I’ve created a MS Word macro that searches for certain text (indicated by markup codes), cuts the text and inserts it into a new footnote, and then deletes the markup codes from the footnote. Now I want the macro to repeat until it doesn’t find any more markup codes in the text.
Here’s the macro below
Sub SearchFN()
'find a footnote
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "&&FB:*&&FE"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
End With
Selection.Find.Execute
'cut the footnote from the text
Selection.Cut
'create a proper Word footnote
With Selection
With .FootnoteOptions
.Location = wdBottomOfPage
.NumberingRule = wdRestartContinuous
.StartingNumber = 1
.NumberStyle = wdNoteNumberStyleArabic
End With
.Footnotes.Add Range:=Selection.Range, Reference:=""
End With
'now paste the text into the footnote
Selection.Paste
'go to the beginning of the newly created footnote
'and find/delete the code for the start of the note (&&FB:)
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
Selection.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "&&FB:"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = False
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
End With
Selection.Find.Execute
With Selection
If .Find.Forward = True Then
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseStart
Else
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
End If
.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceOne
If .Find.Forward = True Then
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
Else
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseStart
End If
.Find.Execute
End With
'do same for ending code (&&FE)
With Selection.Find
.Text = "&&FE"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
End With
Selection.Find.Execute
With Selection
If .Find.Forward = True Then
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseStart
Else
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
End If
.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceOne
If .Find.Forward = True Then
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
Else
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseStart
End If
.Find.Execute
End With
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
'now repeat--but how??
End Sub
shA.t
16.4k5 gold badges53 silver badges111 bronze badges
asked Nov 20, 2012 at 2:24
Good question this one, you can loop through the whole document using the Selection.Find.Found result.
What you do is start a search and if you find a result go into a loop only while the Selection.Find.Found result is true. Once you’ve got through these, you’re done. The following code should do the trick nicely for you.
Sub SearchFN()
Dim iCount As Integer
'Always start at the top of the document
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
'find a footnote to kick it off
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Text = "&&FB:*&&FE"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
.Execute
End With
'If we find one then we can set off a loop to keep checking
'I always put a counter in to avoid endless loops for one reason or another
Do While Selection.Find.Found = True And iCount < 1000
iCount = iCount + 1
'Jump back to the start of the document. Since you remove the
'footnote place holder this won't pick up old results
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
Selection.Find.Execute
'On the last loop you'll not find a result so check here
If Selection.Find.Found Then
''==================================
'' Do your footnote magic here
''==================================
'Reset the find parameters
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Text = "&&FB:*&&FE"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
End With
End If
Loop
End Sub
answered Jan 13, 2013 at 23:20
CuberChaseCuberChase
4,4305 gold badges33 silver badges52 bronze badges
This can be done without using Do while(lots of extra lines, and space/time wastage), It could be as simple as follows:
Sub SearchFN()
'Start from The Top
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
'Find the first search to start the loop
Do
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Replacement.ClearFormatting
.Text = "&&FB:*&&FE"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindstop
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchKashida = False
.MatchDiacritics = False
.MatchAlefHamza = False
.MatchControl = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
.MatchWildcards = True
.Execute
End With
'If we found the result then loop started
If Selection.Find.Found Then
'' Do your work here
' Always end your work after the first found result
' else it will be endless loop
Else
'If we do not found any then it will exit the loop
Exit Do
End If
Loop
End Sub
answered Jun 22, 2018 at 5:51
VBAbyMBAVBAbyMBA
7862 gold badges11 silver badges27 bronze badges
The simplest way to do this is to make the function recursive (the function recalls itself). Add this one line to the bottom of your sub or function:
If (Selection.Find.Found = True) then call SearchFN
answered Jun 8, 2019 at 21:13
In this Article
- INSTR Function
- Instr Example
- Instr Syntax
- Instr Start Position
- Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
- InstrRev Function
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- InString Examples
- If String Contains Substring
- Find Text String in a Cell
- Find Position of a Character in a String
- Search String for Word
- If Variable Contains String
- Instr and the Left Function
- Using Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
INSTR Function
The VBA Instr Function checks if a string of text is found in another string of text. It returns 0 if the text is not found. Otherwise it returns the character position where the text is found.
The Instr Function performs exact matches. The VBA Like Operator can be used instead to perform inexact matches / pattern matching by using Wildcards.
Instr Example
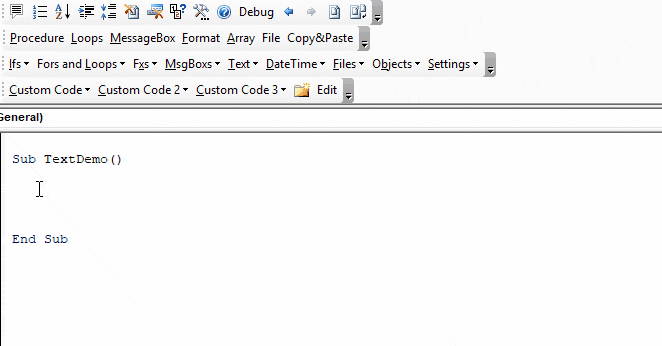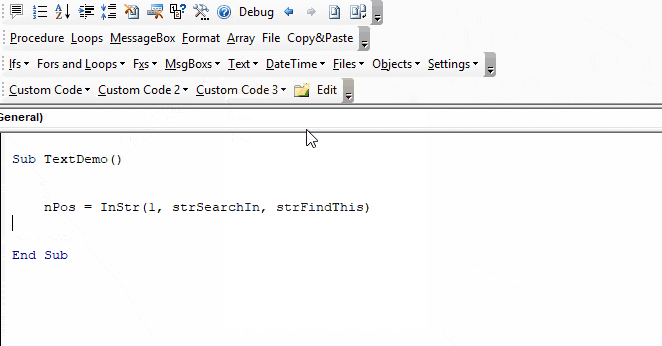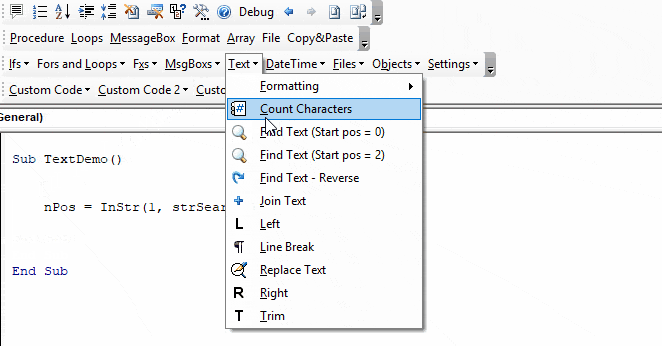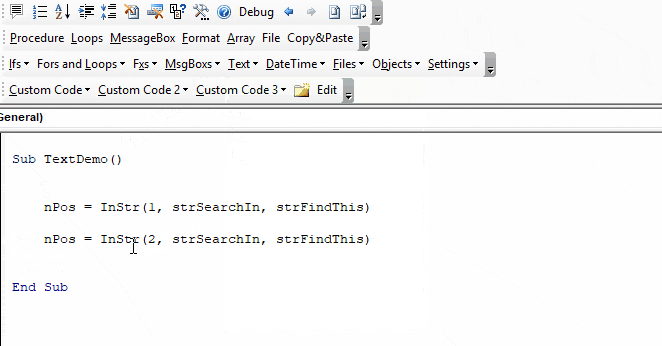
The following code snippet searches the string “Look in this string” for the word “Look”. The Instr Function returns 1 because the text is found in the first position.
Sub FindSomeText()
MsgBox InStr("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubThis second example returns 7 because the text is found starting in the 7th position:
Sub FindSomeText2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "Look")
End SubImportant! The Instr Function is case-sensitive by default. This means “look” will not match with “Look”. To make the test case-insensitive read below.
Instr Syntax
The syntax for the Instr function is as follows:
Instr( [start], string, substring, [compare] )[start] (optional) – This optional argument is the starting position of the search. Enter 1 to start searching from position 1 (or leave blank). Enter 5 to start searching from position 5. Important! The INSTR function calculates the character position by counting from 1 NOT from the [start] position.
string – The string of text to search in.
substring – The string of text to find in the primary string.
[compare] (optional) – By default, Instr is case-sensitive. By setting this argument you can make Instr Case insensitive:
|
Argument vb Value |
Argument Integer | Description |
| vbBinaryCompare |
0 |
(Default) Case-sensitive |
|
vbTextCompare |
1 |
Not Case-sensitive |
|
vbDatabaseCompare |
2 |
MS Access Only. Uses information in the database to perform comparison. |
Instr Start Position
The Instr start position allows you to indicate the character position where you will begin your search. Keep in mind however, the Instr output will always count from 1.
Here we set the start position to 3 to skip the first B:
Sub Instr_StartPosition()
MsgBox InStr(3, "ABC ABC", "B")
End SubThe result is 6 because the second B is the 6th character in the string.
Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
By default, VBA treats “L” different from “l”. In other words, VBA is case-sensitive. This is true of all text functions. To make VBA case-insensitive, set the [compare] argument to 1 or vbTextCompare.
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase()
MsgBox InStr(1, "Don't Look in this string", "look", vbTextCompare)
End SubAlternatively, you can add Option Compare Text to the top of your code module:
Option Compare TextOption Compare Text
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "look")
End SubOption Compare Text will impact all of the code in that module. I personally place this at the top of any module that deals with text because I never care about case differences.
InstrRev Function
The Instr Function searches from the left. Instead you can search from the right using the InstrRev Function. The InstrRev Function works very similarly to the Instr function.
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubJust like the Instr function this will return 1 because there is only one instance of “Look” in the text. But if we add a second “Look”, you’ll see that it returns the position of the right-most “Look”:
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string Look", "Look")
End SubNext we will review more Instr examples.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
InString Examples
If String Contains Substring
Here we will use an If statement to test if a string contains a a substring of text:
Public Sub FindSomeText()
If InStr("Look in this string", "look") = 0 Then
MsgBox "No match"
Else
MsgBox "At least one match"
End If
End SubFind Text String in a Cell
You can also find a string in a cell:
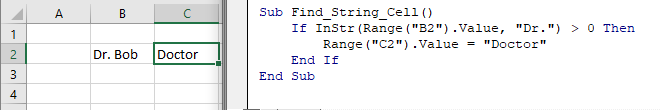
Sub Find_String_Cell()
If InStr(Range("B2").Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
Range("C2").Value = "Doctor"
End If
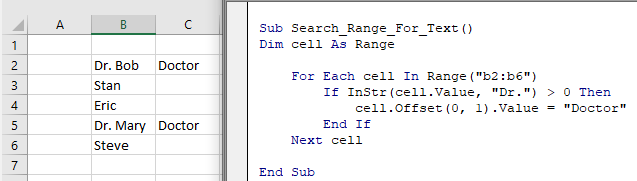
End SubOr loop through a range of cells to test if the cells contain some text:
Sub Search_Range_For_Text()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b6")
If InStr(cell.Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Doctor"
End If
Next cell
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Find Position of a Character in a String
This code will find the position of a single character in a string and assign the position to a variable:
Sub Find_Char()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "L")
End SubSearch String for Word
This code will search a string for a word:
Sub Search_String_For_Word()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "Look")
If n = 0 Then
MsgBox "Word not found"
Else
MsgBox "Word found in position: " & n
End If
End SubIf Variable Contains String
This code will test if a string variable contains a string of text:
Sub Variable_Contains_String()
Dim str As String
str = "Look Here"
If InStr(str, "Here") > 0 Then
MsgBox "Here found!"
End If
End SubInstr and the Left Function
Instr can be used along with other text functions like Left, Right, Len, and Mid to trim text.
With the Left function you can output the text prior to a string of text:
Sub Instr_Left()
Dim str As String
Dim n As Long
str = "Look Here"
n = InStr(str, "Here")
MsgBox Left(str, n - 1)
End SubUsing Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
To learn more, read our article: VBA text functions
<<Return to VBA Examples
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Find.Execute method (Word) |
vbawd10.chm162529724 |
vbawd10.chm162529724 |
word |
Word.Find.Execute |
3b607955-0e82-aa13-dad1-7a5069a57b9d |
06/08/2017 |
medium |
Find.Execute method (Word)
Runs the specified find operation. Returns True if the find operation is successful. Boolean.
Syntax
expression.Execute (FindText, MatchCase, MatchWholeWord, MatchWildcards, MatchSoundsLike, MatchAllWordForms, Forward, Wrap, Format, ReplaceWith, Replace, MatchKashida, MatchDiacritics, MatchAlefHamza, MatchControl)
expression Required. A variable that represents a Find object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FindText | Optional | Variant | The text to be searched for. Use an empty string («») to search for formatting only. You can search for special characters by specifying appropriate character codes. For example, «^p» corresponds to a paragraph mark and «^t» corresponds to a tab character. |
| MatchCase | Optional | Variant | True to specify that the find text be case-sensitive. Corresponds to the Match case check box in the Find and Replace dialog box (Edit menu). |
| MatchWholeWord | Optional | Variant | True to have the find operation locate only entire words, not text that is part of a larger word. Corresponds to the Find whole words only check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| MatchWildcards | Optional | Variant | True to have the find text be a special search operator. Corresponds to the Use wildcards check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| MatchSoundsLike | Optional | Variant | True to have the find operation locate words that sound similar to the find text. Corresponds to the Sounds like check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| MatchAllWordForms | Optional | Variant | True to have the find operation locate all forms of the find text (for example, «sit» locates «sitting» and «sat»). Corresponds to the Find all word forms check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| Forward | Optional | Variant | True to search forward (toward the end of the document). |
| Wrap | Optional | Variant | Controls what happens if the search begins at a point other than the beginning of the document and the end of the document is reached (or vice versa if Forward is set to False). This argument also controls what happens if there is a selection or range and the search text is not found in the selection or range. Can be one of the WdFindWrap constants. |
| Format | Optional | Variant | True to have the find operation locate formatting in addition to, or instead of, the find text. |
| ReplaceWith | Optional | Variant | The replacement text. To delete the text specified by the Find argument, use an empty string («»). You specify special characters and advanced search criteria just as you do for the Find argument. To specify a graphic object or other nontext item as the replacement, move the item to the Clipboard and specify «^c» for ReplaceWith. |
| Replace | Optional | Variant | Specifies how many replacements are to be made: one, all, or none. Can be any WdReplace constant. |
| MatchKashida | Optional | Variant | True if find operations match text with matching kashidas in an Arabic-language document. This argument may not be available to you, depending on the language support (U.S. English, for example) that you have selected or installed. |
| MatchDiacritics | Optional | Variant | True if find operations match text with matching diacritics in a right-to-left language document. This argument may not be available to you, depending on the language support (U.S. English, for example) that you have selected or installed. |
| MatchAlefHamza | Optional | Variant | True if find operations match text with matching alef hamzas in an Arabic-language document. This argument may not be available to you, depending on the language support (U.S. English, for example) that you have selected or installed. |
| MatchControl | Optional | Variant | True if find operations match text with matching bidirectional control characters in a right-to-left language document. This argument may not be available to you, depending on the language support (U.S. English, for example) that you have selected or installed. |
| MatchPrefix | Optional | Variant | True to match words beginning with the search string. Corresponds to the Match prefix check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| MatchSuffix | Optional | Variant | True to match words ending with the search string. Corresponds to the Match suffix check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| MatchPhrase | Optional | Variant | True ignores all white space and control characters between words. |
| IgnoreSpace | Optional | Variant | True ignores all white space between words. Corresponds to the Ignore white-space characters check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
| IgnorePunct | Optional | Variant | True ignores all punctuation characters between words. Corresponds to the Ignore punctuation check box in the Find and Replace dialog box. |
Return value
Boolean
Remarks
If MatchWildcards is True, you can specify wildcard characters and other advanced search criteria for the FindText argument. For example, «*(ing)» finds any word that ends in «ing».
To search for a symbol character, type a caret (^), a zero (0), and then the symbol’s character code. For example, «^0151» corresponds to an em dash (—).
Unless otherwise specified, replacement text inherits the formatting of the text it replaces in the document. For example, if you replace the string «abc» with «xyz», occurrences of «abc» with bold formatting are replaced with the string «xyz» with bold formatting.
Also, if MatchCase is False, occurrences of the search text that are uppercase will be replaced with an uppercase version of the replacement text, regardless of the case of the replacement text. Using the previous example, occurrences of «ABC» are replaced with «XYZ».
Example
This example finds and selects the next occurrence of the word «library».
With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .MatchWholeWord = True .MatchCase = False .Execute FindText:="library" End With
This example finds all occurrences of the word «hi» in the active document and replaces each occurrence with «hello».
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Content myRange.Find.Execute FindText:="hi", _ ReplaceWith:="hello", Replace:=wdReplaceAll
[!includeSupport and feedback]
Bonjour,
Dans son message, < dave55 > écrivait :
In this message, < dave55 > wrote:
|| Hello,
|| I need help in writing a Word Macro that will find text in a paragraph
|| and change the paragraph to a particular font color. I have searched
|| the web and groups but can’t not find any code which I can customize
|| for my use. Any help would be appreciated!
Play around with the following:
‘_______________________________________
Dim SearchedWord As String
Dim CancelOrNot As Integer
Dim DocRange As Range
Dim ParColour As Range
Dim WasFound As Boolean
SearchedWord = «»
CancelOrNot = 0
WasFound = False
Do While SearchedWord = «»
SearchedWord = Trim(InputBox(«What word are you looking for?», _
«Colour paragraphs»))
If SearchedWord = «» Then
CancelOrNot = MsgBox(«You must type a word or cancel.», _
vbOKCancel, «No word»)
‘Ok = 1, Cancel = 2
If CancelOrNot = 2 Then Exit Sub
End If
Loop
Set DocRange = ActiveDocument.Range
With DocRange.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Text = SearchedWord
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindStop
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = True
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
Do While .Execute
WasFound = True
Set ParColour = DocRange.Paragraphs(1).Range
ParColour.Font.Color = wdColorBlue
‘In case word is found more than once in paragraph
‘no need to find the word again in the same paragraph
DocRange.SetRange DocRange.Paragraphs(1).Range.End, _
ActiveDocument.Range.End
Loop
End With
If Not WasFound Then
MsgBox SearchedWord & » was not found in the document.», _
vbExclamation + vbOKOnly, «Word not found»
End If
End Sub
‘_______________________________________
- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
When I do a Selection.find using wildcards, it returns a number of corresponding words. Are those words automatically a Collection? I want to create a list of unique words found at the end of the document with no duplicates in the list (yes, I know that’s
a tautology!) — would that require a dictionary function?-
Изменено
6 февраля 2014 г. 13:52
-
Перемещено
Jeffrey_Chen_
10 февраля 2014 г. 5:52
word development question
-
Изменено
Ответы
-
Hi,
Based on my understanding, Did you want get all of the unique words from a document and create list with these words.
If so , you can just set wildcards to «?*[ |,|.|;|’|:|?]» like below:
Sub Main() Dim List As New Collection Dim r As Range Set r = ActiveDocument.Range r.Select With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .text = "?*[ |,|.|;|'|:|?]" .Forward = True .Wrap = wdFindStop .MatchWildcards = True .MatchCase = False .MatchWholeWord = False .MatchAllWordForms = False .MatchSoundsLike = False .MatchWildcards = True End With Do While Selection.Find.Execute Dim strResult As String strResult = Left(Selection.text, Len(Selection.text) - 1) If (Not IsContainValue(List, strResult)) Then List.Add (strResult) End If Loop End Sub Function IsContainValue(List As Collection, text As String) As Boolean For Each Item In List If (Item = text) Then IsContainValue = True Exit Function End If Next Item IsContainValue = False End FunctionThis sample code can find all of words in document and save these to List collection.
Regards,
We are trying to better understand customer views on social support experience, so your participation in this interview project would be greatly appreciated if you have time. Thanks for helping make community forums a great place.
Click
HERE to participate the survey.-
Помечено в качестве ответа
sluice
11 февраля 2014 г. 10:20
-
Помечено в качестве ответа