Создание таблицы с помощью кода VBA Excel. Создание умной и обычной пользовательской таблицы. Указание стиля умной таблицы, добавление строки итогов. Примеры.
Создание и удаление умной таблицы
Создание умной таблицы
Создается умная таблица Excel с помощью следующего кода:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range(«$A$1:$L$15»), , xlNo).Name _ = «МояТаблица1» |
В данном примере:
ActiveSheet — лист, на котором создается таблица, может быть любой лист рабочей книги Excel.
Range(«$A$1:$L$15») — диапазон, который преобразуется в таблицу. Можно использовать и такую форму: Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(15, 12)), где индексы строк и столбцов можно заменить переменными.
xlNo — указывает, что первая строка выбранного диапазона не содержит заголовки столбцов (граф) будущей таблицы, и их необходимо добавить. В этом случае будет добавлена дополнительная строка с наименованиями столбцов по умолчанию: Столбец1, Столбец2, Столбец3 и т.д., которые в дальнейшем можно переименовать (количество строк в таблице, включая строку заголовков, получится на одну больше, чем в указанном диапазоне). Если в диапазоне уже содержатся заголовки столбцов будущей таблицы, то следует указать вместо xlNo значение xlYes. В этом случае первая строка указанного диапазона будет преобразована в строку заголовков, а если она будет не заполнена, то добавятся названия столбцов по умолчанию: Столбец1, Столбец2, Столбец3 и т.д. (количество строк в таблице, включая строку заголовков, будет то же, что и в указанном диапазоне).
МояТаблица1 — имя, присваиваемое создаваемой таблице. Имя должно быть без пробелов: при указании в коде VBA названия таблицы с пробелами, во время его выполнения Excel заменит пробелы знаками подчеркивания (по крайней мере, так происходит в Excel 2016).
Таблица будет создана со стилем по умолчанию (TableStyleMedium2 в Excel 2016).
Стиль умной таблицы
Присвоение стиля таблице (изменение стиля) осуществляется с помощью свойства TableStyle объекта ListObjects:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«МояТаблица1»).TableStyle = «TableStyleMedium15» |
Свойство TableStyle может принимать следующие значения:
- TableStyleLight (светлый) с индексом от 1 до 21 (в Excel 2016);
- TableStyleMedium (средний) с индексом от 1 до 28 (в Excel 2016);
- TableStyleDark (темный) с индексом от 1 до 11 (в Excel 2016).
Например, TableStyleLight5, TableStyleMedium24, TableStyleDark8.
Чтобы отменить стиль таблицы в коде VBA, необходимо свойству TableStyle присвоить пустую строку:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«МояТаблица1»).TableStyle = «» |
Этому коду соответствует выбор в разделе «Конструктор» на ленте инструментов Excel самого первого значка стилей в разделе «Светлый».
Добавление строки итогов
Строка итогов умной таблицы добавляется следующим образом:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«МояТаблица1»).ShowTotals = True |
Удаляется строка итогов умной таблицы так:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«МояТаблица1»).ShowTotals = False |
Удаление умной таблицы
Удалить умную таблицу очень просто:
|
ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«МояТаблица1»).Delete |
Создание пользовательской таблицы
Мне не приходилось на практике с помощью VBA Excel создавать умные таблицы, в отличие от пользовательских таблиц, которые использовались для улучшения восприятия различных отчетов или сгенерированных документов.
Для создания такой таблицы необходимо:
- определить диапазон, если он заранее не известен (иногда для этого может понадобиться определить номер последней заполненной строки);
- добавить границы ячеек;
- отформатировать строку заголовков;
- добавить строку итогов, если она необходима.
Подробнее о создании пользовательской таблицы в Примере 2.
Примеры создания таблиц
Задание для примеров
Набор данных для примеров создания таблиц
Допустим, на лист Excel переданы данные для заполнения табличной части товарного чека со следующими условиями:
- в табличной части 5 граф: № п/п, Наименование, Количество, Цена и Сумма;
- сколько наименований добавил пользователь неизвестно.
Нам необходимо:
- определить количество строк;
- добавить строку заголовков;
- отобразить сетку (границы ячеек);
- добавить строку итогов.
Таблицу будем оформлять двумя способами: путем создания умной и пользовательской таблиц.
Пример 1 — умная таблица
Упаковываем набор данных из задания в умную таблицу:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
Sub test1() ‘Объявляем переменную для присвоения ей количества строк Dim a As Long ‘Определяем количество строк a = Cells(1, 1).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count ‘Создаем умную таблицу с добавлением строки заголовков ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range(Cells(1, 1),Cells(a, 5)), , xlNo).Name _ = «ТоварныйЧек1» ‘Изменяем названия граф Cells(1, 1) = «№ п/п» Cells(1, 2) = «Наименование» Cells(1, 3) = «Количество» Cells(1, 4) = «Цена» Cells(1, 5) = «Сумма» ‘Добавляем строку итогов ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«ТоварныйЧек1»).ShowTotals = True ‘Стиль оставляем по умолчанию End Sub |
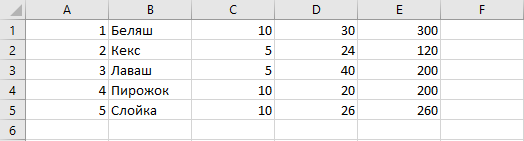
Результат выполнения кода Примера 1 получится такой:
Умная таблица из заданного набора данных
Пример 2 — «обычная» таблица
Упаковываем набор данных из задания в пользовательскую таблицу:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
Sub test2() ‘Объявляем переменную для присвоения ей количества строк Dim a As Long ‘Определяем количество строк a = Cells(1, 1).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count ‘Добавляем строку заголовков Cells(1, 1).EntireRow.Insert ‘Указываем названия граф Cells(1, 1) = «№ п/п» Cells(1, 2) = «Наименование» Cells(1, 3) = «Количество» Cells(1, 4) = «Цена» Cells(1, 5) = «Сумма» ‘Добавляем сетку Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(a + 1, 5)).Borders.LineStyle = True ‘Добавляем строку итогов Cells(a + 2, 4) = «Итого:» With Cells(a + 2, 5) .FormulaR1C1 = «=SUM(R[-« & a & «]C:R[-1]C)» .Borders.LineStyle = True .Font.Bold = True End With ‘Выделяем заголовки жирным шрифтом и ‘применяем автоподстройку ширины столбцов With Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(1, 5)) .Font.Bold = True .EntireColumn.AutoFit End With End Sub |
Результат выполнения кода Примера 2 получится такой:
Пользовательская таблица из заданного набора данных
Если решите поэкспериментировать с моим кодом, добавьте любые данные в пять колонок на активном листе Excel, количество строк может быть любым, в пятой графе должны быть числа.
О работе с умной таблицей (обращение к ячейкам, строкам и столбцам; добавление и удаление строк и столбцов) рассказано в статье VBA Excel. Работа с умной таблицей
In this Article
- VBA Tables and ListObjects
- Create a Table With VBA
- Inserting a Column at the End of the Table with VBA
- Inserting a Row at the Bottom of the Table with VBA
- Adding a Simple Sort with VBA
- Filter a Table With VBA
- Clear the Filter with the ShowAllData Method in VBA
- Clear All Filters From An Excel Table
- Deleting A Row With VBA
- Deleting a Column With VBA
- Converting a Table Back to a Range in VBA
- Adding Banded Columns and formatting to all the Tables in a Worksheet using VBA
- Creating a Table in Access in VBA Using DoCmd.RunSQL
- Filtering a Table in Access Using VBA
This tutorial will demonstrate how to work with Tables and ListObjects in VBA.
VBA Tables and ListObjects
Tables are one of Excel’s most useful and powerful features, in this tutorial, we will go over how to use VBA to create a table, add a simple sort to a table, filter a table and perform other table-related tasks.
Create a Table With VBA
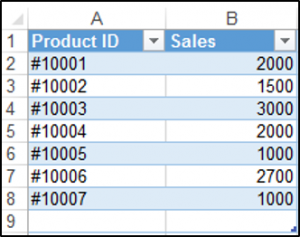
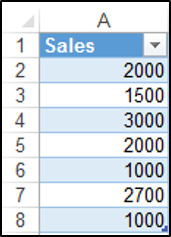
The ListObjects.Add Method can add a table to a worksheet, based on a range in that worksheet. We have the range shown in ($A$1:$B$8) on a worksheet called Sheet1.
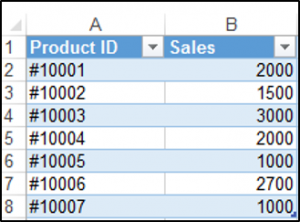
The following code will add a table, called Table1 to your worksheet, based on the range ($A$1:$B$8) using the default Table Style:
Sub CreateTableInExcel()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range("$A$1:$B$8"), , xlYes).Name = _
"Table1"
End SubThe result is:
Inserting a Column at the End of the Table with VBA
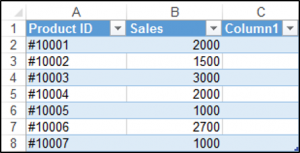
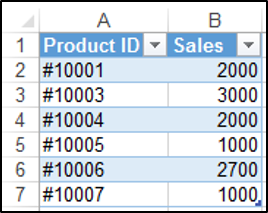
You can use the ListColumns.Add method in order to add a column to the end of your table. We have our table called Table1 shown below.
You can add a column to your table using the following code, which will always add a column to the end of the table:
Sub AddColumnToTheEndOfTheTable()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").ListColumns.Add
End SubThe result is:
Inserting a Row at the Bottom of the Table with VBA
You can use the ListRows.Add method to add a row to the bottom of your table. We have our table called Table1 shown below.
The following code will always add a row to the bottom of your table.
Sub AddRowToTheBottomOfTheTable()
ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table1").ListRows.Add
End SubThe result is:
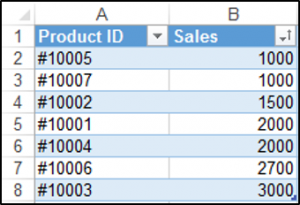
Adding a Simple Sort with VBA
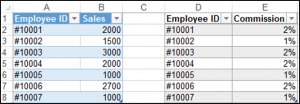
You can sort a table with VBA. We have our table called Table1 shown below and we can use VBA to sort the Sales Column from lowest to highest.
The following code will sort the Sales column in ascending order.
Sub SimpleSortOnTheTable()
Range("Table1[[#Headers],[Sales]]").Select
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").Sort.SortFields.Clear
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").Sort.SortFields.Add _
Key:=Range("Table1[[#All],[Sales]]"), SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:= _
xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").Sort
.Header = xlYes
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.SortMethod = xlPinYin
.Apply
End With
End SubThe result is:
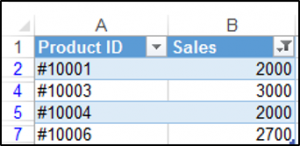
Filter a Table With VBA
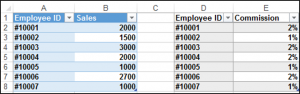
You can also filter an Excel table using VBA. We have our table called Table1 and we would like to filter the table so that only sales of greater than 1500 are shown.
We can use the Autofilter method, which has five optional parameters. Since we’d like to filter the Sales column which is the second column we set the Field to 2, and we use the xlAnd operator parameter, which is used for dates and numbers.
Sub SimpleFilter()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").Range.AutoFilter Field:=2, Criteria1:= _
">1500", Operator:=xlAnd
End SubThe result is:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Clear the Filter with the ShowAllData Method in VBA
You can access the ShowAllData Method of the Worksheet class in order to clear the filter. If it’s a table’s filter(s) that you want to clear, then you first have to select a cell in the table, which you can do in VBA.
The ShowAllData method will generate an error if one does not use conditional logic in order to check if there has been a filter applied in the worksheet. The following code shows you how to do this:
Sub ClearingTheFilter()
Range("Table1[[#Headers],[Sales]]").Select
If ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").FilterMode = True Then
ActiveSheet.ShowAllData
End If
End SubClear All Filters From An Excel Table
You can access the ShowAllData Method of the ListObject class without having to select a cell in the table first. The following code shows you how to do this:
Sub ClearAllTableFilters()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").AutoFilter.ShowAllData
End SubDeleting A Row With VBA
You can delete a row in the databody of your table using the ListRows.Delete method. You have to specify which row using the row number. We have the following table called Table1.
Let’s say you wanted to delete the second row in the databody of your table, the following code would allow you to do this:
Sub DeleteARow()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").ListRows(2).Delete
End SubThe result is:
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Deleting a Column With VBA
You can delete a column from your table using the ListColumns.Delete method. We have the following table called Table1 shown below:
In order to delete the first column, you would use the following code:
Sub DeleteAColumn()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").ListColumns(1).Delete
End SubThe result is:
Converting a Table Back to a Range in VBA
You can convert a table back to a normal range using VBA. The following code shows you how to convert a table called Table1 back to a range:
Sub ConvertingATableBackToANormalRange()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1").Unlist
End SubAdding Banded Columns and formatting to all the Tables in a Worksheet using VBA
You can access all the tables in your worksheet using the ListObjects collection. In the sheet below we have two tables and we would like to add a Banded Column to both the tables at once and change the font of the data section of both tables to bold, using VBA.
Sub AddingBandedColumns()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet
For Each tbl In sht.ListObjects
tbl.ShowTableStyleColumnStripes = True
tbl.DataBodyRange.Font.Bold = True
Next tbl
End SubThe result is:
Creating a Table in Access in VBA Using DoCmd.RunSQL
One of the main ways to create a table in Access in VBA, is through using the DoCmd.RunSQL method to run an action query with a SQL statement.
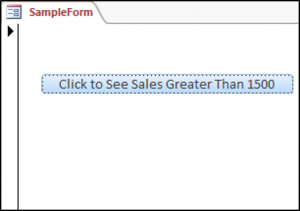
We have a button on our sample form and when we click on the button we’d like to create a table called ProductsTable with two fields or columns, one would be the primary key field called ProductsID and the other would be a field called Sales.
In order to create this table we would use the following code:
Private Sub cmdCreateProductsTable_Click()
DoCmd.RunSQL "CREATE TABLE ProductsTable " _
& "(ProductID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, Sales Integer);"
End SubThe result is:
Filtering a Table in Access Using VBA
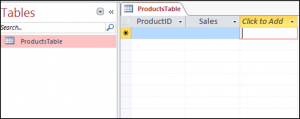
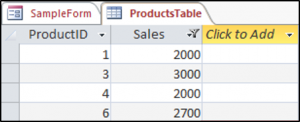
You can also filter a table in Access using the DoCmd.ApplyFilter method. We have our simple table shown below in Access called ProductsTable.
We would like to press this button on our form and then only see Sales that are greater than 1500.
So, we would use the following code to do this:
Private Sub cmdFilter_Click()
DoCmd.OpenTable "ProductsTable"
DoCmd.ApplyFilter , "[Sales]>1500"
End SubThe result is:
VBA Create Table in Excel. In this tutorial we learn how to create table and it’s syntax, different examples using VBA in Excel. Also find and learn step by step instructions to run VBA example macro code.
Table of Contents:
- Objective
- Syntax to create Table in Excel VBA
- Simple example to create Table in Excel
- Example to create Table in Excel
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
VBA Syntax to create Table in Excel
Let us see the syntax to create table in Excel using VBA.
expression.Add (SourceType, Source, LinkSource, XlListObjectHasHeaders, Destination, TableStyleName)
Where expression represents a List-objects object.
SourceType is an optional parameter. It contains XlListObjectSourceType type data. Represents the kind of source for the query.
Source is an optional parameter. It contains variant type data. Represents either xlSrcRange (range object) or xlSrcExternal(An array of String values).
LinkSource is an optional parameter. It contains Boolean type data. specifies whether an external data source is to be linked to the List-object object. It depends on Source. Returns an error if not omitted.
XlListObjectHasHeaders is an optional parameter. It contains variant type data. It is an XlYesNoGuess constant that indicates whether the data being imported has column labels. If the Source data does not contain headers, Excel will automatically generate headers. The default value is xlGuess.
Let us see the XlYesNoGuess constant table.
| Value | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | xlGuess | Excel determines whether there is a header, and its location.Default value. |
| 1 | xlYes | The entire range should not be sorted. |
| 2 | xlNo | The entire range should be sorted. |
Destination is an optional parameter. It contains variant type data. The destination range must be on the worksheet that contains the ListObjects collection specified by expression. New columns will be inserted at the Destination to fit the new list. Therefore, existing data will not be overwritten.
TableStyleName is an optional parameter. It contains string type data. Represents the Table Style.
Simple example to create Table in Excel
Here is a simple example macro statement to create table in Excel.
ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Selection, , xlYes).Name = "MyTable"
Example to create Table in Excel
Let us see another example by using object and create table in Excel. Here you can also set the name and style to the table, .
'VBA Create Table in Excel
Sub VBAF1_Create_Table_in_Excel()
'Variable Declaration
Dim tableListObj As ListObject
Dim sTableName As String
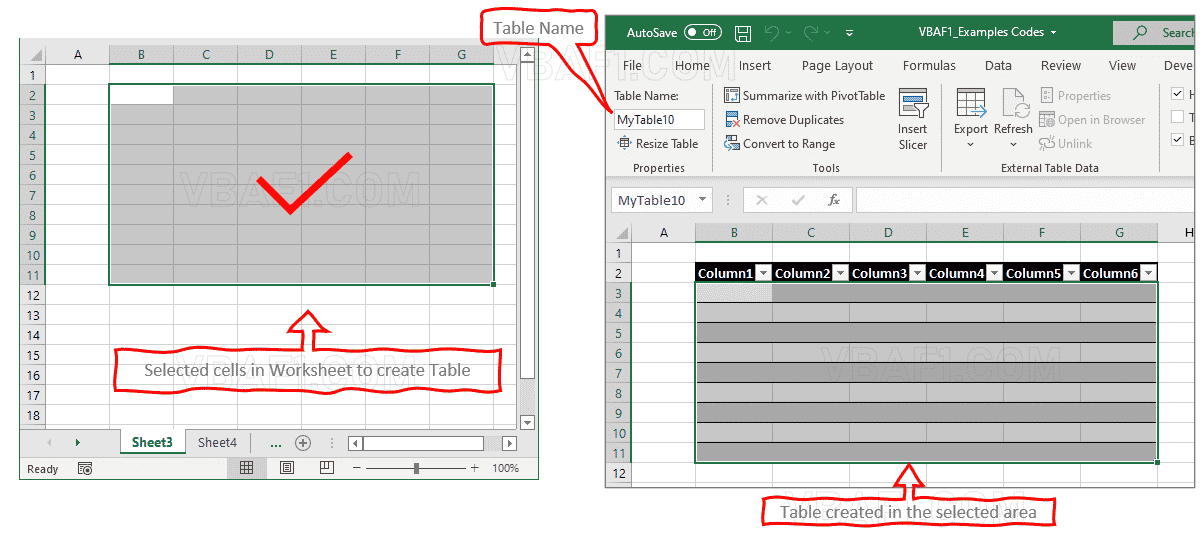
'Define Table Name
sTableName = "MyTable10"
'Create a Table
Set tableListObj = ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Selection, , xlYes)
tableListObj.Name = sTableName
tableListObj.TableStyle = "TableStyleMedium1"
End Sub
Note: The above VBA code macro creates a table in Excel Worksheet.
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays in Excel VBA Tables and ListObjects
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers Blog
Содержание
- Таблицы и объекты VBA
В этом руководстве будет показано, как работать с таблицами и объектами ListObject в VBA.
Таблицы — одна из самых полезных и мощных функций Excel. В этом руководстве мы рассмотрим, как использовать VBA для создания таблицы, добавления простой сортировки в таблицу, фильтрации таблицы и выполнения других задач, связанных с таблицами.
Создать таблицу с VBA
Метод ListObjects.Add может добавлять таблицу на лист на основе диапазона на этом листе. У нас есть диапазон, показанный в ($ A $ 1: $ B $ 
Следующий код добавит на ваш рабочий лист таблицу с именем Table1 в зависимости от диапазона ($ A $ 1: $ B $ 
| 123456 | Подложка CreateTableInExcel ()ActiveWorkbook.Sheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects.Add (xlSrcRange, Range («$ A $ 1: $ B $ 8»),, xlYes) .Name = _»Таблица 1″Конец подписки |
Результат:
Вставка столбца в конец таблицы с помощью VBA
Вы можете использовать метод ListColumns.Add, чтобы добавить столбец в конец вашей таблицы. У нас есть таблица под названием Table1, показанная ниже.
Вы можете добавить столбец в свою таблицу, используя следующий код, который всегда будет добавлять столбец в конец таблицы:
| 12345 | Sub AddColumnToTheEndOfTheTable ()ActiveWorkbook.Sheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). ListColumns.AddКонец подписки |
Результат:
Вставка строки внизу таблицы с помощью VBA
Вы можете использовать метод ListRows.Add, чтобы добавить строку в конец таблицы. У нас есть таблица под названием Table1, показанная ниже.
Следующий код всегда будет добавлять строку в конец таблицы.
| 12345 | Подложка AddRowToTheBottomOfTheTable ()ActiveSheet.ListObjects («Таблица1»). ListRows.AddКонец подписки |
Результат:
Добавление простой сортировки с помощью VBA
Вы можете отсортировать таблицу с помощью VBA. У нас есть таблица с именем Table1, показанная ниже, и мы можем использовать VBA для сортировки столбца продаж от самого низкого до самого высокого.
Следующий код отсортирует столбец «Продажи» в порядке возрастания.
| 12345678910111213141516171819 | Sub SimpleSortOnTheTable ()Диапазон («Таблица1 [[# заголовков], [Продажи]]»). ВыберитеActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). Sort.SortFields.ClearActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). Sort.SortFields.Add _Ключ: = Диапазон («Таблица1 [[# Все], [Продажи]]»), SortOn: = xlSortOnValues, Order: = _xlAscending, DataOption: = xlSortNormalС ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). Sort.Header = xlYes.MatchCase = Ложь.Orientation = xlTopToBottom.SortMethod = xlPinYin.Подать заявлениеКонец сКонец подписки |
Результат:
Фильтрация таблицы с помощью VBA
Вы также можете фильтровать таблицу Excel с помощью VBA. У нас есть таблица с именем Table1, и мы хотели бы отфильтровать ее, чтобы отображались только продажи, превышающие 1500.
Мы можем использовать метод автофильтра, который имеет пять необязательных параметров. Поскольку мы хотим отфильтровать столбец «Продажи», который является вторым столбцом, мы устанавливаем для поля значение 2 и используем параметр оператора xlAnd, который используется для дат и чисел.
| 123456 | Подложка SimpleFilter ()ActiveWorkbook.Sheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1″). Range.AutoFilter Field: = 2, Criteria1: = _»> 1500″, оператор: = xlAndКонец подписки |
Результат:
Очистите фильтр с помощью метода ShowAllData в VBA
Вы можете получить доступ к методу ShowAllData класса Worksheet, чтобы очистить фильтр. Если вы хотите очистить фильтр (-ы) таблицы, вам сначала нужно выбрать ячейку в таблице, что вы можете сделать в VBA.
Метод ShowAllData сгенерирует ошибку, если не использовать условную логику, чтобы проверить, был ли применен фильтр на листе. В следующем коде показано, как это сделать:
| 123456789 | Sub ClearingTheFilter ()Диапазон («Таблица1 [[# заголовков], [Продажи]]»). ВыберитеЕсли ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). FilterMode = True, тоActiveSheet.ShowAllDataКонец, еслиКонец подписки |
Очистить все фильтры из таблицы Excel
Вы можете получить доступ к методу ShowAllData класса ListObject, не выбирая сначала ячейку в таблице. В следующем коде показано, как это сделать:
| 123 | Подложка ClearAllTableFilters ()ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). AutoFilter.ShowAllDataКонец подписки |
Удаление строки с помощью VBA
Вы можете удалить строку в базе данных вашей таблицы с помощью метода ListRows.Delete. Вы должны указать, какая строка используется по номеру строки. У нас есть следующая таблица под названием Table1.
Допустим, вы хотите удалить вторую строку в базе данных вашей таблицы, следующий код позволит вам это сделать:
| 12345 | Sub DeleteARow ()ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). ListRows (2) .DeleteКонец подписки |
Результат:
Удаление столбца с помощью VBA
Вы можете удалить столбец из таблицы с помощью метода ListColumns.Delete. У нас есть следующая таблица под названием Table1, показанная ниже:
Чтобы удалить первый столбец, вы должны использовать следующий код:
| 12345 | Подраздел DeleteAColumn ()ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). ListColumns (1) .DeleteКонец подписки |
Результат:
Преобразование таблицы обратно в диапазон в VBA
Вы можете преобразовать таблицу обратно в нормальный диапазон с помощью VBA. В следующем коде показано, как преобразовать таблицу с именем Table1 обратно в диапазон:
| 12345 | Sub ConvertingATableBackToANormalRange ()ActiveWorkbook.Sheets («Sheet1»). ListObjects («Table1»). UnlistКонец подписки |
Добавление чередующихся столбцов и форматирование ко всем таблицам на листе с помощью VBA
Вы можете получить доступ ко всем таблицам на вашем листе с помощью коллекции ListObjects. На приведенном ниже листе у нас есть две таблицы, и мы хотели бы добавить столбец с чередованием к обеим таблицам сразу и изменить шрифт раздела данных обеих таблиц на полужирный, используя VBA.
| 12345678910111213 | Sub AddingBandedColumns ()Dim tbl As ListObjectТусклый лист как рабочий листУстановить sht = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheetДля каждой табл. В шт.ListObjectstbl.ShowTableStyleColumnStripes = Истинаtbl.DataBodyRange.Font.Bold = ИстинаСледующая таблицаКонец подписки |
Результат:
Создание таблицы в Access в VBA с использованием DoCmd.RunSQL
Одним из основных способов создания таблицы в Access в VBA является использование метода DoCmd.RunSQL для выполнения запроса действия с оператором SQL.
У нас есть кнопка в нашем образце формы, и когда мы нажимаем на кнопку, мы хотим создать таблицу с именем ProductsTable с двумя полями или столбцами, одно будет полем первичного ключа с именем ProductsID, а другое будет полем с именем Sales.
Чтобы создать эту таблицу, мы будем использовать следующий код:
| 123456 | Частная подпрограмма cmdCreateProductsTable_Click ()DoCmd.RunSQL «СОЗДАТЬ ТАБЛИЦУ ProductsTable» _& «(ProductID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, целое число продаж);»Конец подписки |
Результат:
Фильтрация таблицы в доступе с помощью VBA
Вы также можете фильтровать таблицу в Access с помощью метода DoCmd.ApplyFilter. У нас есть наша простая таблица, показанная ниже в Access, которая называется ProductsTable.
Мы хотели бы нажать эту кнопку в нашей форме, и тогда мы увидим только продажи, превышающие 1500.
Итак, мы бы использовали следующий код для этого:
| 1234567 | Частная подпрограмма cmdFilter_Click ()DoCmd.OpenTable «ProductsTable»DoCmd.ApplyFilter, «[Продажи]> 1500»Конец подписки |
Результат:
Tables in Excel VBA – Explained with Examples!
Managing the data with Tables is very easy in Excel. We can do lot more things if your data is in the form of tables. In this section we will show some of the Tables operations using Excel VBA.
- Create Tables in Excel VBA
- Sorting Tables in Excel VBA
- Filtering Tables in Excel VBA
- Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA
Create Tables in Excel VBA:
Sometimes you may want to create Tables in Excel VBA. Please find the following code to Create Tables in Excel VBA.
- Solution
- Code
- Output
- Reset a Table back to Normal Range
- Example File
Create Tables in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
You can use ListObjects.Add method of sheet to create tables in excel VBA. We can create table in the following way. The following code creates a table “myTable1” and referring to sheet1 of a range(“$A$1:$D$10”) .
Code:
'Naming a range
Sub sbCreatTable()
'Create Table in Excel VBA
Sheet1.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range("A1:D10"), , xlYes).Name = "myTable1"
End Sub
Output:
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Double click on ThisWorkbook from Project Explorer
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Press F5
- GoTo Sheet1 and Select Range A1 to D10
- You should see the above output in Sheet1
Reset a Table back to Normal Range
If you want to Reset the table back to original range, you can use Unlist property of table object. Following code will show you how to remove table formats and reset to normal range.
Sub sbReset_Table_BackTo_Range()
'Reset Table Back to Original Range
On Error Resume Next 'If there are no Table ignore the below Statement
Sheet1.ListObjects("myTable1").Unlist
End Sub
Example File
Download the example file and Explore it.
Analysistabs – Create Tables in Excel VBA
Sorting Tables in Excel VBA:
Examples for Sorting Table in Excel VBA with using sort method of ListObjects. You can learn how to sort table with examples.
- Solution
- Code
- Output
Sorting Table in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
You can use sort method of ListObjects for sorting table in Excel VBA. We can do sort data in the following way.
Code:
Sub sbSortTable()
'Naming a range
Sheet1.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("myTable1").Sort.SortFields.Clear
Sheet1.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("myTable1").Sort.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("myTable1[[#All],[EmpName]]"), SortOn:=sortonvalues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
Range("myTable1[#All]").Select
With Sheet1.Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("myTable1").Sort
.Header = xlYes
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.SortMethod = xlPinYin
.Apply
End With
End Sub
Output:
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Double click on ThisWorkbook from Project Explorer
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Press F5
- GoTo Sheet1 and Select Range A1 to D10
- You should see the above output in Sheet1
Filtering Tables in Excel VBA
Sometimes you may want to Filter Tables in Excel VBA. Please find the following code for Filtering Tables in Excel VBA.
- Solution
- Code
- Output
- Example File
Filtering Tables in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
You can use ListObjects(“TableName”).Range.AutoFilter method for Filtering tables in excel VBA. We can filter table in the following way. The following code filters a table “myTable1” and referring to sheet1 of a range(“$A$1:$D$10”).In this Case I am applying filter for second column and looking for description “DDD” in a table.
Code:
'Filtering a table
Sub sbFilterTable()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("myTable1").Range.AutoFilter field:=2, Criteria1:="DDD" 'matched with 4 in column c2 records will be shown
End Sub
Output:
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Double click on ThisWorkbook from Project Explorer
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Press F5 to execute Macro
- GoTo Sheet1 and Select Range A1 to D10
- You should see the above output in Sheet1
Example File
Download the example file and Explore it.
Analysistabs – Filtering Tables in Excel VBA
Clear or Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA:
Examples for Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA with using FilterMode Property and AutoFilter method. You can learn how to Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA with following example.
- Solution
- Code
- Output
- Example File
Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
You can Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA with using FilterMode Property and AutoFilter method in Excel VBA. We can do Clear table filter in the following way.
Code:
'Clear Table Filter
Sub sbClearFilter()
'Check Filter is Exists or Not
If ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").FilterMode = True Then
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("myTable1").Range.AutoFilter
End If
End Sub
Output:
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Double click on ThisWorkbook from Project Explorer
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Press F5 to execute Macro
- GoTo Sheet1 and check the Table Data from A1 to D10
- You should see the above output in Sheet1
Example File
Download the example file and Explore it.
Analysistabs – Clear Tables in Excel VBA
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
-
- Create Tables in Excel VBA:
- Create Tables in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
- Sorting Tables in Excel VBA:
- Sorting Table in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
- Filtering Tables in Excel VBA
- Filtering Tables in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
- Clear or Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA:
- Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA – Solution(s):
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
13 Comments
-
Bruce
January 13, 2014 at 2:20 AM — ReplyExcellent! Now the couple pieces missing:
1) Copying the filtered results to a new sheet Sheet02 (and whether or not the copied area is a range, table or neither at that time)
2)Applying the same process to a new range of data and adding that filtered section to the previously established data on the new sheet Sheet02
3) Sorting the new sheet data every time data is added and removing duplicates based upon one field being used as a key.I am sure I will run into all this, but you folks were off to such a great start of the information being clear and collected in one place, I wanted to place the suggestion, provided you ever have the time!
-
PNRao
January 13, 2014 at 9:14 PM — ReplyHi Bruce,
Thanks for your suggestion, I will add these in couple of weeks.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Nurit
May 27, 2014 at 10:11 PM — ReplyHow do you create a table when the range is dynamic. I want to automate the process of refreshing and opening pivot tables. I need to:
1) import data from a software package (this will be done manually)
2) open the file created in #1 and create and name table. The range of data is unknown.
3) open the pivot table which will refresh automatically using the named table created in #2.I got this far – how do I change the defined range to a dynamic range and do I need the last line?
Sub opengetfile()
Dim strFileName As String
Dim rgData As Range
strFileName = Application.GetOpenFilename
If strFileName = “False” Then Exit Sub
MsgBox strFileName
Workbooks.Open (strFileName)ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range(“$A$1:$AX$224”), , xlYes).Name = “Loans”
Range(“Loans[#All]”).SelectEnd Sub
-
PNRao
May 28, 2014 at 11:45 PM — Reply -
Gejza Horvath
June 16, 2014 at 1:42 AM — ReplyIf all the data on this sheet will be inside a listobject, you can use ActiveSheet.UsedRange property. Instead the Range() object.
-
JonasTiger
December 29, 2014 at 3:44 AM — ReplyHi
Filtering Tables in Excel VBA…
I need to filter my table everytime data changes.
In your example, you filter “DDD”.
In mine, I want filter all options except zero/blank cells of a range, i.e., its like excluding “DDD” and leave remaining data.
please help me changing code for that.
Thank you -
Amy
January 30, 2015 at 5:27 AM — ReplyThis has been very helpful! I needed to create a macro to turn a dynamic range into a table, sort by a specific column, & filter the table based on that same column name. This page had all the information I needed.
I look forward to checking out the other areas of your site.Thanks for sharing.
-
yonsebastian
June 1, 2015 at 5:52 AM — Replyworking for year with VBA now 2013 comes with tables which is awesome!
-
PNRao
June 1, 2015 at 12:20 PM — ReplyYes, Tables or ListObjects in Excel are very handy to deal with the data. We can perform many operations and its fast.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Agni
June 10, 2016 at 12:31 PM — ReplyHi,
How to create a table without default auto filter and header. -
prema
April 2, 2018 at 11:49 AM — ReplyIf ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(“Sheet1”).FilterMode = True Then
is not working for a listobject
-
a
February 17, 2020 at 9:28 AM — Reply[code]
Sub Next ()
If G3=1 Then
Next i
Me.ListBox1.Column = Tbl
End If
End Sub -
a
February 17, 2020 at 9:29 AM — Reply[code]
Sub Next ()
If G3=1 Then
Next i
Me.ListBox1.Column = Tbl
End If
End Sub
[/code]
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top