Удаление пустых строк с помощью кода VBA из всего задействованного диапазона рабочего листа Excel и из отдельного заданного диапазона.
Главный секрет удаления пустых строк кодом VBA Excel – это построчный просмотр диапазона или отдельного столбца снизу вверх, что исключает возможность при удалении найденных пустых строк получить бесконечный цикл и зависание программы.
Удаление пустых строк в используемом диапазоне
Рассмотрим удаление пустых строк из всего используемого диапазона на рабочем листе. Это может быть как таблица, так и любые наборы данных и произвольные записи, внутри которых присутствуют пустые строки, от которых надо избавиться.
Определить границы используемого диапазона на рабочем листе из кода VBA Excel нам поможет последняя ячейка используемого диапазона: Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).
Самый простой код удаления пустых строк
Сначала определяем номер строки последней ячейки задействованного на рабочем листе диапазона. Затем, с этой строки начинаем построчный просмотр используемого диапазона снизу вверх с поиском и удалением пустых строк.
Пример кода VBA Excel для активного листа:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim n As Long, i As Long ‘Определяем номер строки последней ячейки ‘используемого диапазона на рабочем листе n = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row ‘Ищем и удаляем пустые строки For i = n To 1 Step —1 If Rows(i).Text = «» Then Rows(i).Delete Next End Sub |
То же самое, но с указанием книги и рабочего листа:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim n As Long, i As Long With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Лист1») n = .Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row For i = n To 1 Step —1 If .Rows(i).Text = «» Then .Rows(i).Delete Next End With End Sub |
Программа определения времени выполнения макроса показала, что этот код отработал в диапазоне из 3000 строк за 17,5 секунд.
Улучшенный код удаления пустых строк
Предыдущий код VBA Excel анализирует на наличие текста каждую строку по всей длине в пределах рабочего листа. Эта процедура проверяет каждую строку по длине только в переделах используемого диапазона:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim n As Long, i As Long, myRange As Range ‘Присваиваем объектной переменной ссылку на диапазон от первой ячейки ‘рабочего листа до последней ячейки используемого диапазона Set myRange = Range(Range(«A1»), Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell)) With myRange n = .Rows.Count For i = n To 1 Step —1 If .Rows(i).Text = «» Then .Rows(i).Delete Next End With End Sub |
Программа определения времени выполнения макроса показала, что этот код отработал в диапазоне из 3000 строк за 13,3 секунды.
Удаление строк по пустым ячейкам
Иногда может появиться необходимость удалить не только полностью пустые строки, но и строки с пустыми ячейками в определенном столбце. Тогда следует действовать так:
|
Sub Primer4() Dim n As Long, i As Long n = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row For i = n To 1 Step —1 If Cells(i, 1).Text = «» Then Rows(i).Delete Next End Sub |
или так:
|
Sub Primer5() Dim n As Long, i As Long, myRange As Range Set myRange = Range(Range(«A1»), Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell)) With myRange n = .Rows.Count For i = n To 1 Step —1 If .Cells(i, 1).Text = «» Then .Rows(i).Delete Next End With End Sub |
В этих примерах поиск пустой ячейки производится в первом столбце: Cells(i, 1).
Удаление пустых строк в заданном диапазоне
Процедуры VBA Excel для удаления пустых строк из заданного диапазона рассмотрим на примере объекта Selection, который можно заменить на любой диапазон, указанный явно.
Удаление полностью пустых строк в пределах заданного диапазона:
|
Sub Primer6() Dim n As Long, i As Long With Selection n = .Rows.Count For i = n To 1 Step —1 If .Rows(i).Text = «» Then .Rows(i).Delete Next End With End Sub |
Удаление строк по пустым ячейкам в одном из столбцов:
|
Sub Primer7() Dim n As Long, i As Long With Selection n = .Rows.Count For i = n To 1 Step —1 If .Cells(i, 1).Text = «» Then .Rows(i).Delete Next End With End Sub |
I would like to delete the empty rows my ERP Quotation generates. I’m trying to go through the document (A1:Z50) and for each row where there is no data in the cells (A1-B1...Z1 = empty, A5-B5...Z5 = empty) I want to delete them.
I found this, but can’t seem to configure it for me.
On Error Resume Next
Worksheet.Columns("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.Delete
On Error GoTo 0
asked Feb 21, 2012 at 14:55
4
How about
sub foo()
dim r As Range, rows As Long, i As Long
Set r = ActiveSheet.Range("A1:Z50")
rows = r.rows.Count
For i = rows To 1 Step (-1)
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(r.rows(i)) = 0 Then r.rows(i).Delete
Next
End Sub
answered Feb 21, 2012 at 15:15
Alex K.Alex K.
170k30 gold badges263 silver badges286 bronze badges
1
Try this
Option Explicit
Sub Sample()
Dim i As Long
Dim DelRange As Range
On Error GoTo Whoa
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For i = 1 To 50
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range("A" & i & ":" & "Z" & i)) = 0 Then
If DelRange Is Nothing Then
Set DelRange = Range("A" & i & ":" & "Z" & i)
Else
Set DelRange = Union(DelRange, Range("A" & i & ":" & "Z" & i))
End If
End If
Next i
If Not DelRange Is Nothing Then DelRange.Delete shift:=xlUp
LetsContinue:
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Exit Sub
Whoa:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume LetsContinue
End Sub
IF you want to delete the entire row then use this code
Option Explicit
Sub Sample()
Dim i As Long
Dim DelRange As Range
On Error GoTo Whoa
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For i = 1 To 50
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range("A" & i & ":" & "Z" & i)) = 0 Then
If DelRange Is Nothing Then
Set DelRange = Rows(i)
Else
Set DelRange = Union(DelRange, Rows(i))
End If
End If
Next i
If Not DelRange Is Nothing Then DelRange.Delete shift:=xlUp
LetsContinue:
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Exit Sub
Whoa:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume LetsContinue
End Sub
answered Feb 21, 2012 at 15:13
Siddharth RoutSiddharth Rout
146k17 gold badges206 silver badges250 bronze badges
3
I know I am late to the party, but here is some code I wrote/use to do the job.
Sub DeleteERows()
Sheets("Sheet1").Select
Range("a2:A15000").Select
Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.Delete
End Sub
Kingsley
14.3k5 gold badges33 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Dec 12, 2018 at 21:45
3
for those who are intersted to remove «empty» and «blank» rows ( Ctrl + Shift + End going deep down of your worksheet ) .. here is my code.
It will find the last «real»row in each sheet and delete the remaining blank rows.
Function XLBlank()
For Each sh In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
sh.Activate
Cells(1, 1).Select
lRow = Cells.Find(What:="*", _
After:=Range("A1"), _
LookAt:=xlPart, _
LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _
MatchCase:=False).Row
Range("A" & lRow + 1, Range("A1").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Address).Select
On Error Resume Next
Selection.EntireRow.SpecialCells(xlBlanks).EntireRow.Delete
Cells(1, 1).Select
Next
ActiveWorkbook.Save
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Activate
End Function
Open VBA ( ALT + F11 ), Insert -> Module,
Copy past my code and launch it with F5.
Et voila 
answered Mar 5, 2019 at 8:47
I have another one for the case when you want to delete only rows which are complete empty, but not single empty cells. It also works outside of Excel e.g. on accessing Excel by Access-VBA or VB6.
Public Sub DeleteEmptyRows(Sheet As Excel.Worksheet)
Dim Row As Range
Dim Index As Long
Dim Count As Long
If Sheet Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
' We are iterating across a collection where we delete elements on the way.
' So its safe to iterate from the end to the beginning to avoid index confusion.
For Index = Sheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count To 1 Step -1
Set Row = Sheet.UsedRange.Rows(Index)
' This construct is necessary because SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
' always throws runtime errors if it doesn't find any empty cell.
Count = 0
On Error Resume Next
Count = Row.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Count
On Error GoTo 0
If Count = Row.Cells.Count Then Row.Delete xlUp
Next
End Sub
answered Aug 27, 2019 at 11:34
AranxoAranxo
6073 silver badges14 bronze badges
2
To make Alex K’s answer slightly more dynamic you could use the code below:
Sub DeleteBlankRows()
Dim wks As Worksheet
Dim lngLastRow As Long, lngLastCol As Long, lngIdx As Long, _
lngColCounter As Long
Dim blnAllBlank As Boolean
Dim UserInputSheet As String
UserInputSheet = Application.InputBox("Enter the name of the sheet which you wish to remove empty rows from")
Set wks = Worksheets(UserInputSheet)
With wks
'Now that our sheet is defined, we'll find the last row and last column
lngLastRow = .Cells.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
lngLastCol = .Cells.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
'Since we need to delete rows, we start from the bottom and move up
For lngIdx = lngLastRow To 1 Step -1
'Start by setting a flag to immediately stop checking
'if a cell is NOT blank and initializing the column counter
blnAllBlank = True
lngColCounter = 2
'Check cells from left to right while the flag is True
'and the we are within the farthest-right column
While blnAllBlank And lngColCounter <= lngLastCol
'If the cell is NOT blank, trip the flag and exit the loop
If .Cells(lngIdx, lngColCounter) <> "" Then
blnAllBlank = False
Else
lngColCounter = lngColCounter + 1
End If
Wend
'Delete the row if the blnBlank variable is True
If blnAllBlank Then
.rows(lngIdx).delete
End If
Next lngIdx
End With
MsgBox "Blank rows have been deleted."
End Sub
This was sourced from this website and then slightly adapted to allow the user to choose which worksheet they want to empty rows removed from.
answered Dec 18, 2017 at 21:50
RugsKidRugsKid
3247 silver badges25 bronze badges
In order to have the On Error Resume function work you must declare the workbook and worksheet values as such
On Error Resume Next
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet Name").Columns("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.Delete
On Error GoTo 0
I had the same issue and this eliminated all the empty rows without the need to implement a For loop.
answered Apr 30, 2018 at 14:39
This worked great for me (you can adjust lastrow and lastcol as needed):
Sub delete_rows_blank2()
t = 1
lastrow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
lastcol = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count
Do Until t = lastrow
For j = 1 To lastcol
'This only checks the first column because the "Else" statement below will skip to the next row if the first column has content.
If Cells(t, j) = "" Then
j = j + 1
If j = lastcol Then
Rows(t).Delete
t = t + 1
End If
Else
'Note that doing this row skip, may prevent user from checking other columns for blanks.
t = t + 1
End If
Next
Loop
End Sub
answered Feb 27, 2018 at 15:10
Here is the quickest way to Delete all blank Rows ( based on one Columns )
Dim lstRow as integet, ws as worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("NameOfSheet")
With ws
lstRow = .Cells(Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row ' Or Rows.Count "B", "C" or "A" depends
.Range("A1:E" & lstRow).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.Delete
End with
answered Mar 10, 2022 at 15:46
Исходные коды макросов для выделения, удаления, скрытия и добавления пустых строк в таблицу Excel по условию пользователя.
Как выделить все пустые строки макросом
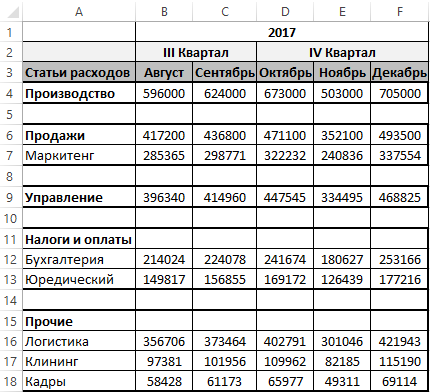
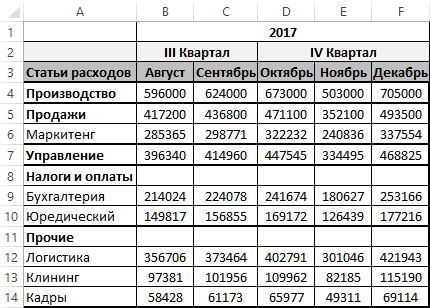
Есть таблица годового бюджета, разделенная на отдельные группы статей расходов и кварталы. Каждая группа статей расходов разделена между собой пустыми строками:
Нам необходимо удалить все пустые строки в таблице. Для этого сначала необходимо их выделить. Если выделять вручную, то потребуется много времени и сил. Кроме того, нужно еще быть уверенным что строка действительно является пустой, чтобы вместе с ней не удалить важную информацию из бюджета или формулу. Для автоматического решения данной задачи лучше написать свой макрос, который сам проверит и выделит все пустые строки в таблице годового бюджета.
Откройте редактор Visual Basic (ALT+F11):
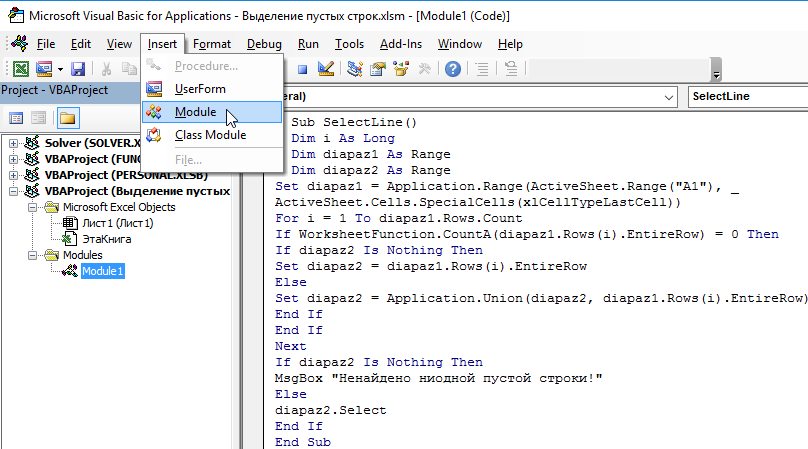
И воздайте в нем новый модуль для текущей книги «Insert»-«Module», а потом запишите в него следующий VBA-код макроса:
Sub SelectLine()
Dim i As Long
Dim diapaz1 As Range
Dim diapaz2 As Range
Set diapaz1 = Application.Range(ActiveSheet.Range("A1"), _
ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell))
For i = 1 To diapaz1.Rows.Count
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow) = 0 Then
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
Set diapaz2 = diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow
Else
Set diapaz2 = Application.Union(diapaz2, diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow)
End If
End If
Next
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Ненайдено ниодной пустой строки!"
Else
diapaz2.Select
End If
End Sub
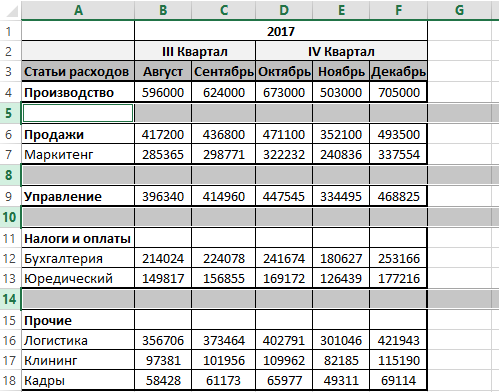
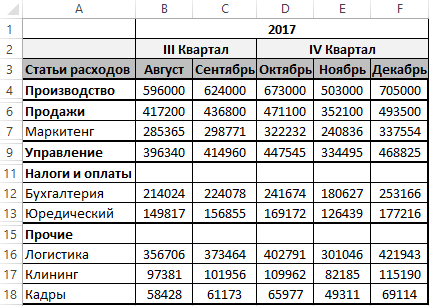
Теперь если нам нужно автоматически выделить все пустые строки в таблице бюджета перед тем как их удалить, выберите инструмент: «РАЗРАБОТЧИК»-«Код»-«Макросы»-«SelectLine»-«Выполнить». В результате выделяться все пустые ячейки только для пустых строк внутри исходной таблицы.
Пример работы первого VBA-кода:
Пустые строки, которые находиться под последними заполненными ячейками не будут выделены. Теперь для удаления выделенных строк пользователю осталось только выбрать инструмент: «ГЛАВНАЯ»-«Ячейки»-«Удалить»-«Удалить строки с листа». Или нажать комбинацию горячих клавиш CTRL+=. А после в появившемся окне «Удаление ячеек» выбрать опцию «строку» и нажать ОК.
Вначале кода присваиваем для переменной diapaz1 диапазон ячеек в границах между A1 и последней используемой ячейкой на рабочем листе Excel.
Примечание. Последняя используемая ячейка на листе — это любая ячейка для, которой были выполнены любые изменения: ввод значений, изменение формата границ или цвета фона и т.п.
Далее в цикле проверяются все строки в этом диапазоне, каждая по отдельности, на количество непустых ячеек. В том случаи если метод CountA возвращает значение 0, то адреса этих ячеек дополняют несмежный диапазон в переменной diapaz2 еще на одну пустую строку.
В конце макроса выделяются все пустые строки, находящиеся внутри диапазона определенным переменной diapaz2. Если же таблица не сдержит ни одной пустой строки, тогда выводиться соответственное сообщение.
Макрос для удаления пустых строк
Как удалить строку макросом? Если нужно сделать так чтобы макрос автоматически не только выделял, но и сам удалял пустые целые и смежные диапазоны ячеек без использования других инструментов, тогда в конце кода для переменной diapaz2.Select следует изменить метод на [Delete]:
diapaz2.[Delete]
Удалить:
Sub DelLine()
Dim i As Long
Dim diapaz1 As Range
Dim diapaz2 As Range
Set diapaz1 = Application.Range(ActiveSheet.Range("A1"), _
ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell))
For i = 1 To diapaz1.Rows.Count
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow) = 0 Then
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
Set diapaz2 = diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow
Else
Set diapaz2 = Application.Union(diapaz2, diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow)
End If
End If
Next
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Ненайдено ниодной пустой строки!"
Else
diapaz2.[Delete]
End If
End Sub
Пример второго VBA-кода:
Макрос для скрытия пустых строк
Как скрыть пустые строки макросом? Но если вам нужно не удалить, а только скрыть (например, при подготовке документа на печать), тогда эту строку кода следует модифицировать несколько иначе:
diapaz2.EntireRow.Hidden = True
Скрыть:
Sub HidLine()
Dim i As Long
Dim diapaz1 As Range
Dim diapaz2 As Range
Set diapaz1 = Application.Range(ActiveSheet.Range("A1"), _
ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell))
For i = 1 To diapaz1.Rows.Count
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow) = 0 Then
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
Set diapaz2 = diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow
Else
Set diapaz2 = Application.Union(diapaz2, diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow)
End If
End If
Next
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Ненайдено ниодной пустой строки!"
Else
diapaz2.EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
End Sub
Пример третьего VBA-кода:
Добавление строк макросом
Как вставить строки макросом? Если мы изменим код в этом же месте как показано ниже, то получиться инструмент для добавления и вставки строк после пустых:
diapaz2.[Insert]
Добавить:
Sub AddLine()
Dim i As Long
Dim diapaz1 As Range
Dim diapaz2 As Range
Set diapaz1 = Application.Range(ActiveSheet.Range("A1"), _
ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell))
For i = 1 To diapaz1.Rows.Count
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow) = 0 Then
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
Set diapaz2 = diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow
Else
Set diapaz2 = Application.Union(diapaz2, diapaz1.Rows(i).EntireRow)
End If
End If
Next
If diapaz2 Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Ненайдено ниодной пустой строки!"
Else
diapaz2.[Insert]
End If
End Sub
Пример четвертого VBA-кода:
Если же вы хотите, чтобы макрос работал исключительно только для пустых строк предварительно выделенного определенного диапазона листа перед запуском макроса, то в начале макроса следует изменить строку создания экземпляра объекта для переменной diapaz1, на:
Set diapaz1 = Selection
Читайте также: Как выделить столбцы в Excel макросом.
Внимание! Следует помнить о том, что если таким образом создавать экземпляр объекта для переменной diapaz1, то тогда нельзя перед запуском макроса выделять все ячейки листа или все ячейки любого столбца. Иначе это затормозит программу Excel, так как один лист содержит аж 1 048 576 строк и тогда они все будут обрабатываться макросом, а пользователь будет ждать.
In this Article
- Delete Entire Row or Column
- Delete Multiple Rows or Columns
- Delete Blank / Empty Rows
- Delete Row if Cell is Blank
- Delete Row Based on Cell Value
- More Delete Row and Column Examples
- Delete Duplicate Rows
- Delete Table Rows
- Delete Filtered Rows
- Delete Rows in Range
- Delete Selected Rows
- Delete Last Row
- Delete Columns by Number
This tutorial will demonstrate different ways to delete rows and columns in Excel using VBA.
Delete Entire Row or Column
To delete an entire row in VBA use this line of code:
Rows(1).DeleteNotice we use the Delete method to delete a row.
Instead of referencing the Rows Object, you can reference rows based on their Range Object with EntireRow:
Range("a1").EntireRow.DeleteSimilarly to delete an entire column, use these lines of code:
Columns(1).DeleteRange("a1").EntireColumn.DeleteDelete Multiple Rows or Columns
Using the same logic, you can also delete multiple rows at once:
Rows("1:3").Deleteor columns:
Columns("A:C").DeleteNotice here we reference the specific row and column numbers / letters surrounded by quotations.
Of course, you can also reference the EntireRow of a range:
Range("a1:a10").EntireRow.DeleteNote: The examples below only demonstrate deleting rows, however as you can see above, the syntax is virtually identically to delete columns.
Delete Blank / Empty Rows
This example will delete a row if the entire row is blank:
Sub DeleteRows_EntireRowBlank()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b20")
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(cell.EntireRow) = 0 Then
cell.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next cell
End SubIt makes use of the Excel worksheet function: COUNTA.
Delete Row if Cell is Blank
This will delete a row if specific column in that row is blank (in this case column B):
Range("b3:b20").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.DeleteDelete Row Based on Cell Value
This will loop through a range, and delete rows if a certain cell value in that row says “delete”.
Sub DeleteRowswithSpecificValue()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b20")
If cell.Value = "delete" Then
cell.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next cell
End SubMore Delete Row and Column Examples
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Delete Duplicate Rows
This code will delete all duplicate rows in a range:
Range("b2:c100").RemoveDuplicates Columns:=2Notice we set Columns:=2. This tells VBA to check both the first two columns of data when considering if rows are duplicates. A duplicate is only found when both columns have duplicate values.
If we had set this to 1, only the first row would’ve been checked for duplicate values.
Delete Table Rows
This code will delete the second row in a Table by referencing ListObjects.
ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("list1").ListRows(2).DeleteDelete Filtered Rows
To delete only rows that are visible after filtering:
Range("b3:b20").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).EntireRow.DeleteVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Delete Rows in Range
This code will delete all rows in range:
Range("a1:a10").EntireRow.DeleteDelete Selected Rows
This code will delete all selected rows:
Selection.EntireRow.DeleteDelete Last Row
This will delete the last used row in column B:
Cells(Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).EntireRow.DeleteBy changing 2 to 1, you can delete the last used row in column A, etc.:
Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).EntireRow.DeleteDelete Columns by Number
To delete a column by it’s number, use a code like this:
Columns (2).DeleteThis is general enough to handle any column of cells with any # of line feeds in each cell. It assumes all your values are in column «A» starting at row 1 of the active sheet:
Public Function RemoveDoubleLfs(str As String) As String
If InStr(str, vbLf & vbLf) > 0 Then
str = RemoveDoubleLfs(Replace(str, vbLf & vbLf, vbLf))
End If
RemoveDoubleLfs = str
End Function
Sub RemoveEmptyLines()
Dim i As Integer, lastRow As Integer
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row '
Dim val As String
For i = 1 To lastRow:
val = Cells(i, "A").Value
If InStr(1, val, vbLf) > 0 Then
val = RemoveDoubleLfs(val)
If Left(val, 1) = vbLf Then val = Right(val, Len(val) - 1)
If Right(val, 1) = vbLf Then val = Left(val, Len(val) - 1)
Cells(i, "A").Value = val
End If
Next
ActiveSheet.Rows.EntireRow.AutoFit
End Sub
The recursive replace function gets rid of double line feeds in the text of the cell. Once that’s done there will be at most one VbLf at the beginning and end of the string. The last two if statements look for and remove the latter.
The autofit at the end is optional and is there purely to prettify the result; it just compacts the cells to their minimum height.