Подсчет количества ячеек в диапазоне, соответствующих заданным критериям, методами CountIf и CountIfs объекта WorksheetFunction из кода VBA Excel.
Metod WorksheetFunction.CountIf
Определение
Определение метода CountIf объекта WorksheetFunction в VBA Excel:
WorksheetFunction.CountIf — это метод, который подсчитывает в указанном диапазоне количество ячеек, соответствующих одному заданному критерию (условию), и возвращает значение типа Double.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис метода CountIf объекта WorksheetFunction:
|
WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Arg1, Arg2) |
Параметры
Параметры метода CountIf объекта WorksheetFunction:
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | Диапазон, в котором необходимо подсчитать количество ячеек, соответствующих заданному критерию. Тип данных — Range. |
| Arg2 | Критерий в виде числа, текста, выражения или ссылки на ячейку, определяющий, какие ячейки будут засчитываться. Тип данных — Variant. |
Примечания
- Метод WorksheetFunction.CountIf позволяет получить количество ячеек, соответствующих заданному критерию, в указанном диапазоне.
- Примеры критериев (условий):
25,"25",">50","<50","береза"илиD5. - В критериях можно использовать знаки подстановки (спецсимволы): знак вопроса (?) и звездочку (*). Знак вопроса заменяет один любой символ, а звездочка соответствует любой последовательности символов. Чтобы знак вопроса (?) и звездочка (*) обозначали сами себя, перед ними указывается тильда (~).
Metod WorksheetFunction.CountIfs
Должен отметить, что у меня в VBA Excel 2016 метод WorksheetFunction.CountIfs не работает. При попытке применить данный метод, генерируется ошибка:
Run-time error '1004':
Невозможно получить свойство CountIfs класса WorksheetFunction
Очевидно, метод WorksheetFunction.CountIfs предусмотрен для более новых версий VBA Excel. Статья на сайте разработчиков датирована 2021 годом.
Определение
Определение метода CountIfs объекта WorksheetFunction в VBA Excel:
WorksheetFunction.CountIfs — это метод, который подсчитывает в указанном диапазоне количество ячеек, соответствующих одному или нескольким заданным критериям (условиям), и возвращает значение типа Double.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис метода CountIfs объекта WorksheetFunction:
|
WorksheetFunction.CountIfs(Arg1, Arg2, ..., Arg30) |
Параметры
Параметры метода CountIfs объекта WorksheetFunction:
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | Диапазон, в котором необходимо подсчитать количество ячеек, соответствующих заданным критериям. Тип данных — Range. |
| Arg2-Arg30 | Один или несколько критериев в виде числа, текста, выражения или ссылки на ячейку, определяющие, какие ячейки будут засчитываться. Тип данных — Variant. |
Примечания
- Метод WorksheetFunction.CountIfs позволяет получить количество ячеек, соответствующих одному или нескольким заданным критериям, в указанном диапазоне.
- Значение пустой ячейки рассматривается как 0.
- Примеры критериев (условий):
25,"25",">50","<50","береза"илиD5. - В критериях можно использовать знаки подстановки (спецсимволы): знак вопроса (?) и звездочку (*). Знак вопроса заменяет один любой символ, а звездочка соответствует любой последовательности символов. Чтобы знак вопроса (?) и звездочка (*) обозначали сами себя, перед ними указывается тильда (~).
Примеры с WorksheetFunction.CountIf
Таблица, на которой тестировались примеры:
|
Sub Primer() Dim n As Double n = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range(«A1:D11»), «<5») MsgBox n ‘Результат: 4 n = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range(«A1:D11»), «>=4500») MsgBox n ‘Результат: 5 n = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range(«A1:D11»), «1600×720») MsgBox n ‘Результат: 4 n = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range(«A1:D11»), «Nokia*») MsgBox n ‘Результат: 2 End Sub |
Предыдущая статья по этой теме: VBA Excel. Методы Count, CountA и CountBlank.
In this Article
- COUNTIF WorksheetFunction
- Assigning a COUNTIF result to a Variable
- Using COUNTIFS
- Using COUNTIF with a Range Object
- Using COUNTIFS on Multiple Range Objects
- COUNTIF Formula
- Formula Method
- FormulaR1C1 Method
This tutorial will show you how to use the Excel COUNTIF and COUNTIFS functions in VBA
VBA does not have an equivalent of Excel’s COUNTIF or COUNTIFS Functions. Instead, you must call the Excel functions by using the WorkSheetFunction object.
COUNTIF WorksheetFunction
The WorksheetFunction object can be used to call most of the Excel functions that are available within the Insert Function dialog box in Excel. The COUNTIF Function is one of them.
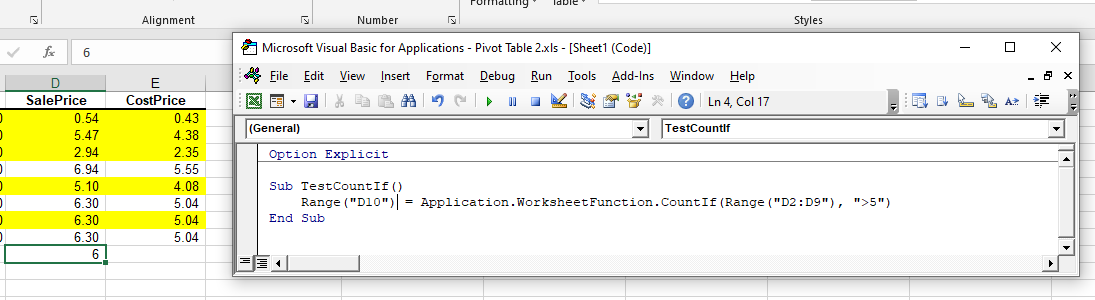
Sub TestCountIf()
Range("D10") = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range("D2:D9"), ">5")
End SubThe procedure above will only count the cells in Range(D2:D9) if they have a value of 5 or greater. Notice that because you are using a greater than sign, the criteria greater than 5 needs to be within parenthesis.
Assigning a COUNTIF result to a Variable
You may want to use the result of your formula elsewhere in code rather than writing it directly back to an Excel Range. If this is the case, you can assign the result to a variable to use later in your code.
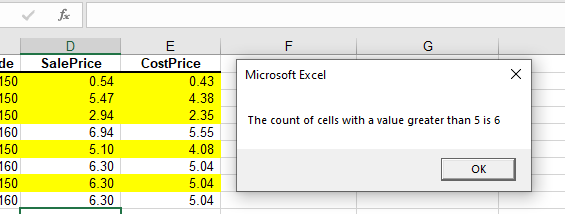
Sub AssignSumIfVariable()
Dim result as Double
'Assign the variable
result = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range("D2:D9"), ">5")
'Show the result
MsgBox "The count of cells with a value greater than 5 is " & result
End SubUsing COUNTIFS
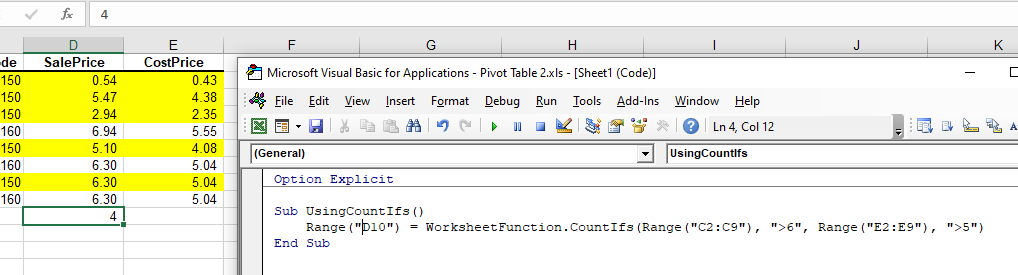
The COUNTIFS function is similar to the COUNTIF WorksheetFunction but it enables you to check for more than one criteria. In the example below, the formula will count up the number of cells in D2 to D9 where the Sale Price is greater than 6 AND the Cost Price is greater than 5.
Sub UsingCountIfs()
Range("D10") = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs(Range("C2:C9"), ">6", Range("E2:E9"), ">5")
End SubUsing COUNTIF with a Range Object
You can assign a group of cells to the Range object, and then use that Range object with the WorksheetFunction object.
Sub TestCountIFRange()
Dim rngCount as Range
'assign the range of cells
Set rngCount = Range("D2:D9")
'use the range in the formula
Range("D10") = WorksheetFunction.SUMIF(rngCount, ">5")
'release the range objects
Set rngCount = Nothing
End SubUsing COUNTIFS on Multiple Range Objects
Similarly, you can use COUNTIFS on multiple Range Objects.
Sub TestCountMultipleRanges()
Dim rngCriteria1 As Range
Dim rngCriteria2 as Range
'assign the range of cells
Set rngCriteria1= Range("D2:D9")
Set rngCriteria2 = Range("E2:E10")
'use the ranges in the formula
Range("D10") = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs(rngCriteria1, ">6", rngCriteria2, ">5")
'release the range objects
Set rngCriteria1 = Nothing
Set rngCriteria2 = Nothing
End SubCOUNTIF Formula
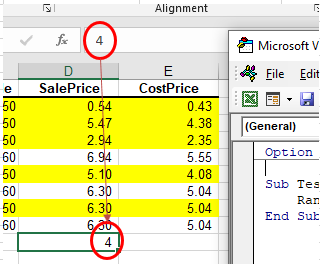
When you use the WorksheetFunction.COUNTIF to add a sum to a range in your worksheet, a static value is returned, not a flexible formula. This means that when your figures in Excel change, the value that has been returned by the WorksheetFunction will not change.
In the example above, the procedure has counted the amount of cells with values in Range(D2:D9) where the Sale Price is greater than 6, and the result was put in D10. As you can see in the formula bar, this result is a figure and not a formula.
If any of the values change in Range(D2:D9), the result in D10 will NOT change.
Instead of using the WorksheetFunction.SumIf, you can use VBA to apply a COUNTIF Function to a cell using the Formula or FormulaR1C1 methods.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Formula Method
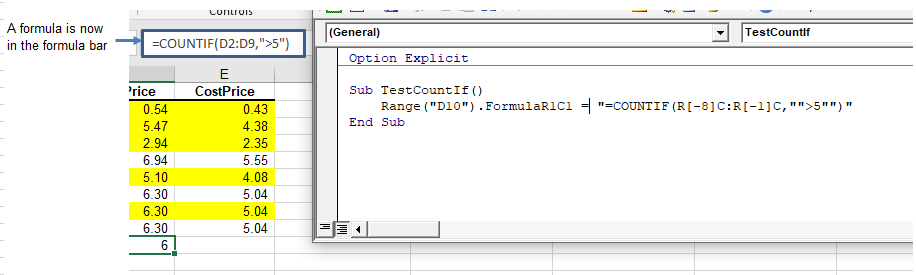
The formula method allows you to point specifically to a range of cells eg: D2:D9 as shown below.
Sub TestCountIf()
Range("D10").FormulaR1C1 ="=COUNTIF(D2:D9, "">5"")"
End SubFormulaR1C1 Method
The FormulaR1C1 method is more flexible in that it does not restrict you to a set range of cells. The example below will give us the same answer as the one above.
Sub TestCountIf()
Range("D10").FormulaR1C1 = "=COUNTIF(R[-8]C:R[-1]C,"">5"")"
End SubHowever, to make the formula even more flexible, we could amend the code to look like this:
Sub TestCountIf()
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=COUNTIF(R[-8]C:R[-1]C,"">5"")"
End SubWherever you are in your worksheet, the formula will then count the cells that meet the criteria directly above it and place the answer into your ActiveCell. The Range inside the COUNTIF function has to be referred to using the Row (R) and Column (C) syntax.
Both these methods enable you to use Dynamic Excel formulas within VBA.
There will now be a formula in D10 instead of a value.
Criteria-based functions are the rulers of Excel in calculations. At the beginning of learning Excel, we must have learned the COUNTIF process in Excel. In our earlier articles, we have shown you how to work with the COUNTIF function in Excel VBA.
Refer to our article on the COUNTIF Formula in ExcelThe COUNTIF function in Excel counts the number of cells within a range based on pre-defined criteria. It is used to count cells that include dates, numbers, or text. For example, COUNTIF(A1:A10,”Trump”) will count the number of cells within the range A1:A10 that contain the text “Trump”
read more to learn the basics of the COUNTIF function in Excel VBA. This article will show you how to use the same function in VBA coding. Now, we will see the same formula in VBA. First, COUNTIF is not a VBA function but a worksheet function that we can access under the worksheet function class.
Table of contents
- VBA COUNTIF
- Example of Excel VBA Countif Function
- Arrive Result with Variables
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA COUNTIF (wallstreetmojo.com)
Example of Excel VBA Countif Function
Let us see a simple example.
You can download this VBA Countif Function Excel Template here – VBA Countif Function Excel Template
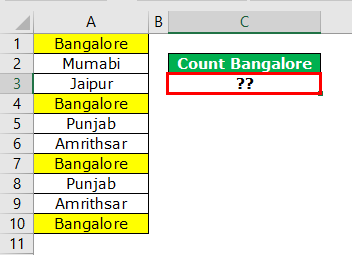
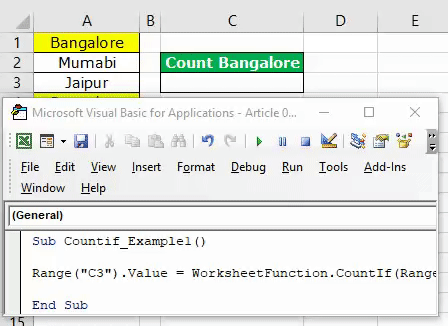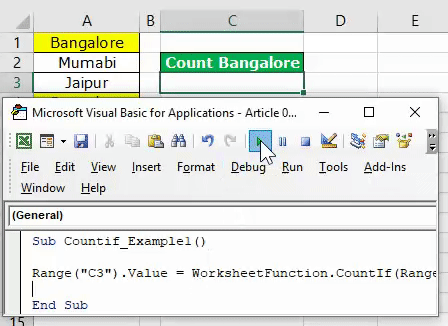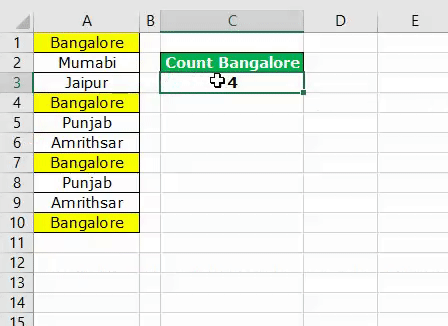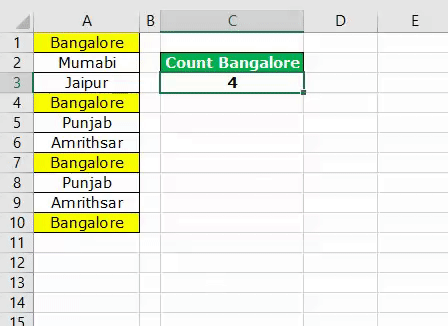
Look at the below example of counting values from the lot.
The above image shows city names from cells A1 to A10. So, for example, in cell C3, we need to count how many times the city name “Bangalore” appears in the range A1 to A10.
Follow the below steps to write the code to apply the COUNTIF function.
Step 1: Start the Sub procedure.
Code:
Option ExplicitVBA option explicitly makes a user mandatory to declare all the variables before using them; any undefined variable will throw an error while coding execution. We can enable it for all codes from options to require variable declaration.read more Sub Countif_Example1() End Sub
Step 2: Since we need to store the result in cell C3, start the Range(“C3”).Value.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Value = End Sub
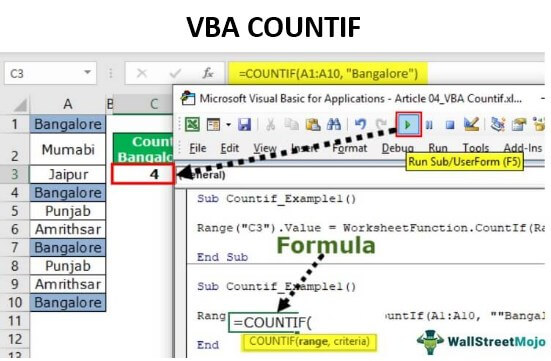
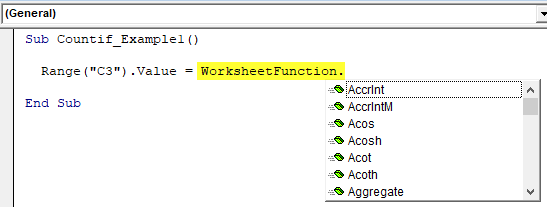
Step 3: In cell C3, by applying the Excel VBA COUNTIF function, we are trying to arrive at the result. So to access the function, we need first to use the Worksheet function class.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction. End Sub
Step 4: From the list, select the Excel VBA COUNTIF function.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction.CountIf( End Sub
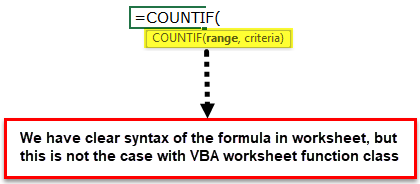
Step 5: If you look at the parameters of the VBA COUNTIF function, we do not see the parameter as we see in the worksheet.
As we can see in the above image in the worksheet, we have exact syntax, but in VBA, we can see only Arg 1 and Arg 2.
Arg 1 is Range, so select the range as A1 to A10.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range("A1:A10"), End Sub
Step 6: Arg 2 is what is the value we need to count from the range A1 to A10. In this example, we need to calculate “Bangalore.”
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range("A1:A10"), "Bangalore") End Sub
We have completed it now.
Run the code to see the result in cell C3.
We got the result as 4. Since the city name “Bangalore” appears in cells A1, A4, A7, and A10 VBA COUNTIF function returns the product as 4.
If you can see VBA code has returned only the result of the formula, we do not get to know the procedure in the formula bar.
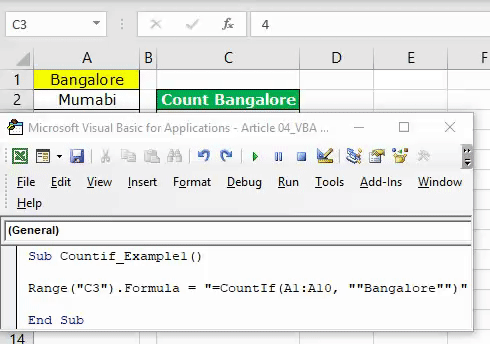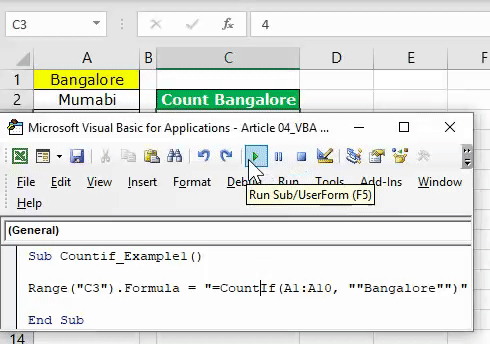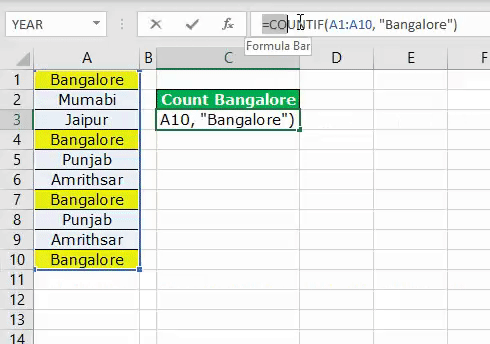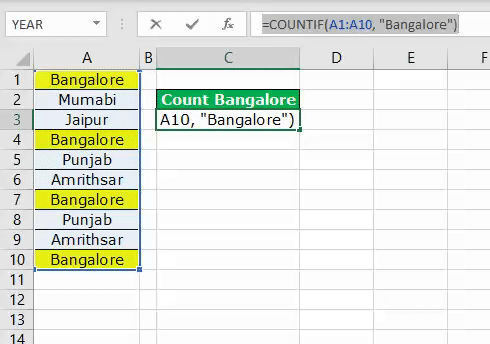
We need to write the code slightly differently to arrive at the formula. Below is the code for applying the formula to the cell.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example1() Range("C3").Formula = "=CountIf(A1:A10, ""Bangalore"")" End Sub
It will apply the formula to cell C3.
Arrive Result with Variables
Variables are an integral part of any coding language. Therefore, we must declare variables to work efficiently with the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more. For example, look at the below code.
Code:
Sub Countif_Example2() Dim ValuesRange As Range Dim ResultCell As Range Dim CriteriaValue As String Set ValuesRange = Range("A1:A10") Set ResultCell = Range("C3") CriteriaValue = "Bangalore" ResultCell = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(ValuesRange, CriteriaValue) End Sub
Let us decode the code for you to understand better.
Firstly, we have declared the two variables as Range.
Dim ValuesRange As Range: This is to reference the list of values.
Dim ResultCell As Range: This to reference the result cell.
Then, we have set the range of references to both variables.
Set ValuesRange = Range(“A1: A10”): This is the range where all the city names are there.
Set ResultCell = Range(“C3”): In this cell, we will store the result of the COUNTIF function.
In the meantime, we have declared one more variable to store the criteria value.
Dim CriteriaValue As String
CriteriaValue = “Bangalore”
So, the variable “CriteriaValue” holds the value “Bangalore.”
As usual, we have applied the COUNTIF function in the next line.
ResultCell = WorksheetFunction.CountIf(ValuesRange, CriteriaValue)
Like this, we can apply the COUNTIF function in Excel VBA to fit our needs.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA COUNTIF. Here, we look at the working of the COUNTIF Function in Excel VBA along with practical examples and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA Like Operator
- Count in VBA
- Countif not Blank in Excel
- COUNTIF Examples in Excel
Содержание
- СЧЕТЕСЛИ Рабочий лист
- Присвоение переменной результата COUNTIF
- Использование СЧЁТЕСЛИМН
- Использование COUNTIF с объектом диапазона
- Использование COUNTIFS для объектов с несколькими диапазонами
- СЧЁТЕСЛИ Формула
Из этого туториала Вы узнаете, как использовать функции Excel СЧЁТЕСЛИ и СЧЁТЕСЛИ в VBA.
VBA не имеет эквивалента функций СЧЁТЕСЛИ или СЧЁТЕСЛИМН, которые вы можете использовать — пользователь должен использовать встроенные функции Excel в VBA, используя Рабочий лист объект.
СЧЕТЕСЛИ Рабочий лист
Объект WorksheetFunction можно использовать для вызова большинства функций Excel, доступных в диалоговом окне «Вставить функцию» в Excel. Функция СЧЁТЕСЛИ — одна из них.
| 123 | Sub TestCountIf ()Range («D10») = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf (Range («D2: D9»), «> 5»)Конец подписки |
Приведенная выше процедура будет подсчитывать только ячейки в диапазоне (D2: D9), если они имеют значение 5 или больше. Обратите внимание: поскольку вы используете знак «больше», критерии больше 5 должны быть заключены в круглые скобки.
Присвоение переменной результата COUNTIF
Возможно, вы захотите использовать результат своей формулы в другом месте кода, а не записывать его непосредственно обратно в Excel Range. В этом случае вы можете присвоить результат переменной, которая будет использоваться позже в вашем коде.
| 1234567 | Sub AssignSumIfVariable ()Тусклый результат как двойной’Назначьте переменнуюresult = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf (Range («D2: D9»), «> 5»)’Показать результатMsgBox «Количество ячеек со значением больше 5 равно» & результатКонец подписки |
Использование СЧЁТЕСЛИМН
Функция СЧЁТЕСЛИМН похожа на функцию СЧЁТЕСЛИ Worksheet, но позволяет вам проверять более одного критерия. В приведенном ниже примере формула подсчитывает количество ячеек от D2 до D9, где цена продажи больше 6, а себестоимость больше 5.
| 123 | Sub UsingCountIfs ()Range («D10») = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs (Range («C2: C9»), «> 6», Range («E2: E9»), «> 5»)Конец подписки |
Использование COUNTIF с объектом диапазона
Вы можете назначить группу ячеек объекту Range, а затем использовать этот объект Range с Рабочий лист объект.
| 123456789 | Sub TestCountIFRange ()Dim rngCount as Range’назначить диапазон ячеекУстановите rngCount = Range («D2: D9»)’используйте диапазон в формулеДиапазон («D10») = WorksheetFunction.SUMIF (rngCount, «> 5»)’освободить объекты диапазонаУстановите rngCount = NothingКонец подписки |
Использование COUNTIFS для объектов с несколькими диапазонами
Точно так же вы можете использовать COUNTIFS для нескольких объектов диапазона.
| 123456789101112 | Sub TestCountMultipleRanges ()Dim rngCriteria1 As ДиапазонDim rngCriteria2 as Range’назначить диапазон ячеекУстановить rngCriteria1 = Range («D2: D9»)Установить rngCriteria2 = Range («E2: E10»)’используйте диапазоны в формулеДиапазон («D10») = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs (rngCriteria1, «> 6», rngCriteria2, «> 5»)’освободить объекты диапазонаУстановить rngCriteria1 = NothingУстановить rngCriteria2 = NothingКонец подписки |
СЧЁТЕСЛИ Формула
Когда вы используете WorksheetFunction.COUNTIF чтобы добавить сумму к диапазону на листе, возвращается статическое значение, а не гибкая формула. Это означает, что при изменении ваших цифр в Excel значение, возвращаемое Рабочий лист не изменится.
В приведенном выше примере процедура подсчитала количество ячеек со значениями в диапазоне (D2: D9), где цена продажи больше 6, и результат был помещен в D10. Как вы можете видеть в строке формул, это число, а не формула.
Если любое из значений изменится в диапазоне (D2: D9), результат в D10 будет НЕТ изменение.
Вместо использования Рабочий лист Функция. Сумма Если, вы можете использовать VBA для применения функции СУММЕСЛИ к ячейке с помощью Формула или Формула R1C1 методы.
Формула Метод
Метод формулы позволяет указать конкретный диапазон ячеек, например: D2: D9, как показано ниже.
| 123 | Sub TestCountIf ()Диапазон («D10»). FormulaR1C1 = «= СЧЁТЕСЛИ (D2: D9,» «> 5» «)»Конец подписки |
Метод FormulaR1C1
Метод FormulaR1C1 более гибкий, поскольку он не ограничивает вас заданным диапазоном ячеек. Пример ниже даст нам тот же ответ, что и приведенный выше.
| 123 | Sub TestCountIf ()Диапазон («D10»). FormulaR1C1 = «= СЧЁТЕСЛИ (R [-8] C: R [-1] C,» «> 5» «)»Конец подписки |
Однако, чтобы сделать формулу еще более гибкой, мы могли бы изменить код, чтобы он выглядел так:
| 123 | Sub TestCountIf ()ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = «= СЧЁТЕСЛИ (R [-8] C: R [-1] C,» «> 5» «)»Конец подписки |
Где бы вы ни находились на своем листе, формула затем подсчитает ячейки, которые соответствуют критериям непосредственно над ней, и поместит ответ в вашу ActiveCell. На диапазон внутри функции СЧЁТЕСЛИ необходимо ссылаться с использованием синтаксиса строки (R) и столбца (C).
Оба эти метода позволяют использовать динамические формулы Excel в VBA.
Теперь вместо значения в D10 будет формула.
Текст вашей ссылки
Вы поможете развитию сайта, поделившись страницей с друзьями
You can use the following methods to write COUNTIF and COUNTIFS functions using VBA in Excel:
Method 1: COUNTIF Function in VBA
Sub Countif_Function()
Range("E2") = WorksheetFunction.Countif(Range("B2:B12"), ">20")
End Sub
This particular example will count the number of values in the range B2:B12 that are greater than 20 and assign the result to cell E2.
Method 2: COUNTIFS Function in VBA
Sub Countifs_Function()
Range("E2") = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs(Range("A2:A12"), "Mavs", Range("B2:B12"), ">20")
End Sub
This particular example will count the number of rows where the value in the range A2:A12 is equal to “Mavs” and the value in the range B2:B12 is greater than 20 and then assign the result to cell E2.
The following examples shows how to use each of these methods in practice with the following dataset in Excel that contains information about various basketball players:
Example 1: COUNTIF Function in VBA
Suppose we would like to count the number of values in the points column that are greater than 20.
We can create the following macro to perform this COUNTIF function:
Sub Countif_Function()
Range("E2") = WorksheetFunction.Countif(Range("B2:B12"), ">20")
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that cell E2 contains a value of 6.
This tells us that there are 6 values in the points column that are greater than 20.
Example 2: COUNTIFS Function in VBA
Suppose we would like to count the number of rows that meet the following criteria:
- Player is on the Mavs team.
- Player scored more than 20 points.
We can create the following macro to perform this COUNTIFS function:
Sub Countifs_Function()
Range("E2") = WorksheetFunction.CountIfs(Range("A2:A12"), "Mavs", Range("B2:B12"), ">20")
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that cell E2 contains a value of 2.
This tells us that there are two rows where the player is on the Mavs team and the player scored more than 20 points.
Note: In this example, we created a COUNTIFS function using two criteria ranges but you can use as many criteria ranges as you’d like within the WorksheetFunction.CountIfs method.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in VBA:
VBA: How to Count Number of Rows in Range
VBA: How to Write SUMIF and SUMIFS Functions
VBA: How to Write AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS Functions