Сохранение файла рабочей книги Excel, существующего или нового, с помощью кода VBA. Методы Save и SaveAs объекта Workbook, параметр SaveChanges метода Close.
Сохранение существующего файла
Сохранить существующий открытый файл рабочей книги Excel из кода VBA можно несколькими способами. В примерах используется выражение ActiveWorkbook, которое может быть заменено на ThisWorkbook, Workbooks(«ИмяКниги.xlsx»), Workbooks(myFile.Name), где myFile — объектная переменная с присвоенной ссылкой на рабочую книгу Excel.
Простое сохранение файла после внесенных кодом VBA Excel изменений:
Сохранение файла под другим именем (исходная рабочая книга будет автоматически закрыта без сохранения внесенных изменений):
|
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
Сохранить файл рабочей книги можно перед закрытием, используя параметр SaveChanges метода Close со значением True:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True |
Чтобы закрыть файл без сохранения, используйте параметр SaveChanges метода Close со значением False:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False |
Сохранение файла под другим именем при закрытии рабочей книги:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True, Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
Если в примерах с методом Close параметр SaveChanges пропустить, будет открыто диалоговое окно с запросом о сохранении файла.
Новая книга сохраняется с указанием полного имени:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
После этого к новой книге можно обращаться по имени: Workbooks ("НоваяКнига.xlsx").
Если не указать полное имя для сохраняемого файла:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.Save |
тогда новая книга будет сохранена с именем и в папке по умолчанию, например: Книга1.xlsx, Книга2.xlsx, Книга3.xlsx и т.д. в папке «Документы».
To save an Excel workbook using VBA, you need to use the SAVE method to write a macro. And in that macro, you need to specify the workbook that you want to save and then use the SAVE method. When you run this code, it works like the keyboard shortcut (Control + S).

- Specify the workbook hat you want to save.
- Type a dot to get the list of all the properties and methods.
- Select the “Save” method out of those or type “Save”
- In the end, run the code to save the workbook.
In this tutorial, we will look at different ways that we can use to save a workbook. So make sure to open the VBA editor from the developer tab to use the code you have in this tutorial.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Save the ActiveWorkbook
If you want to save the active workbook in that case you can use a code like the following code, instead of specifying the workbook by its name.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveWhen you use the ActiveWorkbook as the workbook, VBA always refers to the workbook which is active despite in which file you are writing the code.
Save the Workbook where you are Writing Code
If you want to save the file where you are writing the code you need to use “ThisWorkbook” instead of the workbook name.
ThisWorkbook.SaveSave All the Open Workbooks
Here we can use a loop to loop through all the workbooks that are open and save them one by one. Look at the below code.
Sub vba_save_workbook()
'variable to use as a workbook
Dim wb As Workbook
'For each to loop through each open workbook and save it
For Each wb In Workbooks
wb.Save
Next wb
End SubThe above code uses the FOR EACH loop in each workbook it uses the SAVE method to each file one by one.
Note: If you are trying to save a workbook with the SAVE method that is not saved already, Excel will show a dialog box to ask for your permission to save that file, and then you need to choose if you want to save that file on the default location in the default format.
Now here’s the point: As you are using a macro to save the workbook, that file should be saved in the macro-enabled format and the best way to deal with this situation is to use the SAVE AS method (we’ll see in the next section of this tutorial).
To SAVE a file that is not saved yet, using VBA, you need to use the SAVE AS method. In this method, you can define the file name and the path where you want to save the file, and apart from that, there are ten more arguments that you can define.
expression.SaveAs (FileName, FileFormat, Password, WriteResPassword, ReadOnlyRecommended, CreateBackup, AccessMode, ConflictResolution, AddToMru, TextCodepage, TextVisualLayout, Local)In the following code, you don’t have any argument with the “SAVE AS” method.

When you run this code, it asks you a few things, like, which format you want to use to save the file, do you want to replace the existing file that is already saved with the same name. So it’s better to define the use of some of the arguments.
Save As File on the Current Location
By default, VBA uses the current location to save the file. When you write code with the SAVE AS method and just specify the name that file straight goes to the current folder. You can see in the following code where you have the which saves the active workbook.

Sub save_as_file()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="myNewWorkbook"
End SubSave As File on a Specific Location
The filename argument also allows you to use the location path in case you want to use a different location to save the file.

Sub save_as_file()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs _
Filename:="C:UsersDellDesktopmyNewBook"
End SubIn the above code, you have the path in the FileName argument and VBA uses that path to the file.
Note: You can also use this method to check if a workbook exists in a folder or not before you use the SAVE AS method to save it on a particular location and you can learn more about SAVE AS method from here.
More on VBA Workbooks
VBA Close Workbook | VBA Delete Workbook | VBA ThisWorkbook | VBA Rename Workbook | VBA Activate Workbook | VBA Combine Workbook | VBA Protect Workbook (Unprotect) | VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open | VBA Open Workbook | VBA Check IF an Excel Workbook Exists in a Folder| VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||||||
|
1 |
||||||||
|
13.01.2011, 21:13. Показов 26007. Ответов 27 Метки нет (Все метки)
Вроде изучил этот вопрос Но пишу так
так
вопросов нет, но мне так не надо
0 |
|
Pavel Murtishev 3 / 3 / 0 Регистрация: 29.10.2010 Сообщений: 54 |
||||
|
14.01.2011, 08:51 |
2 |
|||
|
Эндрю, Workbooks — это коллекция объектов Workbook. Попробуйте исполнить данный код:
Должно работать. BR
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||||||||||
|
14.01.2011, 18:53 [ТС] |
3 |
|||||||||||
|
Вы меня не поняли:
затем делаю что хочу
если напишу так:
всё работает, но мне так не надо, так как Эксель спросит, сохранить ли файл, надо чтобы сохранил без вопросов
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
14.01.2011, 19:45 |
4 |
|
oExcel.Workbooks.Close(SaveChanges = True) ‘ошибка аргумент не верный??????? вытащи из скобок и пробелом отбей.
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||
|
14.01.2011, 20:22 [ТС] |
5 |
|||
|
теперь
выделяет .Close и сообщение Wrong number of arguments or invalid property assigment
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
14.01.2011, 21:15 |
6 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю,
0 |
|
Vlanib Частенько бываю 749 / 330 / 42 Регистрация: 20.06.2007 Сообщений: 854 |
||||
|
14.01.2011, 22:25 |
7 |
|||
|
Вот так напиши:
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
14.01.2011, 22:30 |
8 |
|
Vlanib,
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||
|
15.01.2011, 11:36 [ТС] |
9 |
|||
Вот этот скрипт я запускаю в ВБА в Ворде, на двух последних строчках выделяет
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
15.01.2011, 11:46 |
10 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю,
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||||||||||||||
|
15.01.2011, 12:05 [ТС] |
11 |
|||||||||||||||
|
11 строку удалил
надо сравнить с строкой
и найти 10 отличий
Вё мимо, ещё 8 отличий не нашёл Добавлено через 4 минуты
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
15.01.2011, 12:16 |
12 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю,
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||
|
15.01.2011, 12:23 [ТС] |
13 |
|||
|
Ципихович Эндрю, 10 строка в моём 9 м сообщениии, это вот эта:
Во всяком случае она рабочая, ну пусть даже её я заремарчу, ничего ведь не изменится
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
15.01.2011, 12:31 |
14 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю,
0 |
|
1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
|
|
15.01.2011, 12:54 [ТС] |
15 |
|
я её не с потолка взял, искал не могу вспомнить из какого места я её взял
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
||||
|
15.01.2011, 12:56 |
16 |
|||
|
Ципихович Эндрю, Добавлено через 1 минуту
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||||||
|
15.01.2011, 13:04 [ТС] |
17 |
|||||||
|
Я Вас уверяю в Ворде, что так
что так
работает!
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
15.01.2011, 13:10 |
18 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю,
0 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю 1508 / 478 / 56 Регистрация: 10.04.2009 Сообщений: 8,008 |
||||||||||||
|
15.01.2011, 13:22 [ТС] |
19 |
|||||||||||
|
запускаю с Ворда
почему я должен так писать и получать ошибку 91
почему я не должен так писать и не получать ошибку, и получать нужный результат???
0 |
|
Заблокирован |
|
|
15.01.2011, 13:24 |
20 |
|
Ципихович Эндрю, Добавлено через 53 секунды
почему я должен так писать так запрограммировано.
0 |
In this Article
- Save Workbook – VBA
- Save a Specified Workbook
- Save the Active Workbook
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- Save the Workbook Where the Code is Stored
- Save all Open Workbooks
- Save all open workbooks that were not opened ReadOnly
- Save a workbook defined by a variable
- Save a workbook defined by a string variable
- Save a workbook defined by the order it was opened.
- Save a workbook based on a cell value
- Save As – VBA
- SaveAs Syntax:
- Save As Syntax Examples:
- Workbook Save As – Same Directory
- Workbook Save As – New Directory
- Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension
- Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension – Alt Method
- Workbook Save As – Add Password to Open File
- Workbook Save As – Add Password for Write Privileges
- Workbook Save As – Read-Only Recommended
- Other Save As Examples
- Create Save As Dialog Box
- Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
- Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
- Create & Save New Workbook
- Disable Save Alerts
This VBA Tutorial covers how to save a file using the Save and Save As commands in VBA.
Save Workbook – VBA
The VBA Save command saves an Excel file similarly to clicking the Save icon or using the Save Shortcut (CTRL + S).
Save a Specified Workbook
To save a workbook, reference the workbook object and use the Save command.
Workbooks("savefile.xlsm").SaveSave the Active Workbook
Note: This is the current active workbook from with in the VBA code, which is different from ThisWorkbook which contains the running code.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Save the Workbook Where the Code is Stored
ThisWorkbook.saveSave all Open Workbooks
This will loop through all open workbooks, saving each one.
Dim wb as workbook
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
wb.Save
Next wbSave all open workbooks that were not opened ReadOnly
Note: opening a workbook in ReadOnly mode prevents the file from being saved.
To save the file you will need to use Save As and save the file with a different name.
Dim wb as workbook
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
If not wb.ReadOnly then
wb.Save
End if
Next wbSave a workbook defined by a variable
This will save a workbook that was assigned to a workbook object variable.
Dim wb as workbook
set wb = workbooks("savefile.xlsm")
wb.saveSave a workbook defined by a string variable
This will save a workbook that’s name was saved to a string variable.
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "savefile.xlsm"
workbooks(wbstring).saveSave a workbook defined by the order it was opened.
Note: The first workbook opened would have 1, the second 2, etc.
workbooks(1).saveVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Save a workbook based on a cell value
This will save a workbook that’s name is found in a cell value.
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = activeworkbook.sheets("sheet1").range("wb_save").value
workbooks(wbstring).saveSave As – VBA
The VBA Save As command saves an Excel file as a new file, similar to clicking the Save As icon or using the Save As Shortcut (Alt > F > A).
Above, we identified all the ways to specify which workbook to save. You can use those exact same methods to identify workbooks when using Save As.
Save As behaves similarly to Save, except you also need to specify the name of the new file.
In fact, Save As has many potential variables to define:
SaveAs Syntax:
workbook object .SaveAs(FileName, FileFormat, Password, WriteResPassword, _
ReadOnlyRecommended, CreateBackup, AccessMode, ConflictResolution, _
AddToMru,TextCodepage, TextVisualLayout, Local)A full description of all of the SaveAs arguments is included below. For now we will focus on the most common examples.
Note: These arguments can be entered as string with parenthesis or as defined variables.
Save As Syntax Examples:
Workbook Save As – Same Directory
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "new"or
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "new"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "new"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstringAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook Save As – New Directory
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "C:new"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstring=Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "C:new.xlsx"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstringWorkbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension – Alt Method
You can also specify the file format in it’s own argument.
.xlsx = 51 '(52 for Mac)
.xlsm = 52 '(53 for Mac)
.xlsb = 50 '(51 for Mac)
.xls = 56 '(57 for Mac)ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new", FileFormat:= 51Workbook Save As – Add Password to Open File
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", Password:= "password"AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook Save As – Add Password for Write Privileges
If correct password is not supplied then workbook opens as Read-Only
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", WriteRes:= "password"Workbook Save As – Read-Only Recommended
TRUE to display a message box, recommending that the file is opened read-only.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", ReadOnlyRecommended:= TRUEOther Save As Examples
Create Save As Dialog Box
This Generates the Save As Dialog Box, prompting the user to Save the file.
Keep in mind that this simple code may not be appropriate in all cases.
Application.GetSaveAsFilenameAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
Application.GetSaveAsFilename InitialFilename:="test.xlsx"Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
Application.GetSaveAsFilename InitialFilename:="test.xlsx"Create & Save New Workbook
This will create a new workbook and immediately save it.
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Add
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
wb.SaveAs Filename:=”c:Test1.xlsx”
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Disable Save Alerts
As you work with saving in VBA, you may come across various Save Warnings or Prompts. To disable warnings, add this line of code:
Application.DisplayAlerts=Falseand to re-able alerts:
Application.DisplayAlerts=TrueHow to close an Excel workbook using VBA and macros, including how to save the file before you close it or discard any changes.
Sections:
Selecting Which Workbook to Close
Close Workbook While Saving Changes
Close Workbook Without Saving Changes
Let the User Decide to Save Changes or Not
Notes
Selecting Which Workbook to Close
First, we need to tell the macro to choose the current workbook to close or another workbook to close.
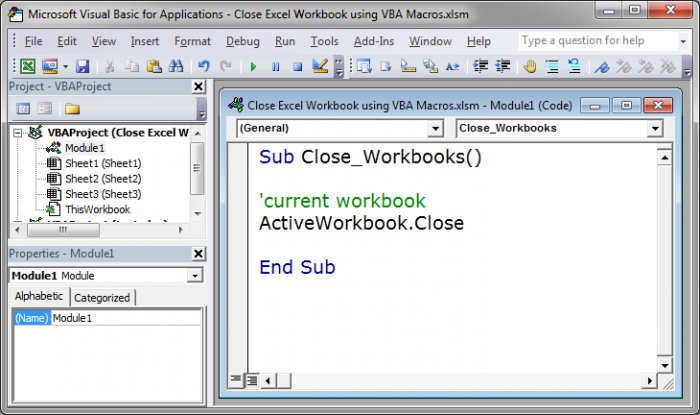
Current Workbook
We use this piece of code to close the current or currently active workbook and close that.
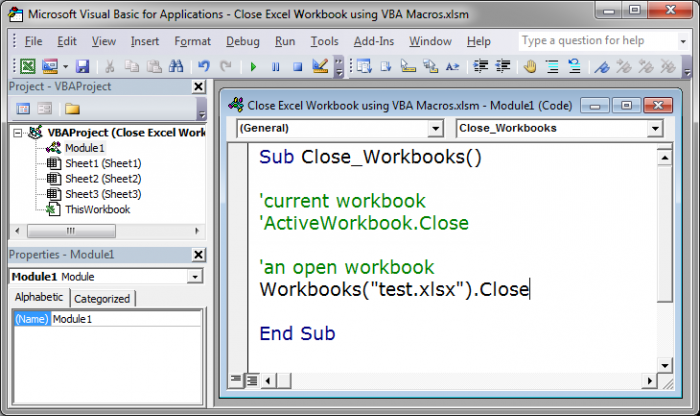
Other Workbook
We use this piece of code to close any specific open workbook.
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close
Replace test.xlsx with the name of the file that you want to close.
Close Workbook While Saving Changes
To have Excel automatically save any changes for the workbook that you want to close, just put True behind the close workbook code from above like this:
ActiveWorkbook.Close True
or, to close a specific file like this:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close True
Close Workbook Without Saving Changes
To have an Excel window close WITHOUT saving any changes, just put False behind the close workbook code from above like this:
ActiveWorkbook.Close False
or, to close a specific file like this:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close False
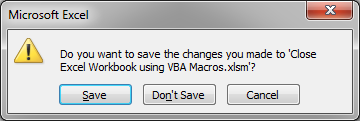
Let the User Decide to Save Changes or Not
You use the basic code from the first section and don’t include a True or False after it and a dialog box will open asking if you want to save the file or not; it looks like this:
Close the currently active or visible workbook:
Close a specific workbook:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close
Notes
You may run into issues with messages popping up depending on your implementation of this code and your setup and it can help to turn off ScreenUpdating for Excel. Make sure to turn it back on when you are finished though.
If Application.DisplayAlerts is set to False before you close the workbook, you won’t see a popup asking if you want to save it or not before closing it. If this is the case, you may lose data if you wanted to save the file before closing it, so test your code on a sample workbook first.
Download the sample files for this tutorial to test everything out.
Similar Content on TeachExcel
Open Excel Workbook Using VBA Macros
Tutorial:
Simple way to open an Excel workbook using VBA and macros.
Syntax
Workbooks.Open («File…
Macro to get Data from Another Workbook in Excel
Tutorial:
Macro to get data from a workbook, closed or open, over a network or locally on your comp…
Get User Submitted Data from a Prompt in Excel using VBA Macros
Tutorial: How to prompt a user for their input in Excel.
There is a simple way to do this using VBA …
Interactive Clickable Buttons and Interface Without Using VBA/Macros in Excel
Tutorial:
How to make your Excel dashboards and worksheets more interactive and easier to view and …
Loop through a Range of Cells in Excel VBA/Macros
Tutorial: How to use VBA/Macros to iterate through each cell in a range, either a row, a column, or …
Kill Command in Excel (Delete Files Using VBA)
Tutorial:
How to safely remove, delete, kill any Excel file, or other file, using VBA Macros in Exc…