Заполнение ListBox данными с помощью кода VBA Excel. Добавление значений в список методом AddItem, с помощью свойств List и RowSource. Примеры.
В примерах используется событие пользовательской формы UserForm_Initialize, реализуемое в модуле формы. Это очень удобно при тестировании, когда запуск формы или кода приводит к одному результату. Кроме того, из модуля формы обращаться к форме можно с помощью ключевого слова «Me».
Создайте в редакторе VBA Excel пользовательскую форму с любым именем и разместите на ней список с именем ListBox1. Вставляйте в модуль формы код примера, запускайте код или форму и смотрите результат.
Чтобы запустить форму, фокус должен быть на ее проекте или на одном из ее элементов управления. Чтобы запустить код, курсор должен быть в одной из его строк. Запускается код или форма нажатием клавиши «F5» или треугольной кнопки «Run Sub/UserForm»:
Заполнение ListBox методом AddItem
Метод AddItem используется для загрузки отдельного элемента в ListBox. Он создает в списке новую строку и записывает в нее значение. Используя цикл, можно загрузить в ListBox одномерный массив.
Пример 1
Загрузка элементов в ListBox по отдельности:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() With Me.ListBox1 .AddItem «Зима» .AddItem «Весна» .AddItem «Лето» .AddItem «Осень» End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода:
Пример 2
Загрузка данных в ListBox из одномерного массива при помощи цикла VBA Excel:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Dim myArray() As Variant, myElement As Variant myArray = Array(«Зима», «Весна», «Лето», «Осень») With Me.ListBox1 For Each myElement In myArray .AddItem myElement Next End With End Sub |
Заполнение ListBox с помощью свойства List
Свойство List позволяет в коде VBA Excel скопировать целиком одномерный или двухмерный массив значений в элемент управления ListBox. А также добавлять данные в элементы двухмерного списка по их индексам в строки, созданные методом AddItem.
Пример 3
Заполнение списка данными из одномерного массива.
Загрузка значений, возвращенных функцией Array:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Me.ListBox1.List = Array(«Зима», «Весна», «Лето», «Осень») End Sub |
Загрузка значений из переменной одномерного массива:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Dim myArray() As Variant myArray = Array(«Январь», «Февраль», «Март», «Апрель», «Май») Me.ListBox1.List = myArray End Sub |
Пример 4
Заполнение списка данными из двухмерного массива.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() ‘Объявляем переменную массива 3×3 Dim myArray(2, 2) As Variant myArray(0, 0) = «Зима» myArray(0, 1) = «Январь» myArray(0, 2) = «Мороз» myArray(1, 0) = «Весна» myArray(1, 1) = «Апрель» myArray(1, 2) = «Теплеет» myArray(2, 0) = «Лето» myArray(2, 1) = «Июль» myArray(2, 2) = «Жара» With Me.ListBox1 ‘Указываем, что у нас 3 столбца .ColumnCount = 3 ‘Задаем ширину столбцов, если надо .ColumnWidths = «50;50;50» .List = myArray End With End Sub |
Результат получается следующий:
Пример 5
Заполнение списка с тремя столбцами по каждому элементу отдельно. Создаем строку и записываем значение в первый столбец методом AddItem. Значения во второй и третий столбцы записываем с помощью свойства List по индексам:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() With Me.ListBox1 ‘Указываем, что у нас 3 столбца .ColumnCount = 3 ‘Задаем ширину столбцов, если надо .ColumnWidths = «50;50;50» .AddItem «Зима» .List(0, 1) = «Январь» .List(0, 2) = «Мороз» .AddItem «Весна» .List(1, 1) = «Апрель» .List(1, 2) = «Теплеет» .AddItem «Лето» .List(2, 1) = «Июль» .List(2, 2) = «Жара» End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода будет таким же, как в Примере 4.
Заполнение ListBox с помощью свойства RowSource
Свойство RowSource позволяет загрузить в элемент управления ListBox значения из диапазона ячеек на рабочем листе Excel. Задать адрес диапазона свойству RowSource можно как в ходе выполнения кода VBA, так и в окне Properties элемента управления ListBox.
Адрес диапазона ячеек для свойства RowSource указывается по следующей формуле: "Имя_листа!Адрес_диапазона". Имя_листа соответствует имени листа по ярлыку. Адрес в окне Properties вводится без парных кавычек.
Если адрес диапазона указать без имени рабочего листа, то данные будут загружаться в список из соответствующего диапазона активного листа. Если имя рабочего листа содержит пробелы, то его следует заключить в одинарные кавычки: "'Данные для списка'!A1:A10".
Пример 6
Импорт данных в одностолбцовый список из диапазона «A1:A7» рабочего листа «Лист1»:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Me.ListBox1.RowSource = «Лист1!A1:A7» End Sub |
Пример 7
Импорт данных в четырехстолбцовый список с заголовками из диапазона «A2:D4» рабочего листа «Лист1» (заголовки импортируются автоматически из диапазона «A1:D1»):
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() With Me.ListBox1 ‘Указываем, что у нас 4 столбца .ColumnCount = 4 ‘Задаем размеры столбцов .ColumnWidths = «50;50;50;50» ‘Указываем, что нужна строка заголовков .ColumnHeads = True ‘Импортируем данные .RowSource = «Лист1!A2:D4» End With End Sub |
Другая информация об элементе управления ListBox представлена в отдельной статье.
|
ListBox таблица |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
The VBA ListBox is a very useful control. If you are creating any kind of UserForm application you will most likely use it.
In this post, I’m going to show you everything you need to know about the VBA ListBox so you can avoid the common pitfalls and get up and running quickly and easily.
What is the VBA ListBox used for?
The ListBox is used to display a list of items to the user so that the user can then select one or more. The ListBox can have multiple columns and so it is useful for tasks like displaying records.
VBA ListBox versus the VBA ComboBox
The ListBox is very similar to the ComboBox which also allows the user to select an item from a list of items. The main differences are:
- The Listbox allows multiple selections. The Combobox only allows one selection.
- Items in the ListBox are always visible. The Combobox items are only visible when you click on the “down” icon.
- The ComboBox has the ability to filter the contents when you type.
The VBA ListBox Properties Quick Guide
| Function | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| AddItem | Add an item | listbox.AddItem «Spain» |
| Clear | Remove all Items | listbox.Clear |
| ColumnCount | Set the number of visible columns | ComboBox1.ColumnCount = 2 |
| ColumnHeads | Make the column row visible | ComboBox1.ColumnHeads = True |
| List | Range to Listbox ListBox to Range |
Listbox.List = Range(«A1:A4»).Value Range(«A1:A4»).Value = Listbox.List |
| List | Update a column value | Listbox.List(1,2) = «New value» |
| ListCount | Get the number of items | cnt = listbox.ListCount |
| ListIndex | Get/set selected item | Idx = listbox.ListIndex combo.ListIndex = 0 |
| RemoveItem | Remove an item | listbox.Remove 1 |
| RowSource | Add a range of values from a worksheet | ComboBox1.RowSource = Sheet1.Range(«A2:B3»).Address |
| Value | Get the value of selected Item | Dim sCountry As String sCountry = listbox.Value |
How to Add Items to the ListBox
There are 3 ways to add items to the VBA Listbox:
- One at a time using the AddItem property.
- Adding an array/range using the List property.
- Adding a Range using the RowSource property.
The List and RowSource properties are the most commonly used. The table below provides a quick comparison of these properties:
| Task | RowSource | List |
|---|---|---|
| Column Headers | Yes | No |
| Update values in ListBox | No | Yes |
| Add new items | No | Yes |
| Data type | Range | Array(including Range.Value) |
| If source data changes | Listbox is automatically updated. | ListBox is not updated. |
VBA ListBox List Property
The List property allows you to add to contents of an array to a ListBox. As Range.Value is an array you can copy the contents of any range to the Listbox.
Here are some examples of using the List property:
' Add the contents of an array ListBox1.List = Array("Apple", "Orange", "Banana") ' Add the contents of a Range ListBox1.List = Range("A1:E5").Value
You can also use the List property to write from the ListBox to an array or range:
Range("A1:B3").Value = ListBox1.List
Important Note: If there is only one item in a range then VBA doesn’t covert it to an array. Instead, it converts the range to a string/double/date etc.
Sheet1.Range("A1:A2").Value ' Array Sheet1.Range("A1").Value ' Single value variable
In this case, you need to use AddItem to add the value to the ListBox:
If myRange.Count = 1 Then ListBox1.AddItem myRange Else ListBox1.List = myRange.Value End If
The List Property and Column Headers
The ListBox only displays column headers if you use RowSource. Otherwise, they are not available. The best way to add column headers(and it’s not a great way) is to add Labels above the ListBox columns. One advantage is that you can use the click event of the Label if you want to implement something like sorting.
Updating Items using the List Property
You can update individual items in the ListBox using the List Property.
Imagine we have a ListBox with data like this:
If we want to change Nelson in row 3, column 2 we do it like this:
ListBox1.List(2, 1) = "SMITH"
The result we get is:
The List property rows and columns are zero-based so this means row 1 is 0, row 2 is 1, row 3 is 2 and so on:
VBA ListBox RowSource
The RowSource property allows us to add a range to the ListBox. This is different from the List Property in that the Range is linked to the ListBox. If data in the Range changes then the data in the ListBox will update automatically.
When we use RowSource the data in the ListBox is read-only. We can change the RowSource range but we cannot change the values in the ListBox.
How to use RowSource
We add the RowSource range as a string like this:
ListBox1.RowSource = "Sheet1!A1:A5"
If you don’t specify the sheet the VBA will use the active sheet
ListBox1.RowSource = "A1:A5"
If you are using the Address of a range object with RowSource then it is important to use the External parameter. This will ensure that RowSource will read from the sheet of the range rather than the active sheet:
' Get the range Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A1:A5") ' Address will be $A$1:$A$5 which will use the active sheet ListBox1.RowSource = rg.Address Debug.Print ListBox1.RowSource ' Address will be [Book2]Sheet1!$A$1:$A$5 which will use Sheet1 ListBox1.RowSource = rg.Address(External:=True) Debug.Print ListBox1.RowSource
RowSource Column Headers
Column headers are automatically added to the ListBox when you use the RowSource property. The ColumnHeads property must be set to True or the headers will not appear. You can set this property in the code or in the properties window of the ListBox.
ListBox1.ColumnHeads = True
The column headers are taken from the row above the range used for the RowSource. For example, if your range is A2 to C5 then the column header will use the range A1 to C1:
Here is an example: We want to add the data below to our ListBox and we want A1 to C1 to be the header.
We set the RowSource property to A2:C5 and set the ColumnHeads property to true:
With ListBox1 .RowSource = "sheet1!A2:C5" .ColumnHeads = True .ColumnWidths = "80;80;80" End With
The result will look like this:
VBA ListBox AddItem
It is very rare that you would use the AddItem property to fill the ListBox. List and RowSource are much more efficient. AddItem is normally used when the Listbox already has items and you want to add a new item.
The AddItem property is simple to use. You provide the item you want to add as a parameter. The ListBox will automatically add it as the last item:
With ListBox .AddItem "Apple" .AddItem "Orange" End With
If you want to Insert the item at a certain position you can use the second parameter. Keep in mind that this is a zero-based position, so if you want the item in position one then the value is 0, position 2 the value is 1, and so on.
With ListBox1 .AddItem "Apple" .AddItem "Orange" ' Add "Banana" to position 1(Index 0) .AddItem "Banana", 0 End With
The order will be:
Banana
Apple
Orange
If you want to add multiple columns with AddItem then you need to use the List property after you use AddItem:
With listboxFruit .List = myRange.Value .AddItem "Banana" ' Add to the second column of 'Banana' row .List(2, 1) = "$2.99" End With
One reason for using AddItem is if you are adding from data that isn’t sequential so you cannot use the List or RowSource properties:
Dim cell As Range ' Fill items with first letter is A For Each cell In Sheet1.Range("A1:A50") If Left(cell.Value, 1) = "A" Then comboBoxFruit.AddItem cell.Value End If Next
Important Note: If you fill a ListBox with RowSource then you cannot use AddItem to add a new item. If you try you will get a “Runtime Error 70 – Permission Denied”.
VBA ListBox Selected Items
If only one item is selected then you can use ListIndex to get the selected row. Remember that it is zero-based so row 1 in the ListBox is at ListIndex 0, row 2 at ListIndex 1 and so on.
MsgBox "The selected item is " & ListBox1.ListIndex
If the ListBox has multiple columns then you can use the ListIndex and List properties together to return a value in the selected row:
' Display the value from the second column of the selected row
MsgBox ListBox1.List(ListBox1.ListIndex, 2)
If multiple items are selected then you can use the GetSelectedRows function which returns a collection of selected rows:
Sub Example() ' Store the row numbers of selected items to a collection Dim selectedRows As Collection Set selectedRows = GetSelectedRows() ' Print the selected rows numbers to the Immediate Window Dim row As Long For Each row In selectedRows ' Print to the Immediate Window Ctrl + G Debug.Print row Next row End Sub ' Returns a collection of all the selected items Function GetSelectedRows() As Collection ' Create the collection Dim coll As New Collection ' Read through each item in the listbox Dim i As Long For i = 0 To listboxFruit.ListCount - 1 ' Check if item at position i is selected If listboxFruit.Selected(i) Then coll.Add i End If Next i Set GetSelectedRows = coll End Function
Reading Data from the VBA Listbox
To read data from the ListBox we can use the ListBox.Value property. This only works when the ListBox is set to only select one item i.e. MultiSelect is set to frmMultiSelectSingle(see the section VBA ListBox MultiSelect below for more about this).
Single selection only with one column
When only one item is selected we can use the Value property to get the currently selected item:
Dim fruit As String fruit = ListBox1.Value
Keep in mind that if there are multiple columns, Value will only return the value in the first column.
Single selection only with multiple columns
If the ListBox has Multiple columns you can use the Value property to get the value in the first column. You need to read through the List property to get the values in the other column(s). The List property is essentially an array so you can treat it like one.
In the example below we read through the columns of row 1(the index of row 1 is 0):
With ListBox1 For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(.List, 2) ' Print the columns of the first row to the Immediate Window Debug.Print .List(0, j) Next j End With
Normally you want to print the values in the selected row. You can use the ListIndex property to get the selected item(Note that ListIndex returns the last selected items so it won’t work where there are multiple items selected):
' ExcelMacroMastery.com
Sub ReadValuesFromSelectedRow()
' Write contents of the row to the Immediate Window(Ctrl G)
With ListBox1
For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(.List, 2)
' Print the columns of the selected row to the Immediate Window
Debug.Print .List(.ListIndex, j) Next j
End With
End Sub
Multiple selections
If the ListBox has multiple selections and you want to get all the data from each then you can use the GetSelectedRows() sub from the section VBA ListBox Selected Items. This will get a collection of all selected rows. You can use this to print the data from the selected rows:
Sub PrintMultiSelectedRows() ' Get all the selected rows Dim selectedRows As Collection Set selectedRows = GetSelectedRows(Me.ListBox1) Dim i As Long, j As Long, currentRow As Long ' Read through the selected rows For i = 1 To selectedRows.Count With ListBox1 ' Get the current row currentRow = selectedRows(i) ' Print row header Debug.Print vbNewLine & "Row : " & currentRow ' Read items in the current row For j = LBound(.List, 2) To UBound(ListBox1.List, 2) ' Print the columns of the first row to the Immediate Window Debug.Print .List(currentRow, j) Next j End With Next i End Sub Function GetSelectedRows(currentListbox As MSForms.ListBox) As Collection ' Create the collection Dim coll As New Collection ' Read through each item in the listbox Dim i As Long For i = 0 To currentListbox.ListCount - 1 ' Check if item at position i is selected If currentListbox.Selected(i) Then coll.Add i End If Next i Set GetSelectedRows = coll End Function
VBA ListBox MultiSelect
We can use the MultiSelect property of the ListBox to allow the user to select either a single item or multiple items:
There are 3 selections:
- 0 = frmMultiSelectSingle – [Default]Multiple selection isn’t allowed.
- 1 = frmMultiSelectMulti – Multiple items are selected or deselected by choosing them with the mouse or by pressing the Spacebar.
- 2 = frmMultiSelectExtended – Multiple items are selected by holding down Shift and choosing them with the mouse, or by holding down Shift and pressing an arrow key to extend the selection from the previously selected item to the current item. You can also select items by dragging with the mouse. Holding down Ctrl and choosing an item selects or deselects that item.
VBA ListBox Columns
You can have multiple columns in a ListBox. For example, you can load a Range or two-dimensional array to a ListBox using List or RowSource.
Often when you load data with multiple columns only one column appears. This can be very confusing when you are using the Listbox. To get the columns to appear you have to set the ColumnCount property to the number of Columns.
You should also make sure that the ColumnWidths property is correct or one of the columns may not appear.
You can do it like this:
With listboxFruit .RowSource = "Sheet1!A2:B4" .ColumnCount = 2 .ColumnWidths = "100,100" End With
In a real-world application, you could set the RowSource and ColumnCount properties like this:
With listboxFruit .RowSource = myRange.Address(External:=True) .ColumnCount = myRange.Columns.Count End With
See the AddItem section for how to add data to the other columns when you are using the AddItem property.
VBA ListBox Column Headers
Column Headers are another confusing element of the ListBox. If you use the RowSource property to add data to the ListBox then the line above the Range will be automatically used as the header.
For the Column headers to appear the ColumnHeads property must be set to true. You can do this in the properties window of the ListBox or in the code list this:
ListBox1.ColumnHeads = True
If you use the List or AddItem property to fill the ListBox then the column headers are not available. The best solution, albeit a frustrating one, is to use labels above the ListBox. I know it sounds crazy but that unfortunately is the reality. The one advantage is that you can use the Label click event which is useful if you plan to sort the data by a column.
Creating a ListBox Dynamically
Controls are normally created at design time but you can also create them dynamically at run time:
Dim myListbox As MSForms.ListBox
Set myListbox = Controls.Add("Forms.ListBox.1")
If you want to add an event to a dynamic control you can do it like this:
- First of all create a Class like this:
Public WithEvents myListBox As MSForms.ListBox Private Sub myListBox_Change() MsgBox "Selection changed" End Sub
- Name the class clsListBoxEvents. Create a variable of this class object in the UserForm like this:
Private listBoxEvents As New clsListBoxEvents
- Attach the events to the ListBox:
Sub CreateDynamicListBox() ' Create the ListBox Dim newListBox As MSForms.ListBox Set newListBox = Controls.Add("Forms.ListBox.1") ' Add some items newListBox.List = Array("Apple", "Orange", "Pear") ' Connect the ListBox to the ListBox events class Set listBoxEvents.myListBox = newListBox End Sub
Note that you can attach events to any ListBox. It doesn’t have to be created dynamically to do this.
Loop through ListBoxes
If you want to loop through all the ListBoxes on a UserForm you can do it like this:
Dim ctrl As Variant For Each ctrl In Me.Controls If TypeName(ctrl) = "ListBox" Then Debug.Print ctrl.Name End If Next ctrl
YouTube Video
Check out this video where I use the ListBox. The source code for the video is available from here
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out this Free VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
Tuesday, September 06, 2011
How to link Excel Table to ListBox using VBA
Fill a ListBox from Excel Table using VBA / Populate a ListBox from Excel Table using VBA
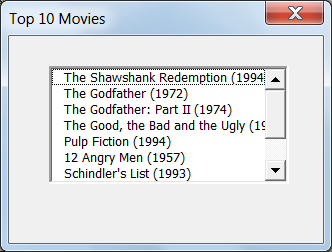
Let us take a Excel table as shown below — a list of Top 10 All time hits .
Let us assume that we need to populate the Listbox with values from Column 2
The following code will help you populate the data
Dim oWS As Worksheet
Set oWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(3)
Me.ListBox1.List = oWS.ListObjects(1).ListColumns("Title").DataBodyRange.Value
End Sub
|
evdvaleri 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 11.04.2015 Сообщений: 3 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
11.04.2015, 08:33. Показов 4790. Ответов 8 Метки нет (Все метки)
Есть таблица в excel, там №, ФИО и группа.
Но не могу понять как сделать выборку по выбранной группе, поиск не помог.
0 |
|
2079 / 1232 / 464 Регистрация: 20.12.2014 Сообщений: 3,237 |
|
|
11.04.2015, 08:43 |
2 |
|
Файл выложите, трудно сделать выборку не зная ячеек
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 11.04.2015 Сообщений: 3 |
|
|
11.04.2015, 10:16 [ТС] |
4 |
|
chumich,
0 |
|
Alex77755 11482 / 3773 / 677 Регистрация: 13.02.2009 Сообщений: 11,145 |
||||
|
11.04.2015, 10:56 |
5 |
|||
|
evdvaleri,
2 |
|
2079 / 1232 / 464 Регистрация: 20.12.2014 Сообщений: 3,237 |
||
|
11.04.2015, 15:20 |
6 |
|
|
Решениеevdvaleri, держите. Alex77755 прав — пример абсолютно идентичен вашему. Но, я сделал через перебор ячеек. А в нем нужно занести данные в массив. Так что выбирайте любой вариант. Вложения
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 11.04.2015 Сообщений: 3 |
|
|
13.04.2015, 03:10 [ТС] |
7 |
|
Спасибо большое
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 09.03.2016 Сообщений: 12 |
|
|
18.05.2016, 17:52 |
8 |
|
Добрый день! пожалуйста можете показать как тоже самое сделать только в visual basic в 2010 студии. Как сделать чтоб, выбирая какую не будь группу из combobox, показывал список студентов этой группы в listbox.
0 |
|
11482 / 3773 / 677 Регистрация: 13.02.2009 Сообщений: 11,145 |
|
|
19.05.2016, 05:39 |
9 |
|
только в visual basic в 2010 студии Может спросишь как в Делфи сделать? Или в С++?
0 |










 :
: 











 Сообщение было отмечено evdvaleri как решение
Сообщение было отмечено evdvaleri как решение