This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the macros, data and formulas I use in the examples below. You can get immediate access to this example workbook by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section that interests you.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about essential VBA terms here.
- Learn how to work in the Visual Basic Editor here.
- Learn how to create Sub procedures here.
- Learn how to create Function procedures here.
- Learn how to work with variables here.
- Learn about VBA data types here.
- Learn about the Range object here.
- Tutorials about other useful topics:
- Learn how to work with the IFERROR worksheet function here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Convert String to Byte
VBA code to convert String to Byte
To convert a string to a number of the Byte data type, use the following statement:
CByte(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Byte
To convert a string to a number of the Byte data type, use the CByte function to convert the String to a number of the Byte data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CByte.
- VBA construct: CByte function.
- Description: The CByte function coerces String to the Byte data type.
CByte is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Byte data type. In other words, CByte generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Byte data type can hold numbers ranging from 0 to 255. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CByte function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Byte data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Byte
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Byte.
Function stringToByte(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Byte
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Byte
stringToByte = CByte(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Byte
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Byte, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#2: Convert String to Integer
VBA code to convert String to Integer
To convert a string to a number of the Integer data type, use the following statement:
CInt(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Integer
To convert a string to a number of the Integer data type, use the CInt function to convert the String to a number of the Integer data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CInt.
- VBA construct: CInt function.
- Description: The CInt function coerces String to the Integer data type.
If String contains a fraction, CInt rounds it. If this fraction is precisely 0.5, CInt rounds to the nearest even number. For example:
- 0.5 is rounded to 0.
- Both 1.5 and 2.5 are rounded to 2.
- Both 3.5 and 4.5 are rounded to 4.
- CInt is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Integer data type. In other words, CInt generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Integer data type can hold numbers ranging from -32,768 to 32,767. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CInt function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Integer data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Integer
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Integer.
Function stringToInteger(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Integer
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Integer
stringToInteger = CInt(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Integer
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Integer, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error. Additionally, if String contains a fraction that’s precisely 0.5, the UDF rounds to the nearest even number.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#3: Convert String to Long
VBA code to convert String to Long
To convert a string to a number of the Long data type, use the following statement:
CLng(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Long
To convert a string to a number of the Long data type, use the CLng function to convert the String to a number of the Integer data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CLng.
- VBA construct: CLng function.
- Description: The CLng function coerces String to the Long data type.
If String contains a fraction, CLng rounds it. If this fraction is precisely 0.5, CLng rounds to the nearest even number. For example:
- 0.5 is rounded to 0.
- Both 1.5 and 2.5 are rounded to 2.
- Both 3.5 and 4.5 are rounded to 4.
CLng is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Long data type. In other words, CLng generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Long data type can hold numbers ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CLng function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Long data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Long
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Long.
Function stringToLong(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Long
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Long
stringToLong = CLng(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Long
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Long, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error. Additionally, if String contains a fraction that’s precisely 0.5, the UDF rounds to the nearest even number.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#4: Convert String to Single
VBA code to convert String to Single
To convert a string to a number of the Single data type, use the following statement:
CSng(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Single
To convert a string to a number of the Single data type, use the CSng function to convert the String to a number of the Single data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CSng.
- VBA construct: CSng function.
- Description: The CSng function coerces String to the Single data type.
CSng is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Single data type. In other words, CSng generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Single data type can hold floating-point numbers ranging from:
- -3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 for negative values; and
- 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CSng function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Single data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Single
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Single.
Function stringToSingle(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Single
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Single
stringToSingle = CSng(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Single
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Single, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#5: Convert String to Double
VBA code to convert String to Double
To convert a string to a number of the Double data type, use the following statement:
CDbl(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Double
To convert a string to a number of the Double data type, use the CDbl to convert the String to a number of the Double data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CDbl.
- VBA construct: CDbl function.
- Description: The CDbl function coerces String to the Double data type.
CDbl is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Double data type. In other words, CDbl generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Double data type can hold floating-point numbers ranging from:
- -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values; and
- 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 for positive values.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CDbl function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Double data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Double
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Double.
Function stringToDouble(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Double
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Double
stringToDouble = CDbl(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Double
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Double, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#6: Convert String to Currency
VBA code to convert String to Currency
To convert a string to a number of the Currency data type, use the following statement:
CCur(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Currency
To convert a string to a number of the Currency data type, use the CCur to convert the String to a number of the Currency data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CCur.
- VBA construct: CCur function.
- Description: The CCur function coerces String to the Currency data type.
CCur is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Currency data type. In other words, CCur generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Currency data type holds integers scaled by 10,000. This results in Currency holding fixed-point numbers with 15 digits to the left of the decimal point and 4 digits to the right of the decimal point. Therefore, Currency can hold numbers ranging from -922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CCur function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Currency data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Currency
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Currency.
Function stringToCurrency(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Currency
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Currency
stringToCurrency = CCur(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Currency
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Currency, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#7: Convert String to Decimal
VBA code to convert String to Decimal
To convert a string to a number of the Decimal data type, use the following statement:
CDec(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Decimal
To convert a string to a number of the Decimal data type, use the CDec function to convert the String to a number of the Decimal data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CDec.
- VBA construct: CDec function.
- Description: From a broad perspective, the CDec function coerces String to the Decimal data subtype of the Variant data type. In other words, CDec doesn’t return a discrete data type, but rather a Variant converted to the Decimal subtype.
CDec is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Decimal data type. In other words, CDec generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Decimal data type holds integers scaled by a variable power of 10. This power of 10 specifies the number of digits to the right of the decimal point. Therefore, the value ranges Decimal can hold are as follows:
- When working with a scale of 0, which results in no decimal places: -79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 to 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335.
- When working with 28 decimal places:
- The largest and smallest values are +7.9228162514264337593543950335 and -7.9228162514264337593543950335.
- The smallest non-zero values are -0.0000000000000000000000000001 and 0.0000000000000000000000000001.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CDec function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the CDec data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Decimal
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Decimal.
Function stringToDecimal(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Decimal
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Decimal
stringToDecimal = CDec(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Decimal
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Decimal, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
String and Integer are common data types. But, often, as part of our data analysis, we may want to convert string data type variables to Integer data type. It is possible by using the CINT function in VBA.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA String to Integer (wallstreetmojo.com)
Table of contents
- Excel VBA String to Integer
- Syntax of CINT Function
- Examples of CINT Function in VBA
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Syntax of CINT Function
The CINT is a data type conversion function. This function converts provided expressions into an Integer data type. When we say “Expression,” it must be a numerical value in the range of Integer data type in VBAIn VBA, an integer is a data type that may be assigned to any variable and used to hold integer values. In VBA, the bracket for the maximum number of integer variables that can be kept is similar to that in other languages. Using the DIM statement, any variable can be defined as an integer variable.read more, i.e., between -32768 to 32767.
Now, look at the syntax of the CINT function in VBA.
- Expression is the value or the variable which contains the value that needs to convert to an Integer data type.
Note 1: When you pass, the expression value must be between -32768 to 32767. Otherwise, it will lead to an “Overflow” error, i.e., assigning the value over the data type’s limit.
Note 2: Expression must be a numerical value. If the expression is string value or text value, it will cause a “Run Time Error 13: Type Mismatch.”
This article will show you the Integer data type conversion from a string to an integer using the function “CINT.”
Examples of CINT Function in VBA
You can download this VBA String to Integer Excel Template here – VBA String to Integer Excel Template
Example #1
Let us perform the first example of converting one fraction number to an Integer data type.
Code:
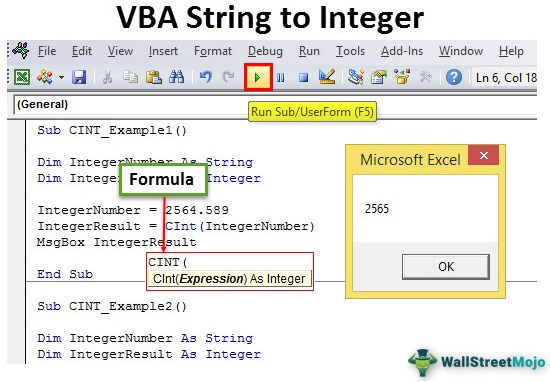
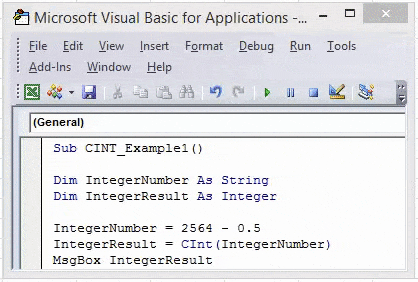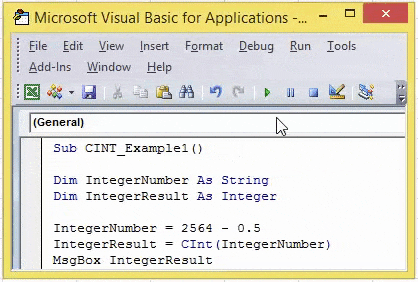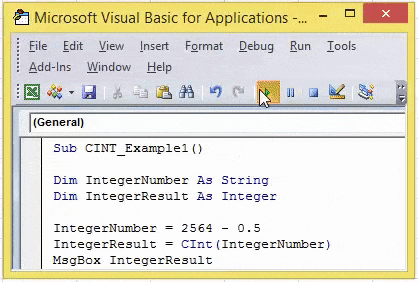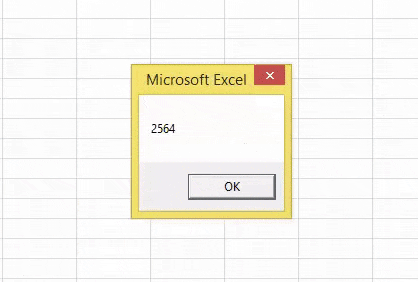
Sub CINT_Example1() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = 2564.589 IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) MsgBox IntegerResult End Sub
- In the above code for the variable “IntegerNumber,” we have assigned the value as “2564.589.”
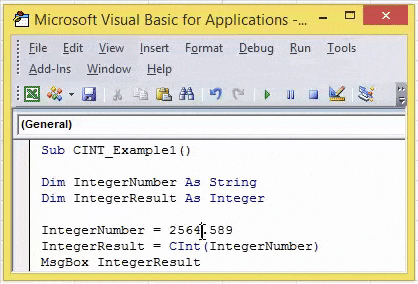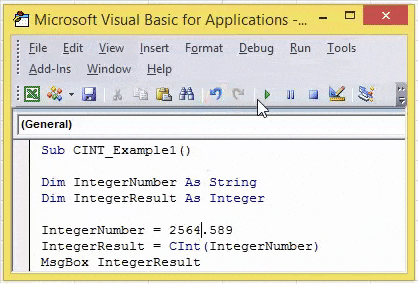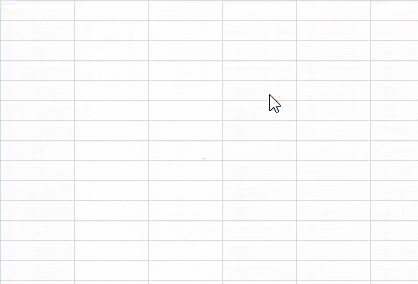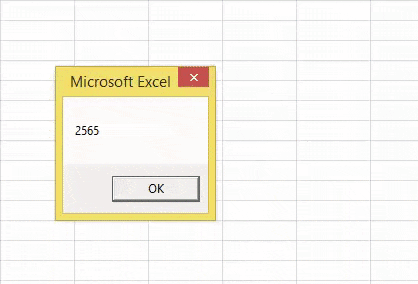
- In the next line, we have applied a CINT function. So, it will convert the provided value to the nearest integer number.
So, we got the result – 2565, and the supplied number is 2564.589. When the decimal value is more than 0.5, the CINT functions round up the number to the next Integer number. When the decimal value is less than or equal to 0.5, CINT functions round down to the same Integer number.
For an example, look at the below code where the number is less than 0.5.
Code:
Sub CINT_Example1() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = 2564 - 0.5 IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) MsgBox IntegerResult End Sub
It should give the result as 2564, not 2565.
Example #2
Now, we will try and assign the number more than the limit of the Integer data type.
Code:
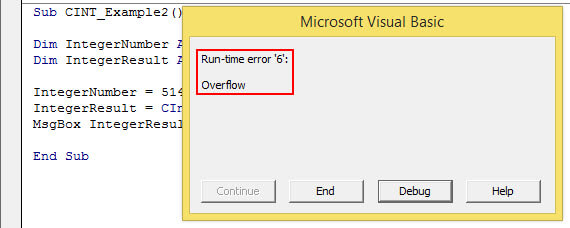
Sub CINT_Example2() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = 51456.785 IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) MsgBox IntegerResult End Sub
We have assigned the “IntegerNumber = 51456.785” more than the Integer data type limit. So now, if we try to run the code, it will throw an overflow error in VBAVBA Overflow Error or «Run Time Error 6: Overflow» occurs when the user inserts a value that exceeds the capacity of a specific variable’s data type. Thus, it is an error that results from the overloading of data beyond the desired data type limit of the variable.read more.
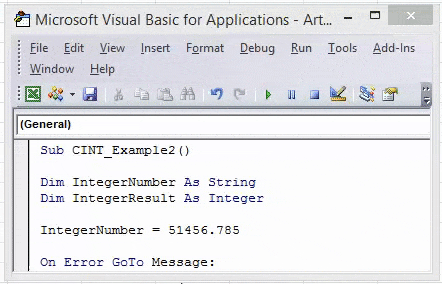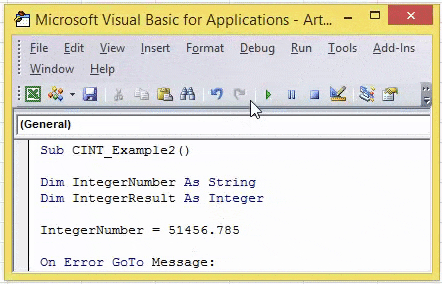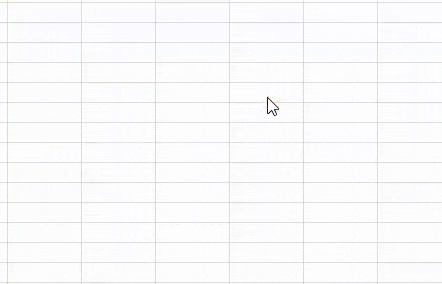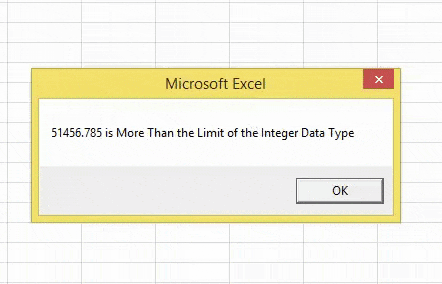
Whenever the provided number is more than the Integer data type, let us show the simple message box saying, “Number is More Than the Limit of the Integer Data Type.”
Code:
Sub CINT_Example2() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = 51456.785 On Error GoTo Message: IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) Message: If Err.Number = 6 Then MsgBox IntegerNumber & " is More Than the Limit of the Integer Data Type" End Sub
It will show the message below whenever the provided number is outside the Integer data type range.
Example #3
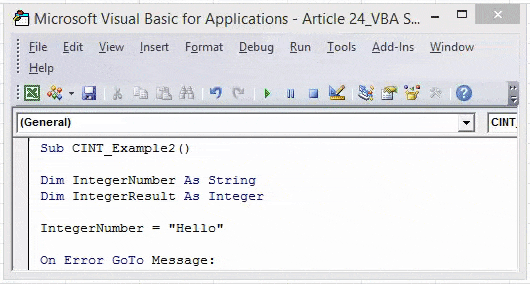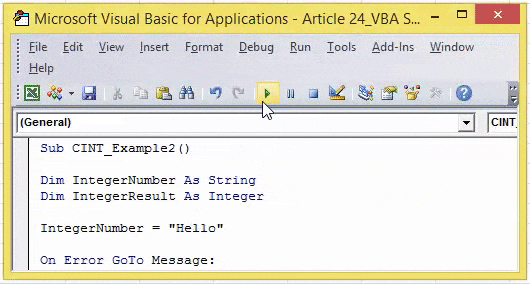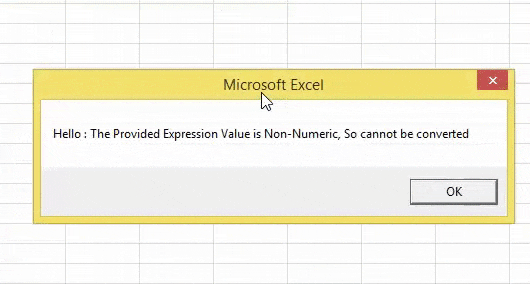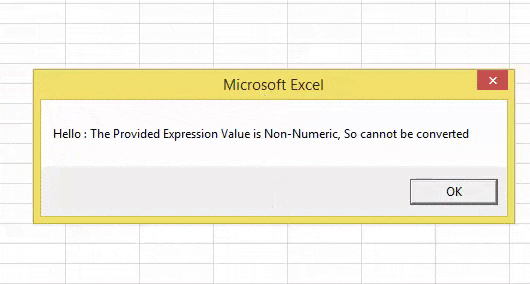
Now, we will try to assign the value which is not numeric.
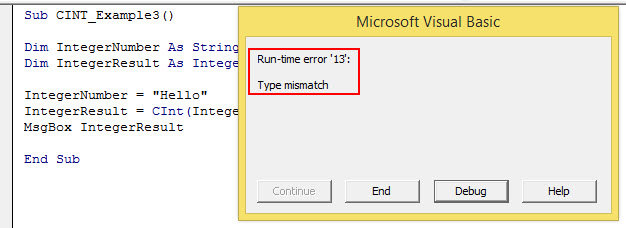
Sub CINT_Example2() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = "Hello" IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) MsgBox IntegerResult End Sub
We have assigned the value “Hello,” which is not numeric. It causes a “Type Mismatch ErrorWhen we assign a value to a variable that is not of its data type, we get Type mismatch Error or Error code 13. For example, if we assign a decimal or long value to an integer data type variable, we will get this error (Error Code 13) when we run the code.read more”.
Instead of showing the error like this, let us put a simple information message box in front of the user. The below code will put the message box saying, “The Provided Expression Value is Non-Numeric, So, cannot be converted.”
Code:
Sub CINT_Example2() Dim IntegerNumber As String Dim IntegerResult As Integer IntegerNumber = "Hello" On Error GoTo Message: IntegerResult = CInt(IntegerNumber) Message: If Err.Number = 13 Then MsgBox IntegerNumber & " : The Provided Expression Value is Non-Numeric, So cannot be converted" End Sub
It will show the message box below.
Things to Remember
- The CINT function converts the value from another data type to an Integer data type.
- Integers can hold values from -32768 to 32767. Anything above these numbers will cause an “Overflow” error.
- Only string data type contains numerical data that will convert to an Integer data type.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA String to Integer. Here, we discuss examples of string to integer in Excel VBA using the CINT function, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA Split String into Array
- VBA String to Date
- VBA String Comparison
- VBA Replace String

This article will discuss how we can convert a string to a number in VBA Excel. There is a step-by-step guide and many examples for our understanding.
Convert String to Number in VBA
In VBA code, converting numbers saved as text to real numbers is obligatory. We have many conversion options.
We can convert strings to numbers of the Byte, Integer, Long, Single, Double, Currency, and Decimal data types. We will discuss each conversion in detail with examples.
Convert String to Byte in VBA
We can easily transform a string into a number of the byte data type with the help of the following code.
# vba
byte = CByte(str)
We can use the CByte() function to achieve this conversion. The above statement has two items: CByte() and string.
CByte() function forces the string to change into a byte type. CByte() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to byte data type.
In simple terms, CByte() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location. The range that a byte data type can hold is 0 to 225. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Here is a macro example in which we have convertStr as an argument to convert a string to a byte.
# vba
Function convertStr(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CByte(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertStr ("12")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Integer in VBA
With the help of the following statement, you can easily convert a string to a number of the integer data type. The syntax of this function is shown below.
# vba
CInt(newStr)
It is recommended to use the Clnt() function to change a string to an integer data type. This function forces the string to change into the integer data type.
If a string holds a fraction, this function will convert it into an integer. If the fraction is precisely 0.4, this function will change it to the closest even number.
For example:
# vba
0.4 will become 0.
1.6 and 2.4 both will become 2.
3.7 and 4.3 will become 4
Clnt() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation into the integer data type. In simple terms, Clnt() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon our computer’s location.
The range between which an integer data type can hold numbers is -32,768 to 32,767. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Let’s go through an example and use the CInt() function as shown below. This example sets newStr as an argument to change a string into an integer, as shown below.
# vba
Function convertToInteger(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CInt(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToInteger ("12.5")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Long in VBA
We can use the CLng() function to achieve this conversion. The syntax of this function is shown below.
# vba
CLng(Str)
We can use the CLng() function when our goal is to change a string into several long data types. The items in this statement are CLng() and string.
This function forces a string to change into the long data type.
If a string holds a fraction, this function will round it. If the fraction is precisely 0.4, this function will change it to the closest even number, as shown below.
# vba
0.4 will become 0.
1.6 and 2.4 both will become 2.
3.7 and 4.3 will become 4
CLng() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to long data types. In simple terms, CLng() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which an integer data type can hold numbers is -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Let’s go through an example and use the CLng() function. In this example, we have set newStr as an argument to change a string into long, as shown below.
# vba
Function convertToLong(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CLng(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToLong ("15.7")
End Sub
Output:
Long data type differs from integer data type by only one thing. Larger numbers are acceptable in long data types.
But there wasn’t enough memory in the old days, and it was not recommended to use long data types.
In modern times, memory is no longer a problem. We can use the long data type instead of an integer.
Convert String to Single in VBA
We can easily transform a string into a number of a single data type with the help of the following syntax, as shown below.
# vba
CSng(str)
We can use the CSng() function to achieve this conversion. There are two items in the above statement, CSng() and string.
This function forces a string to change into a single data type.
CSng() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a single data type. CSng() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which a single data type can hold floating-point numbers is
- 3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 when values are negative
- 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 when values are positive
An error will appear if your string does not fall between this range. As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a single.
# vba
Function convertToSingle(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CSng(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToSingle ("1.3")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Double in VBA
With the help of the following statement, we can easily convert a string to several double data types. The syntax of this function is as shown below.
# vba
CDbl(str)
It is recommended to use the CDbl() function to change a string to a double data type. This function forces a string to change into the double data type.
CDbl() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a double data type.
In simple words, CDbl() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which a double data type can hold floating-point numbers is below.
- -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 when values are negative.
- 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 when values are positive.
An error will appear if our string does not fall between this range. As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a double.
# vba
Function convertToDouble(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CDbl(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToDouble ("1.345")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Currency in VBA
With the help of the following statement, you can easily convert a string to several currency data types. The syntax of the function is shown below.
# vba
CCur(newStr)
It is recommended to use the CCur() function to change a string to a currency data type. This function forces a string to change into the currency data type.
CCur() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a currency data type.
It means CCur() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location. The currency data type can hold integers by 10,000.
As a result, a currency can hold 15 numbers to the left of the decimal point and four numbers to the right of the decimal point. So the range between which a currency can hold numbers is:
-922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807.
An error will appear if your string does not fall between this range.
As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a currency.
# vba
Function convertToCurrency(newStr As Variant)
msgBox(CCur(newStr))
End Function
Convert String to Decimal in VBA
We can use the following statement to achieve this conversion.
# vba
CDec(newStr)
We can use the CDec() function when our goal is to change a string into several decimal data types. This function forces a string to change into the decimal data subtype of the Variant data type.
In simple words, CDec() will return a variant changed to the Decimal subtype.
CDec() is often used to perform the internationally-aware transformation of a string to a decimal data type. It means CDec() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The decimal data type can carry integers having variable power of 10. The power denotes the number of digits that can be present to the right of the decimal point.
The range in which decimals can hold values is shown below.
- When the scale is 0, that is no decimal present the range is from 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 to 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335.
- When there are 28 decimal places, the biggest and smallest values are +7.9228162514264337593543950335 and -7.9228162514264337593543950335.
- The smallest values containing no zero values are -0.0000000000000000000000000001 and 0.0000000000000000000000000001.
As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a decimal.
# vba
Function convertToDecimal(newStr As Variant)
msgBox(CDec(newStr))
End Function
You can use the CInt function in VBA to convert a text string to an integer.
Here are two common ways to use this function in practice:
Method 1: Convert String to Integer in VBA
Sub ConvertStringToInteger() Dim i As Integer For i = 2 To 11 Range("B" & i) = CInt(Range("A" & i)) Next i End Sub
This particular macro will convert each string in the range A2:A11 to an integer and display the integers in the range B2:B11.
Method 2: Convert String to Integer in VBA (Only if String is a Number)
Sub ConvertStringToInteger()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 2 To 11
If IsNumeric(Range("A" & i)) Then
Range("B" & i) = CInt(Range("A" & i))
Else
Range("B" & i) = 0
End If
Next i
End Sub
This particular macro will convert each string in the range A2:A11 to an integer only if the string is a number. Otherwise, the string will be converted to a value of zero.
The following examples show how to use each method in practice.
Suppose we have the following column of values in Excel that are currently formatted as text strings:
Suppose we would like to convert each string to an integer and display the integers in column B.
We can create the following macro to do so:
Sub ConvertStringToInteger() Dim i As Integer For i = 2 To 11 Range("B" & i) = CInt(Range("A" & i)) Next i End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that each text string in column A has been converted to an integer and is displayed in column B.
Example 2: Convert String to Integer in VBA (Only if String is a Number)
Suppose we have the following column of values in Excel that are currently formatted as text strings:
Suppose we would like to convert each string to an integer only if the string is a number and display the integers in column B.
We can create the following macro to do so:
Sub ConvertStringToInteger()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 2 To 11
If IsNumeric(Range("A" & i)) Then
Range("B" & i) = CInt(Range("A" & i))
Else
Range("B" & i) = 0
End If
Next i
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that only the text strings in column A that are numbers are converted to integers in column B.
Otherwise, the text strings are simply converted to a value of zero.
Note: You can find the complete documentation for the VBA Cint function here.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in VBA:
VBA: How to Remove Spaces from String
VBA: How to Count Occurrences of Character in String
VBA: How to Check if String Contains Another String
Функции преобразования типов данных в VBA Excel. Наименования функций, синтаксис, типы возвращаемых данных, диапазоны допустимых значений выражения-аргумента.
Синтаксис функций преобразования
Выражение (аргумент) – это любое строковое или числовое выражение, возвращающее значение, входящее в диапазон допустимых значений для аргумента. Выражение может быть представлено переменной или другой функцией.
Если аргумент, переданный в функцию, не входит в диапазон типа, в который преобразуются данные, происходит ошибка.
Функции преобразования типов
Наименования функций преобразования типов, типы возвращаемых данных, диапазоны допустимых значений для аргумента:
| Функция | Тип данных | Диапазон значений аргумента |
|---|---|---|
| CBool | Boolean | Любое допустимое строковое или числовое выражение. |
| CByte | Byte | От 0 до 255. |
| CCur | Currency | От -922 337 203 685 477,5808 до 922 337 203 685 477,5807. |
| CDate | Date | Любое допустимое выражение даты. |
| CDbl | Double | От -1,79769313486231E308 до -4,94065645841247E-324 для отрицательных значений; от 4,94065645841247E-324 до 1,79769313486232E308 для положительных значений. |
| CDec | Decimal | 79 228 162 514 264 337 593 543 950 335 для чисел без десятичных знаков. Для чисел с 28 десятичными знаками диапазон составляет 7,9228162514264337593543950335. Наименьшим возможным числом, отличным от нуля, является число 0,0000000000000000000000000001. |
| CInt | Integer | От -32 768 до 32 767, дробная часть округляется. |
| CLng | Long | От -2 147 483 648 до 2 147 483 647, дробная часть округляется. |
| CSng | Single | От -3,402823E38 до -1,401298E-45 для отрицательных значений; от 1,401298E-45 до 3,402823E38 для положительных значений. |
| CStr | String | Результат, возвращаемый функцией CStr, зависит от аргумента Выражение. |
| CVar | Variant | Диапазон совпадает с типом Double для числовых значений и с типом String для нечисловых значений. |
Дополнительно для VBA7:
| Функция | Тип данных | Диапазон значений аргумента |
|---|---|---|
| CLngLng | LongLong | От -9 223 372 036 854 775 808 до 9 223 372 036 854 775 807, дробная часть округляется. Действительно только для 64-разрядных платформ. |
| CLngPtr | LongPtr | От -2 147 483 648 до 2 147 483 647 для 32-разрядных платформ, от -9 223 372 036 854 775 808 до 9 223 372 036 854 775 807 для 64-разрядных платформ, дробная часть округляется в обоих типах систем. |
Примеры преобразования типов
Функция CBool
Функция CBool используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Boolean.
|
Dim a a = CBool(10) ‘Результат: True a = CBool(0) ‘Результат: False a = CBool(«True») ‘Результат: True a = CBool(«Test») ‘Результат: Error Dim a, b, c a = «Test1» b = «Test2» c = CBool(a = b) ‘Результат: False c = CBool(a <> b) ‘Результат: True |
Функция CByte
Функция CByte используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Byte.
|
Dim a, b, c a = 654 b = 3.36 c = a / b ‘Результат: 194,642857142857 c = CByte(c) ‘Результат: 195 c = a * b ‘Результат: 2197,44 c = CByte(c) ‘Результат: Error |
Функция CCur
Функция CCur используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Currency.
|
Dim a, b, c a = 254.6598254 b = 569.2156843 c = a + b ‘Результат: 823,8755097 c = CCur(a + b) ‘Результат: 823,8755 |
Функция CDate
Функция CDate используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Date. Она распознает форматы даты в соответствии с национальной настройкой системы.
|
Dim a As String, b As Date, c As Double a = «28.01.2021» b = CDate(a) ‘Результат: #28.01.2021# c = CDbl(b) ‘Результат: 44224 Dim a a = CDate(44298.63895) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021 15:20:05# a = CDate(44298) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021# a = CDate(0.63895) ‘Результат: #15:20:05# |
Функция CDbl
Функция CDbl используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Double.
|
Dim a As String, b As String, c As Double a = «45,3695423» b = «548955,756» c = CDbl(a) + CDbl(b) ‘Результат: 549001,1255423 |
Примечание
Eсли основной язык системы – русский, при записи в редакторе VBA Excel дробного числа в виде текста, ставим в качестве разделителя десятичных разрядов – запятую. Проверьте разделитель по умолчанию для своей национальной системы:
MsgBox Application.DecimalSeparator
Функция CDec
Функция CDec используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Decimal.
|
Dim a As String, b As Double, c a = «5,9228162514264337593543950335» b = 5.92281625142643 c = CDec(a) — CDec(b) ‘Результат: 0,0000000000000037593543950335 Dim a As Double, b As String, c a = 4.2643E—14 b = CStr(a) ‘Результат: «4,2643E-14» c = CDec(a) ‘Результат: 0,000000000000042643 |
Функция CInt
Функция CInt используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Integer.
|
Dim a As String, b As Integer a = «2355,9228» b = CInt(a) ‘Результат: 2356 |
Функция CLng
Функция CLng используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Long.
|
Dim a As Date, b As Long a = CDate(44298.63895) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021 15:20:05# b = CLng(a) ‘Результат: 44299 a = CDate(b) ‘Результат: #13.04.2021# |
Функция CSng
Функция CSng используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Single.
|
Dim a As String, b As Single a = «3,2365625106» b = CSng(a) ‘Результат: 3,236562 |
Функция CStr
Функция CStr используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных String.
|
Dim a As Single, b As String a = 5106.23 b = CStr(a) ‘Результат: «5106,23» |
Функция CVar
Функция CVar используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Variant.
|
Dim a As Double, b As String, c a = 549258.232546 b = «Новое сообщение» c = CVar(a) ‘Результат: 549258,232546 (Variant/Double) c = CVar(b) ‘Результат: «Новое сообщение» (Variant/String) |
Функции преобразования типов данных используются в тексте процедур VBA Excel для того, чтобы указать, что результатом выполнения той или иной операции должны стать данные определенного типа, отличающегося от типа, заданного по умолчанию.