thin
ice — to skate on thin ice (to risk);
§ to wash one’s hands
off dirt — to wash one’s hands off (to withdraw from participance);
§ to play the first
role in the theatre — to play the first role (to dominate).must be not less
than two notional wordsin metaphorical meanings.collocations are partially
motivated but they are made up of words having special lexical valency which is
marked by a certain degree of stability in such word-groups. In phraseological
collocations variability of components is strictly limited. They differ from
phraseological unities by the fact that one of the components in them is used
in its direct meaning, the other — in indirect meaning, and the meaning of the
whole group dominates over the meaning of its components. As figurativeness is
expressed only in one component of the phrase it is hardly felt [14; p. 69].
§ to pay a visit,
tribute, attention, respect;
Conclusions
the course of the present report
writing we have specified the definition of the word-group and determined its
general characteristics. Specific attention has been drawn to the
classification of word-groups. We have thoroughly analyzed semantic features of
word-groups, their motivated and non-motivated types and their specific
subtype, i.e. phraseological word-groups.completed the report writing, we have
come to the following conclusions.word-group is a combination of at least two
notional words which do not constitute the sentence but are syntactically
connected.have concluded that according to the type of syntagmatic relations,
word-groups can be coordinate, subordinate and predicative, according to the
structure they are divided into simple, expanded and extended.lexical meaning
of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of the component words. The
meaning of the word groups is motivated by the meanings of the component
members and is supported by the structural pattern.term motivation is used to
denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition
and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the
other.have come to the conclusion, that here are three main types of
motivation: 1) phonetical; 2) morphological; 3) semantic.have concluded,
phraseological units are created from free word-groups. But in the course of
time some words — constituents of phraseological units may drop out of the
language; the situation in which the phraseological unit was formed can be
forgotten, motivation can be lost and these phrases become phraseological
fusions.
Bibliography
1. Арнольд
И.В. Аспекты семантических исследований. — М., 1980.
2. Арнольд
И.В. Стилистика современного английского языка. — М., 1973.
. Кунин
А.В. Фразеология современного английского языка. — М., 1970
. Маковский
М.М. Английская этимология. — М., 1986
. Мешков
О.Д. Словообразование современного английского языка. -М., 1976
. Мостовий
М.I. Лексикологiя
англiйськоi
мови. — Харькiв, 1993
. Никитин
М.В. Лексическое значение слова (структура и комбинаторика). — М., 1983
Смирницкий А.И. Лексикология английского языка. — М., 1956
. Никитин
М.В. О предмете и понятиях комбинаторной семантики / Проблемы лексической и
грамматической семасиологии. Владимир, 1974 год выпуска
9. Смит
Л.П. Фразеология английского языка. — М., 1959
. Старикова
Е.Н.. Раевская Н.Н., Медведева Л.М. Лингвистические чтения. Проблемы
словообразования. Лингвистика текста. — К., 1985
11. Телия
В.Н. Типы языковых значений. Связанное значение слова в языке — М., 1981
Теоретические проблемы социальной лингвистики. — М., 1981
. Харитончик
З.А. Лексикология английского языка. — Минск, 1992
. Швейцер
А.Д. Очерк современного английского языка США. — М.. 1963
. Akhmanova
O. Lexicology. Theory and Method. — M., 1972 Ginsburg R.S. A Course in Modern
English Lexicology. M., 1979.
. Arnold
I.V. The English Word. — M., 1986
. Kuznetsova
V.S. Notes on English Lexicology.- K., 1968.
. L.P.
Smith, Semantics. An introduction to the science of meaning. Oxford University
Press, 1962.
. Vinogradov
V.V. Pixon P.G. Handbook of American Idioms and Idiomatic Usage, 1973.
1.
Definition and general characteristics of the word-group.
There
are a lot of definitions concerning the word-group. The most adequate
one seems to be the following: the word-group is a combination of at
least two notional words which do not constitute the sentence but are
syntactically connected. According to some other scholars (the
majority of Western scholars and professors B.Ilyish and V.Burlakova
– in Russia), a combination of a notional word with a function word
(on
the table)
may be treated as a word-group as well. The problem is disputable as
the role of function words is to show some abstract relations and
they are devoid of nominative power. On the other hand, such
combinations are syntactically bound and they should belong
somewhere.
General
characteristics of the word-group are:
1)
As a naming unit it differs from a compound word because the number
of constituents in a word-group corresponds to the number of
different denotates:
a
black bird – чорний
птах
(2), a blackbird – дрізд
(1);
a loud speaker (2), a loudspeaker (1).
2)
Each component of the word-group can undergo grammatical changes
without destroying the identity of the whole unit: to
see a house — to see houses.
3)
A word-group is a dependent syntactic unit, it is not a communicative
unit and has no intonation of its own.
2.
Classification of word-groups.
Word-groups
can be classified on the basis of several principles:
-
According
to the type of syntagmatic relations: coordinate
(you
and
me),
subordinate
(to
see a house, a nice dress),
predicative
(him
coming, for him to come), -
According
to the structure: simple
(all elements are obligatory), expanded
(to
read and translate the text
– expanded elements are equal in rank), extended
(a word takes a dependent element and this dependent element becomes
the head for another word: a
beautiful
flower
– a very beautiful flower).
3.
Subordinate word-groups.
Subordinate
word-groups are based on the relations of dependence between the
constituents. This presupposes the existence of a governing
Element
which is called the
head and
the dependent element which is called the
adjunct
(in noun-phrases) or the
complement
(in verb-phrases).
According
to the nature of their heads, subordinate word-groups fall into
noun-phrases
(NP) – a
cup of tea,
verb-phrases
(VP) – to
run fast,
to
see
a house,
adjective
phrases
(AP) – good
for you,
adverbial
phrases
(DP) – so
quickly,
pronoun
phrases
(IP) – something
strange, nothing to
do.
The
formation of the subordinate word-group depends on the valency of its
constituents. Valency
is
a potential ability of words to combine. Actual realization of
valency in speech is called combinability.
4.
The noun-phrase (NP).
Noun
word-groups are widely spread in English. This may be explained by a
potential ability of the noun to go into combinations with
practically all parts of speech. The NP consists of a noun-head and
an adjunct or adjuncts with relations of modification between them.
Three
types of modification are distinguished here:
-
Premodification
that comprises all the units placed before the head:
two
smart hard-working
students. Adjuncts
used in pre-head position are called pre-posed
adjuncts. -
Postmodification
that comprises all the units all the units placed after the head:
students
from
Boston.
Adjuncts used in post-head position are called post-posed
adjuncts. -
Mixed
modification
that comprises all the units in both pre-head and post-head
position: two
smart hard-working
students from
Boston.
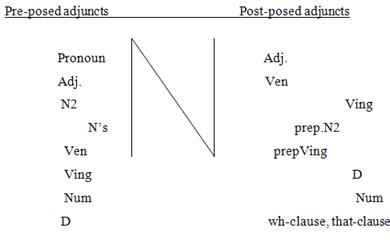
|
Pre-posed |
|
Post-posed |
|
Pronoun |
Adj. |
|
|
Adj. |
Ven |
|
|
N2 |
Ving |
|
|
N`s |
prep.N2 |
|
|
Ven |
prepVing |
|
|
Ving |
D |
|
|
Num |
Num |
|
|
D |
wh-clause, |
X
5.
Noun-phrases with pre-posed adjuncts.
In
noun-phrases with pre-posed modifiers we generally find adjectives,
pronouns, numerals, participles, gerunds, nouns, nouns in the
genitive case (see the table). According to their position all
pre-posed adjuncts may be divided into pre-adjectivals
and adjectiavals.
The position of adjectivals is usually right before the noun-head.
Pre-adjectivals occupy the position before adjectivals. They fall
into two groups: a) lim
iters (to
this
group belong mostly particles): just,
only, even, etc.
and b) determiners
(articles, possessive pronouns, quantifiers – the
first, the last).
Premodification
of nouns by nouns (N+N) is one of the most striking features about
the grammatical organization of English. It is one of devices to make
our speech both laconic and expressive at the same time. Noun-adjunct
groups result from different kinds of transformational shifts. NPs
with pre-posed adjuncts can signal a striking variety of meanings:
world
peace – peace all over the world
silver box – a box made of
silver
table lamp – lamp for tables
table legs – the legs
of the table
river sand – sand from the river
school child
– a child who goes to school
The
grammatical relations observed in NPs with pre-posed adjuncts may
convey the following meanings:
-
subject-predicate
relations: weather
change; -
object
relations: health
service, women hater; -
adverbial
relations:
a)
of time: morning
star,
b) place: world
peace, country house,
c) comparison: button
eyes,
d)
purpose: tooth
brush.
It
is important to remember that the noun-adjunct is usually marked by a
stronger stress than the head.
Of
special interest is a kind of ‘grammatical idiom’ where the
modifier is reinterpreted into the head: a
devil of a man, an angel of a girl.
6.
Noun-phrases with post-posed adjuncts.
NPs
with post-posed may be classified according to the way of connection
into prepositionless
and prepositional.
The basic prepositionless NPs with post-posed adjuncts are: Nadj. –
tea
strong,
NVen – the
shape unknown,
NVing – the
girl smiling,
ND – the
man
downstairs,
NVinf – a
book to read,
NNum – room
ten.
The
pattern of basic prepositional NPs is N1 prep. N2. The most common
preposition here is ‘of’ – a
cup of tea,
a
man of courage.
It may have quite different meanings: qualitative
—
a
woman of sense,
predicative
– the
pleasure of the company,
objective
– the
reading of the newspaper,
partitive
–
the
roof of the house.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
-
Скачать презентацию (0.11 Мб)
-
7 загрузок -
0.0 оценка
Ваша оценка презентации
Оцените презентацию по шкале от 1 до 5 баллов
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Комментарии
Добавить свой комментарий
Аннотация к презентации
Посмотреть и скачать бесплатно презентацию по теме «The word-group theory», состоящую из 28 слайдов. Размер файла 0.11 Мб. Каталог презентаций, школьных уроков, студентов, а также для детей и их родителей.
-
Формат
pptx (powerpoint)
-
Количество слайдов
28
-
Слова
-
Конспект
Отсутствует
Содержание
-
Слайд 1
The Word-Group Theory
Lecture 9
-
Слайд 2
Lecture outline
Syntactic relations.
The definition and general characteristics.
Classification of word-groups. -
Слайд 3
The syntactic notions
Syntactic relations: the syntagmatic (linear) relations between the syntactic units.
1) Coordination and subordination (traditionally);
2) + predication;
3) + accumulation (Burlakova et al.).Barkhudarov: on the basis of equality/inequality of the syntactic function of the whole group and its IC (immediate constituents)
-
Слайд 4
The syntactic relations
Coordination (independence):
word group, sentence, text;
the syntactic function of the whole group coincides with the syntactic function of every IC: pens and pencils were purchased (pens were purchased, pencils were purchased);
symmetric and asymmetric (pens and pencils, ladies and gentlemen);
copulative (you and me), disjunctive (you or me), adversative (strict but just), causative-consecutive (He didn’t come, because…). -
Слайд 5
Subordination (dependence, difference linguistic rank):
word-group and sentence;
the syntactic function of the whole coincides with the function of one of ICs: A tall boy came in (A boy came in, * Tall came in);
adverbial (to run slowly), objective (to help a friend); attributive (a new house) (Burlakova, the functions in a sentences);
the head and the adjunct. -
Слайд 6
Syntactic relations
Predication (interdependence):
the syntactic function of the whole group is different from the syntactic function of every IC: The boy reads well (* the boy well, * reads well);
primary (the subject and the predicate): men worked;
secondary (non-finite forms of the verb and nominal elements): his reading, for me to know, the boy running, I saw him run;
Burlakova: the term is not very good (in not consistent with coordination and subordination; interdependence – the relation b/w the IC). -
Слайд 7
Accumulative
The relations b/w the constituents can be identified only with regard to the word which is not the part of the word combination: (write) his friend a letter; these important (decisions);
the positions of the components are fixed (*important these);
and cannot be used (*these and important; not coordinate). -
Слайд 8
The word-group. The definition.
the basic unit of syntax (as well as the sentence);
2 components minimum;
grammatical structure.No generally accepted definition; negative approach (sth the word-group is not or does not have);
Non-communicative (vs. the sentence). -
Слайд 9
The views on word-groups
Broad (every syntactically organized group, the relations do not matter);
Narrow (two notional words).General characteristics:
As a naming unit it differs from a compound word: two constituents = two denotates (a blackbird, a black bird);
A dependent syntactic unit; non-communicative, no intonation. -
Слайд 10
The broad view: syntagmatic groupings (by Blokh)
Notional words (notional phrases): denote complex phenomena and their properties in their interconnection (a caring mother);
Notional word + functional word (formative combinations): equivalent to separate words in terms of their nominative function, can be expanded (in a box = in an old box);
Functional words: used as connectors or specifiers of notional elements of various status: up to, must be able.
Burlakova supports the broad view. -
Слайд 11
The notional phrases (classification)
Equipotent (words are related on equal rank);
Dominational(words are syntactically unequal).Equipotent syndetic and asyndetic (prose and poetry vs. dark, gloomy);
Equipotent coordinative (quick and careless) and cumulative (agreed, but reluctantly; quick – and careless): equal formally, not in terms of domination.
-
Слайд 12
Dominational connection (Blokh)
The principal (dominating) – kernel, kernel element, head word – and the subordinate constituents (adjunct, adjunct-word, expansion).
Dominational consecutive (a careful observer);
Domination cumulative (an observer, seemingly careful). -
Слайд 13
Dominational bilateral (reciprocal, two-way): predicative (complete and incomplete) – the train arrived, the arrival of the train, the pupil understanding his mistakes.
Dominational mono-lateral (completive): the syntactic status of the whole element is determined by the nature of the head-word.
-
Слайд 14
Dominational completive connection: objective and qualifying.
Objective: direct non-prepositional (saw me), indirect non-prepositional (show me), indirect prepositional (sympathised with the child).
Qualifying: attributive (the woman of strong character; a beautiful ring); adverbial primary (verb+ adverbial modifier = receive with surprise); adverbial secondary (non-verbal kernel + adverbial modifier+ strikingly alike). -
Слайд 15
The narrow view (Barkhudarov)
Word-group (phrase) is a group of syntactically relatednotional words, which is the component of a sentence, but does not constitute a sentence on its own.
According to syntactic relations: subordinate (ready to go, politically active, cold water), co-ordinate (pens and pencils, strict but just), predicative (for you to go).
According to the number of types of relations expresses: elementary (three black dogs – subordination); compound (red and blue pencils – coordination and subordination). -
Слайд 16
The subordinate phrase
Syntactically unequal;
The head and the adjunct.
Types:
The word class to which the head belongs: noun phrases (wonderful weather), verb phrases (run fast), adverb phrases (extremely quickly), pronoun phrases (nothing interesting). -
Слайд 17
The subordinate phrase: types
ICs represented with a word or a word phrase:
simple (cold water);
with the expanded head (saw him there, three black dogs);
with the expanded adjunct (politically active youth);
with the expanded head and adjunct (the reception of the delegation by the President of the republic). -
Слайд 18
ICs separated / non-separated from each other:
Continuous: nicely dressed;
Discontinuous: Slowly, Mr Johnson got out of the chair; Of the threat she said nothing. -
Слайд 19
Noun Phrases
The place of the adjunct:
Noun phrases with pre-posed adjuncts: cold water, her shoulders, thirty-five minutes, slanting stroke, quoted material, Paul’s room, consonant change.Noun phrases with post-posed adjuncts: the roof of the house, the people present, every creature alive, a man hard to please, desire to come, my life as an artist.
-
Слайд 20
Verb Phrases
According to the class of the verb:
Verb phrases with transitive head;
Verb phrases with the intransitive head;
Verb phrases with the transitive or intransitive verb head.The adjuncts are divided accordingly:
Extensions (can be used with any head – transitive or intransitive);
Complements (the distribution is limited, with the verb of a particular class only). -
Слайд 21
Verb phrases
Adjuncts (complements):
object complements (transitive head):
prepositional and non-prepositional (wait for John, insist on doing vs. says not to worry, read a book, turn the page).
!!! Prepositional complements vs. extensions !!!
the preposition is determined by the verb vs. the preposition does not depend on the verb
He believes in God vs. He lives in Chicago.
!!! Non-preposition complements vs. extensions !!!
I came to speak with you vs. I wanted to speak with you
Extension can be substituted for ‘in order to’ -
Слайд 22
Adjuncts (complements):
qualifying complements (intransitive head): rise slowly: seemed quite the best plan, died an old man, look severe, become proficient in. -
Слайд 23
According to the number and type of adjuncts:
simple (see a boy, walk slowly);
verb phrases with two extensions: He ran hastily downstairs;
verb phrases with an extension and a compliments: I watched her closely;
verb phrases with two non-prepositional object complements: gave Tom a book;
verb phrases with a propositional and non-prepositional object complements: explained the whole affair to Mr Jones;
verb phrases with an object complement and a qualifying complement: consider it a privilege. -
Слайд 24
Other types of phrases
Adjective phrases:
Politically active; rich in possible modulations; larger units than the sentence; loudest of all.
Adverb phrases:
Awfully quickly, rather sharply, high in the air.
Pronoun phrases:
Some of the workers, nothing to do, something personal. -
Слайд 25
Coordinate phrases
According to the means used to connect the constituents:
Syndetic (with the conjunction): simple syndetic phrases (with the continuous conjunction) – and, but, yet, or, rather, than, as well as – and correlative syndetic phrases (with the discountinuous conjunction): both … and, either … or, neither … not, from … to.
Harsh and loud, precious nut remote, structural rather than historical.
Either a gerund or a participle, neither reading nor writing. -
Слайд 26
According to the means used to connect the constituents:
Asyndetic: copulative (the co-ordinate conjunction can be used) and appositive (conjunction cannot be used).Hot, dusty, tired…
Bill, the dean’s boy; you young people; the young man Edgar. -
Слайд 27
Predicative phrases
The combinations of the subject and the predicate are not included; The head is only NON-FINITE!
Infinitive predicative phrases (for John to go, for her daughter to look at her);
Gerund predicative phrases (John’s going, John being late);
Absolute predicative phrases: all things considered; (with) his voice trembling.Other opinions: predicative phrases of two times: primary (the boy runs) and secondary (the boy’s running).
-
Слайд 28
Conclusion
The word-group is a combination of at least two notional words (?) which do not constitute the sentence but are syntactically connected.
The type of syntagmatic relations: coordinate, subordinate, predicative.
The internal structure (simple, expanded – to read and translate the text, extended – a very beautiful flower).
Subordinate word-groups: the head and the adjunct; noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun phrases.
Посмотреть все слайды
Сообщить об ошибке
Похожие презентации









Спасибо, что оценили презентацию.
Мы будем благодарны если вы поможете сделать сайт лучше и оставите отзыв или предложение по улучшению.
Добавить отзыв о сайте
Free word groups and phraseological units
A word-group is the largest two-facet lexical unit comprising more than one word but expressing one global concept.
The lexical meaning of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of the component words. The meaning of the word groups is motivated by the meanings of the component members and is supported by the structural pattern. But it’s not a mere sum total of all these meanings! Polysemantic words are used in word groups only in 1 of their meanings. These meanings of the component words in such word groups are mutually interdependent and inseparable (blind man – «a human being unable to see», blind type – «the copy isn’t readable).
Word groups possess not only the lexical meaning, but also the meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of their constituents. The structural pattern of word groups is the carrier of a certain semantic component not necessarily dependent on the actual lexical meaning of its members (school grammar – «grammar which is taught in school», grammar school – «a type of school»). We have to distinguish between the structural meaning of a given type of word groups as such and the lexical meaning of its constituents.
It is often argued that the meaning of word groups is also dependent on some extra-linguistic factors – on the situation in which word groups are habitually used by native speakers.
Words put together to form lexical units make phrases or word-groups. One must recall that lexicology deals with words, word-forming morphemes and word-groups.
The degree of structural and semantic cohesion of word-groups may vary. Some word-groups, e.g. at least, point of view, by means, to take place, etc. seem to be functionally and semantically inseparable. They are usually described as set phrases, word-equivalents or phraseological units and are studied by the branch of lexicology which is known as phraseology. In other word-groups such as to take lessons, kind to people, a week ago, the component-members seem to possess greater semantic and structural independence. Word-groups of this type are defined as free word-groups or phrases and are studied in syntax.
Before discussing phraseology it is necessary to outline the features common to various word-groups irrespective of the degree of structural and semantic cohesion of the component-words.
There are two factors which are important in uniting words into word-groups:
– the lexical valency of words;
– the grammatical valency of words.
Lexical valency
Words are used in certain lexical contexts, i.e. in combinations with other words. E.g. the noun question is often combined with such adjectives as vital, pressing, urgent, delicate, etc.
The aptness of a word to appear in various combinations is described as its lexical valency. The range of the lexical valency of words is delimited by the inner structure of the English words. Thus, to raise and to lift are synonyms, but only the former is collocated with the noun question. The verbs to take, to catch, to seize, to grasp are synonyms, but they are found in different collocations:
to take – exams, measures, precautions, etc.;
to grasp – the truth, the meaning.
Words habitually collocated in speech tend to form a cliche.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical, because as it was said before, it depends on the inner structure of the vocabulary of the language. Both the English flower and the Russian цветок may be combined with a number of similar words, e.g. garden flowers, hot house flowers (cf. the Russian – садовые цветы, оранжерейные цветы), but in English flower cannot be combined with the word room, while in Russian we say комнатные цветы (in English we say pot-flowers).
Words are also used in grammatical contexts. The minimal grammatical context in which the words are used to form word-groups is usually described as the pattern of the word-group. E.g., the adjective heavy can be followed by a noun (A+N) – heavy food, heavy storm, heavy box, heavy eater. But we cannot say «heavy cheese» or «heavy to lift, to carry», etc.
The aptness of a word to appear in specific grammatical (or rather syntactical) structures is termed grammatical valency.
The grammatical valency of words may be different. The grammatical valency is delimited by the part of speech the word belongs to. E.g., no English adjective can be followed by the finite form of a verb.
Then, the grammatical valency is also delimited by the inner structure of the language. E.g., to suggest, to propose are synonyms. Both can be followed by a noun, but only to propose can be followed by the infinitive of a verb – to propose to do something.
Clever and intelligent have the same grammatical valency, but only clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern A+prep+N – clever at maths.
Structurally word-groups can be considered in different ways. Word-groups may be described as for the order and arrangement of the component-members. E.g., the word-group to read a book can be classified as a verbal-nominal group, to look at smb. – as a verbal-prepositional-nominal group, etc.
By the criterion of distribution all word-groups may be divided into two big classes: according to their head-words and according to their syntactical patterns.
Word-groups may be classified according to their head-words into:
nominal groups – red flower;
adjective groups – kind to people;
verbal groups – to speak well.
The head is not necessarily the component that occurs first.
Word-groups are classified according to their syntactical pattern into predicative and non-predicative groups. Such word-groups as he went, Bob walks that have a syntactic structure similar to that of a sentence are termed as predicative, all others are non-predicative ones.
Non-predicative word-groups are divided into subordinative and coordinative depending on the type of syntactic relations between the components. E.g., a red flower, a man of freedom are subordinative non-predicative word-groups, red and freedom being dependent words, while day and night, do and die are coordinative non-predicative word-groups.
The lexical meaning of a word-group may be defined as the combined lexical meaning of the component members. But it should be pointed out, however, that the term «combined lexical meaning» does not imply that the meaning of the word-group is always a simple additive result of all the lexical meanings of the component words. As a rule, the meanings of the component words are mutually dependent and the meaning of the word-group naturally predominates over the lexical meaning of the components. The interdependence is well seen in word-groups made up of polysemantic words. E.g., in the phrases the blind man, the blind type the word blind has different meanings – unable to see and vague.
So we see that polysemantic words are used in word-groups only in one of their meanings.
The term motivation is used to denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the other.
There are three main types of motivation:
1) phonetical
2) morphological
3) semantic
1. Phonetical motivation is used when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word. For example: buzz, cuckoo, gigle. The sounds of a word are imitative of sounds in nature, or smth that produces a characteristic sound. This type of motivation is determined by the phonological system of each language.
2. Morphological motivation – the relationship between morphemic structure and meaning. The main criterion in morphological motivation is the relationship between morphemes. One-morphemed words are non-motivated. Ex – means «former» when we talk about humans ex-wife, ex-president. Re – means «again»: rebuild, rewrite. In borowed words motivation is faded: «expect, export, recover (get better)». Morphological motivation is especially obvious in newly coined words, or in the words created in this century. In older words motivation is established etymologically.
The structure-pattern of the word is very important too: «finger-ring» and «ring-finger». Though combined lexical meaning is the same. The difference of meaning can be explained by the arrangement of the components.
Morphological motivation has some irregularities: «smoker» – si not «the one who smokes», it is «a railway car in which passenger may smoke».
The degree of motivation can be different:
«endless» is completely motivated
«cranberry» is partially motivated: morpheme «cran-» has no lexical meaning.
3. Semantic motivation is based on the co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word within the same synchronous system. «Mouth» denotes a part of the human face and at the same time it can be applied to any opening: «the mouth of a river». «Ermine» is not only the anme of a small animal, but also a fur. In their direct meaning «mouth» and «ermine» are not motivated.
In compound words it is morphological motivation when the meaning of the whole word is based on direct meanings of its components and semantic motivation is when combination of components is used figuratively. For example «headache» is «pain in the head» (morphological) and «smth. annoying» (sematic).
When the connection between the meaning of the word and its form is conventional (there is no perceptible reason for the word having this phonemic and morphemic composition) the word is non-motivated (for the present state of language development). Words that seem non-motivated now may have lost their motivation: «earn» is derived from «earnian – to harvest», but now this word is non-motivated.
As to compounds, their motivation is morphological if the meaning of the whole is based on the direct meaning of the components, and semantic if the combination is used figuratively: watchdog – a dog kept for watching property (morphologically motivated); – a watchful human guardian (semantically motivated).
Every vocabulary is in a state of constant development. Words that seem non-motivated at present may have lost their motivation. When some people recognize the motivation, whereas others do not, motivation is said to be faded.
Semantically all word-groups may be classified into motivated and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological units or idioms.
Word-groups may be described as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the groups is based on the meaning of their components. Thus take lessons is motivated; take place – ‘occur’ is lexically non-motivated.
Word-groups are said to be structurally motivated if the meaning of the pattern is deduced from the order and arrangement of the member-words of the group. Red flower is motivated as the meaning of the pattern quality – substance can be deduced from the order and arrangement of the words red and flower, whereas the seemingly identical pattern red tape (‘official bureaucratic methods’) cannot be interpreted as quality – substance.
Seemingly identical word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on their semantic interpretation. Thus apple sauce, e.g., is lexically and structurally motivated when it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated
Word-groups like words may be also analyzed from the point of view of their motivation. Word-groups may be called as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is deducible from the meaning of the components. All free phrases are completely motivated.
It follows from the above discussion that word-groups may be also classified into motivated and non-motivated units. Non-motivated word-groups are habitually described as phraseological units or idioms.
Investigations of English phraseology began not long ago. English and American linguists as a rule are busy collecting different words, word-groups and sentences which are interesting from the point of view of their origin, style, usage or some other features. All these units are habitually described as «idioms», but no attempt has been made to describe these idioms as a separate class of linguistic units or a specific class of word-groups.
Difference in terminology («set-phrases», «idioms» and «word-equivalents») reflects certain differences in the main criteria used to distinguish types of phraseological units and free word-groups. The term «set phrase» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of word-groups.
There is a certain divergence of opinion as to the essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from other word-groups and the nature of phrases that can be properly termed «phraseological units». The habitual terms «set-phrases», «idioms», «word-equivalents» are sometimes treated differently by different linguists. However these terms reflect to certain extend the main debatable points of phraseology which centre in the divergent views concerning the nature and essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from the so-called free word-groups.
The term «set expression» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of word-groups.
The term «word-equivalent» stresses not only semantic but also functional inseparability of certain word-groups, their aptness to function in speech as single words.
The term «idioms» generally implies that the essential feature of the linguistic units under consideration is idiomaticity or lack of motivation. Uriel Weinreich expresses his view that an idiom is a complex phrase, the meaning of which cannot be derived from the meanings of its elements. He developed a more truthful supposition, claiming that an idiom is a subset of a phraseological unit. Ray Jackendoff and Charles Fillmore offered a fairly broad definition of the idiom, which, in Fillmore’s words, reads as follows: «…an idiomatic expression or construction is something a language user could fail to know while knowing everything else in the language». Chafe also lists four features of idioms that make them anomalies in the traditional language unit paradigm: non-compositionality, transformational defectiveness, ungrammaticality and frequency asymmetry.
Great work in this field has been done by the outstanding Russian linguist A. Shakhmatov in his work «Syntax». This work was continued by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. Great investigations of English phraseology were done by Prof. A. Cunin, I. Arnold and others.
Phraseological units are habitually defined as non-motivated word-groups that cannot be freely made up in speech but are reproduced as ready-made units; the other essential feature of phraseological units is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure.
Unlike components of free word-groups which may vary according to the needs of communication, member-words of phraseological units are always reproduced as single unchangeable collocations. E.g., in a red flower (a free phrase) the adjective red may be substituted by another adjective denoting colour, and the word-group will retain the meaning: «the flower of a certain colour».
In the phraseological unit red tape (bürokratik metodlar) no such substitution is possible, as a change of the adjective would cause a complete change in the meaning of the group: it would then mean «tape of a certain colour». It follows that the phraseological unit red tape is semantically non-motivated, i.e. its meaning cannot be deduced from the meaning of its components, and that it exists as a ready-made linguistic unit which does not allow any change of its lexical components and its grammatical structure.
Grammatical structure of phraseological units is to a certain degree also stable:
red tape – a phraseological unit;
red tapes – a free word-group;
to go to bed – a phraseological unit;
to go to the bed – a free word-group.
Still the basic criterion is comparative lack of motivation, or idiomaticity of the phraseological units. Semantic motivation is based on the coexistence of direct and figurative meaning.
Taking into consideration mainly the degree of idiomaticity phraseological units may be classified into three big groups. This classification was first suggested by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. These groups are:
– phraseological fusions,
– phraseological unities,
– phraseological collocations, or habitual collocations.
Phraseological fusions are completely non-motivated word-groups. Themeaning of the components has no connection at least synchronically with the meaning of the whole group. Idiomaticity is combined with complete stability of the lexical components and the grammatical structure of the fusion.
Phraseological unities are partially non-motivated word-groups as their meaning can usually be understood through (deduced from) the metaphoric meaning of the whole phraseological unit.
Phraseological unities are usually marked by a comparatively high degree of stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure. Phraseological unities can have homonymous free phrases, used in direct meanings.
§ to skate on thin ice – to skate on thin ice (to risk);
§ to wash one’s hands off dirt – to wash one’s hands off (to withdraw from participance);
§ to play the first role in the theatre – to play the first role (to dominate).
There must be not less than two notional wordsin metaphorical meanings.
Phraseological collocations are partially motivated but they are made up of words having special lexical valency which is marked by a certain degree of stability in such word-groups. In phraseological collocations variability of components is strictly limited. They differ from phraseological unities by the fact that one of the components in them is used in its direct meaning, the other – in indirect meaning, and the meaning of the whole group dominates over the meaning of its components. As figurativeness is expressed only in one component of the phrase it is hardly felt.
§ to pay a visit, tribute, attention, respect;
§ to break a promise, a rule, news, silence;
§ to meet demands, requirement, necessity;
§ to set free; to set at liberty;
§ to make money, journey;
§ to fall ill.
The structure V + N (дополнение) is the largest group of phraseological collocations.
Phraseological units may be defined as specific word-groups functioning as word-equivalents; they are equivalent to definite classes of words. The part-of-speech meaning of phraseological units is felt as belonging to the word-group as a whole irrespective of the part-of-speech meaning of component words. Comparing a free word-group, e.g. a long day and a phraseological unit, e.g. in the long run, we observe that in the free word-group the noun day and the adjective long preserve the part-of-speech meaning proper to these words taken in isolation. The whole group is viewed as composed of two independent units (A + N). In the phraseological unit in the long run the part-of-speech meaning belongs to the group as a single whole. In the long run is grammatically equivalent to single adverbs, e.g. finally, firstly, etc.
So, phraseological units are included into the system of parts of speech.
Phraseological units are created from free word-groups. But in the course of time some words – constituents of phraseological units may drop out of the language; the situation in which the phraseological unit was formed can be forgotten, motivation can be lost and these phrases become phraseological fusions.
The vocabulary of a language is enriched not only by words, but also by phraseological units. Phraseological units are word-groups that cannot be made in the process of speech, they exist in the language as ready-made units. They are compiled in special dictionaries. The same as words phraseological units express a single notion and are used in a sentence as one part of it. American and British lexicographers call such units «idioms». We can mention such dictionaries as: L. Smith «Words and Idioms», V. Collins «A Book of English Idioms» etc. In these dictionaries we can find words, peculiar in their semantics (idiomatic), side by side with word-groups and sentences. In these dictionaries they are arranged, as a rule, into different semantic groups.
Phraseological units can be classified according to the ways they are formed, according to the degree of the motivation of their meaning, according to their structure and according to their part-of-speech meaning.
A.V. Koonin classified phraseological units according to the way they are formed. He pointed out primary and secondary ways of forming phraseological units.
Among two-top units A.I. Smirnitsky points out the following structural types:
a) attributive-nominal such as: a month of Sundays, grey matter, a millstone round one’s neck and many others. Units of this type are noun equivalents and can be partly or perfectly idiomatic. In partly idiomatic units (phrasisms) sometimes the first component is idiomatic, e.g. high road, in other cases the second component is idiomatic, e.g. first night. In many cases both components are idiomatic, e.g. red tape, blind alley, bed of nail, shot in the arm and many others.
b) verb-nominal phraseological units, e.g. to read between the lines, to speak BBC, to sweep under the carpet etc. The grammar centre of such units is the verb, the semantic centre in many cases is the nominal component, e.g. to fall in love. In some units the verb is both the grammar and the semantic centre, e.g. not to know the ropes. These units can be perfectly idiomatic as well, e.g. to burn one’s boats, to vote with one’s feet, to take to the cleaners’ etc.
Very close to such units are word-groups of the type to have a glance, to have a smoke. These units are not idiomatic and are treated in grammar as a special syntactical combination, a kind of aspect.
c) phraseological repetitions, such as: now or never, part and parcel, country and western etc. Such units can be built on antonyms, e.g. ups and downs, back and forth; often they are formed by means of alliteration, e.g cakes and ale, as busy as a bee. Components in repetitions are joined by means of conjunctions. These units are equivalents of adverbs or adjectives and have no grammar centre. They can also be partly or perfectly idiomatic, e.g. cool as a cucumber (partly), bread and butter (perfectly).
Phraseological units the same as compound words can have more than two tops (stems in compound words), e.g. to take a back seat, a peg to hang a thing on, lock, stock and barrel, to be a shadow of one’s own self, at one’s own sweet will.
Phraseological units can be classified as parts of speech. This classification was suggested by I.V. Arnold. Here we have the following groups:
a) noun phraseologisms denoting an object, a person, a living being, e.g. bullet train, latchkey child, redbrick university, Green Berets,
b) verb phraseologisms denoting an action, a state, a feeling, e.g. to break the log-jam, to get on somebody’s coattails, to be on the beam, to nose out, to make headlines,
c) adjective phraseologisms denoting a quality, e.g. loose as a goose, dull as lead
d) adverb phraseological units, such as: with a bump, in the soup, like a dream, like a dog with two tails,
e) preposition phraseological units, e.g. in the course of, on the stroke of,
f) interjection phraseological units, e.g. «Catch me!», «Well, I never!» etc.
In I.V. Arnold’s classification there are also sentence equivalents, proverbs, sayings and quotations, e.g. «The sky is the limit», «What makes him tick», «I am easy». Proverbs are usually metaphorical, e.g. «Too many cooks spoil the broth», while sayings are as a rule non-metaphorical, e.g. «Where there is a will there is a way».
Теги:
Free word groups. Phraseological units
Контрольная работа
Английский
Просмотров: 27365
Найти в Wikkipedia статьи с фразой: Free word groups. Phraseological units