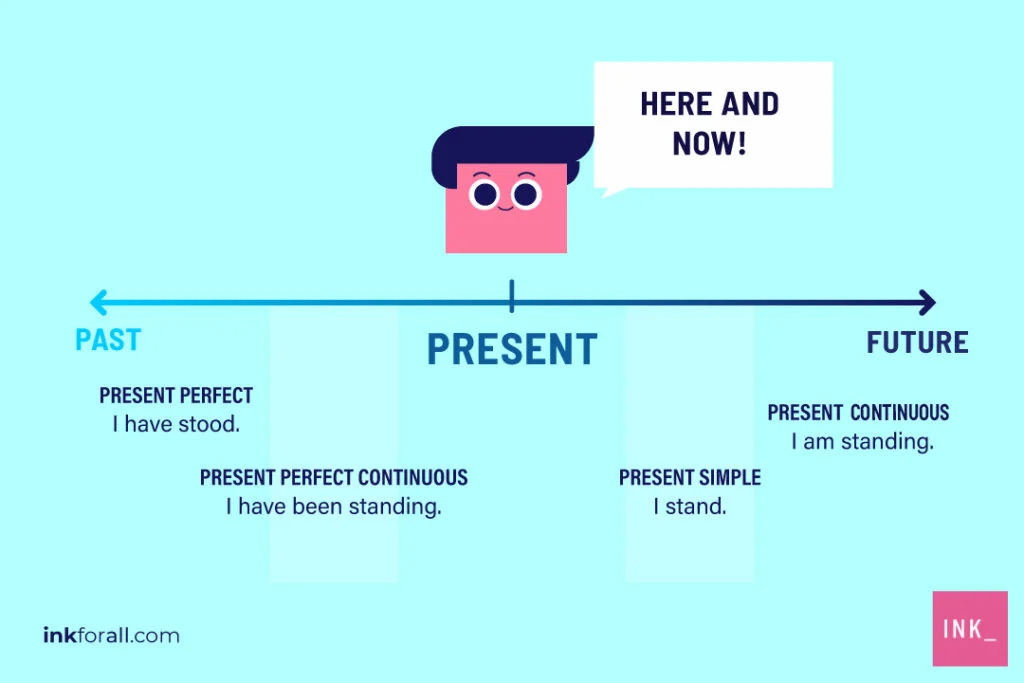
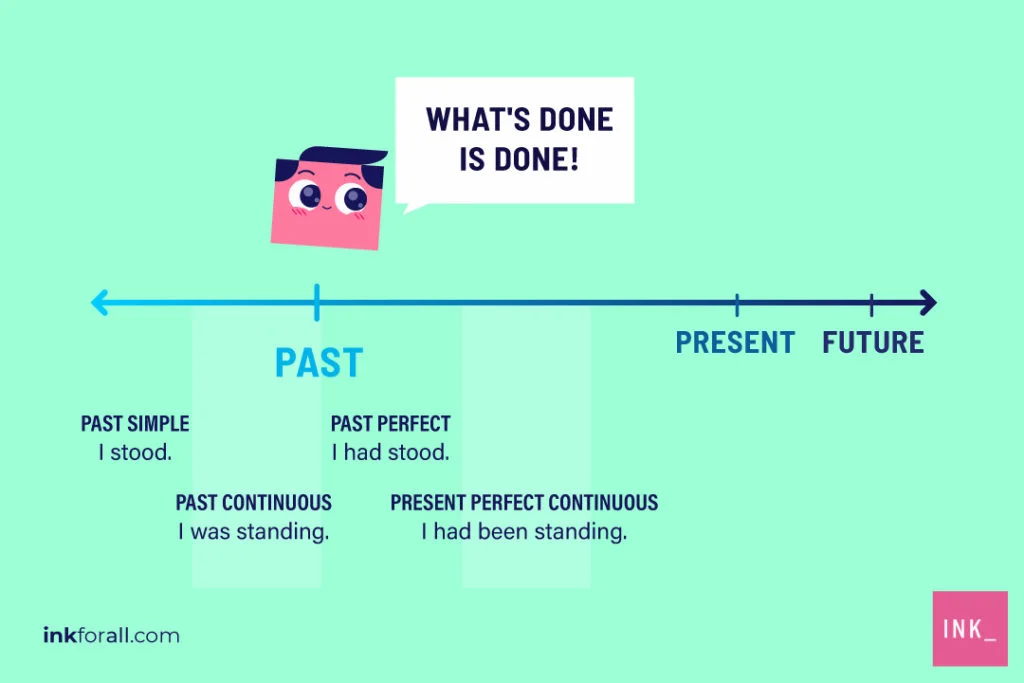
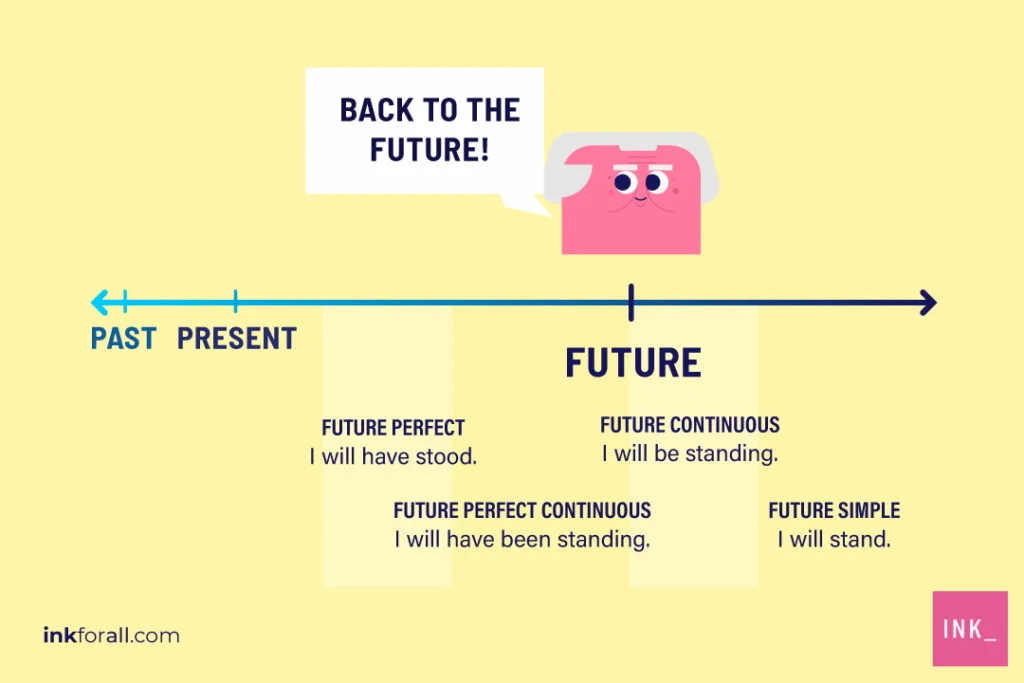
Tense is a modal aspect of the verb. There are 16 tenses in English Grammar in all. The tenses refer to the time of an action or state.
The time of the state is not indicated by the tense. For example, if I say: I run (state); I run (present tense); I ran (past tense); I will run (future tense) – it does not say when I run – right now, yesterday, or tomorrow.
In this blog post, we will look at 16 tenses in English grammar. For each of these 16 tenses, we will see the formula, the structure, and the definition.
English Grammar is a very complex language and tenses are one of the basic things to learn and master the grammar. There are a lot of rules and even more exceptions.
The table of content shows 16 tenses. Let’s explain them briefly one by one.
Past Tense
The past tense is used for events that have already taken place, like “I ate dinner last night”. It has four types, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tense.
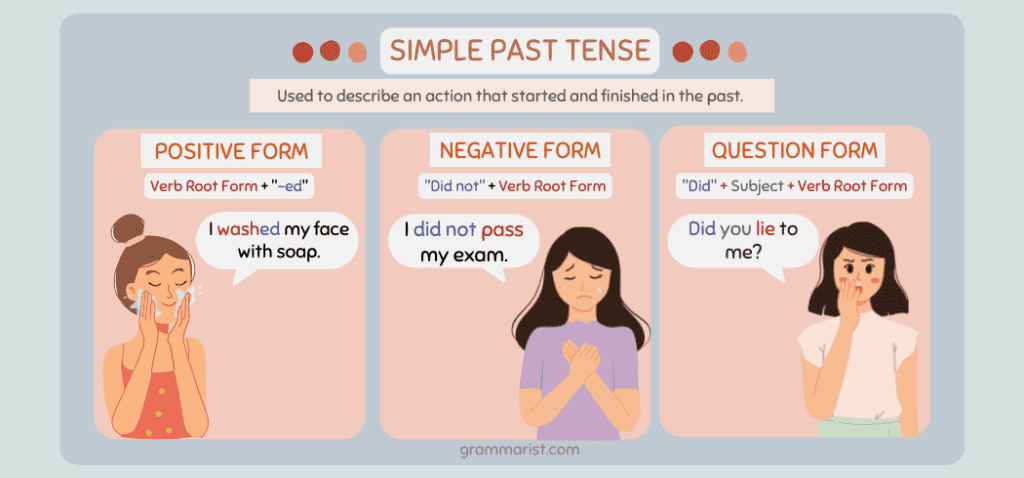
Simple Past Tense
Definition
Simple past tense is used to describe actions that occurred in the past, which were completed at a definite time and are not happening currently.
For example, “I went to school yesterday.”
Simple past tense is used in stories with a definite beginning and end. It’s often used to talk about what someone did or experienced on a particular day or to talk about the weather.
Structure/Formula
Subject + main verb(+ed) or second form of verb
Examples
- Yesterday I went to the market.
- Did you ride your bike this morning?
- The bus was late, so I missed the train.
- She tried to make us feel better, but it didn’t work.
- He did not know you were kidding when you said that.
Past Continuous (Progressive) Tense
Definition
In English, the past continuous tense expresses an action that was in progress at some point in the past.
For example, ‘I was running’.
The past continuous tense is used to talk about an unfinished period of time. It can also refer to a specific action that was happening at a specific point in time.
In the past continuous tense, “was” or “were” is used with an -ing verb to show that something was happening.
Structure/Formula
Subject + was/were + present participle
Examples
He was telling us stories.
- He was telling a story when we came in.
- When we came in, he was telling a story.
- I was bowling when he walked in.
- While we were eating dinner, he went outside to play soccer with his friends.
- He was speaking to you.
Past Perfect Tense
Definition
The past perfect tense uses had and a past participle for the first person, third person singular, and third person plural subjects.
It is also used to describe an action that was completed at some point in the past. It is often used when talking about things that happened before another event in the past.
Structure/Formula
Subject + had + past participle
Examples
- I had finished all my homework.
- Jack had traveled all over Europe by the age of 18.
- Jill had not visited Rome by the time she turned 30.
- The dog had slept for 10 minutes.
- Had she studied for two hours?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The past perfect continuous tense is a verb tense that is used to express an action that started in the past and continued up until another point in the past.
For example, “She had been talking for an hour when I arrived.”
Structure/Formula
Subject + had been + present participle + time reference
Examples
- Betty Ann had been working for many hours that day.
- I had been waiting there since ten o’clock when she entered the room.
- Before they left, my friends had been travelling for two days in the car.
- She had been working for 3 hours before her friend phoned her.
- I had been painting the house when the rain stopped.
Present Tense
We use the present tense to talk about actions or events happening now or completed. It has also four types i.e. simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous.
Simple Present Tense
Definition
Simple present tense is a verb tense that talks about what happens habitually or continually. It can also talk about what is happening right now.
Structure/Formula
Subject + main verb (s/es for third person)
Examples
- Tom works in a garage
- Ali lives in a flat in Brixton
- ‘What do you usually do on Sundays?’ ‘I read.’
- I work in the marketing department.
- We write content for clothing and fashion websites.
Present Continuous (Progressive) Tense
Definition
Present continuous tense is used to describe an action happening now, or an ongoing action. It can also be used to talk about something that will happen in the future. To form present continuous, add “ing” to the base form of a verb (without “to”) and use the following formula:
Structure/Formula
Subject + is/am/are + present participle
Examples
- He is cleaning the windows.
- I am not washing my hands in the sink.
- They are talking to their boss.
- We are having fun with our family.
- Are you saving your money?
Present Perfect Tense
Definition
The present perfect tense is used to emphasize the duration of an action that occurred in a time period before now. When using this tense, you should also provide an additional sentence that describes what happened before now.
Structure/Formula
Subject + has/have + past participle
Examples
- She has visited her grandma.
- I have lived here for twelve years.
- He has bought a new car last week.
- We have listened more than once to the concert.
- We have stopped using the term ‘early retirement’.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The present perfect continuous tense is used for actions that have been going on since the past and up until the present. It can also be used to refer to actions that are still in progress, but still haven’t been finished.
Structure/Formula
Subject + have been + present participle + time reference
Examples
- We have been staying there every day.
- My friend had been waiting for us since morning.
- We have been living in a new house for a month.
- How long has John been working here?
- I have been working hard for this job.
Future Tense
The future tense is used to talk about things that haven’t happened yet like “I will eat dinner tonight”. It four types are simple future tense, future continuous, future perfect and future perfect continuous.
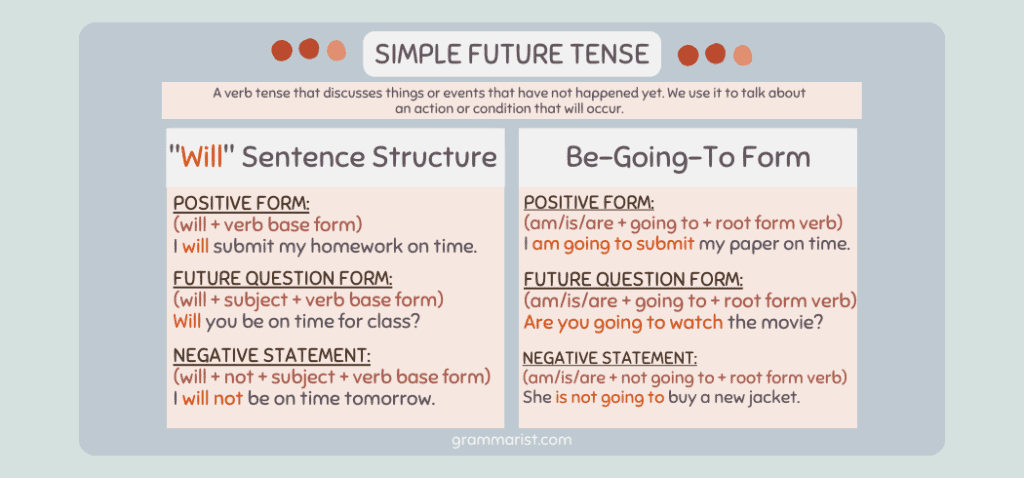
Simple Future Tense
Definition
Simple future tense is a verb tense that is used to describe the things that have not happened yet.
Structure/Formula
Subject + will/shall + main verb
Subject + is/am/are + going to + main verb
Examples
- He will stay here.
- Mark will visit you next month.
- You will go to Jerry’s on Friday.
- They will finish that project before the deadline.
- She is going to apply for the job.
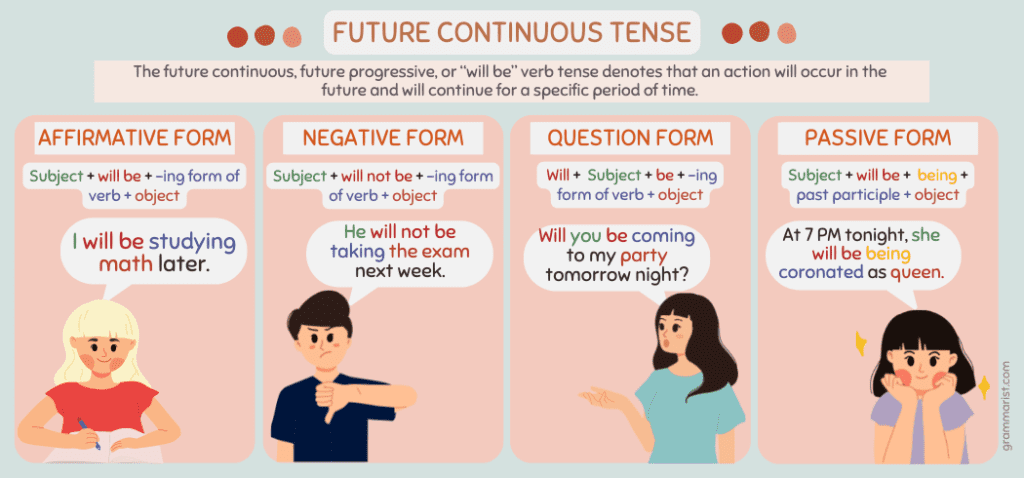
Future Continuous (Progressive) Tense
Definition
Future continuous tense is a verb tense used to express the idea that action will be in progress at some time in the future.
Structure/Formula
Subject + will be + present participle
Examples
- I will be still eating dinner when you arrive.
- You will be seeing him this weekend.
- She will be sleeping for an hour by the time you get back from the office.
- We will be having a quiz tomorrow.
- I will be meeting my husband at the airport.
Future Perfect Tense
Definition
Future perfect tense is a verb tense that indicates an action or event that will be completed by some point in the future.
In the future perfect tense, the action of the verb is completed before some time in the future.
Structure/Formula
Subject + will have + past participle
Examples
- I will have decided to go to the party.
- When will you have finished your essay?
- I will have left by tomorrow morning.
- I will have eaten the sandwich by the time he returns.
- When she arrives, they will have gone to the shops.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The future perfect continuous is a verb tense used to emphasize an action that will be in progress up until another point in time in the future. It’s usually used to describe a situation that started in the past and will continue into the foreseeable future.
The duration of time for the event is not necessary to be specified, but it must take place after a certain time in the future.
Structure/Formula
Subject + will have been + present participle + time reference
Examples
- I will have been working for five years by the time I finish this graduate program.
- Susan will have been living in New York for six months by the time she leaves for London.
- He will have been dozing all morning when the alarm goes off.
- She will have been painting for hours when her dad walks in.
- They will have been talking for over an hour before I arrive.
Past Future Tense
Simple Past Future Tense
Definition
Past Future Tense is a verb tense that expresses the idea that an action or event will occur later in time.
Structure/Formula
Subject + Would + Main Verb
Examples
- Tom and Bob told that they would study twice a week.
- She would tell her boss what she thought.
- We decided that I would go.
Past Future Continuous Tense
Definition
The Past Future Continuous Tense is used to indicate continuous or habitual action in the past that was interrupted by another later action.
Structure/Formula
Subject + should be / would be + Present Participle
Examples
- Tom told that he would be playing football tomorrow.
- I was aware that it would be storming today.
- You planned that you would be eating dinner with your family.
Past Future Perfect Tense
Definition
Past Future Perfect tense is a verb tense that is used to express actions that will happen in the future before something in the past. It is often used as a way to show cause and effect or a sequence of events.
Structure/Formula
Subject + should have/would have + Past Participle
Examples
- He told that he would have completed his task by then.
- They would have sent it to us by now (if they didn’t forget).
- They decided that they would have eaten their dinner before 7pm.
Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to show an action that began in the past and continues up until the present time.
Structure/Formula
Subject + would have been + present participle + time reference
Examples
- He would have been working if we had not come.
- She told that she would have been baking the cookies.
- I would have been swimming in the sea when you called

These are helpful resources to learn tenses with examples, and worksheets.
- 12 Verb Tenses in English Grammar
- Tenses Worksheet (Mixed Tenses Exercise) with Answer
- Examples of Tenses in English
- Tutor teaching tenses in a video
Past Tense
- Simple Past Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Simple Past Tense
- Simple Past Tense Worksheets
- Past Continuous / Progressive Tense
- 50 Sentences of Past Continuous Tense
- Past Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Past Perfect Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets
Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense (Formula, Examples & Exercises)
- 50 Sentences of Simple Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense Worksheets
- Present Continuous Tense Formula, Examples & Usage
- 50 Sentences of Present Continuous Tense
- Present Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Examples, Exercise, & Structure
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets
Future Tense
- Simple Future Tense Explained with Examples, Formula, and Exercise
- 50 Sentences of Simple Future Tense
- Simple Future Tense Worksheets
- Future Continuous Tense Structure, Rules and Examples
- 50 Sentences of Future Continuous Tense
- Future Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Future Perfect Tense Formula and Examples
- 50 Sentences of Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense Structure, Examples and Exercise
- 50 Sentences of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets
A verb tense is a grammatical construct that modifies the verb to represent time. Learning the different tenses of verbs will help you express the reality of time in your speech and writing alongside using time expressions.
Keep reading to learn the uses and examples of verb tenses in English as I break it all down. Then, test your understanding by answering the worksheet I created.
What is a Verb Tense?
Before understanding what a verb tense is, it helps to recall the definition of verbs. Remember that a verb is a part of speech that shows actions, conditions, and the existence of something while showing time.
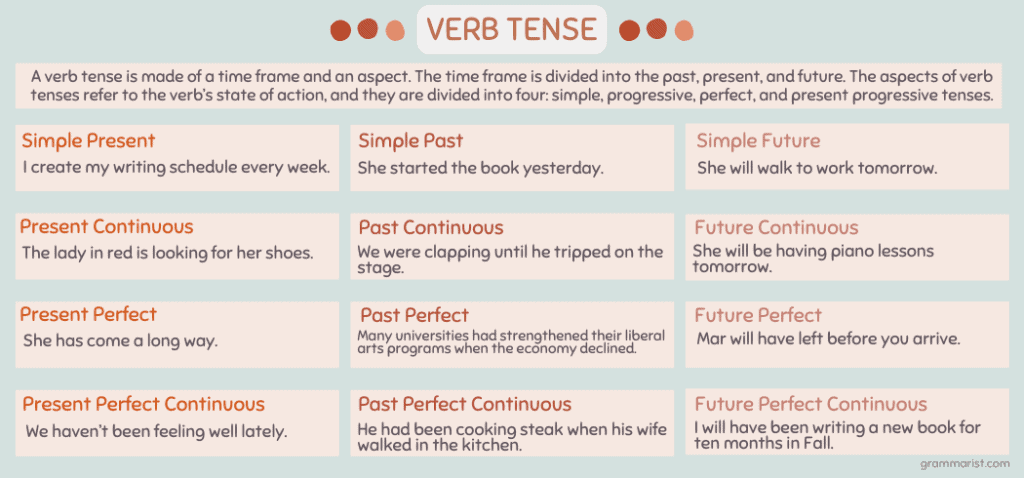
A verb tense is made of a time frame and an aspect. The time frame is divided into the past, present, and future.
The past tenses describe actions in the past, while the present tenses describe activities taking place. Meanwhile, future tenses describe an action that will occur in the future. It’s super important to understand the difference in this, especially if you’re writing.
The aspects of verb tenses refer to the verb’s state of action, and they are divided into four: simple, progressive, perfect, and present progressive tenses.
The simple tenses are for actions occurring at a specific time in the past, future, or present. Progressive tenses indicate ongoing or unfinished action, while perfect tenses describe a finished action. Lastly, the perfect progressive tenses show actions in progress then finished.
How Do You Identify Verb Tenses?
You can understand the types of verb tenses by mastering their different forms. For instance, you should know that the simple past tense usually has a verb that ends in -d or -ed if they are regular verbs.
For progressive tenses, there is an auxiliary verb followed by the present participle verb. The present participle form is also the -ing form of the verb. All of these forms locate an event in time.
It also helps to understand verb tense rules, such as the proper sequence of verb tenses. For example, the verb of the subordinate clause can be in any tense if the independent clause shows future or present tense.
Remember to only show shifts in verb tenses when necessary, such as when you indicate a change in the time of the action.
I find that style guides also vary when it comes to verb tense rules. There may be examples of writing rules in APA that Chicago does not recommend.
What are the 12 Verb Tenses?
Now, let’s discuss the twelve English tenses, their functions, and some sentence examples. I’ve divided them into key sections to make things easier.
Simple Present
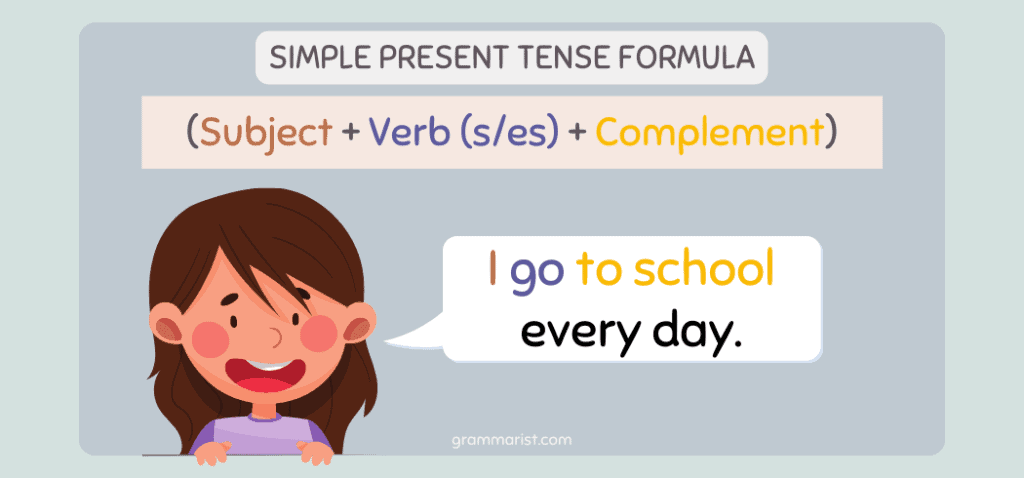
The simple tense is the first big category of verb tenses. The simple present tense shows actions or being that are either happening at the moment or regularly.
We form the simple present tense by adding -s or -es if the subject is singular. But if the subject is plural or I, keep it in its base form. For example:
- I create my writing schedule every week.
- She creates her writing schedule every week.
- They create their writing schedule every week.
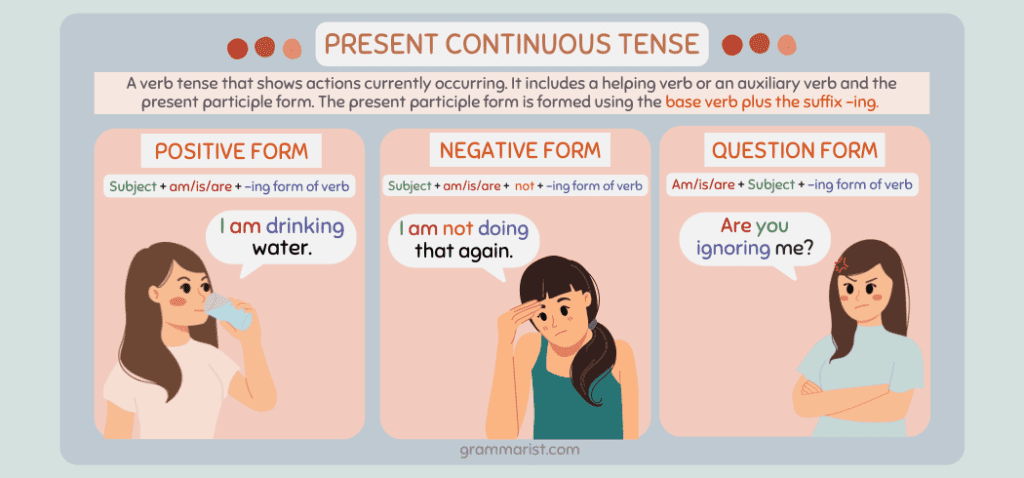
Present Continuous
The present continuous or progressive tense is one of the categories of verb tenses that shows an ongoing action at present. Professional writers also use this verb tense to express habitual action.
We form the present continuous tense using an auxiliary verb in the present tense is/are/am + –ing verb form. For example:
- The previous researchers from Purdue University who wrote thermodynamics are now writing a paper about aerodynamics.
- The lady in red is looking for her shoes.
To understand this verb tense better, we must know the difference between continuous, non-continuous, and mixed verbs. Remember that non-continuous verbs or stative verbs like remember, hate, guess, and seem do not use the present continuous tense. For example:
- Incorrect: I am hating this movie.
Correct: I hate this movie.
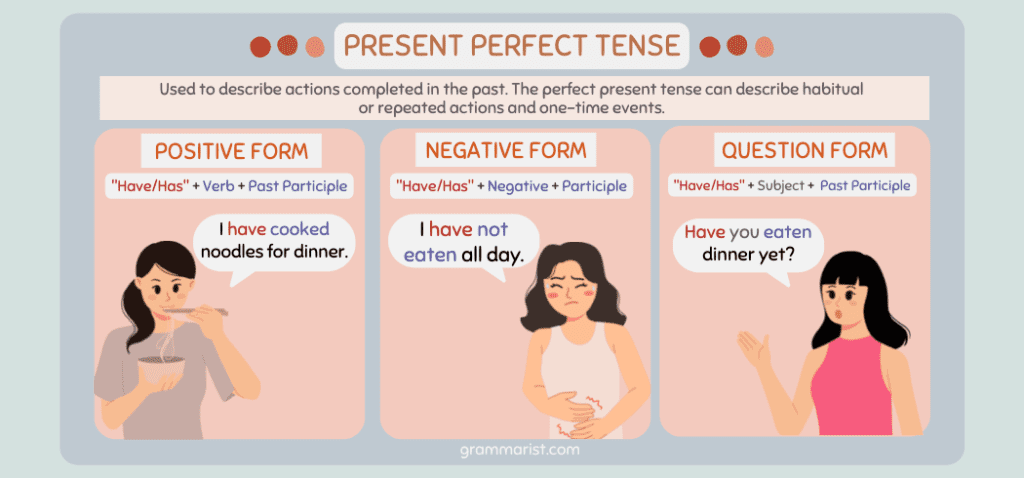
Present Perfect
The perfect verb tenses show actions with complex time relationships. They are either complete, perfected, or finished.
The standard present perfect tense is one of the perfect tenses that shows past actions that continue or are related to the present. They may also show actions recently finished or completed in the past at an indefinite time.
We form it using the popular auxiliary verb, has or have, and the past participle verb form. For example:
- They have come a long way.
- She has come a long way.
Present Perfect Continuous
The present perfect continuous tense shows actions that started in the past and are continuing in the present. This verb tense follows the formula has/have been + present participle of the verb. For example:
- Arnold has been playing the piano recently.
- We haven’t been feeling well lately.
Simple Past
This tense is one of the English verb tenses that show past actions, whether it’s a specific or nonspecific time. They are sometimes formed by adding -d or -ed to the base verb. For example:
- She started the book yesterday.
Some verbs in the simple past form are irregular. An Irregular verb is one of the types of verbs that do not follow the typical simple past and past participle form of verbs. For example:
- We bought new curtains yesterday.
Past Perfect
The perfect aspect of verbs shows perfected or completed action at a specific time.
The past perfect tense is one of the major verb tenses that discuss actions completed before a specific event in the past. Past perfect tense forms require a verbal phrase that includes had and the past participle of the verb. For example:
- Many universities had strengthened their liberal arts programs when the economy declined.
Past Continuous
The past continuous tense shows a continuing action happening at a specific point in the past. We form it by using was/were + -ing form of the verb. For example:
- We were clapping until he tripped on the stage.
- My mom was baking cookies when my friend knocked.
Past Perfect Continuous
The past perfect continuous expresses an action initiated in the past and continued until later in the past. We form it using had been and the present participle form of the verb. For example:
- He had been cooking steak when his wife walked in the kitchen.
Simple Future
The future tense verbs express actions in future events or the future state of being of something.
We form the simple future tense through the verb phrase will plus the root verb. Will is a helping verb that assists the main verb to show the future time, whether it’s a determinate or indeterminate time. It’s one of the modal verbs aside from shall, would, can, etc.
Some examples include will write, will look, will wash, and will buy. Below are some sentence examples that show future action.
- The researcher will submit his paper to the University of Michigan Press tomorrow afternoon.
- She will walk to work tomorrow.
Future Continuous
The future continuous or progressive tense describes an event that is ongoing in the future. Such action is expected to continue over a period of time. Therefore, it’s a future continuous action.
We form a future continuous verb by using will be plus the –ing form of the verb. For example:
- I will be going to the library while you do your homework.
- She will be having piano lessons tomorrow.
Future Perfect
The future perfect tense is for actions that will be finished before another event in the future. This is formed by using the words will + have + past participle of the verb. For example:
- Before school begins in the Fall, they will have gained enough motivation to decide which university they want to attend.
- Mar will have left before you arrive.
Future Perfect Continuous
The future perfect continuous describes an action that will continue in the future. The correct formula is will have been + present participle form of the verb. For example:
- I will have been writing a new book for ten months in Fall.
What are Present Perfect Infinitives?
Infinitives are usually expressed in simple tenses, but they also have perfect tense forms. They occur when the infinitive has the word have before it. Some verbs, such as plan and expect, lead to issues when these future verbs are used with infinitives.
In the sentences below, the actions are expressed in the past. Therefore, they use the simple past verb forms.
- I intended to listen to the new song.
- Ian meant to visit his adviser.
Verb Tenses vs. Time Reference
Verb tenses refer to the grammatical structure of the verb. Meanwhile, the time reference is when the action takes place. Some verb tenses can show a single time reference. Sometimes, different time references use one verb tense.
Can the Verb Tenses Be Expressed in Different Forms?
You can show verb tenses in active and passive verb forms. Negative, affirmative, and interrogative forms also exist in different verb tenses.
What’s the Most Used Verb Tense in English?
The most common verb tenses are simple tenses, especially the simple present and simple past. The present perfect tense is also common in the English language. You’ll find these tenses in both creative and academic writing.
It’s also essential to differentiate between the tenses and mood of verbs. Verbs have three moods: imperative, subjunctive, and indicative.
Verb Tenses Summary
The different verb tenses show any action or condition’s location in time. They include the past, future, and present tenses.
Use different verb tenses to clarify several time periods. Make sure to observe consistency and accuracy in these tenses for verb usage.
Verb tenses can be confusing! So, we’ve created this guide to help you learn the 12 basic types of verb tenses in English, their grammatical structure, and how we use them. Scroll down for paperless worksheets designed for shaping the digital classroom.
What Are The 12 Verb Tenses In English?
Tenses are vital in English for constructing sentences and phrases. There are 12 basic tenses in English, which help us figure out how an action (verb) relates to time.
English tenses are split into three broad time-related categories.
- Past
- Present
- Future
Tenses can be broken down even further. Tap on the links below and see further information about each type of verb tense.
- Present: Simple Present Tense, Present Continuous, Present Perfect, and Present Perfect Continuous.
- Past: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect Tense, and Past Perfect Continuous.
- Future: Future Simple, Future Continuous Tense, Future Perfect, and Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
Types of Tenses in English
Flip the flashcards to get a simple definition of each type of verb tense in English.
Present Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
Learning about the different present tense forms in English is important. Present tenses can be in the simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous. Read about them and then scroll down to take the present tense forms quiz. Here we have focused on the different types of present tenses in the affirmative. For a more in-depth study of each type of present tense, click the links below.
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Present Simple Tense
The simple present tense refers to an action (verb) that occurs in the present— the simple present tense deals with facts and repeated activities.
We use English personal pronouns followed by present tense verbs to form the simple present tense with regular verbs. Note: Singular third-person verbs often change, and an -s is placed at the end of the verb.
- She plays the piano.
- Sarah loves burgers.
- She speaks Spanish.
- Do you speak Spanish?
Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense or present progressive tense refers to an action or state of being. They deal with temporary actions or states and things that are happening now.
In the affirmative, we form the present continuous tense with the subject + am/ is/ are + verb-ing for regular verbs.
- I am working on the report.
- You are playing in the yard.
- What are you doing? I’m eating my dinner.
- My parents are traveling.
Present Perfect Tense
Next up is the present perfect tense! We use it to talk about present experiences that relate to the past. They can refer to present situations that will continue or new information.
In the affirmative, we form the present perfect tense with the subject + have/ has + past participle verb. To form a past participle with regular verbs, we usually add -ed as a suffix.
- The euro has decreased in value lately.
- I haven’t seen her since February.
- I haven’t played football for ages.
- She has forgotten to switch off the light again!
- Have you been to China?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous is an exciting type of tense in English. It refers to a non-specific time that began in the near past but is usually unfinished.
To form this tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + have/has + been + verb-ing.
- I have been living in France since 2018.
- He has been playing football since he was five.
- Our teacher has been talking for too long.
Present Tenses Quiz
Are you a present-tense expert? This present tense paperless worksheet will test your knowledge. Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of present tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
I have ______ living in France since 2018.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She _____ piano.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
___ you been to China?
Choose the best answer from the choices below
Past Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
The past tense generally functions to place an action or situation in the past. They are the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous. Here are some examples suitable for ESL and Grades 3-6 learners. We have focused solely on the past tense in the affirmative. For more examples in interrogative and negative, click on each type of tense below.
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
Past Simple Tense
The past simple tense or preterite refers to a completed action before now.
To form the past simple tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + verb + -ed for regular verbs. For irregular verbs like «sing,» you have to learn the past participle.
- They played soccer.
- She sang songs at our Christmas concert.
Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense or past progressive refers to an action that is ongoing or continues. It is often used to describe something that happened in the past.
To form the past continuous English tense, add the subject + was/were + verb-ing. This is for affirmative sentences, for negative, and for interrogative check out our past continuous page.
- I was making lunch when they arrived.
- I was singing when the doorbell rang.
- She was laughing when she fell over.
Past Perfect Tense
We refer to the past perfect tense when discussing an action completed at a particular time in the past.
To form the past perfect tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + had + past participle + object. Sometimes adverbs are used to give even more information, like ‘just.’
- He had just broken up with her.
- If only I had known how to solve the equation.
- She had almost finished.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
We use the past perfect continuous tense to talk about actions or events that began before a specific time in the past and were ongoing up to that time. It can also be used to describe the cause of a past event.
To form the past perfect continuous tense in the affirmative, we use the subject + had + been + verb-ing
- She had been studying when her mom called her.
- They had been traveling when the doctor called them.
- He was tired because he had been running.
Past Tenses Quiz
Want to test your knowledge of the different past tenses? Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of past tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She had been ______ when her mom called her.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She ____ almost finished.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
She _____ laughing when she fell over.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
Future Tense Forms With Examples and Quiz
A future tense expresses an action that hasn’t happened yet, but might in the future. Here we will talk about future tenses in the affirmative. If you want to learn more about future tenses in the interrogative or negative, check out the future tense guides using the links below.
- Future Simple
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
Future Simple Tense
The future simple tense is one of 5 future tenses. We used it to talk about events that haven’t come about yet.
We use the subject + will / shall + the base verb
- This year, we will go to Disneyland.
- We will come.
- I will go to Japan.
You can also form this tense with «going to,» but this is for more informal language.
Future Continuous Tense
We use the future continuous tense or future progressive when discussing an action that will start in the future and continue for a specific amount of time.
To form the future continuous tense, we use will + be + the present participle of the verb + ing as the suffix.
- We will be buying a house next year.
- We will be going to college.
- They will be starting school next year.
We use the future continuous tense with action verbs and a few stative verbs.
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used when discussing something that will be finished by a specific time in the future. We add expressions of time to help the sentence.
To form the future perfect in the affirmative, we use the subject + will / shall + have + past participle.
- By the year 2050, we will have tackled climate change.
- He will have completed his homework by next week.
- By next year, she will have graduated.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense or future progressive is used to talk about an action or event that will continue up to a specific time in the future. Think of it like projecting yourself to some time in the future.
To form this tense, we use the subject + will / shall + have + been + verb-ing. You can also add an expression of time.
- In January, I will have been studying for 10 years.
- I will have been living in my parent’s house for eighteen years by the time I graduate.
Future Tenses Quiz
Taken it all in? Try our future tenses quiz. Just fill in the sentences with the correct words using the correct form of future tense. Got a question wrong? Press reset and try again.
What is the correct future tense for the sentence?
By next year she ____ have graduated.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
We will be _____ to college.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
What is the correct tense for the sentence?
I _____ to Japan.
Choose the best answer from the choices below
See? Studying the tenses in English doesn’t have to be a headache. To explore more on these topics in detail, click on ELA-related content suitable for grades 4-6+ and ESL learners. We’ve got flashcards, quizzes, and much more to bring inspiration to homeschooling, online tutoring, and for students and your classrooms.
Main Verb Tenses Takeaways:
- Verb tenses indicate whether an event is from the past, present, or future.
- There are 12verb tenses in the English language.
- Auxiliary words follow most verb tenses.
Verb tenses clarify whether an event is from the past, present, or future. They give your audience a better understanding of when something happened. This guide will teach you about each type. Also, we’ve got some nifty formulas and a chart that you can use for future reference.
How Do You Identify a Verb in English?
Before we dive into verb tenses, let us first understand what a verb is and how you can identify it in a sentence. A verb is commonly defined as any word that shows action or a state of being. But is this the most helpful definition of a verb? Consider the example sentence below:
Can you spot the action words in the sentence? You may say it’s “making” and “boost,” but are they verbs? Unfortunately, the verb in this sentence is not an action word, nor is it a state of being.
So, how can you identify the verb in a sentence? In order to do so, you need the working definition of a verb. Verbs tell the time of the sentence, and we refer to them as tenses.
For you to quickly find a verb, use some time words (past or future) like “last week” or “tomorrow.” Then, place your time word in front of your sentence and see which word changes. Let’s use our previous sentence:
The sentence doesn’t sound or look right. As you may have noticed, we need to change “seems” into “seemed.” In this case, “seems” is the verb we’re looking for because it indicates the sentence’s time.
Now that you know this simple trick let’s discuss what verb tenses are.
What are the English Verb Tenses?
In the English language, verb tenses express when an event occurs. We also use verb tenses to convey events from the past, present, or future. These verb tenses typically follow auxiliary words.
An auxiliary word is a helping word, often a verb, that enhances the underlying meaning of a clause’s main verb. Auxiliaries provide information about a verb’s tense. They can also express details about a mood, number, or person. Can, may, must, and will are examples of auxiliary words.
How Do You Use Verb Tenses?
Use verb tenses when you want to show when something has or will happen. Before choosing a tense, consider these tips:
- Know the correct way to express your verb in different tenses, such as adding -ed to a word.
- Also, avoid shifting tenses and remain consistent with verb tense usage.
- Pick the correct auxiliary words, such as will or have.
What are the 12 Tenses of the Verb?
There are 12 verb tenses in the English language:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Future Simple
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
When paired with an auxiliary word, these tenses provide information about the primary verbs in your sentences.
Present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous are tenses that express actions happening right now. Present simple indicates an action that occurs regularly, such as a daily commute to work.
Past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous show actions that happened previously.
Meanwhile, future simple, future perfect, future continuous, and future perfect continuoustenses indicate an action that has not happened yet.
What is the Formula for All Tenses?
Most verb tenses follow a specific formula based on the tense you choose. Keep our handy guide bookmarked until you can easily identify or remember the formulas for verb tenses.
Note the verb form in parentheses in these formulas:
- V1 is the base form of the verb (clean, shop, begin)
- V2 is the past simple form of the verb (cleaned, shopped, began)
- V3 is the past participle form of the verb (cleaned, shopped, begun)
| Verb Tense | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Subject + Verb (v1) + s/es | I play music nearly every day. |
| Past Simple | Subject + Verb (v2) or irregular verb | Yesterday, I playedan entire album. |
| Future Simple | Subject + will/shall + verb (v1) | I will play as many albums as I can this month. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + is/am/are + Verb(+ing) | I am playing The Offspring right now. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + Verb(+ing) | I was playing Marshmello and Halsey last night. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be/shall be + verb(+ing) | I will be playing My Chemical Romance after I download my favorite album. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + Has/have + Verb (v3) | I have played so many songs I can’t keep track. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + Verb (v3) | I had played at least 100 albums by the time I was 10. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will have + verb(v3) | I will have played at least 1,000 songs by the time this year ends. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + Has/have + been + Verb(+ing) | I have been playing music since I was a toddler. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had + been + Verb(+ing) | I had been playing for at least a year before my parents bought me my own iPod. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb(+ing) | I will have been playing songs for at least 3 hours before practice tonight. |

PRESENT TENSE
1. Simple Present Tense
Structure: Subject + Verb (v1) + es/es
2. Present Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + is/am/are + Verb(+ing)
3. Present Perfect Tense
Structure: Subject + Has/have + Verb (v3)
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + Has/have + been + Verb(+ing)
PAST TENSE
5. Simple Past Tense
Structure: Subject + Verb (v2) or irregular verb
6. Past Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + was/were + Verb(+ing)
7. Past Perfect Tense
Structure: Subject + had + Verb (v3)
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + had + been + Verb(+ing)
FUTURE TENSE
9. Simple Future Tense
Structure: Subject+ will/shall+ verb(v1)
10. Future Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + will be/shall be + verb(+ing)
11. Future Perfect Tense
Structure: Subject + will have + verb(v3)
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + will have been + verb(+ing)
Follow these guidelines and formulas, and you’ll never go wrong with your tenses again.
Examples of Common Regular Verbs
Present
abandon
act
abhor
beg
behave
compare
copy
disagree
dry
enjoy
entice
flow
follow
grab
guess
hug
hunt
identify
idolize
jag
jump
kick
knock
laugh
launch
magnify
mark
narrate
need
obey
oblige
order
pacify
pack
paint
sail
slow
tame
turn
use
usher
vacate
vaccinate
wait
walk
yank
yawn
yield
zip
zone
Past
abandoned
acted
abhorred
begged
behaved
compared
copied
disagreed
dried
enjoyed
enticed
flowed
followed
grabbed
guessed
hugged
hunted
identified
idolized
jagged
jumped
kicked
knocked
laughed
launched
magnified
marked
narrated
needed
obeyed
obliged
ordered
pacified
packed
painted
sailed
slowed
tamed
turned
used
ushered
vacated
vaccinated
waited
walked
yanked
yawned
yielded
zipped
zoned
Future
will / shall abandon
will / shall act
will / shall abhor
will / shall beg
will / shall behave
will / shall compare
will / shall copy
will / shall disagree
will / shall dry
will / shall enjoy
will / shall entice
will / shall flow
will / shall follow
will / shall grab
will / shall guess
will / shall hug
will / shall hunt
will / shall identify
will / shall idolize
will / shall jag
will / shall jump
will / shall kick
will / shall knock
will / shall laugh
will / shall launch
will / shall magnify
will / shall mark
will / shall narrate
will / shall need
will / shall obey
will / shall oblige
will / shall order
will / shall pacify
will / shall pack
will / shall paint
will / shall sail
will / shall slow
will / shall tame
will / shall turn
will / shall use
will / shall usher
will / shall vacate
will / shall vaccinate
will / shall wait
will / shall walk
will / shall yank
will / shall yawn
will / shall yield
will / shall zip
will / shall zone
Present Perfect
has/have abandoned
has/have acted
has/have abhorred
has/have begged
has/have behaved
has/have compared
has/have copied
has/have disagreed
has/have dried
has/have enjoyed
has/have enticed
has/have flowed
has/have followed
has/have grabbed
has/have guessed
has/have hugged
has/have hunted
has/have identified
has/have idolized
has/have jagged
has/have jumped
has/have kicked
has/have knocked
has/have laughed
has/have launched
has/have magnified
has/have marked
has/have narrated
has/have needed
has/have obeyed
has/have obliged
has/have ordered
has/have pacified
has/have packed
has/have painted
has/have sailed
has/have slowed
has/have tamed
has/have turned
has/have used
has/have ushered
has/have vacated
has/have vaccinated
has/have waited
has/have walked
has/have yanked
has/have yawned
has/have yielded
has/have zipped
has/have zoned
Past Perfect
had abandoned
had acted
had abhorred
had begged
had behaved
had compared
had copied
had disagreed
had dried
had enjoyed
had enticed
had flowed
had followed
had grabbed
had guessed
had hugged
had hunted
had identified
had idolized
had jagged
had jumped
had kicked
had knocked
had laughed
had launched
had magnified
had marked
had narrated
had needed
had obeyed
had obliged
had ordered
had pacified
had packed
had painted
had sailed
had slowed
had tamed
had turned
had used
had ushered
had vacated
had vaccinated
had waited
had walked
had yanked
had yawned
had yielded
had zipped
had zoned
Future Perfect
will have abandoned
will have acted
will have abhorred
will have begged
will have behaved
will have compared
will have copied
will have disagreed
will have dried
will have enjoyed
will have enticed
will have flowed
will have followed
will have grabbed
will have guessed
will have hugged
will have hunted
will have identified
will have idolized
will have jagged
will have jumped
will have kicked
will have knocked
will have laughed
will have launched
will have magnified
will have marked
will have narrated
will have needed
will have obeyed
will have obliged
will have ordered
will have pacified
will have packed
will have painted
will have sailed
will have slowed
will have tamed
will have turned
will have used
will have ushered
will have vacated
will have vaccinated
will have waited
will have walked
will have yanked
will have yawned
will have yielded
will have zipped
will have zoned
Present Continuous
is/are/am abandoning
is/are/am acting
is/are/am abhoring
is/are/am begging
is/are/am behaving
is/are/am comparing
is/are/am copying
is/are/am disagreeing
is/are/am drying
is/are/am enjoying
is/are/am enticing
is/are/am flowing
is/are/am following
is/are/am grabbing
is/are/am guessing
is/are/am hugging
is/are/am hunting
is/are/am identifying
is/are/am idolizing
is/are/am jagging
is/are/am jumping
is/are/am kicking
is/are/am knocking
is/are/am laughing
is/are/am launching
is/are/am magnifying
is/are/am marking
is/are/am narrating
is/are/am needing
is/are/am obeying
is/are/am obliging
is/are/am ordering
is/are/am pacifying
is/are/am packing
is/are/am painting
is/are/am sailing
is/are/am slowing
is/are/am taming
is/are/am turning
is/are/am using
is/are/am ushering
is/are/am vacating
is/are/am vaccinating
is/are/am waiting
is/are/am walking
is/are/am yanking
is/are/am yawning
is/are/am yielding
is/are/am zipping
is/are/am zoning
Past Continuous
was/were abandoning
was/were acting
was/were abhoring
was/were begging
was/were behaving
was/were comparing
was/were copying
was/were disagreeing
was/were drying
was/were enjoying
was/were enticing
was/were flowing
was/were following
was/were grabbing
was/were guessing
was/were hugging
was/were hunting
was/were identifying
was/were idolizing
was/were jagging
was/were jumping
was/were kicking
was/were knocking
was/were laughing
was/were launching
was/were magnifying
was/were marking
was/were narrating
was/were needing
was/were obeying
was/were obliging
was/were ordering
was/were pacifying
was/were packing
was/were painting
was/were sailing
was/were slowing
was/were taming
was/were turning
was/were using
was/were ushering
was/were vacating
was/were vaccinating
was/were waiting
was/were walking
was/were yanking
was/were yawning
was/were yielding
was/were zipping
was/were zoning
Future Continuous
will be/shall be abandoning
will be/shall be acting
will be/shall be abhoring
will be/shall be begging
will be/shall be behaving
will be/shall be comparing
will be/shall be copying
will be/shall be disagreeing
will be/shall be drying
will be/shall be enjoying
will be/shall be enticing
will be/shall be flowing
will be/shall be following
will be/shall be grabbing
will be/shall be guessing
will be/shall be hugging
will be/shall be hunting
will be/shall be identifying
will be/shall be idolizing
will be/shall be jagging
will be/shall be jumping
will be/shall be kicking
will be/shall be knocking
will be/shall be laughing
will be/shall be launching
will be/shall be magnifying
will be/shall be marking
will be/shall be narrating
will be/shall be needing
will be/shall be obeying
will be/shall be obliging
will be/shall be ordering
will be/shall be pacifying
will be/shall be packing
will be/shall be painting
will be/shall be sailing
will be/shall be slowing
will be/shall be taming
will be/shall be turning
will be/shall be using
will be/shall be ushering
will be/shall be vacating
will be/shall be vaccinating
will be/shall be waiting
will be/shall be walking
will be/shall be yanking
will be/shall be yawning
will be/shall be yielding
will be/shall be zipping
will be/shall be zoning
Present Perfect Continuous
has/have been abandoning
has/have been acting
has/have been abhoring
has/have been begging
has/have been behaving
has/have been comparing
has/have been copying
has/have been disagreeing
has/have been drying
has/have been enjoying
has/have been enticing
has/have been flowing
has/have been following
has/have been grabbing
has/have been guessing
has/have been hugging
has/have been hunting
has/have been identifying
has/have been idolizing
has/have been jagging
has/have been jumping
has/have been kicking
has/have been knocking
has/have been laughing
has/have been launching
has/have been magnifying
has/have been marking
has/have been narrating
has/have been needing
has/have been obeying
has/have been obliging
has/have been ordering
has/have been pacifying
has/have been packing
has/have been painting
has/have been sailing
has/have been slowing
has/have been taming
has/have been turning
has/have been using
has/have been ushering
has/have been vacating
has/have been vaccinating
has/have been waiting
has/have been walking
has/have been yanking
has/have been yawning
has/have been yielding
has/have been zipping
has/have been zoning
Past Perfect Continuous
had been abandoning
had been acting
had been abhoring
had been begging
had been behaving
had been comparing
had been copying
had been disagreeing
had been drying
had been enjoying
had been enticing
had been flowing
had been following
had been grabbing
had been guessing
had been hugging
had been hunting
had been identifying
had been idolizing
had been jagging
had been jumping
had been kicking
had been knocking
had been laughing
had been launching
had been magnifying
had been marking
had been narrating
had been needing
had been obeying
had been obliging
had been ordering
had been pacifying
had been packing
had been painting
had been sailing
had been slowing
had been taming
had been turning
had been using
had been ushering
had been vacating
had been vaccinating
had been waiting
had been walking
had been yanking
had been yawning
had been yielding
had been zipping
had been zoning
Future Perfect Continuous
will have been abandoning
will have been acting
will have been abhoring
will have been begging
will have been behaving
will have been comparing
will have been copying
will have been disagreeing
will have been drying
will have been enjoying
will have been enticing
will have been flowing
will have been following
will have been grabbing
will have been guessing
will have been hugging
will have been hunting
will have been identifying
will have been idolizing
will have been jagging
will have been jumping
will have been kicking
will have been knocking
will have been laughing
will have been launching
will have been magnifying
will have been marking
will have been narrating
will have been needing
will have been obeying
will have been obliging
will have been ordering
will have been pacifying
will have been packing
will have been painting
will have been sailing
will have been slowing
will have been taming
will have been turning
will have been using
will have been ushering
will have been vacating
will have been vaccinating
will have been waiting
will have been walking
will have been yanking
will have been yawning
will have been yielding
will have been zipping
will have been zoning
Examples of Common Irregular Verbs
Present
arise
bear
beat
beget
begin
choose
cling
cost
cut
do
draw
drink
drive
eat
fall
feed
fight
fling
fly
get
give
go
grow
hang
hide
hold
keep
know
lay
lead
lie
light
make
mean
pay
prove
quit
read
ride
say
see
shrink
sleep
take
teach
wake
wear
weep
Past
arose
bore
beat
begot
began
chose
clung
cost
cut
did
drew
drank
drove
ate
fell
fed
fought
flung
flew
got
gave
went
grew
hung
hid
held
kept
knew
laid
led
lay
lit
made
meant
paid
proved
quit
read
rode
said
saw
shrank
slept
took
taught
woke
wore
wept
Future
will / shall arise
will / shall bear
will / shall beat
will / shall beget
will / shall begin
will / shall choose
will / shall cling
will / shall cost
will / shall cut
will / shall do
will / shall draw
will / shall drink
will / shall drive
will / shall eat
will / shall fall
will / shall feed
will / shall fight
will / shall fling
will / shall fly
will / shall get
will / shall give
will / shall go
will / shall grow
will / shall hang
will / shall hide
will / shall hold
will / shall keep
will / shall know
will / shall lay
will / shall lead
will / shall lie
will / shall light
will / shall make
will / shall mean
will / shall pay
will / shall prove
will / shall quit
will / shall read
will / shall ride
will / shall say
will / shall see
will / shall shrink
will / shall sleep
will / shall take
will / shall teach
will / shall wake
will / shall wear
will / shall weep
Present Perfect
has / have arisen
has / have born
has / have beaten
has / have begotten
has / have begun
has / have chosen
has / have clung
has / have cost
has / have cut
has / have done
has / have drawn
has / have drunk
has / have driven
has / have eaten
has / have fallen
has / have fed
has / have fought
has / have flung
has / have flown
has / have gotten
has / have given
has / have gone
has / have grown
has / have hung
has / have hidden
has / have held
has / have kept
has / have known
has / have laid
has / have led
has / have lain
has / have lit
has / have made
has / have meant
has / have paid
has / have proven
has / have quit
has / have read
has / have ridden
has / have said
has / have seen
has / have shrunk
has / have slept
has / have taken
has / have taught
has / have woken
has / have worn
has / have wept
Past Perfect
had arisen
had born
had beaten
had begotten
had begun
had chosen
had clung
had cost
had cut
had done
had drawn
had drunk
had driven
had eaten
had fallen
had fed
had fought
had flung
had flown
had gotten
had given
had gone
had grown
had hung
had hidden
had held
had kept
had known
had laid
had led
had lain
had lit
had made
had meant
had paid
had proven
had quit
had read
had ridden
had said
had seen
had shrunk
had slept
had taken
had taught
had woken
had worn
had wept
Future Perfect
will have arisen
will have born
will have beaten
will have begotten
will have begun
will have chosen
will have clung
will have cost
will have cut
will have done
will have drawn
will have drunk
will have driven
will have eaten
will have fallen
will have fed
will have fought
will have flung
will have flown
will have gotten
will have given
will have gone
will have grown
will have hung
will have hidden
will have held
will have kept
will have known
will have laid
will have led
will have lain
will have lit
will have made
will have meant
will have paid
will have proven
will have quit
will have read
will have ridden
will have said
will have seen
will have shrunk
will have slept
will have taken
will have taught
will have woken
will have worn
will have wept
Present Continuous
is / are / am arising
is / are / am bearing
is / are / am beating
is / are / am begetting
is / are / am beginning
is / are / am choosing
is / are / am clinging
is / are / am costing
is / are / am cutting
is / are / am doing
is / are / am drawing
is / are / am drinking
is / are / am driving
is / are / am eating
is / are / am falling
is / are / am feeding
is / are / am fighting
is / are / am flinging
is / are / am flying
is / are / am getting
is / are / am giving
is / are / am going
is / are / am growing
is / are / am hanging
is / are / am hiding
is / are / am holding
is / are / am keeping
is / are / am knowing
is / are / am laying
is / are / am leading
is / are / am lying
is / are / am lighting
is / are / am making
is / are / am meaning
is / are / am paying
is / are / am proving
is / are / am quitting
is / are / am reading
is / are / am riding
is / are / am saying
is / are / am seeing
is / are / am shrinking
is / are / am sleeping
is / are / am taking
is / are / am teaching
is / are / am waking
is / are / am wearing
is / are / am weeping
Past Continuous
was / were arising
was / were bearing
was / were beating
was / were begetting
was / were beginning
was / were choosing
was / were clinging
was / were costing
was / were cutting
was / were doing
was / were drawing
was / were drinking
was / were driving
was / were eating
was / were falling
was / were feeding
was / were fighting
was / were flinging
was / were flying
was / were getting
was / were giving
was / were going
was / were growing
was / were hanging
was / were hiding
was / were holding
was / were keeping
was / were knowing
was / were laying
was / were leading
was / were lying
was / were lighting
was / were making
was / were meaning
was / were paying
was / were proving
was / were quitting
was / were reading
was / were riding
was / were saying
was / were seeing
was / were shrinking
was / were sleeping
was / were taking
was / were teaching
was / were waking
was / were wearing
was / were weeping
Future Continuous
will be/shall be arising
will be/shall be bearing
will be/shall be beating
will be/shall be begetting
will be/shall be beginning
will be/shall be choosing
will be/shall be clinging
will be/shall be costing
will be/shall be cutting
will be/shall be doing
will be/shall be drawing
will be/shall be drinking
will be/shall be driving
will be/shall be eating
will be/shall be falling
will be/shall be feeding
will be/shall be fighting
will be/shall be flinging
will be/shall be flying
will be/shall be getting
will be/shall be giving
will be/shall be going
will be/shall be growing
will be/shall be hanging
will be/shall be hiding
will be/shall be holding
will be/shall be keeping
will be/shall be knowing
will be/shall be laying
will be/shall be leading
will be/shall be lying
will be/shall be lighting
will be/shall be making
will be/shall be meaning
will be/shall be paying
will be/shall be proving
will be/shall be quitting
will be/shall be reading
will be/shall be riding
will be/shall be saying
will be/shall be seeing
will be/shall be shrinking
will be/shall be sleeping
will be/shall be taking
will be/shall be teaching
will be/shall be waking
will be/shall be wearing
will be/shall be weeping
Present Perfect Continuous
has/have been arising
has/have been bearing
has/have been beating
has/have been begetting
has/have been beginning
has/have been choosing
has/have been clinging
has/have been costing
has/have been cutting
has/have been doing
has/have been drawing
has/have been drinking
has/have been driving
has/have been eating
has/have been falling
has/have been feeding
has/have been fighting
has/have been flinging
has/have been flying
has/have been getting
has/have been giving
has/have been going
has/have been growing
has/have been hanging
has/have been hiding
has/have been holding
has/have been keeping
has/have been knowing
has/have been laying
has/have been leading
has/have been lying
has/have been lighting
has/have been making
has/have been meaning
has/have been paying
has/have been proving
has/have been quitting
has/have been reading
has/have been riding
has/have been saying
has/have been seeing
has/have been shrinking
has/have been sleeping
has/have been taking
has/have been teaching
has/have been waking
has/have been wearing
has/have been weeping
Past Perfect Continuous
had been arising
had been bearing
had been beating
had been begetting
had been beginning
had been choosing
had been clinging
had been costing
had been cutting
had been doing
had been drawing
had been drinking
had been driving
had been eating
had been falling
had been feeding
had been fighting
had been flinging
had been flying
had been getting
had been giving
had been going
had been growing
had been hanging
had been hiding
had been holding
had been keeping
had been knowing
had been laying
had been leading
had been lying
had been lighting
had been making
had been meaning
had been paying
had been proving
had been quitting
had been reading
had been riding
had been saying
had been seeing
had been shrinking
had been sleeping
had been taking
had been teaching
had been waking
had been wearing
had been weeping
Future Perfect Continuous
will have been arising
will have been bearing
will have been beating
will have been begetting
will have been beginning
will have been choosing
will have been clinging
will have been costing
will have been cutting
will have been doing
will have been drawing
will have been drinking
will have been driving
will have been eating
will have been falling
will have been feeding
will have been fighting
will have been flinging
will have been flying
will have been getting
will have been giving
will have been going
will have been growing
will have been hanging
will have been hiding
will have been holding
will have been keeping
will have been knowing
will have been laying
will have been leading
will have been lying
will have been lighting
will have been making
will have been meaning
will have been paying
will have been proving
will have been quitting
will have been reading
will have been riding
will have been saying
will have been seeing
will have been shrinking
will have been sleeping
will have been taking
will have been teaching
will have been waking
will have been wearing
will have been weeping
How Well do you Know the Verb Tenses now?
Verb Tenses Question #1
Please select 2 correct answers
A. Verb tenses express when an event occurs.
B. Verb tenses can convey events from the past only.
C. Verb tenses can convey events from the past, present, and future.
Correct!
Wrong!
The answers are A and C. Verb tenses express when an event occurs and can convey whether an event is from the past, present, or future.
Verbs Question #2
A. Helping
B. Action
C. Linking
D. Past tense
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is A. Helping verbs enhance the underlying meaning of a sentence’s main verb.
Tenses of Verb Question #3
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is FALSE. There are 12 verb tenses in the English Language.
Verb Tense Question #4
A. Future perfect tense
B. Future perfect continuous tense
C. Present simple tense
D. Future simple tense
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. Present simple tense can indicate an event that occurs regularly.
Present Perfect Question #5
A. What do you want to eat?
B. Have you eaten yet?
C. Did you eat before you arrived?
D. He ate already.
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is B. The formula for present perfect tense is has/have + the past participle form of the verb.
Tenses Question #6
A. Future perfect tense
B. Future perfect continuous tense
C. Present simple tense
D. Future simple tense
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. Present simple tense can indicate an event that occurs regularly.
Read More: How To Use The Past Perfect Tense Of A Verb In A Sentence
Tense is the fundamental pillar of English grammar. It’s very important to learn all types of tenses as far as English grammar is concerned. We can indicate the time of action by using a tense. Let us see what the definition of tense in English is.
What is Tense in English Grammar?
The term ‘tense‘ has been taken from the Latin word ‘Tempus,’ which indicates the action time. Now we can say tense is a word that describes the time of a verb. For example:
- I bought a book.
- He reads a novel.
- She will meet with her friends.
Note: All these three sentences refer to the time of action.
Types of Tense
There are three types of tenses in English grammar. They are:
- Past Tense
- Present Tense
- Future Tense
All these three types of tenses have four sub-types. They are:
- Indefinite
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Past Indefinite Tense (simple past)
Past Indefinite Tense is usually used to indicate the completed action in the past or a past habit. For example:
- She described her story.
- I saw this person yesterday.
- He did his job quite easily.
- Mr. George made his statement last week.
- Mrs. Florida participated in the competition last month.
Let us see the different forms of Past Indefinite Tense in English grammar:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I wrote a paragraph. | Did I write a paragraph? | I didn’t write a paragraph. |
| He watched a live cricket match. | Did he watch a live cricket match? | He didn’t watch a live cricket match. |
| You made this mistake. | Did you make this mistake? | You didn’t make this mistake. |
| She found her English lessons. | Did she find her English lessons? | She didn’t find her English lessons. |
| They enjoyed the party. | Did they enjoy the party? | They didn’t enjoy the party. |
Note: Past Indefinite Tense takes ‘did’ as a helping verb before the subject of an interrogative sentence and ‘didn’t after the subject of the negative form of a sentence and the main verb remains unchanged.
Structure: Subject+Verb(past form)+Object
Past Continuous Tense
Past Continuous Tense usually indicates the activity in the past, which was continued for some time. For example:
- I was running in the field.
- He was going to his campus.
- She was holding the mirror.
- They were making a profit from the business.
- Mr. Collin was running the industry.
Let us see the different forms of Past Continuous Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I was playing cards. | Was I playing cards? | I was not playing cards. |
| He was watching the beautiful scenario. | Was he watching the beautiful scenario? | He was not watching the beautiful scenario. |
| She was working as a nurse. | Was she working as a nurse? | She was not working as a nurse. |
| They were looking for a suitable partner. | Were they looking for a suitable partner? | They were not looking for a suitable partner. |
| Mr. Floyd was demanding equal rights. | Was Mr. Floyd demanding equal rights? | Mr. Floyd was not demanding equal rights. |
Note: Past Continuous Tense takes ‘was’ and ‘were’ as helping verbs. ‘Was’ is placed in case of first-person and third-person on the other hand ‘were’ is placed in case of the second person.
Structure: Subject+was/were+Verb(+ing)+Object
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Tense is placed between the two past actions which occurred before, and the later action is called Simple Past or Past Indefinite. For example:
- Selim had left before I came.
- Lina had gone from the program before we attended.
- He had bought some clothes before the shop closed.
- She had cooked good food before the guests came.
- They had played badminton before they took their dinner.
Let us see the different forms of Past Perfect Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I had gone into the market. | Had I gone in the market? | I had not gone to the market. |
| He had met with his teachers. | Had he met with his teachers? | He had not met his teachers. |
| They had planned to make new ideas. | Had they planned to make new ideas? | They had not planned to make new ideas. |
| Mr. Zamal had made a new operating system | Had Mr. Zamal made a new operating system? | Mr. Zamal had not made a new operating system. |
| Mrs. Zarin had got a prize. | Had Mrs. Zarin got a prize? | Mrs. Zarin had not got a prize. |
Note: Past Perfect Tense takes ‘had’ as a helping verb.
Structure: Subject+had+Verb(past participle form)+Object
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense describes an action that started and continued for some time in the past. In Past Perfect Continuous Tense, ‘since’ and ‘for’ can indicate how long the action continued in the past. For example:
- I had been walking since morning.
- He had been reading the book for one week.
- She had been joining the meeting since evening.
- They had been coming for 1 year.
- Mr. Joseph had been attending the class before they left.
Let us see the different forms of Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| We had been playing cricket since morning. | Had we been playing cricket since morning? | We had not been playing cricket since morning. |
| He had been waiting for you for two years. | Had he been waiting for you for two years? | He had not been waiting for you for two years. |
| I had not been running in the field since the afternoon. | Had I been running in the field since the afternoon? | I had not been running in the field since afternoon. |
| She had been looking for a new job. | Had she been looking for a new job? | She had not been looking for a new job. |
| They had been sleeping for 6 hours. | Had they been sleeping for 6 hours? | They had not been sleeping for 6 hours. |
Structure: Subject+had been+Verb(+ing)+Object
Present Indefinite Tense (simple present)
Present Indefinite Tense usually describes an action in the present time or depicts habitual fact or universal truth. For example:
- I read poetry.
- You play a new game.
- She dances well.
- He catches fish in the pond.
- They make a new design.
- The Himalayas is a great mountain.
Note: If a subject starts with a third person singular number, ‘s’ or ‘es’ added after the main verb. Interrogative sentences take ‘do’ and ‘does’ before the subject and Negative sentences takes ‘do not’ and ‘does not’ after the subject.
Let us see the different forms of Present Indefinite Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I see a bird. | Do I see a bird? | I do not see a bird. |
| You look healthy. | Do you look healthy? | You do not look healthy. |
| He recites the holy books. | Does he recite the holy books? | He does not recite the holy books. |
| She enjoys an awesome scenario. | Does she enjoy an awesome scenario? | She does not enjoy an awesome scenario. |
| They plan for a new trip. | Do they plan for a new trip? | They don’t plan for a new trip. |
Structure: Subject+Verb(base form)+Object
Present Continuous Tense
Present Indefinite Tense describes an action that is going on and continues in the near future. For example:
- I’m taking my breakfast.
- You are doing a great job.
- They are helping poor people.
- He is going into the market.
- She is running a shop.
Let us see the different forms of Present Indefinite Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I’m driving a car. | Am I driving a car? | I’m not driving a car. |
| You are looking beautiful. | Are you looking beautiful? | You are not looking beautiful. |
| They are walking on the footpath. | Are they walking on the footpath? | They are not walking on the footpath. |
| He is buying a smartphone. | Is he buying a smartphone? | He is not buying a smartphone. |
| She is reading a poem. | Is she reading a poem? | She is not reading a poem. |
Structure: Subject+am/is/are+Verb(+ing)+Object
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense describes an action that has been finished, but its consequence is still available. For example:
- I have completed my task.
- You have gone to the place.
- He has failed the examination.
- She has missed the train.
- They have won the world cup a few weeks ago.
Let us see the different forms of Present Perfect Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I have left my home. | Have I left my home? | I have not left my home. |
| Mr. Wajid has visited his new office. | Has Mr. Wajid visited his new office? | Mr. Wajid has not visited his new office. |
| He has opened a brand new shop. | Has he opened a brand new shop? | He has not opened a brand new shop. |
| They have achieved their goal. | Have they achieved their goal? | They have not achieved their goal. |
| It has looked pretty well. | Has it looked pretty well? | It has looked pretty well. |
Structure: Subject+have/has+Verb(past participle form)+Object
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense describes an action that started in the past and continues. For example:
- I have been working for three days.
- They have been staying home for six months.
- She has been living this since Friday.
- He has been suffering from mental diseases since Monday.
- The students have been missing their classes for one year.
Let us see the different forms of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I have been reading since morning | Have I been reading since morning? | I have not been reading since morning. |
| He has been driving the car for six hours. | Has he been driving the car for six hours? | He has not been driving the car for six hours. |
| She has been cooking since the evening | Has she been cooking since the evening? | She has not been cooking since the evening. |
| They have been playing for one hour. | Have they been playing for one hour? | They have not been playing for one hour. |
| The Jaw has been waiting for you for one week. | Has Jaw been waiting for you for one week? | The Jaw has not been waiting for you for one week. |
Structure: Subject+have been/has been+Verb(+ing)+Object
Future Indefinite Tense
Future Indefinite Tense describes an action that will occur or happen in the future. For example:
- I will go to my campus.
- You will see the beautiful flower.
- They will attend the meeting.
- She will meet her friends.
- He will be present in the examination hall.
Let us see the different forms of Future Indefinite Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I will see the bird. | Will I see the bird? | I will not see the bird. |
| You will find the place. | Will you find the place? | You will not find the place. |
| The man will contact you later. | Will the man contact you later? | The man will not contact you later. |
| He will provide healthy foods. | Will he provide healthy foods? | He will not provide healthy foods. |
| She will choose an orange color. | Will she choose an orange color? | She will not choose an orange color. |
Structure: Subject+shall/will+Verb(base form)+Object
Note: ‘Will can be used instead of ‘shall’
Future Continuous Tense
Future Indefinite Tense describes an action going on in the future. For example:
- I will be eating pizza.
- He will be walking in the street.
- We shall be running the business.
- They will be coming to my home.
- Luna will be facing the situation.
Let us see the different forms of Future Continuous Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| Walker will be planning a new study plan. | Will Walker be planning a new study plan? | Walker will not be planning a new study plan. |
| I shall be getting my payment. | Shall I be getting my payment? | I shall not be getting my payment. |
| He will be remaining silent. | Will he be remaining silent? | He will not be remaining silent. |
| We shall be going there. | Shall we be going there? | We shall not be going there. |
| You will be missing your sister one day. | Will you be missing your sister one day? | You will not be missing your sister one day. |
Structure: Subject+shall be/will be+Verb(+ing)+Object
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense describes an action that will have occurred by a certain time in the future. When two actions occur in the future, the first is considered Future Perfect Tense, and the second is Simple Present Tense. For example:
- I shall have done my task before you come.
- He will have gone there to meet you.
- She will have written a new story.
- We will have enjoyed the match before you know.
- Ketty will have joined the party.
Let us see the different forms of Future Perfect Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| I will have got the point. | Will I have got the point? | I will not have gotten the point. |
| We shall have missed you. | Shall we have missed you? | We shall not have missed you. |
| You will have made a mistake. | Will you have made a mistake? | You will not have made a mistake. |
| It will have done for you. | Will it have done for you? | It will not have done for you. |
| She will have joined a new job. | Will she have joined a new job? | She will not have joined a new job. |
Structure: Subject+shall have/will have+Verb(past participle form)+Object
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense describes an action that will have been continuing at a certain time in the future. When two actions occur in the future, the first is considered Future Perfect Continuous Tense, and the second is Simple Present Tense. For example:
- I shall have been doing it for you before you want.
- You will have been buying the car before you retire.
- They will have been paying the price for their misdeed.
- He will have been reading the book before Mr. Jim arrives.
- The teacher will have been taking the class for two hours.
Let us see the different forms of Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
| Affirmative | Interrogative | Negative |
| You will have been missing the moment. | Will you have been missing the moment? | You will not have been missing the moment. |
| He will have been staying at home for three months. | Will he have been staying at home for three months? | He will not have been staying at home for three months. |
| I shall have been playing in the field. | Shall I have been playing in the field? | I shall not have been playing in the field. |
| They will have been performing before she comes. | Will they have been performing before she comes? | They will not have been performing before she comes. |
| We shall have been arranging the program since morning. | Shall we have been arranging the program since morning?? | We shall not have been arranging the program since morning. |
Structure: Subject+shall have been/will have been+Verb(+ing)+Object
Tense Quiz
3.9
15
votes
Article Rating
Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com. He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.