Used as a container for Microsoft Excel worksheet functions that can be called from Visual Basic.
Use the WorksheetFunction property of the Application object to return the WorksheetFunction object.
The following example displays the result of applying the Min worksheet function to the range A1:C10.
Set myRange = Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:C10") answer = Application.WorksheetFunction.Min(myRange) MsgBox answer
This example uses the CountA worksheet function to determine how many cells in column A contain a value. For this example, the values in column A should be text. This example does a spell check on each value in column A, and if the value is spelled incorrectly, inserts the text «Wrong» into column B; otherwise, it inserts the text «OK» into column B.
Sub StartSpelling() 'Set up your variables Dim iRow As Integer 'And define your error handling routine. On Error GoTo ERRORHANDLER 'Go through all the cells in column A, and perform a spellcheck on the value. 'If the value is spelled incorrectly, write "Wrong" in column B; otherwise, write "OK". For iRow = 1 To WorksheetFunction.CountA(Columns(1)) If Application.CheckSpelling( _ Cells(iRow, 1).Value, , True) = False Then Cells(iRow, 2).Value = "Wrong" Else Cells(iRow, 2).Value = "OK" End If Next iRow Exit Sub 'Error handling routine. ERRORHANDLER: MsgBox "The spell check feature is not installed!" End Sub
In this Article
- How to Use Worksheet Functions in VBA
- WorksheetFunction Method
- Application.WorksheetFunction vs. Application
- Vlookup WorksheetFunction Error Handling
- VBA Worksheet Functions List
There are many ways to use functions in VBA. VBA comes loaded with many built-in functions. You can even create your own functions (UDFs). However, you can also utilize many of Excel’s functions in VBA by using Application.WorksheetFunction.
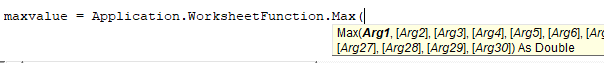
To access an Excel function in VBA add Application.WorksheetFunction in front of the function that you wish to call. In the example below, we’ll call Excel’s Max Function:
Dim maxvalue as long
maxvalue = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)The syntax of the functions are the same, however you will enter the function arguments just like you would any other VBA function.
Notice that the syntax of the Max Function appears when you type (similar to with VBA Functions):
WorksheetFunction Method
WorksheetFunction is a method of Application object. It allows you access to many (not all) of the standard Excel worksheet functions. Generally, you won’t gain access to any worksheet functions that have a corresponding VBA version.
You can see a list of many of the most common Worksheet Functions below.
Application.WorksheetFunction vs. Application
There are actually two ways to access these functions:
Application.WorksheetFunction (as seen above):
maxvalue = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)or you can omit the WorksheetFunction
maxvalue = Application.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)Unfortunately, omitting the WorksheetFunction will eliminate the Intellisense that displays the syntax (see image above). However, it has one big potential advantage: Error Handling.
If you use Application, and your function generates an error it will return the error value. If you use the WorksheetFunction method, VBA will throw a run time error. Of course, you can handle the VBA error, but it’s usually better to avoid the error in the first place.
Let’s look at an example to see the difference:
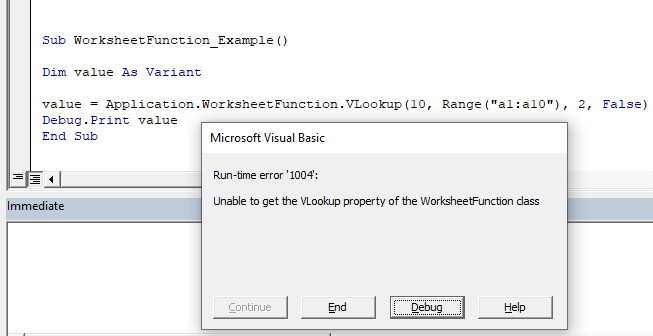
Vlookup WorksheetFunction Error Handling
We will attempt to perform a Vlookup that will not result in a match. So the Vlookup function will return an error.
First, we will use the WorksheetFunction method. Notice how VBA throws an error:
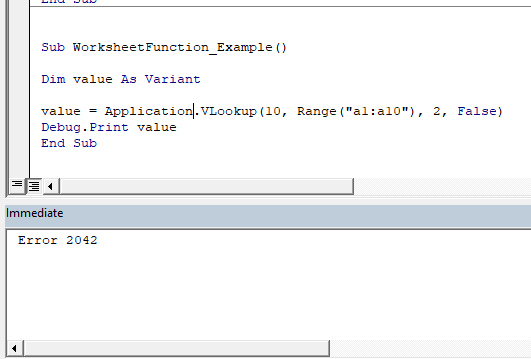
Next we omit the WorksheetFunction. Notice how the
Next we will omit the WorksheetFunction. Notice how no error is thrown and instead the ‘value’ function contains the error value from the Vlookup.
VBA Worksheet Functions List
Below you will find a list of most of the common VBA WorksheetFunctions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Logical | |
| AND | Checks whether all conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| IF | If condition is met, do something, if not, do something else. |
| IFERROR | If result is an error then do something else. |
| OR | Checks whether any conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| Lookup & Reference | |
| CHOOSE | Chooses a value from a list based on it’s position number. |
| HLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first row and return a value. |
| INDEX | Returns a value based on it’s column and row numbers. |
| LOOKUP | Looks up values either horizontally or vertically. |
| MATCH | Searches for a value in a list and returns its position. |
| TRANSPOSE | Flips the oriention of a range of cells. |
| VLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first column and return a value. |
| Date & Time | |
| DATE | Returns a date from year, month, and day. |
| DATEVALUE | Converts a date stored as text into a valid date |
| DAY | Returns the day as a number (1-31). |
| DAYS360 | Returns days between 2 dates in a 360 day year. |
| EDATE | Returns a date, n months away from a start date. |
| EOMONTH | Returns the last day of the month, n months away date. |
| HOUR | Returns the hour as a number (0-23). |
| MINUTE | Returns the minute as a number (0-59). |
| MONTH | Returns the month as a number (1-12). |
| NETWORKDAYS | Number of working days between 2 dates. |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL | Working days between 2 dates, custom weekends. |
| NOW | Returns the current date and time. |
| SECOND | Returns the second as a number (0-59) |
| TIME | Returns the time from a hour, minute, and second. |
| TIMEVALUE | Converts a time stored as text into a valid time. |
| WEEKDAY | Returns the day of the week as a number (1-7). |
| WEEKNUM | Returns the week number in a year (1-52). |
| WORKDAY | The date n working days from a date. |
| YEAR | Returns the year. |
| YEARFRAC | Returns the fraction of a year between 2 dates. |
| Engineering | |
| CONVERT | Convert number from one unit to another. |
| Financial | |
| FV | Calculates the future value. |
| PV | Calculates the present value. |
| NPER | Calculates the total number of payment periods. |
| PMT | Calculates the payment amount. |
| RATE | Calculates the interest Rate. |
| NPV | Calculates the net present value. |
| IRR | The internal rate of return for a set of periodic CFs. |
| XIRR | The internal rate of return for a set of non-periodic CFs. |
| PRICE | Calculates the price of a bond. |
| INTRATE | The interest rate of a fully invested security. |
| Information | |
| ISERR | Test if cell value is an error, ignores #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISERROR | Test if cell value is an error. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISEVEN | Test if cell value is even. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISLOGICAL | Test if cell is logical (TRUE or FALSE). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNA | Test if cell value is #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNONTEXT | Test if cell is not text (blank cells are not text). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNUMBER | Test if cell is a number. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISODD | Test if cell value is odd. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISTEXT | Test if cell is text. TRUE/FALSE |
| TYPE | Returns the type of value in a cell. |
| Math | |
| ABS | Calculates the absolute value of a number. |
| AGGREGATE | Define and perform calculations for a database or a list. |
| CEILING | Rounds a number up, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| COS | Returns the cosine of an angle. |
| DEGREES | Converts radians to degrees. |
| DSUM | Sums database records that meet certain criteria. |
| EVEN | Rounds to the nearest even integer. |
| EXP | Calculates the exponential value for a given number. |
| FACT | Returns the factorial. |
| FLOOR | Rounds a number down, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| GCD | Returns the greatest common divisor. |
| INT | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer. |
| LCM | Returns the least common multiple. |
| LN | Returns the natural logarithm of a number. |
| LOG | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base. |
| LOG10 | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number. |
| MROUND | Rounds a number to a specified multiple. |
| ODD | Rounds to the nearest odd integer. |
| PI | The value of PI. |
| POWER | Calculates a number raised to a power. |
| PRODUCT | Multiplies an array of numbers. |
| QUOTIENT | Returns the integer result of division. |
| RADIANS | Converts an angle into radians. |
| RANDBETWEEN | Calculates a random number between two numbers. |
| ROUND | Rounds a number to a specified number of digits. |
| ROUNDDOWN | Rounds a number down (towards zero). |
| ROUNDUP | Rounds a number up (away from zero). |
| SIN | Returns the sine of an angle. |
| SUBTOTAL | Returns a summary statistic for a series of data. |
| SUM | Adds numbers together. |
| SUMIF | Sums numbers that meet a criteria. |
| SUMIFS | Sums numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| SUMPRODUCT | Multiplies arrays of numbers and sums the resultant array. |
| TAN | Returns the tangent of an angle. |
| Stats | |
| AVERAGE | Averages numbers. |
| AVERAGEIF | Averages numbers that meet a criteria. |
| AVERAGEIFS | Averages numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| CORREL | Calculates the correlation of two series. |
| COUNT | Counts cells that contain a number. |
| COUNTA | Count cells that are non-blank. |
| COUNTBLANK | Counts cells that are blank. |
| COUNTIF | Counts cells that meet a criteria. |
| COUNTIFS | Counts cells that meet multiple criteria. |
| FORECAST | Predict future y-values from linear trend line. |
| FREQUENCY | Counts values that fall within specified ranges. |
| GROWTH | Calculates Y values based on exponential growth. |
| INTERCEPT | Calculates the Y intercept for a best-fit line. |
| LARGE | Returns the kth largest value. |
| LINEST | Returns statistics about a trendline. |
| MAX | Returns the largest number. |
| MEDIAN | Returns the median number. |
| MIN | Returns the smallest number. |
| MODE | Returns the most common number. |
| PERCENTILE | Returns the kth percentile. |
| PERCENTILE.INC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is inclusive. |
| PERCENTILE.EXC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is exclusive. |
| QUARTILE | Returns the specified quartile value. |
| QUARTILE.INC | Returns the specified quartile value. Inclusive. |
| QUARTILE.EXC | Returns the specified quartile value. Exclusive. |
| RANK | Rank of a number within a series. |
| RANK.AVG | Rank of a number within a series. Averages. |
| RANK.EQ | Rank of a number within a series. Top Rank. |
| SLOPE | Calculates the slope from linear regression. |
| SMALL | Returns the kth smallest value. |
| STDEV | Calculates the standard deviation. |
| STDEV.P | Calculates the SD of an entire population. |
| STDEV.S | Calculates the SD of a sample. |
| STDEVP | Calculates the SD of an entire population |
| TREND | Calculates Y values based on a trendline. |
| Text | |
| CLEAN | Removes all non-printable characters. |
| DOLLAR | Converts a number to text in currency format. |
| FIND | Locates position of text within a cell.Case-sensitive. |
| LEFT | Truncates text a number of characters from the left. |
| LEN | Counts number of characters in text. |
| MID | Extracts text from the middle of a cell. |
| PROPER | Converts text to proper case. |
| REPLACE | Replaces text based on it’s location. |
| REPT | Repeats text a number of times. |
| RIGHT | Truncates text a number of characters from the right. |
| SEARCH | Locates position of text within a cell.Not Case-sensitive. |
| SUBSTITUTE | Finds and replaces text. Case-sensitive. |
| TEXT | Converts a value into text with a specific number format. |
| TRIM | Removes all extra spaces from text. |
Excel VBA Worksheet Functions
Worksheet function in VBA one may use when we have to refer to a specific worksheet. Normally, when we create a module, the code executes in the currently active sheet of the workbook. Still, if we want to execute the code in the specific worksheet, we use the Worksheet function. This function has various uses and applications in VBA.
The best thing about VBA is how we use formulas in worksheets. Similarly, VBA too has its functions. However, if this is the best, it also has a beautiful thing. That is, “we can also use Worksheet functions in VBA.”
You heard it right. We can access Worksheet functions in VBA also. We can access some of the worksheet functions while writing and making them part of our code.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Worksheet Functions
- How to use Worksheet Functions in VBA?
- #1 – Simple SUM Worksheet Functions
- #2 – Use VLOOKUP as a Worksheet Function
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- How to use Worksheet Functions in VBA?
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Worksheet Function (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to use Worksheet Functions in VBA?
You can download this VBA WorksheetFunction Template here – VBA WorksheetFunction Template
In the worksheet, all the formulas start with equal (=) sign, similarly, in VBA coding, to access worksheet formulas, we should use the word “WorksheetFunction.“
Before entering any worksheet formula, you need to mention the “WorksheetFunction” object name, put a dot (.), and get a list of all the available functions under this object.
In this article, we will exclusively concentrate on how to use Worksheet functions in VBA codingVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more, which will add more value to your coding knowledge.
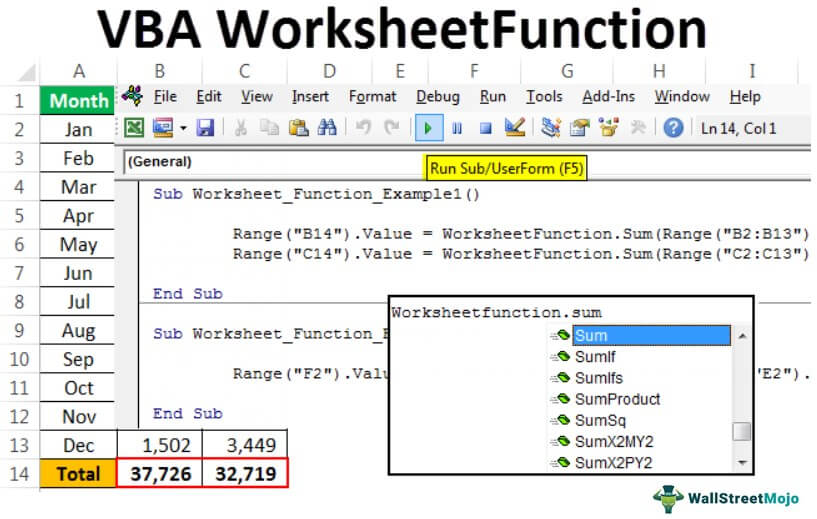
#1 – Simple SUM Worksheet Functions
To start with Worksheet functions, apply the simple SUM function in excelThe SUM function in excel adds the numerical values in a range of cells. Being categorized under the Math and Trigonometry function, it is entered by typing “=SUM” followed by the values to be summed. The values supplied to the function can be numbers, cell references or ranges.read more to add numbers from the worksheet.
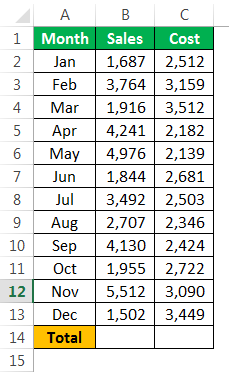
Assume you have monthly sales and cost data in the worksheet like the below one.
In B14 and C14, we need to arrive at the total of the above numbers. Follow the steps below to start applying the SUM function in Excel VBA.
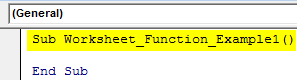
Step 1: Create a simple, excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more name.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() End Sub
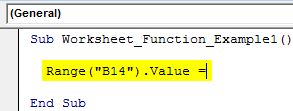
Step 2: Since we need the result in cell B14, start the code as Range (“B14”).Value =
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Range("B14").Value = End Sub
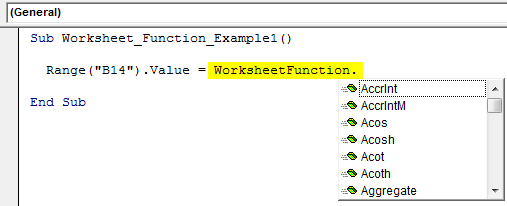
Step 3: In B14, we need the value as the result of the sum of the numbers. So to access the SUM function from the worksheet, start the code as “WorksheetFunction.“
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Range("B14").Value = WorksheetFunction. End Sub
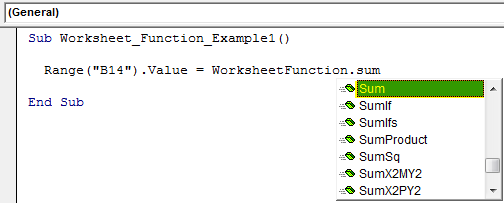
Step 4: The moment you put a dot (.), it will start to display the functions available. So, select SUM from this.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Range("B14").Value = WorksheetFunction.Sum End Sub
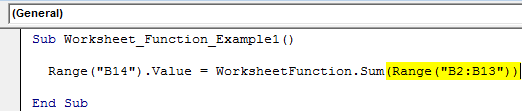
Step 5: Reference the above numbers: Range (“B2:B13”).
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Range("B14").Value = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("B2:B13")) End Sub
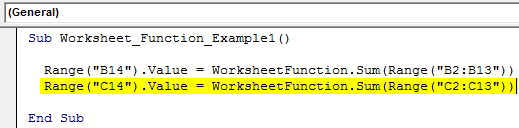
Step 6: Similarly, for the next column, apply a similar code by changing the cell referencesCell reference in excel is referring the other cells to a cell to use its values or properties. For instance, if we have data in cell A2 and want to use that in cell A1, use =A2 in cell A1, and this will copy the A2 value in A1.read more.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Range("B14").Value = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("B2:B13")) Range("C14").Value = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("C2:C13")) End Sub
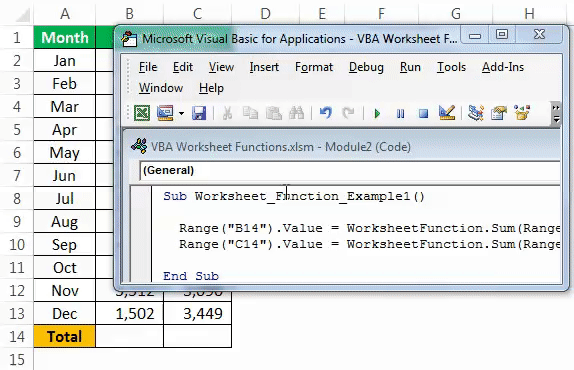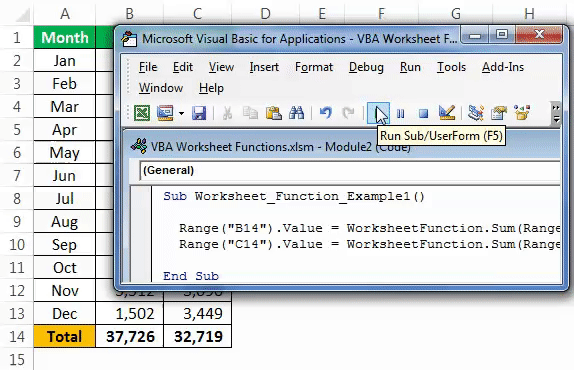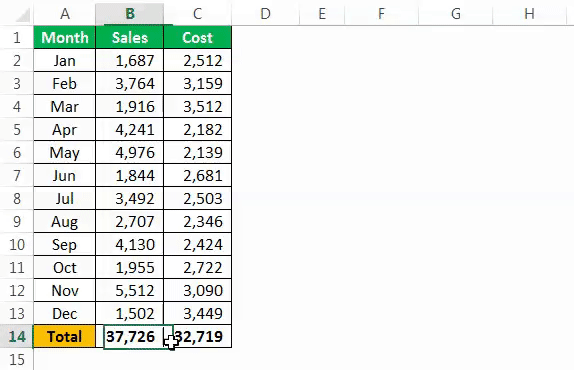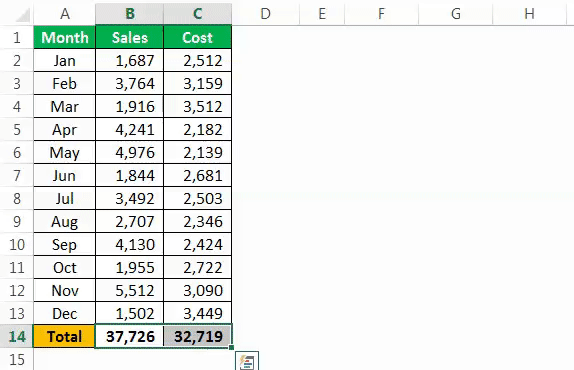
Step 7: Run this code manually or use the F5 key to have a total in B14 and C14 cells.
We got our values. You need to notice that we don’t have any formula in the worksheet, but we just got the result of the SUM function in VBA.
#2 – Use VLOOKUP as a Worksheet Function
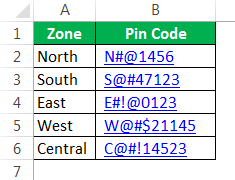
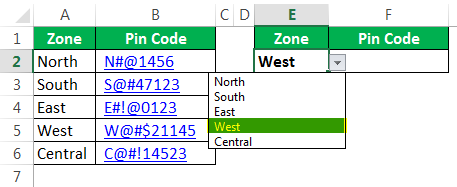
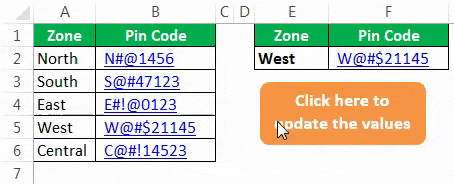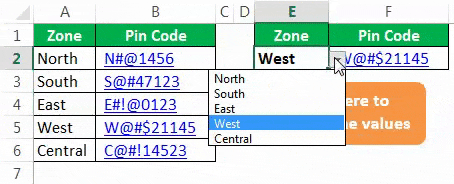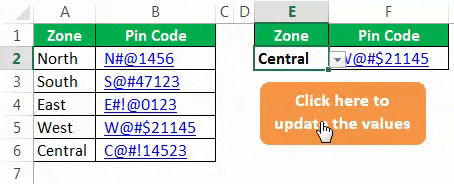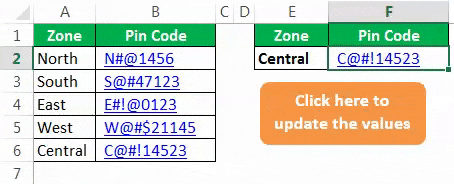
We will see how to use VLOOKUP in VBAThe functionality of VLOOKUP in VBA is similar to that of VLOOKUP in a worksheet, and the method of using VLOOKUP in VBA is through an application. Method WorksheetFunctionread more. Assume below is the data you have in your Excel sheet.
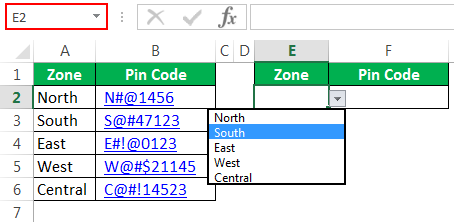
In the E2 cell, you had created a drop-down list of all the zones.
Based on the selection you made in the E2 cell, we need to fetch the pin code for the respective zone. But this time, through VBA VLOOKUP, not worksheet VLOOKUP. So, follow the below steps to apply VLOOKUPThe VLOOKUP excel function searches for a particular value and returns a corresponding match based on a unique identifier. A unique identifier is uniquely associated with all the records of the database. For instance, employee ID, student roll number, customer contact number, seller email address, etc., are unique identifiers.
read more.
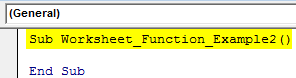
Step 1: Create a simple Macro name in the sub procedure.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() End Sub
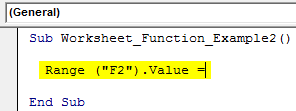
Step 2: We need the result in the F2 cell. So start the code as Range (“F2”).Value =
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range ("F2").Value = End Sub
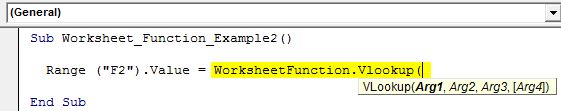
Step 3: To access the worksheet function, VLOOKUP starts the code as “WorksheetFunction.VLOOKUP.”
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range ("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup( End Sub
Step 4: One of the problems here is syntax will not guide you to work with VLOOKUP. It would help if you knew the syntax you were working on.
The first syntax of VLOOKUP is “Lookup Value.” In this case, our lookup value is the E2 cell, so write the code as Range (“E2”).Value
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range ("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup(Range ("E2").Value, End Sub
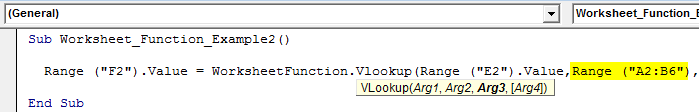
Step 5: Now, the second argument is our table array. In this case, our table array range is from A2 to B6. So the code will be Range (“A2:B6”).
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range ("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup(Range ("E2").Value,Range ("A2:B6"), End Sub
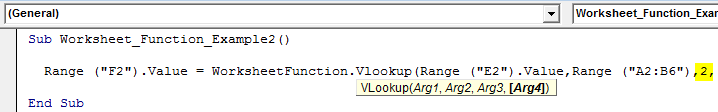
Step 6: The third argument will be from which column we need the data from the table array. Here we need the data from the second column so that the argument will be 2.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range ("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup(Range ("E2").Value,Range ("A2:B6"),2, End Sub
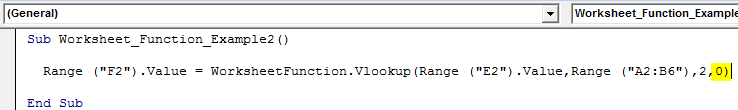
Step 7: The final argument is range lookup, we need an exact match, so the argument is zero (0).
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Range("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Range("E2").Value, Range("A2:B6"), 2, 0) End Sub
So, we have completed the coding part. Now, go to the Worksheet and select any of the ranges.
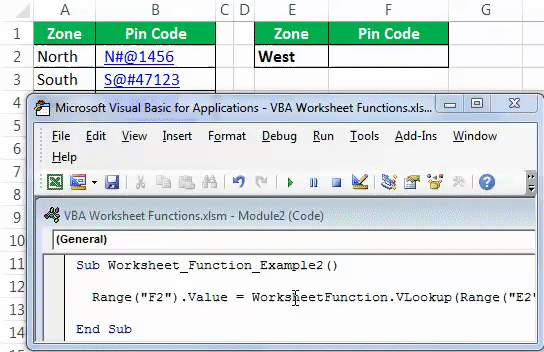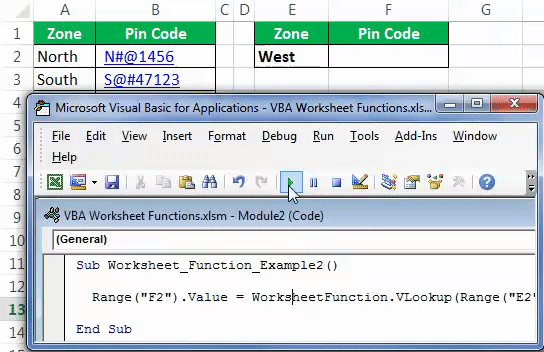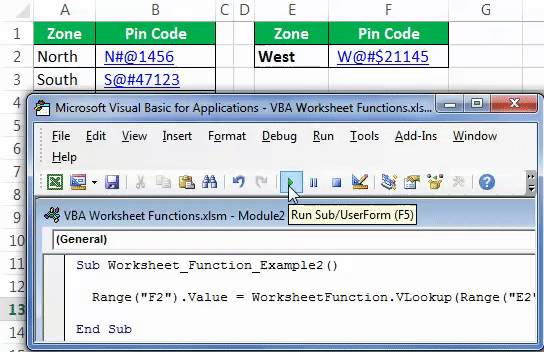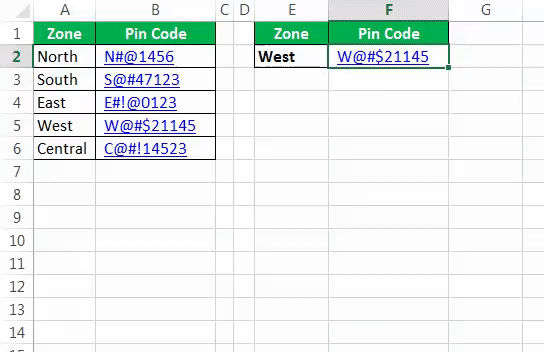
Now, go to your coding module and run the Macro using the F5 key or manually to get the pin code of the selected zone.
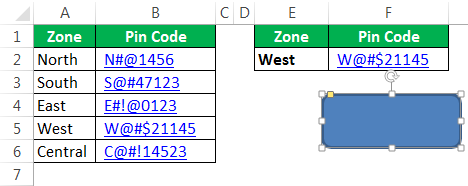
We cannot go back and run the Macro every time, so let’s assign a Macro to shapes. Then, insert one of the shapes into a worksheet.
Add a text value to the inserted shape.
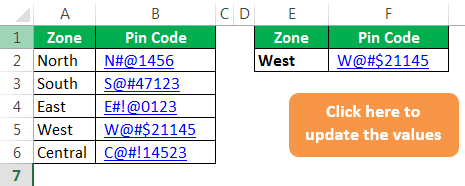
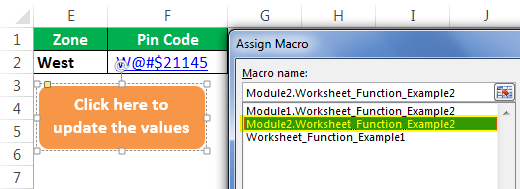
Now, right-click and assign the Macro name to this shape.
Click on “OK” after selecting the Macro name.
Now, this shape holds the code of our VLOOKUP formula. So whenever you change the zone name, click on the button to update the values.
Things to Remember
- To access worksheet functions, we need to write the word “WorksheetFunction” or “Application.WorksheetFunction”
- We do not have access to all the functions, only a few.
- We do not see the actual syntax of Worksheet functions, so we must be sure of the function we are using.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA Worksheet Function. Here, we learn how to use Worksheet functions like SUM and VLOOKUP in Excel VBA and some simple to advanced examples. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- Date Function in VBAVBA Date is a date and time function. It returns only the current date as per the system date you are using and has no arguments whatsoever. This function returns the current system date.read more
- OFFSET in VBAVBA OFFSET function facilitates the user to move down or return to a particular cell at a specific range, i.e., at a distance of a certain number of rows and columns from the current cell.read more
- VBA MODVBA MOD is the same as the application in mathematics. When a number is divided by its divisor, this function gives us the remainder from the division. However, it is not a function in VBA; rather it is an operator.read more
- MID Function in VBAVBA MID function extracts the middle values from the supplied sentence or word. It is categorized under the String and Text function and is a worksheet function.read more
Home / VBA / VBA Worksheet Function (Use Excel Functions in a Macro)
Key Notes
- You can use the WorksheetFunction property to access worksheet functions to use in a macro.
How to use a Worksheet Functions in VBA while Writing a Macro
Use the following steps to use a worksheet function in VBA.
- First, specify the cell where you want to insert the values returned by the function.
- After that, use an equal sign (=) and type Application.WorksheetFunction (as you can already in the Excel application, you can only use WorksheetFunction).
- Next, you need to enter a dot (.), and the moment you do that, you’ll get a list of functions that you have in the worksheet.
- From here, let’s use the TextJoin function to join text from the cell A1 and B1. Just like that, you use a function in the worksheet; when you enter starting parentheses, it shows you the arguments that you need to specify in the cell.
- As you can see in the above screenshot, it shows you the argument that you need to specify, but not the name of the arguments. So, you need to know the arguments before using them. Here are the arguments that you need to use in TextJoin.
- Now, let’s enter arguments in the function.
- delimiter: “ “
- ignore_empty: True
- text1: Range(“A1”)
- text2: Range(“B1”)
Here’s the full code.
Sub MyMacro()
Range("A1") = _
Application.WorksheetFunction.TextJoin _
(" ", True, Range("A2"), Range("A3"))
End SubAnd when you run this macro:
There is a total of 387 worksheet functions that you can use in VBA. But there are a few functions (Example: LEFT) that are not available to use.
Reason? There are In-Built functions in VBA that you can use while writing a VBA code.
Let’s if you want to use a message box to get the value for a function. Lets you want to get the maximum value from the named range “myValues”.
The code would be:
Sub MyMacro()
MsgBox Prompt:=WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("myValues"))
End SubAnd here’s how you get a message box:

Application.WorksheetFunction vs. Application
There are two different ways to refer to a worksheet function. Below are the two different lines of code that perform the same activity.

Sub MyMacro()
MsgBox Prompt:= _
Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("myValues"))
MsgBox Prompt:= _
Application.Max(Range("myValues"))
End SubBut there’s a benefit to using the second method. It returns an error code instead of showing the error directly.
previous page
next page
WorksheetFunction Object
Application
Used as a container for Microsoft Excel worksheet functions that can be called from Visual Basic.
Using the WorksheetFunction Object
Use the WorksheetFunction property to return the WorksheetFunction object. The following example displays the result of applying the Min worksheet function to the range A1:A10.
Set myRange = Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:C10")
answer = Application.WorksheetFunction.Min(myRange)
MsgBox answer