Word для Microsoft 365 Word для Microsoft 365 для Mac Word для Интернета Word 2021 Word 2021 для Mac Word 2019 Word 2019 для Mac Word 2016 Word 2016 для Mac Еще…Меньше
Для использования версий в Word необходимо хранить документы в OneDrive или в SharePoint библиотеке.
Если документы хранятся в Интернете, вы можете включить автосохранения для автоматического сохранения в качестве работы. Вы также можете предоставить доступ к документам, пригласив кого-либо в библиотеку или предоставив ссылку, а не отправляя отдельные копии документа. Наконец, вы можете работать над документом одновременно с другими людьми.
Дополнительные сведения о сохранении в OneDrive или SharePoint, совместном использовании или использовании автосохранения см. в:
OneDrive и SharePoint
-
Сохранение документа в OneDrive
-
Следует ли сохранять в OneDrive или SharePoint
-
Как работает работа с версиями в SharePoint списке или библиотеке
-
Восстановление предыдущей версии элемента или файла в SharePoint
-
Включение и настройка управления версиями для списка или библиотеки
Совместное репроизводение и автоскрытие
-
Совместное редактирование и совместная работа над документами
-
Видео: совместное Office файлов
-
Что такое автоскрытие
-
Включить автоскрытие
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Содержание
- 1 Режимы работы с документами и совместимость
- 1.1 Доступные компоненты в каждом из режимов
- 2 Преобразование документа в режиме Word 2016
- 3 Как создать документ «Word» стандартным способом?
- 4 Как открыть документ «Word»?
Совет. Если вы долго работаете с одним документом, вам, возможно, понадобится вернуться к одному из предыдущих вариантов файла. Для этого нужно воспользоваться возможностью создания версий документа. Версии позволяют фиксировать изменения, внесенные в документ в определенный момент времени. При использовании версий экономится место на диске, так как сохраняется не полное содержимое документа, а только различия между ними. Если сохранены несколько вариантов документа, то у вас всегда будет возможность вернуться к предыдущему и открыть, или удалить его.
В редакторе Word в любой момент можно, например, сохранить вариант текста, отправленный на рецензирование, а после внесения всех исправлений сохранить его как другую версию. Для управления версиями необходимо выбрать «Файл | Версии». В открывшемся окне «Версии документа» будет отображен список всех ранее сохраненных версий. Для сохранения версий необходимо нажать кнопку «Сохранить» и в появившемся окне сделать комментарии (заметки) к сохраняемой версии. Открыть любую из ранее сохраненных ранее версий можно воспользовавшись пунктом «Открыть» окна «Версии». А кнопка «Заметки» позволит отобразить заметки выделенной версии документа. В MS Word можно включить режим автоматического сохранения версии документа при каждом его закрытии. Это бывает полезно, если необходимо фиксировать информацию о том, кто и когда вносил исправления. Для этого отметьте галочкой опцию «Автоматически сохранять версию при закрытии» в окне «Версии». Кроме сохранения версий в Word можно делать резервную копию документа. Если по какой-то причине изменения в вашем документе не были сохранены, можно восстановить хотя бы некоторые из них, воспользовавшись резервной копией. Для автоматического создания резервной копии выберите пункт меню «Сервис | Параметры». В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Сохранение» и пометьте переключатель «Всегда создавать резервную копию». Сохраненная резервная копия – это файл с именем «Копия имя_файла». Ее можно отыскать в любой момент в той же папке, в которой сохранен основной файл, и работать с ней точно так же, как с обычным документом.
Когда вы открываете в Word 2016 документ, созданный в Word 2010 или более ранней версии, в строке заголовка окна документа отображается надпись Режим ограниченной функциональности.В режиме совместимости (или ограниченной функциональности) новые и улучшенные возможности Word 2016 временно отключаются, чтобы пользователям Word 2010 или более ранних версий были доступны все возможности редактирования. В режиме совместимости также сохраняется структура документа.
Если вы открываете в Word 2016 документ Word 2013, надпись Режим ограниченной функциональности в строке заголовка не появляется, поскольку версии Word 2013 и Word 2016 совместимы.
Режимы работы с документами и совместимость
В Word 2016 документ может быть открыт в одном из трех режимов.
- Режим Word 2013–2016
- Режим совместимости Word 2010
- Режим совместимости Word 2007
- Режим совместимости Word 97—2003
Если в строке заголовка отображается надпись Режим ограниченной функциональности, определить текущий режим можно следующим образом:
- Щелкните Файл > Сведения.
- В разделе Инспектор документов выберите команду Поиск проблем > Проверка совместимости.
- Нажмите кнопку Выберите отображаемые версии. Версии приложения, в режиме совместимости с которыми открыт документ, будут отмечены флажками.
Доступные компоненты в каждом из режимов
Преобразование документа в режиме Word 2016
Можно продолжать работу с документом в режиме совместимости или преобразовать его в формат файла Word 2016. Команда Преобразовать в Word очищает параметры совместимости, после чего макет документа выглядит так, как если бы он был создан в приложении Word 2016. Если файл имеет формат DOC, команда Преобразовать преобразует его в формат DOCX.
После преобразования документа можно использовать новые и улучшенные возможности Word 2016. Однако для пользователей более ранних версий Word это может затруднить или сделать невозможным редактирование отдельных частей документа, созданных с использованием этих функций Word 2016.
- Откройте вкладку Файл.
- Выполните одно из указанных ниже действий.
- Чтобы преобразовать документ без сохранения копии, выберите пункт Сведения, а затем — командуПреобразовать.
- Чтобы создать копию документа в режиме Word 2016, выберите команду Сохранить как и укажите расположение и папку для сохранения копии. В поле Имя файла введите имя нового документа, а в списке Тип файла выберите пункт Документ Word. Убедитесь, что флажок Поддерживать совместимость с предыдущими версиями Word снят.
Статья расскажет, как создать и открыть документ «Word».
Новые пользователи текстового редактора «Word» нуждаются в освоении этой не совсем простой программы. Прежде чем начать изучать все ее возможности, необходимо научиться самым простым и первоочередным вещам. В сегодняшнем обзоре мы научимся создавать и открывать документ «Word».
Как создать и открыть документ «Word»?
Для того чтобы создать документ «Word», вы можете воспользоваться самым простым и быстрым способом:
- На Рабочем столе или в любой папке, где вам нужно создать документ, кликните по пустой области правой кнопкой мышки, в контекстном меню пройдите в пункт «Создать» и выберите «Документ Microsoft Word». После этого пустой документ будет создан. Далее вы сможете его переименовать, открыть (об этом скажем ниже) и набирать тексты.
Производим действия по созданию документа «Word»
Производим действия по созданию документа «Word»
В принципе, вам должно быть известно, что таким методом можно создавать также новую папку, блокнот, архив и так далее.
Если же вы по каким-то причинам не смогли установить платную версию «Word» на компьютере, то можем рекомендовать воспользоваться бесплатным аналогом в виде программы «Office Word» (скачать здесь). С ее помощью будет доступно открывать и файлы «Word».
Как открыть документ «Word»?
Открываем документ «Word»
Как известно, текстовой редактор «Word» очень популярен, им пользуются в том числе и профессионалы. Для открытия документа «Word» необходимо, как обычно, дважды кликнуть мышкой по файлу. Но бывают ситуации, когда документ не открывается по тем или иным причинам.
Мы приведем способ, с помощью которого документ «Word» можно будет открыть, если это не получается сделать стандартным способом. Дело в том, что при установке программы может случиться так, что файлы «Word» не ассоциируются с ней, поэтому их невозможно открыть.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, сделайте следующее:
- Кликните по файлу правой кнопкой мышки, далее в контекстном меню нажмите на пункт «Открыть с помощью» и, в итоге, кликните на «Выбрать программу».
Открываем документ «Word»
- Затем в открывшемся окошке выберите программу «Word» (если ее не будет в списке, нажмите на кнопку «Обзор» и найдите «exe» файл в папке установки текстового редактора «Word») и нажмите на «Ок» (не забудьте поставить галку напротив пункта «Использовать выбранную программу для всех файлов такого типа», как указано на скриншоте).
Открываем документ «Word»
После этого документ «Word» откроется и в нем можно будет работать. Таким образом вы сможете открывать файлы старых версий текстового редактора «Word» при наличии у вас на компьютере установленной новой версии.
Видео: Как создать документ Word?
Microsoft Word exists in many different versions. Sometimes you need to know what Word version you have installed. For example, you may find add-ins on this site that are relevant only for specific versions of Word.
The information below will help you answer the question: «What version of Word do I have?«.
Latest updated 18-Oct-2021: Updated with information about the new Word 2021 that was released as part of Microsoft Office 2021 in October 2021.
NOTE – Microsoft has changed product names as of April 21, 2020
Office 365 has been renamed to Microsoft 365.
Correspondingly, Word for Office 365 has been renamed to Word for Microsoft 365.
How to detect the version of Word just by looking at the Word window
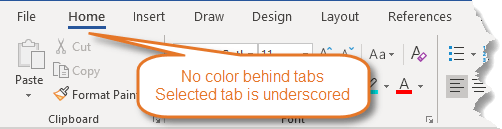
Figure 1. Word 2021 and Word for Microsoft 365 – no color behind Ribbon tabs – selected tab is underscored.
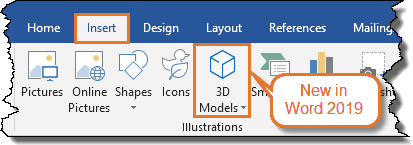
Figure 2. Word 2016 and Word 2019 – color behind the Ribbon tabs – selected tab has no background color. In Word 2019, you will find 3D Models on the Insert tab – it is not found in Word 2016.
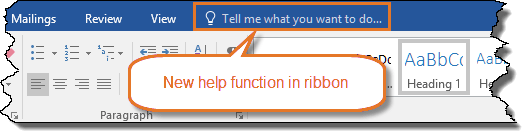
Figure 3. Word 2016 and Word 2019 – Help added after the tab names in the Ribbon.
Figure 4. In Word 2021 and Word for Microsoft 365, you will see only the magnifier icon without text, and it has been moved to the Title bar.
Figure 5. Word for Microsoft 365 has Editor group on Home tab – not found in Word 2021.
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2016, Word 2019, Word 2021
There are only a few visible differences between Word 2016 and Word 2019. Correspondingly, there are only a few visible differences between Word 2021 and Word for Microsoft 365.
All four versions have a Ribbon with several tabs, starting with the File tab followed by Home, Insert, etc.
Word 2021 and Word for Microsoft 365 have no special background color behind the Ribbon tabs. The selected tab is underlined. See Figure 1.
Word 2016 and Word 2019 have a colored background behind the Ribbon tabs. The selected tab has no background color. Word 2019 has a new command, 3D Models, on the Insert tab. It is not found in Word 2016. See Figure 2.
Word 2016 and Word 2019 have a Tell me what you want to do… help in the Ribbon. See Figure 3.
In Word 2021 and Word for Microsoft 365, you will see only the magnifier icon without text and it has been moved to the Title bar. A Search field appears when you click the icon. See Figure 4.
Word for Microsoft 365 has e.g. an Editor group on the Home tab that is not found in Word 2021. See Figure 5.
Word for Microsoft 365 is the version you have if you have Microsoft 365 installed. With Microsoft 365 you will automatically have the latest Word version. However, you may have the version updated with a delay depending on which Channel you are on, i.e. how often your Microsoft 365 is updated (Monthly Channel, Semi-Annual Channel).
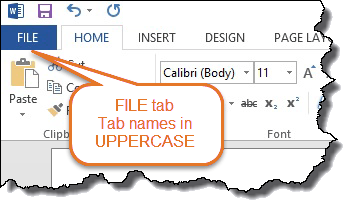
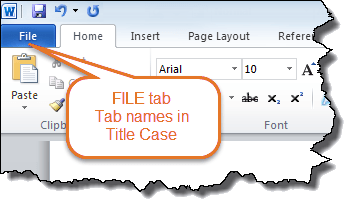
Word version – Word 2013 – tab names in uppercase.
Word 2013
Has FILE tab
Has ribbon with HOME, INSERT, PAGE LAYOUT, etc.
Names of tabs are in UPPERCASE
Word version – Word 2010 – tab names in Title Case.
Word 2010
Has File tab
Has ribbon with Home, Insert, Page Layout, etc.
Does not have Tell me what you want to do… help in the ribbon
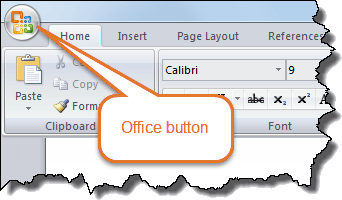
Word version – Word 2007 – Office button.
Word 2007
Has Office button
Has ribbon with Home, Insert, Page Layout, etc.
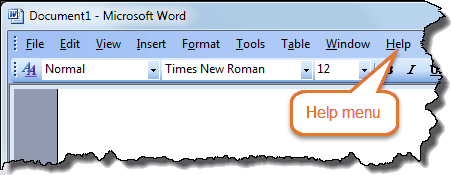
Word version – Word 2003 – Menu bar with Help menu.
Word 2003 or earlier version
Has menu bar with Help menu
Menu bar includes File, Edit, View, etc.
How to find more details about your Word version – version number and 32-bit / 64-bit information
Once you know which version of Word you have, you can find more details about the specific version by following the relevant information below.
Note that Microsoft Office 2010 and all newer versions of Office exist in both a 32-bit version and a 64-bit version. Previously, Microsoft recommended to install the 32-bit version. Now, the 64-bit version is the default. However, not all computers can run the 64-bit versions.
Word for Microsoft 365
Word 2021
Word 2019
Word 2016
Word 2013
Select File > Account category (left side of dialog box). You will now see the version number in the right side of the dialog box. See the examples below.
Word 2013
Word 2013 version details.
Word 2019
Word 2019 version details.
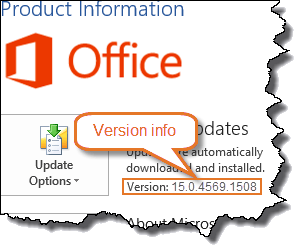
Select File tab > Help category (left side of dialog box). You will now see the version number and more information in the right side of the dialog box.
Microsoft Office 2010 was the first version that exists in both a 32-bit version and a 64-bit version. The illustration below is from a 32-bit version. You will see that information at the end of the version number. See more about 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
Word 2010 version details.
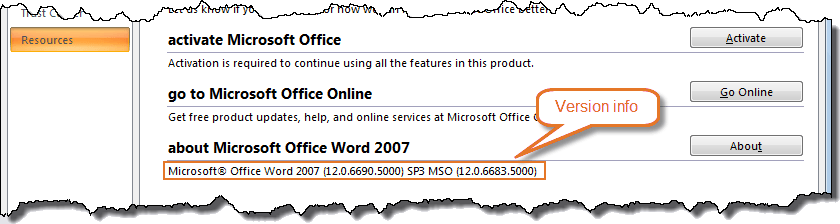
Select Office button > Word Options > Resources category (left side of dialog box). You will now see the version number in the bottom right of the dialog box. Click the About button next to the version information to open a dialog box with more details.
Word 2007 version details.
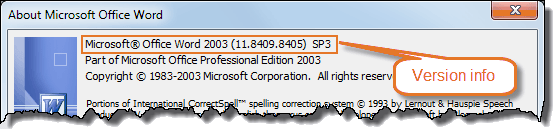
Select Help menu > About Microsoft Office Word. You will see the version information in top of the dialog box that opens.
The illustration below tells it is Word 2003. If you have e.g. Word 2002 or Word 2000, you will see that.
Word 2003 version details.
.
How to find more details about Word versions and version numbers
We talk about e.g. Word 2010 or Word 2019 or Word for Microsoft 365 (or just Word 365). Each version of Word has a version number that used to be unique. However, after the launch of Office 2019 in October 2018, this is not exactly true anymore: Word 2016, Word 2019, Word 2021, and Word for Microsoft 365 share the same number!
In the illustrations above for Word 2010, Word 2007, and Word 2003, you see a long number, e.g. 14.0.7116.5000 for Word 2010. The leftmost part of the long number (here 14) is the version number for the Word version.
In case of Word 2013, Word 2016, Word 2019, and Word 2021, you must select File > Account category and click the About Word button to see the corresponding number. It is shown in top of the dialog box that opens.
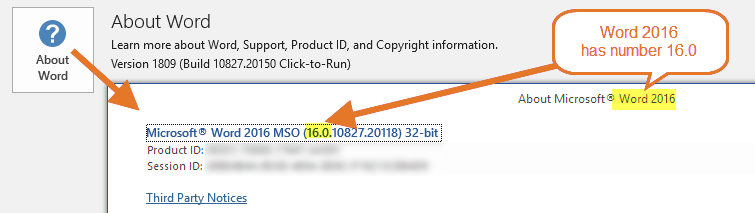
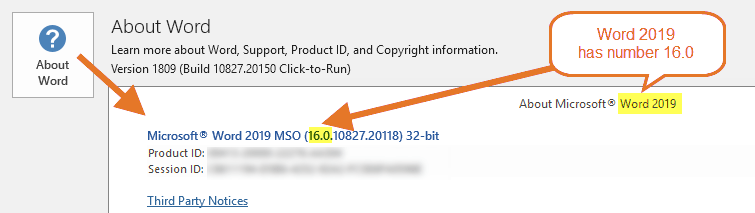
Below are illustrations from Word 2016, Word 2019, Word 2021, and Word for Microsoft 365. As you can see, all four versions have number 16.0 which can lead to a lot of confusion. As you can see in the illustrations for Word 2016 and 2019 below, they even had the entire long version and build number in common at the time when I made the illustrations:
NOTE: The information in the dialog box that opens when you click About Word may not look exactly as shown in the illustrations below. Microsoft seems to move the information around from time to time.
Word 2016 has number 16.0
Word 2019 has number 16.0
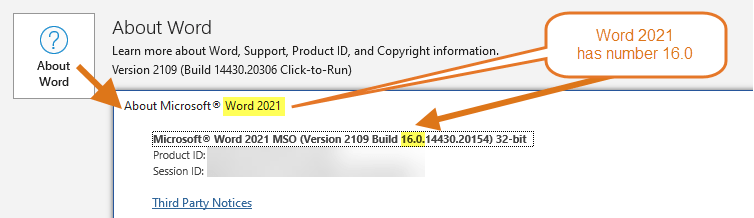
Word 2021 has number 16.0
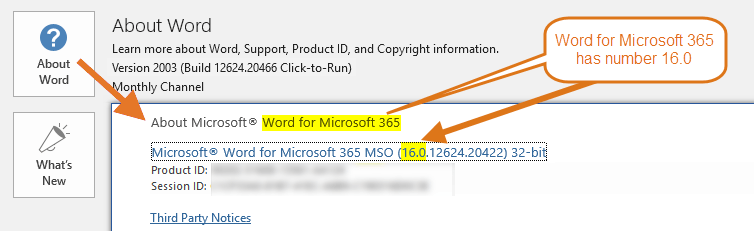
Word for Microsoft 365 has number 16.0
The number must be used e.g. in macros.
The last two groups of digits in the long number contains information about which updates have been installed.
For Word 2003, you also see SP3 after the version number. It tells that Service Pack 3 has been installed.
Overview of the Word version numbers
Which version
Word 2000
Word 2002
Word 2003
Word 2007
Word 2010
Word 2013
Word 2016
Word 2019
Word 2021
Word for Microsoft 365
Version number
9.0
10.0
11.0
12.0
14.0
15.0
16.0
16.0
16.0
16.0
Comments
Sometimes called Word XP
Microsoft skipped 13
As explained above, Word 2016, Word 2019, Word 2021, and Word for Microsoft 365 have the same number. This is not practical for developers but that is how Microsoft has implemented it.
If you have Microsoft 365 installed, you will automatically have the latest Word version. However, you may have the version updated with a delay depending on which Channel you are on.
How to detect the version of Word by looking at the splash screen that appears when you start Word
When you start Word, a splash screen (i.e. a window with an image showing information about the product) is shown while the program is launching. You may be able to detect the version of Word by looking at the splash screen. However, as you will see from the illustrations below, you may to be able to distinguish between all versions of Word that way.
The splash screen may disappear too quickly for you to catch the information you need. If you have installed one or more add-ins, this will normally make the splash screen stay on screen a little longer since Word needs time to load the add-ins.
The illustrations below show the splash screens from different versions of Word.
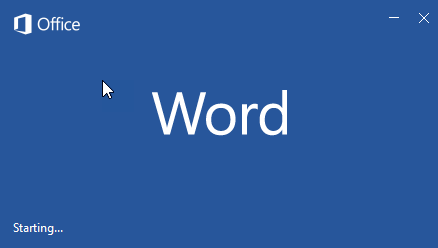
Word for Microsoft 365
Splash screen
Late in 2021, Microsoft has introduced a new look that also affects the splash screen.
You may see either the blue (old) or the white (new) splash screen depending on your Office version.
Notice the text Microsoft 365 in both versions.
As explained above, the name was changed from Office 365 to Microsoft 365 as of April 21, 2020.
Word 2021
Splash screen
Notice both text Office 2021 and a totally new look compared to earlier Office versions.
Word 2019
Splash screen
Notice the text Office 2019.
Word 2016 and Word 2013
Splash screen
Notice that no useful version information is shown – you can’t see whether it is Word 2016 or Word 2013. You need to use one of the methods above to find out
Word 2010
Splash screen
Notice the text Word 2010.
Word 2007
Splash screen
Notice the text Word 2007.
Word 2003
Splash screen
Notice the text Word 2003.
How to find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Microsoft 365 or Microsoft Office
The versions listed in the leftmost column below exist in both a 32-bit version and a 64-bit version:
|
Version |
How to find the 32-bit / 64-bit information |
|---|---|
|
Microsoft 365 Microsoft Office 2021 Microsoft Office 2019 |
To find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version installed, select File > Account category (left side of dialog box). Click the About Word button. You will find the information in top of the dialog box that opens as illustrated below: Click About Word to find info about 32-bit or 64-bit |
|
Microsoft Office 2010 |
You will find the information via File tab > Help as illustrated in Figure 9 above. |
For more details about 32-bit and 64-bit versions, see: Choose the 32-bit or 64-bit version of Office
How to find the Word version number and build number in VBA (macros)
Find Word version number as string in VBA
You can find the version number of Word with the following VBA code:
Example of result is the string:
«16.0»
Find Word version number as numeric value in VBA
If you need to find out e.g. whether the Word version number is lower or higher than a specific number, you need a numeric value and not a string. For that purpose, you can use the Val function:
Example of result is the numeric value:
16
Find first part of Word build number as string in VBA
You can find the first part of the build number with the following VBA code:
Example of result:
16.0.10827
If you compare the result with the number you see in the About dialog box (see illustrations above), you will see that the last part of the build number is missing. See below for a method to find the full build number.
Find full Word build number as string in VBA
You can find the full build number with the following function:
Function fncGetFullWordBuildNumber_String() As String
'Returns string with the full Word build number
fncGetFullWordBuildNumber_String = _
CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") _
.GetFileVersion(Application.Path & "WINWORD.exe")
End Function
Example of result:
16.0.10827.20150
Generate complete documents in seconds from re-usable text or graphics
Manage comments in Word fast and easy – review comments, extract comments to Word or Excel, etc.
Simplify and speed up the management of cross-references even in your most complex documents
Manage and repeat data in Word fast and easy with custom document properties and DocProperty fields
Extract insertions, deletions and comments from any Word document, incl. context and headings
Apply any highlight color or remove highlight in Word with a single click – customizable shortcuts
Browse pages, sections, headings, tables, graphics, etc. and find text in Word with a single click
Check safety-critical procedure documents for human factor issues in minutes – improve quality and help prevent errors
Create screen tips in Word fast and easy – with up to 2040 characters
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated December 17, 2022)
This tip applies to Word 97 and 2000
In many office environments, different people probably use many different versions of Word to create their documents. At some time you may want to know which version of Word was used to create a particular document.
It is not possible to be absolutely sure which version of Word was used to create a document. It is possible, however, to identify which version of Word was last used to modify a document. This is because every time a document is saved, Word (whichever version you are using) rewrites the format and some of the identifying information saved within a file.
Each time a document is modified and saved, a host of data is written into the actual document file. The data mostly consists of internal information Word needs when working with the file—stuff like style definitions, macros, and the whole gambit of document properties. This data also includes the name of the last version of Word to save the file and the file version or ‘class.’
Most of this information is not visible when the file is open in Word because Word reads what it needs to know and just displays the document content in the editing window. You can, however, use a plain text editor to look at the document file and examine the version information stored within it.
The default text editor that ships with Windows is Notepad. Depending on your version of Windows, Notepad isn’t the tool of choice to view a large document file, however. Why? Because in some versions of Windows there is a size limit on the documents you can open in Notepad. If you try to open a file that is too large, Notepad helpfully volunteers to open the file in WordPad. This won’t do you any good, since you want to view the plain ASCII characters in the file, not the document itself (which is how WordPad would display it).
This means that if you are using a version of Windows that has a limited version of Notepad, you need some other text editor without a size limit. You can find a variety on the Internet, including TextPad, TextEdit, UltraEdit, or NotepadPlus. You can install and use one of these programs, and then use it to open the document in question. Be careful, however, that you don’t actually change anything within the file. You are just looking around, and changing anything (and resaving the file within the text editor) is a sure recipe to make the file unusable within Word.
Having opened the file, look towards the end for some short sections of text that are actually readable. If the text editor has a search feature, then search for «Microsoft Word.» The area you are looking for is in a section that is obviously the common document properties (template name, author, document title, etc) and the version information will be displayed nearby. This information will consist of one of the following:
- Microsoft Word 6.0
- Microsoft Word 95
- Microsoft Word 8.0
- Microsoft Word 9.0
- Microsoft Word 10.0
This covers versions of Word up through Word 2002. If the document was saved in Word 2003, then the version number is not saved in the document. Instead, you’ll find the text «Microsoft Office Word» and «Microsoft Office Word Document.»
Later readable sections of the file also reveal the file version—which is not necessarily the same thing as the Word version since some Word versions can write binary files of earlier versions and the same file version is used for both Word 97 and Word 2000. The file versions are:
- Word.Document.6 (Word 6 format)
- Word.Document.7 (Word 95 format)
- Word.Document.8 (Word 97 or later format)
Now, having said all this (which is a great way to understand a little more about the inside workings of Word), there is something you can try within Word itself. If you are using Word 2000 or a later version, follow these steps:
- Start Word.
- Click on the Open tool, or choose Open from the File menu. Word displays the Open dialog box.
- Use the controls in the dialog box to locate and select the file in question. (Don’t open it; just select it.)
- Click on the down arrow next to the Views tool on the toolbar in the Open dialog box. This displays a small drop-down menu.
- Choose Properties from the drop-down menu.
If you are using Word 97, the steps are only slightly different.
- Start Word.
- Click on the Open tool, or choose Open from the File menu. Word displays the Open dialog box.
- Use the controls in the dialog box to locate and select the file in question. (Don’t open it; just select it.)
- Click on the Properties tool on the toolbar in the Open dialog box.
The information that appears at the right side of the dialog box shows a multitude of properties for the selected document file. One of the properties is called Application. This lists the version information for the document—the same information you located using the text editor earlier in this tip.
WordTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Word training.
(Microsoft Word is the most popular word processing software in the world.)
This tip (601) applies to Microsoft Word 97 and 2000.
Author Bio
With more than 50 non-fiction books and numerous magazine articles to his credit, Allen Wyatt is an internationally recognized author. He is president of Sharon Parq Associates, a computer and publishing services company. Learn more about Allen…
MORE FROM ALLEN
Quickly Removing Table Borders
Insert a table in your document and Word assumes that you want borders around the table and its cells. Here’s a shortcut …
Discover More
Determining the Length of a Non-Document Text File
If you use a macro to create and work with text files, you can find out the length of those files using a simple command. …
Discover More
Entering a Name in the Header of a Locked Form
When you lock a document as a form, then Word limits what you can do with that document. That includes not being able to …
Discover More
For the last lesson in this Geek School series, we’re going to talk about keeping track of versions in Word and comparing and combining documents.
The Versions feature in Word was removed in recent versions of Word. In Word 2013, the only way you can access previous versions of a document in Word is to open previous automatically saved (autosaved) versions of the document. You can also open recent unsaved documents. However, there is no formal versioning feature in Word. We will show you an alternative you can easily add to Word for free that will provide this capability.
If multiple people have worked on different copies of the same file, instead of using the Track Changes feature on one copy of the file, you can compare the two versions of the file to see the differences. Word contains a comparison tool that allows you to compare two files, as long as they have different file names. We will show you how to use this feature and how to read the results of the comparison.
In addition to comparing documents, you can combine documents after comparing them. We will show you how to merge two versions of the same document and also how to easily merge two different documents, in case multiple authors have worked on separate parts of a document.
Once all changes have been made, the necessary comparisons made, and combining of documents done, you can easily share your document using Microsoft OneDrive. You can also use OneDrive at any point in the collaboration process to provide access to the document for other reviewers.
Keep Track of Versions of a Document
Word used to have a formal versioning feature that allowed you to save different versions of a document within the document itself. That feature has gone away and the only way you can retrieve previous versions of a document is through the Auto-Save feature or by accessing unsaved documents, if available.
By default, Word automatically saves your document at certain intervals. This is the Auto-Save feature. To go back to a previously, automatically saved copy of your document, click the “File” tab and select an “(autosave)” item from the list under “Versions.”
You can also increase or decrease the interval for the Auto-Save feature in Word.
If you have closed your document by accident without saving, or you lost power and the computer unexpectedly turned off, you can recover unsaved documents. To do this, click the “File” tab and click the “Manage Versions” button on the “Info” screen. Select “Recover Unsaved Documents” from the drop-down menu.
If any unsaved files were available, they would be listed on the “Open” dialog box that displays.
Alternatives for Saving Versions of a Word Document
There are alternatives for adding a versioning system to Word. One is an add-in for Word, called Save Versions, and another is a plugin that works with an external version control program called Perforce.
The Save Versions add-in allows you to easily save numbered versions of a Word document from within the file.
Perforce is a version control program that is available for free for up to 20 users. They provide a plugin for Microsoft Office that allows Microsoft Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Project files to be easily stored and managed in Perforce from within the programs.
Compare Two Versions of the Same Document
If a reviewer has forgotten to use the “Track Changes” feature, and you didn’t lock it on in the document, you can still compare the two versions of the document and accept and reject changes based on the comparison. All you need is your original document and the revised document. Each file must have a different name.
The “Compare” and “Combine” features are similar, but each has its purpose. If you only have two documents you want to compare, and the neither one contains tracked changes, use the “Compare” feature. If you have two or more documents that contain tracked changes, and you need to keep track of who changed what and when, use the “Combine” feature, described later in this lesson.
To compare the original and revised versions of a document, click “Compare” in the “Compare” section of the “Review” tab and select “Compare” from the drop-down menu.
NOTE: You can’t compare two documents if either of them is protected for tracked changes or has any kind of document protection applied. Remove the document protection to continue comparing the documents. See Lesson 2 for information on how to unlock the tracked changes feature and Lesson 4 for information about removing formatting and editing restrictions from a document and a password assigned to a document to open it.
On the “Compare Documents” dialog box, select the “Original document” from the drop-down list.
Select the “Revised document” from the drop-down list. Under the “Revised document,” specify a label to apply to the changes so you know who made them in the “Label changes with” edit box. It can be a user’s name or whatever you like.
Click “More” to access more options.
In the “Comparison settings” section, select the items you want to compare in the two documents. By default, all items are selected.
NOTE: The “Insertions and deletions” item is always grayed out and always checked. When you use “Compare” or “Combine”, insertions and deletions will always be compared.
In the “Show changes at” section, choose to compare character by character (“Character Level”) or word by word (“Word level”). “Character level” allows you to see the exact changes that were made. For example, if the original document has the word “to” and the revised document has the word “too,” to which an “o” was added, the “Word level” setting would show you that “to” was replaced with “too.” However, the “Character level” setting would show the fact that an “o” was added.
By default, the “Compare” feature puts the changes into a new document, as shown in the “Show changes in” section. However, you can choose to put the changes into the “Original document” or the “Revised document.”
Click “OK” once you’ve made your selections.
The comparison between the two documents is made and the changes are displayed in the specified document. In our example, we chose to accept the default of showing the changes in a new document. The “Original document” and the “Revised document” both display in a pane to the right of the “Compared Document” to be used for reference. They cannot be edited.
If you don’t see the pane containing the original and revised documents, click “Compare” in the “Compare” section of the “Review” tab. Then, select “Show Source Document” and then “Show Both.” You can also choose to “Show Original” or the “Show Revised,” if you don’t want to view both.
The “Reviewing pane”, discussed briefly in Lesson 2 and in more detail in Lesson 3, also displays to the left of the “Compared document.”
In the “Compared document,” you can go through the tracked changes, just as discussed in Lesson 2, accepting or rejecting each change.
Then, save the compared document with a different name and you’ll have a document containing changes from both the original and revised documents.
Combine documents
When you have multiple documents containing tracked changes that you need to compare, it helps to be able to keep track of who made which changes and when. The “Combine” command allows you to merge the tracked changes from each document, two at a time, until all changes from all documents have been incorporated into one document.
NOTE: This is not the best way to review documents and incorporate changes. It’s best to share documents and have other people review them sequentially, using “Track Changes.” However, if that was not done, the “Combine” feature can help you gather and incorporate changes made by all reviewers.
Also, as with the “Compare” feature, you can’t combine documents if any of the documents are protected in any way. Remove protection from the documents before combining them.
Combine Multiple Versions of the Same Document
To start combining the first two documents, click “Compare” in the “Compare” section of the “Review” tab and select “Combine” from the drop-down menu.
The “Combine Documents” dialog box is essentially the same as the “Compare Documents” dialog box discussed in the previous section.
For the “Original document” select the earliest version of the original document and then select one of the reviewers’ versions of the document as the “Revised document.” Enter labels for the “Original document” and the “Revised document” using the corresponding “Label unmarked changes with” edit box. This allows you to see who made which changes.
Just as you did when comparing documents, select the “Comparison settings,” the level for “Show changes at,” and which document to “Show changes in.” When combining more than two documents, it might be a good idea to show the changes in the “Original document,” making sure you make a copy of it first, and use the same original document when comparing to each reviewer’s document. This allows you to “gather” all the changes into the original document.
The “Combined Document” displays with all the changes tracked and marked with the specified labels and times. If the changes in the “Revised document” were not tracked, the revision time will be the time the documents were combined, which will be essentially useless.
You can wait until combining all the reviewers’ documents before reviewing and accepting and rejecting editing changes. However, before combining additional documents, you must resolve all formatting changes because Word cannot retain multiple formatting revisions.
The easiest way to do this is to use the “Show Markup” menu to only show the “Formatting” markup. Select “Comments,” “Ink,” and “Insertions and Deletions” so there are no check marks to the left of those options. Only the “Formatting” option should have a check mark. Then, review all the tracked formatting changes and accept or reject each change.
NOTE: If you’re not using tablet, the “Ink” option is irrelevant. It does not matter if that option is on or off.
Once you have resolved all the formatting changes, you can compare the new original document with the next revised document. Continue until all the revised documents have been combined into the original. When this is done, you’ll have a version that contains all of the changes and each change will be marked with who made it. Again, the times when the changes were made are only accurate if the changes were tracked in each revised document.
Now, you can show all the markup using the “Show Markup” menu (turn “Comments” and “Insertions and Deletions” back on – turn on “Ink” only if you are using a tablet) and review all the changes, accepting or rejecting each change.
Merge Two Different Documents
There may be times when multiple authors are working on different parts of a document and you need to combine those separate parts into one document. That’s easily accomplished in Word. Open the main document into which you want to add the other documents and place the cursor at the point where you want to insert another file. Click the “Insert” tab.
In the “Text” section, click the down-arrow on the “Object” button and select “Text from File” from the drop-down list.
On the “Insert File” dialog box, navigate to the location of the file you want to insert, select the file, and click “Insert.”
NOTE: You can also insert a link to a file, which is recommended if that file is going to change. Instead of clicking the “Insert” button, click the down-arrow on the “Insert” button and select “Insert as Link.” An “INCLUDETEXT” field code is inserted, rather than the file’s contents.
When you insert the contents of a file using the “Text from File” option, the styles of the current document are applied to the contents of the incoming file. If styles were used in the incoming file, the formatting of the inserted text will most likely change to the formatting of the current document. However, any information about paper size, orientation, margins, and other Page Layout settings will be discarded and replaced with the settings from the current document.
Share a Document Using Microsoft OneDrive
You can use OneDrive to share your document with other reviewers. A document can be saved to and opened from your OneDrive account directly from within Word, as long as you’re signed into your Microsoft account. To share your document with others, simply click the “File” tab and then click “Save As” from the list of options on the left. On the “Save As” screen, click the “OneDrive” option and then click the “Browse” button on the right.
As long as you have an internet connection, the “Save As” dialog box displays showing you the files and folders in your OneDrive account. Choose a folder in which to save your document (or create a new folder), enter a file name, and click “Save.”
For other people to be able to access the document on OneDrive, you must share the file, or the folder containing the file. See the help on OneDrive’s site for information on how to do this.
Conclusion
And that’s it for the How-To Geek School’s Guide to Using Word in a Team Setting!
It’s been fun, we’ve learned a lot, and hope you did too! If you missed any part of this series, or simply want to review something again, you can easily do so by clicking any of the links in the table of contents at the beginning of the article.
READ NEXT
- › Save Hundreds on Elegoo’s New PHECDA Laser Engraver Through Kickstarter
- › How to Get a Refund on the PlayStation Store
- › Five Types of Phone Damage That Aren’t Covered by Your Free Warranty
- › Spotify Is Shutting Down Its Free Online Game
- › Android’s Nearby Share Has (Unofficially) Arrived on Mac
- › This 64 GB Flash Drive From Samsung Is Just $8 Right Now