I just came to know that macros in Word/Excel/PowerPoint can be programmed. That is awesome because I’ve a Word document with 70 tables for styling.
I’m a programmer but I don’t know VB, VBA or VB .NET. I’m confused with these three. I’m familiar with .NET programming using C#. Now I want to write new macros. Where should I get started? What are VB, VBA, VB.NET and which one should I learn? Please suggest some material.
If I learn for Word 2007 will that help with other Office applications life Excel & PowerPoint?
Robert Harvey
177k47 gold badges333 silver badges499 bronze badges
asked Jul 9, 2010 at 6:23
0
Here’s a brief explanation of the different Visual Basics:
- Visual Basic 6 (VB6, or classic VB)
- Released around 1998, this was the last iteration of Microsoft’s original «Visual Basic.» It has the beginnings of object-oriented development, but it requires the Visual Basic Runtime for applications to run. A lot of companies have used VB6 for internal business applications. It was superceded by VB.NET and the .NET Framework.
- Visual Basic for Applications (VBA)
- VBA shares the same code base as VB6 and in 1996 was available to be licensed to developers to include in their own applications. This is how VBA appears in Microsoft Office, as an embedded language that can be used to control Office’s various applications. It’s important to remember that VBA, which is still used to code office applications, is over a decade old and may feel as such when one is used to working with .NET.
- Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET)
- VB.NET was a radical departure from VB6. Though subsequent iterations of VB.NET have been referred to in sequence (e.g. VB7, VB8, etc.) by many developers, VB.NET shares very little with VB6 and VBA other than the BASIC syntax. Many consider it more of a new evolution in BASIC rather than an evolution in Visual Basic. Because it’s entirely different from VBA and VB6, you cannot not use VB.NET code directly in VBA.
- Because VB.NET code compiles down to the same managed intermediate language code as C# and shares the same .NET APIs, you may feel more commonality between C# and VB.NET than VB6 and VB.NET from a programming perspective.
If you anticipate doing a lot of development in VBA, I would highly recommend the VBA Developer’s Handbook, Second Edition, by Getz and Gilbert.
Learning the VBA syntax for Word will certainly help you when you go to use Excel, Access, etc. However, each application has its own API that provides a set of objects and methods unique to its domain. For example, I’m very familiar with programming in VBA in Excel and Access, but I have never done macro programming in Word. Although the code syntax would be the same, I’d have to learn Word’s API to be able to program against it.
The nice thing about some of the Office applications (Excel, for example) is that you can record a macro, see what code it generates, and then tweak that code to do what you want. That’s largely how I got started in programming.
answered Jul 9, 2010 at 15:29
Ben McCormackBen McCormack
31.8k46 gold badges145 silver badges221 bronze badges
There are some good answers here — I’d like to offer one more set of suggestions:
First, if supported in your environment, you can use Visual Studio 2005/8/10 and your C# skills to program against Office with «Visual Studio Tools for Office». See this thread for more details.
If you want to delve into VBA instead (which I personally love because development is so fast compared to VS), start with this article Ten Code Conversions for VBA, Visual Basic .NET, and C# which will show you samples from all three languages. Next, watch this webcast: Using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) Every Day Is Easier Than You Think.
Thirdly- MSDN, read through this: Getting Started with VBA in Word 2010. 99% of it applies to Word 2007. There are many other articles linked from this one or you can always go to the main page of Office VBA Developer Center as a single jump page.
Then it’s probably time to get started to directly program. See how things work, learn Word’s Object Model, etc. You can always browse SO under the word-vba tag to see what other people are trying to do and the answers.
answered Jul 10, 2010 at 2:41
Todd MainTodd Main
28.9k11 gold badges82 silver badges146 bronze badges
3
You always have MSDN.
If you go to Microsoft Word > Developer > Visual Basic and open up ThisDocument in the left menu, you will have the editor. If you press F2 you will get the libraries that can be used in Microsoft Word (the Object Browser). The easiest program would be the following:
Sub Hello()
MsgBox "Hello World"
End Sub
When you have the sub marked, press F5 (to run).
In the Object Browser you will have three different objects, properties, functions and events. When you see something that strikes your interest, go to the reference for word vba and locate it.
[If the link changes, you can find it in the tree under MSDN Library > Office Development > 2007 Microsoft Office System > Word 2007 > Word 2007 Developer Reference > Word Object Model Reference]
I think the easiest thing to do is to define a problem you need fixed and try to program it, similar to learning any other language. Don’t make the problem to easy, but not to hard that you give up.
answered Jul 9, 2010 at 7:08
defaultdefault
11.3k8 gold badges67 silver badges102 bronze badges
In Word, you can use compatibility options to change the way Word handles the layout of a document. Instead of turning on and off compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, you can handle the settings via VBA (macros). This requires that you know the name (or number) to use in the VBA code to set a specific option.
This article helps you find the names to use in VBA macros to set any compatibility option in Word. You will also find macros ready for use, including code for setting all compatibility options in different versions of Word. In addition, you will find VBA macros that show how to change the Compatibility Mode of a Word document.
The article covers all the following Word versions: Word 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Word for Microsoft 365. See How to find out what version of Word you have, if needed.
For details about how to access the compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, see my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. That article also includes descriptions of the options and a list showing the names of all compatibility options in English and Danish side by side.
For information about Compatibility Mode in Word, see my article Word Compatibility Mode – What Is It?.
This article was first published March 5, 2020.
List of all 70 Word compatibility option names and the related VBA names
The WdCompatibility Enumeration includes constant names and values you can use to set the individual compatibility options via VBA in Word. For example, all compatibility options in the active document can be set via VBA by calling ActiveDocument.Compatibility with the appropriate WdCompatibility constant.
The list below shows the English compatibility option names (column 2) together with the related WdCompatibility Enumeration values (column 3) and WdCompatibility Enumeration names (column 4).
The numbers in the first column are only added for easier reference. Note that the numbers correspond to the numbers used in the lists in my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. This means that you can quickly find the same option in the different lists.
In cases where the same option has been renamed between Word versions, the old name is shown in parentheses below the new name, incl. information about to which Word version(s) the old name applies.
Important differences between Word 2007 and other Word versions when setting some compatibility options via VBA
For unknown reasons, some compatibility options behave differently in Word 2007 than in other Word versions when setting the options via VBA. It seems to be a bug in Word 2007. The following applies:
- In Word 2007, you must set any compatibility option to TRUE to turn it ON. Correspondingly, you must set any compatibility option to FALSE to turn it OFF. This seems logical at first glance. However, it is not. If you note the names of the VBA members of the WdCompatibility Enumeration listed below, you will see that some names in VBA are opposite to the names in the user interface. For example, if the user interface name says «Do…», the corresponding WdCompatibility Enumeration constant says «Don’t…».
- In all other version of Word than Word 2007, some compatibility options must be set to FALSE to be turned ON and TRUE to be turned OFF.
These differences in behavior of some compatibility options mean that you need to check any code for setting compatibility options to make sure the TRUE/FALSE settings are correct for the version of Word in use. If the same VBA code is to be used both in Word 2007 and other versions of Word and if you need to set any of the compatibility options that differ, your code must check for the Word version and handle the settings depending on whether it is Word 2007 or another Word version. See VBA the example below.
In the macros available in this article, I have set the TRUE/FALSE values correctly for the version(s) of Word each of the macros is created for.
In the list below, I have added a note below the options that must be FALSE to be turned ON and TRUE to be turned OFF in all versions except Word 2007.
Note that the list below does not show to which version(s) of Word each compatibility applies. To go to a page with an extended list that shows both the information below plus information about which Word version(s) each of the compatibility option applies to, click the button below.
|
No. |
Compatibility option names |
VBA |
VBA |
|
1 |
Add space for underlines |
21 |
wdNoSpaceForUL NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
2 |
Adjust line height to grid height in the table |
36 |
wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
3 |
Align table rows independently |
39 |
wdAlignTablesRowByRow |
|
4 |
Allow hyphenation between pages or columns |
71 |
wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom |
|
5 |
Allow space between paragraphs of the same style in a table |
54 |
wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable |
|
6 |
Allow table rows to lay out apart |
41 |
wdLayoutTableRowsApart |
|
7 |
Allow tables to extend into margins |
50 |
wdGrowAutofit |
|
8 |
Auto space the way Word 95 does (Word 2003: Auto space like Word 95) |
38 |
wdAutospaceLikeWW7 |
|
9 |
Balance SBCS characters and DBCS characters |
16 |
wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
10 |
Combine table borders the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does |
9 |
wdOrigWordTableRules |
|
11 |
Convert backslash characters into yen signs |
13 |
wdLeaveBackslashAlone NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
12 |
Disable OpenType Font Formatting Features |
66 |
wdDisableOTKerning |
|
13 |
Do full justification the way WordPerfect 6.x for Windows does |
31 |
wdWPJustification |
|
14 |
Don’t add automatic tab stop for hanging indent |
1 |
wdNoTabHangIndent |
|
15 |
Don’t add extra space for raised/lowered characters |
2 |
wdNoSpaceRaiseLower |
|
16 |
Don’t add leading (extra space) between rows of text |
20 |
wdNoLeading |
|
17 |
Don’t allow hanging punctuation with character grid |
47 |
wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation |
|
18 |
Don’t autofit tables next to wrapped objects |
56 |
wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables |
|
19 |
Don’t balance columns at the start of Continuous sections |
5 |
wdNoColumnBalance |
|
20 |
Don’t blank the area behind metafile pictures |
10 |
wdTransparentMetafiles |
|
21 |
Don’t break constrained tables forced onto the page |
62 |
wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables |
|
22 |
Don’t break wrapped tables across pages |
43 |
wdDontBreakWrappedTables |
|
23 |
Don’t center «exact line height» lines |
28 |
wdExactOnTop |
|
24 |
Don’t expand character spaces on a line that ends with SHIFT+RETURN |
14 |
wdExpandShiftReturn NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
25 |
Don’t snap text to grid inside table with inline objects |
44 |
wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects |
|
26 |
Don’t use Asian rules for line breaks with character grid |
48 |
wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid |
|
27 |
Don’t use hanging indent as tab stop for bullets and numbering |
52 |
wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop |
|
28 |
Don’t use HTML paragraph auto spacing |
35 |
wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing |
|
29 |
Don’t use proportional width for Korean characters |
59 |
wdHangulWidthLikeWW11 |
|
30 |
Don’t vertically align inside of textboxes |
63 |
wdDontVertAlignInTextbox |
|
31 |
Don’t vertically align table cells containing shapes |
61 |
wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape |
|
32 |
Draw underline on trailing spaces |
15 |
wdDontULTrailSpace NOTE: False = ON, True = OFF (except Word 2007) |
|
33 |
Expand/condense by whole number of points |
18 |
wdSpacingInWholePoints |
|
34 |
Forget last tab alignment |
37 |
wdForgetLastTabAlignment |
|
35 |
Lay out AutoShapes the way Word 97 does |
33 |
wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8 |
|
36 |
Lay out footnotes the way Word 6.x/95/97 does |
34 |
wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8 |
|
37 |
Lay out tables with raw width |
40 |
wdLayoutRawTableWidth |
|
38 |
Print body text before header/footer |
19 |
wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader |
|
39 |
Print colors as black on noncolor printers |
3 |
wdPrintColBlack |
|
40 |
Select entire field with first or last character |
45 |
wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter |
|
41 |
Set the width of a space like WordPerfect 5.x |
30 |
wdWPSpaceWidth |
|
42 |
Show hard page or column breaks in frames |
11 |
wdShowBreaksInFrames |
|
43 |
Split apart page break and paragraph mark |
60 |
wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark |
|
44 |
Substitute fonts based on font size |
25 |
wdSubFontBySize |
|
45 |
Suppress extra line spacing at bottom of page |
29 |
wdSuppressBottomSpacing |
|
46 |
Suppress extra line spacing at top of page |
8 |
wdSuppressTopSpacing |
|
47 |
Suppress extra line spacing at top of page the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does (Word 2003: Suppress extra line spacing at top of page like Word 5.x for the Mac) |
17 |
wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5 |
|
48 |
Suppress extra line spacing the way WordPerfect 5.x does (Word 2003: Suppress extra line spacing like WordPerfect 5.x) |
23 |
wdNoExtraLineSpacing |
|
49 |
Suppress Space Before after a hard page or column break |
7 |
wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk |
|
50 |
Swap inside and outside mirror indents and relative positioning |
67 |
wdFlipMirrorIndents |
|
51 |
Swap left and right borders on odd facing pages |
12 |
wdSwapBordersFacingPages |
|
52 |
Treat * as ** in mail merge data sources |
6 |
wdConvMailMergeEsc |
|
53 |
Truncate font height |
24 |
wdTruncateFontHeight |
|
54 |
Underline tab character in numbered lists |
58 |
wdUnderlineTabInNumList |
|
55 |
Use cached paragraph information for column balancing |
65 |
wdCachedColBalance |
|
56 |
Use larger small caps the way Word 5.x for the Macintosh does |
22 |
wdMWSmallCaps |
|
57 |
Use line-breaking rules |
46 |
wdApplyBreakingRules |
|
58 |
Use Normal style for bulleted and numbered lists |
51 |
wdUseNormalStyleForList |
|
59 |
Use printer metrics to lay out document |
26 |
wdUsePrinterMetrics |
|
60 |
Use Word 2002 table style rules |
49 |
wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules |
|
61 |
Use Word 2002-2007 style evaluation rules for font size and paragraph justification in tables |
68 |
wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification |
|
62 |
Use Word 2003 hanging-punctuation rules |
53 |
wdFELineBreak11 |
|
63 |
Use Word 2003 indent rules for text next to wrapped objects |
55 |
wdWW11IndentRules |
|
64 |
Use Word 2003 kerning pair rules |
64 |
wdWord11KerningPairs |
|
65 |
Use Word 2013 rules for hyphenation between pages and columns |
72 |
wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation |
|
66 |
Use Word 2003 table autofit rules |
57 |
wdAutofitLikeWW11 |
|
67 |
Use Word 6.x/95 border rules |
27 |
wdWW6BorderRules |
|
68 |
Use Word 97 line-breaking rules for Asian text |
42 |
wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules |
|
69 |
Wrap lines the way Word 6.0 does (Word 2003: Lines wrap like Word 6.0) |
32 |
wdLineWrapLikeWord6 |
|
70 |
Wrap trailing spaces to next line |
4 |
wdWrapTrailSpaces |
VBA macros – detect or change the compatibility mode of a document
If a Word document shows the text Compatibility Mode in the title bar, it means that the document was created or last saved in an earlier version of Word than the version you are using.
- You can use VBA to find out which version of Word a document is compatible with.
- You can use VBA to change the compatibility mode of a document.
See the VBA examples below.
The WdCompatibilityMode enumeration
The WdCompatibilityMode enumeration specifies the compatibility mode that Word uses when opening a document.
In the VBA code, you can use either the name or the value.
- The code is easier to read for others (and for yourself later) if you use the names.
- On the other hand, the code will fail with run-time error 5843 if you use a name from a newer version of Word than the version in which the code is running.
See the rules described below for more details.
|
Name |
Value |
Description – Long, read-only |
|
wdWord2003 |
11 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2003. If opened in Word 2007 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2003 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2007 |
12 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2007. If opened in Word 2010 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2007 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2010 |
14 |
Mode that is most compatible with Word 2010. If opened in Word 2013 or newer version, features new to Word compared to Word 2010 are disabled. |
|
wdWord2013 |
15 |
Common mode for Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and 365. All features in the Word version in question are enabled. |
|
wdCurrent |
65535 |
Compatibility mode equivalent to the current version of Word, i.e. the version in use when running the VBA code. |
RULE 1 no. 1– You can’t set the compatibility mode to a version newer than the current Word version
You can’t set the Compatibility Mode of a document to a version newer than the current Word version in which the VBA code is running.
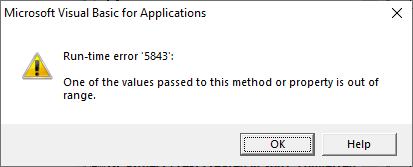
If, for example, you are using Word 2010 and attempt to set the compatibility mode to wdWord2013, the macro will fail with run-time error 5843, «One of the values passed to this method or property is out range.» (see the illustration below).
If you use the value instead (i.e. 15 instead of wdWord2013 in the example used here), no run-time error will occur but the code will do nothing!
Run-time error 5843 occurs if you try to set the compatibility mode to a Word version never than the current version.
RULE no. 2 – You can’t set a compatibility option if that option is not available in the current compatibility mode
You can’t set a compatibility option if that option is not available in the current Compatibility Mode. You will need to first change the Compatibility mode and then set the Compatibility option.
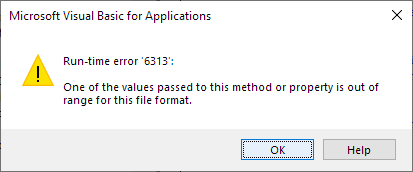
If, for example, you are using Word 2019 and attempt to set a compatibility option that is not found in Word 2019, the macro will fail with run-time error 6213, «One of the values passed to this method or property is out range for this file format.» (see the illustration below).
Run-time error 6313 occurs if you try to set a compatibility option that is not available in the current compatibility mode of the document.
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2003
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2003
In this example and the examples for other Word versions below, you may add the parameter name, Mode, if you want. The result is the same:
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode Mode:=wdWord2003
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2007
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2007
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2010
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2010
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2013
VBA – Set the active document to be compatible with the current version of Word
The current Word version is the version in use when running the VBA code.
ActiveDocument.SetCompatibilityMode wdCurrent
VBA – Find out whether the active document is compatible with the current version of Word
Before running VBA code that only works with documents in a specific Compatibility Mode, you should add code to check the mode before running such code.
Each Word version has an Application.Version number. In Word 2013 and earlier versions, the Application.Version number match the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value. However, Application.Version is in the format ##.0 (e.g. 11.0 for Word 2003, 14.0 for Word 2010). Therefore, the Val function is used in the VBA code below in order to compare the values of Application.Version and the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value.
You will find an overview of Word version numbers in my wordaddins.com article here.
Since Word 2013 and newer versions share the same WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value, the VBA code can’t just compare Val(Application.Version) with the WdCompatibilityMode enumeration value. Therefore, the example below operates on Word 2010 and earlier versus Word 2013 and newer versions.
The VBA code below can be used with Word 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and 365. The code sets blnIsCompatible to True if the active document is compatible with the current Word version and False if not. You can the use the result to determine what to do next.
In the VBA code below, 15 is used instead of wdWord2013 to prevent a run-time error in case the code is running in Word 2010 or earlier version.
Dim lngVersion As Long
Dim blnIsCompatible As Boolean
lngVersion = Val(Application.Version)
If lngVersion <= 14 Then
If lngVersion = ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode Then
blnIsCompatible = True
Else
blnIsCompatible = False
End If
ElseIf lngVersion >= 15 Then
If ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode = 15 Then
blnIsCompatible = True
Else
blnIsCompatible = False
End If
End If
If blnIsCompatible = True Then
Else
End If
VBA – Find the actual compatibility mode of the active document
Dim lngCompMode As Long
lngCompMode = ActiveDocument.CompatibilityMode
VBA – Find out whether the active document is in a specific compatibility mode, e.g. Word 2010
In the example below, it is checked whether the active document is in Word 2010 compatibility mode. Replace wdWord2010 with another WdCompatibilityMode enumeration constant to check for another version.
With ActiveDocument
If .CompatibilityMode = wdWord2010 Then
Else
End If
End With
VBA – Change the Compatibility Mode and turn on a compatibility option available in the new mode
If you need to set a compatibility option that is not available in the actual Compatibility Mode of a document but in earlier Word version, you can get access to that compatibility option by changing the Compatibility Mode of the document.
Note that setting the Compatibility Mode to an earlier version of Word may influence other layout details too in addition to the one(s) you specifically want to change.
In the example below, the Compatibility Mode of the active document is set to Word 2010 and the compatibility option Select entire field with first or last character is turned on.
With ActiveDocument
.SetCompatibilityMode wdWord2010
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
End With
VBA – Set a compatibility option that acts differently in Word 2007 in code that is to be used in both Word 2007 and other Word versions
As described above, some compatibility options are to be set to True in Word 2007 and False in other Word versions (or vice versa) to obtain the same result.
If you are writing VBA code that is to be used both Word 2007 and other versions of Word, you need to take this into account.
The example below turns ON one of the compatibility options that behaves differently in Word 2007, wdExpandShiftReturn (option no. 24 in the lists). The code checks for the Word version in order to apply True or False as needed:
If Val(Application.Version) = 12 Then
ActiveDocument.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
Else
ActiveDocument.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
End If
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2003
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2003 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2003 includes 50 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2003 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2003_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdTransparentMetafiles) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPSpaceWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2003 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2003_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdTransparentMetafiles) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPSpaceWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2007
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2007 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2007 includes 63 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2007 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: As opposed to all the other versions of Word, all compatibility options In Word 2007 must be set to True to be turned ON.
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2007_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = True
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = True
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2007 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: As opposed to all the other versions of Word, all compatibility options In Word 2007 must be set to False to be turned OFF.
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2007_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = False
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = False
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2010
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2010 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2010 includes 66 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2010 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2010_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = True
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdDisableOTKerning) = True
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = True
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = True
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = True
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = True
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = True
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = True
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = True
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = True
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = True
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = True
.Compatibility(wdFlipMirrorIndents) = True
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = True
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = True
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = True
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = True
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = True
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = True
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification) = True
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = True
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = True
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = True
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2010 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2010_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAlignTablesRowByRow) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowSpaceOfSameStyleInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutTableRowsApart) = False
.Compatibility(wdGrowAutofit) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutospaceLikeWW7) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdOrigWordTableRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdDisableOTKerning) = False
.Compatibility(wdWPJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoTabHangIndent) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceRaiseLower) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoLeading) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontWrapTextWithPunctuation) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAutofitConstrainedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoColumnBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakConstrainedForcedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBreakWrappedTables) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontSnapTextToGridInTableWithObjects) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseAsianBreakRulesInGrid) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseIndentAsNumberingTabStop) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdHangulWidthLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignInTextbox) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontVertAlignCellWithShape) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSpacingInWholePoints) = False
.Compatibility(wdForgetLastTabAlignment) = False
.Compatibility(wdShapeLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdFootnoteLayoutLikeWW8) = False
.Compatibility(wdLayoutRawTableWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintBodyTextBeforeHeader) = False
.Compatibility(wdPrintColBlack) = False
.Compatibility(wdSelectFieldWithFirstOrLastCharacter) = False
.Compatibility(wdShowBreaksInFrames) = False
.Compatibility(wdSplitPgBreakAndParaMark) = False
.Compatibility(wdSubFontBySize) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacingMac5) = False
.Compatibility(wdNoExtraLineSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressSpBfAfterPgBrk) = False
.Compatibility(wdFlipMirrorIndents) = False
.Compatibility(wdSwapBordersFacingPages) = False
.Compatibility(wdConvMailMergeEsc) = False
.Compatibility(wdTruncateFontHeight) = False
.Compatibility(wdUnderlineTabInNumList) = False
.Compatibility(wdCachedColBalance) = False
.Compatibility(wdMWSmallCaps) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseNormalStyleForList) = False
.Compatibility(wdUsePrinterMetrics) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2002TableStyleRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontOverrideTableStyleFontSzAndJustification) = False
.Compatibility(wdFELineBreak11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW11IndentRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdWord11KerningPairs) = False
.Compatibility(wdAutofitLikeWW11) = False
.Compatibility(wdWW6BorderRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord97LineBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdLineWrapLikeWord6) = False
.Compatibility(wdWrapTrailSpaces) = False
End With
End Sub
VBA – set all compatibility options – Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365
Below, you will find two macros, each including code for setting all compatibility options in documents in Word 2013, 2016, 2019, or 365 format. MACRO 1 turns on all compatibility options in the active document. MACRO 2 turns off all compatibility options in the active document.
- Word 2013, 2016, 2019, and 365 include 13 compatibility options. For each compatibility option, the macros below include a comment showing the related English (US) name used in the user interface of Word.
- You can adjust each individual setting in the macros as desired by changing True to False of vice versa.
MACRO 1 Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365 – turn ON all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to False to be turned ON!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2013_2016_2019_2021_365_TurnON()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = False
.Compatibility(wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = False
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = False
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = True
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = True
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = True
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation) = True
End With
End Sub
MACRO 2 Word 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 365 – turn OFF all compatibility options
IMPORTANT: Note that some of the compatibility options must be set to True to be turned OFF!
Sub SetAllCompatibilityOptions_Word2013_2016_2019_2021_365_TurnOFF()
With ActiveDocument
.Compatibility(wdNoSpaceForUL) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontAdjustLineHeightInTable) = True
.Compatibility(wdAllowHyphenationAtTrackBottom) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontBalanceSingleByteDoubleByteWidth) = True
.Compatibility(wdLeaveBackslashAlone) = True
.Compatibility(wdExactOnTop) = False
.Compatibility(wdExpandShiftReturn) = True
.Compatibility(wdDontUseHTMLParagraphAutoSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdDontULTrailSpace) = True
.Compatibility(wdSuppressBottomSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdSuppressTopSpacing) = False
.Compatibility(wdApplyBreakingRules) = False
.Compatibility(wdUseWord2013TrackBottomHyphenation) = False
End With
End Sub
Related information
Overview of all compatibility options and information about in which Word versions each option is found: For details about how to access the compatibility options manually via the user interface in Word, see my article Word Layout Options & Compatibility Options. The article also includes lists showing which layout options and compatibility options are found in the different versions of Word.
Show Extended List of Compatibility Options, incl. Word Version Info.
Finding Word terms in another language than your Word: You can use the Microsoft Language Portal to look up Word terminology in another language than your Word version.
For information about Compatibility Mode in Word, see my article Word Compatibility Mode – What Is It?.
ВикиЧтение
Word 2007.Популярный самоучитель
Краинский И
9.3. Редактор Visual Basic
После записи рассмотренного выше макроса к шаблону Normal добавился следующий текст макроса:
Sub Arial_10_bold()
“
“ Arial_10_bold Macro
“ Arial 10 Полужирный
“
With Selection.Font
.Name = «Arial»
.Size = 10
.Bold = True
.Italic = False
.Underline = wdUnderlineNone
.UnderlineColor = wdColorAutomatic
.StrikeThrough = False
.DoubleStrikeThrough = False
.Outline = False
.Emboss = False
.Shadow = False
.Hidden = False
.SmallCaps = False
.AllCaps = False
.Color = wdColorAutomatic
.Engrave = False
.Superscript = False
.Subscript = False
.Spacing = 0
.Scaling = 100
.Position = 0
.Kerning = 0
.Animation = wdAnimationNone
End With
End Sub
Наверняка пользователям, незнакомым с программированием, такой текст покажется очень сложным, однако при ближайшем рассмотрении оказывается, что это простой набор параметров, которые установлены или не установлены. Установленный параметр обозначается словом True, а неустановленный – False.
Для записи макросов, как и для других команд, в Microsoft Word используется язык Visual Basic for Applications (VBA, Visual Basic для приложений). Макрос представляет собой набор команд и операторов на VBA. Каждая команда и действие в Microsoft Word представлены в виде строк формата VBA, процесс записи макроса тоже представляет собой формирование таких строк. Таким образом, пользователь имеет возможность изменить или создать макрос без повторного выполнения всей процедуры. Хотя макрос VBA можно создать в любом текстовом редакторе, не стоит пренебрегать возможностью записи макроса в Word. Макросу, созданному при помощи Microsoft Word, можно добавлять новые команды и функции, а также на таких макросах можно изучать язык VBA.
Макросы можно редактировать, используя специальную утилиту, которая входит в поставку Microsoft Office, – редактор Visual Basic (рис. 9.10).
Рис. 9.10. Окно редактора Visual Basic
Данная программа содержит возможности, которые позволяют работать с макросом: тестировать, отлаживать, запускать на выполнение. Используя этот редактор, можно добавлять, изменять и удалять объекты в макросах, создавать пользовательские диалоговые окна, отлаживать код программных процедур, просматривать и выбирать компоненты текущих проектов и библиотек, определять вид и поведение объектов макроса во время выполнения и выполнять многое другое.
Окно редактора Visual Basic можно открыть несколькими способами, например нажав кнопку Visual Basic на панели Разработчик.
Данный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.
Читайте также
Visual Basic 6.0
Visual Basic 6.0
В Visual Basic 6.0 в отличие от пятой версии окна Code и Object появляются в нормальном, не в раскрытом виде. И приходится при каждом запуске VB6 раскрывать эти окна. Можно заставить автоматически раскрывать эти окна при каждом запуске. Создайте в соответствующем разделе
Visual Basic
Visual Basic
Регистрация dll- и ocx-файловДанная заметка будет полезна разработчикам. Если вам часто приходится работать с ocx-файлами (а также с dll-файлами), которые требуют регистрации в реестре с помощью REGSVR.EXE, то будет гораздо удобнее внести соответствующую запись в реестр, чем
Delphi и Visual Basic
Delphi и Visual Basic
1. Есть ли в Delphi эквивалент массива элементов управления из Visual Basic? Hет. Компоненты Delphi не имеют свойства Index, подобное VB. Однако, имеются три основные причины, почему вы хотите использовать их в VB, и для каждой из них есть решение в Delphi. Причина 1. Вы хотите
3. Переменные Visual Basic
3. Переменные Visual Basic
В Visual Basic переменные накапливают информацию (значения). При их применении Visual Basic занимают область в памяти компьютера, которая предназначена для сохранения этой информации. Имена переменных, составленные из символов, могут иметь длину в 255 символов.
Что визуального в Visual Basic для приложений?
Что визуального в Visual Basic для приложений?
К счастью, VBA во многом избавляет от необходимости нудного печатания программного кода. В одних случаях вы записываете команды, которые нужны в приложении, и используете их в качестве отправной точки при создании новой программы.В
VBA против Visual Basic
VBA против Visual Basic
Помимо того, что VBA не позволяет вам создавать отдельные приложения, одно из основных отличий состоит в том, что программы, написанные на VBA, работают медленнее, чем программы, написанные на Visual
Различия между VBA и Visual Basic
Различия между VBA и Visual Basic
VBA имеет очень много общего с Visual Basic, своим старшим братом, предназначенным для создания независимых приложений. А раз языки похожи, вы можете перенести большую часть своих навыков в программировании на VBA в Visual Basic. Однако вам следует помнить о
Вызов редактора Visual Basic
Вызов редактора Visual Basic
Редактор Visual Basic служит командным центром для работы в VBA. В нем вы должны находиться при разработке VBA-форм, создании VBA-кода, тестировании и отладке VBA программ. Экспертом по использованию редактора Visual Basic вы станете после прочтения главы 5, а пока
Краткое знакомство с редактором Visual Basic
Краткое знакомство с редактором Visual Basic
Первые обращения к редактору Visual Basic могут вас озадачить. Наверное, присутствие меню и панелей инструментов вверху экрана покажется вам привычным, но вот что означает это обилие окон? Предсказать их взаимное расположение
Глава 5. Редактор Visual Basic к вашим услугам.
Глава 5. Редактор Visual Basic к вашим услугам.
В этой главе …~ Поиск команд в системе меню редактора Visual Basic~ Отображение, перемещение и настройка панелей инструментов~ Понимание и использование закрепления панелей инструментов и окон~ Сражение с толпами окон редактора Visual Basic~
Пользовательский интерфейс редактора Visual Basic
Пользовательский интерфейс редактора Visual Basic
Редактор Visual Basic является стандартным блюдом Microsoft- меню, панели инструментов и комбинации клавиш выглядят и работают очень похоже на Microsoft Office. Вы будете чувствовать себя как дома, если используете VBA с приложениями из Office.С
Подход Visual Basic 6.0
Подход Visual Basic 6.0
Благодаря искреннему желанию насладиться более простой жизнью, многие программисты ушли от «мира каркасов» приложений на базе C(++) к более дружественным языкам, таким, как, например, Visual Basic 6.0 (VB6). Язык VB6 стал популярным благодаря тому, что он дает
Среда разработки eMbedded Visual Basic 3.0
Среда разработки eMbedded Visual Basic 3.0
Для краткости в этой главе для обозначения среды eMbedded Visual Basic 3.0 будет использовано сокращение eVB.Запустить eVB можно либо при помощи команды меню Пуск (Пуск ? Программы ? Microsoft eMbedded Visual Tools ? eMbedded Visual Basic 3.0), либо найти в папке установки
Отличия eVB и Visual Basic для. NET
Отличия eVB и Visual Basic для. NET
В основном отличия VB.NET от eVB связаны с интеграцией языка VB с Compact Framework и определяются именно внутренней структурой самой CF.Типы данныхВ eVB был один-единственный тип данных на все случаи жизни, Variant, который достался eVB по наследству от VB Script. Visual
2.4.2. Генерация кода в Visual Basic
2.4.2. Генерация кода в Visual Basic
ERwin поддерживает генерацию кода для MS Visual Basic версий 4.0 и 5.0. В качестве источника информации при генерации форм служит модель ERwin. Использование ERwin позволяет одновременно описывать как клиентскую часть (объекты, отображающие данные на экране),
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I’m sure the answer to this is very easy, but I can’t find it in any documentation I have. I am automating a Word 2007 document and would like to give the user the ability to update the document properties (e.g., «Title», «Subject», «Keywords», or
custom properties like «Role») using VBA. I am thinking of using InputBox, but can’t seem to figure out how to access and change the document properties.Thanks!
mlr
Answers
-
Finally figured it out. Here’s what I came up with:
Sub SetVersion()
‘
‘ CustomDocumentProperties
‘
‘ 3 = Team
‘ 4 = Role
‘ 5 = Address
‘ 6 = City
‘ 7 = State
‘ 8 = Zip5
‘ 9 = Phone
‘ 10 = Web Address
‘ 11 = Version
‘
Dim myPrompt As String
Dim myTitle As String
Dim myVersion As StringmyPrompt = «Enter new Version number: «
myTitle = «Modify Version»myVersion = InputBox(myPrompt, myTitle)
Application.ActiveDocument.CustomDocumentProperties.Item(11).Value = myVersion
End Sub
mlr
-
Edited by
Monday, June 7, 2010 5:28 PM
missing 1 line of code in example -
Marked as answer by
mlr_gb
Monday, June 7, 2010 5:28 PM
-
Edited by