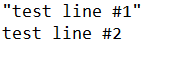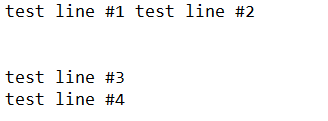Редактирование документов Word из кода VBA Excel. Добавление и форматирование текста. Объект Word.Range, свойство Text, методы InsertAfter и InsertBefore.
Работа с Word из кода VBA Excel
Часть 3. Редактирование документов Word
[Часть 1] [Часть 2] [Часть 3] [Часть 4] [Часть 5] [Часть 6]
Добавление текста в новый документ
Основные объекты, использующиеся в VBA Word для определения места вставки, добавления и форматирования текста – это Selection (выделение), Range (диапазон) и Bookmark (закладка).
Selection и Range позволяют заполнять текстом новые документы или редактировать существующие. Закладки можно использовать для вставки изменяемых реквизитов в шаблоны различных документов: договоры, акты, справки.
Объект Range имеет преимущество перед объектом Selection, так как он может быть создан только программно и не зависит от действий пользователя. Если для вставки и форматирования текста будет использоваться объект Selection, а пользователь во время работы программы просто поставит курсор в другое место документа, результат будет непредсказуем.
Word.Range кардинально отличается от объекта Range в Excel. В приложении Word он представляет из себя набор из одного или множества символов. А также он может вообще не содержать ни одного символа, а быть указателем ввода текста (виртуальным курсором).
Объект Range возвращается свойством Range других объектов приложения Word: Document, Selection, Bookmark, Paragraph, Cell (объект Table).
Вставка текста без форматирования
Если текст вставляется без форматирования, достаточно одной строки кода (myDocument – это переменная):
- Вставка текста с заменой имеющегося:
myDocument.Range.Text = "Вставляемый текст" - Добавление текста после имеющегося:
myDocument.Range.InsertAfter "Добавляемый текст" - Добавление текста перед имеющимся:
myDocument.Range.InsertBefore "Добавляемый текст"
Методами InsertAfter и InsertBefore можно вставить текст и на пустую страницу, также, как с помощью свойства Text. Перейти на новый абзац и начать предложение с красной строки можно с помощью ключевых слов vbCr (vbNewLine, vbCrLf) и vbTab.
Вставка текста с форматированием
Для форматирования отдельных участков текста необходимо указать диапазон символов, входящих в этот участок. Здесь нам также поможет объект Range, которому можно задать любой набор символов, содержащихся в документе Word.
Синтаксис присвоения диапазона символов объекту Range:
|
myDocument.Range(Start:=n, End:=m) ‘или без ключевых слов Start и End myDocument.Range(n, m) |
- myDocument – переменная;
- n – номер точки перед начальным символом;
- m – номер точки после конечного символа.
Счет точек вставки начинается с нуля. Знаки переноса строки, возврата каретки и табуляции учитываются как отдельные символы. 0 – это для объекта Word.Range виртуальная точка вставки на пустом документе, 1 – точка между первым и вторым символом, 2 – точка между вторым и третьим символом и т.д.
На пустом документе объекту Range можно присвоить только виртуальную точку вставки:
myDocument.Range(Start:=0, End:=0)
Первый символ в документе с текстом:
myDocument.Range(Start:=0, End:=1)
Диапазон с 11 по 20 символ:
myDocument.Range(Start:=10, End:=20)
Реальная точка вставки (курсор) принадлежит объекту Selection, который создается вручную или программно с помощью метода Select.
Вставка курсора в начало документа:
myDocument.Range(Start:=0, End:=0).Select
Эта строка вставит курсор между пятым и шестым символами:
myDocument.Range(Start:=5, End:=5).Select
Вставка курсора в конец документа:
myDocument.Range(.Range.Characters.Count - 1, .Range.Characters.Count - 1).Select
Ссылку на объект Range можно присвоить переменной, но при форматировании ее придется каждый раз переопределять и код получится длиннее. Пример присвоения ссылки объектной переменной:
|
Dim myRange As Word.Range Set myRange = myDocument.Range(Start:=0, End:=20) |
Для Range(Start:=0, End:=20) в документе должно быть как минимум 20 символов.
Однострочные примеры редактирования и форматирования текста
Вставка дополнительного текста внутри имеющегося после заданной точки:
myDocument.Range(Start:=10, End:=10).InsertAfter "Вставляемый текст"
Новый абзац с красной строки (предыдущая строка должна заканчиваться символом возврата каретки или переноса строки):
myDocument.Range.InsertAfter vbTab & "Красная строка"
Присвоение шрифту заданного диапазона зеленого цвета:
myDocument.Range(Start:=10, End:=65).Font.ColorIndex = wdGreen
Меняем обычное начертание на курсив:
myDocument.Range(Start:=10, End:=65).Font.Italic = True
Указываем размер шрифта:
myDocument.Range(Start:=10, End:=65).Font.Size = 22
Применение стандартных стилей:
myDocument.Range(Start:=0, End:=16).Style = "Заголовок 1"
Если вас заинтересуют другие команды форматирования текста, запишите их макрорекордером в VBA Word и примените к объекту Range.
Пример 1
Добавление текста в новый документ без форматирования:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
Sub Primer1() On Error GoTo Instr Dim myWord As New Word.Application, _ myDocument As Word.Document Set myDocument = myWord.Documents.Add myWord.Visible = True With myDocument .Range.Text = «Заголовок по центру» & vbCr .Range(Start:=0, End:=19).ParagraphFormat.Alignment _ = wdAlignParagraphCenter .Range.InsertAfter _ vbTab & «Первый абзац с красной строки» & vbCr & _ «Второй абзац не с красной строки» & vbCr & _ vbTab & «Третий абзац с красной строки» End With Set myDocument = Nothing Set myWord = Nothing Exit Sub Instr: If Err.Description <> «» Then MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End If If Not myWord Is Nothing Then myWord.Quit Set myDocument = Nothing Set myWord = Nothing End If End Sub |
Пример 2
Добавление текста в новый документ с форматированием:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
Sub Primer2() On Error GoTo Instr Dim myWord As New Word.Application, _ myDocument As Word.Document Set myDocument = myWord.Documents.Add myWord.Visible = True With myDocument .Range.Text = «Заголовок по центру» & vbCr .Range(Start:=0, End:=19).Style = «Заголовок» .Range(Start:=0, End:=19).ParagraphFormat.Alignment _ = wdAlignParagraphCenter .Range.InsertAfter «Заголовок 1 не по центру» & vbCr .Range(Start:=20, End:=44).Style = «Заголовок 1» .Range.InsertAfter vbTab & «Шрифт по умолчанию « _ & «с красной строки» & vbCr .Range.InsertAfter «Зеленый курсив, размер 20» .Range(Start:=82, End:=107).Font.Italic = True .Range(Start:=82, End:=107).Font.Size = 20 .Range(Start:=82, End:=107).Font.ColorIndex = wdGreen End With Set myDocument = Nothing Set myWord = Nothing Exit Sub Instr: If Err.Description <> «» Then MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End If If Not myWord Is Nothing Then myWord.Quit Set myDocument = Nothing Set myWord = Nothing End If End Sub |
Вы можете запустить эти примеры в редакторе VBA Excel на своем компьютере и посмотреть результаты.
|
Здравствуйте, здесь на форуме узнал как читать, писать в файле txt. |
|
|
The_Prist Пользователь Сообщений: 14182 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
Как из Excel обратиться к другому приложению
Если коротко: так же, как из Word. Хотя смотря какие цели преследуются и что подразумевается под запись, чтение…Читать можно и бинарно — и разницы не будет, хоть картинка, хоть файл Word. Только надо четко понимать структуру документа в этом случае и уметь преобразовывать биты в нормальное представление. Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
|
usersuperpupsik Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#3 02.12.2013 23:19:05 Спасибо, The_Prist, Я почитал, немного прояснилось.Уточню вопрос.
2.Как Все удалить в docx файле и записать туда новый массив?
(Всё делается из excel с помощью vba!) |
||||
|
usersuperpupsik Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#4 02.12.2013 23:39:44 И еще у меня не получается использовать ThisWorkbook.Path:
|
||
|
The_Prist Пользователь Сообщений: 14182 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
Может в форум по Word тогда? Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
|
usersuperpupsik Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#6 03.12.2013 00:12:14 Спасибо за совет, The_Prist. Записывать в файл получилось построчно! Чтобы этот код работал нужно добавить библиотеку Microsoft Word:
А какой Вы посоветуете форум по Word VBA? Изменено: usersuperpupsik — 10.12.2013 14:20:24 |
||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
Говорят, неплохой ресурс Wordexpert |
|
Игорь Пользователь Сообщений: 3631 |
А зачем считывать и записывать файл Word построчно? Вот простой пример макроса для работы с файлами Word: http://excelvba.ru/programmes/Notepad |
|
usersuperpupsik Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#9 06.12.2013 01:50:24 Игорь, http://excelvba.ru/programmes/Notepad , что-то я не вижу модуля с кодом в этом файле.
Зарегистрировался. Буду спрашивать здесь http://wordexpert.ru Изменено: usersuperpupsik — 06.12.2013 01:51:10 |
||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
|
|
usersuperpupsik Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#11 06.12.2013 14:58:10 У меня microsoft office 2007, Чтобы посмотреть код формы нужно выделить её, а потом нажать на F7! |
I have a file which is manually added or modified based on the inputs. Since most of the contents are repetitive in that file, only the hex values are changing, I want to make it a tool generated file.
I want to write the c codes which are going to be printed in that .txt file.
What is the command to create a .txt file using VBA, and how do I write to it
ashleedawg
20k8 gold badges73 silver badges104 bronze badges
asked Jul 16, 2012 at 11:20
2
To elaborate on Ben’s answer:
If you add a reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime and correctly type the variable fso you can take advantage of autocompletion (Intellisense) and discover the other great features of FileSystemObject.
Here is a complete example module:
Option Explicit
' Go to Tools -> References... and check "Microsoft Scripting Runtime" to be able to use
' the FileSystemObject which has many useful features for handling files and folders
Public Sub SaveTextToFile()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = "C:tempMyTestFile.txt"
' The advantage of correctly typing fso as FileSystemObject is to make autocompletion
' (Intellisense) work, which helps you avoid typos and lets you discover other useful
' methods of the FileSystemObject
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
Dim fileStream As TextStream
' Here the actual file is created and opened for write access
Set fileStream = fso.CreateTextFile(filePath)
' Write something to the file
fileStream.WriteLine "something"
' Close it, so it is not locked anymore
fileStream.Close
' Here is another great method of the FileSystemObject that checks if a file exists
If fso.FileExists(filePath) Then
MsgBox "Yay! The file was created! :D"
End If
' Explicitly setting objects to Nothing should not be necessary in most cases, but if
' you're writing macros for Microsoft Access, you may want to uncomment the following
' two lines (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/517202/2822719 for details):
'Set fileStream = Nothing
'Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
answered Apr 5, 2018 at 14:16
3
an easy way with out much redundancy.
Dim fso As Object
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Dim Fileout As Object
Set Fileout = fso.CreateTextFile("C:your_pathvba.txt", True, True)
Fileout.Write "your string goes here"
Fileout.Close
answered Feb 23, 2016 at 17:01
pelospelos
1,6743 gold badges24 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
Dim SaveVar As Object
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine("Enter Text")
Console.WriteLine("")
SaveVar = Console.ReadLine
My.Computer.FileSystem.WriteAllText("N:A-Level Computing2017!PPESaveFileSaveData.txt", "Text: " & SaveVar & ", ", True)
Console.WriteLine("")
Console.WriteLine("File Saved")
Console.WriteLine("")
Console.WriteLine(My.Computer.FileSystem.ReadAllText("N:A-Level Computing2017!PPESaveFileSaveData.txt"))
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub()
BDL
20.7k19 gold badges52 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Feb 10, 2017 at 13:16
5
I have a file which is manually added or modified based on the inputs. Since most of the contents are repetitive in that file, only the hex values are changing, I want to make it a tool generated file.
I want to write the c codes which are going to be printed in that .txt file.
What is the command to create a .txt file using VBA, and how do I write to it
ashleedawg
20k8 gold badges73 silver badges104 bronze badges
asked Jul 16, 2012 at 11:20
2
To elaborate on Ben’s answer:
If you add a reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime and correctly type the variable fso you can take advantage of autocompletion (Intellisense) and discover the other great features of FileSystemObject.
Here is a complete example module:
Option Explicit
' Go to Tools -> References... and check "Microsoft Scripting Runtime" to be able to use
' the FileSystemObject which has many useful features for handling files and folders
Public Sub SaveTextToFile()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = "C:tempMyTestFile.txt"
' The advantage of correctly typing fso as FileSystemObject is to make autocompletion
' (Intellisense) work, which helps you avoid typos and lets you discover other useful
' methods of the FileSystemObject
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
Dim fileStream As TextStream
' Here the actual file is created and opened for write access
Set fileStream = fso.CreateTextFile(filePath)
' Write something to the file
fileStream.WriteLine "something"
' Close it, so it is not locked anymore
fileStream.Close
' Here is another great method of the FileSystemObject that checks if a file exists
If fso.FileExists(filePath) Then
MsgBox "Yay! The file was created! :D"
End If
' Explicitly setting objects to Nothing should not be necessary in most cases, but if
' you're writing macros for Microsoft Access, you may want to uncomment the following
' two lines (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/517202/2822719 for details):
'Set fileStream = Nothing
'Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
answered Apr 5, 2018 at 14:16
3
an easy way with out much redundancy.
Dim fso As Object
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Dim Fileout As Object
Set Fileout = fso.CreateTextFile("C:your_pathvba.txt", True, True)
Fileout.Write "your string goes here"
Fileout.Close
answered Feb 23, 2016 at 17:01
pelospelos
1,6743 gold badges24 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
Dim SaveVar As Object
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine("Enter Text")
Console.WriteLine("")
SaveVar = Console.ReadLine
My.Computer.FileSystem.WriteAllText("N:A-Level Computing2017!PPESaveFileSaveData.txt", "Text: " & SaveVar & ", ", True)
Console.WriteLine("")
Console.WriteLine("File Saved")
Console.WriteLine("")
Console.WriteLine(My.Computer.FileSystem.ReadAllText("N:A-Level Computing2017!PPESaveFileSaveData.txt"))
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub()
BDL
20.7k19 gold badges52 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Feb 10, 2017 at 13:16
5
In this Article
- Write to a Text File
- Write to New Text File
- Write to Existing Text File
- Append to Text File
- WriteLine Method
- Write Method
- WriteBlankLines
- Data Range to Text File
- Array to Text File
This tutorial will demonstrate how to write to text files using VBA.
Write to a Text File
The below codes use the FileSystemObject (learn more). In order to use it, you will need to set a reference to the VB script run-time library.
Write to New Text File
With the CreateTextFile method of FileSystemObject you can create and then add content to a text file:
Sub FSOCreateAndWriteToTextFile()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToCreate = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt")
FileToCreate.Write "test line"
FileToCreate.Close
End Sub
Please note that content will not be enclosed by quotes.
Write to Existing Text File
To write to an existing text file you can use the OpenTextFile method of FileSystemObject with ForWriting mode.
Sub FSOWriteToTextFile()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForWriting)
FileToWrite.Write "test line"
FileToWrite.Close
End Sub
Please note that you do not necessarily need FileSystemObject to write to an existing text file. The above example is shown in another way in this code below (see other example in the Data Range to Text File section):
Sub WriteToTextFile()
Dim FileName As String
FileName = "C:TestTestFile.txt"
Open FileName For Output As #1
Print #1, "test line"
Close #1
End SubPlease note that using Write command instead of Print will result in having the added content enclosed by quotes. Having both commands in your macro
Write #1, "test line #1"
Print #1, "test line #2"will result in a text file like this:
Append to Text File
By changing the mode in the above code to ForAppending, a line can be added to the end of the text file:
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForAppending)WriteLine Method
This method appends the input string as a separate line to the existing content.
Write Method
The input string is appended on the same line as the existing content.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
WriteBlankLines
This method takes the number of blank lines to be written to the text file as a parameter.
This code below illustrates the difference between the different write methods:
Sub WriteMethods()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForAppending)
FileToWrite.Write "test line #1 "
FileToWrite.Write "test line #2"
FileToWrite.WriteBlankLines (3)
FileToWrite.WriteLine "test line #3"
FileToWrite.WriteLine "test line #4"
FileToWrite.Close
End SubAnd the result:
Data Range to Text File
If you want to output a data range from your worksheet to a text file, you can use this code:
Sub OutputToTextFile()
Dim FileName As String, LineText As String
Dim MyRange As Range, i, j
FileName = "C:TestTestFile.txt" 'you can specify here the text file name you want to create
Open FileName For Output As #1
Set MyRange = Range("data") 'it assumes you have a data range named “data” on your worksheet
For i = 1 To MyRange.Rows.Count
For j = 1 To MyRange.Columns.Count
LineText = IIf(j = 1, "", LineText & ",") & MyRange.Cells(i, j) 'the text file creating will have a comma separator
Next j
Print #1, LineText 'using Write command instead of Print will result in having your data in quotes in the output text file
Next i
Close #1
End Sub
Array to Text File
You can also save your array of data into a text file like this:
Sub SaveArrayToTextFile()
Dim MyArray As Variant
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
MyArray = Array(Array("00", "01"), Array("10", "11"), Array("20", "21"))
Set FileToCreate = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt")
For n = 0 To UBound(MyArray)
FileToCreate.WriteLine MyArray(n)(0) & "," & MyArray(n)(1)
Next
FileToCreate.Close
End Sub