How do I get to the VBA editor in MS Word 2013? All my searches return information on Excel.
asked Apr 23, 2014 at 15:11
0
First you need to enable the Developer button in Word.
Click File, then Options, Customize Ribbon.
Then Select the Developer tab checkbox.
Developer will appear is a menu option now. Select it and you can the select Visual Basic to open the VBA editor.
answered Apr 23, 2014 at 15:24
KeltariKeltari
71.4k26 gold badges178 silver badges228 bronze badges
I think you can access it via the visual basic button under the Developer tab as above
answered Apr 23, 2014 at 15:17
SimkillSimkill
1,62711 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I have a word 2013 document that I believe has some vba code somehow embedded in the word document. I would like to know how to obtain a tool to edit the vba code behind the word document. What tool is used? I have an msdn license and I can download tools
if I need to. I am guessing that I will need some version of visual studio 2008.Just let me know what tool is needed.
Answers
-
Your document is evidently a mailmerge main document — it contains mergefields. When opening such a document you will normally get an SQL prompt. If you answer ‘Yes’ to that prompt, the document will connect to the data source so the mailmerge can be completed;
otherwise, it will disconnect from the data source. No VBA code is involved. The values with which mergefields are populated are those contained in the data source.If you open the document and answer ‘Yes’ to the SQL prompt, the following macro can be used to tell you the key mailmerge parameters, all of which are stored in the document’s metadata:
Sub GetMailMergeParameters()
With ActiveDocument.MailMerge
If .MainDocumentType <> wdNotAMergeDocument Then
MsgBox «Mail Merge Data Source Name:» & vbCr & .DataSource.Name
MsgBox «Mail Merge Connect String:» & vbCr & .DataSource.ConnectString
MsgBox «Mail Merge Query String:» & vbCr & .DataSource.QueryString
Else
MsgBox «Not A Merge Document»
End If
End With
End Sub
Cheers
Paul Edstein
[MS MVP — Word]-
Marked as answer by
Thursday, February 9, 2017 4:13 PM
-
Marked as answer by
In Word, you can use compatibility options to change the way Word handles the layout of a document. Instead of turning on and off compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, you can handle the settings via VBA (macros). This requires that you know the name (or number) to use in the VBA code to set a specific option.
This article helps you find the names to use in VBA macros to set any compatibility option in Word. You will also find macros ready for use, including code for setting all compatibility options in different versions of Word. In addition, you will find VBA macros that show how to change the Compatibility Mode of a Word document.
The article covers all the following Word versions: Word 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Word for Microsoft 365. See How to find out what version of Word you have, if needed.
For details about how to access the compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, see my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. That article also includes descriptions of the options and a list showing the names of all compatibility options in English and Danish side by side.
For information about Compatibility Mode in Word, see my article Word Compatibility Mode – What Is It?.
This article was first published March 5, 2020.
List of all 70 Word compatibility option names and the related VBA names
The WdCompatibility Enumeration includes constant names and values you can use to set the individual compatibility options via VBA in Word. For example, all compatibility options in the active document can be set via VBA by calling ActiveDocument.Compatibility with the appropriate WdCompatibility constant.
The list below shows the English compatibility option names (column 2) together with the related WdCompatibility Enumeration values (column 3) and WdCompatibility Enumeration names (column 4).
The numbers in the first column are only added for easier reference. Note that the numbers correspond to the numbers used in the lists in my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. This means that you can quickly find the same option in the different lists.
In cases where the same option has been renamed between Word versions, the old name is shown in parentheses below the new name, incl. information about to which Word version(s) the old name applies.
Important differences between Word 2007 and other Word versions when setting some compatibility options via VBA
For unknown reasons, some compatibility options behave differently in Word 2007 than in other Word versions when setting the options via VBA. It seems to be a bug in Word 2007. The following applies:
- In Word 2007, you must set any compatibility option to TRUE to turn it ON. Correspondingly, you must set any compatibility option to FALSE to turn it OFF. This seems logical at first glance. However, it is not. If you note the names of the VBA members of the WdCompatibility Enumeration listed below, you will see that some names in VBA are opposite to the names in the user interface. For example, if the user interface name says «Do…», the corresponding WdCompatibility Enumeration constant says «Don’t…».
- In all other version of Word than Word 2007, some compatibility options must be set to FALSE to be turned ON and TRUE to be turned OFF.
These differences in behavior of some compatibility options mean that you need to check any code for setting compatibility options to make sure the TRUE/FALSE settings are correct for the version of Word in use. If the same VBA code is to be used both in Word 2007 and other versions of Word and if you need to set any of the compatibility options that differ, your code must check for the Word version and handle the settings depending on whether it is Word 2007 or another Word version. See VBA the example below.
In the macros available in this article, I have set the TRUE/FALSE values correctly for the version(s) of Word each of the macros is created for.
In the list below, I have added a note below the options that must be FALSE to be turned ON and TRUE to be turned OFF in all versions except Word 2007.
Note that the list below does not show to which version(s) of Word each compatibility applies. To go to a page with an extended list that shows both the information below plus information about which Word version(s) each of the compatibility option applies to, click the button below.
|
No. |
Compatibility option names |
VBA |
VBA |
|
1 |
Add space for underlines |
21 |
wdNoSpaceForUL NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
2 |
Adjust line height to grid height in the table |
36 |
wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
3 |
Align table rows independently |
39 |
wdAlignTablesRowByRow |
|
4 |
Allow hyphenation between pages or columns |
71 |
wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom |
|
5 |
Allow space between paragraphs of the same style in a table |
54 |
wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable |
|
6 |
Allow table rows to lay out apart |
41 |
wdLayoutTableRowsApart |
|
7 |
Allow tables to extend into margins |
50 |
wdGrowAutofit |
|
8 |
Auto space the way Word 95 does (Word 2003: Auto space like Word 95) |
38 |
wdAutospaceLikeWW7 |
|
9 |
Balance SBCS characters and DBCS characters |
16 |
wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
10 |
Combine table borders the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does |
9 |
wdOrigWordTableRules |
|
11 |
Convert backslash characters into yen signs |
13 |
wdLeaveBackslashAlone NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
12 |
Disable OpenType Font Formatting Features |
66 |
wdDisableOTKerning |
|
13 |
Do full justification the way WordPerfect 6.x for Windows does |
31 |
wdWPJustification |
|
14 |
Don’t add automatic tab stop for hanging indent |
1 |
wdNoTabHangIndent |
|
15 |
Don’t add extra space for raised/lowered characters |
2 |
wdNoSpaceRaiseLower |
|
16 |
Don’t add leading (extra space) between rows of text |
20 |
wdNoLeading |
|
17 |
Don’t allow hanging punctuation with character grid |
47 |
wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation |
|
18 |
Don’t autofit tables next to wrapped objects |
56 |
wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables |
|
19 |
Don’t balance columns at the start of Continuous sections |
5 |
wdNoColumnBalance |
|
20 |
Don’t blank the area behind metafile pictures |
10 |
wdTransparentMetafiles |
|
21 |
Don’t break constrained tables forced onto the page |
62 |
wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables |
|
22 |
Don’t break wrapped tables across pages |
43 |
wdDontBreakWrappedTables |
|
23 |
Don’t center «exact line height» lines |
28 |
wdExactOnTop |
|
24 |
Don’t expand character spaces on a line that ends with SHIFT+RETURN |
14 |
wdExpandShiftReturn NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
25 |
Don’t snap text to grid inside table with inline objects |
44 |
wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects |
|
26 |
Don’t use Asian rules for line breaks with character grid |
48 |
wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid |
|
27 |
Don’t use hanging indent as tab stop for bullets and numbering |
52 |
wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop |
|
28 |
Don’t use HTML paragraph auto spacing |
35 |
wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing |
|
29 |
Don’t use proportional width for Korean characters |
59 |
wdHangulWidthLikeWW11 |
|
30 |
Don’t vertically align inside of textboxes |
63 |
wdDontVertAlignInTextbox |
|
31 |
Don’t vertically align table cells containing shapes |
61 |
wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape |
|
32 |
Draw underline on trailing spaces |
15 |
wdDontULTrailSpace NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
33 |
Expand/condense by whole number of points |
18 |
wdSpacingInWholePoints |
|
34 |
Forget last tab alignment |
37 |
wdForgetLastTabAlignment |
|
35 |
Lay out AutoShapes the way Word 97 does |
33 |
wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8 |
|
36 |
Lay out footnotes the way Word 6.x/95/97 does |
34 |
wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8 |
|
37 |
Lay out tables with raw width |
40 |
wdLayoutRawTableWidth |
|
38 |
Print body text before header/footer |
19 |
wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader |
|
39 |
Print colors as black on noncolor printers |
3 |
wdPrintColBlack |
|
40 |
Select entire field with first or last character |
45 |
wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter |
|
41 |
Set the width of a space like WordPerfect 5.x |
30 |
wdWPSpaceWidth |
|
42 |
Show hard page or column breaks in frames |
11 |
wdShowBreaksInFrames |
|
43 |
Split apart page break and paragraph mark |
60 |
wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark |
|
44 |
Substitute fonts based on font size |
25 |
wdSubFontBySize |
|
45 |
Suppress extra line spacing at bottom of page |
29 |
wdSuppressBottomSpacing |
|
46 |
Suppress extra line spacing at top of page |
8 |
wdSuppressTopSpacing |
|
47 |
Suppress extra line spacing at top of page the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does (Word 2003: Suppress extra line spacing at top of page like Word 5.x for the Mac) |
17 |
wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5 |
|
48 |
Suppress extra line spacing the way WordPerfect 5.x does (Word 2003: Suppress extra line spacing like WordPerfect 5.x) |
23 |
wdNoExtraLineSpacing |
|
49 |
Suppress Space Before after a hard page or column break |
7 |
wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk |
|
50 |
Swap inside and outside mirror indents and relative positioning |
67 |
wdFlipMirrorIndents |
|
51 |
Swap left and right borders on odd facing pages |
12 |
wdSwapBordersFacingPages |
|
52 |
Treat * as ** in mail merge data sources |
6 |
wdConvMailMergeEsc |
|
53 |
Truncate font height |
24 |
wdTruncateFontHeight |
|
54 |
Underline tab character in numbered lists |
58 |
wdUnderlineTabInNumList |
|
55 |
Use cached paragraph information for column balancing |
65 |
wdCachedColBalance |
|
56 |
Use larger small caps the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does |
22 |
wdMWSmallCaps |
|
57 |
Use line-breaking rules |
46 |
wdApplyBreakingRules |
|
58 |
Use Normal style for bulleted and numbered lists |
51 |
wdUseNormalStyleForList |
|
59 |
Use printer metrics to lay out document |
26 |
wdUsePrinterMetrics |
|
60 |
Use Word 2002 table style rules |
49 |
wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules |
|
61 |
Use Word 2002-2007 style evaluation rules for font size and paragraph justification in tables |
68 |
wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification |
|
62 |
Use Word 2003 hanging-punctuation rules |
53 |
wdFELineBreak11 |
|
63 |
Use Word 2003 indent rules for text next to wrapped objects |
55 |
wdWW11IndentRules |
|
64 |
Use Word 2003 kerning pair rules |
64 |
wdWord11KerningPairs |
|
65 |
Use Word 2013 rules for hyphenation between pages and columns |
72 |
wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation |
|
66 |
Use Word 2003 table autofit rules |
57 |
wdAutofitLikeWW11 |
|
67 |
Use Word 6.x/95 border rules |
27 |
wdWW6BorderRules |
|
68 |
Use Word 97 line-breaking rules for Asian text |
42 |
wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules |
|
69 |
Wrap lines the way Word 6.0 does (Word 2003: Lines wrap like Word 6.0) |
32 |
wdLineWrapLikeWord6 |
|
70 |
Wrap trailing spaces to next line |
4 |
wdWrapTrailSpaces |
VBA macros – detect or change the compatibility mode of a document
If a Word document shows the text Compatibility Mode in the title bar, it means that the document was created or last saved in an earlier version of Word than the version you are using.
- You can use VBA to find out which version of Word a document is compatible with.
- You can use VBA to change the compatibility mode of a document.
See the VBA examples below.
The WdCompatibilityMode enumeration
The WdCompatibilityMode enumeration specifies the compatibility mode that Word uses when opening a document.
In the VBA code, you can use either the name or the value.
- The code is easier to read for others (and for yourself later) if you use the names.
- On the other hand, the code will fail with run-time error 5843 if you use a name from a newer version of Word than the version in which the code is running.
See the rules described below for more details.
|
Name |
Value |
Description – Long, read-only |
|
wdWord2003 |
11 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2003. If opened in Word 2007 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2003 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2007 |
12 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2007. If opened in Word 2010 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2007 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2010 |
14 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2010. If opened in Word 2013 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2010 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2013 |
15 |
Common mode for Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and 365. All features in the Word version in question are enabled. |
|
wdCurrent |
65535 |
Compatibility mode equivalent to the current version of Word, i.e. the version in use when running the VBA code. |
RULE 1 no. 1– You can’t set the compatibility mode to a version newer than the current Word version
You can’t set the Compatibility Mode of a document to a version newer than the current Word version in which the VBA code is running.
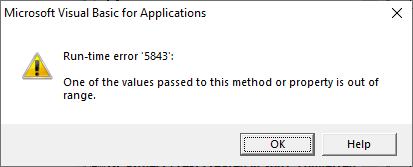
If, for example, you are using Word 2010 and attempt to set the compatibility mode to wdWord2013, the macro will fail with run-time error 5843, «One of the values passed to this method or property is out range.» (see the illustration below).
If you use the value instead (i.e. 15 instead of wdWord2013 in the example used here), no run-time error will occur but the code will do nothing!
Run-time error 5843 occurs if you try to set the compatibility mode to a Word version never than the current version.
RULE no. 2 – You can’t set a compatibility option if that option is not available in the current compatibility mode
You can’t set a compatibility option if that option is not available in the current Compatibility Mode. You will need to first change the Compatibility mode and then set the Compatibility option.
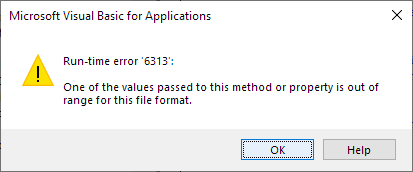
If, for example, you are using Word 2019 and attempt to set a compatibility option that is not found in Word 2019, the macro will fail with run-time error 6213, «One of the values passed to this method or property is out range for this file format.» (see the illustration below).
Run-time error 6313 occurs if you try to set a compatibility option that is not available in the current compatibility mode of the document.
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2003
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2003
In this example and the examples for other Word versions below, you may add the parameter name, Mode, if you want. The result is the same:
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode Mode:=wdWord2003
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2007
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2007
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2010
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2010
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2013
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with the current version of Word
The current Word version is the version in use when running the VBA code.
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdCurrent
VBA – Find out whether the active document is compatible with the current version of Word
Before running VBA code that only works with documents in a specific Compatibility Mode, you should add code to check the mode before running such code.
Each Word version has an Application.Version number. In Word 2013 and earlier versions, the Application.Version number match the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value. However, Application.Version is in the format ##.0 (e.g. 11.0 for Word 2003, 14.0 for Word 2010). Therefore, the Val function is used in the VBA code below in order to compare the values of Application.Version and the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value.
You will find an overview of Word version numbers in my wordaddins.com article here.
Since Word 2013 and newer versions share the same WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value, the VBA code can’t just compare Val(Application.Version) with the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value. Therefore, the example below operates on Word 2010 and earlier versus Word 2013 and newer versions.
The VBA code below can be used with Word 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and 365. The code sets blnIsCompatible to True if the active document is compatible with the current Word version and False if not. You can the use the result to determine what to do next.
In the VBA code below, 15 is used instead of wdWord2013 to prevent a run-time error in case the code is running in Word 2010 or earlier version.
Dim lngVersion As Long
Dim blnIsCompatible As Boolean
lngVersion = Val(Application.Version)
If lngVersion <= 14 Then
If lngVersion = ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode Then
blnIsCompatible = True
Else
blnIsCompatible = False
End If
ElseIf lngVersion >= 15 Then
If ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode = 15 Then
blnIsCompatible = True
Else
blnIsCompatible = False
End If
End If
If blnIsCompatible = True Then
Else
End If
VBA – Find the actual compatibility mode of the active document
Dim lngCompMode As Long
lngCompMode = ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode
VBA – Find out whether the active document is in a specific compatibility mode, e.g. Word 2010
In the example below, it is checked whether the active document is in Word 2010 compatibility mode. Replace wdWord2010 with another WdCompatibilityMode enumeration constant to check for another version.
With ActiveDocument
If .CompatibilityMode = wdWord2010 Then
Else
End If
End With
VBA – Change the Compatibility Mode and turn on a compatibility option available in the new mode
If you need to set a compatibility option that is not available in the actual Compatibility Mode of a document but in earlier Word version, you can get access to that compatibility option by changing the Compatibility Mode of the document.
Note that setting the Compatibility Mode to an earlier version of Word may influence other layout details too in addition to the one(s) you specifically want to change.
In the example below, the Compatibility Mode of the active document is set to Word 2010 and the compatibility option Select entire field with first or last character is turned on.
With ActiveDocument
.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2010
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
End With
VBA – Set a compatibility option that acts differently in Word 2007 in code that is to be used in both Word 2007 and other Word versions
As described above, some compatibility options are to be set to True in Word 2007 and False in other Word versions (or vice versa) to obtain the same result.
If you are writing VBA code that is to be used both Word 2007 and other versions of Word, you need to take this into account.
The example below turns ON one of the compatibility options that behaves differently in Word 2007, wdExpandShiftReturn (option no. 24 in the lists). The code checks for the Word version in order to apply True or False as needed:
If Val(Application.Version) = 12 Then
ActiveDocument.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
Else
ActiveDocument.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
End If
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2003
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2003 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2003 includes 50 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2003 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2003_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdTransparentMetafiles) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPSpaceWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2003 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2003_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdTransparentMetafiles) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPSpaceWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2007
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2007 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2007 includes 63 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2007 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: As opposed to all the other versions of Word, all compatibility options In Word 2007 must be set to True to be turned ON.
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2007_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = True
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = True
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2007 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: As opposed to all the other versions of Word, all compatibility options In Word 2007 must be set to False to be turned OFF.
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2007_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = False
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = False
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2010
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2010 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2010 includes 66 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2010 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2010_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdDisableOTKerning) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdFlipMirrorIndents) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = True
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2010 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2010_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdDisableOTKerning) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdFlipMirrorIndents) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = False
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2013, 2016, 2019, or 365 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2013, 2016, 2019, and 365 include 13 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2013_2016_2019_2021_365_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2013_2016_2019_2021_365_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation) = False
End With
End Sub
Related information
Overview of all compatibility options and information about in which Word versions each option is found: For details about how to access the compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, see my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. The article also includes lists showing which layout options and compatibility options are found in the different versions of Word.
Show Extended List of Compatibility Options, incl. Word Version Info.
Finding Word terms in another language than your Word: You can use the Microsoft Language Portal to look up Word terminology in another language than your Word version.
For information about Compatibility Mode in Word, see my article Word Compatibility Mode – What Is It?.
Как установить VBA в приложениях Microsoft Office
Некоторые приложения пакета Microsoft Office, такие как Word, Excel, Access, Outlook, позволяют использовать для решения пользовательских задач язык программирования Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Для того чтобы использовать возможности VBA, макросы, процедуры и надстройки, написанные на этом языке программирования, необходимо чтобы компонент Visual Basic для приложений был установлен вместе с приложениями пакета Microsoft Office.
Как проверить установлен ли Visual Basic для приложений?
Самый простой способ проверить наличие либо отсутствие установленного VBA это попробовать его запустить. Запустить VBA можно сочетанием клавиш Alt+F11 на клавиатуре, либо кнопкой «Visual Basic» на вкладке «Разработчик». По умолчанию вкладка «Разработчик» отключена во всех приложениях пакета Microsoft Office, поэтому предварительно ее нужно отобразить в настройках ленты.
Итак, если VBA установлен, то нажатие горячих клавиш либо кнопки «Visual Basic» на ленте приложения приводит к появлению окна редактора Visual Basic на экране монитора. Выглядит редактор примерно так, как показано на изображении ниже.
В случае, если окно редактора не появилось, то компонент Visual Basic для приложений необходимо установить.
Как установить Visual Basic для приложений?
Чтобы установить компонент пакета Visual Basic for Applications, необходимо нажать кнопку Пуск, зайти в Панель управления/Программы и компоненты, выбрать программу Microsoft Office и нажать кнопку «Изменить», либо запустить установочный файл Setup.exe.
Далее выбрать опцию «Добавить или удалить компоненты», в параметрах установки выбрать компонент Visual Basic для приложений и доустановить его.
How to Run VBA Code in Your Word
For most cases, you are often using VBA code to do various tasks in Your Word. However, do you really get hang of the steps to run VBA code? Therefore, in this article, we offer a detailed description of those steps for you.
In the followings, we take Word 2010 as an example to show the detailed steps. And you can easily apply the method to other versions in a similar way.
Step 1 Open the “Developer”
- First of all, go to the “File”, and click “Options”.
- Next click “Customize Ribbon” to check whether the “Developer” is selected.
If checked, you can go to the Step 2; if not, you need do the followings:
(1). On the right sections of Word Options, you need choose “Main Tabs” under the “Customize Ribbon”.
(2). Now you will find the “Developer”, and then check it.
(3). Finally, click “OK” to close the window.
(4). Back to the home screen of your word, you can easily find the “Developer” tab.
Step 2 Check Securities for the Macro
Before running VBA code, you need follow this step to check whether the operating environment is secure to run your macro.
- After enabling the “Developer”, you need click “Macro Security” in the “Code” group.
- Then make sure the “Disable all macro with notifications” is checked in “Macro Setting”.
Step 3 Edit the VBA code
- Firstly, click “Visual Basic” in the “Code” group, on “Developer” tab or you can press “Alt” + “F11” in your keyboard to open the VBA editor.
- Then click “Insert”, in the drop-down menu, you can click “Module”.
- Next double click to open a new module.
- Finally, in the empty area of this project, you can edit your VBA code in it.
Step 4 Run VBA code
After editing the VBA code you need, next comes to run it.
- Chick “Run” (the green triangle like bellowed picture) in the toolbar or hit “F5” in your keyboard in the current module.
Alternative Option: Add Macro Buttons to the Quick Access Toolbar
When finishing above steps, you can also add shortcut button for your macro.
- Similarly, click “Options” in the “File” tab, and then click “Quick Access Toolbar”.
- Choose “Macros” and click “Add” to the toolbar after selecting “All Commands” from the “Choose commands from” drop down list.
- Then click “Ok” to close the window.
- Back to the document, you can find the macro is already in the Quick Access Toolbar. Therefore, you can easily click it to run your code.
How do you open the VBA editor in MS Word 2013? [duplicate]
How do I get to the VBA editor in MS Word 2013? All my searches return information on Excel.
2 Answers 2
First you need to enable the Developer button in Word.
Click File , then Options , Customize Ribbon .
Then Select the Developer tab checkbox.
Developer will appear is a menu option now. Select it and you can the select Visual Basic to open the VBA editor.
I think you can access it via the visual basic button under the Developer tab as above
2 ответа
6
Сначала вам нужно включить кнопку разработчика в Word.
Нажмите File , затем Options , Customize Ribbon .
Затем установите флажок на вкладке « Developer ».
Developer появится это опция меню сейчас. Выберите его, и вы можете выбрать Visual Basic чтобы открыть редактор VBA.
поделиться|источник
ответ дан Keltari51k
0
Я думаю, что вы можете получить к нему доступ через кнопку Visual Basic на вкладке разработчика, как указано выше
поделиться|источник
ответ дан Simkill2k