Thanks Harry Spier, even though I had to modify your code a little — finally it works great!
Sub FindReplaceAnywhere()
Dim pOldFontName As String
Dim pNewFontName As String
Dim rngStory As Word.Range
Dim lngJunk As Long
Dim oShp As Shape
pOldFontName = "FontDoe" 'replace with the font you want to replace
pNewFontName = "Font Dolores" 'replace with the font you really need to have in your doc
'Fix the skipped blank Header/Footer problem
lngJunk = ActiveDocument.Sections(1).Headers(1).Range.StoryType
'Iterate through all story types in the current document
For Each rngStory In ActiveDocument.StoryRanges
'Iterate through all linked stories
Do
SearchAndReplaceInStory rngStory, pOldFontName, pNewFontName, pFindTxt, pReplaceTxt
On Error Resume Next
Select Case rngStory.StoryType
Case 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
If rngStory.ShapeRange.Count > 0 Then
For Each oShp In rngStory.ShapeRange
If oShp.TextFrame.HasText Then
SearchAndReplaceInStory oShp.TextFrame.TextRange, pOldFontName, pNewFontName, pFindTxt, pReplaceTxt
End If
Next
End If
Case Else
'Do Nothing
End Select
On Error GoTo 0
'Get next linked story (if any)
Set rngStory = rngStory.NextStoryRange
Loop Until rngStory Is Nothing
Next
End Sub
Sub SearchAndReplaceInStory( _
ByVal rngStory As Word.Range, _
ByVal FindFontName As String, _
ByVal ReplaceFontName As String, _
ByVal strSearch As String, _
ByVal strReplace As String)
With rngStory.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Replacement.ClearFormatting
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Font.Name = FindFontName
.Replacement.Font.Name = ReplaceFontName
.Text = strSearch
.Replacement.Text = strReplace
.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End With
End Sub
| title | ms.prod | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Finding and Replacing Text or Formatting |
word |
9ab9f4a7-9833-5a78-56b0-56a161480f18 |
06/08/2019 |
medium |
Finding and replacing is exposed by the Find and Replacement objects. The Find object is available from the Selection object and the Range object. The find action differs slightly depending upon whether you access the Find object from the Selection object or the Range object.
Finding text and selecting it
If the Find object is accessed from the Selection object, the selection is changed when the find criteria is found. The following example selects the next occurrence of the word «Hello.» If the end of the document is reached before the word «Hello» is found, the search is stopped.
With Selection.Find .Forward = True .Wrap = wdFindStop .Text = "Hello" .Execute End With
The Find object includes properties that relate to the options in the Find and Replace dialog box. You can set the individual properties of the Find object or use arguments with the Execute method, as shown in the following example.
Selection.Find.Execute FindText:="Hello", _ Forward:=True, Wrap:=wdFindStop
Finding text without changing the selection
If the Find object is accessed from a Range object, the selection is not changed but the Range is redefined when the find criteria is found. The following example locates the first occurrence of the word «blue» in the active document. If the find operation is successful, the range is redefined and bold formatting is applied to the word «blue.»
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find .Text = "blue" .Forward = True .Execute If .Found = True Then .Parent.Bold = True End With
The following example performs the same result as the previous example, using arguments of the Execute method.
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Content myRange.Find.Execute FindText:="blue", Forward:=True If myRange.Find.Found = True Then myRange.Bold = True
Using the Replacement object
The Replacement object represents the replace criteria for a find and replace operation. The properties and methods of the Replacement object correspond to the options in the Find and Replace dialog box (Edit menu).
The Replacement object is available from the Find object. The following example replaces all occurrences of the word «hi» with «hello». The selection changes when the find criteria is found because the Find object is accessed from the Selection object.
With Selection.Find .ClearFormatting .Text = "hi" .Replacement.ClearFormatting .Replacement.Text = "hello" .Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll, Forward:=True, _ Wrap:=wdFindContinue End With
The following example removes bold formatting in the active document. The Bold property is True for the Find object and False for the Replacement object. To find and replace formatting, set the find and replace text to empty strings («») and set the Format argument of the Execute method to True. The selection remains unchanged because the Find object is accessed from a Range object (the Content property returns a Range object).
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find .ClearFormatting .Font.Bold = True With .Replacement .ClearFormatting .Font.Bold = False End With .Execute FindText:="", ReplaceWith:="", _ Format:=True, Replace:=wdReplaceAll End With
[!includeSupport and feedback]
Word VBA Find
This example is a simple word macro find the text “a”:
Sub SimpleFind()
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "a"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindAsk
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
End With
Selection.Find.Execute
End SubFind and Replace
This simple macro will search for the word “their” and replace it with “there”:
Sub SimpleReplace()
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
Selection.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "their"
.Replacement.Text = "there"
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
End With
Selection.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End SubFind and Replace Only in Selection
This VBA macro will find and replace text in a selection. It will also italicize the replaced text.
Sub ReplaceInSelection()
'replaces text JUST in selection . in adittion it makes replaced text italic
Selection.Find.ClearFormatting
Selection.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "their"
With .Replacement
.Font.Italic = True
.Text = "there"
End With
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindStop 'this prevents Word from continuing to the end of doc
.Format = True 'we want to replace formatting of text as well
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = True
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
End With
Selection.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End SubThis line of code prevents VBA from continuing to the end of the Word document:
.Wrap = wdFindStop 'this prevents Word from continuing to the end of docThis line of code indicates to replace the formatting of the text as well:
.Format = True 'we want to replace formatting of text as wellFind and Replace Only In Range
Instead of replacing text throughout the entire document, or in a selection, we can tell VBA to find and replace only in range. In this example we defined the range as the first paragraph:
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).RangeSub ReplaceInRange()
'replaces text JUST in range [in this example just in the first paragraph]
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Range
oRange.Find.ClearFormatting
oRange.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With oRange.Find
.Text = "their"
.Replacement.Text = "there"
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindStop 'this prevent Word to continue to the end of doc
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
End With
oRange.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End Sub
In today’s article, we would like to explain to you of how to find and replace multiple items in your Word document.
The built-in function in Word, “Find and Replace”, allows us to find and replace a word or a phrase at a time. This certainly cannot meet our need for batch processing.
As a matter of fact, we’ve extended the function to find multiple items in one time in one of our previous article. For more details, you can refer to this article: 2 Quick Ways to Find Multiple Items in One Word Document at the Same Time
The above link discussed how to find multiple items at the same time. And this article will also show you how to replace each item with a different new one respectively.
Run Word VBA to Find and Replace Multiple Items
Macro is the only way left to do customized and batch processing tasks in Word. Just follow bellowing steps to accomplish your mission.
- First and foremost, open your target document.
- Then click “Developer” tab if it’s available in the Ribbon.
- And click “Visual Basic” next to open the VBA editor in Word. Or you can choose to press “Alt+ F11” instead.
- Next click “Normal” on the left column.
- And go to menu bar to click “Insert”.
- On its drop-down menu, choose “Module”.
- Then double click on the new module as to open it.
- Paste following codes on module:
Sub FindAndReplaceMultiItems()
Dim strFindText As String
Dim strReplaceText As String
Dim nSplitItem As Long
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
' Enter items to be replaces and new ones.
strFindText = InputBox("Enter items to be found here,seperated by comma: ", "Items to be found")
strReplaceText = InputBox("Enter new items here, seperated by comma: ", "New items")
nSplitItem = UBound(Split(strFindText, ","))
' Find each item and replace it with new one respectively.
For nSplitItem = 0 To nSplitItem
With Selection
.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Replacement.ClearFormatting
.Text = Split(strFindText, ",")(nSplitItem)
.Replacement.Text = Split(strReplaceText, ",")(nSplitItem)
.Format = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
End With
Selection.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End With
Next nSplitItem
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
- Press “F5” to run the macro.
- Now there will be the first input box. Enter items to be found and use comma to separate. Don’t enter a space after comma.
- Then click “OK” to proceed.
- In the second input box, enter new items and separate them with comma.
- Finally, click “OK”.
In the Face of Data Loss
It’s hard to be cheerful in the face of a data disaster which might destroy valuable information. However, there is no need to be panic since you can obtain a Word repair utility by shelling out a small amount of money.
Author Introduction:
Vera Chen is a data recovery expert in DataNumen, Inc., which is the world leader in data recovery technologies, including excel corruption and pdf repair software products. For more information visit www.datanumen.com
The Microsoft Word Find and Replace feature is very powerful and a great time saver for the more skilled user. You can use Find and Replace to locate exact words, phrases and even patterns matching various scenarios.
Let us start with exploring how to do a regular Find and Replace in Word.
Click the Find or Replace buttons in the Home ribbon Editing section
If you want to Find a word or sentence in your Word file go to the Home ribbon tab and go to the Editing section.
- If you want to Find click Find
- If you want to Find and Replace click Replace
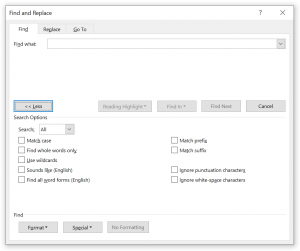
- Match case – will only find words/sentences that match the letter case (e.g. A vs a)
- Find whole words only – will only find whole words (if looking for “ate” will only match ” ate “ and not “late”)
- Use wildcards – allows you to use wildcards (click the Special button for list of wildcard special characters that can be used
- Sounds like – matches expressions that sound like provided text
- Find all word forms – matches all words/sentences that match a word form (e.g. “doyle” will also match “doyl” as it sounds similar)
- Match prefix – match text matching a prefix of a word
- Match suffix – match text matching a suffixof a word
- Ignore punctuation characters – will ignore punctionation
- Ignore white-space characters – will ignore white-space (” “)
This will open the Find and Replace window.
You can also use the CTRL+F keyboard shortcut to Find and the CTRL+H keyboard shortcut to do a Find and Replace.
If you click More > > you will see the full set of options below:
The following options are available:
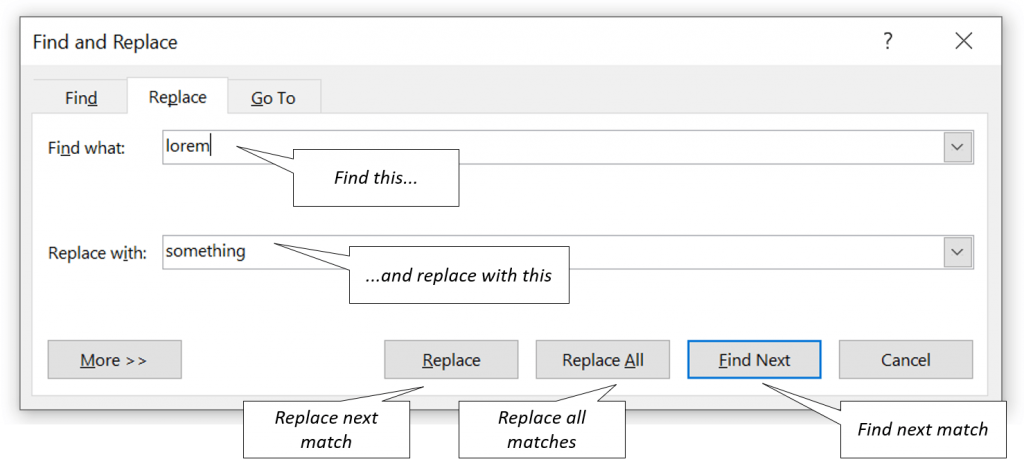
Provide a word, sentence and/or wildcard special characters
Provide a word/sentence you want to Find in the Find what text field and the word/sentence you want to replace it with in the Replace with text field.
Below and explanation of key buttons used to Find or Replace text:
Although Find and Replace is a basic and very easy to use function it is often underestimated. Especially that many users do not know that you can easily use wildcards to replace more complex text patterns.
Using Wilcards
You can also you wildcards to replace various complex patterns such as sequences of numbers or specific number of occurances, letter cases, characters use to replace any characters and much more. To use wilcards click More > > and select the Use wilcards checkbox.
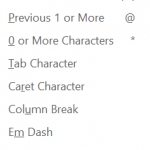
On the right you should see all available wildcard characters.
For more information on Special Characters that can be used in Wildcard Find and Replace read this
Let us explore some example common scenarios below:
Match any word made of A-Z characters, any letter case
<[A-z]@>
This matches any single word that contains A-z letters.
The < character indicate the beginning, while > the end of a word. The [A-z] brackets indicate a series of characters, using the hyphen allows you specify the whole range of A-z letters. Lastly the @ character indicates that the previous expression may repeat 0 to any number of times.
Match an email from the .com domain
<[A-z,0-9]@@[A-z,0-9]@.com>
This matches only emails with A-z letters and 0-9 numbers in their login and domain name. Again the [A-z,0-9] bracket specifies we are listing several ranges of acceptable characters, following this with the @ characters tells that any number of these characters may appear. To use the @ character explicitly we need to escape it with a backslash . We use the similar patter for the domain name. Finally notice again I am using < and > to indicate the beginning or end of a word as emails are not separated by spaces.
Match a phone number split with hyphens
[0-9]@-[0-9]@-[0-9]@
The above matches any 3 series of digits separated by hyphens.
Using Wildcards to Capture and Replace text
In some cases you will want to not only capture a pattern but replace it with part of its content. For this you need to use Expressions (). Expressions let you mark a specific group in the “Find what” text field, that you want to reuse in your “Replace with” text field. Below a simple example:
Example: Switch places of 2 numbers
In this example we have a pattern of numbers separated by hyphens. Let us assume we want to switch places of these two 3-digit numbers.
Text:
Some text 123-456, some other text 789-012. Something else 345-678
Find what:
([0-9]{3})-([0-9]{3})
Replace with:
-
The resulting Text:
Some text 456-123, some other text 012-789. Something else 678-345
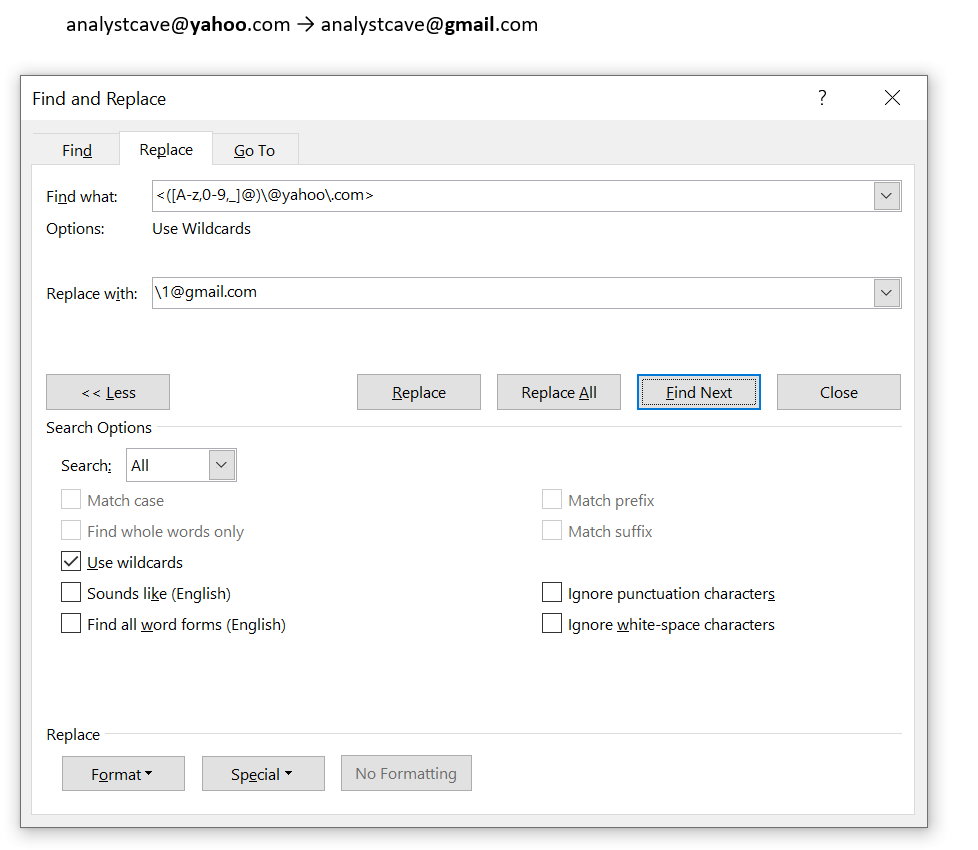
Example: Replace Email domain
Imagine you want to replace an email domain from yahoo to gmail on all emails in your Word document. If you didn’t know Expressions you would use wildcards to find a match an manually replace all such cases. However below an example that will replace this automatically:
All Expressions () are numbered by the sequence in which they are used. This allows us to reference the first part of the email by using the backslash and number 1.
VBA Find and Replace
You can also execute a Find and Replace sequence using a VBA Macro:
Find a single match
The below procedure will print out all occurances of “Find Me” phrases.
ActiveDocument.Content.Select
With Selection.Find
.Text = "Find Me"
.Forward = True
.Execute
End With
If Selection.Find.Found Then
Debug.Print "Found: " & Selection.Range 'Print the found match
Else
Debug.Print "Not Found"
End If
Find all matches
Below VBA macro will find all emails in a Word document with their mailto hyperlinks. This is a good example of fixing hyperlinks in Word documents.
ActiveDocument.Content.Select
Do
With Selection.Find
.Text = "<[A-z,0-9]@@[A-z,0-9]@.com>"
.MatchWildcards = True
.Forward = True
.Execute
End With
If Selection.Find.Found Then
ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection.Range, Address:="mailto:" & Selection.Range
Else
Exit Do 'If not found then end the loop
End If
Loop
Conclusions
Here are my main takeaways from using Find and Replace in Microsoft Word