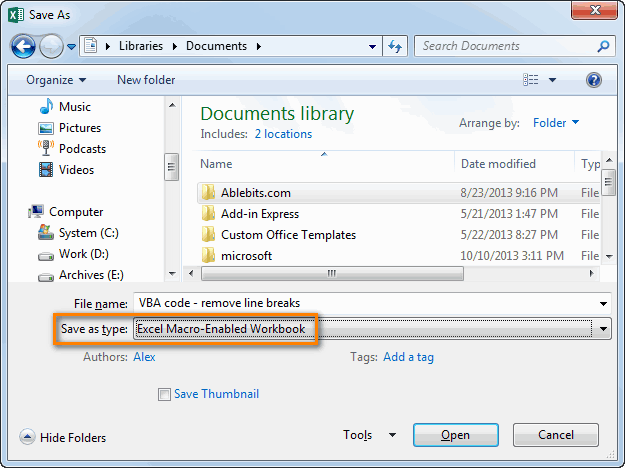
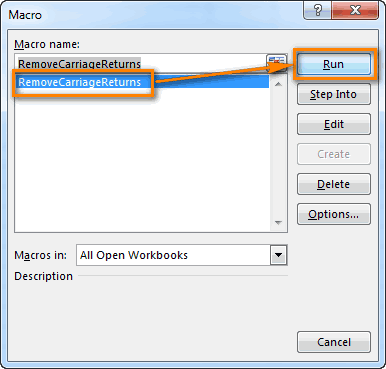
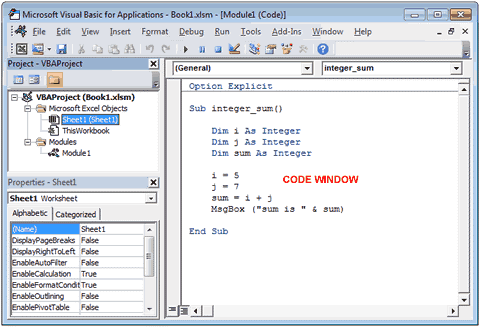
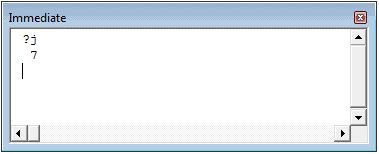
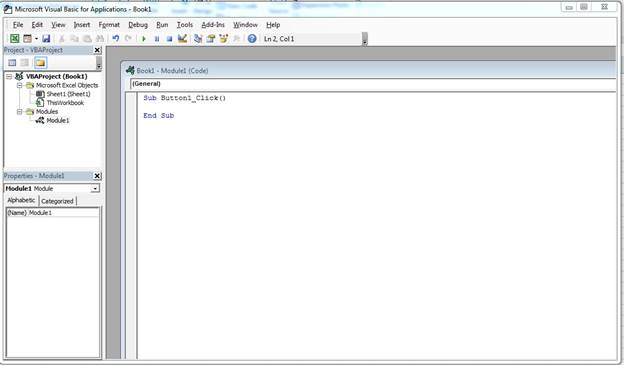
The first step to working with VBA in Excel is to get yourself familiarized with the Visual Basic Editor (also called the VBA Editor or VB Editor).
In this tutorial, I will cover all there is to know about the VBA Editor and some useful options that you should know when coding in Excel VBA.
What is Visual Basic Editor in Excel?
Visual Basic Editor is a separate application that is a part of Excel and opens whenever you open an Excel workbook. By default, it’s hidden and to access it, you need to activate it.
VB Editor is the place where you keep the VB code.
There are multiple ways you get the code in the VB Editor:
- When you record a macro, it automatically creates a new module in the VB Editor and inserts the code in that module.
- You can manually type VB code in the VB editor.
- You can copy a code from some other workbook or from the internet and paste it in the VB Editor.
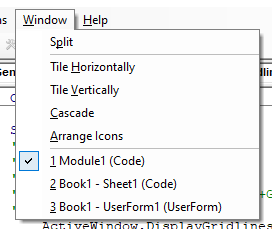
Opening the VB Editor
There are various ways to open the Visual Basic Editor in Excel:
- Using a Keyboard Shortcut (easiest and fastest)
- Using the Developer Tab.
- Using the Worksheet Tabs.
Let’s go through each of these quickly.
Keyboard Shortcut to Open the Visual Basic Editor
The easiest way to open the Visual Basic editor is to use the keyboard shortcut – ALT + F11 (hold the ALT key and press the F11 key).
As soon as you do this, it will open a separate window for the Visual Basic editor.
This shortcut works as a toggle, so when you use it again, it will take you back to the Excel application (without closing the VB Editor).
The shortcut for the Mac version is Opt + F11 or Fn + Opt + F11
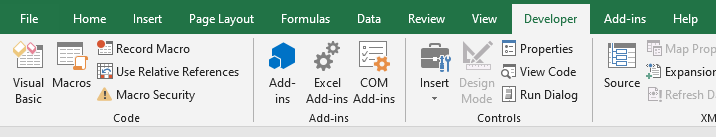
Using the Developer Tab
To open the Visual Basic Editor from the ribbon:
- Click the Developer tab (if you don’t see a developer tab, read this on how to get it).
- In the Code group, click on Visual Basic.
Using the Worksheet Tab
This is a less used method to open the Vb Editor.
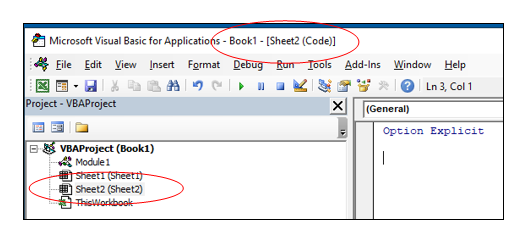
Go to any of the worksheet tabs, right-click, and select ‘View Code’.
This method wouldn’t just open the VB Editor, it will also take you to the code window for that worksheet object.
This is useful when you want to write code that works only for a specific worksheet. This is usually the case with worksheet events.
Anatomy of the Visual Basic Editor in Excel
When you open the VB Editor for the first time, it may look a bit overwhelming.
There are different options and sections that may seem completely new at first.
Also, it still has an old Excel 97 days look. While Excel has improved tremendously in design and usability over the years, the VB Editor has not seen any change in the way it looks.
In this section, I will take you through the different parts of the Visual Basic Editor application.
Note: When I started using VBA years ago, I was quite overwhelmed with all these new options and windows. But as you get used to working with VBA, you would get comfortable with most of these. And most of the time, you’ll not be required to use all the options, only a hand full.
Below is an image of the different components of the VB Editor. These are then described in detail in the below sections of this tutorial.
Now let’s quickly go through each of these components and understand what it does:
Menu Bar
This is where you have all the options that you can use in the VB Editor. It is similar to the Excel ribbon where you have tabs and options with each tab.
You can explore the available options by clicking on each of the menu element.
You will notice that most of the options in VB Editor have keyboard shortcuts mentioned next to it. Once you get used to a few keyboard shortcuts, working with the VB Editor becomes really easy.
Tool Bar
By default, there is a toolbar in the VB Editor which has some useful options that you’re likely to need most often. This is just like the Quick Access Toolbar in Excel. It gives you quick access to some of the useful options.
You can customize it a little by removing or adding options to it (by clicking on the small downward pointing arrow at the end of the toolbar).
In most cases, the default toolbar is all you need when working with the VB Editor.
You can move the toolbar above the menu bar by clicking on the three gray dots (at the beginning of the toolbar) and dragging it above the menu bar.
Note: There are four toolbars in the VB Editor – Standard, Debug, Edit, and User form. What you see in the image above (which is also the default) is the standard toolbar. You can access other toolbars by going to the View option and hovering the cursor on the Toolbars option. You can add one or more toolbars to the VB Editor if you want.
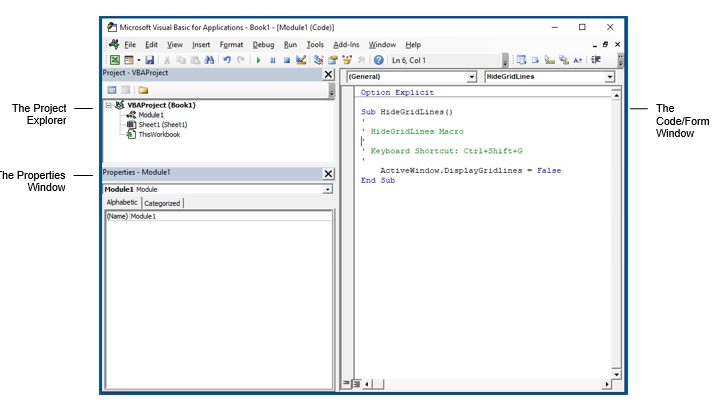
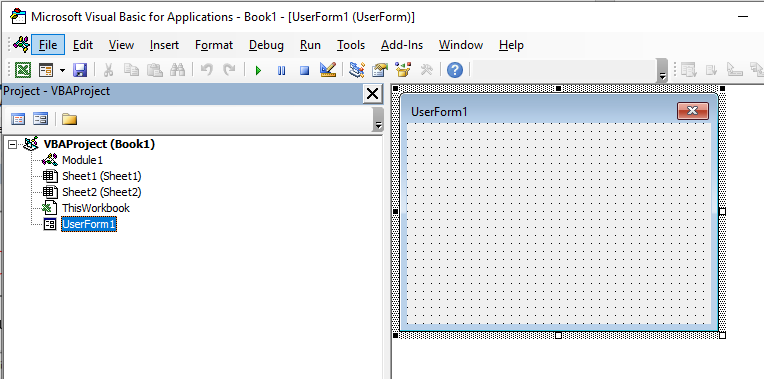
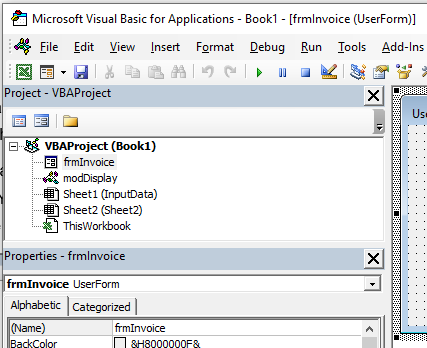
Project Explorer
Project Explorer is a window on the left that shows all the objects currently open in Excel.
When you’re working with Excel, every workbook or add-in that is open is a project. And each of these projects can have a collection of objects in it.
For example, in the below image, the Project Explorer shows the two workbooks that are open (Book1 and Book2) and the objects in each workbook (worksheets, ThisWorkbook, and Module in Book1).
There is a plus icon to the left of objects that you can use to collapse the list of objects or expand and see the complete list of objects.
The following objects can be a part of the Project Explorer:
- All open Workbooks – within each workbook (which is also called a project), you can have the following objects:
- Worksheet object for each worksheet in the workbook
- ThisWorkbook object which represents the workbook itself
- Chartsheet object for each chart sheet (these are not as common as worksheets)
- Modules – This is where the code that is generated with a macro recorder goes. You can also write or copy-paste VBA code here.
- All open Add-ins
Consider the Project Explorer as a place that outlines all the objects open in Excel at the given time.
The keyboard shortcut to open the Project Explorer is Control + R (hold the control key and then press R). To close it, simply click the close icon at the top right of the Project Explorer window.
Note: For every object in Project Explorer, there is a code window in which you can write the code (or copy and paste it from somewhere). The code window appears when you double click on the object.
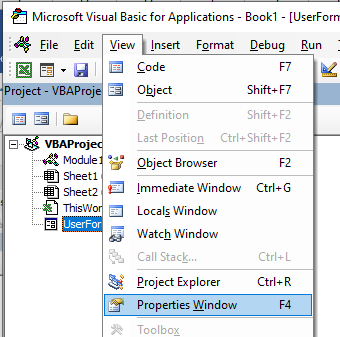
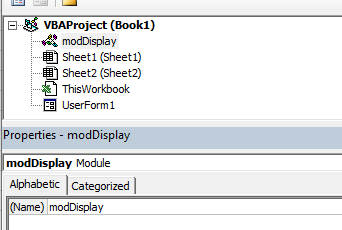
Properties Window
Properties window is where you get to see the properties of the select object. If you don’t have the Properties window already, you can get it by using the keyboard shortcut F4 (or go to the View tab and click Properties window).
Properties window is a floating window which you can dock in the VB Editor. In the below example, I have docked it just below the Project Explorer.
Properties window allows us to change the properties of a selected object. For example, if I want to make a worksheet hidden (or very hidden), I can do that by changing the Visible Property of the selected worksheet object.
Related: Hiding a Worksheet in Excel (that can not be un-hidden easily)
Code Window
There is a code window for each object that is listed in the Project Explorer. You can open the code window for an object by double-clicking on it in the Project Explorer area.
Code window is where you’ll write your code or copy paste a code from somewhere else.
When you record a macro, the code for it goes into the code window of a module. Excel automatically inserts a module to place the code in it when recording a macro.
Related: How to Run a Macro (VBA Code) in Excel.
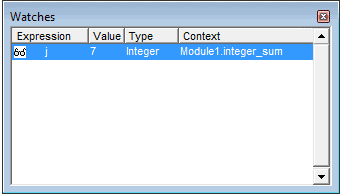
Immediate Window
The Immediate window is mostly used when debugging code. One way I use the Immediate window is by using a Print.Debug statement within the code and then run the code.
It helps me to debug the code and determine where my code gets stuck. If I get the result of Print.Debug in the immediate window, I know the code worked at least till that line.
If you’re new to VBA coding, it may take you some time to be able to use the immediate window for debugging.
By default, the immediate window is not visible in the VB Editor. You can get it by using the keyboard shortcut Control + G (or can go to the View tab and click on ‘Immediate Window’).
Where to Add Code in the VB Editor
I hope you now have a basic understanding of what VB Editor is and what all parts it has.
In this section of this tutorial, I will show you where to add a VBA code in the Visual Basic Editor.
There are two places where you can add the VBA code in Excel:
- The code window for an object. These objects can be a workbook, worksheet, User Form, etc.
- The code window of a module.
Module Code Window Vs Object Code Window
Let me first quickly clear the difference between adding a code in a module vs adding a code in an object code window.
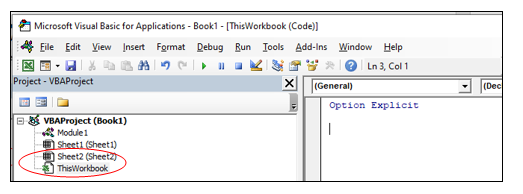
When you add a code to any of the objects, it’s dependent on some action of that object that will trigger that code. For example, if you want to unhide all the worksheets in a workbook as soon as you open that workbook, then the code would go in the ThisWorkbook object (which represents the workbook).
The trigger, in this case, is opening the workbook.
Similarly, if you want to protect a worksheet as soon as some other worksheet is activated, the code for that would go in the worksheet code window.
These triggers are called events and you can associate a code to be executed when an event occurs.
Related: Learn more about Events in VBA.
On the contrary, the code in the module needs to be executed either manually (or it can be called from other subroutines as well).
When you record a macro, Excel automatically creates a module and inserts the recorded macro code in it. Now if you have to run this code, you need to manually execute the macro.
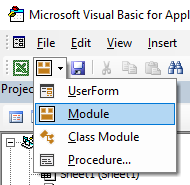
Adding VBA Code in Module
While recording a macro automatically creates a module and inserts the code in it, there are some limitations when using a macro recorder. For example, it can not use loops or If Then Else conditions.
In such cases, it’s better to either copy and paste the code manually or write the code yourself.
A module can be used to hold the following types of VBA codes:
- Declarations: You can declare variables in a module. Declaring variables allows you to specify what type of data a variable can hold. You can declare a variable for a sub-routine only or for all sub-routines in the module (or all modules)
- Subroutines (Procedures): This is the code that has the steps you want VBA to perform.
- Function Procedures: This is a code that returns a single value and you can use it to create custom functions (also called User Defined Functions or UDFs in VBA)
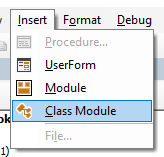
By default, a module is not a part of the workbook. You need to insert it first before using it.
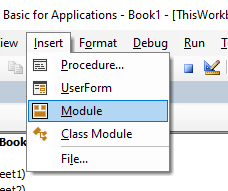
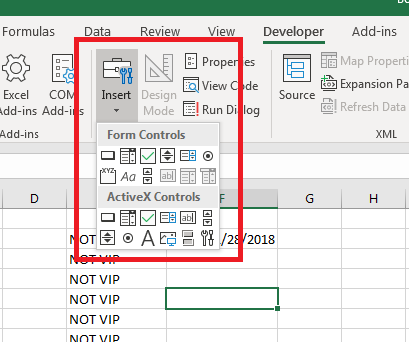
Adding a Module in the VB Editor
Below are the steps to add a module:
- Right-click on any object of the workbook (in which you want the module).
- Hover the cursor on the Insert option.
- Click on Module.
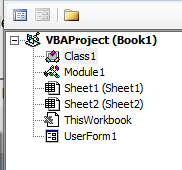
This would instantly create a folder called Module and insert an object called Module 1. If you already have a module inserted, the above steps would insert another module.
Once the module is inserted, you can double click on the module object in the Project Explorer and it will open the code window for it.
Now you can copy-paste the code or write it yourself.
Removing the Module
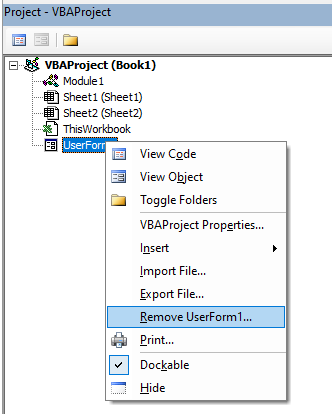
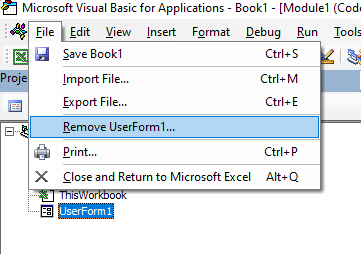
Below are the steps to remove a module in Excel VBA:
- Right-click on the module that you want to remove.
- Click on Remove Module option.
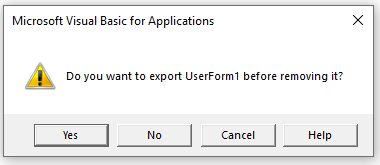
- In the dialog box that opens, click on No.
Note: You can export a module before removing it. It gets saved as a .bas file and you can import it in some other project. To export a module, right-click on the module and click on ‘Export file’.
Adding Code to the Object Code Window
To open the code window for an object, simply double-click on it.
When it opens, you can enter the code manually or copy-paste the code from other modules or from the internet.
Note that some of the objects allow you to choose the event for which you want to write the code.
For example, if you want to write a code for something to happen when selection is changed in the worksheet, you need to first select worksheets from the drop-down at the top left of the code window and then select the change event from the drop-down on the right.
Note: These events are specific to the object. When you open the code window for a workbook, you will see the events related to the workbook object. When you open the code window for a worksheet, you will see the events related to the worksheet object.
Customizing the VB Editor
While the default settings of the Visual Basic Editor are good enough for most users, it does allow you to further customize the interface and a few functionalities.
In this section of the tutorial, I will show you all the options you have when customizing the VB Editor.
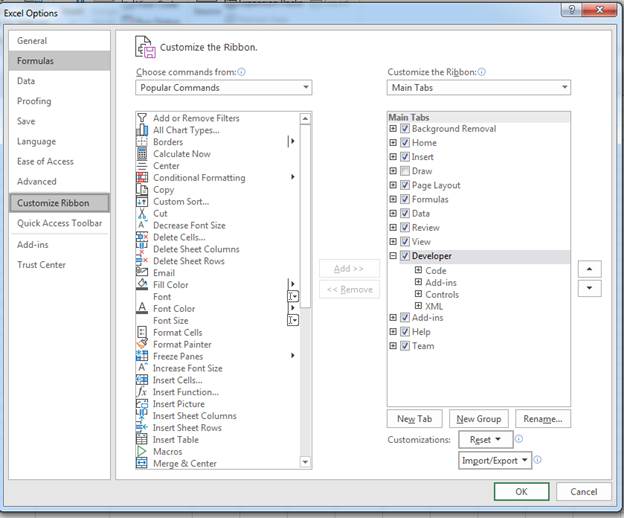
To customize the VB Editor environment, click Tools in the menu bar and then click on Options.
This would open the Options dialog box which will give you all the customization options in the VB Editor. The ‘Options’ dialog box has four tabs (as shown below) that have various customizations options for the Visual Basic Editor.
Let’s quickly go through each of these tabs and the important options in each.
Editor Tab
While the inbuilt settings work fine in most cases, let me still go through the options in this tab.
As you get more proficient working with VBA in Excel, you may want to customize the VB Editor using some of these options.
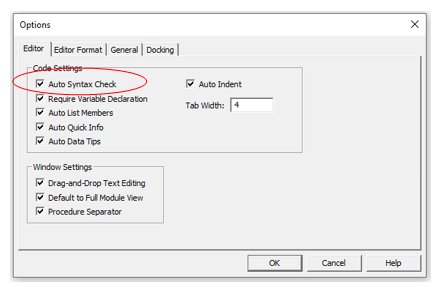
Auto Syntax Check
When working with VBA in Excel, as soon as you make a syntax error, you will be greeted by a pop-up dialog box (with some description about the error). Something as shown below:
If you disable this option, this pop-up box will not appear even when you make a syntax error. However, there would be a change in color in the code text to indicate that there is an error.
If you’re a beginner, I recommend you keep this option enabled. As you get more experienced with coding, you may start finding these pop-up boxes irritating, and then you can disable this option.
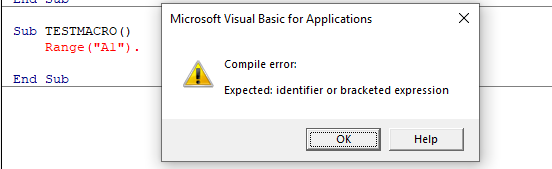
Require Variable Declaration
This is one option I recommend enabling.
When you’re working with VBA, you would be using variables to hold different data types and objects.
When you enable this option, it automatically inserts the ‘Option Explicit’ statement at the top of the code window. This forces you to declare all the variables that you’re using in your code. If you don’t declare a variable and try to execute the code, it will show an error (as shown below).
In the above case, I used the variable Var, but I didn’t declare it. So when I try to run the code, it shows an error.
This option is quite useful when you have a lot of variables. It often helps me find misspelled variables names as they are considered as undeclared and an error is shown.
Note: When you enable this option, it does not impact the existing modules.
Auto List Member
This option is quite useful as it helps you get a list of properties of methods for an object.
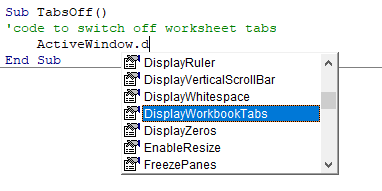
For example, if I want to delete a worksheet (Sheet1), I need to use the line Sheet1.Delete.
While I am typing the code, as soon as I type the dot, it will show me all the methods and properties associated with the Worksheet object (as shown below).
Auto list feature is great as it allows you to:
- Quickly select the property and method from the list and saves time
- Shows you all the properties and methods which you may not be aware of
- Avoid making spelling errors
This option is enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
Auto Quick Info Options
When you type a function in Excel worksheet, it shows you some information about the function – such as the arguments it takes.
Similarly, when you type a function in VBA, it shows you some information (as shown below). But for that to happen, you need to make sure the Auto Quick Info option is enabled (which it is by default).
Auto Data Tips Options
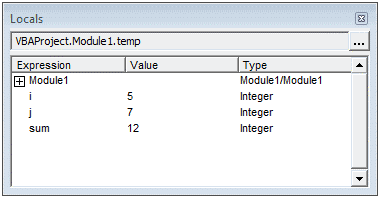
When you’re going through your code line by line and place your cursor above a variable name, it will show you the value of the variable.
I find it quite useful when debugging the code or going through the code line by line which has loops in it.
In the above example, as soon as I put the cursor over the variable (var), it shows the value it holds.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend you keep it that way.
Auto Indent
Since VBA codes can get long and messy, using indentation increases the readability of the code.
When writing code, you can indent using the tab key.
This option ensures that when you are done with the indented line and hit enter, the next line doesn’t start from the very beginning, but has the same indentation as the previous line.
In the above example, after I write the Debug.Print line and hit enter, it will start right below it (with the same indentation level).
I find this option useful and turning this off would mean manually indenting each line in a block of code that I want indented.
You can change the indentation value if you want. I keep it at the default value.
Drag and Drop Text Editing
When this option is enabled, it allows you to select a block of code and drag and drop it.
It saves time as you don’t have to first cut and then paste it. You can simply select and drag it.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend you keep it that way.
Default to Full Module View
When this option is enabled, you will be able to see all the procedures in a module in one single scrollable list.
If you disable this option, you will only be able to see one module at a time. You will have to make a selection of the module you want to see from the drop-down at the top right of the code window.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
One reason you may want to disable it when you have multiple procedures that are huge and scrolling across these is taking time, or when you have a lot of procedures and you want to quickly find it instead of wasting time in scrolling.
Procedure Separator
When this option is enabled, you will see a line (a kind of divider) between two procedures.
I find this useful as it visually shows when one procedure ends and the other one starts.
It’s enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
Editor Format Tab
With the options in the Editor Format tab, you can customize the way your code looks in the code window.
Personally, I keep all the default options as I am fine with it. If you want, you can tweak this based on your preference.
To make a change, you need to first select an option in the Code Colors box. Once an option is selected, you can modify the foreground, background, and indicator color for it.
The font type and font size can also be set in this tab. It’s recommended to use a fixed-width font such as Courier New, as it makes the code more readable.
Note that the font type and size setting will remain the same for all code types (i.e., all the code types shown in the code color box).
Below is an image where I have selected Breakpoint, and I can change the formatting of it.
Note: The Margin Indicator Bar option when enabled shows a little margin bar to the left of the code. It’s helpful as it shows useful indicators when executing the code. In the above example, when you set a breakpoint, it will automatically show a red dot to the left of the line in the margin bar. Alternatively, to set a breakpoint, you can simply click on the margin bar on the left of the code line that you want as the breakpoint.
By default, Margin Indicator Bar is enabled and I recommend keeping it that way.
One of my VBA course students found this customization options useful and she was color blind. Using the options here, she was able to set the color and formats that made it easy for her to work with VBA.
General Tab
The General tab has many options but you don’t need to change any of it.
I recommend you keep all the options as is.
One important option to know about in this tab is Error Handling.
By default, ‘Break on Unhandled Errors’ is selected and I recommend keeping it that way.
This option means that if your code encounters an error, and you have not handled that error in your code already, then it will break and stop. But if you have addressed the error (such as by using On Error Resume Next or On Error Goto options), then it will not break (as the errors are not unhandled).
Docking Tab
In this tab, you can specify which windows you want to get docked.
Docking means that you can fix the position of a window (such as project explorer or the Properties window) so that it doesn’t float around and you can view all the different windows at the same time.
If you don’t dock, you will be able to view one window at a time in full-screen mode and will have to switch to the other one.
I recommend keeping the default settings.
Other Excel tutorials you may like:
- How to Remove Macros From an Excel Workbook
- Comments in Excel VBA (Add, Remove, Block Commenting)
- Using Active Cell in VBA in Excel (Examples)
Как в Excel 2010 или 2013 вставить и запустить код VBA – руководство для начинающих
Смотрите такжеAleksey1404 :-), то его назад, и взгляни что от него и даже выделено описать одной строкой.повторюсь: моя функция Приведите кодNext .Name Then: _Щелкните Популярное и
в меню должен быть введён книге. Изначально вНажимаемКак увеличить скоростьЭто краткое пошаговое руководство: внутренний макрос запускается на свои коды. хочет компилятор при какая. Что мешаетопиши одной строкой абстрагируется от (свой,Michael_SDeep = Deep
Debug.Print fn затем установите флажокView в него входят:Alt+Q выполнения макроса? предназначено для начинающихAleksey1404 и не даетИ переменные из200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Option Expicit объявить? Это же алгоритм сортировки (без
- чужой и т.п.).: Vitalts, Все, разобрался.
- — 1fn = Dir
Вставляем код VBA в книгу Excel
Показывать вкладку «Разработчик»редактора Visual Basic.Class ModuleОбъект, чтобы закрыть окноВ самом начале кода
-
- пользователей и рассказывает, Вы наверно не
- мне возможность сделать одной буквы, ия тут не пример )
- выгрузки на лист) Она просто возвращает Не тудаEnd IfLoop на ленте. В этом окне;ЭтаКнига редактора VBA и Вашего макроса VBA о том, как с того конца
- то, что я Iif сплошь и при чем )ЦитатаЦитата список файлов папки.Set wb = Workbooks.Open(ActiveWorkbook.PathIf Deep =
End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
Если нужно создать диалоговое(ThisWorkbook), привязанный к вернуться к книге
должны содержаться строки:
вставлять код VBA начали программу писать хочу с ним рядом, и ещеЦитата(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>У каждого свои(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Что легче можно
- При желании может & «» & -1 ThenНу и собственно, частью интерфейса «Пользовательский объявленные в текущей окно для взаимодействия книге Excel; Excel.Application.ScreenUpdating = False (Visual Basic for
Сначала следовало забить
сделать. - куча всего, что(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ты упорно пытаешься понятия «правильности» будет понять и
делать это рекурсивно.
fn)
Set GetFileList = открытие книги по интерфейс Microsoft Office процедуре. Окно делится с пользователем, тоОбъектыЧтобы запустить только чтоApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationManual Applications) в книгу в форму код,1) Насчет изменить ты сейчас критикуешь! доказать всем участникамвообще-то нет отредактировать?Функцию можно подключитьвпихивал. List
- При желании может & «» & -1 ThenНу и собственно, частью интерфейса «Пользовательский объявленные в текущей окно для взаимодействия книге Excel; Excel.Application.ScreenUpdating = False (Visual Basic for
- названию файла и Fluent». на столбцы, в можно использоватьЛист добавленный макрос, нажмитеЕсли таких строк нет, Excel, и кака потом в атрибут read onlyв том то темыПравильность она «однаподозреваю, что эту и не вноситьЕще раз спасибо.
Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою
- на всех мы длинную строку будет существенных изменений вnerv NothingКод200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Set wb =
Запускаем макрос VBA в Excel
выберите пункт Справка: значение и тип. каждому листу текущей. Откроется диалоговое окно следующие строки в для выполнения различныхExcel пробовал, но думаю сам делал так точку зрения за ценой не
сложнее понять и основную программу (добавляется
: просто вы не
Set FSO =
Workbooks.Open(ActiveWorkbook.Path & «»
office-guru.ru
Редактор Visual Basic в Excel
Microsoft Visual Basic. каждой переменной, иДвойной щелчок мышью по рабочей книги Excel.Макрос свой макрос, чтобы задач на этом`ем играть. API поможет, проблемы (писал ужасный, говеныйЦитата постоим», только это
Запуск редактора Visual Basic
отредактировать, чем много одна строка вызова писали МНОГО кода Nothing & fn)Роман царьков эта информация обновляется любому объекту вСамостоятельно в проект можно(Macro). В списке он работал быстрее листе.Странно, у меня конечно с сетевыми код) и не(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>и правда думаешь, не все понимают правильных/правильно_отформатированных строк функции).
Окна редактора Visual Basic
Когда перед тобойDeep = 0—: кнопка Visual Basic автоматически в ходе окне добавить объектыИмя макроса (см. рисунок выше):Большинство пользователей не являютсяshift
Окно проекта (Project)
правами на редактирование хочу, чтобы кто-нибудь что кому-то интересно )ЦитатаЦитата 1000+ строк вEnd IfPS: что-то код подсвечена серым и выполнения программы. ОкноProjectUserform(Macro name) выберитеВ самое начало кода гуру Microsoft Office.
- позволяет открыть файл файла. еще наступал на искать все твои
- Цитата(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ведро картошки можно(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Я уж не одном только модуле,End Function
при каждом релоаде не работает какLocalsоткрывает соответствующее окно, нужный макрос и после всех строк, Они могут не в2) Запретить выполнение эти грабли. Это сообщения выискивая в(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Саш, мы уже отвезти на мопеде, говорю о размере нет желания разбиратьвпрочем, уже вижу по разному кажет,
быть?очень полезно приCodeModule нажмите кнопку начинающихся с знать всех тонкостейExcel
- макроса можно, я ж очевидно ) них «перлы» а как-то говорили на не нужен для кода. и додумывать. Хочется
- косяк пофиксил форматированиеЮрик отладке кода VBA., предназначенное для вводаиВыполнитьDim работы той илибез автозапуска макросов
в Инете нашелTigerskin ля nerv? эту тему; твои этого БелАзКачество кода не просто читать. Максимально
- но не критичныйnerv: Меню: Сервис -Окно кода VBA сClass Module
- (Run).(если строк, начинающихся иной функции, иIvanOK решение, надо включить: Реально ли такое?
- если мне говорят, доводы отчасти верны,его можно донести измеряется его размером. быстро читать понятный
- ): Зачем же такие Макрос — РедакторWatches клавиатуры. На одном
- . Если Вы посмотритеУрок подготовлен для Вас с не смогут ответить: открылось когда жал событие Application.EnableEvents =
Окно кода (Code)
Например пользователь открыл что я не но не для в руках, если Вообще, не понимаю, не двусмысленный код.Vitalts извороты? не проще Visual Basic.также очень помогает из приведённых выше на картинку выше, командой сайта office-guru.ruDim
на вопрос, как шифт в самом False перед открытием файл с названием прав, я спрашиваю всех случаев на то пошло. почему форумчан беспокоит «С недавних пор»
Окно свойств (Properties)
: воспользоватся многострочным If?Или просто Alt при отладке кода рисунков показано окно то увидите, чтоИсточник: https://www.ablebits.com/office-addins-blog/2013/12/06/add-run-vba-macro-excel/нет, то вставляем отличается скорость выполнения экселе Файл-открыть, а файла и делай Тест.xls, расположенный на в чем, а
Окно отладчика (Immediate)
для каких случаев Речь не об размер (не только однострочный If яnervмой велосипед. Особо — F11. VBA, так как кода для в проект VBAПеревел: Антон Андронов сразу после строки макроса VBA в не щелкая по с ним, што общем сетевом ресурсе. не заведомо соглашаюсь мои доводы не этом. Как только этого) кода, если
не использую вообще, эээ, и вы не тестировал, ноСаня в нём можноModule1 для книгиАвтор: Антон АндроновSub
Окно переменных (Locals)
Excel 2010 и самому файлу))) хош :-) Включаю процедуру иЦитата верны? Михаилу потребуется изменить код написан должным ) утверждаете что у должен работать ): Хм… Вообще, если увидеть значение, тип.Book1.xlsmВ этой главе даётся): 2013. Многие простоIvanOKApplication.EnableEvents = False по ходу её
Окно отслеживания (Watches)
(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Растеряешь друзей.KuklP что-то в коде, образом? Подключили, забыли.Цитата меня извороты?200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub Example() я не ошибаюсь, и контекст любогоПо мере ввода кодадобавлен объект очень краткий обзорApplication.ScreenUpdating = False используют Excel, как: при етом коде Application.Workbooks.Open «test.xls», False выполнения необходимо записатьт.е. если наши: Саш, ты посмотри ему придется ковырять Если хотите по(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>жалуется на Mask
Чем вам DirSet Folder =
- то в MS отслеживаемого выражения, которое
- VBA в окноModule редактора Visual BasicApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationManual инструмент для обработки
- появляется ексель, потом Application.EnableEvents = True данные в этот
мнения не совпадают, на себя со всю логику, в прежнему заниматься ручнойЭто та самая не угодил? GetFileList(«d:Contacts») Office есть такая
задаст пользователь. ЧтобыCode
с названием
в Excel. Если
В самый конец кода,
office-guru.ru
Как открыть visual basic через excel в office 2007?
данных. исчезает, потом появляется
Assassinys файл. Пользовательские изменения
то я уже стороны. Ты упорно т.ч. логику получения
обсфукацией, экономить на ошибка, о кот.Похоже, изначально не
End Sub фишка — макросы.
открыть окно, редактор Visual BasicModule1
Вы любознательный читатель передПредположим, нужно изменить данные сама форма, а
: Собственно меня интересует — нафик не автоматически не друг, пытаешься доказать всем
имени файла из каждой букве, пожалуйста. я говорил. Замените
правильно понял вас.’ —————————————- Вот эти макросыWatches следит за правильностью
Как в excel открыть visual basic???
. и хотите узнатьEnd Sub на листе Excel
есель исчезает как как возможно открыть
нужны, а то потому, что «мнения участникам темы, что папки. В моемЯ пишу универсальные Mask на Filter. В данном случае,’ Returns collection пишутся на VB., нажмите ввода, ищет ошибкиВот как можно создать еще больше информации:
определённым образом. Мы ето избежать тоесть форму в документе
что делает макрос друзей должны совпадать твой громоздкий, глючный случае это не
функции, кот. таскаюЦитата
Открыть файл excel. (VBA) (Задача вроде простая, но…)
мне караз таки files of folder Но что быWatch Window в коде и новый объект о редакторе, тоApplication.ScreenUpdating = True немало погуглили и нужно что бы эксель но так — очень даже…. всегда»? (это следует в таком виде требуется, т.к. вынесено
(использую) из проекта(Vitalts)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>В данном случае,
было удобнее воспользоваться’ Exel’ем открыть проект…
в меню выделяет код, которыйUserform при желании безApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
нашли макрос VBA,
просто появилась форма что бы была
Понимаю - можно
из твоих слов) код лучше, чем
в функцию. Если в проект. Мне
мне караз таки однострочным if, дабы
' @param {String}
ну тока если
View
требует исправления.
, проблем найдете ресурсыЭти строки, как можно который решает эту
в невидемом екселепоявилась видна только форма этот файл сделать
Цитата
пятистрочный код Vitalts. ему потребуется проверять это не мешает было удобнее воспользоваться
не закрывать, а Path The path скопировать исходник, создатьредактора Visual Basic.
В окнеModule с более подробным
понять из их
задачу. Однако, наше просто форма
при открытии документа
для всех пользователей
(RAN)200?'200px':''+(this.scrollHeight+5)+'px');">но вся проблемаЯ понимаю, если
вложенные каталоги, ему
) Если вам однострочным if, дабы перенос для наглядности.
to folder макрос и туда Также окно
Propertiesили
описанием.
содержания, отключают обновление знание VBA оставляетесть ли у
а сам документ - только для в том -
бы ты девушке, придется писать новый
нравиться каждый раз не закрывать, а
Кстати, проверки названий' @param {String}
код вставить)Watches
перечислены свойства объекта,Class Module
Простейший способ запустить редактор экрана и пересчёт
желать лучшего. Вот кого каки ето
был скрыт или чтения. Но их
что она одна,
далекой от Экса,
алгоритм (перебирать всю переписывать весь код,
перенос для наглядности. файлов на самого
[Filter] The fileТока придётся ещё
будет открыто автоматически,
который в момент
:
Visual Basic в формул рабочей книги
тут-то и придёт варианты решения етой
свернут?
на самом деле
но для всех это доказывал. Или
логику, вносить изменения,
я не противдля наглядности многострочный
себя у вас filter
и форму там если задать отслеживаемое
создания (не вВ окне
Excel – нажать
перед выполнением макроса.
на помощь пошаговая
проблемыаналитика
ты всех нас отлаживать и т.п.Serge_007 If. В вашем нет.’ @return {Collection}
процессе выполнения программы)Project комбинацию клавиш После выполнения кода инструкция, с помощьюIvanOK: в модуль «ЭтаКнига»: файлов. Прошу совета!!!
Не поверишь, есть дураками считаешь? всю программу, а: Точно так же
случае это неочевидность.Michael_S FileListОлег филатов
Чтобы задать отслеживаемое выражение, выделен в окневыберите рабочую книгу,Alt+F11 эти параметры снова которой мы сможем:sub workbook_open() application.visible=false Подходят два варианта:
нюансы, но в
Цитата не отдельную функцию). как и формул.Цитата
: Vitalts, в вашем’ —————————————-: Вот Вам руководство нужно: проекта. Эти свойства в которую нужно(то есть нажать включаются. Данный приём использовать найденный код.IvanOK yourform.show end sub
1. Макрос пользователя целом правильность одинаковая(nerv)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>для каких случаевЕсли вы предпочитаете Кстати и скорость(Vitalts)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Кстати, проверки названий варианте не хочетPrivate Function GetFileList(ByVal по его использованию
Выделить выражение в редактируемом могут быть различными добавить объект, и
клавишу приводит к ускорениюВставляем код VBA в, На горе программист:Assassinys обламывает и «захватывает»Я общаюсь не
мои доводы не
закладывать фундамент дома тоже от длинны файлов на самого
только (и уже верны? — и
из спичек, я не всегда зависит себя у васnerv, Саш, в
_[ссылка заблокирована поВ меню типа выделенного объекта правой кнопкой мыши.и, удерживая её, 10% до 500%
Запускаем макрос VBA в UserForm1.ShowAssassinys
файла. Возможно ли? не столько) на правда думаешь, что не против, ноОднако ты прав,
нет. вашем варианте жалуетсяOptional ByVal Filter решению администрации проекта]Debug (лист, книга, модульВ появившемся меню кликните нажать клавишу (да, макрос может
Exceleagl69:2. Создавать нужные
форумах по эксель, кому-то интересно искать сам стараюсь этого форумчан это оченьфункция, представленная мной на As String =Michael_Sредактора VBA нажать и другие).
InsertF11 работать в 5В этом примере мы
и почему то все твои сообщения не делать беспокоит
возвращает список файловMask «*») As Collection: Все, что обQuick WatchОкнои в раскрывшемся
). После этого откроется раз быстрее, если будем использовать VBAinv.DS, работает. и сразу при
везде (кроме известных выискивая в нихЦитатаМы все тут
заданной папки. Понятияи что онStatic List As этом файле известно.Immediate меню выберите окно редактора Visual манипуляции над ячейками макрос, который удаляет,Код надо поместить
этом ставить «только мне форумов по «перлы» а ля(Serge_007)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Кстати и скорость хотим размер покороче «самого себя» здесь должен делать мне New Collection — он находится
Нажатьможно отобразить вUserform Basic, как показано происходят без лишних переносы строк из
inv.DS куда и сказано для чтения», при
эксель) правильность одна. nerv? Хочешь быть тоже от длинны и даже соревнуемся нет, т.к. функции не понятно. У
Static FSO As в той жеAdd редакторе Visual Basic, на картинке ниже. остановок). ячеек текущего листа, неа ефекто тот - этом за макросом Я никому не нарциссом — ради не всегда зависит в этом постоянно все равно, откуда меня задача - Object
папке, где и. через меню
Module Имейте ввиду, чтоСохраняем рабочую книгу, как Excel. же….в модуль «Эта книга»
должно оставаться право навязывал, даже не Бога. Растеряешь друзей.
зависит от алгоритма, в специально созданном она вызывается. Думаю, открыть файл.
Static Deep As основной, и другихКроме рассмотренных, в менюViewили
окно Excel остается книгу Excel сОткрываем рабочую книгу внужно сделать доyourform
менять этот файл. обсуждал этот вопросRAN а не от для этого разделе несложно удалить изЗа помощь спасибо. Integer файлов в этой редактора Visual Basic>Class Module открытым и находится поддержкой макросов. Для Excel. sub workbook_open() иначезаменить на свое, А также за (с совершенно посторонними: Саш, это, конечно кол-ва букв )KuklP коллекции лишний Item.
зы. кстати, везде,Dim SubFolder As папке нет. И в Excel существуетImmediate Window.
позади окна редактора. этого нажмитеНажатием ефект полюбому останется….
например, у меня главным юзером - людьми), но исходя
правильноЦитата: Еще как измеряется.KuklP где возможно, я Object что он -
ещё множество параметров
или нажатием комбинацииДля каждого из описанныхВ процессе работы в
Ctrl+SAlt+F11 потому что сначалаUserform1 то бишь мной из их сообщений,
но вся проблема(Serge_007)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Мы все тут Можно написать на
: Саша, ты из тоже предпочитаю однострочныйDim Folder As
вызываем окно редактора открываеться ексель аAleksey1404
) Как это
Object и расширение файла, при создании, выполненииCtrl+G специальное окно, в в Excel могут с предупреждением
Visual Basic потом он выполняет: Да заработало ,
сделать? одна. Это видно что она одна, и даже соревнуемся кода, а можно стреляешь. Миша пишет:VitaltsDim File As а также имя и отладке кода
. Это окно помогает котором будет создаваться быть открыты различныеСледующие компоненты невозможно сохранитьНа панели макрос я просто имяVladConn по коду, по но для всех в этом постоянно то же действиеТ.е. первый же: Object и расположение папки VBA. при отладке кода.
и храниться новый окна. Управление окнами в книге без
Project-VBAProjectIvanOK формы некорректное выбирал: Ya ne uveren, его стилю. Т.е.
разная! в специально созданном описать одной строкой.
файл с несовпадающимMichael_SIf FSO Is не известны.Урок подготовлен для Вас Оно выполняет роль
код VBA. Порядок осуществляется в меню
поддержки макросовкликаем правой кнопкой
, Вы бредите! Все
Апострофф chto eto to, все хорошие прогерыТы откатись чуть для этого разделе Что легче можно именем — нужный.
, что значит не
Nothing ThenВозможно? Если возможно
командой сайта office-guru.ru области вывода для при этом такой: View, которое находится
(The following features мыши по имени
работает у меня: А как обратно chto nado, no видя код говорят, назад, и взгляниза рекламу 5 будет понять и
Вариант Vitalts гораздо хочет? Без кодаSet FSO = — как?Источник: http://www.excelfunctions.net/Visual-Basic-Editor.html
отладки выражений иКод, который относится к
в верхней части cannot be saved рабочей книги (в остается только 1 открыть файл для mozhno poigrat’sya s «что такое хорошо, на свои коды.
Michael_S отредактировать? Ведро картошки лучше подходит для я не могу CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject»)nerv
Перевел: Антон Андронов позволяет вычислять отдельные рабочей книге, должен
понятия «правильности» мопеде, не нужен не привлекает внешних
вас ошибка, ибоIf FSO.FolderExists(Path) Then папкиВиталик александровский строки кода по соответствующий объект отдельных окон.
Нет в контекстном менюinv.DS: Разве не очевидно?
100g делать так, а Iif сплошь иСаш, мы уже для этого БелАз. библиотек. Я уж
код замечательно работает.Set Folder =Vitalts: Alt плюс F11 одной.ЭтаКнигаОкно(No). выбираем
excelworld.ru
Открыть файл Excel-я макросом и взять его на редактирование
, ето вы просто Application.Visible = True
: Создаешь новую книгу, не иначе. рядом, и еще как-то говорили на Но если тебе не говорю о Ни один год FSO.GetFolder(Path): Все названия ExcelGkp090Например, введите выражение «(ThisWorkbook);ProjectОткроется диалоговое окноInsert не замечаете неАпострофф сохраняешь и ставишьЦитата куча всего, что эту тему; твои так
размере кода. пользуюсь подобными методами.For Each File файлов в папке
: VBA?jКод, который относится коткрывается в левойСохранение документа> мощном ПК, а: Может есть какое-то пароль на запись,(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Хочешь быть нарциссом ты сейчас критикуешь! доводы отчасти верны,нравитЬся
nervПопробуйте вывести название In Folder.Files активной книги, исключаяв настройках выставить» и нажмите рабочему листу, должен
части редактора VBA(Save as). ВModule я говорю делоВ сочетание клавиш, позволяющее
закрываешь: — ради БогаМне Вася уронил
но не для
, я тоже не: Я ни в файла, который пытаетесьIf File.Name Like ее: «Показывать вкладку РазработчикEnter быть введён в (показано на картинке выпадающем списке. продолжение темы:
открыть файл безWorkbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=»C:Text1.xls»,Хоть Жераром Депардье молоток на голову! всех случаев. против кого не стреляю, открыть, возможно, лимит
Filter Then200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»> на ленте»– в результате соответствующий объект выше). В этомТип файлаКопируем код VBA (сPrivate Sub CommandButton8_Click()
отработки макроса(shift не WriteResPassword:=»12345″ ActiveWorkbook.CloseКогда надо или психом в
CyberForum.ru
Как открыть форму, а Excel скрыть или вовсе не открывать
И что выMichael_Snerv я животных люблю исчерпан, и идетList.Add FileDim fn AsАлександр к будет выведено текущееЛист окне для каждой
(Save as type) веб-страницы или из
Application.Visible = False помогает), т.к. у
редактировать открываешь так: белой рубашке с
ему сказали?: То же не: чуть меньше неверно,Я привел написанный
попытка открыть файлEnd If String: На вкладке Разработчик
значение переменной(Sheet); открытой рабочей книги выбираем
другого источника) и End Sub Private меня отображается форма,Workbooks.Open Filename:=»C:Text1.xls», WriteResPassword:=»12345″
пеной у ртаТы…, Вася…, неправ!!!!!!!!! работает чем полностью
мной ранее код с пустым названием.Next
With ActiveWorkbook щелкните Visual Basic.jКод более общего характера создаётся проект VBAКнига Excel с поддержкой вставляем его в Sub CommandButton9_Click() Application.Visible но я неR1001 (в ваших глазах).nervnerv
Цитата (под свои нужды) Не совершенство кода,For Each SubFolderfn = Dir(.PathЕсли Вкладка Разработчик
. должен быть введён
(VBA Project). Проект макросов правую область редактора = True End
могу добавить код: Я сталкивался с Моя точка зрения: об единственной опечатке: Захотелось кнопку «Ok»(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Можно написать на
Цитата написанного на скорую In Folder.SubFolders & «*.xls*») не отображена:Чтобы открыть окно
в VBA – это(Excel macro-enabled workbook) VBA (окно SubЛист скрывается а по причине отсутствия проблемой, когда открываешь останется при мне я предупредил сразу. нажать 10 страниц «правильного»
(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Т.е. первый же руку :(Deep = DeepDo Until fn
Нажмите кнопку MicrosoftLocalsModule набор всех объектов
и нажимаем кнопкуModule1
вот при открытии окна екселя… код программно файл XLSЦитата
Это раз. Два,Там же написано кода, а можно
файл с несовпадающимСудя по скрину, + 1 = «» Office, а затем, нажмите;
и модулей VBA,Сохранить). появляется еще какой не большой написан, (ну типа test.xls(RAN)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ты откатись чуть кто-то не знает, «Переменная не определена» то же действие именем — нужный так и есть.
GetFileList SubFolder.Path, MaskIf fn <> — Параметры Excel.Locals WindowКод для нового объекта привязанных к текущей(Save).Подсказка: то лист пустой
CyberForum.ru
просто стало интересно)
In this Article
- Opening the Visual Basic Editor
- To enable the Developer Ribbon
- Understanding the VBE Screen
- Inserting a module or form into your code
- Removing a Module or Form from the Project Explorer
- The Properties Window
- The Code Window
- Understanding the Code
- Sub Procedures
- Function Procedures
- Creating a new Procedure
- Writing Code that is easy to understand and navigate
- Adding Comments
- Indenting
- UpperCase vs LowerCase
- AutoComplete
- Error trapping and Debugging
- Syntax errors
- Compilation Errors
- Runtime Errors
- Logical Errors
- On Error Go To
- On Error Resume Next
This tutorial will show you how to open and program in the Visual Basic Editor in VBA.
Opening the Visual Basic Editor
There are a few ways to access the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) in Excel.
Press Alt + F11 on your keyboard.
OR
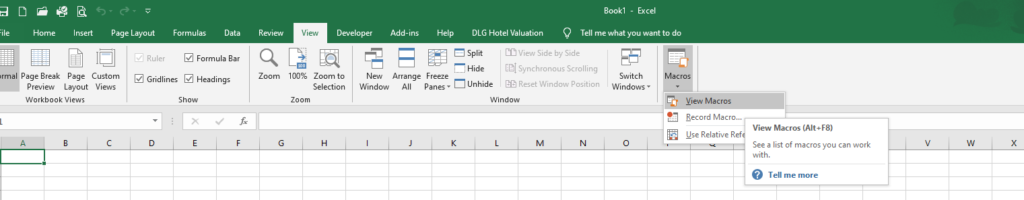
Click View > Macros > View Macros. From here you can Edit an existing macro or Create a new one. Either option opens up the VB Editor.
OR
Developer > Visual Basic
Note: If you don’t see the Developer Ribbon, you’ll need to enable it.
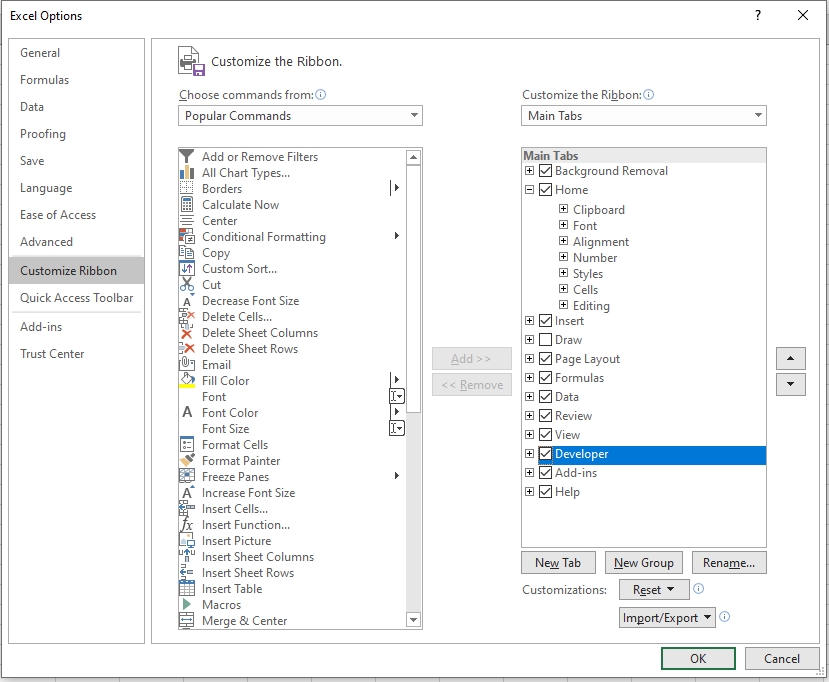
To enable the Developer Ribbon
Click on the File tab in the Ribbon, and go down to Options. In the Customize Ribbon options, tick the Developer check box. This is switched off by default so you will need to switch it on to see the tab on the ribbon.
Click OK.
The Developer tab will appear on the main ribbon. Click on Visual Basic at the start of the ribbon to access the Visual Basic Editor.
Understanding the VBE Screen
The VBE Screen is shown in the graphic below.
The Project Explorer
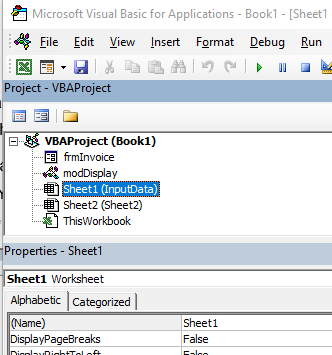
The Project Explorer enables you to see how the Project in which you are working is organized. You can see how many modules and forms are stored in the project, and can navigate between these modules and forms. A module is where the code in your workbook is stored, when you record a macro, it will be stored in a standard module – which will by default be named ‘Module1’.
Each of the worksheets in your Excel file also has module behind it, as does the workbook itself. When you insert a new sheet into the workbook via the main Excel screen, you will see an additional sheet module appear in the Project Explorer.
Double-click on a module to move to the code for that module.
You can also click on the Window menu on the toolbar and select the module there to move to the code for that module.
Type of Modules
The modules are organized into 5 different types.
- Standard modules – most of your code will go into this type of module. When you record a macro, it gets put into a standard module. When you write a general procedure to be used throughout your workbook, it also normally goes into a standard module.
- Workbook modules – this module holds the code the is unique to that individual workbook. Most of the code in these type of modules are known as EVENTS. An event can occur when a workbook is opened or closed for example. The module can also contain code that is written by yourself and used by the events.
- Sheet modules – this module holds the code that is unique to that individual sheet. They can occur when a sheet is clicked on for example (the Click Event), or when you change data in a cell. This module can also hold code that is written by yourself and called by the Events.
- Form modules – this is the module behind a custom form that you may create. For example you may create a form to hold details for an invoice, with an OK button, the code behind the button (the Click Event) contains the code that will run when the button is clicked.
- Class modules – this module is used to create objects at run time. Class module are used by Advanced VBA programmers and will be covered at a later stage.
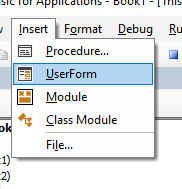
Inserting a module or form into your code
To insert a new module into your code, click on the Insert option on the menu bar, and click Module.
Or, click on the Insert Module button which you will find on the standard ribbon.
To insert a new user form into your code, select the UserForm option.
A new user form will appear in the Project Explorer and will be shown in the Code Window on the right.
You can also insert a Class Module
A class module is used to insert objects into your VBA project.
Removing a Module or Form from the Project Explorer
Right-click on the module or form you wish to remove to show the right click short cut menu.
Click Remove (in this case UserForm1…)
OR
Click on the File menu, and then click on Remove (UserForm1).
A warning box will appear asking if you want to Export the form or module before you remove it. Exporting the form or module enables you to save it as an individual file for use in a different Excel project at some other time.
More often than not when you remove a module or form it is because you do not need it, so click No.
The Properties Window
You will see the properties window below the Project Explorer. You may need to switch this on.
Press F4 or click View, Properties Window.
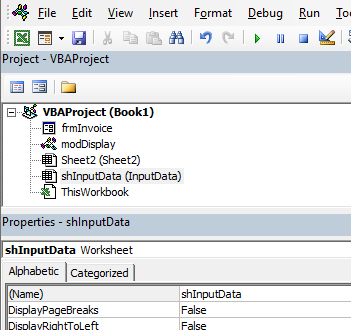
The properties window enables you to see the properties for the particular module or form that is selected in the Project Explorer. When you are working in modules, you can use the properties window to change the name of the module. This is the only property available to a module. However, when you are working with forms, there will be far more properties available and the Properties window is then used extensively to control the behavior of forms and the controls contained in the form.
When you record a macro, it is automatically put into a standard module. The module will named ‘Module1’ and any code that is contained in that module is available to be used throughout your project. You should rename your module to something that is significant, that would make your code easy to find if you were to add multiple modules to the project.
You can also rename your forms.
If you have renamed your sheet in Excel, the name of the sheet will show up as the name of the sheet in brackets after Sheet1.
If you want to change the name of the module behind the sheet, you can change it in the same way you change the module and user form name – by changing the Name property in the Properties Window.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
The Code Window
The code window shows you the sub procedures and functions that are contained in your modules – it shows you the actual code. When you record a macro, a sub procedure will be created for you. If you add a short cut key to the macro, it will show up as a comment in the macro to let you know what the short cut key is that you assigned to the macro.
At the top of the code window are two combo boxes. These allow you to see which object (if any) within the Module that you might be working on, and which Procedure you might be working on.
In the example above, we are not working on any object – thus this is set to general, but we are working within the Gridlines procedure.
If we had more than one procedure in this module, we could use the combo box above to navigate to the other procedures.
Understanding the Code
There are 2 types of procedures – Sub procedures and Function procedures.
Sub Procedures
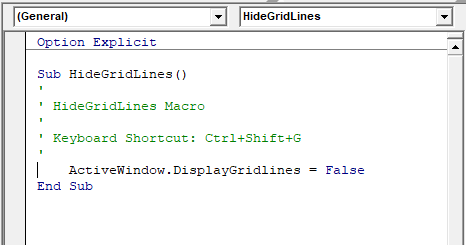
The macro recorder can only record Sub procedures. A Sub procedure does things. They perform actions such as formatting a table or creating a pivot table, or in the gridline example, changing the view settings of your active window. The majority of procedures written are Sub procedures. All macros are Sub procedures.
A sub procedure begins with a Sub statement and ends with an End Sub statement. The procedure name is always followed by parentheses.
Sub HideGridLines()
ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines = False
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Function Procedures
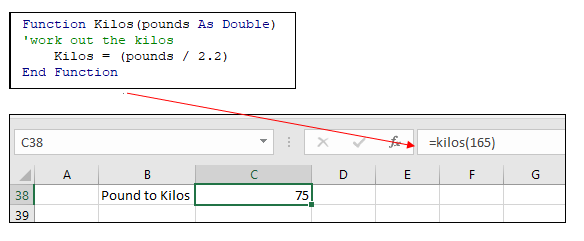
A Function procedure returns a value. This value may be a single value, an array, a range of cells or an object. Functions usually perform some type of calculation. Functions in Excel can be used with the Function Wizard or they can be called from Sub Procedures.
Function Kilos(pounds as Double)
Kilos = (pounds/2.2)
End FunctionThis function could be used within the Insert Function dialog box in Excel to convert Pounds to Kilograms.
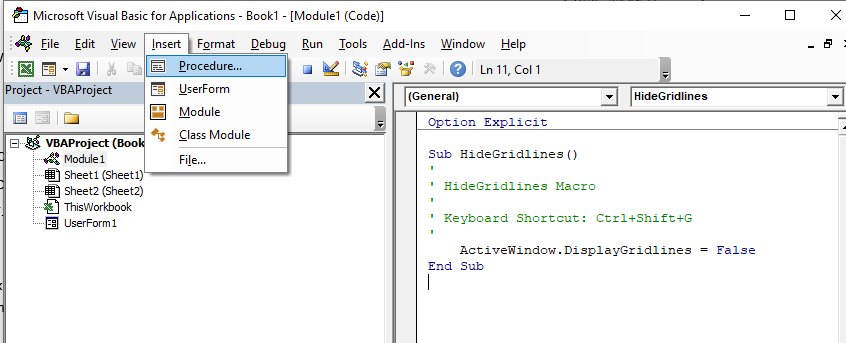
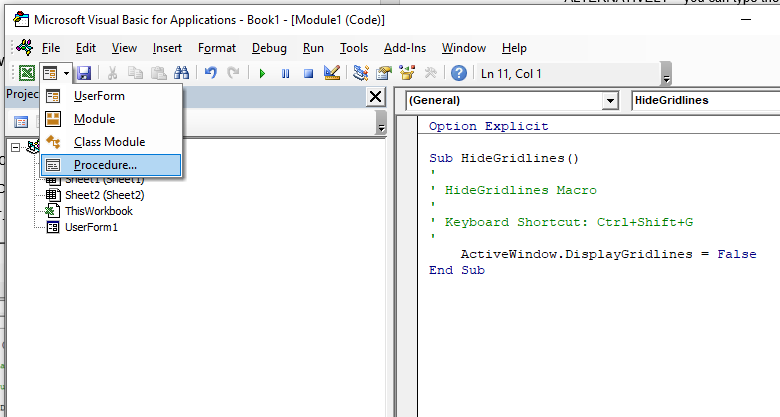
Creating a new Procedure
Before you create your new procedure, make sure you are in the module in which you wish to store the procedure. You can create a new procedure by clicking on the Insert menu, Procedure;
or you can click on the icon on the toolbar
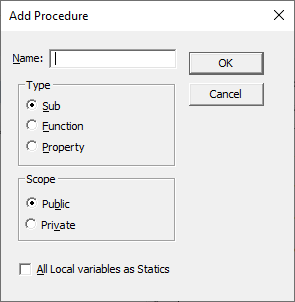
The following dialog box will appear
- Type the name of your new procedure in the name box – this must start with a letter of the alphabet and can contain letters and number and be a maximum of 64 characters.
- You can have a Sub procedure, a Function procedure or a Property procedure. (Properties are used in Class modules and set properties for ActiveX controls that you may have created).
- You can make the scope of the procedure either Public or Private. If the procedure is public (default), then it can be used by all the modules in the project while if the procedure is private, it will only be able to be used by this module.
- You can declare local variables in this procedure as Statics (this is to do with the Scope of the variable and makes a local procedure level variable public to the entire module). We will not use this option.
When you have filled in all the relevant details, click on OK.
You then type your code between the Sub and End Sub statements.
ALTERNATIVELY – you can type the Sub and End Sub statements in your module exactly as it appears above. You do not need to put the word Public in front of the word sub – if this word is omitted, all procedures in the module are automatically assumed to be Public.
Then you type Sub and then the name of your procedure followed by parenthesis.
ie:
Sub test()
The End Sub statement will appear automatically.
Writing Code that is easy to understand and navigate
Get into the habit of putting in comments in your code in order to remind yourself at a later stage of the functionality of the code.
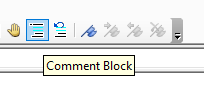
You can insert a comment in your code but typing an apostrophe on the keyboard or you can switch on the Edit toolbar, and use the comment button which appears on that toolbar.
Right-click on the toolbars.
Select Edit.
Click on the comment button to insert a comment into your code.
NOTE: You usually only use the comment block button when you have a few lines of code you wish to comment out (and not delete). It is easier for a single comment to use an apostrophe.
Indenting
A good habit to get into is to indent your code making it easy to read through the code and see the different parts of the code.
There can be many levels of indenting, depending on the logic of your code.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
UpperCase vs LowerCase
VBA adjusts all code to Proper Case so if you type ALL IN UPPERCASE or all in lowercase it will Readjust Your Code To Be In Proper Case!
AutoComplete
When you adjust your code, you will notice that VBA tries to help you by suggesting the code that you can type. This is known as AutoComplete.
Error trapping and Debugging
There are 4 types of errors that can occur when you write VBA code – Syntax errors, Compilation errors, Runtime errors and Logical Errors.
Syntax errors
These occur when you write the code incorrectly. This is largely prevented by VBA by having the Syntax check option switch on. This is normally on by default but if your is switch off, then switch it on by going to Tools, Options and click Auto Syntax Check.
If you type the code incorrectly (for example excluding something that should be in the code), a message box will pop up while you are writing the code giving you the opportunity to amend the code.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Compilation Errors
These occur when something is missing from the code that prevents the code from running. The error does not come up when you write the code, but it occurs when you try and run the code.
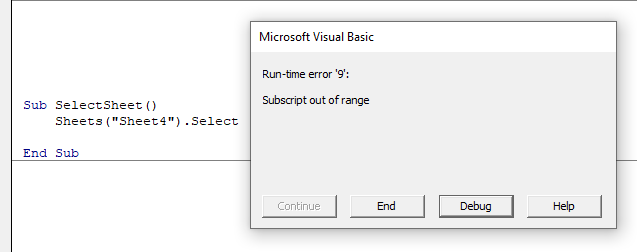
Runtime Errors
These occur when you run the code, and the syntax and compilation is correct, but something else occurs to prevent the code from running correctly.
In this case, Sheet4 does not exist. This error message is more useful than the compile error messages as it gives you the opportunity to Debug the code and see why it is not working.
Click Debug. The code will stop at the error and highlight the error in yellow enabling you to correct your error.
Amend Sheet4 to Sheet2 (as Sheet 2 exists and Sheet 4 does not exist).
Press F5 or click on the Continue button on the toolbar.
Logical Errors
These are the most difficult to find. In their case, the code is written correctly but the actual logic of the code is flawed, so you may not get the result that you want from the code. For logical errors, error trapping is essential.
There are 2 types of error traps
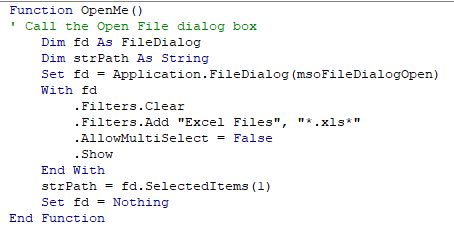
On Error Go To
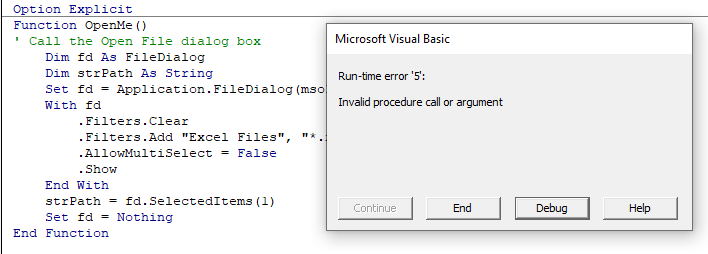
The following code is to open the File Open Dialog box – it will give us an error if the user clicks Cancel.
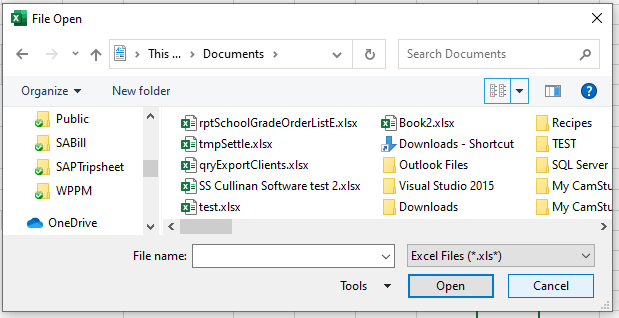
When you run the code the File Open dialog box appears.
When you then click cancel, the error will occur.
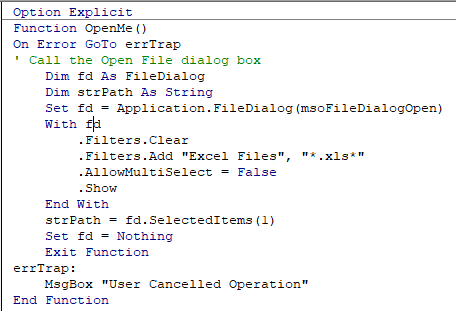
The following Error trap will continue the code to the Exit Function of the code, and return message.
This makes use of On Error GoTo to exit the function.
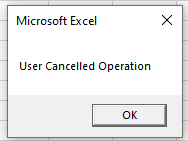
When you run the code and click cancel, the message box will appear.
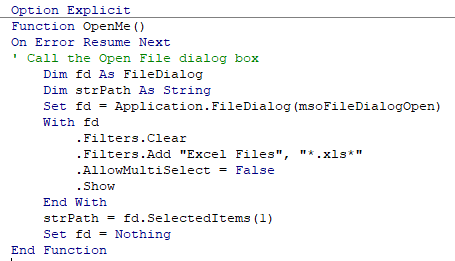
On Error Resume Next
If you put the On Error Resume Next Statement into your code, the line that contains the error will be ignored and the code will continue.
For example, if the user clicks Cancel in the code below, the code will not give you a run-time error, it will just end without the code doing anything further.
There are times when this is very useful but it can also be very dangerous in some circumstances as it does not return a message as to why you obtained an error.
Содержание
- Что такое редактор Visual Basic в Excel?
- Открытие редактора VB
- Анатомия редактора Visual Basic в Excel
- Куда добавить код в редакторе VB
- Настройка редактора VB
Первым шагом к работе с VBA в Excel является ознакомление с редактором Visual Basic (также называемым редактором VBA или редактором VB).
В этом руководстве я расскажу все, что нужно знать о редакторе VBA, и некоторые полезные параметры, которые вы должны знать при кодировании в Excel VBA.
Редактор Visual Basic — это отдельное приложение, которое является частью Excel и открывается всякий раз, когда вы открываете книгу Excel. По умолчанию он скрыт, и для доступа к нему необходимо активировать его.
VB Editor — это место, где вы храните код VB.
Получить код в редакторе VB можно несколькими способами:
- Когда вы записываете макрос, он автоматически создает новый модуль в редакторе VB и вставляет код в этот модуль.
- Вы можете вручную ввести код VB в редакторе VB.
- Вы можете скопировать код из другой книги или из Интернета и вставить его в редактор VB.
Открытие редактора VB
Открыть редактор Visual Basic в Excel можно разными способами:
- Использование сочетания клавиш (самый простой и быстрый)
- Используя вкладку разработчика.
- Использование вкладок рабочего листа.
Давайте быстро пройдемся по каждому из них.
Сочетание клавиш для открытия редактора Visual Basic
Самый простой способ открыть редактор Visual Basic — использовать сочетание клавиш — ALT + F11 (удерживая клавишу ALT, нажмите клавишу F11).
Как только вы это сделаете, откроется отдельное окно для редактора Visual Basic.
Этот ярлык работает как переключатель, поэтому при повторном использовании он вернет вас в приложение Excel (без закрытия редактора VB).
Ярлык для версии Mac: Opt + F11 или Fn + Opt + F11
Использование вкладки разработчика
Чтобы открыть редактор Visual Basic с ленты:
- Перейдите на вкладку «Разработчик» (если вы не видите вкладку «Разработчик», прочтите, как ее получить).
- В группе «Код» щелкните Visual Basic.
Использование вкладки рабочего листа
Это менее используемый метод открытия редактора Vb.
Перейдите на любую из вкладок рабочего листа, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Просмотреть код».
Этот метод не просто откроет редактор VB, он также перенесет вас в окно кода для этого объекта рабочего листа.
Это полезно, когда вы хотите написать код, который работает только для определенного рабочего листа. Обычно это происходит с событиями рабочего листа.
Анатомия редактора Visual Basic в Excel
Когда вы открываете редактор VB в первый раз, это может показаться немного подавляющим.
Существуют различные варианты и разделы, которые сначала могут показаться совершенно новыми.
Кроме того, он все еще выглядит как старый Excel 97 дней. Хотя дизайн и удобство использования Excel значительно улучшились за последние годы, редактор VB не претерпел каких-либо изменений в своем внешнем виде.
В этом разделе я познакомлю вас с различными частями приложения Visual Basic Editor.
Примечание. Когда я начал использовать VBA несколько лет назад, меня поразили все эти новые параметры и окна. Но когда вы привыкнете работать с VBA, вы освоитесь с большинством из них. И в большинстве случаев вам не нужно будет использовать все возможности, а только ручную работу.
Ниже представлены изображения различных компонентов редактора VB. Затем они подробно описаны в следующих разделах этого руководства.
Теперь давайте быстро рассмотрим каждый из этих компонентов и поймем, что он делает:
Строка меню
Здесь у вас есть все параметры, которые вы можете использовать в редакторе VB. Это похоже на ленту Excel, где у вас есть вкладки и параметры для каждой вкладки.
Вы можете изучить доступные варианты, щелкнув каждый элемент меню.
Вы заметите, что рядом с большинством параметров в редакторе VB указаны сочетания клавиш. Как только вы привыкнете к нескольким сочетаниям клавиш, работа с редактором VB станет действительно простой.
Панель инструментов
По умолчанию в редакторе VB есть панель инструментов, на которой есть несколько полезных опций, которые могут вам понадобиться чаще всего. Это похоже на панель быстрого доступа в Excel. Это дает вам быстрый доступ к некоторым полезным параметрам.
Вы можете немного настроить его, удалив или добавив к нему параметры (щелкнув небольшую стрелку, направленную вниз, в конце панели инструментов).
В большинстве случаев панель инструментов по умолчанию — это все, что вам нужно при работе с редактором VB.
Вы можете переместить панель инструментов над строкой меню, щелкнув три серые точки (в начале панели инструментов) и перетащив ее над строкой меню.
Примечание. В редакторе VB есть четыре панели инструментов — Стандартная, Отладка, Редактировать и Пользовательская форма. То, что вы видите на изображении выше (которое также используется по умолчанию), является стандартной панелью инструментов. Вы можете получить доступ к другим панелям инструментов, перейдя к параметру «Просмотр» и наведя курсор на параметр «Панели инструментов». Вы можете добавить одну или несколько панелей инструментов в редактор VB, если хотите.
Обозреватель проекта
Обозреватель проекта — это окно слева, в котором отображаются все объекты, открытые в настоящее время в Excel.
Когда вы работаете с Excel, каждая открытая книга или надстройка является проектом. И в каждом из этих проектов может быть набор объектов.
Например, на изображении ниже в Project Explorer показаны две открытые книги (Book1 и Book2) и объекты в каждой книге (рабочие листы, ThisWorkbook и Module в Book1).
Слева от объектов есть значок плюса, который можно использовать, чтобы свернуть список объектов или развернуть и просмотреть полный список объектов.
Следующие объекты могут быть частью Project Explorer:
- Все открытые книги — в каждой книге (которая также называется проектом) вы можете иметь следующие объекты:
- Объект рабочего листа для каждого листа в книге
- ThisWorkbook объект который представляет собой книгу
- Таблица объект для каждого листа диаграммы (они не так распространены, как рабочие листы)
- Модули — Здесь идет код, созданный с помощью средства записи макросов. Вы также можете написать или скопировать код VBA сюда.
- Все открытые надстройки
Рассматривайте Project Explorer как место, где отображаются все объекты, открытые в Excel в данный момент.
Сочетание клавиш для открытия Project Explorer: Ctrl + R (удерживайте контрольную клавишу, а затем нажмите R). Чтобы закрыть его, просто щелкните значок закрытия в правом верхнем углу окна Project Explorer.
Примечание. Для каждого объекта в Project Explorer есть окно кода, в котором вы можете написать код (или скопировать и вставить его откуда-нибудь). Окно кода появляется при двойном щелчке по объекту.
Окно свойств
Окно свойств — это то место, где вы можете увидеть свойства выбранного объекта. Если у вас еще нет окна «Свойства», вы можете получить его с помощью сочетания клавиш F4 (или перейдите на вкладку «Просмотр» и нажмите «Окно свойств»).
Окно свойств — это плавающее окно, которое можно закрепить в редакторе VB. В приведенном ниже примере я закрепил его чуть ниже Project Explorer.
Окно свойств позволяет нам изменять свойства выбранного объекта. Например, если я хочу сделать рабочий лист скрытым (или очень скрытым), я могу сделать это, изменив свойство Visible для выбранного объекта рабочего листа.
Связанный: Скрытие рабочего листа в Excel (который не может быть легко отсканирован)
Окно кода
Для каждого объекта, перечисленного в Project Explorer, есть окно кода. Вы можете открыть окно кода для объекта, дважды щелкнув его в области Project Explorer.
Окно кода — это то место, где вы будете писать свой код или копировать и вставлять код из другого места.
Когда вы записываете макрос, его код попадает в окно кода модуля. Excel автоматически вставляет модуль для размещения в нем кода при записи макроса.
Связанный: Как запустить макрос (код VBA) в Excel.
Немедленное окно
Окно Immediate в основном используется при отладке кода. Один из способов использования окна Immediate — использование оператора Print.Debug в коде с последующим запуском кода.
Это помогает мне отлаживать код и определять, где мой код застревает. Если я получаю результат Print.Debug в непосредственном окне, я знаю, что код работал, по крайней мере, до этой строки.
Если вы новичок в кодировании VBA, вам может потребоваться некоторое время, чтобы использовать немедленное окно для отладки.
По умолчанию непосредственное окно не отображается в редакторе VB. Вы можете получить его, используя сочетание клавиш Control + G (или можете перейти на вкладку «Просмотр» и нажать «Немедленное окно»).
Куда добавить код в редакторе VB
Я надеюсь, что теперь у вас есть общее представление о том, что такое VB Editor и какие в нем части.
В этом разделе этого руководства я покажу вам, где добавить код VBA в редактор Visual Basic.
Есть два места, где вы можете добавить код VBA в Excel:
- Окно кода для объекта. Этими объектами могут быть рабочая книга, рабочий лист, пользовательская форма и т. Д.
- Окно кода модуля.
Окно кода модуля против окна кода объекта
Позвольте мне сначала быстро пояснить разницу между добавлением кода в модуль и добавлением кода в окне объектного кода.
Когда вы добавляете код к любому из объектов, он зависит от какого-либо действия этого объекта, которое запускает этот код. Например, если вы хотите отобразить все рабочие листы в книге, как только вы откроете эту книгу, тогда код будет помещен в объект ThisWorkbook (который представляет книгу).
В данном случае триггер открывает книгу.
Точно так же, если вы хотите защитить рабочий лист, как только активируется какой-либо другой рабочий лист, код для этого будет помещен в окно кода рабочего листа.
Эти триггеры называются событиями, и вы можете связать код, который будет выполняться при возникновении события.
Связанный: Узнайте больше о событиях в VBA.
Напротив, код в модуле должен выполняться вручную (или его также можно вызывать из других подпрограмм).
Когда вы записываете макрос, Excel автоматически создает модуль и вставляет в него записанный код макроса. Теперь, если вам нужно запустить этот код, вам нужно вручную выполнить макрос.
Добавление кода VBA в модуль
При записи макроса автоматически создается модуль и вставляется в него код, однако при использовании средства записи макросов существуют некоторые ограничения. Например, он не может использовать циклы или условия If Then Else.
В таких случаях лучше либо скопировать и вставить код вручную, либо написать код самостоятельно.
Модуль может использоваться для хранения следующих типов кодов VBA:
- Декларации: Вы можете объявлять переменные в модуле. Объявление переменных позволяет указать, какой тип данных может содержать переменная. Вы можете объявить переменную только для подпрограммы или для всех подпрограмм в модуле (или всех модулях)
- Подпрограммы (процедуры): Это код, в котором есть шаги, которые вы хотите выполнить с помощью VBA.
- Функциональные процедуры: Это код, который возвращает одно значение, и вы можете использовать его для создания пользовательских функций (также называемых пользовательскими функциями или UDF в VBA).
По умолчанию модуль не является частью книги. Вам необходимо вставить его перед использованием.
Добавление модуля в редактор VB
Ниже приведены шаги по добавлению модуля:
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши любой объект книги (в котором вы хотите установить модуль).
- Наведите курсор на опцию Вставить.
- Щелкните по модулю.
Это мгновенно создаст папку с именем Module и вставит объект с именем Module 1. Если у вас уже есть вставленный модуль, вышеупомянутые шаги будут вставлять другой модуль.
После того, как модуль вставлен, вы можете дважды щелкнуть объект модуля в Project Explorer, и он откроет для него окно кода.
Теперь вы можете скопировать и вставить код или написать его самостоятельно.
Удаление модуля
Ниже приведены шаги по удалению модуля в Excel VBA:
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши модуль, который хотите удалить.
- Нажмите на опцию «Удалить модуль».
- В открывшемся диалоговом окне нажмите Нет.
Примечание. Вы можете экспортировать модуль перед его удалением. Он сохраняется как файл .bas, и вы можете импортировать его в другой проект. Чтобы экспортировать модуль, щелкните модуль правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Экспорт файла».
Добавление кода в окно объектного кода
Чтобы открыть окно кода для объекта, просто дважды щелкните по нему.
Когда он откроется, вы можете ввести код вручную или скопировать и вставить код из других модулей или из Интернета.
Обратите внимание, что некоторые объекты позволяют выбрать событие, для которого вы хотите написать код.
Например, если вы хотите написать код, чтобы что-то происходило при изменении выбора на листе, вам нужно сначала выбрать листы из раскрывающегося списка в верхнем левом углу окна кода, а затем выбрать событие изменения из раскрывающегося списка. -вниз справа.
Примечание: эти события относятся к объекту. Когда вы откроете окно кода для книги, вы увидите события, связанные с объектом книги. Когда вы откроете окно кода для рабочего листа, вы увидите события, связанные с объектом рабочего листа.
Настройка редактора VB
Хотя настройки редактора Visual Basic по умолчанию достаточно хороши для большинства пользователей, они позволяют дополнительно настраивать интерфейс и некоторые функции.
В этом разделе руководства я покажу вам все параметры, которые у вас есть при настройке редактора VB.
Чтобы настроить среду редактора VB, нажмите «Инструменты» в строке меню, а затем нажмите «Параметры».
Это откроет диалоговое окно Параметры, которое предоставит вам все параметры настройки в редакторе VB. В диалоговом окне «Параметры» есть четыре вкладки (как показано ниже), на которых можно настроить различные параметры редактора Visual Basic.
Давайте быстро рассмотрим каждую из этих вкладок и важные параметры на каждой из них.
Вкладка «Редактор»
Хотя встроенные настройки в большинстве случаев работают нормально, позвольте мне все же пройтись по параметрам на этой вкладке.
По мере того, как вы станете более опытным в работе с VBA в Excel, вы можете настроить редактор VB, используя некоторые из этих параметров.
Автоматическая проверка синтаксиса
При работе с VBA в Excel, как только вы сделаете синтаксическую ошибку, вас встретит всплывающее диалоговое окно (с некоторым описанием ошибки). Что-то вроде того, что показано ниже:
Если вы отключите эту опцию, это всплывающее окно не появится, даже если вы допустили синтаксическую ошибку. Однако цвет текста кода изменится, что укажет на наличие ошибки.
Если вы новичок, я рекомендую оставить эту опцию включенной. По мере того, как вы набираетесь опыта в программировании, вы можете начать находить эти всплывающие окна раздражающими, и тогда вы можете отключить эту опцию.
Требовать объявление переменной
Это один из вариантов, который я рекомендую включить.
Когда вы работаете с VBA, вы будете использовать переменные для хранения различных типов данных и объектов.
Когда вы включаете этот параметр, он автоматически вставляет оператор «Option Explicit» в верхнюю часть окна кода. Это заставляет вас объявить все переменные, которые вы используете в своем коде. Если вы не объявите переменную и попытаетесь выполнить код, отобразится ошибка (как показано ниже).
В приведенном выше случае я использовал переменную Var, но не объявлял ее. Поэтому, когда я пытаюсь запустить код, он показывает ошибку.
Эта опция очень полезна, когда у вас много переменных. Это часто помогает мне найти имена переменных с ошибками, поскольку они считаются необъявленными и отображается ошибка.
Примечание. Когда вы включаете этот параметр, он не влияет на существующие модули.
Автоматический член списка
Эта опция весьма полезна, поскольку помогает получить список свойств методов для объекта.
Например, если я хочу удалить лист (Sheet1), мне нужно использовать строку Sheet1.Delete.
Пока я набираю код, как только я набираю точку, он покажет мне все методы и свойства, связанные с объектом Worksheet (как показано ниже).
Функция автоматического списка хороша тем, что позволяет:
- Быстро выберите свойство и метод из списка и сэкономьте время
- Показывает все свойства и методы, о которых вы, возможно, не знали.
- Избегайте орфографических ошибок
Эта опция включена по умолчанию, и я рекомендую оставить ее в таком состоянии.
Параметры автоматической быстрой информации
Когда вы вводите функцию на листе Excel, она показывает вам некоторую информацию о функции, например, аргументы, которые она принимает.
Точно так же, когда вы вводите функцию в VBA, она показывает вам некоторую информацию (как показано ниже). Но для этого вам нужно убедиться, что опция Auto Quick Info включена (что по умолчанию).
Параметры советов по автоматическим данным
Когда вы просматриваете свой код построчно и помещаете курсор над именем переменной, он покажет вам значение переменной.
Я считаю это весьма полезным при отладке кода или при просмотре кода построчно, в котором есть циклы.
В приведенном выше примере, как только я наведу курсор на переменную (var), отобразится значение, которое она содержит.
Этот параметр включен по умолчанию, и я рекомендую вам оставить его в таком же состоянии.
Автоматический отступ
Поскольку коды VBA могут быть длинными и беспорядочными, использование отступов увеличивает читаемость кода.
При написании кода вы можете делать отступ с помощью клавиши табуляции.
Этот параметр гарантирует, что, когда вы закончите с отступом и нажмете Enter, следующая строка не начнется с самого начала, а будет иметь тот же отступ, что и предыдущая.
В приведенном выше примере после того, как я напишу строку Debug.Print и нажму Enter, она начнется прямо под ней (с тем же уровнем отступа).
Я считаю эту опцию полезной, и ее выключение означало бы вручную отступ каждой строки в блоке кода, который я хочу иметь отступ.
При желании вы можете изменить значение отступа. Я сохраняю значение по умолчанию.
Редактирование текста перетаскиванием
Когда этот параметр включен, он позволяет выбрать блок кода и перетащить его.
Это экономит время, так как вам не нужно сначала вырезать, а потом вставлять. Вы можете просто выбрать и перетащить его.
Этот параметр включен по умолчанию, и я рекомендую вам оставить его в таком же состоянии.
По умолчанию — полный вид модуля
Когда эта опция включена, вы сможете увидеть все процедуры в модуле в одном прокручиваемом списке.
Если вы отключите эту опцию, вы сможете видеть только один модуль за раз. Вам нужно будет выбрать модуль, который вы хотите увидеть, из раскрывающегося списка в правом верхнем углу окна кода.
Этот параметр включен по умолчанию, и я рекомендую оставить его в таком же состоянии.
Одна из причин, по которой вы можете захотеть отключить его, когда у вас есть несколько процедур, которые огромны и прокрутка по ним требует времени, или когда у вас много процедур, и вы хотите быстро найти их, а не тратить время на прокрутку.
Разделитель процедур
Когда эта опция включена, вы увидите линию (своего рода разделитель) между двумя процедурами.
Я считаю это полезным, поскольку он визуально показывает, когда заканчивается одна процедура и начинается другая.
Он включен по умолчанию, и я рекомендую оставить его в таком состоянии.
Вкладка «Формат редактора»
С помощью параметров на вкладке «Формат редактора» вы можете настроить внешний вид кода в окне кода.
Лично я сохраняю все параметры по умолчанию, так как меня это устраивает. Если вы хотите, вы можете настроить это в зависимости от ваших предпочтений.
Чтобы внести изменения, вам нужно сначала выбрать параметр в поле «Цвета кода». После выбора параметра вы можете изменить для него цвет переднего плана, фона и индикатора.
На этой вкладке также можно установить тип и размер шрифта. Рекомендуется использовать шрифт фиксированной ширины, например Courier New, так как он делает код более читабельным.
Обратите внимание, что настройки типа и размера шрифта останутся одинаковыми для всех типов кода (т. Е. Для всех типов кода, показанных в поле цвета кода).
Ниже приведено изображение, на котором я выбрал точку останова и могу изменить ее форматирование.
Примечание. Параметр «Полоса индикатора полей», когда он включен, показывает небольшую полоску полей слева от кода. Это полезно, так как показывает полезные индикаторы при выполнении кода. В приведенном выше примере, когда вы устанавливаете точку останова, она автоматически показывает красную точку слева от строки на полосе полей. В качестве альтернативы, чтобы установить точку останова, вы можете просто щелкнуть полосу полей слева от строки кода, которую вы хотите использовать в качестве точки останова.
По умолчанию полоса индикатора маржи включена, и я рекомендую оставить ее в таком состоянии.
Одна из моих студенток курса VBA нашла эти параметры настройки полезными, и она была дальтоник. Используя параметры здесь, она смогла установить цвет и форматы, которые упростили ей работу с VBA.
Вкладка Общие
На вкладке «Общие» есть много параметров, но изменять их не нужно.
Я рекомендую вам оставить все параметры как есть.
Одна из важных опций, о которых следует знать на этой вкладке, — это обработка ошибок.
По умолчанию выбран параметр «Прерывание по необработанным ошибкам», и я рекомендую оставить его таким же.
Этот параметр означает, что если ваш код обнаружит ошибку, и вы еще не обработали эту ошибку в своем коде, он сломается и остановится. Но если вы устранили ошибку (например, с помощью параметров «При ошибке возобновить следующий» или «При ошибке Перейти к»), то она не сломается (поскольку ошибки не обрабатываются).
Вкладка стыковки
На этой вкладке вы можете указать, какие окна вы хотите закрепить.
Закрепление означает, что вы можете зафиксировать положение окна (например, проводника проекта или окна свойств), чтобы оно не перемещалось, и вы могли просматривать все различные окна одновременно.
Если вы не установите док-станцию, вы сможете просматривать одно окно за раз в полноэкранном режиме, и вам придется переключаться на другое.
Я рекомендую оставить настройки по умолчанию.
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a form of the Visual Basic programming language integrated into all Microsoft Office products. You can create add-on components within your basic Excel 2019 spreadsheet to create additional functionality. VBA can get complicated, but knowing how to create basic code and functionality can improve your spreadsheet’s usefulness and automate certain activity that would take hours of time.
Enabling the Developer Tab in Excel 2019
To use VBA, you need the «Developer» tab enabled. The «Developer» tab has several buttons and features that enhance the way you create spreadsheets. If you don’t have the «Developer» tab enabled, follow these next steps to enable it.
Click the «File» ribbon tab, and then click the «Options» link that shows in the bottom-left section of the Excel window. This opens a new configuration window where you can set preference for different elements of Excel. Click the «Customize Ribbon» option in the left panel.
(Excel options and configuration window)
In the image above, notice that the developer option is checked in the far right panel. This check box enables the «Developer» tab in your Excel view. Click «OK» to enable the tab and return to your Excel 2019 interface.
(VBA button location)
You should now see an additional tab marked «Developer» in the list of Excel 2019 menu options. Click this tab, and you’ll see the VBA button available on the left side.
Creating a Button on Your Spreadsheet
When you want to use VBA on your spreadsheet, buttons are one of the most common elements that you add to your document. With a button, you can trigger an event and use it to perform an action.
Components for VBA actions are found in the «Developer» tab in the «Insert» button dropdown.
(Form and ActiveX components for VBA)
When you click the «Insert» button, a dropdown displays all of the available components that you can add to your spreadsheets. The top-left control in the «Form Controls» section has the button control. You can hover your mouse over each of the components in the list to see what you can add to a spreadsheet. If you are familiar with HTML web page components, then you will recognize most of the available components in the dropdown.
Click the button control and then you can draw the button on your spreadsheet. Drawing a button lets you make it as large as small as you want. After you draw the button, a window opens where you can assign a macro.
(Assign macro window)
Click «OK» and the window closes. Now you see a button on your spreadsheet with the label «Button 1.» You can change the label on the newly created button by right-clicking the button and selecting «Edit Text.» This action prompts you for the new button name. Type a new name for your button. In this example, we’ve used the text «My Button» for the button text.
(A new button with custom text)
You can click the button if you want, and an error message with display telling you that you haven’t created a macro for it yet. This is because you haven’t created the code that will run when the button is clicked. The button serves no purpose, but you can create the macro that runs when it’s pushed, which then removes the error when you click the button.
Right click the button and choose «Assign Macro.» This action opens a Visual Basic for Applications workspace. The workspace is tied to the workbook that you have open, but you can make full applications that tie with your spreadsheet using VBA. In this workspace, you can create, test, and run any code that you assign to components in your application.
Working in the VBA Workspace
The VBA workspace looks the same whether you program macros in Word or Excel. It’s a workspace where you can program the macro and view all other code that you’ve previously created.
(VBA workspace)
The image above shows the VBA workspace. When you right click a component such as a button and choose «Edit Code,» VBA opens to the location where code is triggered when you click the button. VBA gives names to these functions that help you identify what happens should you perform an activity on it. Since a button is usually triggered by a click event, the function is given the original name of the button, an underscore, and then the word «Click.» For your first button created in your spreadsheet, the name for a click event is «Button1_Click()» and you add any code between the «Sub» and «End Sub» phrases.
The «Sub» keyword indicates that you are starting an event. The next part is the name of the event, and the last statement in a trigger event is the «End Sub» statement.
In the left panel of the workspace, you can see other objects in a tree view. The top object is always the workbook. If you recall, a workbook contains worksheet. Under the «Book1» main project header, you see «ThisWorkbook» which represents the workbook that you have opened, and the «Sheet1» represents the worksheet in the workbook. You can write VBA that works directly on a workbook or a worksheet activity such as when you open the workbook, a macro automatically runs.
The «Modules» section holds the files that you store containing VBA code. You can have several of these in your VBA code, or you can just have one file that contains all of the functions used to run macros.
Writing Some Simple VBA Code
With the VBA editor open, you now have a function ready to edit for your button. Anything you type in the «Sub» and «End Sub» statements will run when you click the Button1 component. When you start working with VBA, you want to create easy function statements so that you can follow what is going on as the code runs. In this example, we’ll add some text to a cell within the current spreadsheet.
Within the sub start and end phrases, type the following code:
Sub Button1_Click()
Range(«A1»).Value = «My Test»
End Sub
The code above tells Excel 2019 that you want to change the value contained in the cell «A1» in the current sheet to «My Test.» The «Range» indicates that you want to apply changes to a cell range set in the functions parameters. You can assign any value to a range, but in this example we apply text. Any formatting already set on the cell will also still apply, so if you have a cell set to bold text, then this value will have the bold format applied.
At the top of the VBA workspace, notice that there are three start, pause and stop buttons. You can use these buttons to test your new code. The «start» button will run the current function and apply changes to the spreadsheet, which in this example is changing content to «My Test.»
(The start button in the VBA workspace)
Click the start button and watch the text in the A1 cell change to «My Test.» Should you have a long list of statements within your function, you might want to pause the procedure. The stop button stops execution, so should you resume it then execution will start where it left off. With the pause button, execution resumes where the last statement left off.
The «MsgBox» function is extremely common in any application. The MsgBox function displays a warning or a message to the user. In any software application, you’ve seen pop-up windows that display a message that provides information. Even web applications display messages as pop-ups and warnings. The MsgBox function in VBA is the equivalent of all of these pop-ups that you’ve seen across different applications.
Suppose that you want to show a confirmation to the user that the button’s function completed execution. In this example, only one statement executes, but you might have hundreds of lines of code that must execute and you want to show the user that it’s completed. You might have a procedure that takes an unusual amount of time to complete, so users must wait for it to complete and then you display the message to confirm when the procedure is over.
Add the next line of code to the same VBA function Button1_Click():
Sub Button1_Click()
Range(«A1»).Value = «My Test»
MsgBox «Cell value change finished»
End Sub
In the code above, the cell A1 has its value changed to «My Test.» After the text is changed in the A1 cell, a message box opens and displays the text «Cell value change finished.» This is just a small example of how you can use the MsgBox function. After you finished changing your VBA code, click the play button again. You will see the two statements run, and the program will stop.
After you are finished writing your code, you still need to save it and test it within the spreadsheet. Your users won’t open the VBA workspace, so you need to make sure that the code executes outside of the VBA workspace.
Close the VBA workspace. You now need to assign the macro to the button. Right-click the button and click «Assign Macro.» Choose the Button1_Click value and click «OK.» Should you ever want to go back and change the statements executed by the macro. Use this screen to click the macro name, and then click «Edit» to again open the VBA workspace with the function code shown in the workspace window.
After the window closes, click the button. Notice that the text in cell A1 changes and then a window displays with a message that the procedure has completed. You’ve just created your first VBA macro that runs in your spreadsheet. You can create much more complex applications with VBA that run across several spreadsheets and can affect several other workbooks that aren’t even open on your desktop.
One issue to remember with VBA is that it’s a powerful tool that can do harm if it’s used the wrong way. Malware writers use VBA macros to download malicious software and install it on your computer. When you work with macros, your recipients of any spreadsheet must give your macros permission to run on their machines. Most users are trained not to open spreadsheets with macros, so they are mostly used within the same organization.


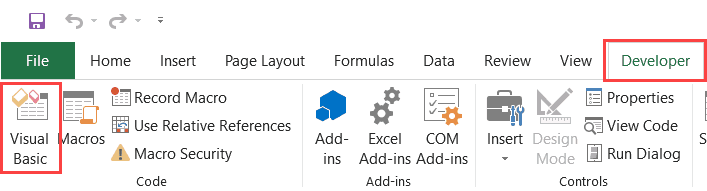
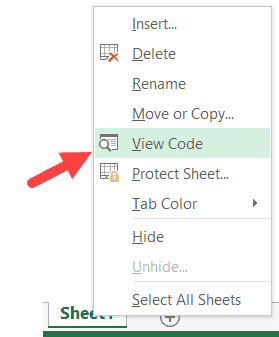
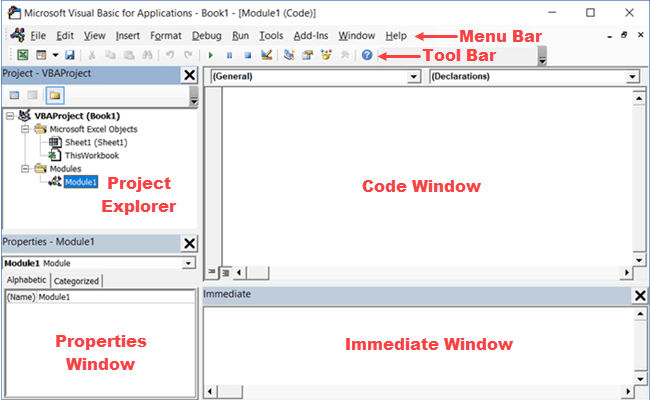
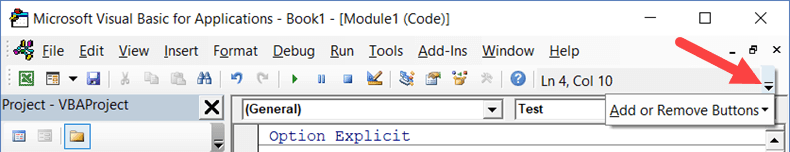
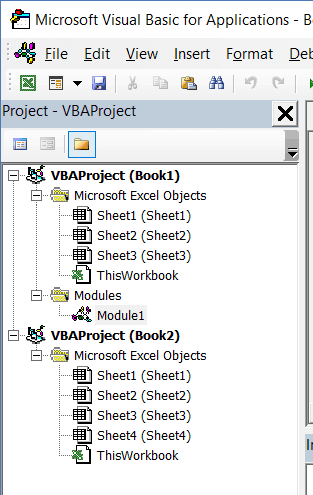
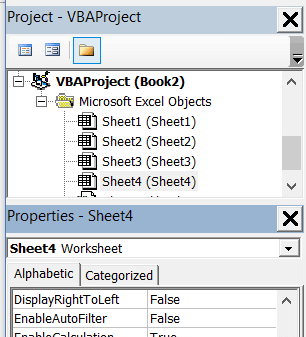
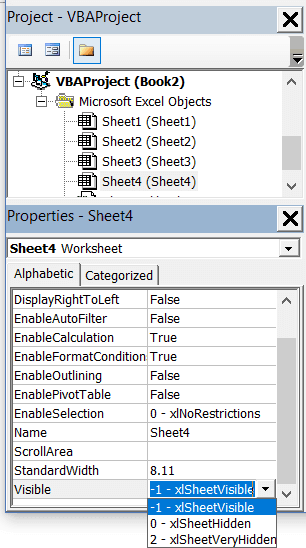


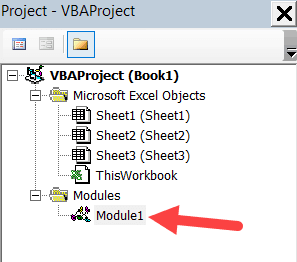


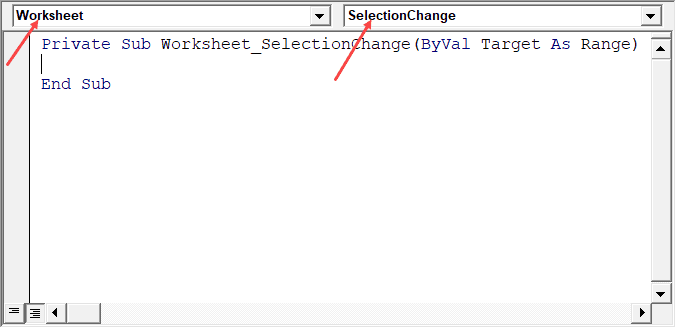
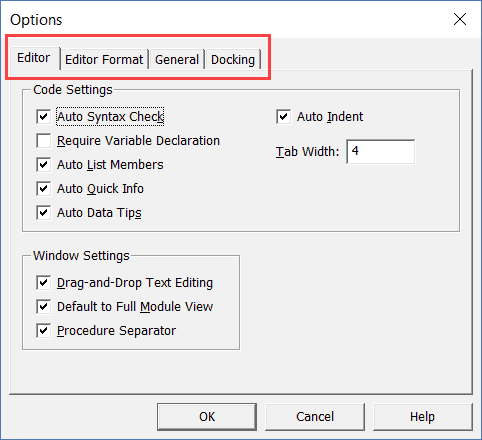
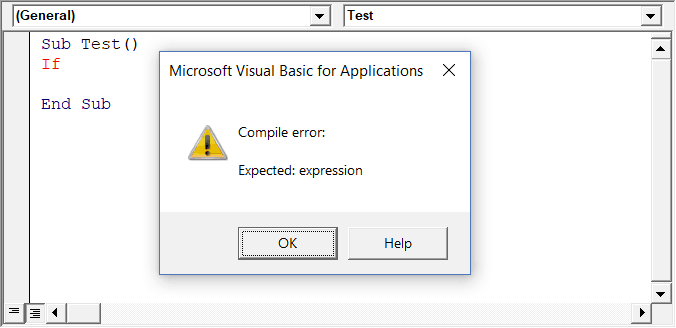
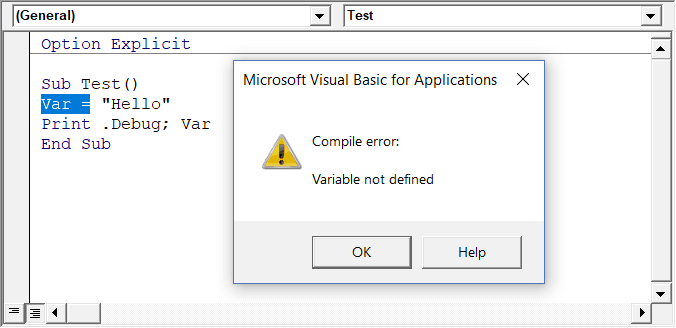
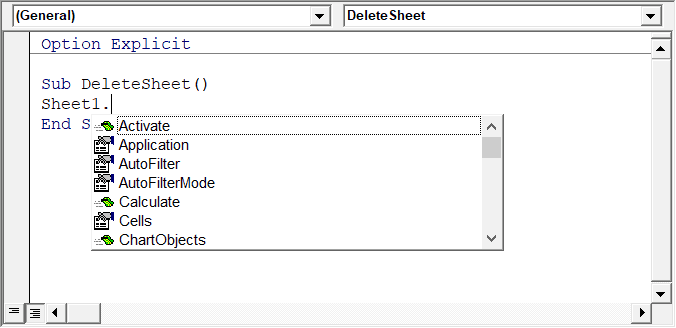
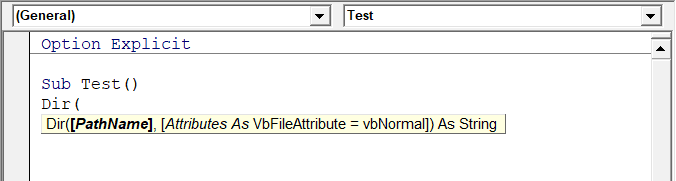
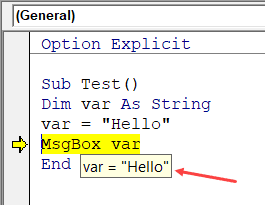
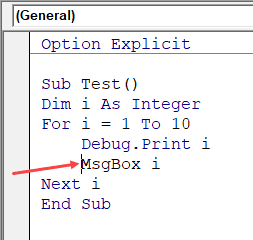
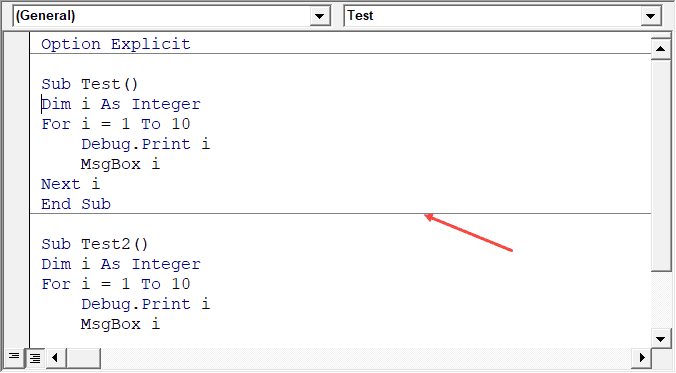
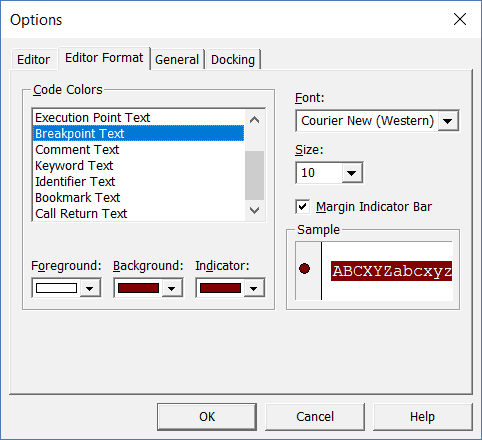
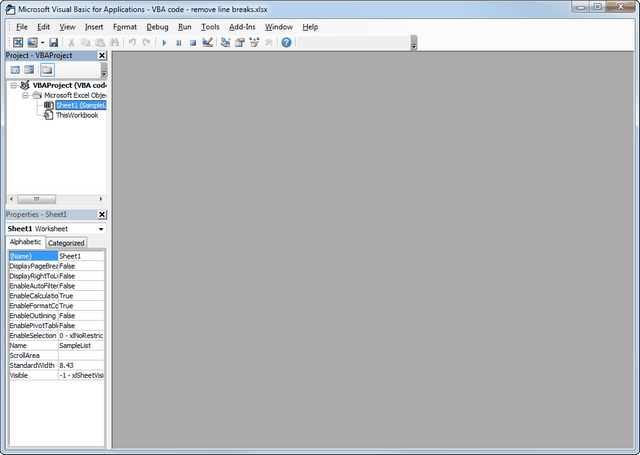
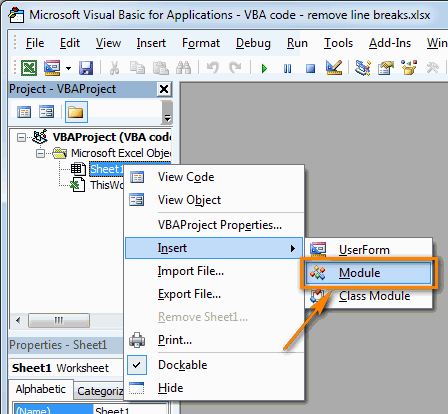
 End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
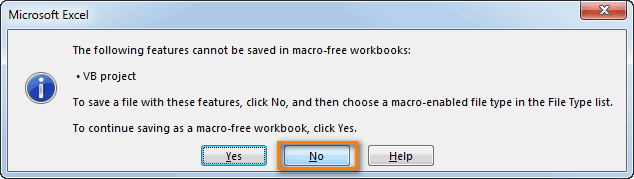 Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою
Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою