Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will demonstrate how to get today’s date in VBA.
There are a couple of ways to obtain today’s date in VBA code, namely using the VBA Date() function or the VBA Now() functions.
Date() function
The Date() Function returns today’s date. In the example below, we assign today’s date to a variable and then display the date in the immediate window in the VBE Editor.
Dim dtToday as Date
dtToday = Date()
Debug.Print dtTodayAlternatively, we can display the date in a message box.
Sub TestDate
Dim dtToday as Date
dtToday = Date()
Msgbox "Today's date is " & dtToday
End SubNow() Function
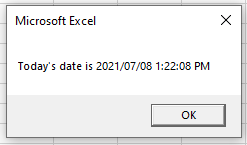
The Now() Function works in the same way as the date function, but it includes the time.
Sub TestDate()
Dim dtToday As Date
dtToday = Now()
MsgBox "Today's date is " & dtToday
End SubFormatting Dates with VBA
In both the Date() and the Now() functions, the date is formatted in a default style as determined by the settings on our PC. We can customize this formatting using the VBA Format function. As the format function will return a string, we need to declare a STRING variable rather than a DATE variable.
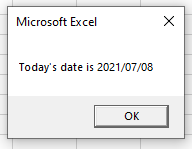
Sub TestDate()
Dim dtToday As String
dtToday = Format (Date, "dd mmmm yyyy")
MsgBox "Today's date is " & dtToday
End SubWe can also format the Now() function to include the time portion in a customized format.
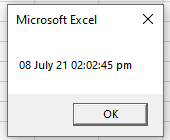
Sub FormatNow()
Dim dtToday As String
dtToday = Format(Now(), "dd mmmm yy hh:mm:ss am/pm")
MsgBox dtToday
End SubComparing 2 Dates with VBA
We can also use the Date function to compare today’s date with a different date – we might want to calculate how many days there are until an event! We can do this using the VBA DateDiff() function which will return a number. We can therefore declare an INTEGER variable to store the returned value in.
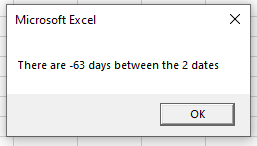
Sub TestDateDiff()
Dim dtToday As Date
Dim dtSomeDay As Date
Dim iDays As Integer
dtToday = Date
dtSomeDay = "05/06/2021"
iDays = DateDiff("d", dtToday, dtSomeDay)
MsgBox "There are " & iDays & " days between the 2 dates"
End SubAs Dates are stored as numbers, we could also minus the second date from the first to obtain the same answer.
iDays = dtToday - dtSomeDayVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Функции для работы с датой и временем в VBA Excel. Синтаксис, параметры, спецсимволы, примеры. Функции, возвращающие текущие дату и время по системному таймеру.
Функция Date
Date – это функция, которая возвращает значение текущей системной даты. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDate() MsgBox «Сегодня: « & Date End Sub |
Функция DateAdd
DateAdd – это функция, которая возвращает результат прибавления к дате указанного интервала времени. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
DateAdd(interval, number, date) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее интервал времени, который требуется добавить. |
| number | Обязательный параметр. Числовое выражение, задающее количество интервалов, которые необходимо добавить. Может быть как положительным (возвращается будущая дата), так и отрицательным (возвращается предыдущая дата). |
| date | Обязательный параметр. Значение типа Variant/Date или литерал, представляющий дату, к которой должен быть добавлен интервал. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1».
Примечание к таблице аргументов: три символа – y, d, w – указывают функции DateAdd на один день, который необходимо прибавить к исходной дате number раз.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateAdd() MsgBox «31.01.2021 + 1 месяц = « & DateAdd(«m», 1, «31.01.2021») ‘Результат: 28.02.2021 MsgBox «Сегодня + 3 года = « & DateAdd(«yyyy», 3, Date) MsgBox «Сегодня — 2 недели = « & DateAdd(«ww», —2, Date) MsgBox «10:22:14 + 10 минут = « & DateAdd(«n», 10, «10:22:14») ‘Результат: 10:32:14 End Sub |
Функция DateDiff
DateDiff – это функция, которая возвращает количество указанных интервалов времени между двумя датами. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Long.
Синтаксис
|
DateDiff(interval, date1, date2, [firstdayofweek], [firstweekofyear]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее интервал времени, количество которых (интервалов) требуется вычислить между двумя датами. |
| date1, date2 | Обязательные параметры. Значения типа Variant/Date, представляющие две даты, между которыми вычисляется количество указанных интервалов. |
| firstdayofweek | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
| firstweekofyear | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первую неделю года. По умолчанию – неделя, в которую входит 1 января. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1».
Примечание к таблице аргументов: в отличие от функции DateAdd, в функции DateDiff спецсимвол "w", как и "ww", обозначает неделю. Но расчет осуществляется по разному. Подробнее об этом на сайте разработчиков.
Параметры firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear определяют правила расчета количества недель между датами.
Таблицы констант из коллекций firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear смотрите в параграфах «Приложение 2» и «Приложение 3».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateDiff() ‘Даже если между датами соседних лет разница 1 день, ‘DateDiff с интервалом «y» покажет разницу — 1 год MsgBox DateDiff(«y», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1 год MsgBox DateDiff(«d», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1 день MsgBox DateDiff(«n», «31.12.2020», «01.01.2021») ‘Результат: 1440 минут MsgBox «Полных лет с начала века = « & DateDiff(«y», «2000», Year(Now) — 1) End Sub |
Функция DatePart
DatePart – это функция, которая возвращает указанную часть заданной даты. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Есть предупреждение по использованию этой функции.
Синтаксис
|
DatePart(interval, date, [firstdayofweek], [firstweekofyear]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| interval | Обязательный параметр. Строковое выражение из спецсимволов, представляющее часть даты, которую требуется извлечь. |
| date | Обязательные параметры. Значение типа Variant/Date, представляющее дату, часть которой следует извлечь. |
| firstdayofweek | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
| firstweekofyear | Необязательный параметр. Константа, задающая первую неделю года. По умолчанию – неделя, в которую входит 1 января. |
Таблицу аргументов (значений) параметра interval смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 1». В третьей графе этой таблицы указаны интервалы значений, возвращаемых функцией DatePart.
Таблицы констант из коллекций firstdayofweek и firstweekofyear смотрите в параграфах «Приложение 2» и «Приложение 3».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDatePart() MsgBox DatePart(«y», «31.12.2020») ‘Результат: 366 MsgBox DatePart(«yyyy», CDate(43685)) ‘Результат: 2019 MsgBox DatePart(«n», CDate(43685.45345)) ‘Результат: 52 MsgBox «День недели по счету сегодня = « & DatePart(«w», Now, vbMonday) End Sub |
Функция DateSerial
DateSerial – это функция, которая возвращает значение даты для указанного года, месяца и дня. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
DateSerial(year, month, day) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| year | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее значение от 100 до 9999 включительно. |
| month | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 1 до 12.* |
| day | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 1 до 31.* |
* Функция DateSerial автоматически пересчитывает общее количество дней в полные месяцы и остаток, общее количество месяцев в полные годы и остаток (подробнее в примере).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateSerial() MsgBox DateSerial(2021, 2, 10) ‘Результат: 10.02.2020 MsgBox DateSerial(2020, 1, 400) ‘Результат: 03.02.2021 End Sub |
Разберем подробнее строку DateSerial(2020, 1, 400):
- 400 дней = 366 дней + 31 день + 3 дня;
- 366 дней = 1 год, так как по условию month:=1, значит февраль 2020 входит в расчет, а в нем – 29 дней;
- 31 день = 1 месяц, так как сначала заполняется январь (по условию month:=1);
- 3 дня – остаток.
В итоге получается:
DateSerial(2020+1, 1+1, 3) = DateSerial(2021, 2, 3)
Функция DateValue
DateValue – это функция, которая преобразует дату, указанную в виде строки, в значение типа Variant/Date (время игнорируется).
Синтаксис
Параметр date – строковое выражение, представляющее дату с 1 января 100 года по 31 декабря 9999 года.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDateValue() MsgBox DateValue(«8 марта 2021») ‘Результат: 08.03.2021 MsgBox DateValue(«17 мая 2021 0:59:15») ‘Результат: 17.05.2021 End Sub |
Функция DateValue игнорирует время, указанное в преобразуемой строке, но если время указано в некорректном виде (например, «10:60:60»), будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Функция Day
Day – это функция, которая возвращает день месяца в виде числа от 1 до 31 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerDay() MsgBox Day(Now) End Sub |
Функция IsDate
IsDate – это функция, которая возвращает True, если выражение является датой или распознается как допустимое значение даты или времени. В остальных случаях возвращается значение False.
Синтаксис
Параметр expression – это переменная, возвращающая дату или строковое выражение, распознаваемое как дата или время.
Значение, возвращаемое переменной expression, не должно выходить из диапазона допустимых дат: от 1 января 100 года до 31 декабря 9999 года (для Windows).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerIsDate() MsgBox IsDate(«18 апреля 2021») ‘Результат: True MsgBox IsDate(«31 февраля 2021») ‘Результат: False MsgBox IsDate(«4.10.20 11:12:54») ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция Hour
Hour – это функция, которая возвращает количество часов в виде числа от 0 до 23 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerHour() MsgBox Hour(Now) MsgBox Hour(«22:36:54») End Sub |
Функция Minute
Minute – это функция, которая возвращает количество минут в виде числа от 0 до 59 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMinute() MsgBox Minute(Now) MsgBox Minute(«22:36:54») End Sub |
Функция Month
Month – это функция, которая возвращает день месяца в виде числа от 1 до 12 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMonth() MsgBox Month(Now) End Sub |
Функция MonthName
MonthName – это функция, которая возвращает название месяца в виде строки.
Синтаксис
|
MonthName(month, [abbreviate]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| month | Обязательный параметр. Числовое обозначение месяца от 1 до 12 включительно. |
| abbreviate | Необязательный параметр. Логическое значение: True – возвращается сокращенное название месяца, False (по умолчанию) – название месяца не сокращается. |
Пример
|
Sub PrimerMonthName() MsgBox MonthName(10) ‘Результат: Октябрь MsgBox MonthName(10, True) ‘Результат: окт End Sub |
Функция Now
Now – это функция, которая возвращает текущую системную дату и время. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerNow() MsgBox Now MsgBox Day(Now) MsgBox Hour(Now) End Sub |
Функция Second
Second – это функция, которая возвращает количество секунд в виде числа от 0 до 59 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр time – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее время.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerSecond() MsgBox Second(Now) MsgBox Second(«22:30:14») End Sub |
Функция Time
Time – это функция, которая возвращает значение текущего системного времени. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTime() MsgBox «Текущее время: « & Time End Sub |
Функция TimeSerial
TimeSerial – это функция, которая возвращает значение времени для указанного часа, минуты и секунды. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Date.
Синтаксис
|
TimeSerial(hour, minute, second) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| hour | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее значение от 0 до 23 включительно. |
| minute | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 0 до 59.* |
| second | Обязательный параметр типа Integer. Числовое выражение, возвращающее любое значение (в пределах Integer), а не только от 0 до 59.* |
* Функция TimeSerial автоматически пересчитывает общее количество секунд в полные минуты и остаток, общее количество минут в полные часы и остаток (подробнее в примере).
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTime() MsgBox TimeSerial(5, 16, 4) ‘Результат: 5:16:04 MsgBox TimeSerial(5, 75, 158) ‘Результат: 6:17:38 End Sub |
Разберем подробнее строку TimeSerial(5, 75, 158):
- 158 секунд = 120 секунд (2 минуты) + 38 секунд;
- 75 минут = 60 минут (1 час) + 15 минут.
В итоге получается:
TimeSerial(5+1, 15+2, 38) = TimeSerial(6, 17, 38)
Функция TimeValue
TimeValue – это функция, которая преобразует время, указанное в виде строки, в значение типа Variant/Date (дата игнорируется).
Синтаксис
Параметр time – строковое выражение, представляющее время с 0:00:00 по 23:59:59 включительно.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerTimeValue() MsgBox TimeValue(«6:45:37 PM») ‘Результат: 18:45:37 MsgBox TimeValue(«17 мая 2021 3:59:15 AM») ‘Результат: 3:59:15 End Sub |
Функция TimeValue игнорирует дату, указанную в преобразуемой строке, но если дата указана в некорректном виде (например, «30.02.2021»), будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Функция Weekday
Weekday – это функция, которая возвращает день недели в виде числа от 1 до 7 включительно. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
|
Weekday(date, [firstdayofweek]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| date | Обязательный параметр. Любое выражение (числовое, строковое), отображающее дату. |
| firstdayofweek | Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
Таблицу констант из коллекции firstdayofweek смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 2».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerWeekday() MsgBox Weekday(«23 апреля 2021», vbMonday) ‘Результат: 5 MsgBox Weekday(202125, vbMonday) ‘Результат: 6 End Sub |
Функция WeekdayName
WeekdayName – это функция, которая возвращает название дня недели в виде строки.
Синтаксис
|
WeekdayName(weekday, [abbreviate], [firstdayofweek]) |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| weekday | Обязательный параметр. Числовое обозначение дня недели от 1 до 7 включительно. |
| abbreviate | Необязательный параметр. Логическое значение: True – возвращается сокращенное название дня недели, False (по умолчанию) – название дня недели не сокращается. |
| firstdayofweek | Константа, задающая первый день недели. По умолчанию – воскресенье. |
Таблицу констант из коллекции firstdayofweek смотрите в параграфе «Приложение 2».
Пример
|
Sub PrimerWeekdayName() MsgBox WeekdayName(3, True, vbMonday) ‘Результат: Ср MsgBox WeekdayName(3, , vbMonday) ‘Результат: среда MsgBox WeekdayName(Weekday(Now, vbMonday), , vbMonday) End Sub |
Функция Year
Year – это функция, которая возвращает номер года в виде числа. Тип возвращаемого значения – Variant/Integer.
Синтаксис
Параметр date – любое числовое или строковое выражение, представляющее дату.
Пример
|
Sub PrimerYear() MsgBox Year(Now) End Sub |
Приложение 1
Таблица аргументов (значений) параметраinterval для функций DateAdd, DateDiff и DatePart:
| Аргумент | Описание | Интервал значений |
|---|---|---|
| yyyy | Год | 100 – 9999 |
| q | Квартал | 1 – 4 |
| m | Месяц | 1 – 12 |
| y | День года | 1 – 366 |
| d | День месяца | 1 – 31 |
| w | День недели | 1 – 7 |
| ww | Неделя | 1 – 53 |
| h | Часы | 0 – 23 |
| n | Минуты | 0 – 59 |
| s | Секунды | 0 – 59 |
В третьей графе этой таблицы указаны интервалы значений, возвращаемых функцией DatePart.
Приложение 2
Константы из коллекции firstdayofweek:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Используются системные настройки |
| vbSunday | 1 | Воскресенье (по умолчанию) |
| vbMonday | 2 | Понедельник |
| vbTuesday | 3 | Вторник |
| vbWednesday | 4 | Среда |
| vbThursday | 5 | Четверг |
| vbFriday | 6 | Пятница |
| vbSaturday | 7 | Суббота |
Приложение 3
Константы из коллекции firstweekofyear:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Используются системные настройки. |
| vbFirstJan1 | 1 | Неделя, в которую входит 1 января (по умолчанию). |
| vbFirstFourDays | 2 | Неделя, в которую входит не менее четырех дней нового года. |
| vbFirstFullWeek | 3 | Первая полная неделя года. |
Home / VBA / How to Get Today’s Date and Current Time using VBA
In this tutorial, we will learn different ways to get today’s date and current time using a VBA code.
In VBA, there’s a function called “DATE” that you can use to get the current date. When you use this function, just like the following example, it returns the current date according to the date setting of the system.
Sub myMacro()
Range("A1") = Date
End SubWhen you run this code, it enters the current date into cell A1 and uses the current format of the date that you have in Excel.

You can also use this function to get today’s date into a message box, just like the following code.
Sub myMacro()
MsgBox Date
End SubToday’s Date and Current Time
In the same way, there’s a function called “NOW” that you can use to get today’s date and current time. As you can see, we have used it in the following code to get the current date and time into cell A1.

Sub myMacro()
Range("A1") = Now
End SubCurrent Time
Now if you want to get the current time only instead of date and time you need to use another function “Format” (you can learn more about this function from here) along with the now function.

In the above code, we have used the now function to provide the value for the format function and then used a format for the time only.
Sub myMacro()
Range("A1") = Format(Now, "HH:MM Am/Pm")
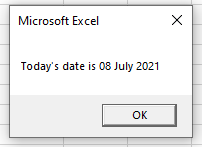
End SubChanging Today’s Date Format (Example: YYYYMMDD)
You can also use the format function to change the format of the current date. In the following code, we have used the format function and specify the format as “YYYYMMDD”.
Sub myMacro()
Range("A1").Value = Format(Date, "YYYY/MM/DD")
End SubNote: In the above code, we have used value property to enter the date into cell A1.

VBA Today Function
Today means the current date. In the worksheet, the NOW function does the same thing, which gives us the current date and time, but there is no built-in Today function in VBA. So instead, the method to get the system’s current date is by using the Date function. However, unlike the NOW function, the Date function only gives us the current date.
In Excel, we have several useful functions that can help us daily. Excel made all of our lives easy at the workplace. When we say “daily,” Excel also has the formula to return today’s date. Not only the date, but we can also get the current date and time together. Such is the variety of excel formulas. If you are a regular user of Excel, we hope you have come across the formula “TODAY” in excel to insert the current date as shown on your working computer. But we do not have the TODAY function in VBA. So then, how do we get the TODAY date from VBA? This article will show you how to work with the TODAY date in VBA. Read on.
Table of contents
- VBA Today Function
- What is the Formula to get Today’s Date in VBA?
- What Date Function Does in VBA?
- Examples of Date Function in VBA
- Example #1
- Date Function to find the Due is Today.
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Today (wallstreetmojo.com)
What is the Formula to get Today’s Date in VBA?
If there is no formula called TODAY, how do we get today’s date from VBA? It is the common question everybody asks, but the solution is simple: we have a formula with a different name, i.e., the DATE function.
What Date Function Does in VBA?
The DATE function is the same as the VBA TODAY function. But this is not a volatile function unless you run the Macro or trigger the Macro.
The syntax of the DATE function does not have any arguments. So, we need to pass the function DATE. That is all.
DATE ()
Examples of Date Function in VBA
The DATE function returns the current date of the system. Using this as part of the big VBA project is very useful. To have proper knowledge about this, first, we will show you simple examples of the DATE function.
Example #1
Let us create a simple DATE function to show the current date in the message box. Then, follow the below steps to write the excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more.
Step 1: Create a sub procedure by naming the macro.
Step 2: Declare the variable as “Date.” The DATE function returns the result as a date only, so the variable data type should be “Date.”
Code:
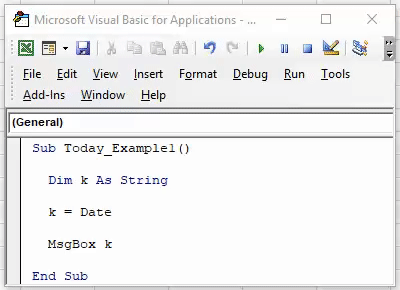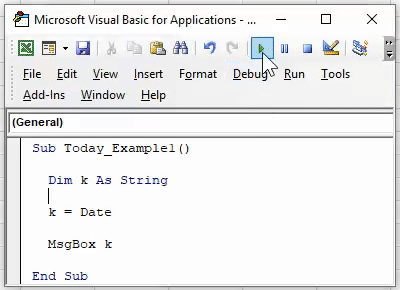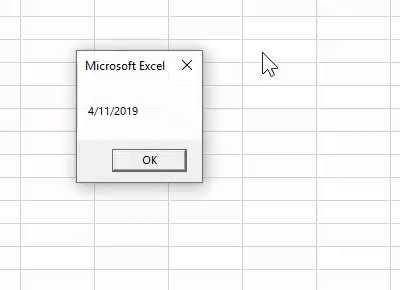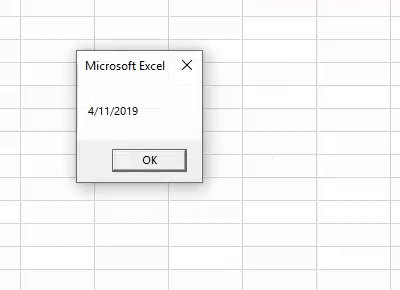
Sub Today_Example1() Dim K As String End Sub
Step 3: Assign the value to variable “k” as the DATE function.
Code:
Sub Today_Example1() Dim K As String K = Date End Sub
Step 4: Now, the value of the variable “k” in the message box in VBA.
Code:
Sub Today_Example1() Dim K As String K = Date MagBox K End Sub
Run the code. We should see the current date showing in the system.
Note: Date format could vary based on the system settings. It could be in “mm-dd-yy,” “dd-mm-yy.”
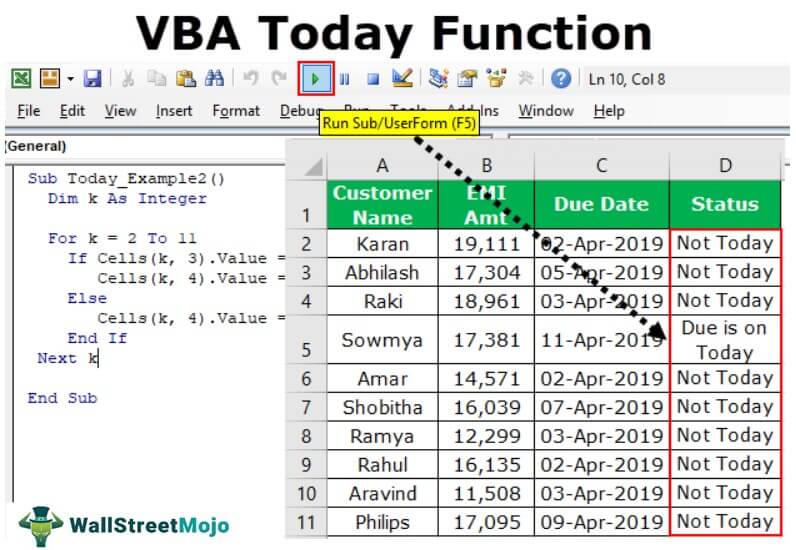
Date Function to find the Due is Today.
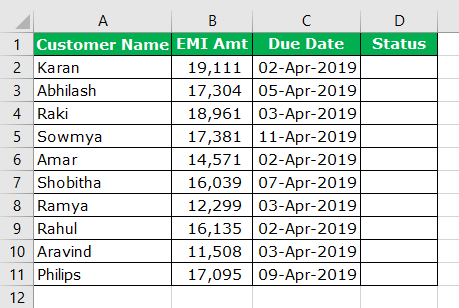
The Date function is more helpful in finding the due dates of EMI, credit card payments, insurance payments, etc.
Assume you are working as a loan recovery officer and have a list of customers with their due amount and due date.
In the status column, you need the result as “Due is Today” if the due date is equal to the current system date.
We can do this by using the IF condition and loops in VBAA VBA loop in excel is an instruction to run a code or repeat an action multiple times.read more. Below is the readymade code for you to arrive at the results.
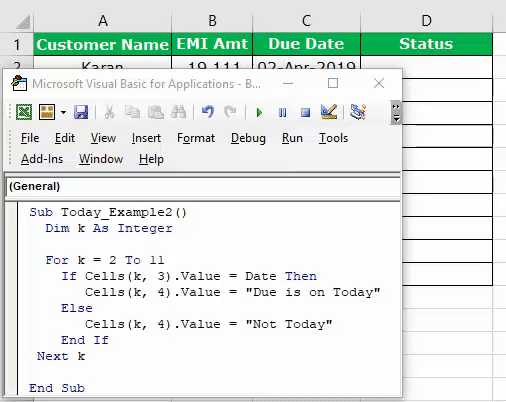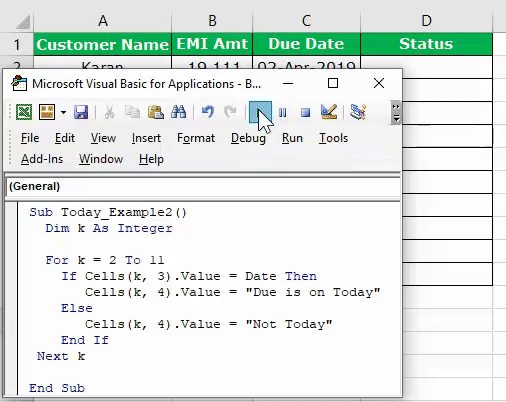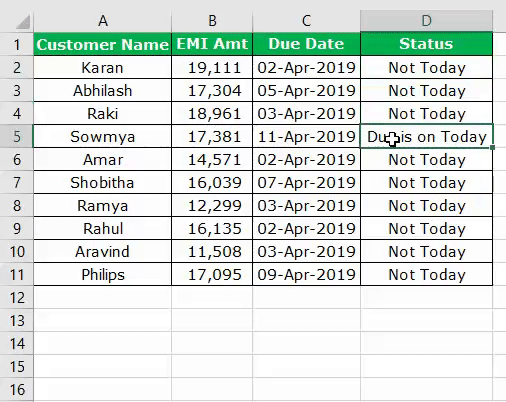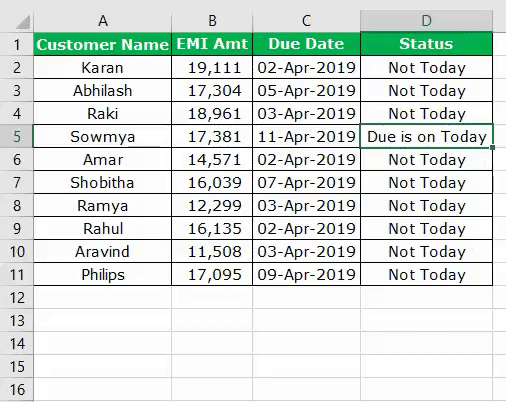
Code:
Sub Today_Example2() Dim K As Integer For K = 2 To 11 If Cells(K, 3).Value = Date Then Cells(K, 4).Value = "Due is on Today" Else Cells(K, 4).Value = "Not Today" End If Next K End Sub
It will arrive at the results in the status column.
Like this in many scenarios, we can use the DATE function to check the dates and perform some action.
You can download this VBA Today Function here. VBA Today Function Excel Template
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to the VBA Today function. Here, we learn how to find today’s date in VBA using the Date function, practical examples, and downloadable Excel templates. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- DateDiff function in VBA
- DateAdd in VBA
- VBA Functions List
- Weekday Function in VBA
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I’ve been trying to get the current date a few ways in VBA. I tried using the today() function in a spreadsheet and getting the data from that cell and also calling it explicitly in a vba script and have had no success. any help will be appreciated.
Answers
-
Offcourse. (^_^ ) The only difference between Now and the one’s i’ve suggested is that Now contains both the current date and time while Date and Time are seperate commands for the date and time. (^_^ ) It all depends on which information you need.
Главная » Функции VBA »
28 Апрель 2011 326682 просмотров
- Date() — возвращает текущую системную дату. Установить ее можно при помощи одноименного оператора, например, так:
- Time() — возвращает текущее системное время
- Now() — возвращает дату и время вместе.
- DateAdd() — возможность добавить к дате указанное количество лет, кварталов, месяцев и так далее — вплоть до секунд. Интервалы(год, месяц и т.д.) указываются в текстовом формате. Список допустимых значений:
«yyyy» Год
«q» Квартал
«m» Месяц
«y» День года
«d» День
«w» День недели
«ww» Неделя
«h» Час
«n» Минута
«s» Секунда
Сам синтаксис обращения незамысловат. Сначала указываем интервал, затем сколько единиц добавить и самый последний аргумент — к какой дате(включая время, кстати). Например, чтобы добавить 3 года к текущей дате-времени, надо записать функцию так:
MsgBox DateAdd(«yyyy», 3, Now)
Но что интереснее — можно не только добавлять, но и отнимать. Функция не изменится, мы просто должны записать кол-во добавляемых периодов со знаком минус. Отнимем три года от текущей даты-времени:
MsgBox DateAdd(«yyyy», -3, Now) - DateDiff() — возможность получить разницу между датами (опять таки в единицах от лет до секунд).
Dim lDaysCnt As Long lDaysCnt = DateDiff("d", "20.11.2012", Now) MsgBox "С 20.11.2012 прошло дней: " & lDaysCnt
Первый аргумент определяет период времени, в котором необходимо вернуть разницу между датами. Допустимые значения:
«yyyy» Год
«q» Квартал
«m» Месяц
«y» День года
«d» День
«w» День недели
«ww» Неделя
«h» Час
«n» Минута
«s» Секунда
Наиболее полезна DateDiff при вычислении полных лет. Например, чтобы вычислить сколько лет на текущий момент человеку, в зависимости от даты рождения, можно использовать функцию так:MsgBox DateDiff("yyyy", "20.12.1978", Now)
Без этой функции вычислить кол-во полных лет гораздо сложнее.
- DatePart() — функция возвращает указанную часть даты (например, только год, только месяц или только день недели), на основании заданной даты. Часто применяется для получения номера недели для даты.
Первый аргумент — период времени. Принимаемые значения те же, что и для функции DateDiff(годы, месяцы, недели и т.д.)
Второй аргумент — непосредственно дата, часть которой необходимо получить:MsgBox "Номер недели года: " & DatePart("ww", Now)
- DateSerial() — возможность создать значение даты, задавая месяц, год и день числовыми значениями:
- DateValue()— делает то же, что и DateSerial(). Отличия — в формате принимаемых значений. Эта функция в качестве аргумента принимает дату в текстовом формате и преобразует её в формат даты:
MsgBox DateValue("07.06.12")Аналогичным образом (для времени) работают TimeSerial() и TimeValue()
- Day(), Year(), Month(), Weekday(), Hour(), Minute(), Second() — специализированные заменители функции DatePart(), которые возвращают нужную часть даты/времени (которую именно — видно из названия).
- MonthName() — возвращает имя месяца словами по его номеру. Возвращаемое значение зависит от региональных настроек. Если они русские, то вернется русское название месяца.
- Timer() — возвращает количество секунд, прошедших с полуночи.
MsgBox DateSerial(2012, 6, 7)
Статья помогла? Сделай твит, поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
I have a dialog box that appears when the user clicks a macro button. This dialog box is mostly filled out (date, email, producer, website, etc are filled) and all the user needs to do is enter their name. The problem is that the date entered is static, so if I entered «3/3/11» it’ll stay that way until someone changes it.
I was wondering if there was some way for that text box to always display the current date (unless the user decides to change it for whatever reason). I’ve tried putting different things into the «Value» section of the text box (such as «getDate()» and «= Date()») but so far haven’t been successful.
Thank you,
Jesse Smothermon
H.B.
160k28 gold badges316 silver badges390 bronze badges
asked May 3, 2011 at 20:38
Jesse SmothermonJesse Smothermon
1,04110 gold badges25 silver badges36 bronze badges
Use the form Initialize event, e.g.:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
TextBox1.Value = Format(Date, "mm/dd/yyyy")
End Sub
answered May 3, 2011 at 21:17
4
The easy way to do this is to put the Date function you want to use in a Cell, and link to that cell from the textbox with the LinkedCell property.
From VBA you might try using:
textbox.Value = Format(Date(),"mm/dd/yy")
answered May 3, 2011 at 21:08
Lance RobertsLance Roberts
22.2k32 gold badges112 silver badges129 bronze badges
1
Set the value from code on showing the form, not in the design-timeProperties for the text box.
Private Sub UserForm_Activate()
Me.txtDate.Value = Format(Date, "mm/dd/yy")
End Sub
answered May 3, 2011 at 21:20
Tim WilliamsTim Williams
150k8 gold badges96 silver badges124 bronze badges
Here’s a more simple version. In the cell you want the date to show up just type
=Today()
Format the cell to the date format you want and Bob’s your uncle. 
Udo Held
12.3k11 gold badges69 silver badges93 bronze badges
answered Mar 29, 2012 at 20:46
2
You were close. Add this code in the UserForm_Initialize() event handler:
tbxDate.Value = Date
Gaffi
4,3118 gold badges45 silver badges73 bronze badges
answered May 3, 2011 at 21:12
Arnoud KooiArnoud Kooi
1,5584 gold badges17 silver badges25 bronze badges
2
Actually, it is less complicated than it seems.
Sub
today_1()
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=TODAY()"
ActiveCell.Value = Date
End Sub
Timothy
1,9703 gold badges26 silver badges28 bronze badges
answered Jun 2, 2016 at 6:27
1
I know this is extremely old post, but I’ve used this before
You can always adjust to activate. Now method is another way. Just an option
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
Textbox1.Text = Format(Now(), "mmddyyyhhmmss")
End Sub
answered Jan 17, 2018 at 17:12
Year, Month, Day of a Date | DateAdd | Current Date and Time | Hour, Minute, Second | TimeValue
Learn how to work with dates and times in Excel VBA.
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the code lines below. To execute the code lines, click the command button on the sheet.
Year, Month, Day of a Date
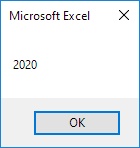
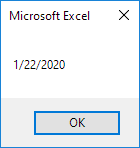
The following macro gets the year of a date. To declare a date, use the Dim statement. To initialize a date, use the DateValue function.
Code:
Dim exampleDate As Date
exampleDate = DateValue(«Jan 19, 2020»)
MsgBox Year(exampleDate)
Result:
Note: Use Month and Day to get the month and day of a date.
DateAdd
To add a number of days to a date, use the DateAdd function. The DateAdd function has three arguments. Fill in «d» for the first argument to add days. Fill in 3 for the second argument to add 3 days. The third argument represents the date to which the number of days will be added.
Code:
Dim firstDate As Date, secondDate As Date
firstDate = DateValue(«Jan 19, 2020»)
secondDate = DateAdd(«d», 3, firstDate)
MsgBox secondDate
Result:
Note: Change «d» to «m» to add a number of months to a date. Place your cursor on DateAdd in the Visual Basic Editor and click F1 for help on the other interval specifiers. Dates are in US Format. Months first, Days second. This type of format depends on your windows regional settings.
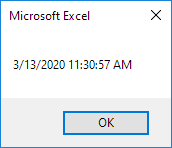
Current Date and Time
To get the current date and time, use the Now function.
Code:
MsgBox Now
Result:
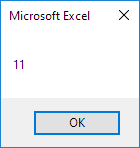
Hour, Minute, Second
The get the hour of a time, use the Hour function.
Code:
MsgBox Hour(Now)
Result:
Note: Use Minute and Second to get the minute and second of a time.
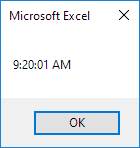
TimeValue
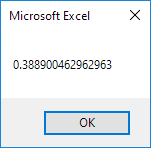
The TimeValue function converts a string to a time serial number. The time’s serial number is a number between 0 and 1. For example, noon (halfway through the day) is represented as 0.5.
Code:
MsgBox TimeValue(«9:20:01 am»)
Result:
Now, to clearly see that Excel handles times internally as numbers between 0 and 1, add the following code lines:
Dim y As Double
y = TimeValue(«09:20:01»)
MsgBox y
Result:
Date and Time Functions are the inbuilt functions that give us the opportunity to see the date or time according to the user’s need. Suppose a user needs to see the month or the day or the year then it can be easily seen by different date functions. Similarly, for the time function, also we can manipulate it according to the need of the user. Date and Time functions are used to interconvert date and time in different formats. In this article, we will learn about the most commonly used date and time functions.
VBA Date Functions
There are fifteen-plus different date functions in VBA, but here we will talk about some of the most commonly used date functions.
VBA Date Function
The Date() function returns the current date. The Date() function does not require any arguments. For example, declare a variable name date_1 of Date data type, call the Date() function, and store the return value in date_1, then print the date_1 in the console.
Syntax of the function: Date()
VBA DateAdd Function
The DateAdd() function is used to add an interval of date/time to the respective date or time. The function will return the resulting date or time. The function takes three arguments, Interval, Number, and Date/Time.
Syntax of the function: DateAdd(Interval, Number, Date/Time)
Interval: The first argument, represents, which part of the Date/Time, you want the interval to be added.
Types of intervals are discussed in the following table:
| Intervals | Specification |
| “d” | Day |
| “ww” | Week |
| “m” | Month |
| “q” | Quarter |
| “yyyy” | Year |
| “y” | Day of the year |
| “h” | Hour |
| “n” | Minute |
| “s” | Second |
Number: The second argument represents, the number of Intervals we want to add to the Date/Time.
Date/Time: The third argument represents, the Date/Time on which the changes have to occur.
For example, the current date is “20/11/2020”, and we want to increase the month count by 8. Then use, DateAdd(“m”, 8, “20/11/2020”), and the final output date will be “20/07/2021”.
VBA DateDiff Function
The DateDiff() function is used to get the difference between two dates, in terms of the year, month, day, hours, seconds, etc. The function will return the resulting Date/Time. The functions take three mandatory arguments, Interval, Date1, and Date2.
Syntax of the function: DateDiff(Interval, Date1, Date2)
Interval: The first argument, represents, the part of the Date/Time, you want to see the difference. For example, in terms of the year, day, month, etc. Refer to the table in VBADateAdd() function, for the values of Interval.
Date1: Date1 is the second argument. It tells the start date in an interval.
Date 2: Date2 is the third argument. It tells the end date in an interval.
For example, consider Date1 as “20/10/2020”, and Date2 as “20/12/2021”, and the difference in terms of “d”(days). The final output of the function will be 426.
VBA DatePart Function
The DatePart() function is used to get a particular part(day, week, year) from the date. The function returns the part of date in asked format by the user. The function takes two mandatory arguments, Interval, Date.
Syntax of the function: DatePart(Interval, Date)
Interval: The first argument, represents, the part of the Date/Time, one wants to see. For example, “yyyy” represents the year, and tells the DatePart function to return the year of an input Date.
Date: The second argument, which represents the date user will enter, to check a particular part of a date.
For example, consider the Date as “10/10/2020”, and it has been asked to print the year of this particular date. So, we will use “yyyy” as the first argument. The final output is 2020.
VBA MonthName Function
The MonthName() function returns the name of the month according to the integer value. The function takes one mandatory argument, a number.
Syntax of the function: MonthName(number)
number: The first argument, which tells about the number of the month.
For example, 11 is the argument of the MonthName() function, the function returns “November”.
VBA Time Functions
There are ten-plus different time functions in VBA, but here we will talk about some of the most commonly used time functions.
VBA Now Function
The Now() function is used to get the current date and time of the system. The function does not take any arguments. For example, declare a variable name date_2 of Date data type, call the Now() function, and store the return value in date_2, then print the date_2 in the console.
Syntax of the function: Now()
VBA Time Function
The Time() function is used to get the current time of your system. The function does not take any arguments. For example, call the Time() function, and the system will return the current time i.e. 5:20:20 PM.
Syntax of the function: Time()
VBA Hour Function
The hour() function is used to get the hour from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: hour(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the hour of this particular time. The final output will be 1.
VBA Minute Function
The minute() function is used to get the minute from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: minute(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the minute of this particular time. The final output will be 08.
VBA Second Function
The second() function is used to get the seconds from the time. The function takes one mandatory argument, Time.
Syntax of the function: second(Time)
Time: The first argument, which represents the time user will enter.
For example, consider the time “1:08:42 PM”, and it has been asked to print the seconds of this particular time. The final output will be 42.